Submarine fresh groundwater discharge estimation in the intertidal zone based on dynamic salinity simulation
-
摘要:
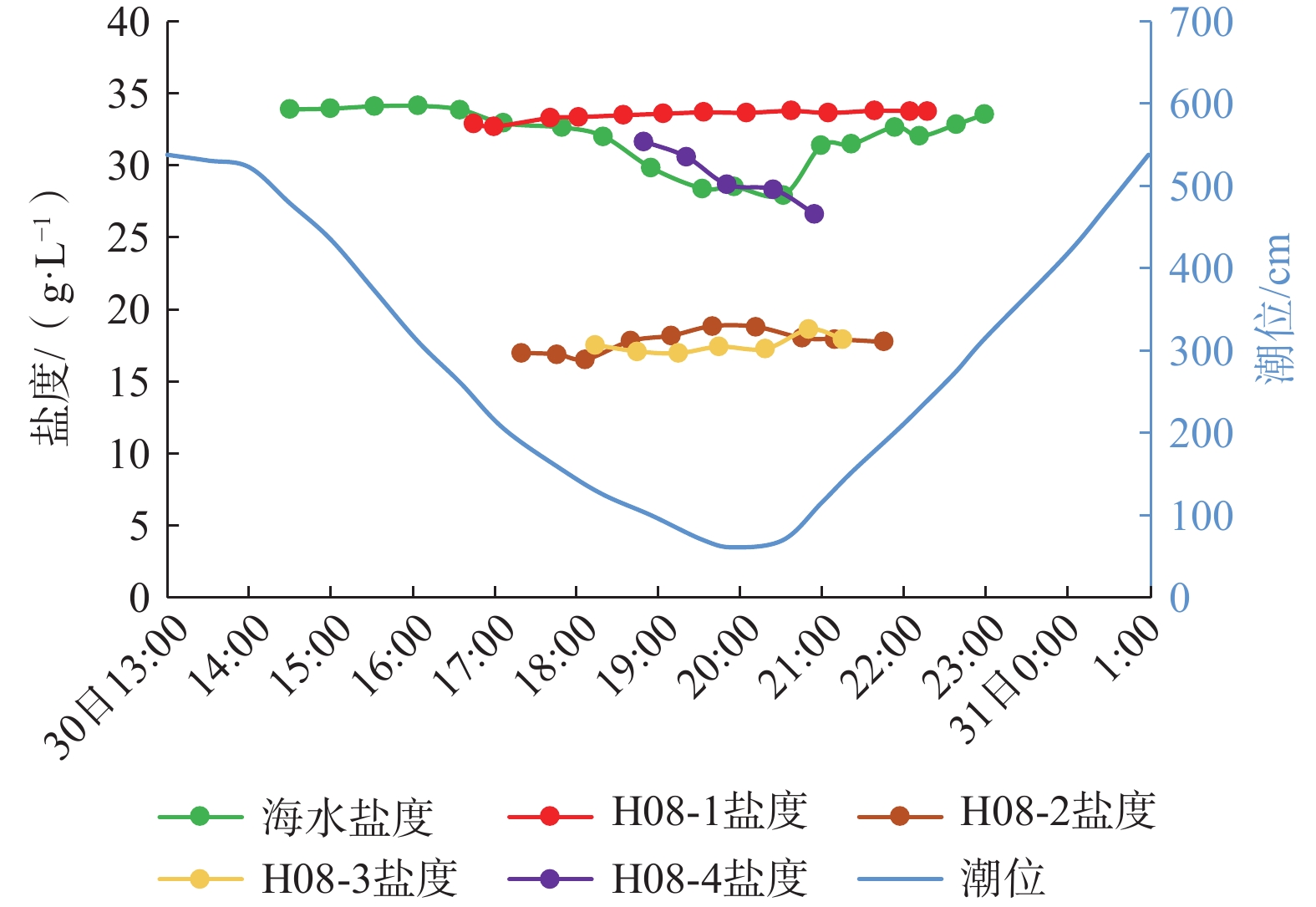
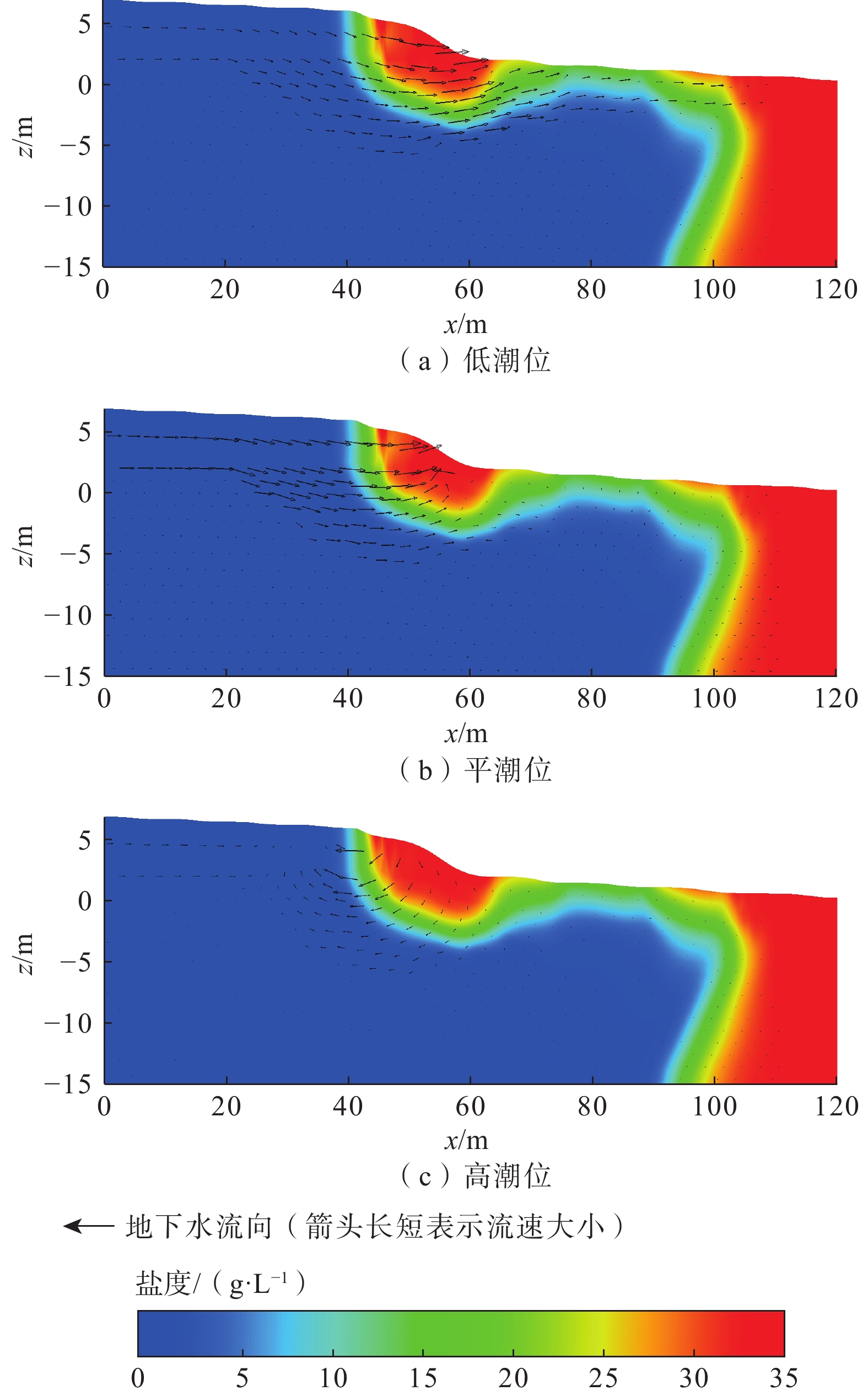
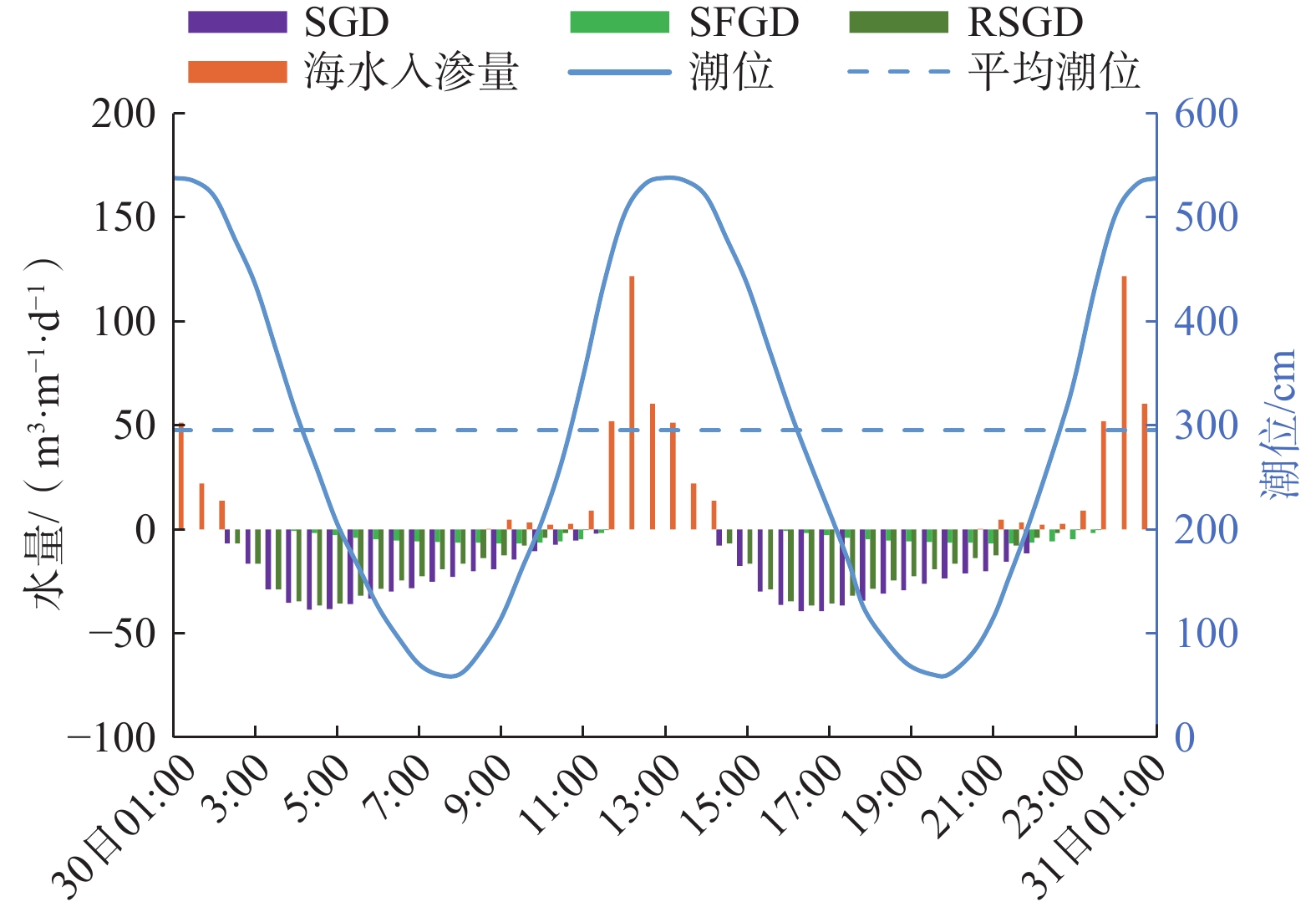
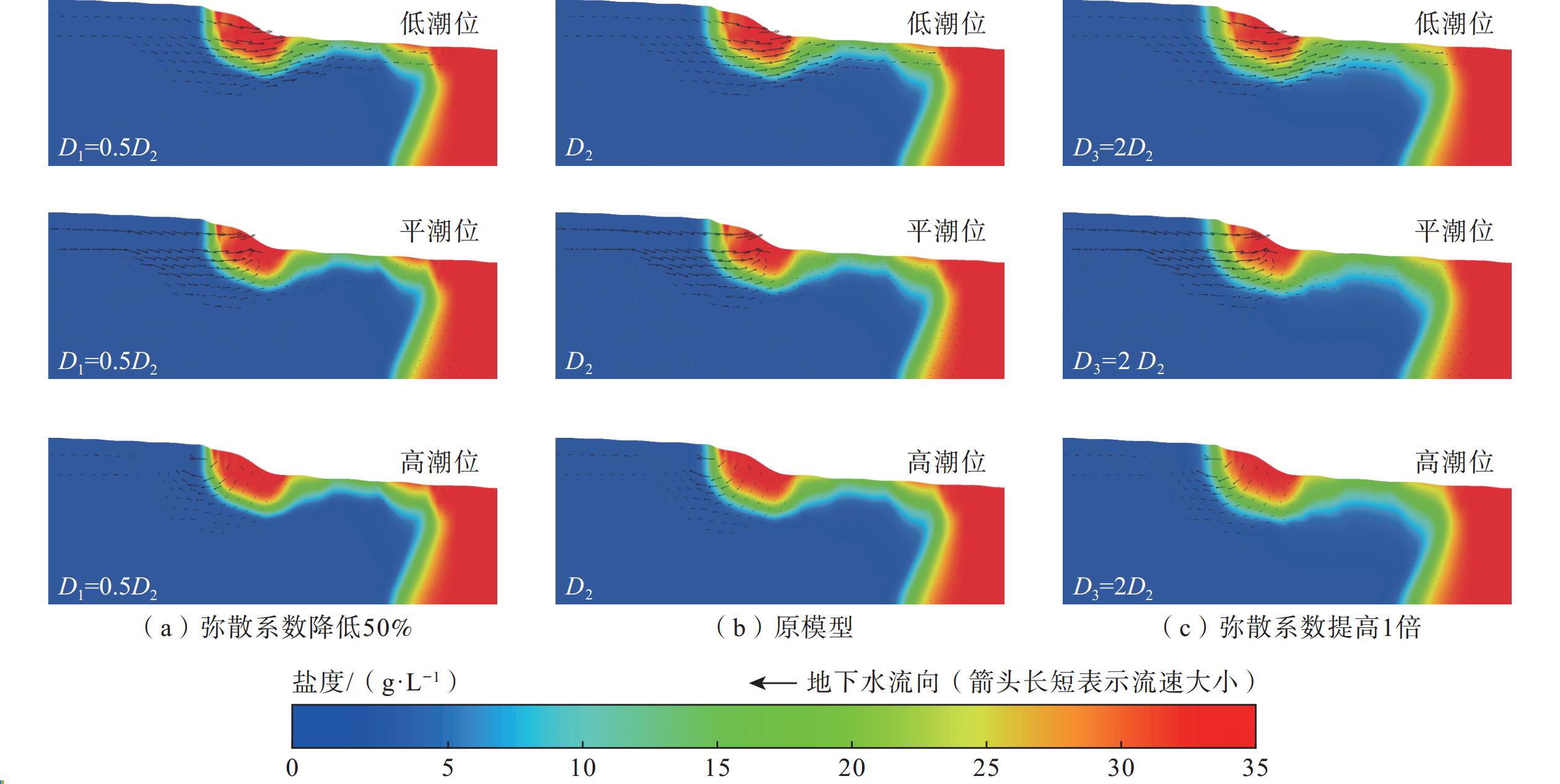
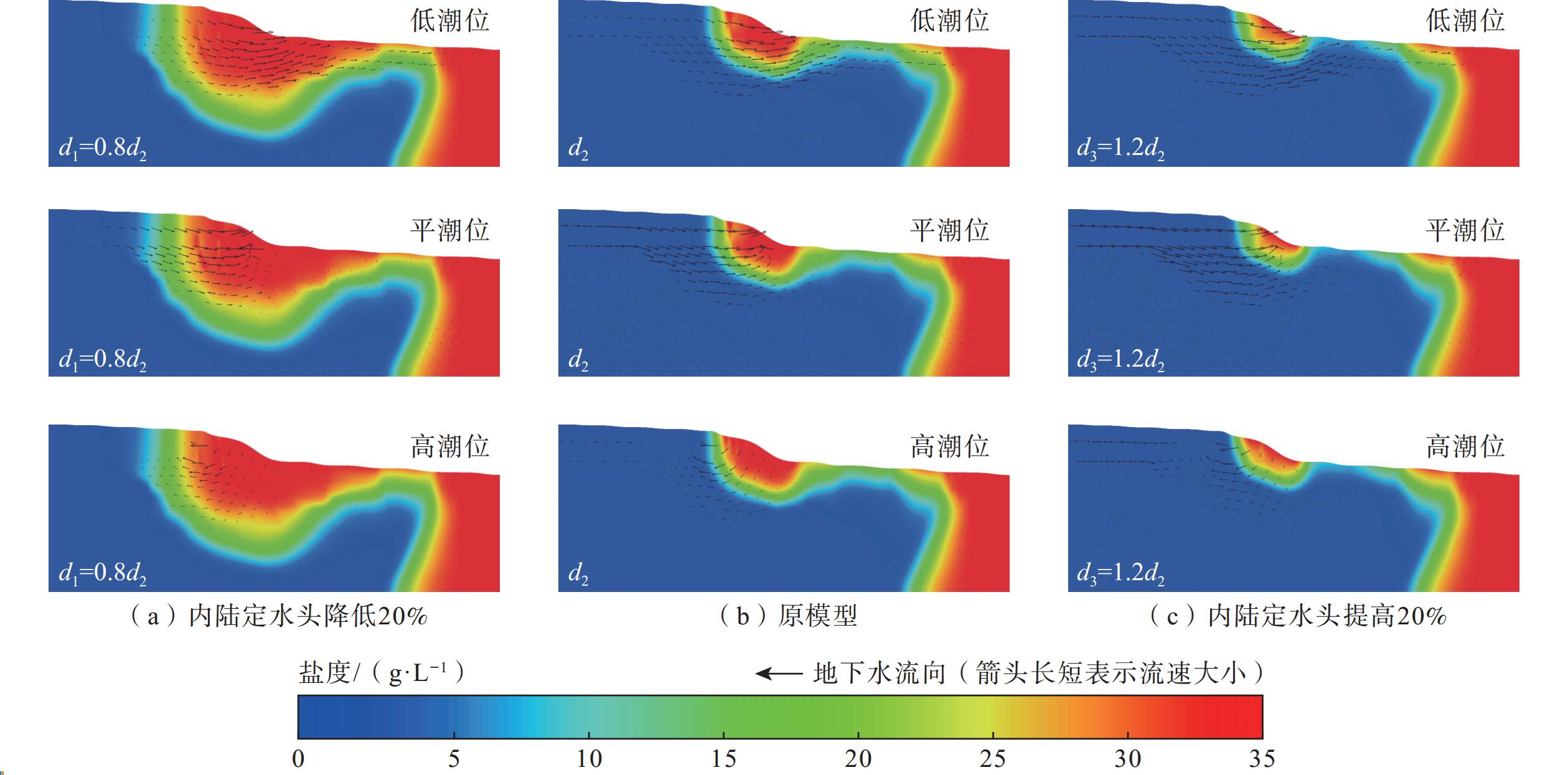
目前关于砂质潮间带海底地下淡水排泄速率、海水再循环速率及相应比例随潮位的变化研究较少。文章以厦门湾某砂质潮滩为例,对地下水渗出面的盐度进行实地动态监测,采用变密度流数值模拟技术,对潮间带地下水盐度变化过程进行动态模拟,以此反演潮间带海底地下淡水排泄量。研究结果显示:(1)潮间带不同位置地下水盐度随潮汐发生不同规律的变化,通过数值模型估算出典型剖面海底地下水排泄量为17.47 m3/(m·d),其中海底地下淡水排泄量为3.19 m3/(m·d),占海底地下水排泄总量的18.26%,海水再循环量为14.28 m3/(m·d),占海底地下水排泄总量的81.74%,处于主导地位;(2)潮汐作用下,海水入渗与海底地下水排泄交替发生,落潮阶段发生交替的时间略早于平潮位,涨潮阶段发生交替的时间略晚于平潮位,海水入渗速率与海底地下水排泄速率达到峰值时刻分别早于潮位达到高潮和低潮时刻,整个潮汐周期内(从高潮时刻到下一个高潮时刻)海底地下淡水排泄量比例逐渐增大;(3)潮间带地下水盐度的变化可间接反映海底地下淡水排泄量的变化,与其他研究相比,该典型剖面的海底地下淡水排泄量占海底地下水排泄总量比例相对较高,显示潮间带存在着大量海底地下淡水排泄;(4)通过敏感性分析可知,内陆水头对海底地下淡水排泄量及盐度空间分布有重要影响。研究可为海岸带地下水开发利用和滨海环境管理提供一定参考。
Abstract:Currently, limited studies focused on the variations in submarine fresh groundwater discharge rates, seawater recirculation rates, and their respective proportions with tidal level change in sandy intertidal zones. This study conducted in-situ dynamic monitoring of the salinity at the groundwater seepage face in a sandy tidal flat in Xiamen Bay. Using variable-density flow numerical model, the dynamic groundwater salinity in the intertidal zone was simulated to calculate the submarine fresh groundwater discharge in the intertidal zone. The results show that groundwater salinity at different locations in the intertidal zone exhibits varying patterns with the tides. The submarine groundwater discharge at a typical profile was estimated to be 17.47 m3/(m·d), in which the submarine fresh groundwater discharge was calculated to be 3.19 m3/(m·d), accounting for 18.26% of the total submarine groundwater discharge. In contrast, recirculated submarine groundwater discharge was estimated to be 14.28 m3/(m·d), constituting 81.74% of the total submarine groundwater discharge and thus playing a dominant role. Under the influence of tides, seawater infiltration and submarine groundwater discharge are alternate. The alternation during ebb tide occurs slightly earlier than the slack water level, while during flood tide, it occurs slightly later. The peak moment of seawater infiltration rate and submarine groundwater discharge rate precede the tidal peaks at high and low tides, respectively. Throughout the tidal cycle (from high tide to the next high tide), the proportion of submarine fresh groundwater discharge gradually increases. The variation in groundwater salinity in the intertidal zone can represent the changes in submarine fresh groundwater discharge. The proportion of submarine fresh groundwater discharge in the total submarine groundwater discharge is relatively high in this typical profile than that in the previous studies. It indicates the presence of a substantial amount of submarine fresh groundwater discharge in the intertidal zone. Through sensitivity analysis, it reveals that inland hydraulic head has significant influences on submarine fresh groundwater discharge and spatial distribution of salinity. This study can provide scientific information for the development and utilization of coastal groundwater and the management of coastal environments.
-

-
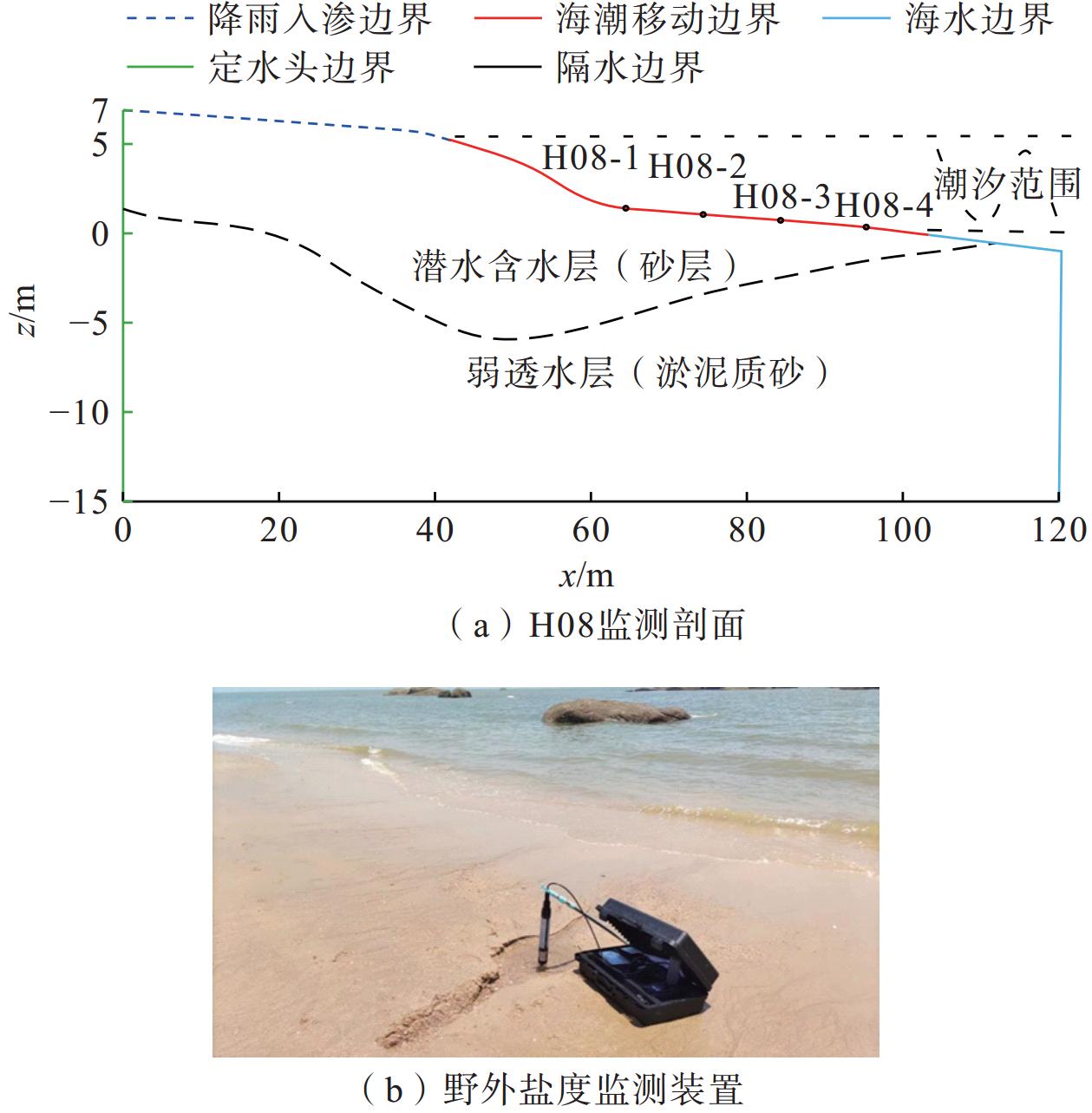
表 1 含水层水文地质参数
Table 1. Hydrogeological parameters of aquifer
位置 水平渗透系数/
(m·h−1)垂向渗透系数/
(m·h−1)贮水系数/
m−1给水度 孔隙度 弥散度 第一层 1.25 0.625 0.0005 0.2 0.3 0.5 第二层 0.08 0.008 0.0005 0.1 0.3 0.5 表 2 已有研究SGD案例中SFGD的贡献度
Table 2. The contribution of SFGD in studies on SGD
-
[1] MOORE W S. The effect of submarine groundwater discharge on the ocean[J]. Annual Review of Marine Science,2010,2:59 − 88. doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-120308-081019
[2] 李海龙,王学静. 海底地下水排泄研究回顾与进展[J]. 地球科学进展,2015,30(6):636 − 646. [LI Hailong,WANG Xuejing. Submarine groundwater discharge:A review[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2015,30(6):636 − 646. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Hailong, WANG Xuejing. Submarine groundwater discharge: A review[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2015, 30(6): 636 − 646. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 王一清,吴自军. 海底地下水排泄对海洋锶储库的影响[J]. 地质论评,2022,68(3):1079 − 1088. [WANG Yiqing,WU Zijun. The effect of submarine groundwater discharge on marine strontium budget[J]. Geological Review,2022,68(3):1079 − 1088. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Yiqing, WU Zijun. The effect of submarine groundwater discharge on marine strontium budget[J]. Geological Review, 2022, 68(3): 1079 − 1088. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] BURNETT W C,BOKUNIEWICZ H,HUETTEL M,et al. Groundwater and pore water inputs to the coastal zone[J]. Biogeochemistry,2003,66(1):3 − 33.
[5] SANTOS I R,EYRE B D,HUETTEL M. The driving forces of porewater and groundwater flow in permeable coastal sediments:A review[J]. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science,2012,98:1 − 15. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2011.10.024
[6] SANTOS I R,BURNETT W C,CHANTON J,et al. Land or ocean? :Assessing the driving forces of submarine groundwater discharge at a coastal site in the Gulf of Mexico[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans,2009,114(C4):1 − 11.
[7] ABBOTT B W,BISHOP K,ZARNETSKE J P,et al. Human domination of the global water cycle absent from depictions and perceptions[J]. Nature Geoscience,2019,12(7):533 − 540. doi: 10.1038/s41561-019-0374-y
[8] LUIJENDIJK E,GLEESON T,MOOSDORF N. Fresh groundwater discharge insignificant for the world’s oceans but important for coastal ecosystems[J]. Nature Communications,2020,11(1):1260. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15064-8
[9] BAUDRON P,COCKENPOT S,LOPEZCASTEJON F,et al. Combining radon,short-lived radium isotopes and hydrodynamic modeling to assess submarine groundwater discharge from an anthropized semiarid watershed to a Mediterranean lagoon (Mar Menor,SE Spain)[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2015,525:55 − 71. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.03.015
[10] KWON E Y,KIM G,PRIMEAU F,et al. Global estimate of submarine groundwater discharge based on an observationally constrained radium isotope model[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2014,41(23):8438 − 8444. doi: 10.1002/2014GL061574
[11] SANTOS I R,CHEN Xiaogang,LECHER A L,et al. Submarine groundwater discharge impacts on coastal nutrient biogeochemistry[J]. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment,2021,2(5):307 − 323.
[12] TAMBORSKI J J,ROGERS A D,BOKUNIEWICZ H J. Investigation of submarine groundwater discharge to tidal rivers:Evidence for regional and local scale seepage[J]. Hydrological Processes,2017,31(3):716 − 730. doi: 10.1002/hyp.11079
[13] CHENG K H,LUO X,JIAO J J. Two-decade variations of fresh submarine groundwater discharge to Tolo Harbour and their ecological significance by coupled remote sensing and radon-222 model[J]. Water Research,2020,178:115866. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.115866
[14] FU Tengfei,ZHANG Yufeng,XU Xingyong,et al. Assessment of submarine groundwater discharge in the intertidal zone of Laizhou Bay,China,using electrical resistivity tomography[J]. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science,2020,245:106972. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2020.106972
[15] KURYLYK B L,IRVINE D J,MOHAMMED A A,et al. Rethinking the use of seabed sediment temperature profiles to trace submarine groundwater flow[J]. Water Resources Research,2018,54(7):4595 − 4614. doi: 10.1029/2017WR022353
[16] LEROUX N K,KURYLYK B L,BRIGGS M A,et al. Using heat to trace vertical water fluxes in sediment experiencing concurrent tidal pumping and groundwater discharge[J]. Water Resources Research,2021,57(2):e2020WR027904. doi: 10.1029/2020WR027904
[17] LIU Jun,CHENG Yanpei,ZHANG Feng’e,et al. Research hotspots and trends of groundwater and ecology studies:Based on a bibliometric approach[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering,2023,11(1):20 − 36. doi: 10.26599/JGSE.2023.9280003
[18] BAKHTYAR R,BROVELLI A,BARRY D A,et al. Transport of variable-density solute plumes in beach aquifers in response to oceanic forcing[J]. Advances in Water Resources,2013,53:208 − 224. doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2012.11.009
[19] WERNER A D,BAKKER M,POST V E A,et al. Seawater intrusion processes,investigation and management:Recent advances and future challenges[J]. Advances in Water Resources,2013,51:3 − 26. doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2012.03.004
[20] ROBINSON C,XIN Pei,LI Ling,et al. Groundwater flow and salt transport in a subterranean estuary driven by intensified wave conditions[J]. Water Resources Research,2014,50(1):165 − 181. doi: 10.1002/2013WR013813
[21] 中国海湾志编纂委员会. 中国海湾志(第八分册)[M]. 北京:海洋出版社,1993. [China Gulf Chronicles Compilation Committee. China gulf chronicles(Volume 8)[M]. Beijing:China Ocean Press,1993. (in Chinese)]
China Gulf Chronicles Compilation Committee. China gulf chronicles(Volume 8)[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1993. (in Chinese)
[22] WANG Jining,MENG Yonghui. Characteristics analysis and model prediction of sea-salt water intrusion in lower reaches of the Weihe River,Shandong Province,China[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering,2016,4(2):149 − 156. doi: 10.26599/JGSE.2016.9280018
[23] CHANG Yawen,HU B X,XU Zexuan,et al. Numerical simulation of seawater intrusion to coastal aquifers and brine water/freshwater interaction in south coast of Laizhou Bay,China[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology,2018,215:1 − 10. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2018.06.002
[24] 王佳琪,郭芷琳,田勇,等. 海水入侵模拟方法VFT3D及应用[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(2):184 − 194. [WANG Jiaqi,GUO Zhilin,TIAN Yong,et al. Development and application of sea water intrusion models[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(2):184 − 194. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Jiaqi, GUO Zhilin, TIAN Yong, et al. Development and application of sea water intrusion models[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(2): 184 − 194. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 李英豪,韩冬梅,曹天正,等. 边坡防渗增加灰沙岛地下淡水的试验与数值模拟研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(2):13 − 22. [LI Yinghao,HAN Dongmei,CAO Tianzheng,et al. A study of the increase in subsurface freshwater on coral islands by slope seepage control:Experiment and modeling[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(2):13 − 22. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Yinghao, HAN Dongmei, CAO Tianzheng, et al. A study of the increase in subsurface freshwater on coral islands by slope seepage control: Experiment and modeling[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(2): 13 − 22. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] BAKHTYAR R,BROVELLI A,BARRY D A,et al. Wave-induced water table fluctuations,sediment transport and beach profile change:Modeling and comparison with large-scale laboratory experiments[J]. Coastal Engineering,2011,58(1):103 − 118. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2010.08.004
[27] 常雅雯,胡晓农,张汉雄,等. 泥质潮滩的海水-地下水交换量化研究——以莱州湾南岸为例[J]. 海洋通报,2018,37(4):450 − 458. [CHANG Yawen,HU B X,ZHANG Hanxiong,et al. Quantifying seawater-groundwater exchange rates in muddy tidal flat:A case study of the south coast of the Laizhou Bay[J]. Marine Science Bulletin,2018,37(4):450 − 458. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2018.04.011
CHANG Yawen, HU B X, ZHANG Hanxiong, et al. Quantifying seawater-groundwater exchange rates in muddy tidal flat: A case study of the south coast of the Laizhou Bay[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2018, 37(4): 450 − 458. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2018.04.011
[28] 黄文辉,林国平,郑祖南. 厦门市区域水文地质调查报告[R]. 厦门:厦门地质工程勘察院,1999. [HUANG Wenhui,LIN Guoping,ZHENG Zunan. Regional hydrogeological survey report of Xiamen City[R]. Xiamen:Xiamen Geological Engineering Survey Institute,1999. (in Chinese)]
HUANG Wenhui, LIN Guoping, ZHENG Zunan. Regional hydrogeological survey report of Xiamen City[R]. Xiamen: Xiamen Geological Engineering Survey Institute, 1999. (in Chinese)
[29] 李亚松,刘春雷,郝奇琛,等. 厦漳泉同城化地区综合地质调查报告[R]. 石家庄:中国地质科学院水文地质环境地质研究所, 2022. [LI Yasong,LIU Chunlei,HAO Qichen et al. Comprehensive geological survey of Xiamen-Zhangzhou-Quanzhou integration region project[R]. Shijiazhuang:Institute of Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology,Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences,2022. (in Chinese with English abstract))]
LI Yasong, LIU Chunlei, HAO Qichen et al. Comprehensive geological survey of Xiamen-Zhangzhou-Quanzhou integration region project[R]. Shijiazhuang: Institute of Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract))
[30] 郑涛. 曹妃甸地区海底地下水排泄的定量化研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2014. [ZHENG Tao. Quantitative submarine groundwater discharges in Caofeidian[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences,2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHENG Tao. Quantitative submarine groundwater discharges in Caofeidian[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] LIU Jianan,DU Jinzhou,YU Xueqing. Submarine groundwater discharge enhances primary productivity in the Yellow Sea,China:Insight from the separation of fresh and recirculated components[J]. Geoscience Frontiers,2021,12(6):101204. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2021.101204
[32] WANG Qianqian,ZHANG Xiaolang,WANG Xuejing,et al. Quantification of the water age and submarine groundwater discharge in a typical semi-enclosed bay using stable oxygen (18O) and radioactive radium (228Ra) isotopes[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2021,603:127088. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.127088
[33] LI L,BARRY D A,STAGNITTI F,et al. Submarine groundwater discharge and associated chemical input to a coastal sea[J]. Water Resources Research,1999,35(11):3253 − 3259. doi: 10.1029/1999WR900189
[34] MICHAEL H A. Seasonal dynamics in costal aquifers:Investigation of submarine groundwater discharge through field measurements and numerical models[D]. Cambridge:Massachusetts Institute of Technology,2005.
[35] MICHAEL H A,CHARETTE M A,HARVEY C F. Patterns and variability of groundwater flow and radium activity at the coast:A case study from Waquoit Bay,Massachusetts[J]. Marine Chemistry,2011,127(1/2/3/4):100 − 114.
[36] KIM G,LEE K K,PARK K S,et al. Large submarine groundwater discharge (SGD) from a volcanic island[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2003,30(21):2098.
[37] BECK A J,RAPAGLIA J P,COCHRAN J K,et al. Submarine groundwater discharge to Great South Bay,NY,estimated using Ra isotopes[J]. Marine Chemistry,2008,109(3/4):279 − 291.
[38] WANG Xuejing,LI Hailong,JIAO J J,et al. Submarine fresh groundwater discharge into Laizhou Bay comparable to the Yellow River flux[J]. Scientific Reports,2015,5(1):8814. doi: 10.1038/srep08814
[39] 李露露,张秋兰,李星宇,等. 高放废物深地质处置地下水数值模拟应用综述[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(2):43 − 53. [LI Lulu,ZHANG Qiulan,LI Xingyu,et al. Review of groundwater numerical simulation for deep geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(2):43 − 53. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Lulu, ZHANG Qiulan, LI Xingyu, et al. Review of groundwater numerical simulation for deep geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(2): 43 − 53. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[40] HENRY H R. Interfaces between salt water and fresh water in coastal aquifers[J]. US Geological Survey Water-Supply Paper,1964:C35-70.
-




 下载:
下载: