Construction of three-dimensional model and stability analysis of dangerous rock mass based on nap-of-the-object photogrammetry and LiDAR technology
-
摘要:
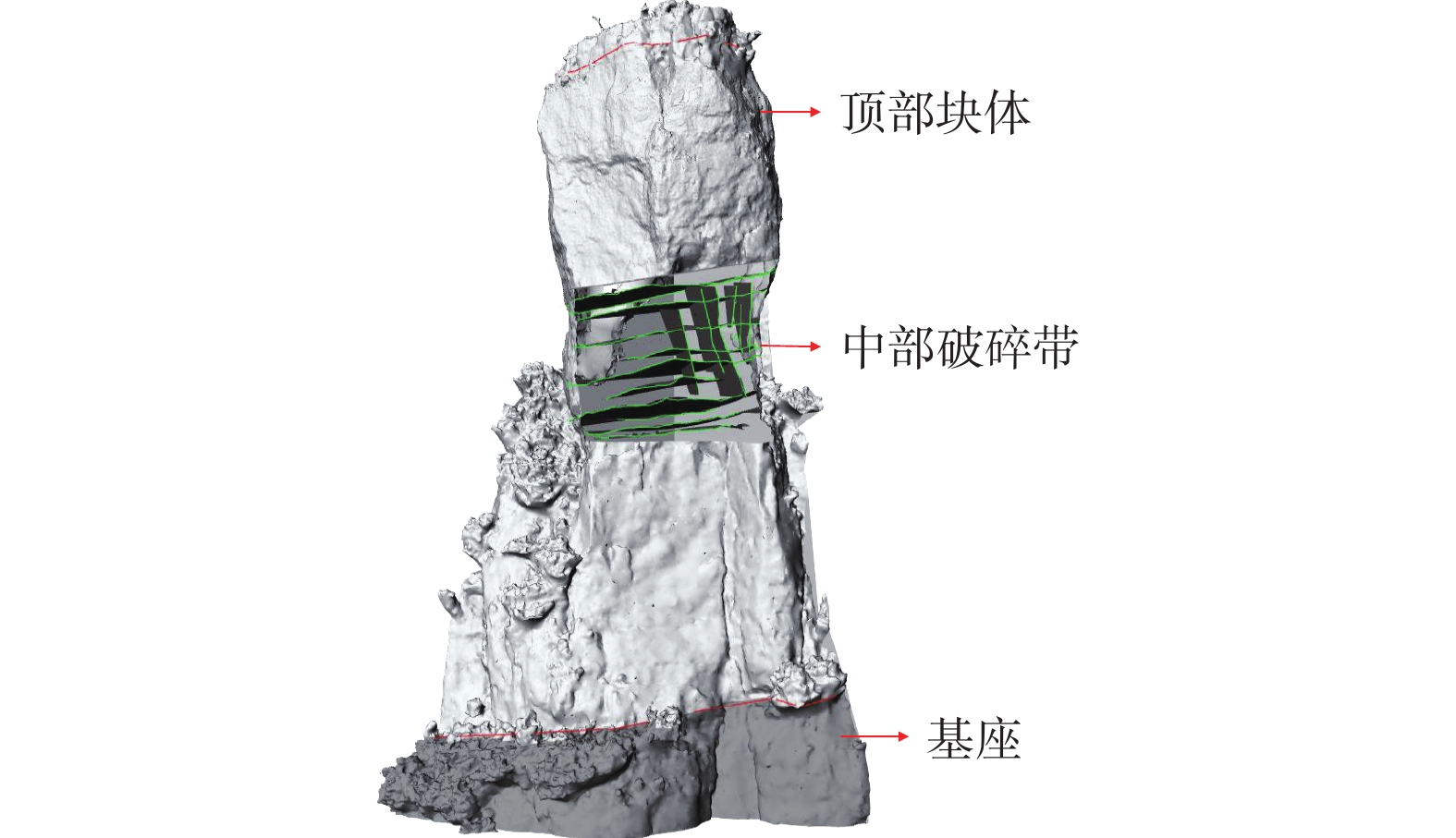
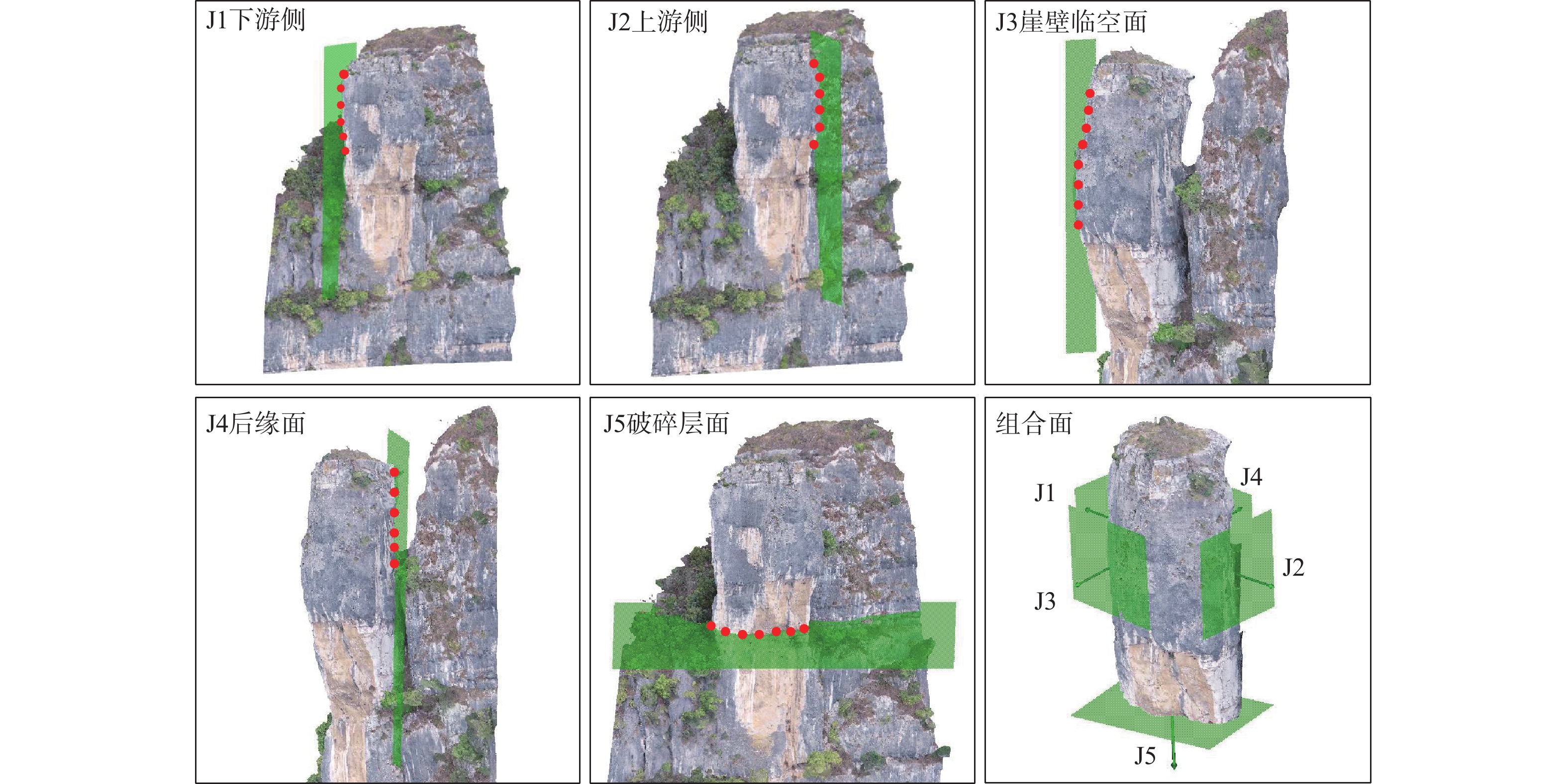
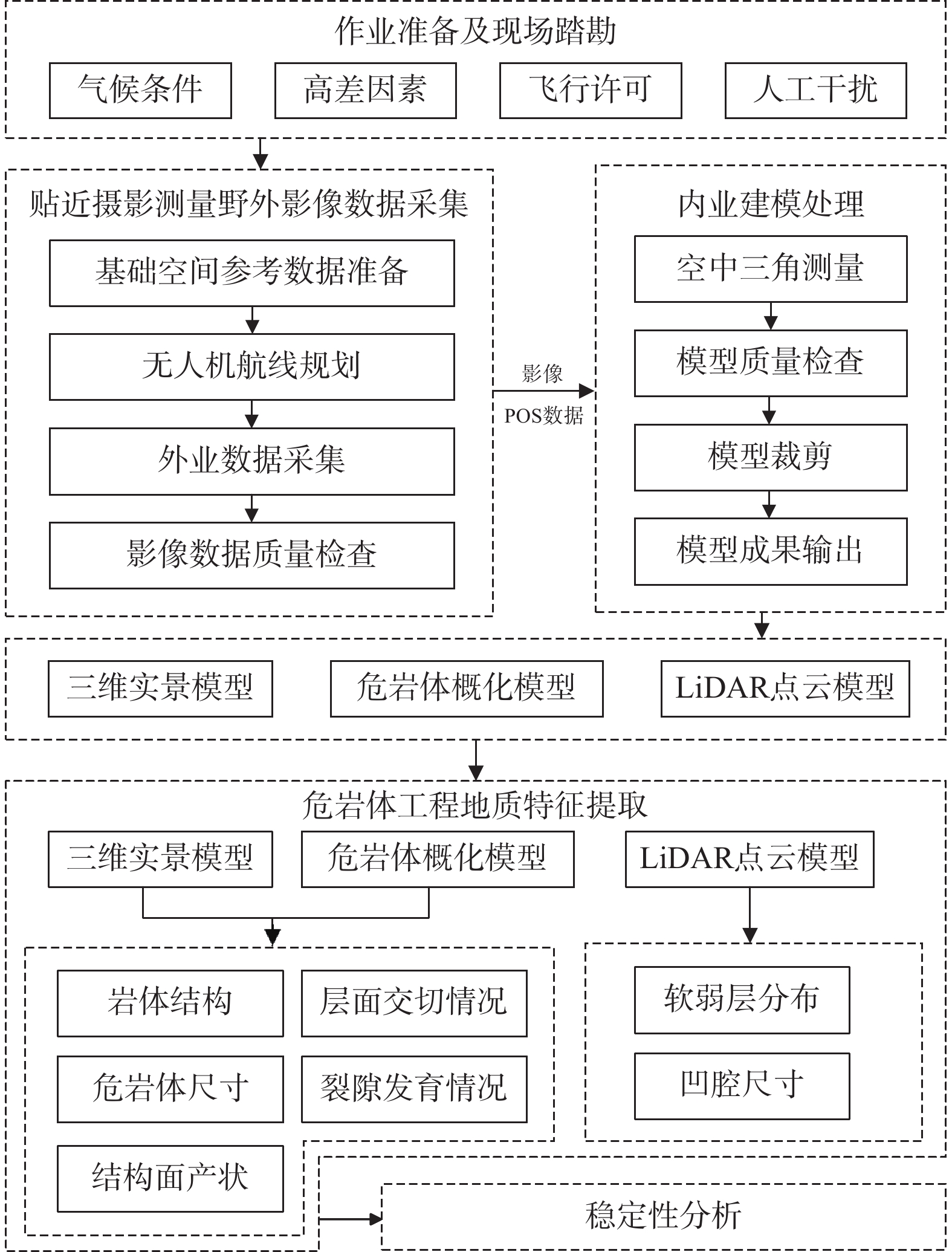
高陡危岩崩塌是我国山区常见的一种地质灾害,但由于通行困难等客观因素的限制,导致人工地质勘查工作效率低,安全风险高,存在调查死角。以三峡库区老鼠错3号高陡危岩体为例,融合无人机贴近摄影测量和机载LiDAR技术,建立了高陡危岩体调查分析方法体系。在此基础上,系统构建了老鼠错3号危岩体的三维地质模型,获取了该危岩体工程地质特征。研究显示老鼠错3号危岩体发育有5条控制结构面,软弱层最宽27.30 m,凹腔最深2.19 m,崩塌类型为倾倒式崩塌;危岩体稳定性系数在自然工况下为1.375,处于稳定状态,暴雨工况下为1.01,处于欠稳定状态,需进行治理。结果表明融合贴近摄影和LiDAR技术方法对高陡危岩体调查具有较好的互补性,可为高陡危岩体的非接触式测量、地质信息获取及稳定性分析提供一种新的调查思路,为库区的防灾减灾工作提供一定的技术支撑。
Abstract:The collapse of high-steep dangerous rock is a common geological disaster in the mountainous areas of China. However, due to the limitation of objective factors such as traffic difficulties, the efficiency of artificial geological exploration is low and the safety risk is high, and the investigation in some places is unreachable. Based on the Laoshucuo 3# high-steep dangerous rock mass in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, this study established an analysis method system of high-steep dangerous rock mass by integrating UAV nap-of-the-object photogrammetry and airborne LiDAR technology. The three-dimensional geological model of Laoshucuo 3# dangerous rock mass was constructed systematically, and the engineering geological characteristics of the dangerous rock mass were characterized. The results show that there are five structural planes in the dangerous rock mass of Laoshucuo 3#, with the widest weak layer of 27.30 m and the deepest cavity of 2.19 m. The collapse type is toppling collapse. The stability coefficient of the dangerous rock mass is 1.375 under the natural condition, which is in a stable state, and 1.01 under the rainstorm condition, which is in an unstable state and needs to be treated. The technical method in this study has good complementarity to the investigation of high-steep dangerous rock mass, providing a new investigation method for non-contact measurement, geological information acquisition, and stability analysis of high-steep dangerous rock mass, and technical support for disaster prevention and mitigation in the reservoir area.
-
Key words:
- low-altitude remote sensing /
- nap-of-the-object photogrammetry /
- LiDAR /
- unstable rock mass /
- stability
-

-
表 1 计算工况
Table 1. Calculation conditions
工况 受力情况 天然工况 自重 暴雨工况 自重+强降雨 -
[1] 葛大庆,戴可人,郭兆成,等. 重大地质灾害隐患早期识别中综合遥感应用的思考与建议[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):949 − 956. [GE Daqing,DAI Keren,GUO Zhaocheng,et al. Early identification of serious geological hazards with integrated remote sensing technologies:Thoughts and recommendations[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):949 − 956. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
GE Daqing, DAI Keren, GUO Zhaocheng, et al. Early identification of serious geological hazards with integrated remote sensing technologies: Thoughts and recommendations[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(7): 949 − 956. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 黄波林,殷跃平,李滨,等. 柱状危岩体坐落式崩塌产生涌浪的简化数值模型与校验[J]. 岩土力学,2021,42(8):2269 − 2278. [HUANG Bolin,YIN Yueping,LI Bin,et al. Simplified numerical model and verification for the impulse wave generated by situated collapse of a dangerous columnar rock mass[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2021,42(8):2269 − 2278. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HUANG Bolin, YIN Yueping, LI Bin, et al. Simplified numerical model and verification for the impulse wave generated by situated collapse of a dangerous columnar rock mass[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2021, 42(8): 2269 − 2278. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 许强,董秀军,李为乐. 基于天-空-地一体化的重大地质灾害隐患早期识别与监测预警[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):957 − 966. [XU Qiang,DONG Xiujun,LI Weile. Integrated space-air-ground early detection,monitoring and warning system for potential catastrophic geohazards[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):957 − 966. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
XU Qiang, DONG Xiujun, LI Weile. Integrated space-air-ground early detection, monitoring and warning system for potential catastrophic geohazards[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(7): 957 − 966. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 何佳男. 贴近摄影测量及其关键技术研究[D]. 武汉:武汉大学,2019. [HE Jianan. Nap-of-the-Object Photogrammetry and Its Key Techniques[D]. Wuhan:Wuhan University,2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HE Jianan. Nap-of-the-Object Photogrammetry and Its Key Techniques[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] WANG Wei,ZHAO Wenbo,CHAI Bo,et al. Discontinuity interpretation and identification of potential rockfalls for high-steep slopes based on UAV nap-of-the-object photogrammetry[J]. Computers mp; Geosciences,2022,166:105191.
[6] 梁京涛,铁永波,赵聪,等. 基于贴近摄影测量技术的高位崩塌早期识别技术方法研究[J]. 中国地质调查,2020,7(5):107 − 113. [LIANG Jingtao,TIE Yongbo,ZHAO Cong,et al. Technology and method research on the early detection of high-level collapse based on the nap-of-the-object photography[J]. Geological Survey of China,2020,7(5):107 − 113. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIANG Jingtao, TIE Yongbo, ZHAO Cong, et al. Technology and method research on the early detection of high-level collapse based on the nap-of-the-object photography[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2020, 7(5): 107 − 113. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 姚富潭,吴明堂,董秀军,等. 基于贴近摄影测量技术的高陡危岩体结构面调查方法[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2023,50(2):218 − 228. [YAO Futan,WU Mingtang,DONG Xiujun,et al. Investigation method of discontinuity in high and steep dangerous rock mass based on nap of the object photogrammetry[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition),2023,50(2):218 − 228. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2023.02.09
YAO Futan, WU Mingtang, DONG Xiujun, et al. Investigation method of discontinuity in high and steep dangerous rock mass based on nap of the object photogrammetry[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2023, 50(2): 218 − 228. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2023.02.09
[8] 贾虎军,王立娟,范冬丽. 无人机载LiDAR和倾斜摄影技术在地质灾害隐患早期识别中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(2):60 − 65. [JIA Hujun,WANG Lijuan,FAN Dongli. The application of UAV LiDAR and tilt photography in the early identification of geo-hazards[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(2):60 − 65. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
JIA Hujun, WANG Lijuan, FAN Dongli. The application of UAV LiDAR and tilt photography in the early identification of geo-hazards[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(2): 60 − 65. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 陈洁,高子弘,王珊珊,等. 三峡库区航空遥感地质调查技术发展综述[J]. 国土资源遥感,2020,32(2):1 − 10. [CHEN Jie,GAO Zihong,WANG Shanshan,et al. A review on the development of aerial remote sensing geological survey technology in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources,2020,32(2):1 − 10. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHEN Jie, GAO Zihong, WANG Shanshan, et al. A review on the development of aerial remote sensing geological survey technology in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 2020, 32(2): 1 − 10. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] GUILLAUME A S,LEEMPOEL K,ROCHAT E,et al. Multiscale very high resolution topographic models in alpine ecology:Pros and cons of airborne LiDAR and drone-based stereo-photogrammetry technologies[J]. Remote Sensing,2021,13(8):1588. doi: 10.3390/rs13081588
[11] ABU DABOUS S,AL-RUZOUQ R,LLORT D. Three-dimensional modeling and defect quantification of existing concrete bridges based on photogrammetry and computer aided design[J]. Ain Shams Engineering Journal,2023,14(12):102231. doi: 10.1016/j.asej.2023.102231
[12] 贾曙光,金爱兵,赵怡晴. 无人机摄影测量在高陡边坡地质调查中的应用[J]. 岩土力学,2018,39(3):1130 − 1136. [JIA Shuguang,JIN Aibing,ZHAO Yiqing. Application of UAV oblique photogrammetry in the field of geology survey at the high and steep slope[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2018,39(3):1130 − 1136. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
JIA Shuguang, JIN Aibing, ZHAO Yiqing. Application of UAV oblique photogrammetry in the field of geology survey at the high and steep slope[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(3): 1130 − 1136. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] LI Xiaolu,LIU Chang,WANG Zining,et al. Airborne LiDAR:State-of-the-art of system design,technology and application[J]. Measurement Science and Technology,2021,32(3):032002. doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/abc867
[14] LOWE D G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision,2004,60(2):91 − 110. doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94
[15] 宣程强,章杨松,许文涛. 基于数字表面模型的岩体结构面产状获取[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(1):75 − 83. [XUAN Chengqiang,ZHANG Yangsong,XU Wentao. Extraction of the discontinuity orientation from a digital surface model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(1):75 − 83. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
XUAN Chengqiang, ZHANG Yangsong, XU Wentao. Extraction of the discontinuity orientation from a digital surface model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(1): 75 − 83. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] DEROSE R C,GOMEZ B,MARDEN M,et al. Gully erosion in Mangatu Forest,New Zealand,estimated from digital elevation models[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,1998,23(11):1045 − 1053. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9837(1998110)23:11<1045::AID-ESP920>3.0.CO;2-T
[17] 吴秀坤,谭礼金,吴本林,等. 遥感技术在地质灾害调查、监测和防治中的应用[J]. 工程技术研究,2021,6(3):103 − 104. [WU Xiukun,TAN Lijin,WU Benlin,et al. Application of remote sensing technology in geological disaster investigation,monitoring and prevention[J]. Engineering and Technological Research,2021,6(3):103 − 104. (in Chinese)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3818.2021.03.044
WU Xiukun, TAN Lijin, WU Benlin, et al. Application of remote sensing technology in geological disaster investigation, monitoring and prevention[J]. Engineering and Technological Research, 2021, 6(3): 103 − 104. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3818.2021.03.044
[18] 徐画,陈建平,张权平,等. 无人机点云数据的危岩体结构信息提取[J]. 测绘科学,2021,46(7):137 − 144. [XU Hua,CHEN Jianping,ZHANG Quanping,et al. Application of UAV photogrammetry in investigation of high and steep dangerous rock mass[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping,2021,46(7):137 − 144. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
XU Hua, CHEN Jianping, ZHANG Quanping, et al. Application of UAV photogrammetry in investigation of high and steep dangerous rock mass[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2021, 46(7): 137 − 144. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 李长青,曹明兰,李亚东,等. 低空无人机航测露天矿三维重构方法与试验[J]. 测绘通报,2018(3):89 − 92. [LI Changqing,CAO Minglan,LI Yadong,et al. 3D reconstruction method and experiment of aerial survey of low-altitude uav for open-pit mine[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping,2018(3):89 − 92. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Changqing, CAO Minglan, LI Yadong, et al. 3D reconstruction method and experiment of aerial survey of low-altitude uav for open-pit mine[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2018(3): 89 − 92. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 邵延秀,张波,邹小波,等. 采用无人机载LiDAR进行快速地质调查实践[J]. 地震地质,2017,39(6):1185 − 1197. [SHAO Yanxiu,ZHANG Bo,ZOU Xiaobo,et al. Application of uavls to rapid geological surveys[J]. Seismology and Geology,2017,39(6):1185 − 1197. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2017.06.007
SHAO Yanxiu, ZHANG Bo, ZOU Xiaobo, et al. Application of uavls to rapid geological surveys[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2017, 39(6): 1185 − 1197. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2017.06.007
[21] 党杰,董吉,何松标,等. 机载LiDAR与地面三维激光扫描在贵州水城独家寨崩塌地质灾害风险调查中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(4):106 − 113. [DANG Jie,DONG Ji,HE Songbiao,et al. Application of airborne LiDAR and ground 3D laser scanning in geological hazard risk investigation of Dujiazhai collapse in Shuicheng,Guizhou[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(4):106 − 113. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
DANG Jie, DONG Ji, HE Songbiao, et al. Application of airborne LiDAR and ground 3D laser scanning in geological hazard risk investigation of Dujiazhai collapse in Shuicheng, Guizhou[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(4): 106 − 113. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 国家质量监督检验检疫总局,中国国家标准化管理委员会. 数字航空摄影测量 空中三角测量规范:GB/T 23236—2009[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社,2009. [General Administration of Quality Supervision,Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China,Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Specifications for aerotriangulation of digital aerophotogrammetry:GB/T 23236—2009[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China,2009. (in Chinese)]
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Specifications for aerotriangulation of digital aerophotogrammetry: GB/T 23236—2009[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2009. (in Chinese)
[23] DU Yixin,WAN Luhe,LI Xiaoyi,et al. High-precision DEM extraction by region segmentation-based progressive triangulation encryption filtering[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences,2021,14(6):415. doi: 10.1007/s12517-021-06635-0
[24] LI Wenyu. Application of multimedia tilt photogrammetry technology based on unmanned aerial vehicle in geological survey[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering,2022,2022:4616119.
[25] 郭健. 库水位波动下塔柱状危岩体失稳过程研究[D]. 宜昌:三峡大学,2021. [GUO Jian. Research on the Instability Process of Tower Rocks under the Fluctuation Levels of Water Reservoirs[D]. Yichang:China Three Gorges University,2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
GUO Jian. Research on the Instability Process of Tower Rocks under the Fluctuation Levels of Water Reservoirs[D]. Yichang: China Three Gorges University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 胡刘洋,张鹏,黄波林. 三峡库区消落带岩体劣化下危岩体长期变形破坏机理——以冠木岭为例[J]. 工程地质学报,2023,31(6):1891 − 1900. [HU Liuyang,ZHANG Peng,HUANG Bolin. Long-term deformation and failure mechanism of dangerous rock mass in water-level-fluctuation zone of Three Gorges Reservoir Area:A case study of guanmuling[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2023,31(6):1891 − 1900. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HU Liuyang, ZHANG Peng, HUANG Bolin. Long-term deformation and failure mechanism of dangerous rock mass in water-level-fluctuation zone of Three Gorges Reservoir Area: A case study of guanmuling[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2023, 31(6): 1891 − 1900. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] XIA Yuelin,FENG Xiating,YANG Chengxiang,et al. Mechanism of excavation-induced cracking of the protective layer of a rock bench in a large underground powerhouse under high tectonic stress[J]. Engineering Geology,2023,312:106951. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2022.106951
[28] 铁永波,徐伟,梁京涛,等. 川藏铁路卡子拉山滑坡发育特征与防灾减灾对策[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(5):129 − 136. [TIE Yongbo,XU Wei,LIANG Jingtao,et al. Characteristics of Kazila Mountain landslide and its mitigation measures on the Sichuan-Tibet Railway[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(5):129 − 136. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
TIE Yongbo, XU Wei, LIANG Jingtao, et al. Characteristics of Kazila Mountain landslide and its mitigation measures on the Sichuan-Tibet Railway[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(5): 129 − 136. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: