Attribution analysis of water-sediment variation under the influence of climate change and human activities in the Kuye River Basin
-
摘要:
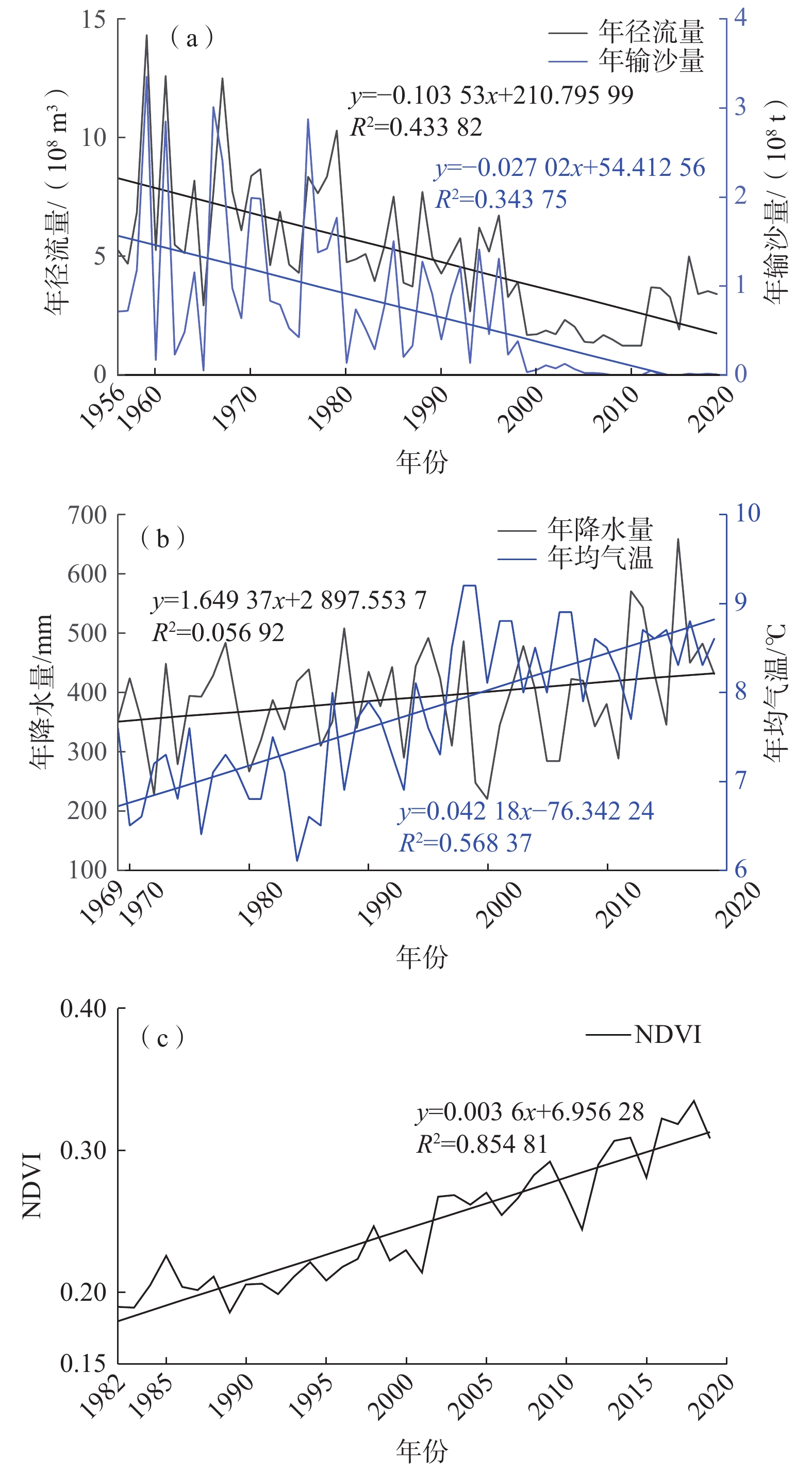
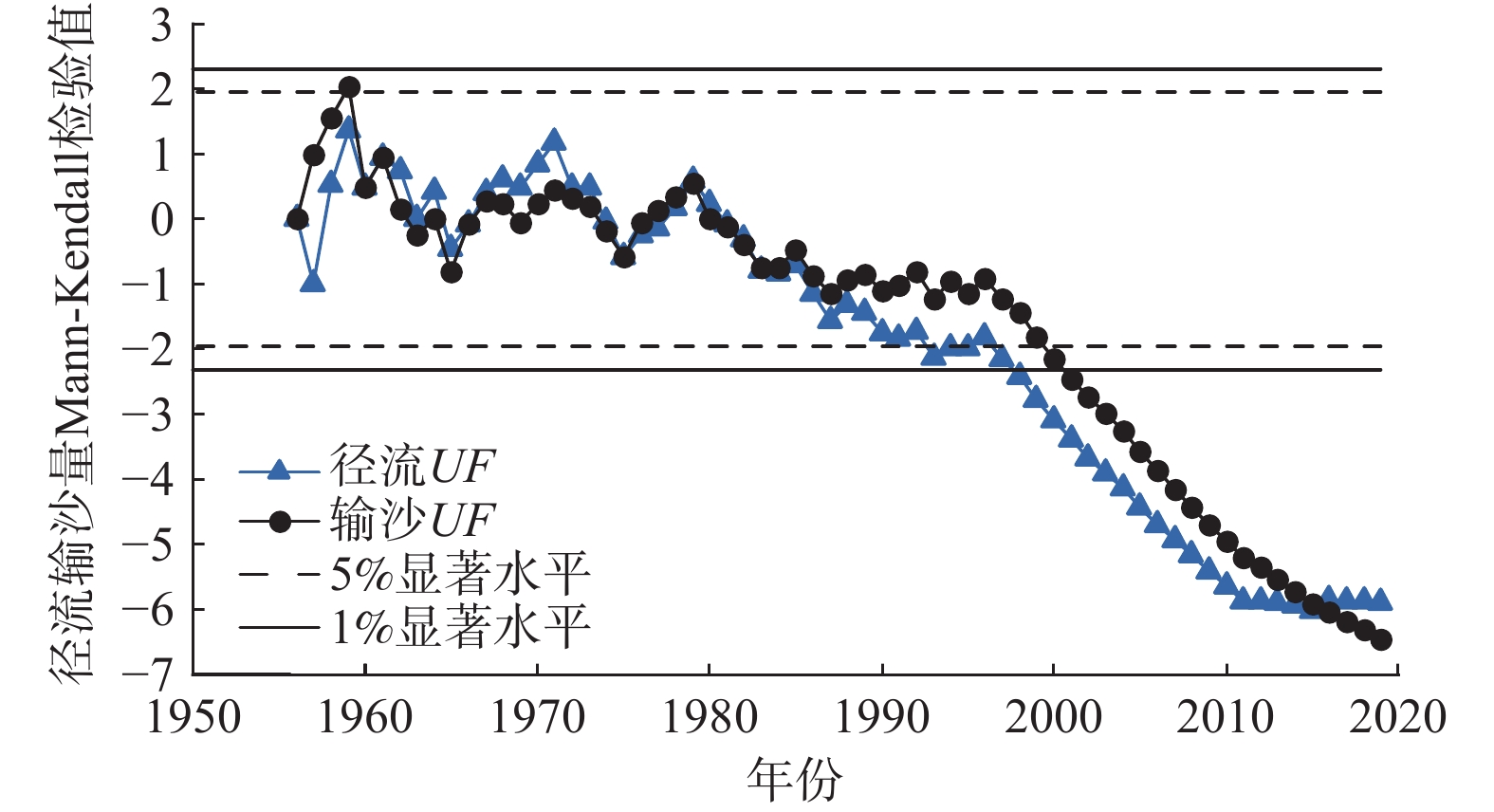
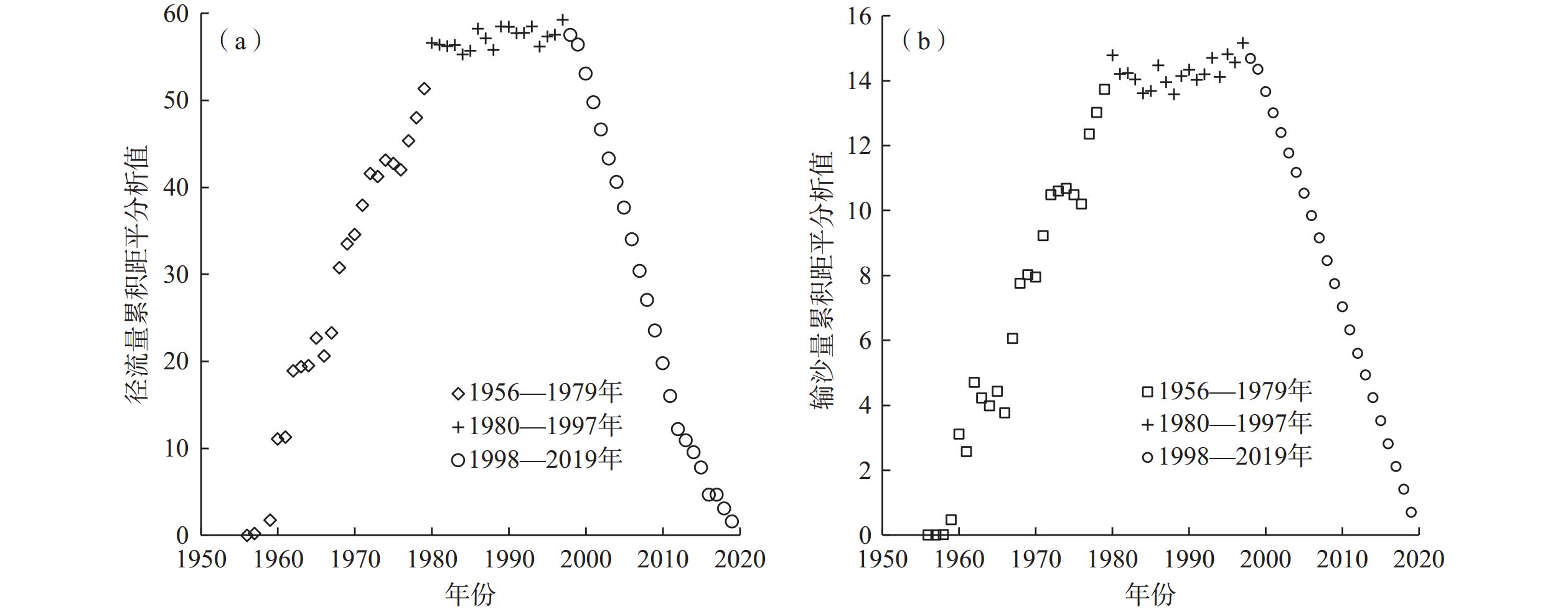
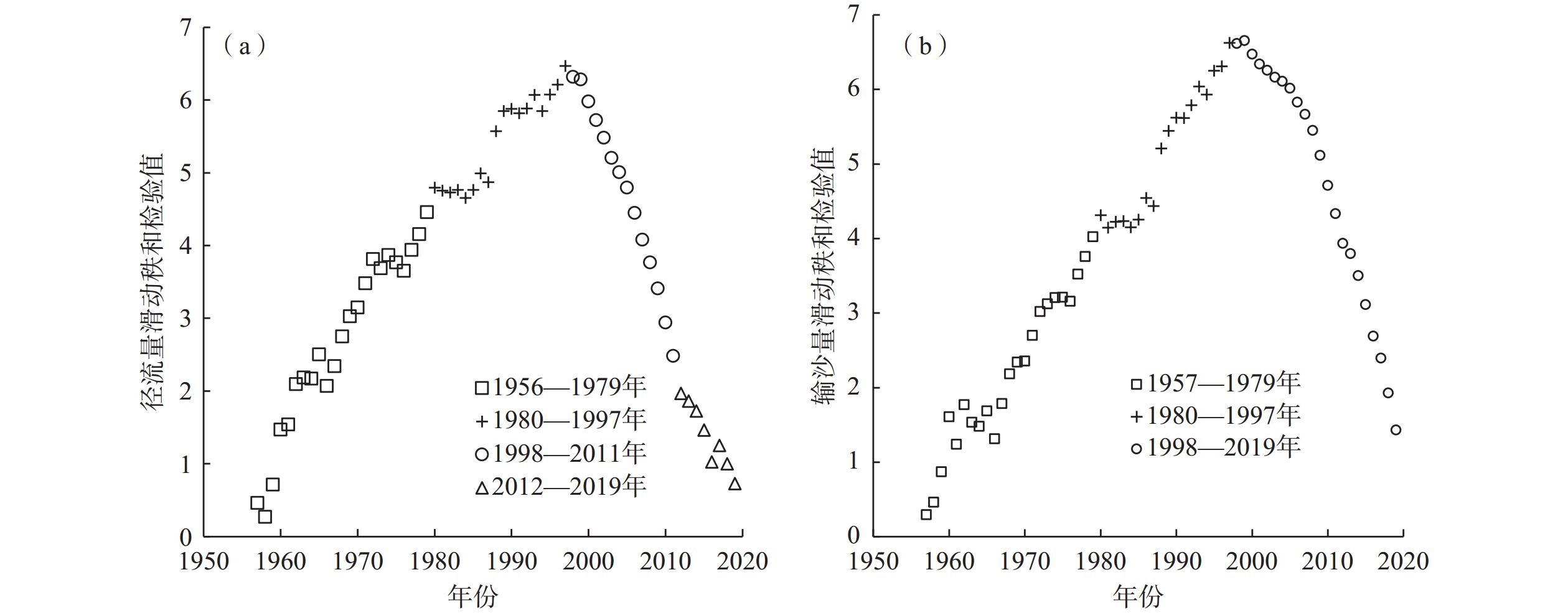
流域水沙情势演变归因是水文地质学的研究重点之一。为了深入理解窟野河流域水沙变化规律,并为水资源管理和生态保护提供科学依据,以应对气候变化和人类活动的影响,基于水文、气象、归一化植被指数、土地利用等数据信息,运用累积量斜率变化率分析法、Mann-Kendall非参数检验法、双累积曲线法、累积距平法、滑动秩和检验法等方法,定量研究气候变化和人类活动综合作用下流域水沙变化趋势及其影响归因。结果表明:(1)窟野河流域1956—2019年的年径流量、年输沙量呈显著减少趋势,年径流量和年输沙量平均每年减少约0.104×108 m3和0.027×108 t,突变年为1997年,通过了5%显著性水平检验;(2)1998—2011年间,气候变化和人类活动对流域年径流量减少的贡献率分别为36.06%和63.94%,对年输沙量减少的贡献率分别为26.11%和73.89%,其中径流量减少主要与退耕还林还草工程导致的植被、土地利用/覆被变化有关;(3)以1998—2011年为基准期,2012—2019年累积径流量斜率变化率高达109%,径流量反弹明显,可能与矿井封存水外溢有关,同时,累积输沙量斜率接近零,输沙量无显著变化,说明研究区土壤侵蚀得到有效控制。研究成果为窟野河流域水文预测与管理提供科学依据,未来需重点关注生态恢复和煤炭开采活动对水资源变化的复合影响。
Abstract:The attribution of the evolution of water and sediment in a river basin is an important theoretical issue in hydrogeology. To understand the change patterns of water and sediment in the Kuye River Basin and provide scientific basis for water resources management and ecological protection under the impacts of climate change and human activities, based on hydrological and meteorological observation data, NDVI (normalized difference vegetation index), and land use change data, this study quantitatively analyzed the trends of water and sediment changes in the basin and their attributed influences using the Mann-Kendall non-parametric test, double mass curve method, cumulative anomaly analysis, sliding rank-sum test, and cumulative quantity slope change rate analysis. The results indicate that from 1956 to 2019, the annual runoff and sediment yield in the Kuye River Basin showed a significant decreasing trend, with an average annual decrease of approximately 10.4 million m3 and 2.7 million tons. The abrupt change year was 1997, verified by the 95% significance level test. From 1998 to 2011, the contribution rates of climate change and human activities to the decrease in annual runoff were 36.06% and 63.94%, respectively. The contribution rates to the decrease in sediment transport were 26.11% and 73.89%, respectively. The decrease in runoff is mainly related to vegetation and land use/cover changes caused by the Grain for Green Program. Using 1998—2011 as the base period, the cumulative slope change rate of runoff reached 109% during 2012—2019. It indicates a significant rebound in runoff, possibly related to the overflow of mine sealing water. The cumulative slope of sediment yield approached 0, indicating no significant change in sediment yield and effective control of soil erosion in the study area. The analysis method of slope change rate of cumulative quantity has good applicability and provides scientific basis for hydrological prediction and management in the Kuye River basin. In the future. It is necessary to pay more attention to the combined effects of ecological restoration and coal mining activities on water resources change.
-

-
表 1 年径流量、输沙量、降水量和年均气温、年最大NDVI值的Mann-Kendall趋势检验结果
Table 1. Mann-Kendall trend test results of annual runoff, sediment transport, precipitation, air temperature, and NDVI
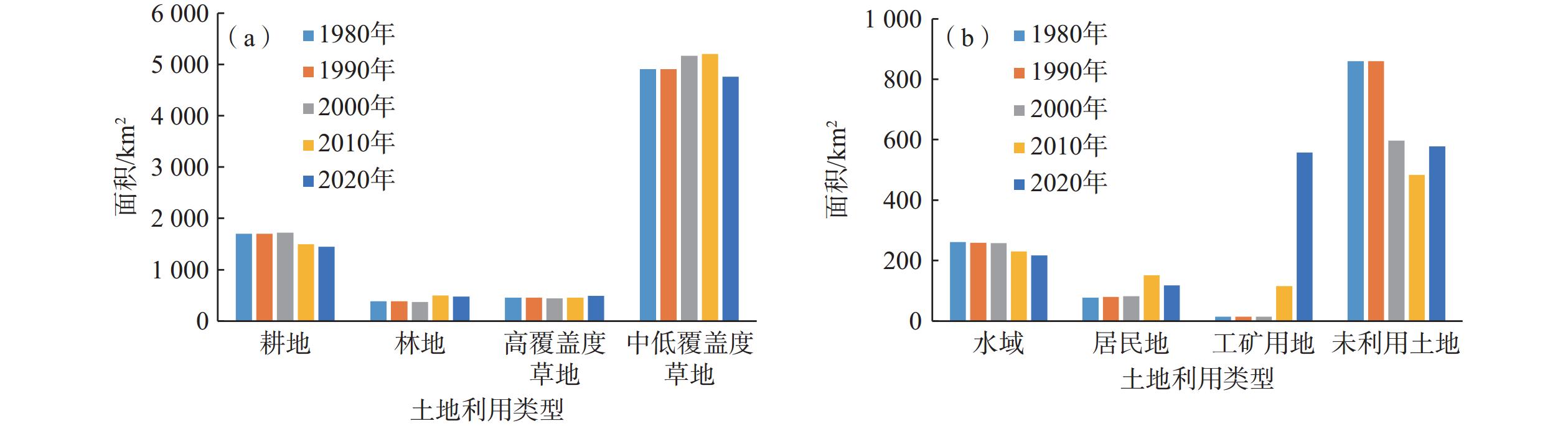
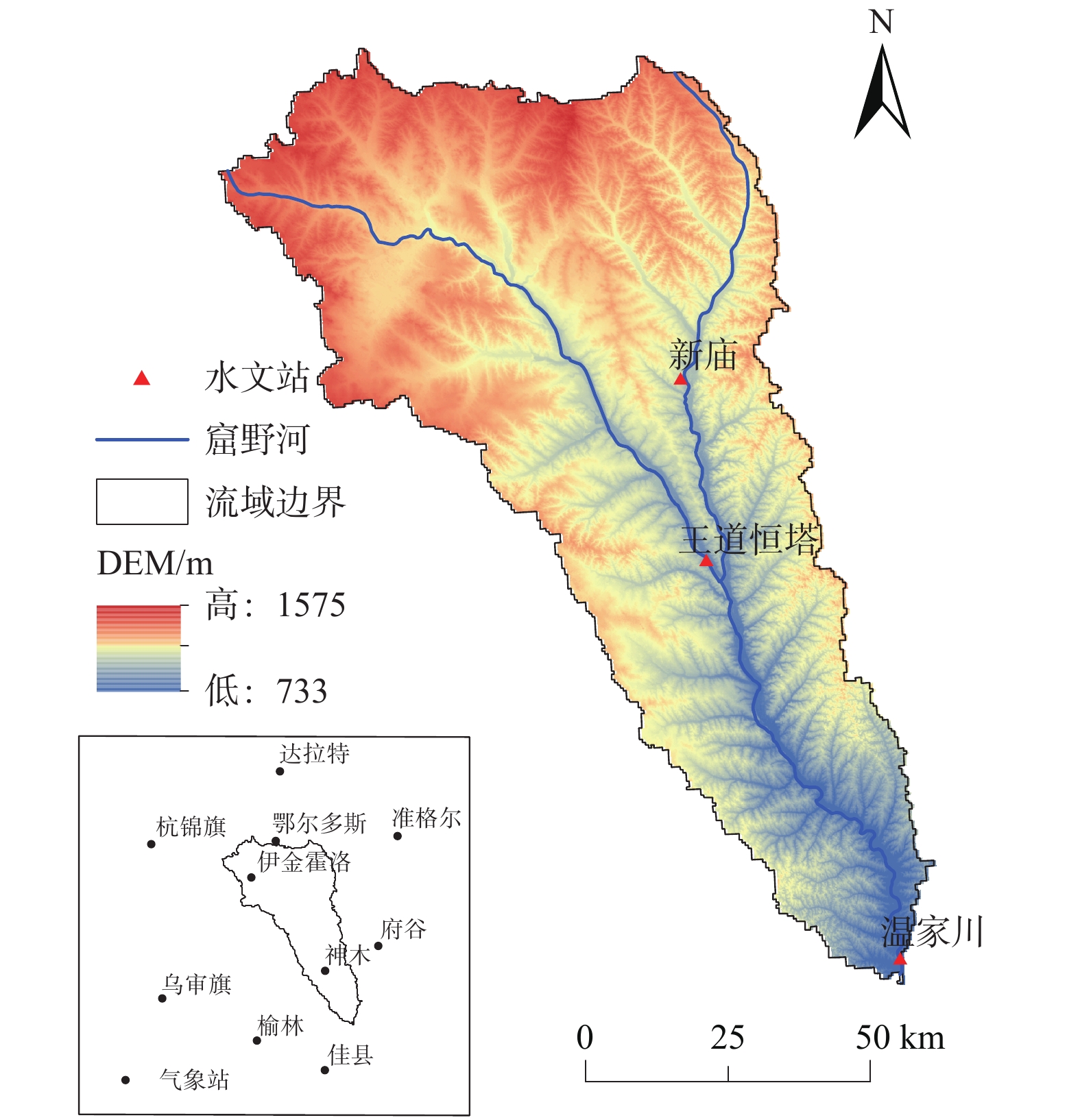
水文站 年径流量Z值 年输沙量Z值 年降水量Z值 年均气温Z值 年最大NDVI的Z值 温家川 −5.887 −6.471 1.606 5.179 6.587 表 2 1995—2020年土地利用类型转移矩阵
Table 2. Land-use transfer matrix from 1995 to 2020
/km2 时间 土地利用类型 高覆盖度草地 耕地 工矿用地 居民地 林地 水域 未利用土地 中低覆盖度草地 1995—2010年 高覆盖度草地 325.44 76.87 0.00 0.16 10.19 1.63 2.45 40.48 耕地 5.57 1411.23 0.00 1.17 3.13 7.57 2.47 67.98 工矿用地 18.17 11.85 1.54 0.77 6.57 2.95 5.43 68.26 居民地 6.16 36.61 0.01 76.81 4.96 4.18 1.53 21.29 林地 28.45 67.27 0.00 0.16 282.60 9.65 5.56 105.25 水域 2.48 3.03 0.07 0.10 2.56 193.41 7.62 21.37 未利用土地 7.99 10.25 0.01 0.04 1.55 10.10 270.93 182.93 中低覆盖度草地 323.57 133.90 0.21 1.17 21.67 27.10 66.42 4630.83 2010—2020年 高覆盖度草地 407.07 4.40 4.38 6.95 6.86 0.56 1.25 55.93 耕地 2.74 1323.52 6.94 19.61 5.36 3.89 1.88 81.66 工矿用地 18.31 66.92 59.43 6.68 25.66 22.10 33.56 324.93 居民地 5.39 2.47 0.82 98.63 1.34 0.46 0.33 9.01 林地 2.27 3.84 3.41 3.03 434.47 1.27 1.53 25.61 水域 0.77 3.60 1.08 2.71 1.38 196.18 3.36 8.18 未利用土地 1.27 2.03 5.02 0.66 2.89 1.28 421.18 143.57 中低覆盖度草地 19.21 91.82 34.43 13.18 20.79 4.70 20.61 4554.07 表 3 窟野河流域各变化期累积年径流量、年输沙量、年降水量、年平均气温、年最大NDVI的斜率及变化率
Table 3. Accumulated annual runoff, sediment load, precipitation, air temperature, and NDVI slope change rate in each variation period of the Kuye River Basin
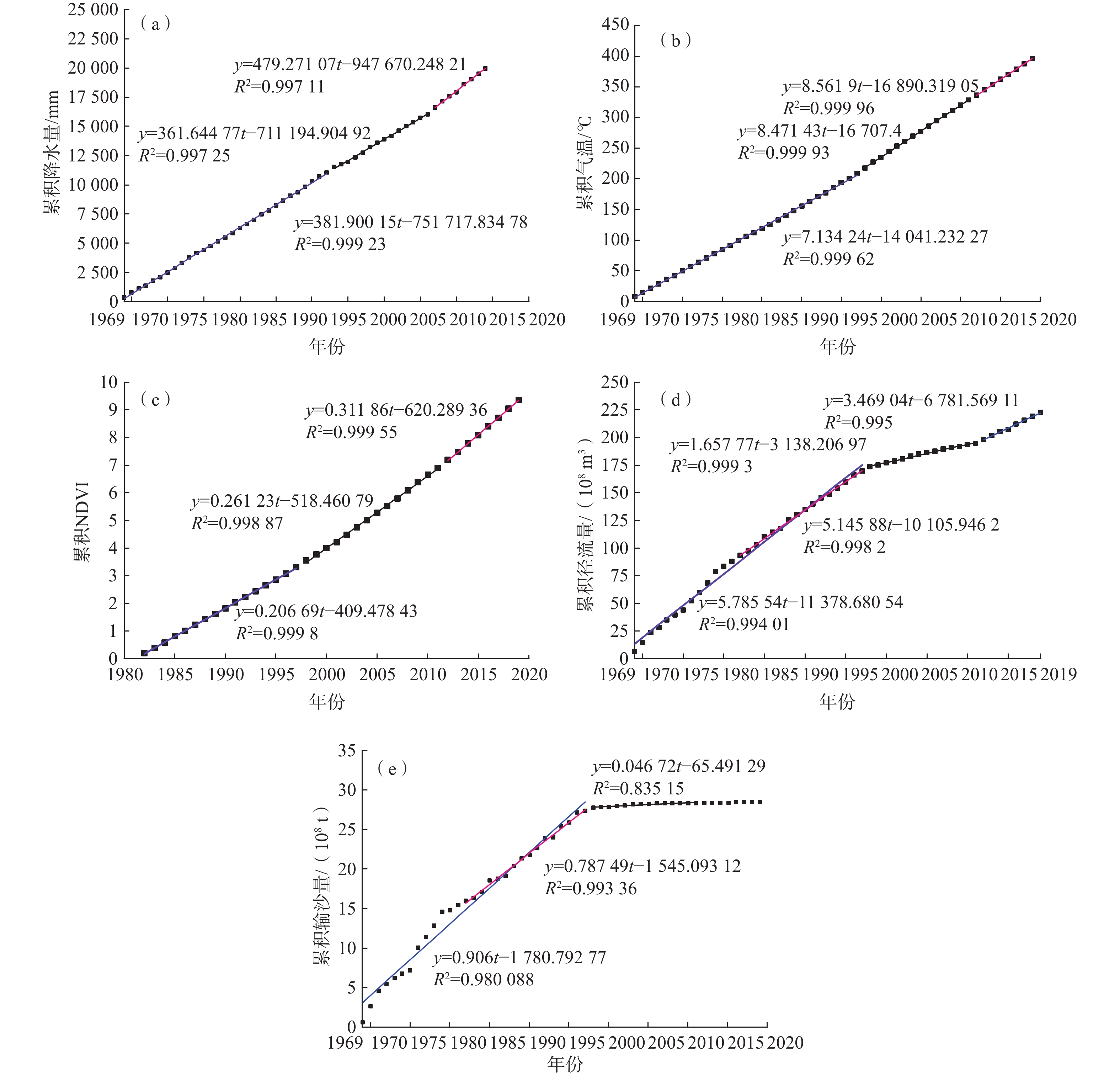
时期 时段 年累积径流量 年累积输沙量 累积年降水量 累积年平均气温 累积年最大NDVI S ΔS ΔS/S S ΔS ΔS/S S ΔS ΔS/S S ΔS ΔS/S S ΔS ΔS/S A1—B A1(1969—1997年) 5.79 −4.13 −0.71 0.91 −0.86 −0.95 381.90 −20.26 −0.05 7.13 1.34 0.19 0.21 0.05 0.24 B(1998—2011年) 1.66 0.05 361.64 8.47 0.26 A2—B A2(1980—1997年) 5.14 −3.48 −0.68 0.77 −0.72 −0.94 394.76 −33.12 −0.08 7.30 1.17 0.16 0.21 0.05 0.26 B—C C(2012—2019年) 3.47 1.81 1.09 0.00 479.27 117.63 0.33 8.56 0.09 0.01 0.31 0.05 0.19 注: S为斜率;ΔS为斜率变化量;ΔS/S为斜率变化率。 表 4 窟野河流域气候变化和人类活动对径流量和输沙量变化的贡献率
Table 4. Contribution rates of climate change and human activities to changes in runoff and sediment load in the Kuye River Basin
计算方案 年径流量 年输沙量 仅考虑降水/% 综合考虑降水和气温/% 仅考虑降水/% 综合考虑降水和气温/% A1—B时期 A2—B时期 B—C时期 A1—B时期 A2—B时期 B—C时期 A1—B时期 A2—B时期 A1—B时期 A2—B时期 气候变化 7.44 12.39 29.83 33.79 36.06 28.86 5.60 8.97 25.42 26.11 年降水量 7.44 12.39 29.83 7.44 12.39 29.83 5.60 8.97 5.60 8.97 年平均气温 — — — 26.35 23.67 −0.97 — — 19.82 17.14 人类活动 92.56 87.61 70.17 66.21 63.94 71.14 94.40 91.03 74.58 73.89 年最大NDVI 33.38 38.97 −17.78 33.38 38.97 −17.78 25.11 25.46 25.11 25.46 -
[1] LI Huijuan,SHI Changxing,ZHANG Yusheng,et al. Using the Budyko hypothesis for detecting and attributing changes in runoff to climate and vegetation change in the soft sandstone area of the middle Yellow River Basin,China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,703:135588. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135588
[2] PARK E,HO H L,VAN BINH D,et al. Impacts of agricultural expansion on floodplain water and sediment budgets in the Mekong River[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2022,605:127296. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.127296
[3] FANOS A M. The impact of human activities on the erosion and accretion of the Nile delta coast[J]. Journal of Coastal Research,1995,11(3):821 − 833.
[4] CARRIQUIRY J D,SÁNCHEZ A. Sedimentation in the Colorado River delta and upper gulf of California after nearly a century of discharge loss[J]. Marine Geology,1999,158(1/2/3/4):125 − 145.
[5] 赵芳芳,徐宗学. 黄河源区未来气候变化的水文响应[J]. 资源科学,2009,31(5):722 − 730. [ZHAO Fangfang,XU Zongxue. Hydrological response to climate change in headwater catchment of the Yellow River Basin[J]. Resources Science,2009,31(5):722 − 730. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-7588.2009.05.002
ZHAO Fangfang, XU Zongxue. Hydrological response to climate change in headwater catchment of the Yellow River Basin[J]. Resources Science, 2009, 31(5): 722 − 730. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-7588.2009.05.002
[6] FANG Haiyan. Water erosion research in China:A review[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences Discussions,2020:1-53.
[7] CHANG Jianxia,WANG Yimin,ISTANBULLUOGLU E,et al. Impact of climate change and human activities on runoff in the Weihe River Basin,China[J]. Quaternary International,2015,380:169 − 179.
[8] GUO Qiaoling,YANG Yunsong,XIONG Xinzhi. Using hydrologic simulation to identify contributions of climate change and human activity to runoff changes in the Kuye River Basin,China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2016,75(5):417. doi: 10.1007/s12665-016-5280-7
[9] LUAN Jinkai,ZHANG Yongqiang,TIAN Jing,et al. Coal mining impacts on catchment runoff[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2020,589:125101. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125101
[10] 鲍振鑫,张建云,王国庆,等. 基于水文模型与机器学习集合模拟的水沙变异归因定量识别——以黄河中游窟野河流域为例[J]. 水科学进展,2021,32(4):485 − 496. [BAO Zhenxin,ZHANG Jianyun,WANG Guoqing,et al. Quantitative assessment of the attribution of runoff and sediment changes based on hydrologic model and machine learning:A case study of the Kuye River in the Middle Yellow River Basin[J]. Advances in Water Science,2021,32(4):485 − 496. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
BAO Zhenxin, ZHANG Jianyun, WANG Guoqing, et al. Quantitative assessment of the attribution of runoff and sediment changes based on hydrologic model and machine learning: A case study of the Kuye River in the Middle Yellow River Basin[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2021, 32(4): 485 − 496. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] LOTFIRAD M,ADIB A,SALEHPOOR J,et al. Simulation of the impact of climate change on runoff and drought in an arid and semiarid basin (the Hablehroud,Iran)[J]. Applied Water Science,2021,11(10):168. doi: 10.1007/s13201-021-01494-2
[12] 李慧娟,师长兴,马小晴,等. 黄河中游窟野河流域水沙变化影响因素定量评估[J]. 资源科学,2020,42(3):499 − 507. [LI Huijuan,SHI Changxing,MA Xiaoqing,et al. Quantification of the influencing factors of runoff and sediment discharge changes of the Kuye River catchment in the middle reaches of the Yellow River[J]. Resources Science,2020,42(3):499 − 507. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.18402/resci.2020.03.08
LI Huijuan, SHI Changxing, MA Xiaoqing, et al. Quantification of the influencing factors of runoff and sediment discharge changes of the Kuye River catchment in the middle reaches of the Yellow River[J]. Resources Science, 2020, 42(3): 499 − 507. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.18402/resci.2020.03.08
[13] 韩双宝,王赛,赵敏敏,等. 北洛河流域生态环境变迁及对水资源和水沙关系的影响[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(6):14 − 24. [HAN Shuangbao,WANG Sai,ZHAO Minmin,et al. Ecological environmental changes and its impact on water resources and water-sediments relationship in Beiluo River Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(6):14 − 24. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HAN Shuangbao, WANG Sai, ZHAO Minmin, et al. Ecological environmental changes and its impact on water resources and water-sediments relationship in Beiluo River Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(6): 14 − 24. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 赵娜娜,王贺年,于一雷,等. 基于Budyko假设的若尔盖流域径流变化归因分析[J]. 南水北调与水利科技,2018,16(6):21 − 26. [ZHAO Nana,WANG Henian,YU Yilei,et al. The attribution analysis of streamflow changes in the Zoige Basin based on the Budyko hypothesis[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology,2018,16(6):21 − 26. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHAO Nana, WANG Henian, YU Yilei, et al. The attribution analysis of streamflow changes in the Zoige Basin based on the Budyko hypothesis[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 2018, 16(6): 21 − 26. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] WANG Suiji,YAN Ming,YAN Yunxia,et al. Contributions of climate change and human activities to the changes in runoff increment in different sections of the Yellow River[J]. Quaternary International,2012,282:66 − 77. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2012.07.011
[16] WANG Suiji,YAN Yunxia,YAN Ming,et al. Quantitative estimation of the impact of precipitation and human activities on runoff change of the Huangfuchuan River Basin[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences,2012,22(5):906 − 918. doi: 10.1007/s11442-012-0972-8
[17] CHENG Qingping,ZUO Xiaoan,ZHONG Fanglei,et al. Runoff variation characteristics,association with large-scale circulation and dominant causes in the Heihe River Basin,Northwest China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2019,688:361 − 379. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.397
[18] HU Didi,XU Min,KANG Shichang,et al. Impacts of climate change and human activities on runoff changes in the Ob River Basin of the Arctic region from 1980 to 2017[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology,2022,148(3):1663 − 1674.
[19] MIAO Chiyuan,NI Jinren,BORTHWICK A G L,et al. A preliminary estimate of human and natural contributions to the changes in water discharge and sediment load in the Yellow River[J]. Global and Planetary Change,2011,76(3/4):196 − 205.
[20] SHI Hongling,HU Chunhong,WANG Yangui,et al. Analyses of trends and causes for variations in runoff and sediment load of the Yellow River[J]. International Journal of Sediment Research,2017,32(2):171 − 179. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsrc.2016.09.002
[21] GU Chaojun,MU Xxingmin. ,GAO Peng,et al. Changes in run‐off and sediment load in the three parts of the Yellow River basin,in response to climate change and human activities[J]. Hydrological Processes,2019,33(4):585 − 601. doi: 10.1002/hyp.13345
[22] LIU Yu,SONG Huiming,AN Zhisheng,et al. Recent anthropogenic curtailing of Yellow River runoff and sediment load is unprecedented over the past 500 y[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2020,117(31):18251 − 18257.
[23] WANG Hong,SUN Fubao. Variability of annual sediment load and runoff in the Yellow River for the last 100 years (1919–2018)[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2021,758:143715. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143715
[24] WANG Junjie,SHI Bing,ZHAO Enjin,et al. The long-term spatial and temporal variations of sediment loads and their causes of the Yellow River Basin[J]. Catena,2022,209:105850. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2021.105850
[25] HE Yi,MU Xingmin,JIANG Xiaohui,et al. Runoff variation and influencing factors in the Kuye River basin of the middle Yellow River[J]. Frontiers in Environmental Science,2022,10:877535. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2022.877535
[26] HUANG Tingting,WANG Zhihui,WU Zhiyong,et al. Attribution analysis of runoff evolution in Kuye River Basin based on the time-varying budyko framework[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science,2023,10:1092409. doi: 10.3389/feart.2022.1092409
[27] 刘晓燕,李皓冰,李晓宇,等. 黄河流域窟野河入黄水沙锐减成因分析[J]. 水利学报,2022,53(3):296 − 305. [LIU Xiaoyan,LI Haobing,LI Xiaoyu,et al. Analysis on the cause of sharp decrease of runoff and sediment from Kuye River in Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2022,53(3):296 − 305. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Xiaoyan, LI Haobing, LI Xiaoyu, et al. Analysis on the cause of sharp decrease of runoff and sediment from Kuye River in Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2022, 53(3): 296 − 305. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] GUO Qiaoling,SU Ning,YANG Yunsong,et al. Using hydrological simulation to identify contribution of coal mining to runoff change in the Kuye River Basin,China[J]. Water Resources,2017,44(4):586 − 594. doi: 10.1134/S0097807817040054
[29] ZHANG Jiankang,DONG Hua,CHENG Yanpei et al. Compilation of hydrogeological map of China[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering. 2020,8(4):381 − 395.
[30] WANG Zhaosheng. Satellite-observed effects from ozone pollution and climate change on growing-season vegetation activity over China during 1982–2020[J]. Atmosphere,2021,12(11):1390. doi: 10.3390/atmos12111390
[31] LIU Jiyuan,KUANG Wenhui,ZHANG Zengxiang,et al. Spatiotemporal characteristics,patterns,and causes of land-use changes in China since the late 1980s[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences,2014,24(2):195 − 210. doi: 10.1007/s11442-014-1082-6
[32] YUE Sheng,PILON P,PHINNEY B,et al. The influence of autocorrelation on the ability to detect trend in hydrological series[J]. Hydrological Processes,2002,16(9):1807 − 1829. doi: 10.1002/hyp.1095
[33] 穆兴民,张秀勤,高鹏,等. 双累积曲线方法理论及在水文气象领域应用中应注意的问题[J]. 水文,2010,30(4):47 − 51. [MU Xingmin,ZHANG Xiuqin,GAO Peng,et al. Theory of double mass curves and its applications in hydrology and meteorology[J]. Journal of China Hydrology,2010,30(4):47 − 51. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0852.2010.04.011
MU Xingmin, ZHANG Xiuqin, GAO Peng, et al. Theory of double mass curves and its applications in hydrology and meteorology[J]. Journal of China Hydrology, 2010, 30(4): 47 − 51. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0852.2010.04.011
[34] 刘强,李苗苗,罗霞飞,等. 黄河中游河龙区间水沙变化特征及其对降雨和人类活动的响应[J]. 天水师范学院学报,2021,41(5):22 − 28. [LIU Qiang,LI Miaomiao,LUO Xiafei,et al. Variation characteristics of runoff and sediment in the Helong Region of the middle Yellow River and its response to climate change and human activities[J]. Journal of Tianshui Normal University,2021,41(5):22 − 28. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Qiang, LI Miaomiao, LUO Xiafei, et al. Variation characteristics of runoff and sediment in the Helong Region of the middle Yellow River and its response to climate change and human activities[J]. Journal of Tianshui Normal University, 2021, 41(5): 22 − 28. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[35] 赵溦,王向东,张晓明,等. 窟野河流域水沙演变的尺度效应驱动因素研究[J]. 水文,2016,36(2):56 − 61. [ZHAO Wei,WANG Xiangdong,ZHANG Xiaoming,et al. Scale effect driving factors of runoff and sediment evolution in Kuye River basin[J]. Journal of China Hydrology,2016,36(2):56 − 61. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0852.2016.02.011
ZHAO Wei, WANG Xiangdong, ZHANG Xiaoming, et al. Scale effect driving factors of runoff and sediment evolution in Kuye River basin[J]. Journal of China Hydrology, 2016, 36(2): 56 − 61. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0852.2016.02.011
[36] 魏宣,王宁,周明通,等. 气候变化和人类活动对克里雅河径流变化影响定量研究[J]. 灌溉排水学报,2022,41(8):80 − 86. [WEI Xuan,WANG Ning,ZHOU Mingtong,et al. Combined impact of climate change and human activities on runoff in the Kriya river[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage,2022,41(8):80 − 86. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WEI Xuan, WANG Ning, ZHOU Mingtong, et al. Combined impact of climate change and human activities on runoff in the Kriya river[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2022, 41(8): 80 − 86. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[37] 田甜,黄强,郭爱军,等. 基于标准化降雨蒸散指数的渭河流域干旱演变特征分析[J]. 水力发电学报,2016,35(2):16 − 27. [TIAN Tian,HUANG Qiang,GUO Aijun,et al. Drought evolution characteristics in Wei River Basin based on standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering,2016,35(2):16 − 27. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.11660/slfdxb.20160202
TIAN Tian, HUANG Qiang, GUO Aijun, et al. Drought evolution characteristics in Wei River Basin based on standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering, 2016, 35(2): 16 − 27. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11660/slfdxb.20160202
[38] MANN H B,WHITNEY D R. On a test of whether one of two random variables is stochastically larger than the other[J]. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics,1947,18(1):50 − 60. doi: 10.1214/aoms/1177730491
[39] 姚惠明,秦福兴,沈国昌,等. 黄河宁蒙河段凌情特性研究[J]. 水科学进展,2007,18(6):893 − 899. [YAO Huiming,QIN Fuxing,SHEN Guochang,et al. Ice regime characteristics in the Ningxia-Inner Mongolia reach of Yellow River[J]. Advances in Water Science,2007,18(6):893 − 899. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6791.2007.06.017
YAO Huiming, QIN Fuxing, SHEN Guochang, et al. Ice regime characteristics in the Ningxia-Inner Mongolia reach of Yellow River[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2007, 18(6): 893 − 899. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6791.2007.06.017
[40] 赵益平,王文圣,张丹,等. 累积量斜率变化分析法及其在径流变化归因中的应用[J]. 水电能源科学,2019,37(10):17 − 20. [ZHAO Yiping,WANG Wensheng,ZHANG Dan,et al. Slope change analysis method of cumulative quantity and its application in runoff change attribution[J]. Water Resources and Power,2019,37(10):17 − 20. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHAO Yiping, WANG Wensheng, ZHANG Dan, et al. Slope change analysis method of cumulative quantity and its application in runoff change attribution[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2019, 37(10): 17 − 20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[41] 赵晓坤,王随继,范小黎. 1954—1993年间窟野河径流量变化趋势及其影响因素分析[J]. 水资源与水工程学报,2010,21(5):32 − 36. [ZHAO Xiaokun,WANG Suiji,FAN Xiaoli. Analysis on the change trend of runoff and influence factors in Kuye River Basin from 1954 to 1993[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering,2010,21(5):32 − 36. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHAO Xiaokun, WANG Suiji, FAN Xiaoli. Analysis on the change trend of runoff and influence factors in Kuye River Basin from 1954 to 1993[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 2010, 21(5): 32 − 36. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[42] 杨洁,金继明,邵进,等. 黄土高原中部典型流域植被恢复对径流的影响[J]. 农业机械学报,2021,52(5):258 − 266. [YANG Jie,JIN Jiming,SHAO Jin,et al. Vegetation restoration and its impact on runoff in typical areas of middle Loess Plateau[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery,2021,52(5):258 − 266. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2021.05.028
YANG Jie, JIN Jiming, SHAO Jin, et al. Vegetation restoration and its impact on runoff in typical areas of middle Loess Plateau[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2021, 52(5): 258 − 266. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2021.05.028
[43] 陈国光,刘红樱,陈进全,等. 福建长汀县水土流失的地质影响因素及防治对策[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(6):26 − 35. [CHEN Guoguang,LIU Hongying,CHEN Jinquan,et al. Geological influence factors of soil erosion in Changting County,Fujian Province and the countermeasures to prevent and control[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(6):26 − 35. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHEN Guoguang, LIU Hongying, CHEN Jinquan, et al. Geological influence factors of soil erosion in Changting County, Fujian Province and the countermeasures to prevent and control[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(6): 26 − 35. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: