Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of iron-rich groundwater in Xining City
-
摘要:
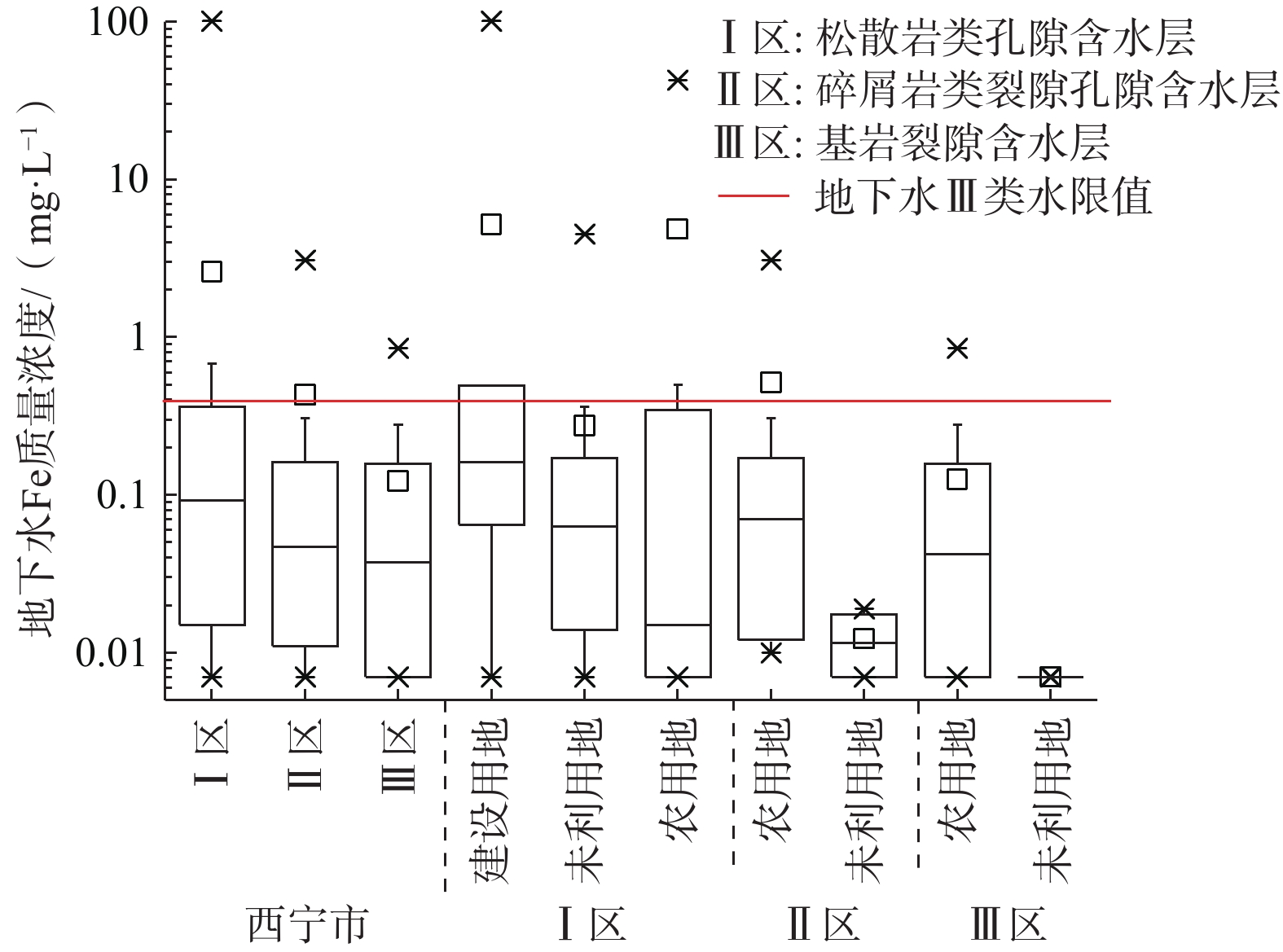
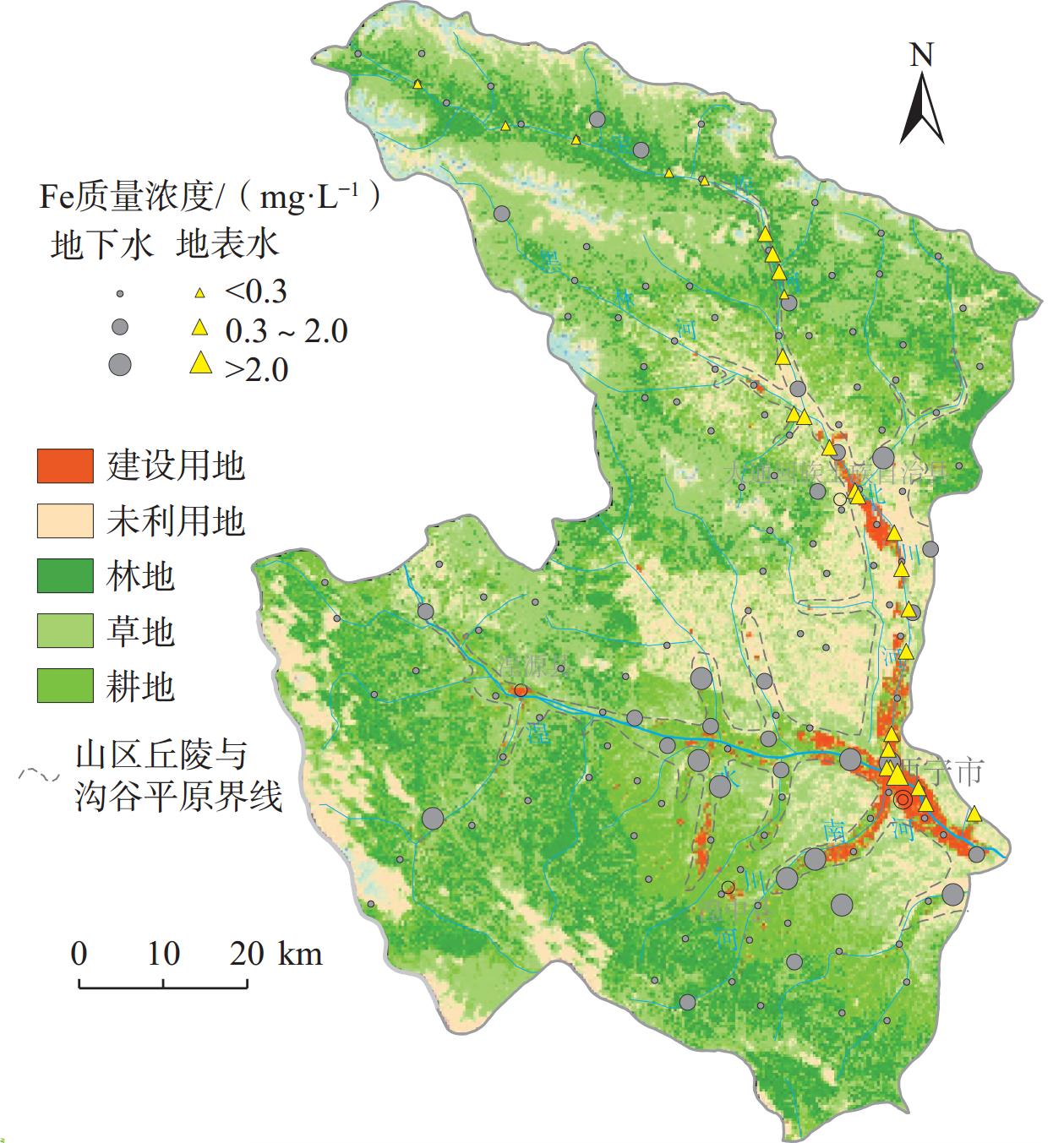
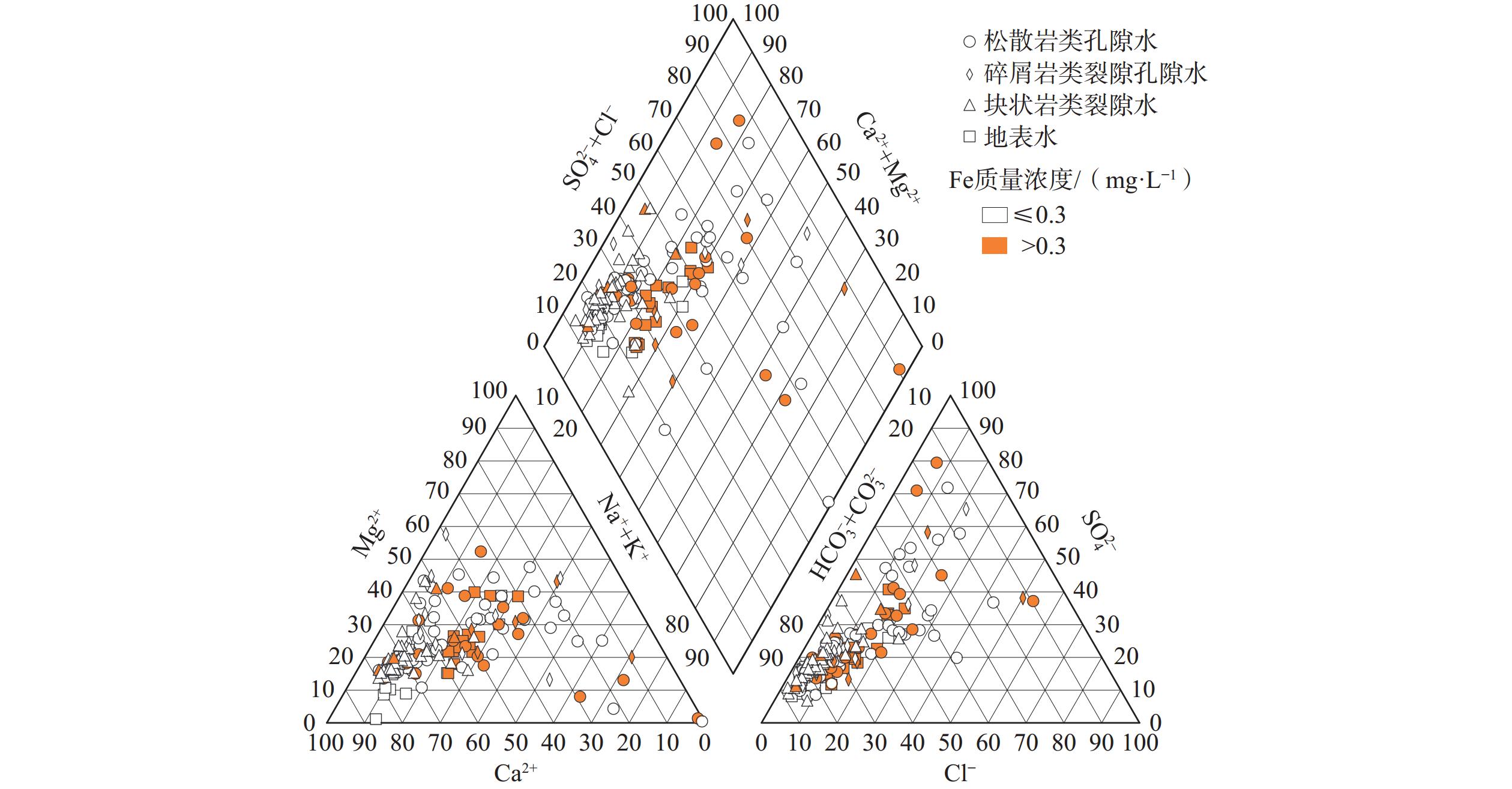
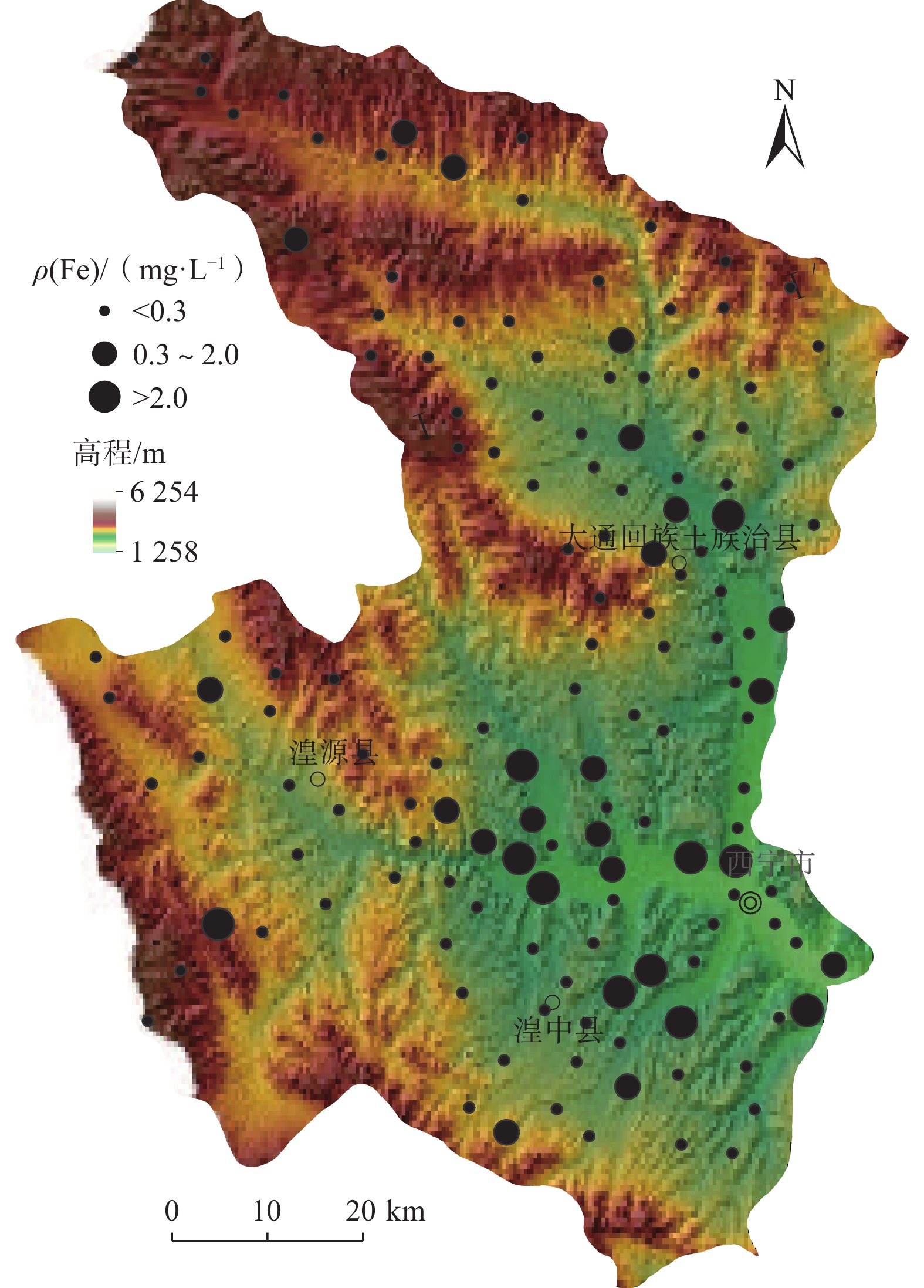
地下水是西宁市的重要供水水源,调查发现其地下水中富铁,限制了开发利用,而针对不同类型含水层中富铁地下水分布特征及其成因缺乏研究。以144组地下水样品水化学测试数据为基础,结合地质和水文地质条件特征,借助统计学和地统计学等方法,研究了不同类型含水层地下水中铁含量的分布特征及其影响因素。结果表明:松散岩类孔隙含水层(Ⅰ区)地下水中Fe超过质量浓度0.3 mg/L的水占27.85%,分别是碎屑岩类裂隙孔隙含水层(Ⅱ区)和基岩裂隙含水层(Ⅲ区)的1.6倍和2.7倍,富铁地下水(质量浓度大于0.3 mg/L)在建设用地中的比例明显高于其他土地利用类型区;还原环境和人类活动(如工业废水、生活污水、富铁河水的入渗)可能是影响Ⅰ区地下水中铁含量升高的主要因素,Ⅱ区中富铁地下水除了受还原环境的影响外,农业氮肥的施用和生活污水的排放也是重要影响因素,Ⅲ区中富铁地下水主要受控于还原条件;在区域尺度上,富铁地下水沿河流呈条带或斑状分布,原生地层中铁矿床和人类活动(工业废水)释放的铁是研究区浅层地下水中铁离子的主要来源,地下水中铁离子的迁移和富集主要受还原条件的控制,径流条件也起到一定作用,与pH无明显相关性,未引起明显的“盐效应”。研究结果可为西宁市及类似干旱—半干旱区城市水环境管理提供科学依据。
Abstract:Groundwater is an important water supply source in Xining City. Previous works have found that iron-rich groundwater limits water development and utilization. However, few studies focus on the distribution characteristics and mechanism of iron-rich groundwater in different types of aquifers in Xining City. Based on the hydrochemical data of 144 groundwater samples, combined with the geological and hydrogeological conditions, the distribution characteristics and influencing factors of iron content in groundwater in different aquifers were analyzed by methods of statistics and geostatistics. The results show that the exceeding standard ratio of iron in groundwater of unconsolidated sediments aquifer (Area Ⅰ) is 27. 85%, which is 1. 6 times and 2. 7 times higher than that of clastic rocks fissure-pore aquifer (Area Ⅱ) and bedrock aquifer (Area Ⅲ), respectively. The proportion of iron-rich groundwater (concentration greater than 0. 3 mg/L) in construction land area is significantly higher than in areas with other land use types. The redox environment and human activities (such as industrial wastewater, domestic sewage, and infiltration of iron-rich river water) may be the main factors affecting the increase of iron content in groundwater in Area I. In addition to the redox environment, Agricultural nitrogen fertilizer use and domestic sewage discharge are also important factors affecting iron-rich groundwater in Area Ⅱ. The iron-rich groundwater in Area Ⅲ is mainly controlled by redox conditions. On the regional scale, the distribution of iron-rich groundwater presents in bands or spots along the river. The iron deposits releasing in the primary strata and human activities (industrial wastewater) are the main source of iron ions in the shallow groundwater in the study area. The migration and enrichment of iron in groundwater are mainly controlled by redox conditions, and affected by the runoff condition, without relation to pH and salt effect. This study can provide scientific basis for urban water environment management in Xining City and similar arid and semi-arid areas.
-
Key words:
- groundwater /
- human activities /
- aquifers /
- Fe distribution characteristics /
- influencing factors /
- Xining City
-

-
表 1 水环境中铁质量浓度统计
Table 1. Statistics of iron concentration in groundwater
水点类型 类型区编号 Fe质量浓度/(mg·L−1) 变异系数/% 超标率/% 最大值 最小值 平均值 中位值 地下水 Ⅰ区(n=79) 100.80 <0.01 2.58 0.09 480.46 27.85 Ⅱ区(n=23) 3.09 <0.01 0.41 0.01 238.71 17.39 Ⅲ区(n=40) 0.85 <0.01 0.12 0.04 148.42 10.00 Ⅳ区(n=2) 0.09 <0.01 0.04 0.04 148.42 0.00 整区(n=144) 100.80 <0.01 1.52 0.05 609.17 20.83 地表水 北川河、湟水河(n=27) 2.04 0.04 0.76 0.68 72.64 77.78 注:计算统计Fe的测试数据时,未检出以0.7倍检出限替代;n为样品数量。 -
[1] JIA Yongfeng,XI Beidou,JIANG Yonghai,et al. Distribution,formation and human-induced evolution of geogenic contaminated groundwater in China:A review[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,643:967 − 993. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.201
[2] SHARMA G K,JENA R K,RAY P,et al. Evaluating the geochemistry of groundwater contamination with iron and manganese and probabilistic human health risk assessment in endemic areas of the world’s largest River Island,India[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology,2021,87:103690. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2021.103690
[3] CARRETERO S,KRUSE E. Iron and manganese content in groundwater on the northeastern coast of the Buenos Aires Province,Argentina[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2015,73(5):1983 − 1995. doi: 10.1007/s12665-014-3546-5
[4] ZHANG Ming,HUANG Guanxing,LIU Chunyan,et al. Distributions and origins of nitrate,nitrite,and ammonium in various aquifers in an urbanized coastal area,South China[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2020,582:124528. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124528
[5] REHMAN I U,ISHAQ M,ALI L,et al. Enrichment,spatial distribution of potential ecological and human health risk assessment via toxic metals in soil and surface water ingestion in the vicinity of Sewakht mines,district Chitral,Northern Pakistan[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2018,154:127 − 136. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.02.033
[6] 余东,周金龙,张杰,等. 新疆喀什地区地下水铁锰水文地球化学及演化规律[J]. 环境科学学报,2021,41(6):2169 − 2181. [YU Dong,ZHOU Jinlong,ZHANG Jie,et al. Hydrogeochemistry and evolution of iron and manganese in groundwater in Kashgar,Xinjiang[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2021,41(6):2169 − 2181. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YU Dong, ZHOU Jinlong, ZHANG Jie, et al. Hydrogeochemistry and evolution of iron and manganese in groundwater in Kashgar, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2021, 41(6): 2169 − 2181. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] BENOIT B,ANNIE C,MARYSE F B. Spatial and temporal variations of manganese concentrations in drinking water[J]. Journal of Environmental Science & Health,Part A:Toxic/Hazardous Substances & Environmental Engineering,2011,46(6):608 − 616.
[8] BONDU R,CLOUTIER V,ROSA E. Occurrence of geogenic contaminants in private wells from a crystalline bedrock aquifer in western Quebec,Canada:Geochemical sources and health risks[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2018,559:627 − 637. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.02.042
[9] YADAV K K,KUMAR S,PHAM Q B,et al. Fluoride contamination,health problems and remediation methods in Asian groundwater:A comprehensive review[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2019,182:109362. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.06.045
[10] EPA. Secondary drinking water standards:Guidance for nuisance chemicals[EB/OL]. 2024. https://www.epa.gov/sdwa/secondary-drinking-water-standards-guidance-nuisance-chemicals#table
[11] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局,中华人民共和国国家标准化管理委员会. 地下水质量标准:GB/T 14848—2017[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社,2017. [General Administration of Quality Supervision,Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China,Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Standard for groundwater quality:GB/T 14848—2017[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China,2017. (in Chinese)]
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Standard for groundwater quality: GB/T 14848—2017[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2017. (in Chinese)
[12] 吕晓立,刘景涛,周冰,等. 新疆塔城盆地地下水中铁锰分布特征及人类活动的影响[J]. 中国地质,2020,47(6):1765 − 1775. [LÜ Xiaoli,LIU Jingtao,ZHOU Bing,et al. Fe and Mn distribution of groundwater in the Tacheng Basin,Xinjiang and its impact of human activities[J]. Geology in China,2020,47(6):1765 − 1775. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LÜ Xiaoli, LIU Jingtao, ZHOU Bing, et al. Fe and Mn distribution of groundwater in the Tacheng Basin, Xinjiang and its impact of human activities[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(6): 1765 − 1775. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 曾昭华. 长江中下游地区地下水中Mn元素的背景特征及其形成[J]. 上海地质,2004,25(1):9 − 12. [ZENG Zhaohua. The background characteristics and formation of Mn element of groundwater in the area of the middle and lower veaches of the yangfze river[J]. Shanghai Geology,2004,25(1):9 − 12. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZENG Zhaohua. The background characteristics and formation of Mn element of groundwater in the area of the middle and lower veaches of the yangfze river[J]. Shanghai Geology, 2004, 25(1): 9 − 12. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] ZHAI Yuanzheng,ZHENG Fuxin,ZHAO Xiaobing,et al. Identification of hydrochemical genesis and screening of typical groundwater pollutants impacting human health:A case study in Northeast China[J]. Environmental Pollution,2019,252:1202 − 1215. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.05.158
[15] 李英,李洁,薛忠歧,等. 银川平原浅层地下水Fe、Mn空间分布及影响因素研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境,2018,32(5):110 − 115. [LI Ying,LI Jie,XUE Zhongqi,et al. Spatial distribution of iron and manganese in shallow groundwater in Yinchuan Plain[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment,2018,32(5):110 − 115. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Ying, LI Jie, XUE Zhongqi, et al. Spatial distribution of iron and manganese in shallow groundwater in Yinchuan Plain[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2018, 32(5): 110 − 115. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 梁国玲,孙继朝,黄冠星,等. 珠江三角洲地区地下水锰的分布特征及其成因[J]. 中国地质,2009,36(4):899 − 906. [LIANG Guoling,SUN Jichao,HUANG Guanxing,et al. Origin and distribution characteristics of manganese in groundwater of the Zhujiang River Delta[J]. Geology in China,2009,36(4):899 − 906. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIANG Guoling, SUN Jichao, HUANG Guanxing, et al. Origin and distribution characteristics of manganese in groundwater of the Zhujiang River Delta[J]. Geology in China, 2009, 36(4): 899 − 906. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] PAN Xinhao,WANG Yihang,LIU Zhifeng,et al. Understanding urban expansion on the Tibetan Plateau over the past half century based on remote sensing:The case of Xining City China[J]. Remote Sensing,2021,13(1):1 − 24.
[18] 李梦洁. 基于TOD模式的西宁市土地利用效益评价研究[D]. 西宁:青海师范大学,2020. [LI Mengjie. Study on land use benefit evaluation of Xining City based on TOD model[D]. Xining:Qinghai Normal University,2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Mengjie. Study on land use benefit evaluation of Xining City based on TOD model[D]. Xining: Qinghai Normal University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 谢丹,宋卓玛. 西宁市土地利用与生态环境耦合关系[J]. 内江师范学院学报,2017,32(4):89 − 95. [XIE Dan,SONG Zhuoma. Coupling relationship between land use and eco-environment in Xining City[J]. Journal of Neijiang Normal University,2017,32(4):89 − 95. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
XIE Dan, SONG Zhuoma. Coupling relationship between land use and eco-environment in Xining City[J]. Journal of Neijiang Normal University, 2017, 32(4): 89 − 95. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 规划科技处国土规划研究院. 《青海省土地利用总体规划》(2006年—2020年)具体内容[J]. 青海国土经略,2010(4):6 − 8. [Land Planning Research Institute of Planning and Technology Division. The specific contents of the Master Plan of Land Use in Qinghai Province (2006—2020)[J]. Management & Strategy of Qinghai Land & Resources,2010(4):6 − 8. (in Chinese)]
Land Planning Research Institute of Planning and Technology Division. The specific contents of the Master Plan of Land Use in Qinghai Province (2006—2020)[J]. Management & Strategy of Qinghai Land & Resources, 2010(4): 6 − 8. (in Chinese)
[21] MENDIETA-MENDOZA A,HANSON R T,RENTERIA-VILLALOBOS M. Potential adverse impacts on vulnerability and availability of groundwater from climate-change and land use[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2021,594:125978. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.125978
[22] MEKONNEN M M,HOEKSTRA A Y. Four billion people facing severe water scarcity[J]. Science Advances,2016,2(2):e1500323. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1500323
[23] 孙思奥,任宇飞,张蔷. 多尺度视角下的青藏高原水资源短缺估算及空间格局[J]. 地球信息科学学报,2019,21(9):1308 − 1317. [SUN Siao,REN Yufei,ZHANG Qiang. A multi-scale perspective on water scarcity assessment in the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science,2019,21(9):1308 − 1317. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
SUN Siao, REN Yufei, ZHANG Qiang. A multi-scale perspective on water scarcity assessment in the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 2019, 21(9): 1308 − 1317. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 刘春燕,刘景涛,朱亮,等. 高原河谷城市浅层地下水铁锰分布特征、影响因素及其对生态环境的影响——以西宁市为例[J/OL]. 中国地质,(2023-06-14)[2023-11-18]. [LIU Chunyan,LIU Jingtao,ZHU Liang,et al. Distribution characteristics,influencing factors and impacts on ecological environment of Fe and Mn in shallow groundwater of Plateau Valley-City:A case study of Xining city[J/OL]. Geology in China,(2023-06-14)[2023-11-18]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/detail/11.1167.P.20230613.1552.004.html. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Chunyan, LIU Jingtao, ZHU Liang, et al. Distribution characteristics, influencing factors and impacts on ecological environment of Fe and Mn in shallow groundwater of Plateau Valley-City: A case study of Xining city[J/OL]. Geology in China, (2023-06-14)[2023-11-18]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/detail/11.1167.P.20230613.1552.004.html. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] FAN Yupeng,FANG Chuanglin. Evolution process analysis of urban metabolic patterns and sustainability assessment in Western China,a case study of Xining city[J]. Ecological Indicators,2020,109:105784. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105784
[26] 刘春燕,于开宁,张英,等. 西宁市浅层地下水化学特征及形成机制[J]. 环境科学,2023,44(6):3228 − 3236. [LIU Chunyan,YU Kaining,ZHANG Ying,et al. Characteristics and driving mechanisms of shallow groundwater chemistry in Xining city[J]. Environmental Science,2023,44(6):3228 − 3236. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Chunyan, YU Kaining, ZHANG Ying, et al. Characteristics and driving mechanisms of shallow groundwater chemistry in Xining city[J]. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(6): 3228 − 3236. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 国家环境保护总局,国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 地表水环境质量标准:GB 3838—2002[S]. 北京:中国环境科学出版社,2002. [State Environmental Protection Administration of the Peoples Republic of China,General Administration of Quality Supervision,Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. Environmental quality standards for surface water:GB 3838—2002[S]. Beijing:China Environmental Science Press,2002. (in Chinese)]
State Environmental Protection Administration of the Peoples Republic of China, General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. Environmental quality standards for surface water: GB 3838—2002[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2002. (in Chinese)
[28] ZHANG Bing,SONG Xianfang,ZHANG Yinghua,et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality assessment of surface water and groundwater in Songnen Plain,Northeast China[J]. Water Research,2012,46(8):2737 − 2748. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2012.02.033
[29] LI Zijun,YANG Qingchun,YANG Yuesuo,et al. Isotopic and geochemical interpretation of groundwater under the influences of anthropogenic activities[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2019,576:685 − 697. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.06.037
[30] 陈毓川. 中国新疆战略性固体矿产大型矿集区研究[M]. 北京:地质出版社,2007. [CHEN Yuchuan. Research on large scale ore concentration area of strategic mineral resources in Xinjiang,China[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House,2007. (in Chinese)]
CHEN Yuchuan. Research on large scale ore concentration area of strategic mineral resources in Xinjiang, China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2007. (in Chinese)
[31] 张爱奎,马生龙,刘光莲,等. 青海省铁矿时空分布、成矿系列及成矿模式[J]. 矿物学报,2019,39(1):41 − 54. [ZHANG Aikui,MA Shenglong,LIU Guanglian,et al. The spatial-temporal distribution,minerogenic series and metallogenic models of iron deposits,Qinghai Province,China[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica,2019,39(1):41 − 54. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Aikui, MA Shenglong, LIU Guanglian, et al. The spatial-temporal distribution, minerogenic series and metallogenic models of iron deposits, Qinghai Province, China[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2019, 39(1): 41 − 54. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] ADEYEYE O,XIAO Changlai,ZHANG Zhihao,et al. State,source and triggering mechanism of iron and manganese pollution in groundwater of Changchun,Northeastern China[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment,2020,192(10):619. doi: 10.1007/s10661-020-08571-0
[33] JIA Yongfeng,GUO Huaming,JIANG Yuxiao,et al. Hydrogeochemical zonation and its implication for arsenic mobilization in deep groundwaters near alluvial fans in the Hetao Basin,Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2014,518:410 − 420. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.02.004
[34] KOIT O,BARBERÁ J A,MARANDI A,et al. Spatiotemporal assessment of humic substance-rich stream and shallow Karst aquifer interactions in a boreal catchment of northern Estonia[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2020,580:124238. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124238
[35] ZHAI Yuanzheng,HAN Yifan,XIA Xuelian,et al. Anthropogenic organic pollutants in groundwater increase releases of Fe and Mn from aquifer sediments:Impacts of pollution degree,mineral content,and pH[J]. Water,2021,13:1 − 15.
[36] ZHAI Yuanzheng,CAO Xinyi,XIA Xuelian,et al. Elevated Fe and Mn concentrations in groundwater in the Songnen Plain,Northeast China,and the factors and mechanisms involved[J]. Agronomy,2021,11:2392. doi: 10.3390/agronomy11122392
[37] 蔡玲,胡成,陈植华,等. 江汉平原东北部地区高铁锰地下水成因与分布规律[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(4):18 − 25. [CAI Ling,HU Cheng,CHEN Zhihua,et al. Distribution and genesis of high Fe and Mn groundwater in the northeast of the Jianghan Plain[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(4):18 − 25. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CAI Ling, HU Cheng, CHEN Zhihua, et al. Distribution and genesis of high Fe and Mn groundwater in the northeast of the Jianghan Plain[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2019, 46(4): 18 − 25. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[38] HUANG Guanxing,HAN Dongya,SONG Jiangmin,et al. A sharp contrasting occurrence of iron-rich groundwater in the Pearl River Delta during the past dozen years (2006–2018):The genesis and mitigation effect[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2022,829:154676. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154676
[39] 黄冠星,孙继朝,荆继红,等. 珠江三角洲地区地下水铁的分布特征及其成因[J]. 中国地质,2008,35(3):531 − 538. [HUANG Guanxing,SUN Jichao,JING Jihong,et al. Distribution and origin of iron in groundwater of the Zhujiang delta[J]. Geology in China,2008,35(3):531 − 538. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HUANG Guanxing, SUN Jichao, JING Jihong, et al. Distribution and origin of iron in groundwater of the Zhujiang delta[J]. Geology in China, 2008, 35(3): 531 − 538. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[40] ZHAI Yuanzheng,MA Tianyi,ZHOU Jingjing,et al. Impacts of leachate of landfill on the groundwater hydrochemistry and size distributions and heavy metal components of colloids:A case study in NE China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International,2019,26(6):5713 − 5723. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-4053-0
[41] DU Yao,DENG Yamin,MA Teng,et al. Enrichment of geogenic ammonium in quaternary alluvial-lacustrine aquifer systems:Evidence from carbon isotopes and DOM characteristics[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2020,54(10):6104 − 6114.
[42] MCMAHON P B,BELITZ K,REDDY J E,et al. Elevated manganese concentrations in United States groundwater,role of land surface-soil-aquifer connections[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2019,53(1):29 − 38.
[43] ZHANG Zhihao,XIAO Changlai,YANG Weifei,et al. Effects of the natural environment and human activities on iron and manganese content in groundwater:A case study of Changchun city,Northeast China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International,2021,28(30):41109 − 41119. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-13576-4
-




 下载:
下载: