Mechanisms controlling seasonal variations of hydrochemistry in a typical river of the Baiyangdian Basin
-
摘要:
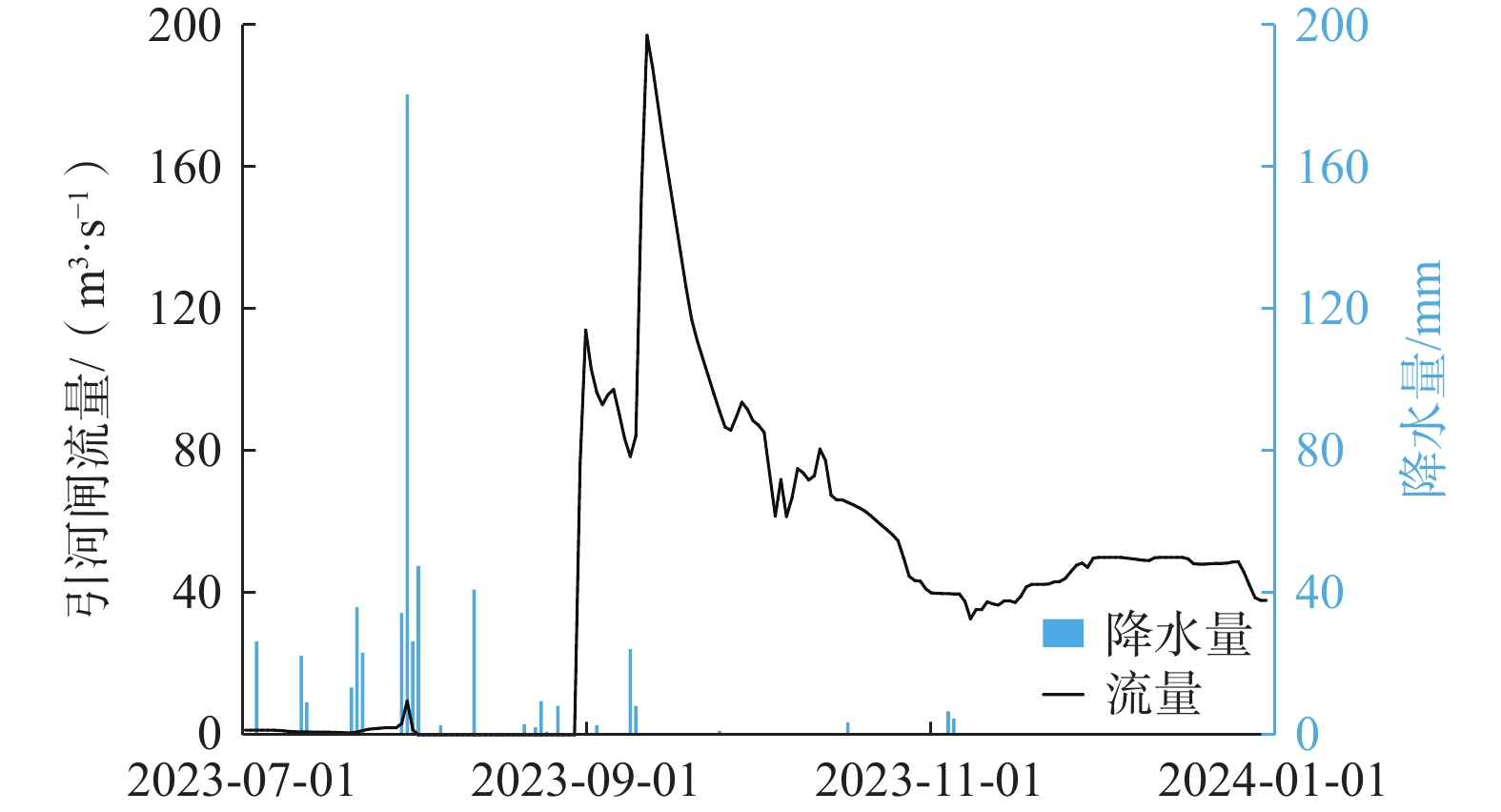
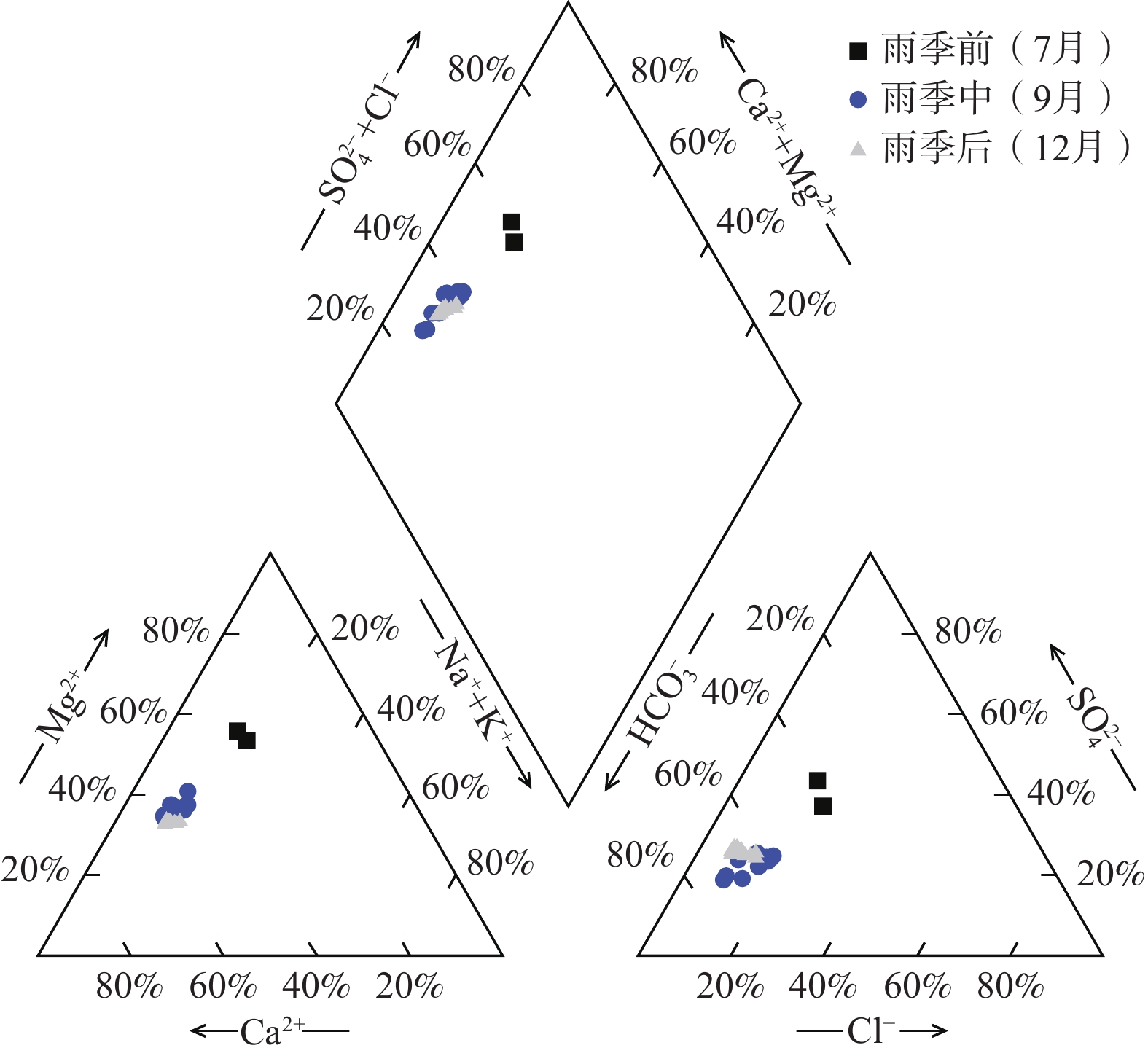
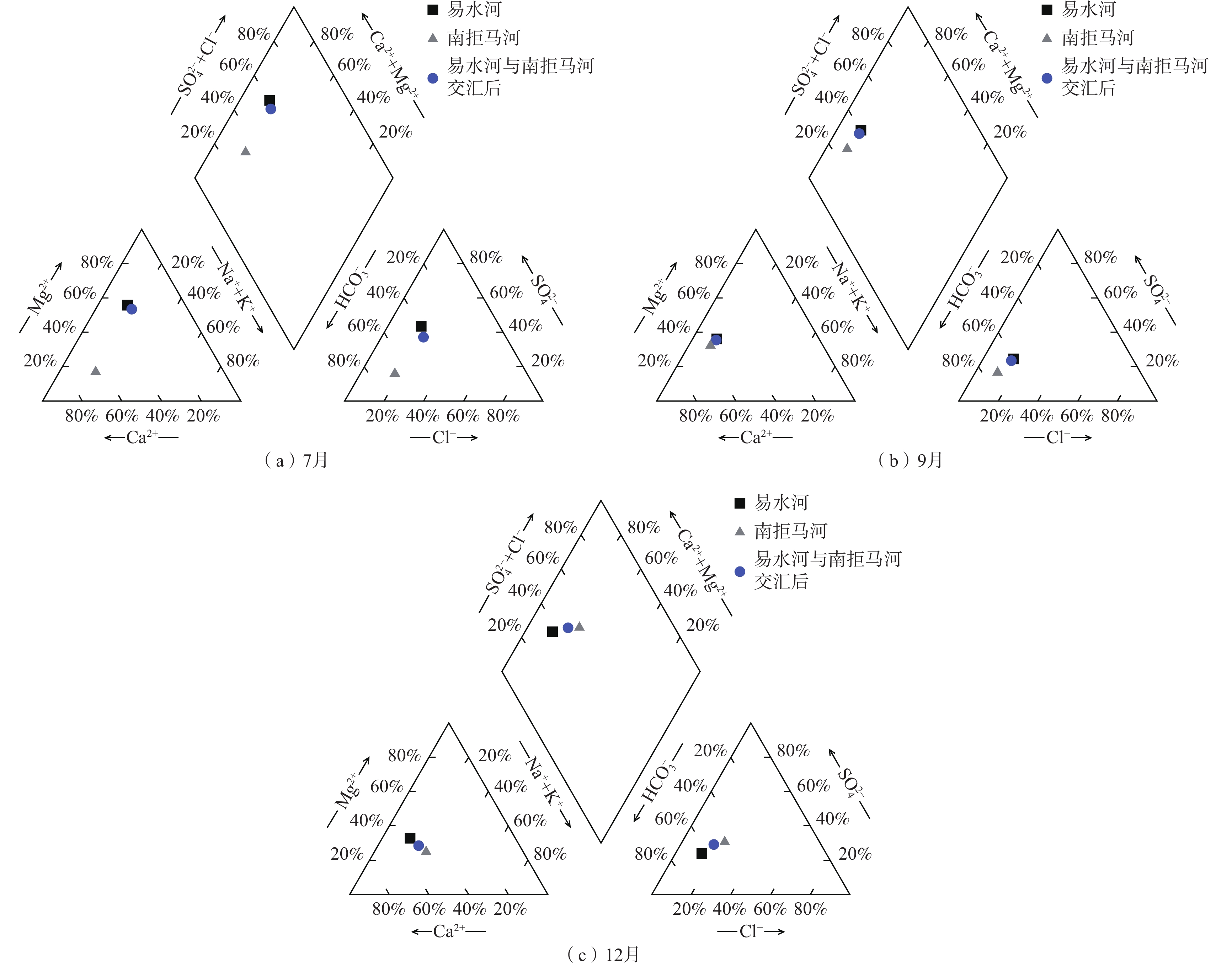
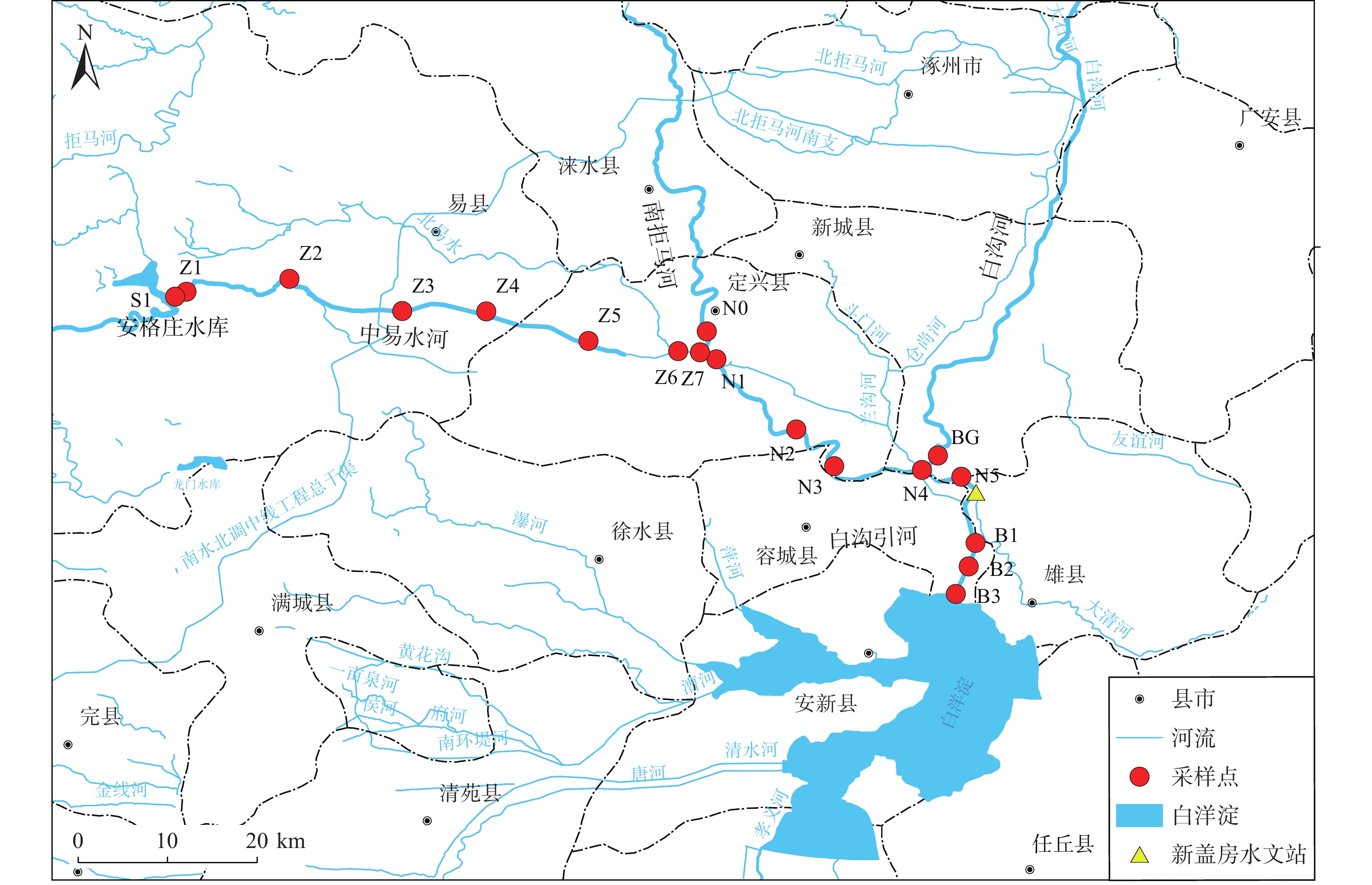
为查明白洋淀入淀河流水化学组分的季节性变化特征及控制机理,选择白洋淀流域的安格庄水库—中易水河—南拒马河—白沟引河为研究对象,对比2023年雨季前、雨季和雨季后的河流水化学组成,利用描述性统计、Piper三线图、Gibbs图、端元图以及PHREEQC模拟等方法进行分析。结果表明:上游安格庄水库水化学组分在2023年具有明显的季节性变化特征,在很大程度上控制了下游河流水化学组成;易水河与南拒马河交汇后水化学组分与易水河更接近,指示易水河流量占优并控制了两者混合后的南拒马河水化学组分;易水河—南拒马河在雨季前、雨季后因流量小、风化作用弱表现出主要离子随径流距离无明显变化,而在雨季水库大流量放水期间,河道内碳酸盐岩矿物的强烈风化导致主要离子浓度随径流距离急剧增大。端元分析和PHREEQC模拟结果表明雨季河水主要发生的水文地球化学过程为方解石、石膏、石盐和白云石的溶解/风化。作为直接汇入白洋淀的河流,白沟引河在雨季前的水化学组分受蒸发浓缩作用控制,而在雨季和雨季后的水化学组分受南拒马河与白沟河混合作用控制。该研究加深了对河流水化学组分控制机理的认识,有助于分析白洋淀的水化学季节性变化特征。
Abstract:To investigate the seasonal variation characteristics and controlling mechanism of the hydrochemistry of rivers that flow into the Baiyangdian Basin, the Angezhuang Reservoir—Zhongyishui River—Nanjuma River—Baigou Canal was selected to compare the hydrochemical composition of the rivers pre and post-rainy season in 2023. Various methods, including mathematical statistics, Piper diagrams, Gibbs diagrams, end-member analysis, and PHREEQC simulation, were employed. The results indicate that the hydrochemical characteristic of the Angezhuang Reservoir exhibited seasonal variation in the year 2023, which significantly influenced the hydrochemistry of the downstream river. At the confluence of the Yishui River and the Nanjuma River, the hydrochemical components were predominantly similar to those of the Yishui River, indicating that the Yishui River's flow primarily governs the mixed hydrochemistry composition of the Nanjuma River. Before and after the rainy season, due to low flow rates and weak weathering, the primary ions in the Yishui-Nanjuma River showed minimal changes with the runoff distance. During the rainy season, however, the large discharge flow from the reservoir and intense rock weathering resulted in a sharp increase in the concentration of major ions with the runoff distance. End-member analysis and PHREEQC simulation results indicated that the main hydrogeochemical processes occurring in river water during the rainy season were the dissolution/weathering of calcite, gypsum, halite, and dolomite. As a river that directly flows into Baiyangdian Basin, the hydrochemical composition of the Baigou Canal was influenced by evaporation and concentration before the rainy season, while during and after the rainy season, it was controlled by the mixing of the Nanjuma River and Baigou River. This study enhances the understanding of the mechanisms controlling river hydrochemical composition and aids in analyzing the origins of Baiyangdian Lake’s water quality.
-
Key words:
- Baiyangdian Basin /
- surface water /
- hydrochemistry /
- seasonal variation /
- chemical weathering
-

-
表 1 白洋淀流域主要河流的水化学特征
Table 1. Hydrochemical data of the main rivers in the Baiyangdian Basin
编号 采样点 月份 距水库
距离/kmpH 质量浓度(ρ)/(mg·L−1) 电荷平衡
误差/%Ca2+ Mg2+ Na+ K+ ${\mathrm{HCO}}_3^- $ ${\mathrm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ Cl− ${\mathrm{NO}}_3^- $ S1 安格庄水库 7 0.0 9.70 20.8 24.3 11.6 1.8 62.0 53.5 15.7 3.5 7 N2 南拒马河 7 59.6 9.41 22.1 25.6 14.4 3.8 80.8 56.8 24.1 2.9 2 N5 南拒马河 7 75.9 10.14 20.7 26.1 17.5 3.3 71.4 64.5 28.1 3.1 3 B1 白沟引河 7 83.5 9.20 28.8 27.4 25.4 4.9 116.8 72.4 28.1 3.8 3 B2 白沟引河 7 86.2 9.06 30.2 26.8 28.1 4.9 114.7 73.5 30.6 4.6 4 B3 白沟引河 7 89.9 8.93 32.3 26.8 32.6 5.1 129.8 76.1 34.0 3.8 2 N0 南拒马河 9 — 8.17 25.8 4.0 5.4 5.0 88.0 16.3 13.4 5.7 −6 S1 安格庄水库 9 0.0 7.85 44.1 16.8 8.4 3.4 148.6 41.6 13.0 13.3 2 Z1 中易水河 9 1.2 7.82 43.1 15.9 7.3 3.4 158.0 34.4 12.1 11.6 1 Z2 中易水河 9 10.2 7.91 51.0 19.2 8.4 3.3 184.6 38.1 13.5 14.5 2 Z2 中易水河 9 20.6 8.06 67.1 25.5 11.2 3.7 245.2 54.6 27.4 23.0 −2 Z4 中易水河 9 27.9 8.19 71.2 30.8 13.4 4.0 223.6 63.6 31.6 28.7 −1 Z5 中易水河 9 37.4 8.07 74.9 32.2 14.1 3.8 238.7 66.3 33.0 30.5 1 Z6 中易水河 9 45.3 8.09 52.8 27.5 13.1 3.6 190.4 61.5 23.2 19.7 0 Z7 中易水河 9 47.6 8.21 70.6 29.9 17.0 4.0 227.2 73.3 34.3 27.2 −1 N1 南拒马河 9 48.6 8.23 70.4 29.0 16.7 4.3 240.2 71.5 34.0 26.7 −2 N2 南拒马河 9 59.6 8.16 63.7 29.5 18.5 3.6 213.5 68.5 34.8 23.7 0 N3 南拒马河 9 65.0 8.19 64.8 29.9 18.3 3.8 207.0 68.6 34.5 24.1 1 N4 南拒马河 9 72.3 8.06 66.0 28.7 17.8 4.4 214.2 66.0 34.0 21.7 1 N5 南拒马河 9 75.9 7.89 77.7 26.5 23.4 3.9 230.1 86.2 36.6 16.7 2 B1 白沟引河 9 83.5 8.57 73.4 24.6 21.9 3.8 200.5 83.5 36.4 11.6 2 B2 白沟引河 9 86.2 8.05 74.5 24.9 21.8 3.7 199.8 84.9 35.6 10.8 3 B3 白沟引河 9 89.9 8.12 73.9 24.9 21.9 4.1 209.9 84.8 35.7 11.7 3 N0 南拒马河 9 — 8.42 58.6 19.9 10.5 4.5 196.2 34.9 18.4 1.7 2 S1 安格庄水库 12 0.0 8.14 52.0 18.0 9.6 4.4 175.3 53.7 11.5 14.3 0 Z1 中易水河 12 1.2 8.02 52.8 18.5 9.8 4.3 177.4 52.9 11.4 14.1 1 Z2 中易水河 12 10.2 8.24 53.0 18.6 9.9 4.5 176.0 55.2 11.8 14.5 −2 Z2 中易水河 12 20.6 8.17 53.3 18.8 9.9 4.6 181.0 55.7 12.4 15.7 −1 Z4 中易水河 12 27.9 8.28 53.1 19.0 10.1 4.6 172.4 55.1 12.7 15.4 −1 Z5 中易水河 12 37.4 8.07 54.4 19.3 10.0 4.5 186.1 56.2 12.6 15.5 0 Z6 中易水河 12 45.3 8.15 53.7 19.2 10.0 4.2 189.7 55.2 12.7 15.5 −2 Z7 中易水河 12 47.6 8.31 56.9 20.6 12.1 4.5 194.0 60.9 16.2 18.5 −1 N1 南拒马河 12 48.6 8.29 59.1 21.1 12.8 3.3 202.7 60.7 20.0 19.6 −2 N2 南拒马河 12 59.6 8.21 61.6 22.3 15.1 3.7 207.7 62.8 22.7 20.4 −1 N3 南拒马河 12 65.0 8.01 61.8 22.4 15.8 4.0 199.8 64.0 24.2 21.0 −2 N4 南拒马河 12 72.3 8.38 63.3 23.7 17.0 3.9 211.3 63.0 26.4 22.9 0 N5 南拒马河 12 75.9 8.27 75.2 25.5 32.3 4.7 220.4 94.0 40.3 22.3 0 B1 白沟引河 12 83.5 8.17 72.0 25.1 32.2 5.7 225.0 85.7 42.7 24.0 0 B2 白沟引河 12 86.2 8.38 74.2 25.7 32.8 4.4 218.5 89.5 43.8 24.3 1 B3 白沟引河 12 89.9 8.14 74.0 25.8 33.2 5.4 211.3 87.3 43.9 24.6 −1 BG 白沟河 12 — 8.36 86.2 26.4 49.5 6.5 238.7 118.7 62.8 24.8 1 表 2 水流路径上矿物的溶解-沉淀量
Table 2. Dissolution and precipitation of minerals along the flow path
/(mol·L−1) 矿物 溶解量(Z1→Z2) 方解石 4.640×10−5 石膏 4.796×10−5 石盐 4.121×10−5 白云石 1.014×10−4 CO2(g) 2.634×10−4 NaX — CaX2 — MgX2 — 钾长石 — 钠长石 8.408×10−6 高岭石 −4.204×10−6 石英 −1.682×10−5 注:正值表示矿物的溶解;负值表示矿物的沉淀;“—”表示未发生该反应。 -
[1] HU Minghui,STALLARD R F,EDMOND J M. Major ion chemistry of some large Chinese rivers[J]. Nature,1982,298(5874):550 − 553. doi: 10.1038/298550a0
[2] STETS E G,KELLY V J,CRAWFORD C G. Long-term trends in alkalinity in large rivers of the conterminous US in relation to acidification,agriculture,and hydrologic modification[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2014,488/489:280 − 289. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.04.054
[3] HINDSHAW R S,TIPPER E T,REYNOLDS B C,et al. Hydrological control of stream water chemistry in a glacial catchment (Damma Glacier,Switzerland)[J]. Chemical Geology,2011,285(1-4):215 − 230. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2011.04.012
[4] JIANG Liguang,YAO Zhijun,LIU Zhaofei,et al. Hydrochemistry and its controlling factors of rivers in the source region of the Yangtze River on the Xizang Plateau[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration,2015,155:76 − 83. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.04.009
[5] 解晨骥,高全洲,陶贞. 流域化学风化与河流水化学研究综述与展望[J]. 热带地理,2012,32(4):331 − 337. [JIE Chenji,GAO Quanzhou,TAO Zhen,et al. Review and perspectives of the study on chemical weathering and hydrochemistry in river basin[J]. Tropical Geography,2012,32(4):331 − 337. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5221.2012.04.001
JIE Chenji, GAO Quanzhou, TAO Zhen, et al. Review and perspectives of the study on chemical weathering and hydrochemistry in river basin[J]. Tropical Geography, 2012, 32(4): 331 − 337. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5221.2012.04.001
[6] 霍俊伊,于奭,张清华,等. 湘西峒河流域水化学特征及无机碳通量计算[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(4):64 − 72. [HUO Junyi,YU Shi,ZHANG Qinghua,et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and estimation of the dissolved inorganic carbon flux in the Donghe River Basin of western Hunan[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(4):64 − 72. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HUO Junyi, YU Shi, ZHANG Qinghua, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and estimation of the dissolved inorganic carbon flux in the Donghe River Basin of western Hunan[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2019, 46(4): 64 − 72. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] OUYANG Ying,NKEDI-KIZZA P WU Qitang,et al. Assessment of seasonal variations in surface water quality[J]. Water Research,2006,40(20):3800 − 3810. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2006.08.030
[8] 罗进,安艳玲,吴起鑫,等. 赤水河中下游冬季河水化学空间分布特征分析[J]. 地球与环境,2014,42(3):297 − 305. [LUO Jin,AN Yanling,WU Qixin,et al. Spatial distribution of surface water chemical components in the middle and lower reaches of the Chishui River Basin[J]. Earth and Environment,2014,42(3):297 − 305. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LUO Jin, AN Yanling, WU Qixin, et al. Spatial distribution of surface water chemical components in the middle and lower reaches of the Chishui River Basin[J]. Earth and Environment, 2014, 42(3): 297 − 305. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 王雨山,韩双宝,邓启军,等. 马莲河流域化学风化的季节变化和影响因素[J]. 环境科学,2018,39(9):4132 − 4141. [WANG Yushan,HAN Shuangbao,DENG Qijun,et al. Seasonal variations in river water chemical weathering and its influence factors in the Malian River Basin[J]. Environmental Science,2018,39(9):4132 − 4141. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Yushan, HAN Shuangbao, DENG Qijun, et al. Seasonal variations in river water chemical weathering and its influence factors in the Malian River Basin[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(9): 4132 − 4141. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] OLLIVIER P,HAMELIN B,RADAKOVITCH O. Seasonal variations of physical and chemical erosion:A three-year survey of the Rhone River (France)[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2010,74(3):907 − 927. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2009.10.037
[11] 肖琼,沈立成,杨雷,等. 西南喀斯特流域风化作用季节性变化研究[J]. 环境科学,2012,33(4):1122 − 1128. [XIAO Qiong,SHEN Licheng,YANG Lei,et al. Weathering seasonal variations in Karst valley in Southwest China[J]. Environmental Science,2012,33(4):1122 − 1128. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
XIAO Qiong, SHEN Licheng, YANG Lei, et al. Weathering seasonal variations in Karst valley in Southwest China[J]. Environmental Science, 2012, 33(4): 1122 − 1128. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] WEI Gangjian,MA Jinlong,LIU Ying,et al. Seasonal changes in the radiogenic and stable strontium isotopic composition of Xijiang River water:Implications for chemical weathering[J]. Chemical Geology,2013,343:67 − 75. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.02.004
[13] ZHANG Qianqian,JIN Zhangdong,ZHANG Fei,et al. Seasonal variation in river water chemistry of the middle reaches of the Yellow River and its controlling factors[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration,2015,156:101 − 113. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.05.008
[14] 孟俊伦,郭建阳,吴婕,等. 青藏高原尼洋河流域化学风化的季节变化特征和影响因素[J]. 地球环境学报,2020,11(2):190 − 203. [MENG Junlun,GUO Jianyang,WU Jie,et al. Seasonal variations of chemical weathering and its controlling factors of Nyang River in the Xizang Plateau[J]. Journal of Earth Environment,2020,11(2):190 − 203. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
MENG Junlun, GUO Jianyang, WU Jie, et al. Seasonal variations of chemical weathering and its controlling factors of Nyang River in the Xizang Plateau[J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 2020, 11(2): 190 − 203. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] GAILLARDET J,DUPRÉ B,LOUVAT P,et al. Global silicate weathering and CO2 consumption rates deduced from the chemistry of large rivers[J]. Chemical Geology,1999,159(1/2/3/4):3 − 30.
[16] WU Lingling,HUH Y,QIN Jianhua,et al. Chemical weathering in the Upper Huang He (Yellow River) draining the eastern Qinghai-Xizang Plateau[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2005,69(22):5279 − 5294. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2005.07.001
[17] WEST A J,GALY A,BICKLE M. Tectonic and climatic controls on silicate weathering[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2005,235(1/2):211 − 228.
[18] 王雅宁,饶文波,郑芳文,等. 赣江河水主离子化学特征和径流效应以及控制机制[J]. 人民长江,2020,51(4):26 − 34. [WANG Yaning,RAO Wenbo,ZHENG Fangwen,et al. Major ion chemical characteristics,runoff effect and controlling mechanism of Ganjiang River[J]. Yangtze River,2020,51(4):26 − 34. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Yaning, RAO Wenbo, ZHENG Fangwen, et al. Major ion chemical characteristics, runoff effect and controlling mechanism of Ganjiang River[J]. Yangtze River, 2020, 51(4): 26 − 34. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 刘文景,孙会国,李源川,等. 怒江水化学与碳同位素组成对青藏高原岩石风化碳汇效应的指示[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,2023,53(12):2992 − 3009. [LIU Wenjing,SUN Huiguo,LI Yuanchuan. Hydrochemistry and carbon isotope characteristics of Nujiang River water:Implications for CO2 budgets of rock weathering in the Xizang Plateau[J]. Science China Earth Sciences,2023,53(12):2992 − 3009. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Wenjing, SUN Huiguo, LI Yuanchuan. Hydrochemistry and carbon isotope characteristics of Nujiang River water: Implications for CO2 budgets of rock weathering in the Xizang Plateau[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2023, 53(12): 2992 − 3009. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] JHA P K,TIWARI J,SINGH U K,et al. Chemical weathering and associated CO2 consumption in the Godavari river basin,India[J]. Chemical Geology,2009,264(1/2/3/4):364 − 374.
[21] SUN Huiguo,HAN Jingtai,LI Dong,et al. Chemical weathering inferred from riverine water chemistry in the lower Xijiang basin,South China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2010,408(20):4749 − 4760. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.06.007
[22] 蒲焘,何元庆,朱国锋,等. 玉龙雪山周边典型河流雨季水化学特征分析[J]. 地理科学,2011,31(6):734 − 740. [PU Tao,HE Yuanqing,ZHU Guofeng,et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of three rivers around Yulong Mountain in rainy season[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica,2011,31(6):734 − 740. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
PU Tao, HE Yuanqing, ZHU Guofeng, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of three rivers around Yulong Mountain in rainy season[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2011, 31(6): 734 − 740. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 王君波,鞠建廷,朱立平. 季风期前后西藏纳木错湖水及入湖河流水化学特征变化[J]. 地理科学,2013,33(1):90 − 96. [WANG Junbo,JU Jianting,ZHU Liping. Water chemistry variations of lake and inflowing rivers between pre- and post-monsoon season in Nam Co,Xizang[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica,2013,33(1):90 − 96. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Junbo, JU Jianting, ZHU Liping. Water chemistry variations of lake and inflowing rivers between pre- and post-monsoon season in Nam Co, Xizang[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2013, 33(1): 90 − 96. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 黄露,刘丛强,CHETELAT Benjamin,等. 中国西南三江流域风化的季节性变化特征[J]. 地球与环境,2015,43(5):512 − 521. [HUANG Lu,LIU Congqiang,CHETELAT Benjamin,et al. Seasonal variation characteristics of weathering in the three rivers basin,southwestern China[J]. Earth and Environment,2015,43(5):512 − 521. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HUANG Lu, LIU Congqiang, CHETELAT Benjamin, et al. Seasonal variation characteristics of weathering in the three rivers basin, southwestern China[J]. Earth and Environment, 2015, 43(5): 512 − 521. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] LI Xiaoqiang,HAN Guilin,LIU Man,et al. Potassium and its isotope behaviour during chemical weathering in a tropical catchment affected by evaporite dissolution[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2022,316:105 − 121. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2021.10.009
[26] 陈文婷,郑明霞,夏青,等. 基于产业细化和多要素约束的白洋淀流域水环境承载力系统动力学模拟与调控[J]. 长江流域资源与环境,2022,31(2):345 − 357. [CHEN Wenting,ZHENG Mingxia,XIA Qing,et al. System dynamics simulation and control strategy of water environment carrying capacity in Baiyangdian Basin based on industry refinement and multifactor constraint[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin,2022,31(2):345 − 357. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHEN Wenting, ZHENG Mingxia, XIA Qing, et al. System dynamics simulation and control strategy of water environment carrying capacity in Baiyangdian Basin based on industry refinement and multifactor constraint[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2022, 31(2): 345 − 357. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 余杰,李祎飞,王衫允,等. 白洋淀流域岸边带土壤全程氨氧化菌的分布特征及其生态网络研究[J]. 环境科学学报,2023,43(4):359 − 367. [YU Jie,LI Yifei,WANG Shanyun,et al. Distribution characteristics and ecological network analysis of complete ammonia oxidizers and other nitrifiers in the riparian zone of Baiyangdian Basin[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2023,43(4):359 − 367. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YU Jie, LI Yifei, WANG Shanyun, et al. Distribution characteristics and ecological network analysis of complete ammonia oxidizers and other nitrifiers in the riparian zone of Baiyangdian Basin[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2023, 43(4): 359 − 367. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 陈毅. 白洋淀流域平原区地下水—孔隙水的水化学特征和水文地球化学过程[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2018. [CHEN Yi. Pore-water and groundwater hydrochemical characteristics and hydrogeochemical processes in Baiyangdian Lake Basin[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences (Beijing),2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHEN Yi. Pore-water and groundwater hydrochemical characteristics and hydrogeochemical processes in Baiyangdian Lake Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 刘志远,李晓,张云鹏,等. 河北省顺平县太行山山前平原区浅层地下水及界河冲积扇电性特征研究[J]. 工程地球物理学报,2021,18(6):930 − 937. [LIU Zhiyuan,LI Xiao,ZHANG Yunpeng et al. Research on characteristics of shallow groundwater and Jiehe alluvial fan in piedmont plain of Taihang Mountain in Shunping County,Hebei Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics,2021,18(6):930 − 937(in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7940.2021.06.016
LIU Zhiyuan, LI Xiao, ZHANG Yunpeng et al. Research on characteristics of shallow groundwater and Jiehe alluvial fan in piedmont plain of Taihang Mountain in Shunping County, Hebei Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2021, 18(6): 930 − 937(in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7940.2021.06.016
[30] 何登发,单帅强,张煜颖,等. 雄安新区的三维地质结构:来自反射地震资料的约束[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,2018,48(9):1207 − 1222. [HE Dengfa,SHAN Shuaiqiang,ZHANG Yuying,et al. 3-D geologic architecture of Xiong’an New Area:Constraints from seismic reflection data[J]. Scientia Sinica(Terrae),2018,48(9):1207 − 1222. (in Chinese)]
HE Dengfa, SHAN Shuaiqiang, ZHANG Yuying, et al. 3-D geologic architecture of Xiong’an New Area: Constraints from seismic reflection data[J]. Scientia Sinica(Terrae), 2018, 48(9): 1207 − 1222. (in Chinese)
[31] 孔晓乐,王仕琴,丁飞,等. 基于水化学和稳定同位素的白洋淀流域地表水和地下水硝酸盐来源[J]. 环境科学,2018,39(6):2624 − 2631. [KONG Xiaole,WANG Shiqin,DING Fei,et al. Source of nitrate in surface water and shallow groundwater around Baiyangdian Lake area based on hydrochemical and stable isotopes[J]. Environmental Science,2018,39(6):2624 − 2631. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
KONG Xiaole, WANG Shiqin, DING Fei, et al. Source of nitrate in surface water and shallow groundwater around Baiyangdian Lake area based on hydrochemical and stable isotopes[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(6): 2624 − 2631. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 李刚,马佰衡,周仰效,等. 白洋淀湖岸带地表水与地下水垂向交换研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(4):48 − 54. [LI Gang,MA Baiheng,ZHOU Yangxiao,et al. A study of vertical exchange between surface water and groundwater around the banks of Baiyangdian Lake[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(4):48 − 54. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Gang, MA Baiheng, ZHOU Yangxiao, et al. A study of vertical exchange between surface water and groundwater around the banks of Baiyangdian Lake[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(4): 48 − 54. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 欧阳恺皋,蒋小伟,杜亚楠,等. 华北“23•7”强降雨事件对不同埋深地下水的补给机理:以雄安新区为例[J/OL]. 地学前缘,(2024-06-14)[2024-06-15]. [OUYANG Kaigao,JIANG Xiaowei,DU Ya’nan,et al. The responses of groundwater with different water table depths in the North China Plain to the “23•7” extreme rainfall event:An example in the Xiongan New Area[J/OL]. Earth Science Frontiers,(2024-06-14)[2024-06-15]. Https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=sKJ9SXrFdEpEIGpXECx2s34eVSZIIUJzReMdjiEitz8tzT7-XsOW9ZZy745Zfr3LW4ZEb1psgA7ogt03lL2NpiUc_RGZjfnnH1SU9bY3xhVJohGR8ZrGmOEP-K0gbO-G9bMimKgqO4MDzVISW76UetTmP8e1Zq7YDMJ-eqN34kgNiQ97rWeuvaDxyCtwgmrp&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
OUYANG Kaigao, JIANG Xiaowei, DU Ya’nan, et al. The responses of groundwater with different water table depths in the North China Plain to the “23•7” extreme rainfall event: An example in the Xiongan New Area[J/OL]. Earth Science Frontiers, (2024-06-14)[2024-06-15]. Https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=sKJ9SXrFdEpEIGpXECx2s34eVSZIIUJzReMdjiEitz8tzT7-XsOW9ZZy745Zfr3LW4ZEb1psgA7ogt03lL2NpiUc_RGZjfnnH1SU9bY3xhVJohGR8ZrGmOEP-K0gbO-G9bMimKgqO4MDzVISW76UetTmP8e1Zq7YDMJ-eqN34kgNiQ97rWeuvaDxyCtwgmrp&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[34] WHITE A F,BLUM A E,SCHULZ M S,et al. Chemical weathering in a tropical watershed,Luquillo Mountains,Puerto Rico:I. long-term versus short-term weathering fluxes[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1998,62(2):209 − 226. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00335-9
[35] ROY S,GAILLARDET J,ALLÈGRE C J. Geochemistry of dissolved and suspended loads of the Seine River,France:anthropogenic impact,carbonate and silicate weathering[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1999,63(9):1277 − 1292. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00099-X
[36] HUA Kun,XIAO Jun,LI Shujian,et al. Analysis of hydrochemical characteristics and their controlling factors in the Fen River of China[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society,2020,52:101827. doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2019.101827
[37] 李永柳,周忠发,孔杰,等. 喀斯特地区河流水化学季节变化特征及成因分析——以平寨水库上游流域为例[J]. 环境化学,2023,42(2):478 − 486. [LI Yongliu,ZHOU Zhongfa,KONG Jie,et al. Seasonal variation characteristics and causes of river water chemistry in Karst:Taking the area of Pingzhai Reservoir as an example[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2023,42(2):478 − 486. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021092405
LI Yongliu, ZHOU Zhongfa, KONG Jie, et al. Seasonal variation characteristics and causes of river water chemistry in Karst: Taking the area of Pingzhai Reservoir as an example[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2023, 42(2): 478 − 486. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021092405
[38] 李思悦,谭香,徐志方,等. 湖北丹江口水库主要离子化学季节变化及离子来源分析[J]. 环境科学,2008(12):3353 − 3359. [LI Siyue,TAN Xiang,XU Zhifang,et al. Seasonal variation in the major ion chemistry and their sources in the Hubei Danjiangkou Reservoir China[J]. Environmental Science,2008(12):3353 − 3359. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2008.12.010
LI Siyue, TAN Xiang, XU Zhifang, et al. Seasonal variation in the major ion chemistry and their sources in the Hubei Danjiangkou Reservoir China[J]. Environmental Science, 2008(12): 3353 − 3359. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2008.12.010
[39] TIPPER E T,BICKLE M J,GALY A,et al. The short term climatic sensitivity of carbonate and silicate weathering fluxes:Insight from seasonal variations in river chemistry[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2006,70(11):2737 − 2754. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2006.03.005
[40] MILLOT R,GAILLARDET J,DUPRÉ B,et al. The global control of silicate weathering rates and the coupling with physical erosion:New insights from rivers of the Canadian Shield[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2002,196(1/2):83 − 98.
[41] CLOW D W,MAST M A. Mechanisms for chemostatic behavior in catchments:Implications for CO2 consumption by mineral weathering[J]. Chemical Geology,2010,269(1/2):40 − 51.
[42] SUMMERFIELD M A,HULTON N J. Natural controls of fluvial denudation rates in major world drainage basins[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,1994,99(B7):13871 − 13883. doi: 10.1029/94JB00715
[43] 李晶莹,张经. 流域盆地的风化作用与全球气候变化[J]. 地球科学进展,2002,17(3):411 − 419. [LI Jingying,ZHANG Jing. Weathering of watershed basins and global climatic change[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2002,17(3):411 − 419. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2002.03.018
LI Jingying, ZHANG Jing. Weathering of watershed basins and global climatic change[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2002, 17(3): 411 − 419. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2002.03.018
[44] YU Zhengliang,WU Guangjian,KEYS L,et al. Seasonal variation of chemical weathering and its controlling factors in two alpine catchments,Nam Co basin,central Xizang Plateau[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2019,576:381 − 395. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.06.042
[45] GIBBS R J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry[J]. Science,1970,170(3962):1088 − 1090. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1088
-



 下载:
下载: