Current situation and scientific challenge of soil and water erosion in Gully Consolidation and Highland Protection Project of DongZhi Loess Plateau
-
摘要:
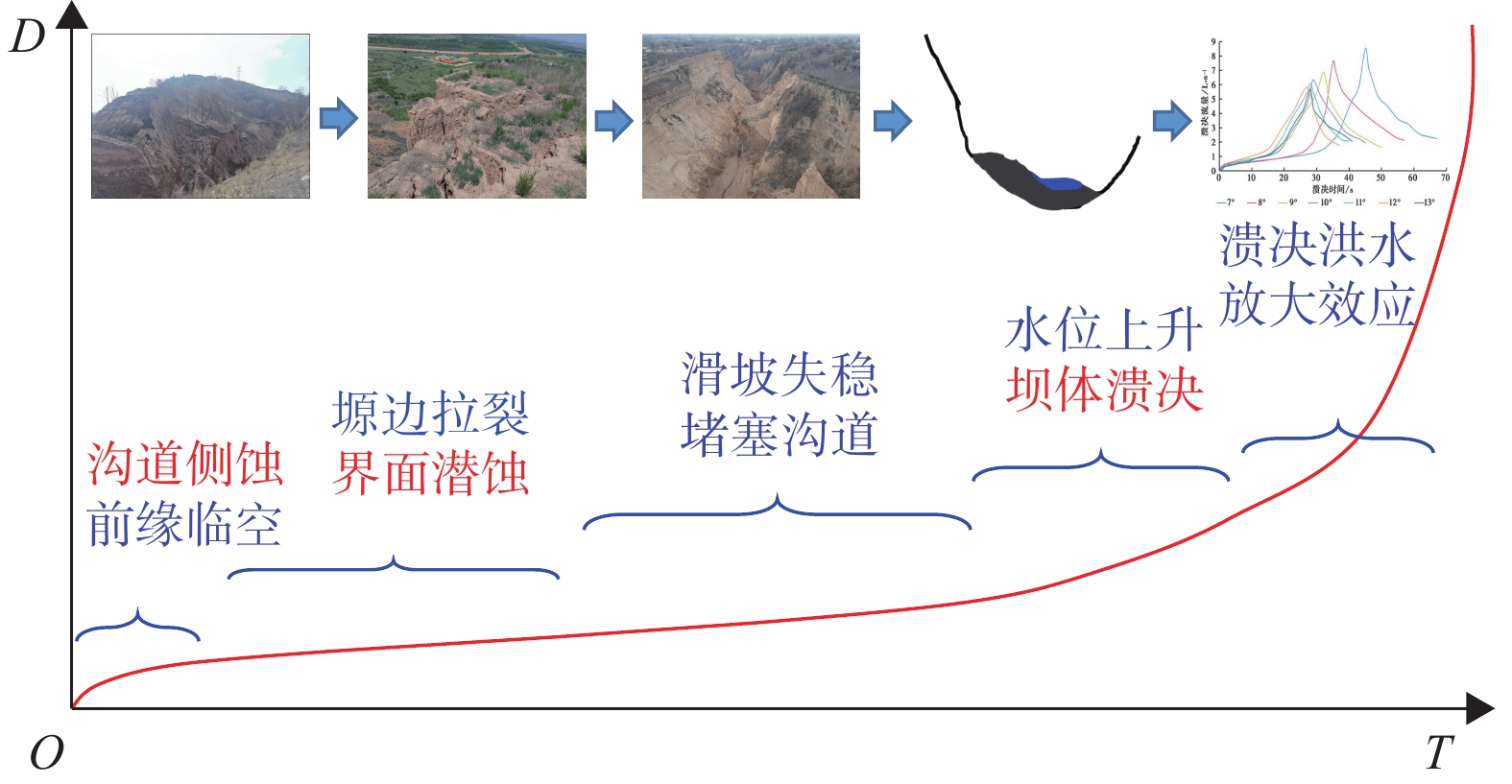
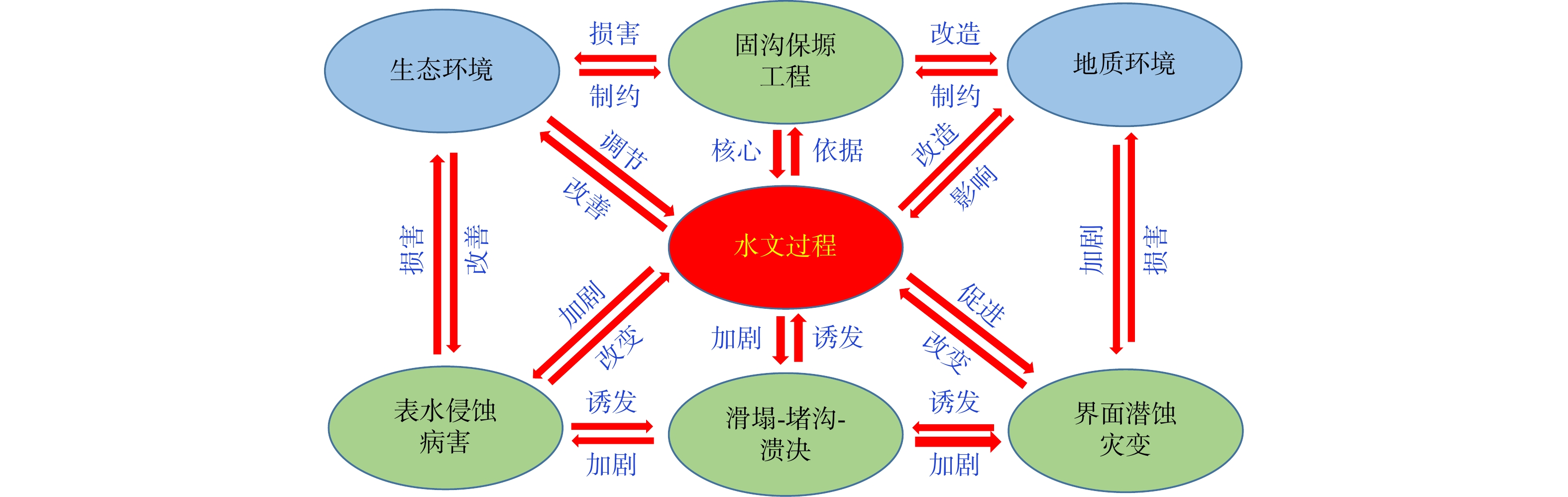
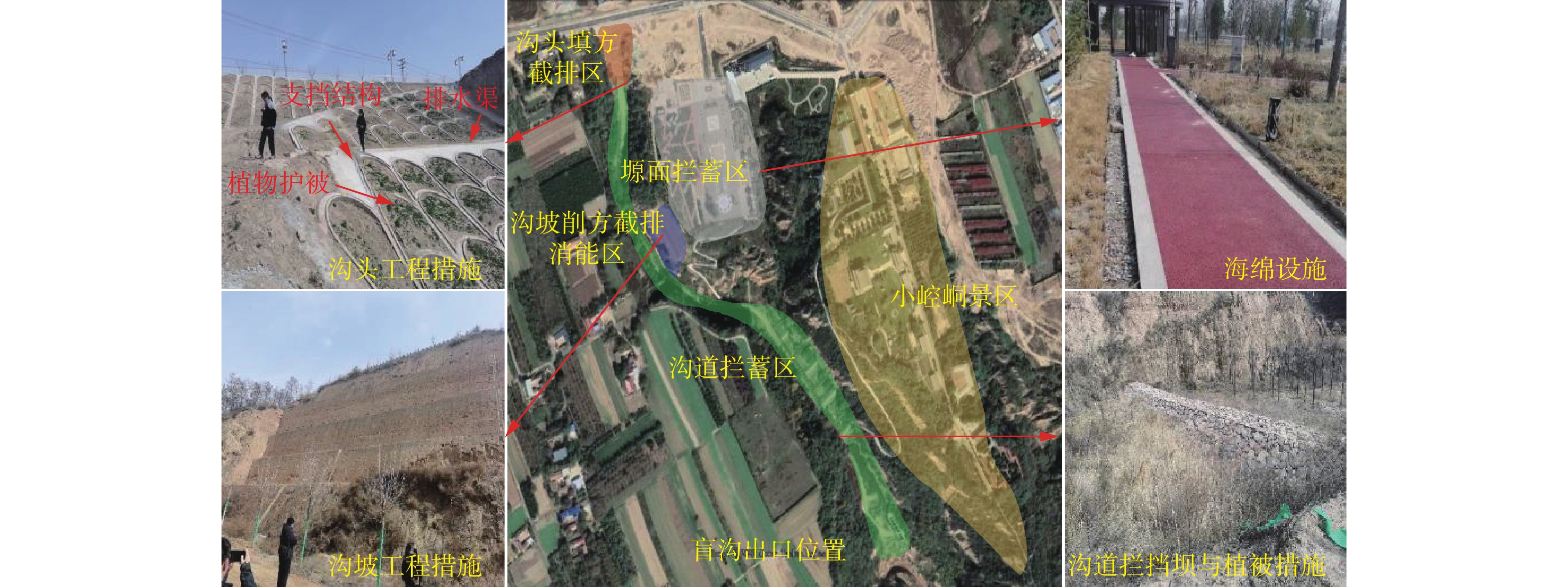
由于极端降雨和高强度人类工程活动的影响,黄土塬区沟头前进速度加剧,严重威胁黄土塬区经济社会发展。近年来实施的大规模固沟保塬工程虽然有效抑制了黄土塬区溯源侵蚀的发展,但是仍然存在严重的水土侵蚀病害问题。基于这一现状,以陇东黄土高原董志塬地区典型固沟保塬工程为研究对象,通过野外实地考察、查阅文献和综合分析等研究方法,对董志塬地区典型固沟保塬工程水土侵蚀病害进行调查分析。结果表明:固沟保塬工程水文调控功能可分为塬面拦蓄区、沟头填方截排区、沟坡削方截排消能区和沟道拦蓄区;固沟保塬工程目前遭受表水侵蚀病害、黄土工程地质界面潜蚀病害、截排水渠淤积堵塞病害及黄土沟谷灾害链等4大类病害;固沟保塬工程水文调控机制不明和水土互馈侵蚀灾变机理不清是当前面临的关键科学挑战;未来固沟保塬工程水土侵蚀病害的防治应重视生物土壤结皮、新型土壤改良材料的研发应用以及固沟保塬工程全过程质量监督。研究成果可为未来固沟保塬工程水土侵蚀灾变机理研究和工程规划设计提供借鉴。
Abstract:Due to the influence of extreme rainfall and high intensity human engineering activities, the advance speed of the gully head in the Loess Tableland is intensified, which seriously threatens the economic and social development of the Loess Tableland. In recent years, although large-scale Gully Consolidation and Highland Protection (GCHP) projects have effectively inhibited the development of traceable erosion on Loess tableland, there are still serious problems of soil and water erosion. Based on this situation, this study investigated and analyzed the soil erosion diseases of the typical GCHP Projects through field investigation, literature review, and comprehensive analysis. The results show that the hydrology regulation function of GCHP Projects can be divided into the table-land intercept area, gully head cut row area, gully slope cutting line of energy dissipation, and channel held area. Currently, the GCHP suffers from surface water erosion, subsurface erosion of loess engineering geological interface, blockage of drainage channels, and disaster chain of loess gully. The unclear hydrological control mechanism and the mechanism of soil and water mutual feeding erosion disasters are the key scientific challenges of the project. In the future, attention should be paid to the application of biological soil crust, new soil improvement materials, and the complete quality supervision of gully protection tableland engineering. This study can provide basic information for future research on the mechanism of soil and water erosion disasters and engineering planning and design of the Gugou Plateau.
-

-
表 1 典型固沟保塬工程水土侵蚀病害发育特征统计表
Table 1. Development characteristics of soil and water erosion diseases in typical GCHP
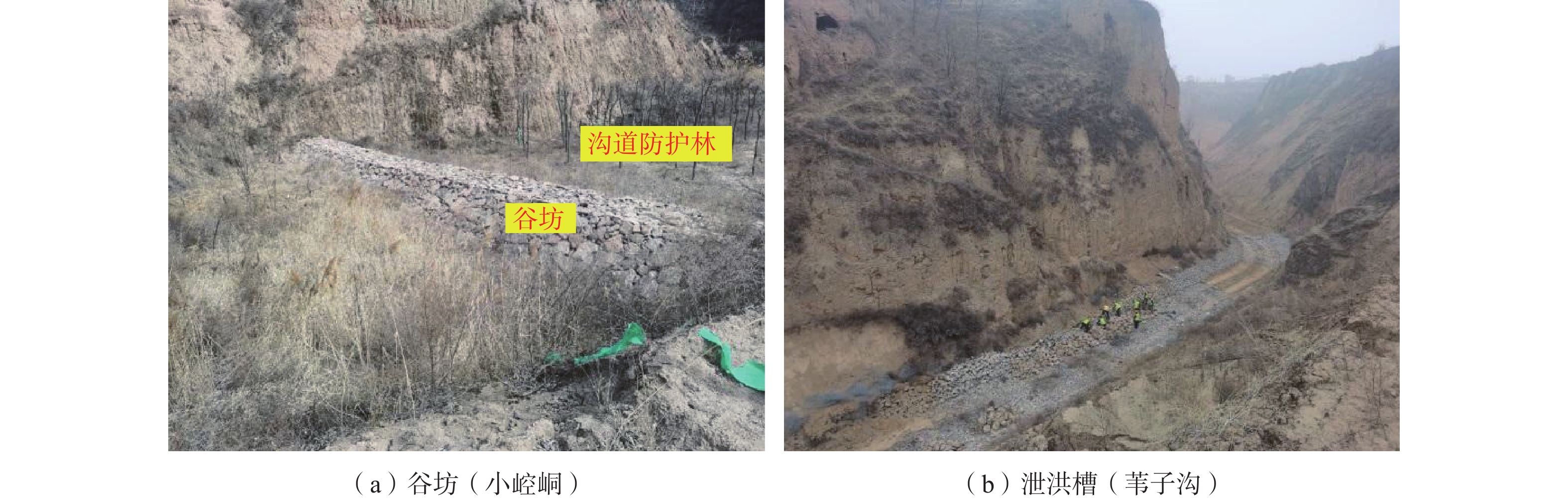
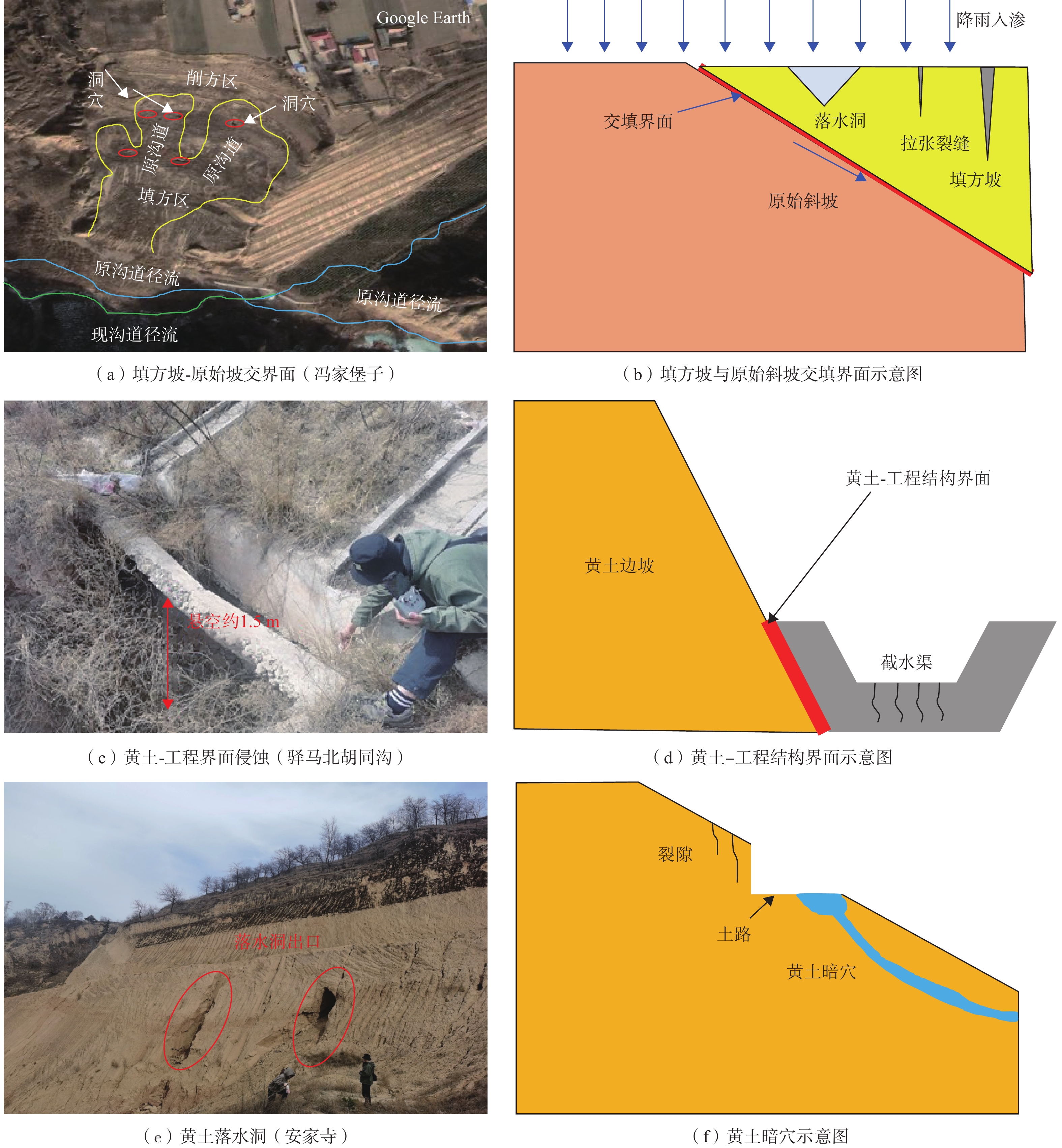
工程地点 沟头高程/m 塬面拦蓄区 沟头填方截排区 沟坡削方截排区 沟道拦蓄区 冯家堡子 1343 1.塬边裂缝
2.塬边落水洞发育1.填方体沉降开裂
2.落水洞发育
3.冲沟发育1.差异性侵蚀
2.浅层滑移
3.截排水渠淤积堵塞1.截排水渠潜蚀悬空
2.淤积堵塞
3.侧蚀滑塌堵沟小崆峒沟 1354 新建海绵设施未见明显病害 1.表水冲沟侵蚀发育
2.轻微界面潜蚀1.冲沟侵蚀极为发育
2.界面潜蚀发育
3.局部浅层滑塌1.多处小型重力失稳
2.大规模边坡滑塌堵沟
3.泄洪渠侵蚀悬空折断火巷沟 1364 1.沉降变形明显
2.未见落水洞1.表水冲沟侵蚀发育
2.界面潜蚀发育
3.溯源侵蚀致路面悬空1.冲沟侵蚀发育
2.界面潜蚀发育
3.局部浅层滑塌1.多处小规模滑塌
2.沟坡削方堆积体滑移驿马沟 1481 1.沉降变形
2.未见落水洞1.表水冲沟侵蚀发育
2.界面潜蚀发育1.苔藓发育较好,未见明显病害 1.截排水渠潜蚀悬空
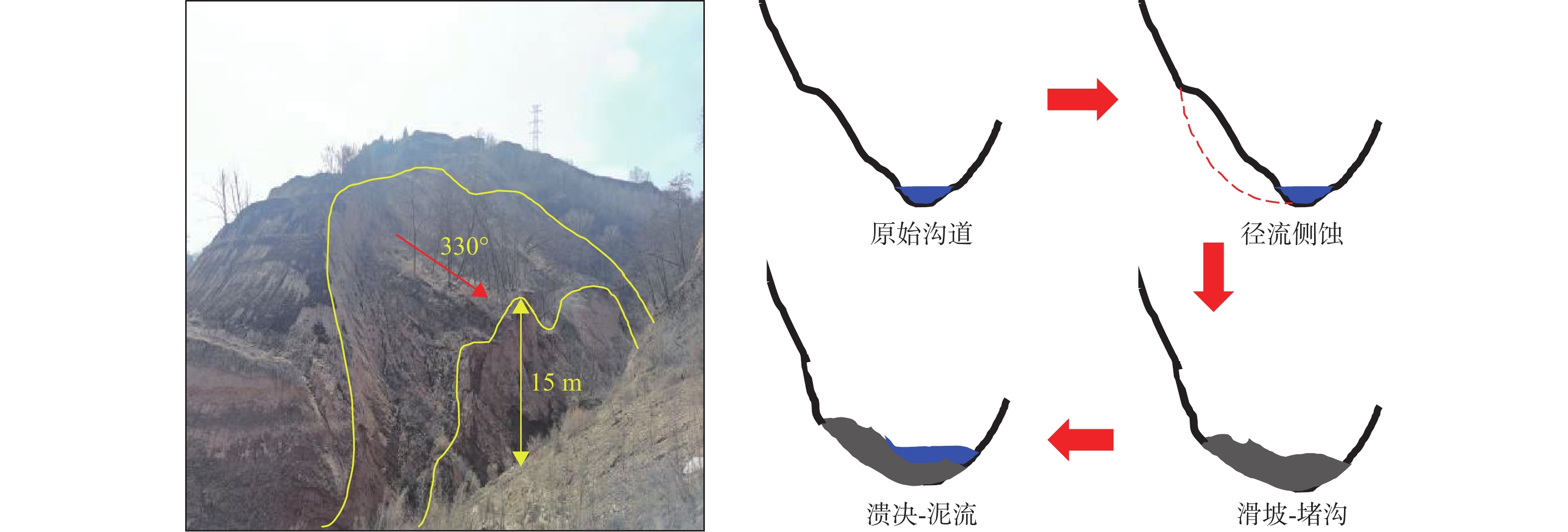
2.小规模滑塌安家寺 1497 1.串珠状落水洞
2.溯源侵蚀1.冲沟侵蚀严重 1.冲沟侵蚀极为发育
2.潜蚀落水洞极为发育1.小规模滑塌病害 -
[1] 金钊. 黄土塬——千沟万壑之中的平坦之地[J]. 地球环境学报,2020,11(1):119 − 124. [JIN Zhao. Loess tableland:A flat land among thousands of valleys and valleys[J]. Journal of Earth Environment,2020,11(1):119 − 124. (in Chinese)]
JIN Zhao. Loess tableland: A flat land among thousands of valleys and valleys[J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 2020, 11(1): 119 − 124. (in Chinese)
[2] 王小帆,霍艾迪,朱兴华,等. 陇东黄土塬区固沟保塬工程治理模式研究[J]. 人民黄河,2019,41(9):106 − 109. [WANG Xiaofan,HUO Aidi,ZHU Xinghua,et al. Study on governance mode of gully consolidation and highland protection project in East Gansu[J]. Yellow River,2019,41(9):106 − 109. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Xiaofan, HUO Aidi, ZHU Xinghua, et al. Study on governance mode of gully consolidation and highland protection project in East Gansu[J]. Yellow River, 2019, 41(9): 106 − 109. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] JIN Zhao,PENG Jianbing,ZHUANG Jianqi,et al. Gully erosion and expansion mechanisms in loess tablelands and the scientific basis of gully consolidation and tableland protection[J]. Science China Earth Sciences,2023,66(4):821 − 839. doi: 10.1007/s11430-022-1020-2
[4] WANG Jiaxi,ZHANG Yan,LI Kunheng,et al. Gully internal erosion triggered by a prolonged heavy rainfall event in the tableland region of China’s Loess Plateau[J]. International Soil and Water Conservation Research,2023,11(4):610 − 621. doi: 10.1016/j.iswcr.2022.12.003
[5] LIU Wanfeng,ZHANG Huyuan,ZHU Jianghong,et al. Strategies for gully stabilization and highland protection in Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science,2022,10:812609. doi: 10.3389/feart.2022.812609
[6] 曹国帆,金钊,杨思齐,等. 近60年人类活动对洛川塬典型沟道侵蚀演化的影响[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报,2022,41(5):1041 − 1050. [CAO Guofan,JIN Zhao,YANG Siqi,et al. Impacts of human activities on gully erosion on the Luochuan tableland of the Chinese Loess Plateau during the past 60 years[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy,Petrology and Geochemistry,2022,41(5):1041 − 1050. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CAO Guofan, JIN Zhao, YANG Siqi, et al. Impacts of human activities on gully erosion on the Luochuan tableland of the Chinese Loess Plateau during the past 60 years[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2022, 41(5): 1041 − 1050. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 赵景波,朱显谟. 黄土高原的演变与侵蚀历史[J]. 土壤侵蚀与水土保持学报,1999(2):58 − 63. [ZHAO Jingbo,ZHU Xianmo. Evolution and erodind histry of Loess Plateau[J]. Joural of Soil and Water Conservation,1999(2):58 − 63. (in Chinese)]
ZHAO Jingbo, ZHU Xianmo. Evolution and erodind histry of Loess Plateau[J]. Joural of Soil and Water Conservation, 1999(2): 58 − 63. (in Chinese)
[8] 史念海. 历史时期黄土高原沟壑的演变[J]. 中国历史地理论丛,1987,2(2):3 − 54. [SHI Nianhai. Evolution of gully in Loess Plateau in historical period[J]. Journal of Chinese Historical Geography,1987,2(2):3 − 54. (in Chinese)]
SHI Nianhai. Evolution of gully in Loess Plateau in historical period[J]. Journal of Chinese Historical Geography, 1987, 2(2): 3 − 54. (in Chinese)
[9] 庆阳市水土保持监督局. 庆阳市固沟保塬综合治理实施规划(2015—2020)[R]. 庆阳,2014. [Qingyang City Soil and Water Conservation Supervision Bureau. Qingyang City Gugou Baoyuan comprehensive treatment implementation plan (2015—2020)[R]. Qingyang,2014.(in Chinese)]
Qingyang City Soil and Water Conservation Supervision Bureau. Qingyang City Gugou Baoyuan comprehensive treatment implementation plan (2015—2020)[R]. Qingyang, 2014.(in Chinese)
[10] ZHU Yi,ZHUANG Jianqi,ZHAO Yong. Evaluation of loess-filled slope failure triggered by groundwater rise using a flume test[J]. Geomatics,Natural Hazards and Risk,2022,13(1):2471 − 2488. doi: 10.1080/19475705.2022.2122592
[11] 张智锋. 黄土边坡不同土层差异性侵蚀模式与土性改良试验研究[D]. 西安:长安大学,2022. [ZHANG Zhifeng. Experimental study on differential erosion patterns and soil property improvement in different soil layers of loess slope[D]. Xi’an:Chang’an University,2022. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Zhifeng. Experimental study on differential erosion patterns and soil property improvement in different soil layers of loess slope[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract)
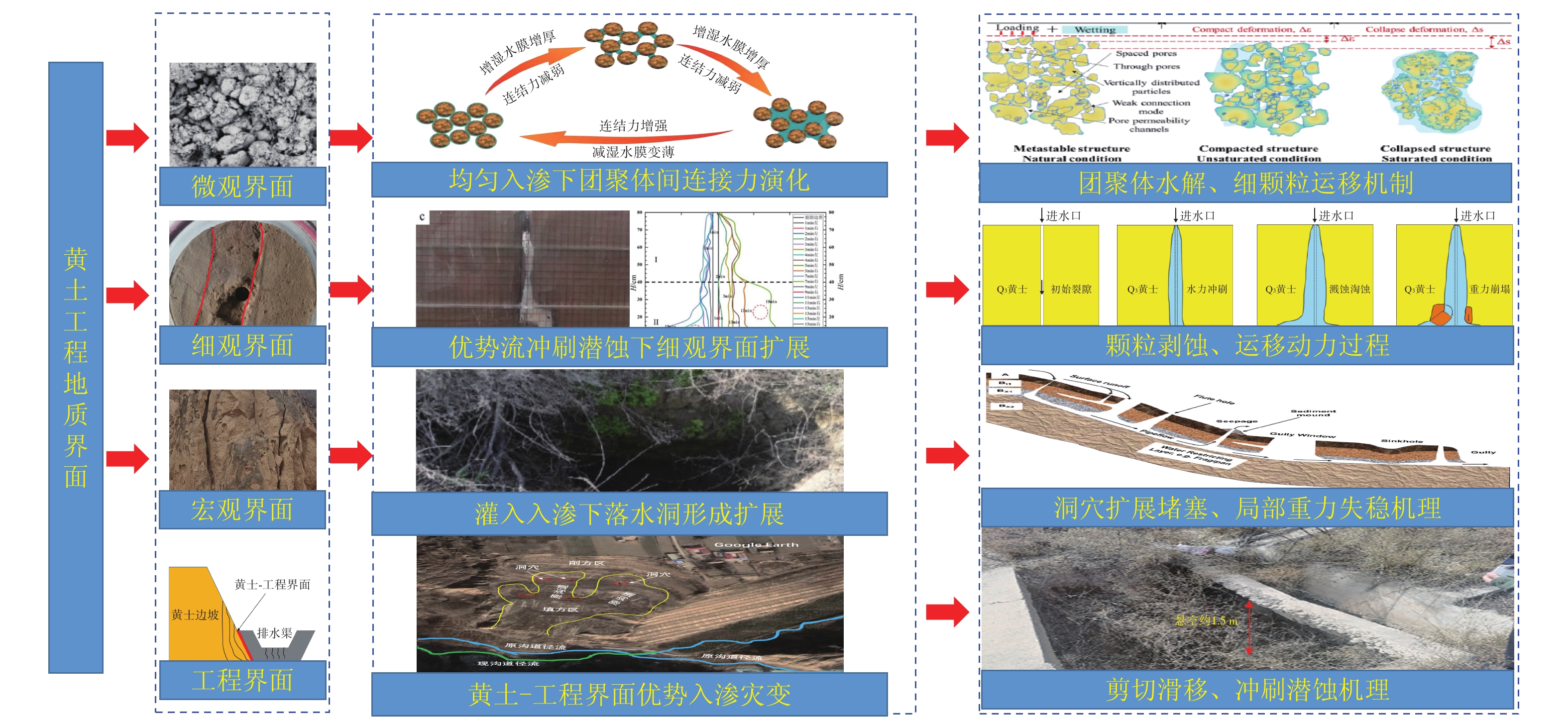
[12] 朱鸿鹄. 工程地质界面:从多元表征到演化机理[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(1):1 − 19. [ZHU Honghu. Engineering geological interface:From multivariate characterization to evolution mechanism[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(1):1 − 19. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHU Honghu. Engineering geological interface: From multivariate characterization to evolution mechanism[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(1): 1 − 19. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 余岱金,黄强兵,康孝森,等. 黄土填方边坡界面渗流破坏机制模型试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(5):119 − 128. [YU Daijin,HUANG Qiangbing,KANG Xiaosen,et al. A model test study of the interface seepage and failure mechanism of loess-filled slope[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(5):119 − 128. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YU Daijin, HUANG Qiangbing, KANG Xiaosen, et al. A model test study of the interface seepage and failure mechanism of loess-filled slope[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(5): 119 − 128. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 龚伟翔,张晓超,裴向军,等. 基于高陡交填界面软弱带影响下黄土填方边坡失稳模式研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2023,31(1):288 − 298. [GONG Weixiang,ZHANG Xiaochao,PEI Xiangjun,et al. Instability modelling of loess fill slope with influence of weak zone of high and steep filling interface[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2023,31(1):288 − 298. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
GONG Weixiang, ZHANG Xiaochao, PEI Xiangjun, et al. Instability modelling of loess fill slope with influence of weak zone of high and steep filling interface[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2023, 31(1): 288 − 298. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 张卜平,朱兴华,成玉祥,等. 黄土潜蚀机理及其致灾效应研究综述[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(6):41 − 52. [ZHANG Buping,ZHU Xinghua,CHENG Yuxiang,et al. A review on loess subsurface-erosion mechanism and it’s hazard effects[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(6):41 − 52. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Buping, ZHU Xinghua, CHENG Yuxiang, et al. A review on loess subsurface-erosion mechanism and it’s hazard effects[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(6): 41 − 52. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 彭建兵,吴迪,段钊,等. 典型人类工程活动诱发黄土滑坡灾害特征与致灾机理[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(5):971 − 980. [PENG Jianbing,WU Di,DUAN Zhao,et al. Disaster characteristics and destructive mechanism of typical loess landslide cases triggered by human engineering activities[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University,2016,51(5):971 − 980. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
PENG Jianbing, WU Di, DUAN Zhao, et al. Disaster characteristics and destructive mechanism of typical loess landslide cases triggered by human engineering activities[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(5): 971 − 980. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] XIE Quanyi,LIU Jian,HAN Bo,et al. Critical hydraulic gradient of internal erosion at the soil–structure interface[J]. Processes,2018,6(7):92. doi: 10.3390/pr6070092
[18] KIM H J,PARK J M,SHIN J H. Flow behaviour and piping potential at the soil–structure interface[J]. Géotechnique,2019,69(1):79 − 84.
[19] 彭建兵,王启耀,庄建琦,等. 黄土高原滑坡灾害形成动力学机制[J]. 地质力学学报,2020,26(5):714 − 730. [PENG Jianbing,WANG Qiyao,ZHUANG Jianqi,et al. Dynamic formation mechanism of landslide disaster on the Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2020,26(5):714 − 730. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
PENG Jianbing, WANG Qiyao, ZHUANG Jianqi, et al. Dynamic formation mechanism of landslide disaster on the Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2020, 26(5): 714 − 730. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] WANG Shaokai,PENG Jianbing,ZHUANG Jianqi,et al. Underlying mechanisms of the geohazards of macro Loess discontinuities on the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Engineering Geology,2019,263:105357. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105357
[21] FENG Li,ZHANG Maosheng,JIN Zhao,et al. The genesis,development,and evolution of original vertical joints in loess[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2021,214:103526. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2021.103526
[22] 朱兴华,彭建兵,同霄,等. 黄土地区地质灾害链研究初探[J]. 工程地质学报,2017,25(1):117 − 122. [ZHU Xinghua,PENG Jianbing,TONG Xiao,et al. Preliminary research on geological disaster chains in loess area[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2017,25(1):117 − 122. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHU Xinghua, PENG Jianbing, TONG Xiao, et al. Preliminary research on geological disaster chains in loess area[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2017, 25(1): 117 − 122. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] HUO Aidi,ZHAO Zhixin,LUO Pingping,et al. Assessment of spatial heterogeneity of soil moisture in the critical zone of gully consolidation and highland protection[J]. Water,2022,14(22):3674. doi: 10.3390/w14223674
[24] HUO Aidi,PENG Jianbing,CHENG Yuxiang,et al. Hydrological analysis of Loess Plateau highland control schemes in Dongzhi Plateau[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science,2020,8:637.
[25] 史倩华. 黄土塬区溯源侵蚀水动力过程与形态演化试验研究[D]. 杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2021. [SHI Qianhua. Experimental Study of hydrodynamic processes and gully head morphological evolution in the loess yuan[D]. Yangling:Northwest A & F University,2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
SHI Qianhua. Experimental Study of hydrodynamic processes and gully head morphological evolution in the loess yuan[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 姜程. 黄土高塬沟壑区固沟保塬(沟头填埋)与水力侵蚀的互馈机制[D]. 西安:长安大学,2020. [JIANG Cheng. Dynamic interaction mechanism of gully consolidation and highland protection(gully head landfill) and hydraulic erosion in gully region of loess plateau[D]. Xi’an:Chang’an University,2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
JIANG Cheng. Dynamic interaction mechanism of gully consolidation and highland protection(gully head landfill) and hydraulic erosion in gully region of loess plateau[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 王小帆. 基于水文特征分析的固沟保塬综合治理方案优化研究[D]. 西安:长安大学,2020. [WANG Xiaofan. Study on optimization of comprehensive treatment plan of gully consolidation and highland protection based on analysis of hydrological characteristics[D]. Xi’an:Chang’an University,2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Xiaofan. Study on optimization of comprehensive treatment plan of gully consolidation and highland protection based on analysis of hydrological characteristics[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 赵勇. 水动力作用下不同防护措施的黄土填方边坡失稳过程研究[D]. 西安:长安大学,2020. [ZHAO Yong. Study on instability process of loess filled slope under different protective measures under hydrodynamic force[D]. Xi’an:Chang’an University,2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHAO Yong. Study on instability process of loess filled slope under different protective measures under hydrodynamic force[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] BELNAP J,WILCOX B P,VAN SCOYOC M W,et al. Successional stage of biological soil crusts:An accurate indicator of ecohydrological condition[J]. Ecohydrology,2013,6(3):474 − 482. doi: 10.1002/eco.1281
[30] 高丽倩,赵允格,秦宁强,等. 黄土丘陵区生物结皮对土壤可蚀性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报,2013,24(1):105 − 112. [GAO Liqian,ZHAO Yunge,QIN Ningqiang,et al. Effects of biological soil crust on soil erodibility in Hilly Loess Plateau Region of Northwest China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2013,24(1):105 − 112. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
GAO Liqian, ZHAO Yunge, QIN Ningqiang, et al. Effects of biological soil crust on soil erodibility in Hilly Loess Plateau Region of Northwest China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2013, 24(1): 105 − 112. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 张丙昌,武志芳,李彬. 黄土高原生物土壤结皮研究进展与展望[J]. 土壤学报,2021,58(5):1123 − 1131. [ZHANG Bingchang,WU Zhifang,LI Bin. Progress and prospect of biological soil crusts in Loess Plateau[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica,2021,58(5):1123 − 1131. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Bingchang, WU Zhifang, LI Bin. Progress and prospect of biological soil crusts in Loess Plateau[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2021, 58(5): 1123 − 1131. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 张侃侃,卜崇峰,高国雄. 黄土高原生物结皮对土壤水分入渗的影响[J]. 干旱区研究,2011,28(5):808 − 812. [ZHANG Kankan,BU Chongfeng,GAO Guoxiong. Effect of microbiotic crust on soil water infiltration in the Loess Plateau[J]. Arid Zone Research,2011,28(5):808 − 812. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Kankan, BU Chongfeng, GAO Guoxiong. Effect of microbiotic crust on soil water infiltration in the Loess Plateau[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2011, 28(5): 808 − 812. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] SUN Jiqiang,LI Xi’an,LI Jie,et al. Numerical investigation of characteristics and mechanism of tunnel erosion of loess with coupled CFD and DEM method[J]. CATENA,2023,222:106729. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2022.106729
[34] YANG Hui,XIE Wanli,LIU Qiqi,et al. Three-stage collapsibility evolution of Malan loess in the Loess Plateau[J]. CATENA,2022,217:106482. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2022.106482
[35] WILSON G V,WELLS R,KUHNLE R,et al. Sediment detachment and transport processes associated with internal erosion of soil pipes[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,2018,43(1):45 − 63. doi: 10.1002/esp.4147
[36] 王力. 基于微结构单元理论的黄土湿陷性预测模型研究[D]. 西安:长安大学,2021. [WANG Li. Research on prediction model of loess collapsibility based on microstructure unit Theory[D]. Xi’an:Chang’an University,2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Li. Research on prediction model of loess collapsibility based on microstructure unit Theory[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[37] 成玉祥,张卜平,唐亚明. 溯源侵蚀引发的拉裂-倾倒型黄土崩塌形成机制[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(5):86 − 91. [CHENG Yuxiang,ZHANG Buping,TANG Yaming. The mechanism of bending-toppling loess collapse caused by headward erosion[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(5):86 − 91. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHENG Yuxiang, ZHANG Buping, TANG Yaming. The mechanism of bending-toppling loess collapse caused by headward erosion[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(5): 86 − 91. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[38] FELL R,WAN C F. Investigation of internal erosion and piping of soils in embankment dams by the slot erosion test and the hole erosion test - interpretative report[R]. NSW:School of Civil and Environmental Engineering,University of New South Wales,2002
[39] BRIAUD J L,SHAFII I,CHEN H C,et al. Relationship between erodibility and properties of soils[M]. Washington DC:The National Academies Press,2019.
[40] 兰恒星,彭建兵,祝艳波,等. 黄河流域地质地表过程与重大灾害效应研究与展望[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,2022,52(2):199 − 221. [LAN Hengxing,PENG Jianbing,ZHU Yanbo,et al. Research and prospect of geological surface processes and major disaster effects in the Yellow River Basin[J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae),2022,52(2):199 − 221. (in Chinese)] doi: 10.1360/SSTe-2021-0115
LAN Hengxing, PENG Jianbing, ZHU Yanbo, et al. Research and prospect of geological surface processes and major disaster effects in the Yellow River Basin[J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 2022, 52(2): 199 − 221. (in Chinese) doi: 10.1360/SSTe-2021-0115
[41] 祝艳波,兰恒星,彭建兵,等. 黄河中游地区水土灾害机理与灾害链效应研究进展[J]. 人民黄河,2021,43(8):108 − 116. [ZHU Yanbo,LAN Hengxing,PENG Jianbing,et al. Research progress of water-soil disaster mechanism and disaster chain effect in the middle reaches of the Yellow River Basin[J]. Yellow River,2021,43(8):108 − 116. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHU Yanbo, LAN Hengxing, PENG Jianbing, et al. Research progress of water-soil disaster mechanism and disaster chain effect in the middle reaches of the Yellow River Basin[J]. Yellow River, 2021, 43(8): 108 − 116. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[42] 崔鹏,邓宏艳,王成华,等. 山地灾害[M]. 北京:高等教育出版社,2018. [CUI Peng,DENG Hongyan,WANG Chenghua et al. Mountain disaster [M]. Beijing:Higher Education Press,2018.(in Chinese)]
CUI Peng, DENG Hongyan, WANG Chenghua et al. Mountain disaster [M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2018.(in Chinese)
-



 下载:
下载: