Landslide susceptibility evaluation based on FR-DNN coupling model: A case study on Yanyuan County
-
摘要:
盐源县位于青藏高原东南边缘,区域构造活动强烈,在内外动力共同作用下,境内滑坡灾害极其发育,已经造成了巨大的人员伤亡和经济损失,有必要开展滑坡易发性评价,对区域滑坡灾害进行科学管控。依据盐源县1∶5万地质灾害调查成果,选取高程、坡度、坡向、地形曲率、距断层距离、地层岩性、距水系距离、年平均降雨量、地形湿度指数、水流强度指数、归一化植被指数、距道路距离、土地利用类型等13个滑坡易发性评价因子,基于
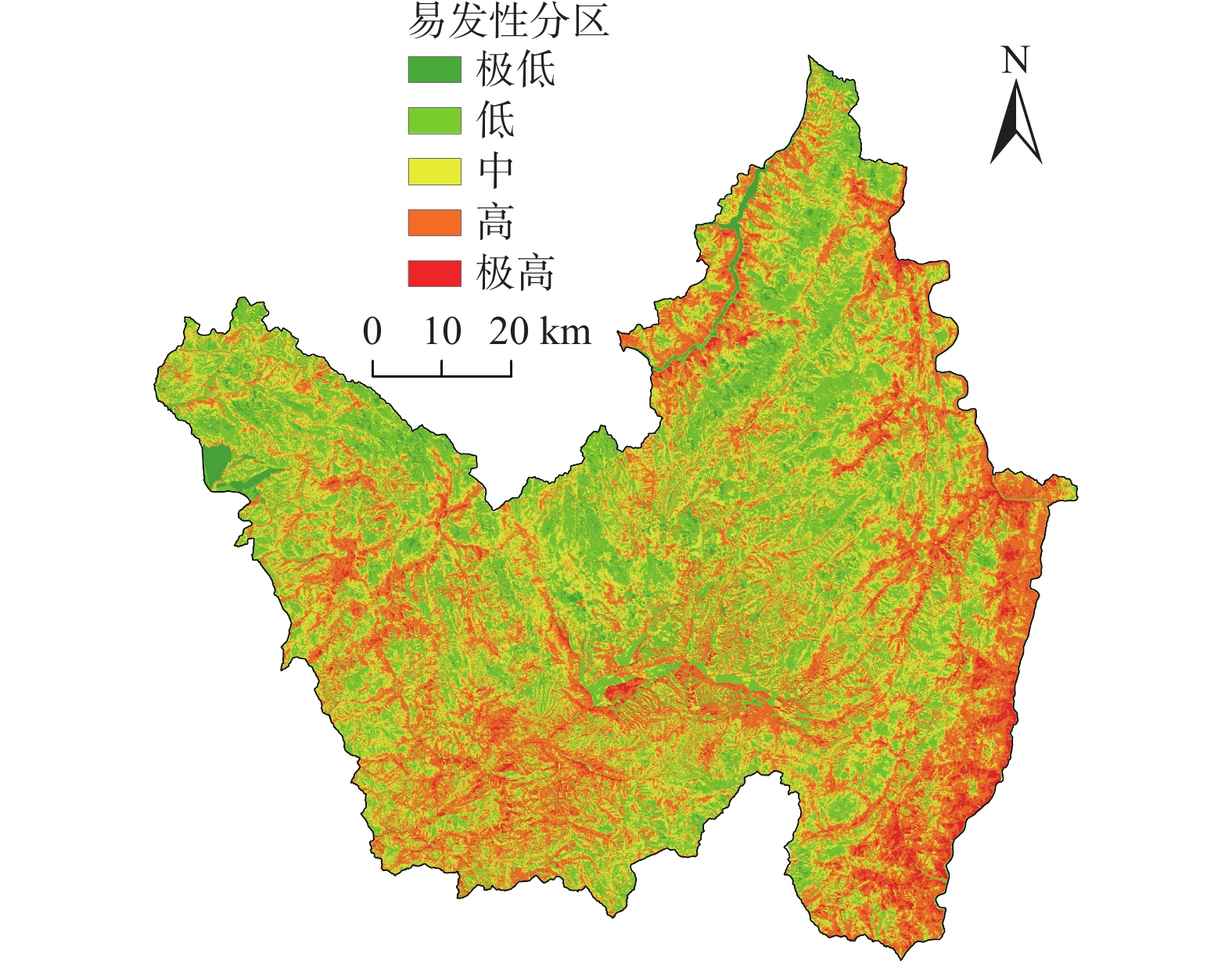
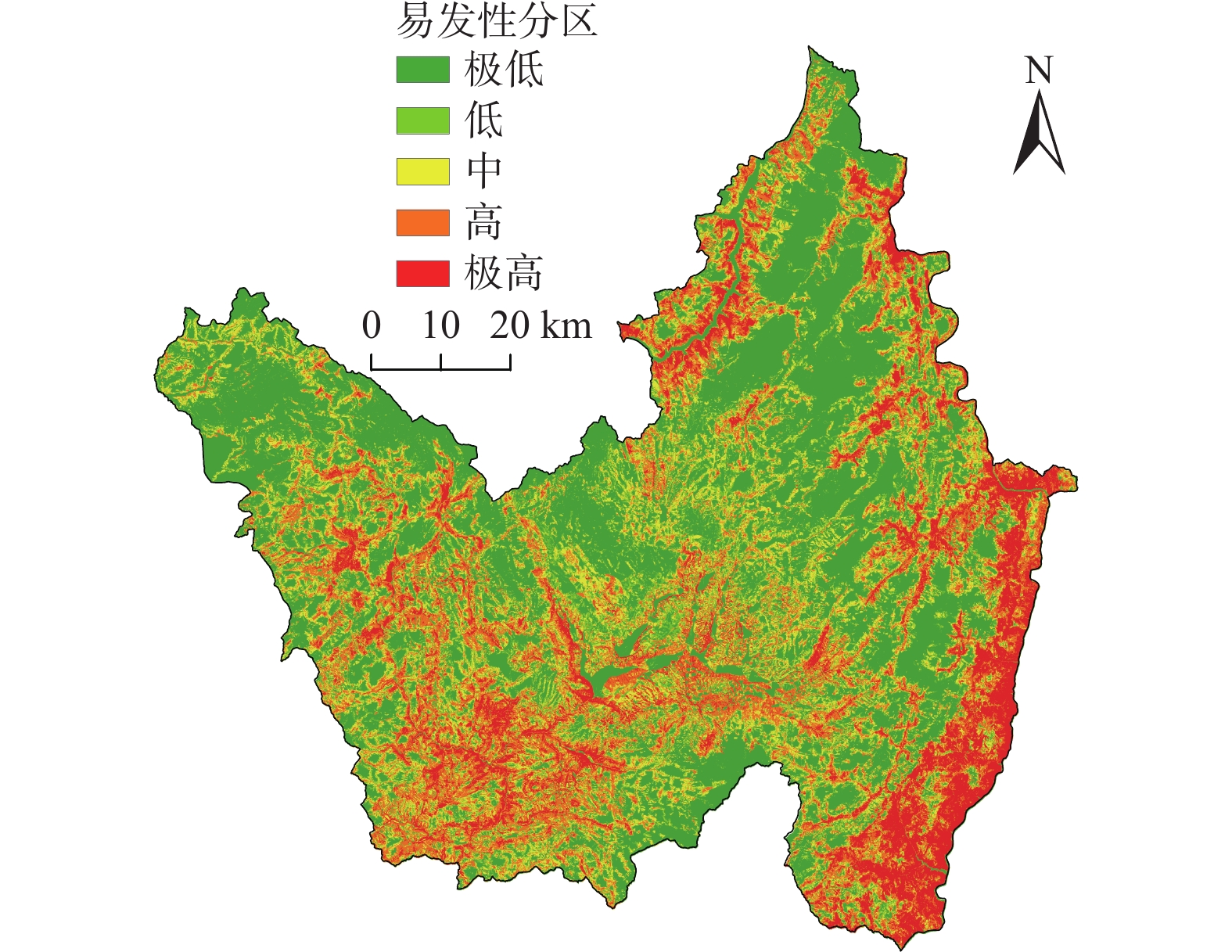
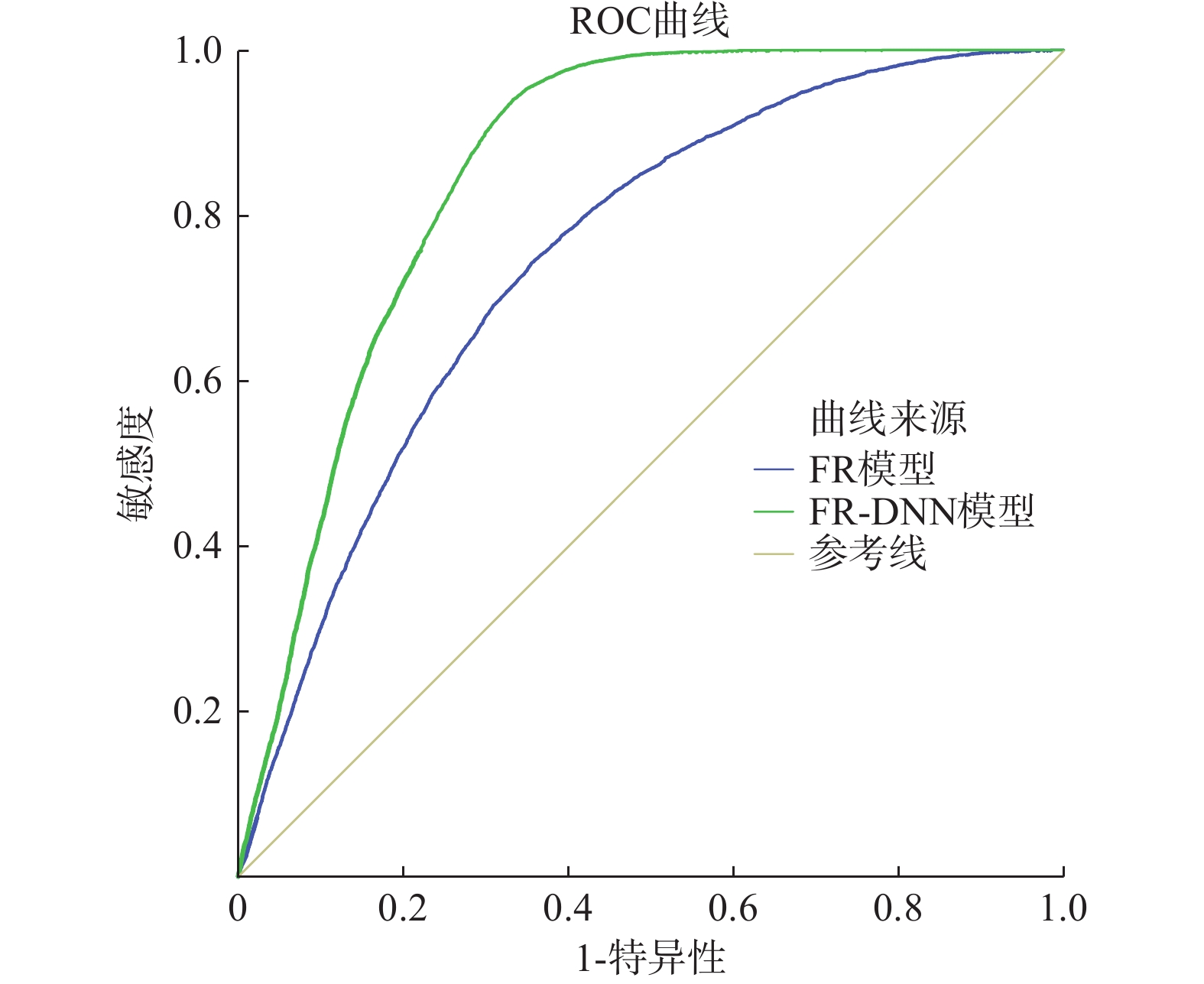
27596 个滑坡灾害栅格点数据,将传统频率比(frequency ratio,FR)模型定量分析及数据量化优势,与新兴深度神经网络(deep neural network,DNN)模型强大的非线性学习和拟合能力相结合,构建FR-DNN耦合模型进行滑坡易发性评价,将研究区划分为极高易发区、高易发区、中易发区、低易发区、极低易发区5个等级,面积占比分别为11.90%、18.38%、18.34%、9.13%、42.25%,并与传统FR模型进行对比,用ROC曲线的AUC值进行精度验证。结果表明,FR模型与FR-DNN耦合模型的AUC值分别为0.754、0.859,FR-DNN耦合模型相对于FR模型预测精度提高了10.5%,由此说明FR-DNN耦合模型具有更好的预测能力,更适用于研究区滑坡易发性评价。Abstract:Yanyuan County is located on the southeastern edge of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, with strong regional tectonic activities. Under the internal and external dynamics actions, landslide disasters are extremely developed in the country, which has caused huge casualties and economic losses. It is necessary to carry out landslide susceptibility assessment and then control the regional landslide disasters scientifically. Based on the 1∶
50000 geological disaster survey in Yanyuan County, this study selected 13 landslide susceptibility evaluation factors, including elevation, slope, slope direction, terrain curvature, distance from fault, stratigraphic lithology, distance from water body, average annual rainfall, topographic wetness index, stream power index, normalized difference vegetation index, distance from road, and land use type. Based on27596 grid points of landslide disaster data, combining the traditional Frequency Ratio (FR) model with the advantages of quantitative analysis and data quantification and the emerging Deep Neural Network (DNN) model with the powerful nonlinear learning and fitting ability, The FR-DNN coupling model was constructed to evaluate landslide susceptibility. The study area is divided into five levels: extremely high susceptibility area, high susceptibility area, medium susceptibility area, low susceptibility area, and extremely low susceptibility area, with an area percentage of 11.90%, 18.38%, 18.34%, 9.13%, and 42.25%, respectively. The accuracy was verified by the AUC value of the ROC curve. The AUC values of the FR model and the FR-DNN coupling model are 0.754 and 0.859, respectively. The prediction accuracy of the FR-DNN coupling model is improved by 10.5% compared with that of the FR model, indicating that the FR-DNN coupling model has better prediction ability and is more suitable for landslide susceptibility evaluation in the study area.-
Key words:
- landslide /
- frequency ratio method /
- deep neural network /
- susceptibility
-

-
表 1 Pearson相关性分析
Table 1. Pearson correlation analysis
评价因子 高程 坡度 坡向 地形
起伏度地形
曲率距断层
距离地层
岩性距水系
距离年平均
降雨量TWI SPI NDVI 距道路
距离土地利用
类型高程 1 坡度 −0.02 1 坡向 0.06 0.13 1 地形起伏度 −0.03 0.78 0.09 1 地形曲率 0.01 0.33 0.00 0.02 1 距断层距离 0.18 −0.15 −0.01 −0.09 0.00 1 地层岩性 −0.35 −0.19 −0.09 −0.12 0.00 0.04 1 距水系距离 0.34 −0.11 0.03 −0.11 −0.03 0.02 −0.16 1 年平均降雨量 0.22 0.15 0.04 0.12 0.02 0.00 −0.08 −0.03 1 TWI −0.11 −0.48 −0.29 −0.33 −0.26 0.11 0.21 0.00 −0.13 1 SPI −0.01 0.44 −0.20 0.30 −0.28 −0.11 −0.17 −0.02 0.10 0.00 1 NDVI 0.14 0.29 −0.09 0.20 0.00 −0.09 −0.09 0.02 0.20 −0.21 0.20 1 距道路距离 0.24 0.24 0.02 0.19 0.02 0.03 −0.19 0.10 0.02 −0.12 0.10 0.09 1 土地利用类型 −0.83 −0.09 0.00 −0.06 −0.03 0.06 0.08 0.00 0.02 0.06 0.00 −0.23 −0.13 1 表 2 各评价因子频率比值
Table 2. Frequency ratios of various evaluation factors
评价因子 分级 频率比 赋值 滑坡易发性指数 评价因子 分级 频率比 赋值 滑坡易发性指数 高程/m < 1500 8.5747 4 11.1237 年平均降雨量/mm [890,984) 0.4341 2 3.0467 [ 1500 ,2500 )2.2051 3 [984, 1078 )1.5039 4 [ 2500 ,3500 )0.3439 2 [ 1078 ,1172 )0.6866 3 ≥ 3500 0.0000 1 [ 1172 ,1278 ]0.4222 1 坡度/(°) [0,15) 0.9418 3 4.3800 地形湿度指数 [0.8,4.7) 0.7858 3 3.9352 [15,25) 1.7588 5 [4.7,7.1) 1.2536 4 [25,35) 0.9775 4 [7.1,11.3) 1.3801 5 [35,45) 0.4331 2 [11.3,16.2) 0.3212 2 ≥45 0.2688 1 [16.2,30.8] 0.1945 1 坡向/(°) 平面 0.2070 1 8.5809 水流强度指数 [−10.4,−2.4) 0.2057 1 4.2803 北 1.1573 8 [−2.4,2.4) 0.9672 3 东北 1.1432 7 [2.4,4.2) 0.9947 4 东 1.1349 6 [4.2,6.8) 1.2303 5 东南 1.0428 5 [6.8,19.8] 0.8825 2 南 1.0136 4 归一化植被指数 [0,0.2) 0.0000 1 3.8407 西南 0.8851 3 [0.2,0.4) 0.6901 3 西 0.8389 2 [0.4,0.6) 1.6129 5 西北 1.1582 9 [0.6,0.8) 1.0796 4 地形曲率 <0 1.1118 3 2.7600 [0.8,1] 0.4581 2 0 0.6610 1 距道路距离/m <100 1.9028 6 4.3969 >0 0.9872 2 [100,200) 1.2285 5 距断层距离/m <500 1.5481 5 5.4673 [200,300) 0.5030 4 [500, 1000 )1.3203 4 [300,400) 0.4139 3 [ 1000 ,1500 )0.8863 2 [400,500) 0.2298 2 [ 1500 ,2000 )1.0683 3 ≥500 0.1189 1 ≥ 2000 0.6442 1 土地利用类型 水体 0.0000 1 11.6200 地层岩性 硬岩 0.6593 1 3.7818 林地 0.1849 2 软硬相间 1.7231 3 淹没植被 0.0000 1 软岩 1.3994 2 耕地 1.0825 3 距水系距离/m <500 1.8563 5 4.1476 建筑 8.7269 5 [500, 1000 )1.0599 4 雪/冰 0.0000 1 [ 1000 ,1500 )0.5320 3 裸地 1.6258 4 [ 1500 ,2000 )0.3891 2 ≥ 2000 0.3103 1 -
[1] 黄润秋. 20世纪以来中国的大型滑坡及其发生机制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2007,26(3):433 − 454. [HUANG Runqiu. Large-scale landslides and their sliding mechanisms in China since the 20th century[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2007,26(3):433 − 454. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.03.001
HUANG Runqiu. Large-scale landslides and their sliding mechanisms in China since the 20th century[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 26(3): 433 − 454. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.03.001
[2] 殷跃平. 中国地质灾害减灾战略初步研究[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2004,15(2):1 − 8. [YIN Yueping. Initial study on the hazard-relief strategy of geological hazard in China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2004,15(2):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2004.02.001
YIN Yueping. Initial study on the hazard-relief strategy of geological hazard in China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2004, 15(2): 1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2004.02.001
[3] 余祥伟. 盐源地区雷达遥感滑坡灾害识别与形变监测研究[D]. 成都:成都理工大学,2021. [YU Xiangwei. Research on radar remote sensing landslide disaster identification and deformation monitoring in Yanyuan area [D]. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Technology,2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YU Xiangwei. Research on radar remote sensing landslide disaster identification and deformation monitoring in Yanyuan area [D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 孙长明,马润勇,尚合欣,等. 基于滑坡分类的西宁市滑坡易发性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(3):173 − 181. [SUN Changming,MA Runyong,SHANG Hexin,et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment in Xining based on landslide classification[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(3):173 − 181. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
SUN Changming, MA Runyong, SHANG Hexin, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment in Xining based on landslide classification[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(3): 173 − 181. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] POURGHASEMI H R,PRADHAN B,GOKCEOGLU C,et al. Application of weights-of-evidence and certainty factor models and their comparison in landslide susceptibility mapping at Haraz watershed,Iran[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences,2013,6(7):2351 − 2365. doi: 10.1007/s12517-012-0532-7
[6] 张艳玲,南征兵,周平根. 利用证据权法实现滑坡易发性区划[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2012,39(2):121 − 125. [ZHANG Yanling,NAN Zhengbing,ZHOU Pinggen. Division of landslide susceptibility based on weights of evidence model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2012,39(2):121 − 125. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Yanling, NAN Zhengbing, ZHOU Pinggen. Division of landslide susceptibility based on weights of evidence model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2012, 39(2): 121 − 125. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] PANCHAL S,SHRIVASTAVA A K. Landslide hazard assessment using analytic hierarchy process (AHP):A case study of National Highway 5 in India[J]. Ain Shams Engineering Journal,2022,13(3):101626. doi: 10.1016/j.asej.2021.10.021
[8] 杜国梁,杨志华,袁颖,等. 基于逻辑回归-信息量的川藏交通廊道滑坡易发性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(5):102 − 111. [DU Guoliang,YANG Zhihua,YUAN Ying,et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping in the Sichuan-Tibet traffic corridor using logistic regression-information value method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(5):102 − 111. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
DU Guoliang, YANG Zhihua, YUAN Ying, et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping in the Sichuan-Tibet traffic corridor using logistic regression-information value method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(5): 102 − 111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 胡涛. 贵州省思南县地质灾害危险性评价研究[D]. 武汉:中国地质大学,2020. [HU Tao. Study of Geological Disasters Hazard Assessment in Sinan County of Guizhou Province[D]. Wuhan:China University of Geosciences,2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HU Tao. Study of Geological Disasters Hazard Assessment in Sinan County of Guizhou Province[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 刘福臻,王灵,肖东升. 机器学习模型在滑坡易发性评价中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(6):98 − 106. [LIU Fuzhen,WANG Ling,XIAO Dongsheng. Application of machine learning model in landslide susceptibility evaluation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(6):98 − 106. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Fuzhen, WANG Ling, XIAO Dongsheng. Application of machine learning model in landslide susceptibility evaluation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(6): 98 − 106. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] TEHRANI F S,CALVELLO M,LIU Zhongqiang,et al. Machine learning and landslide studies:Recent advances and applications[J]. Natural Hazards,2022,114(2):1197 − 1245. doi: 10.1007/s11069-022-05423-7
[12] AGEENKO A,HANSEN L C,LYNG K L,et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping using machine learning:A Danish case study[J]. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information,2022,11(6):324. doi: 10.3390/ijgi11060324
[13] KIM J C,LEE Sunmin,JUNG H S,et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping using random forest and boosted tree models in Pyeong-Chang,Korea[J]. Geocarto International,2018,33(9):1000 − 1015. doi: 10.1080/10106049.2017.1323964
[14] XIE Wei,NIE Wen,SAFFARI P,et al. Landslide hazard assessment based on Bayesian optimization–support vector machine in Nanping City,China[J]. Natural Hazards,2021,109(1):931 − 948. doi: 10.1007/s11069-021-04862-y
[15] 张林梵,王佳运,张茂省,等. 基于BP神经网络的区域滑坡易发性评价[J]. 西北地质,2022,55(2):260 − 270. [ZHANG Linfan,WANG Jiayun,ZHANG Maosheng,et al. Evaluation of regional landslide susceptibility assessment based on BP neural network[J]. Northwestern Geology,2022,55(2):260 − 270. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Linfan, WANG Jiayun, ZHANG Maosheng, et al. Evaluation of regional landslide susceptibility assessment based on BP neural network[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2022, 55(2): 260 − 270. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] YAO Jingyu,QIN Shengwu,QIAO Shuangshuang,et al. Assessment of landslide susceptibility combining deep learning with semi-supervised learning in Jiaohe County,Jilin Province,China[J]. Applied Sciences,2020,10(16):5640. doi: 10.3390/app10165640
[17] HUANG Faming,YAO Chi,LIU Weiping,et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment in the Nantian Area of China:A comparison of frequency ratio model and support vector machine[J]. Geomatics,Natural Hazards and Risk,2018,9(1):919 − 938. doi: 10.1080/19475705.2018.1482963
[18] 王世宝,庄建琦,郑佳,等. 基于深度学习的CZ铁路康定—理塘段滑坡易发性评价[J]. 工程地质学报,2022,30(3):908 − 919. [WANG Shibao,ZHUANG Jianqi,ZHENG Jia,et al. Landslide susceptibility evaluation based on deep learning along Kangding-Litang section of cz railway[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2022,30(3):908 − 919. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Shibao, ZHUANG Jianqi, ZHENG Jia, et al. Landslide susceptibility evaluation based on deep learning along Kangding-Litang section of cz railway[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2022, 30(3): 908 − 919. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 王毅,方志策,牛瑞卿,等. 基于深度学习的滑坡灾害易发性分析[J]. 地球信息科学学报,2021,23(12):2244 − 2260. [WANG Yi,FANG Zhice,NIU Ruiqing,et al. Landslide susceptibility analysis based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science,2021,23(12):2244 − 2260. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.12082/dqxxkx.2021.210057
WANG Yi, FANG Zhice, NIU Ruiqing, et al. Landslide susceptibility analysis based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 2021, 23(12): 2244 − 2260. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12082/dqxxkx.2021.210057
[20] 郭子正,殷坤龙,黄发明,等. 基于滑坡分类和加权频率比模型的滑坡易发性评价[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2019,38(2):287 − 300. [GUO Zizheng,YIN Kunlong,HUANG Faming,et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility based on landslide classification and weighted frequency ratio model[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2019,38(2):287 − 300. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
GUO Zizheng, YIN Kunlong, HUANG Faming, et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility based on landslide classification and weighted frequency ratio model[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2019, 38(2): 287 − 300. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] HONG Haoyuan,CHEN Wei,XU Chong,et al. Rainfall-induced landslide susceptibility assessment at the Chongren Area (China) using frequency ratio,certainty factor,and index of entropy[J]. Geocarto International,2016:1-16.
[22] AKINCI H,YAVUZ OZALP A. Landslide susceptibility mapping and hazard assessment in Artvin (Turkey) using frequency ratio and modified information value model[J]. Acta Geophysica,2021,69(3):725 − 745. doi: 10.1007/s11600-021-00577-7
[23] 庄育龙,田原,程楚云. 基于深度神经网络的滑坡危险性评价——以深圳市为例[J]. 地理与地理信息科学,2019,35(2):104 − 110. [ZHUANG Yulong,TIAN Yuan,CHENG Chuyun. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on deep neural network:A case study of Shenzhen[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science,2019,35(2):104 − 110. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0504.2019.02.016
ZHUANG Yulong, TIAN Yuan, CHENG Chuyun. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on deep neural network: A case study of Shenzhen[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 2019, 35(2): 104 − 110. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0504.2019.02.016
[24] 吴常润,角媛梅,王金亮,等. 基于频率比-逻辑回归耦合模型的双柏县滑坡易发性评价[J]. 自然灾害学报,2021,30(4):213 − 224. [WU Changrun,JIAO Yuanmei,WANG Jinliang,et al. Frequency ratio and logistic regression models based coupling analysis for susceptibility of landslide in Shuangbai County[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2021,30(4):213 − 224. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WU Changrun, JIAO Yuanmei, WANG Jinliang, et al. Frequency ratio and logistic regression models based coupling analysis for susceptibility of landslide in Shuangbai County[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2021, 30(4): 213 − 224. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] ITO R,NAKAE K,HATA J,et al. Semi-supervised deep learning of brain tissue segmentation[J]. Neural Networks,2019,116:25 − 34. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2019.03.014
[26] REICHENBACH P,ROSSI M,MALAMUD B D,et al. A review of statistically-based landslide susceptibility models[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2018,180:60 − 91. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.03.001
[27] 王进,郭靖,王卫东,等. 权重线性组合与逻辑回归模型在滑坡易发性区划中的应用与比较[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2012,43(5):1932 − 1939. [WANG Jin,GUO Jing,WANG Weidong,et al. Application and comparison of weighted linear combination model and logistic regression model in landslide susceptibility mapping[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology),2012,43(5):1932 − 1939. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Jin, GUO Jing, WANG Weidong, et al. Application and comparison of weighted linear combination model and logistic regression model in landslide susceptibility mapping[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2012, 43(5): 1932 − 1939. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 张钟远,邓明国,徐世光,等. 镇康县滑坡易发性评价模型对比研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2022,41(1):157 − 171. [ZHANG Zhongyuan,DENG Mingguo,XU Shiguang,et al. Comparison of landslide susceptibility assessment models in Zhenkang County,Yunnan Province,China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2022,41(1):157 − 171. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Zhongyuan, DENG Mingguo, XU Shiguang, et al. Comparison of landslide susceptibility assessment models in Zhenkang County, Yunnan Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2022, 41(1): 157 − 171. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 张洪吉,赵铮,陈建华,等. 面向滑坡危险性评价的深度一维卷积神经网络方法——以四川省芦山县为例[J]. 自然灾害学报,2021,30(3):191 − 198. [ZHANG Hongji,ZHAO Zheng,CHEN Jianhua,et al. A deep one-dimensional convolutional neural network method for landslide risk assessment:A case study in Lushan,Sichuan,China[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2021,30(3):191 − 198. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Hongji, ZHAO Zheng, CHEN Jianhua, et al. A deep one-dimensional convolutional neural network method for landslide risk assessment: A case study in Lushan, Sichuan, China[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2021, 30(3): 191 − 198. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 闫举生,谭建民. 基于不同因子分级法的滑坡易发性评价——以湖北远安县为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(1):52 − 60. [YAN Jusheng,TAN Jianmin. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on different factor classification methods:A case study in Yuan’an County of Hubei Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(1):52 − 60. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YAN Jusheng, TAN Jianmin. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on different factor classification methods: A case study in Yuan’an County of Hubei Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2019, 30(1): 52 − 60. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] COSTACHE R,NGO P T T,BUI D T. Novel ensembles of deep learning neural network and statistical learning for flash-flood susceptibility mapping[J]. Water,2020,12(6):1549. doi: 10.3390/w12061549
[32] LEE Sunmin,BAEK W K,JUNG H S,et al. Susceptibility mapping on urban landslides using deep learning approaches in Mt. Umyeon[J]. Applied Sciences,2020,10(22):8189. doi: 10.3390/app10228189
[33] 刘坚,李树林,陈涛. 基于优化随机森林模型的滑坡易发性评价[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2018,43(7):1085 − 1091. [LIU Jian,LI Shulin,CHEN Tao. Landslide susceptibility assesment based on optimized random forest model[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2018,43(7):1085 − 1091. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Jian, LI Shulin, CHEN Tao. Landslide susceptibility assesment based on optimized random forest model[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2018, 43(7): 1085 − 1091. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[34] 任敬,范宣梅,赵程,等. 贵州省都匀市滑坡易发性评价研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(5):165 − 172. [REN Jing,FAN Xuanmei,ZHAO Cheng,et al. Evaluation of the landslide vulnerability in Duyun of Guizhou Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(5):165 − 172. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
REN Jing, FAN Xuanmei, ZHAO Cheng, et al. Evaluation of the landslide vulnerability in Duyun of Guizhou Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2018, 45(5): 165 − 172. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[35] LIU Yanrong,MENG Zhongqiu,ZHU Lei,et al. Optimizing the sample selection of machine learning models for landslide susceptibility prediction using information value models in the Dabie Mountain Area of Anhui,China[J]. Sustainability,2023,15(3):1971. doi: 10.3390/su15031971
-




 下载:
下载: