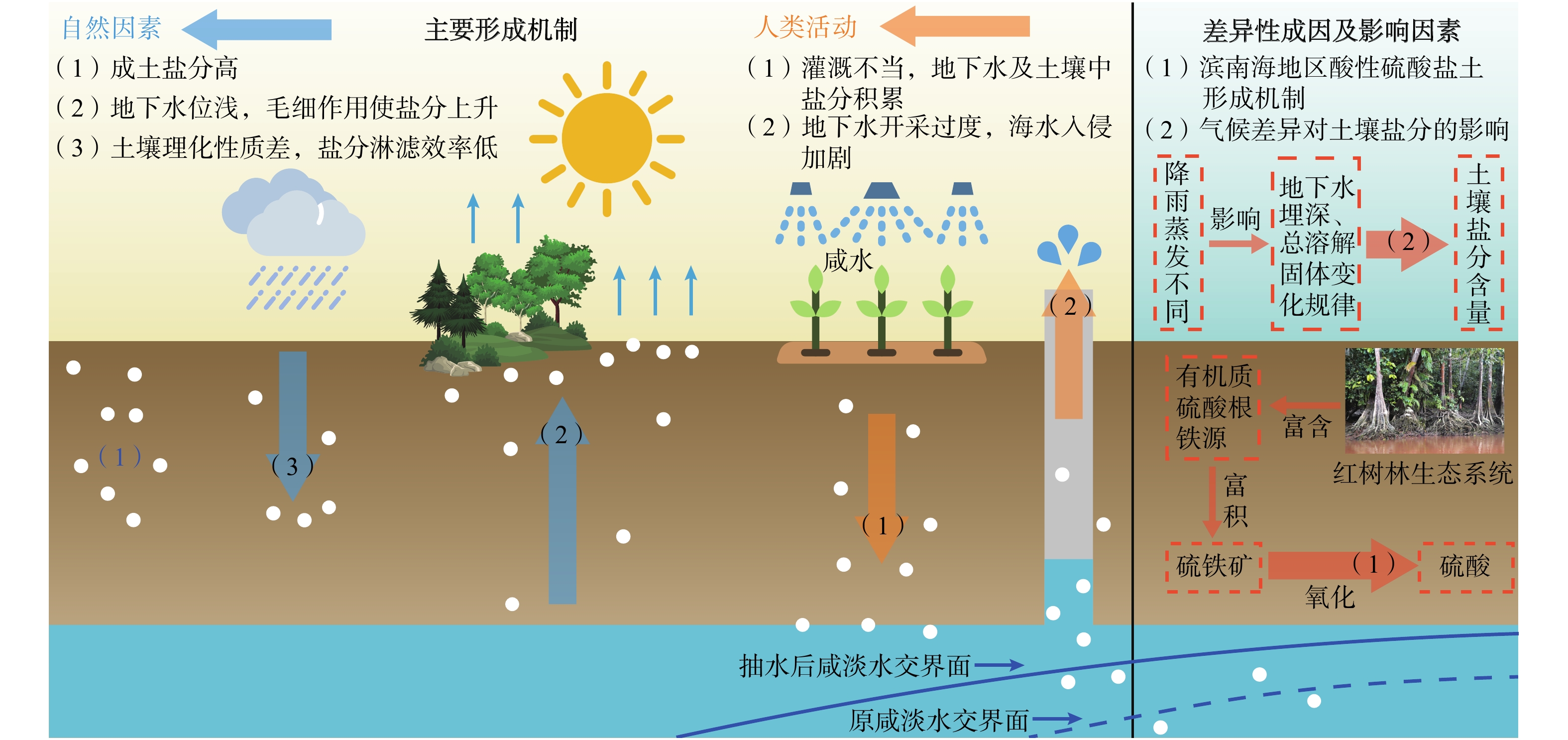
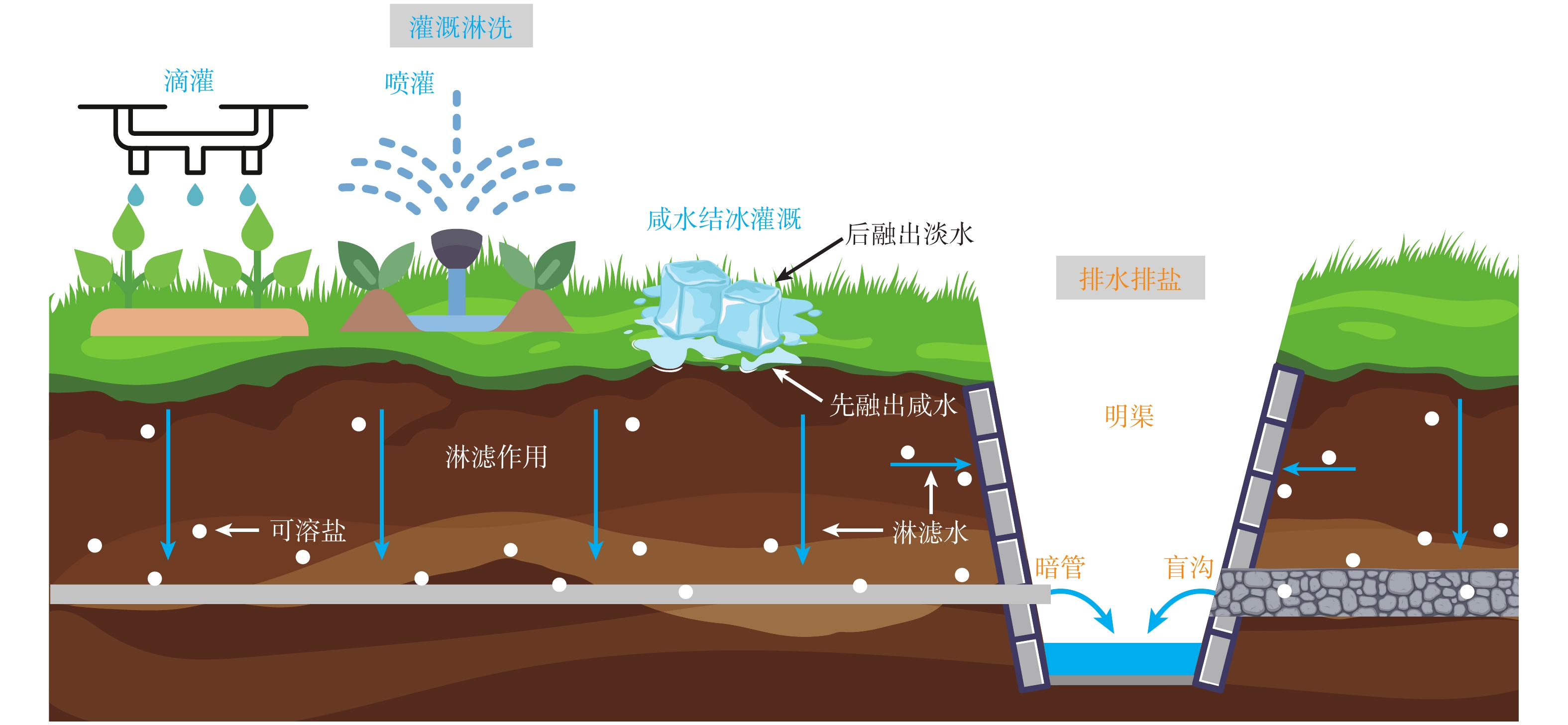
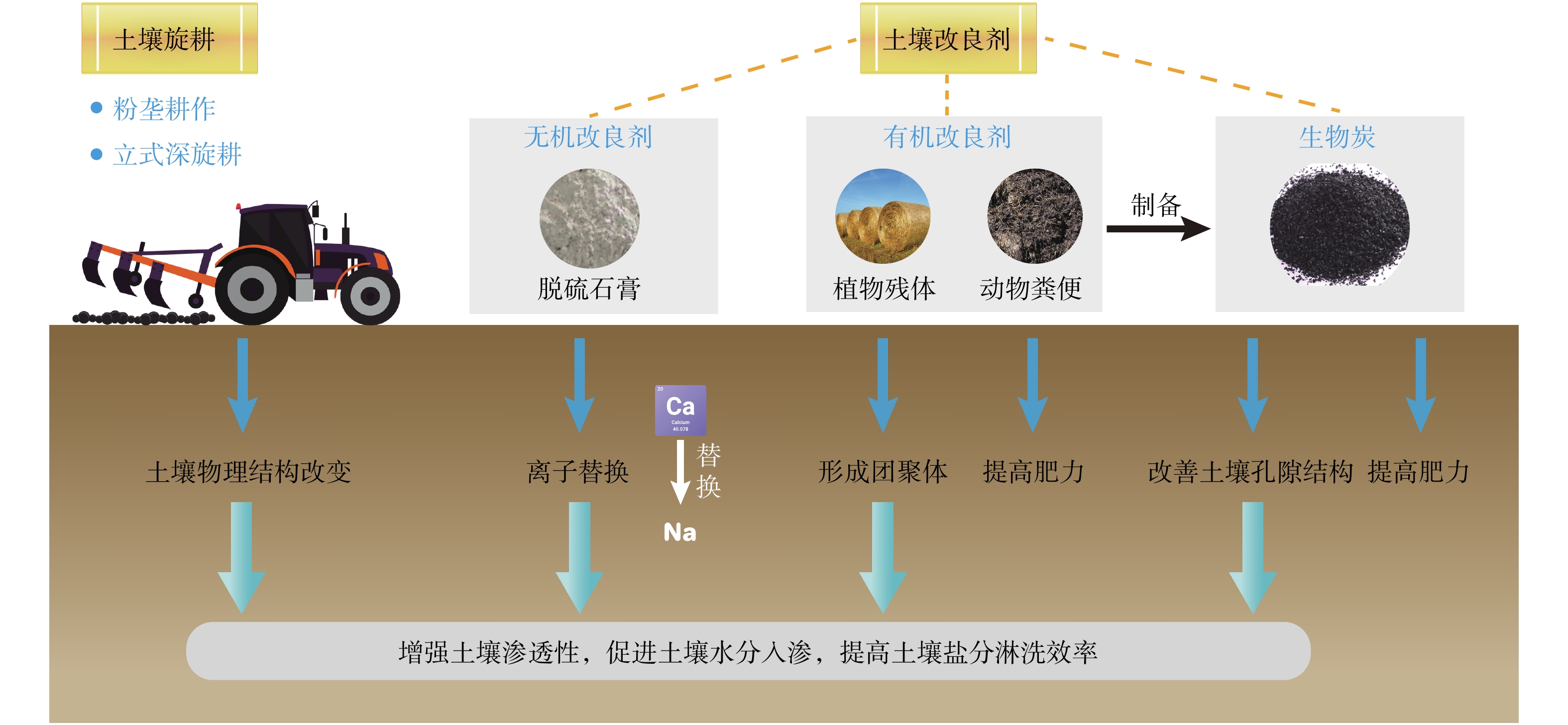
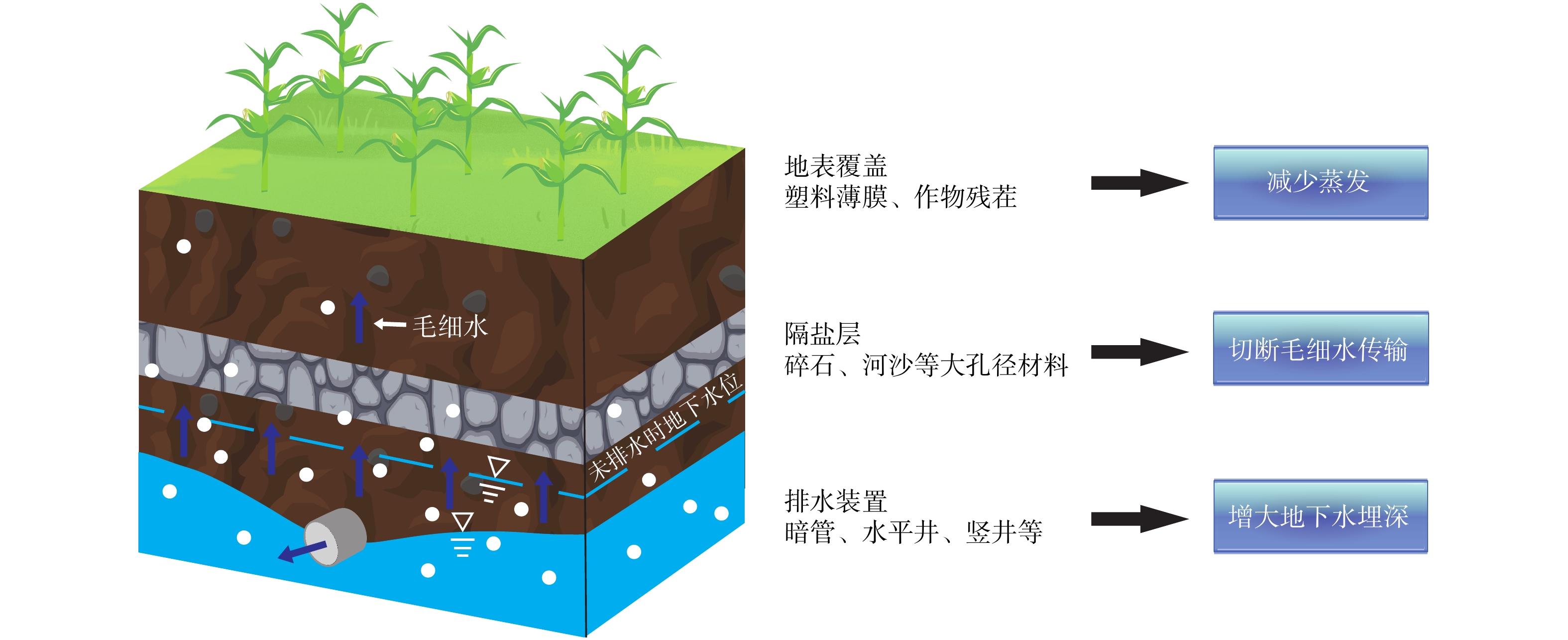
Review of techniques and case studies for saline-alkali land amelioration in the coastal regions of China
-
摘要:
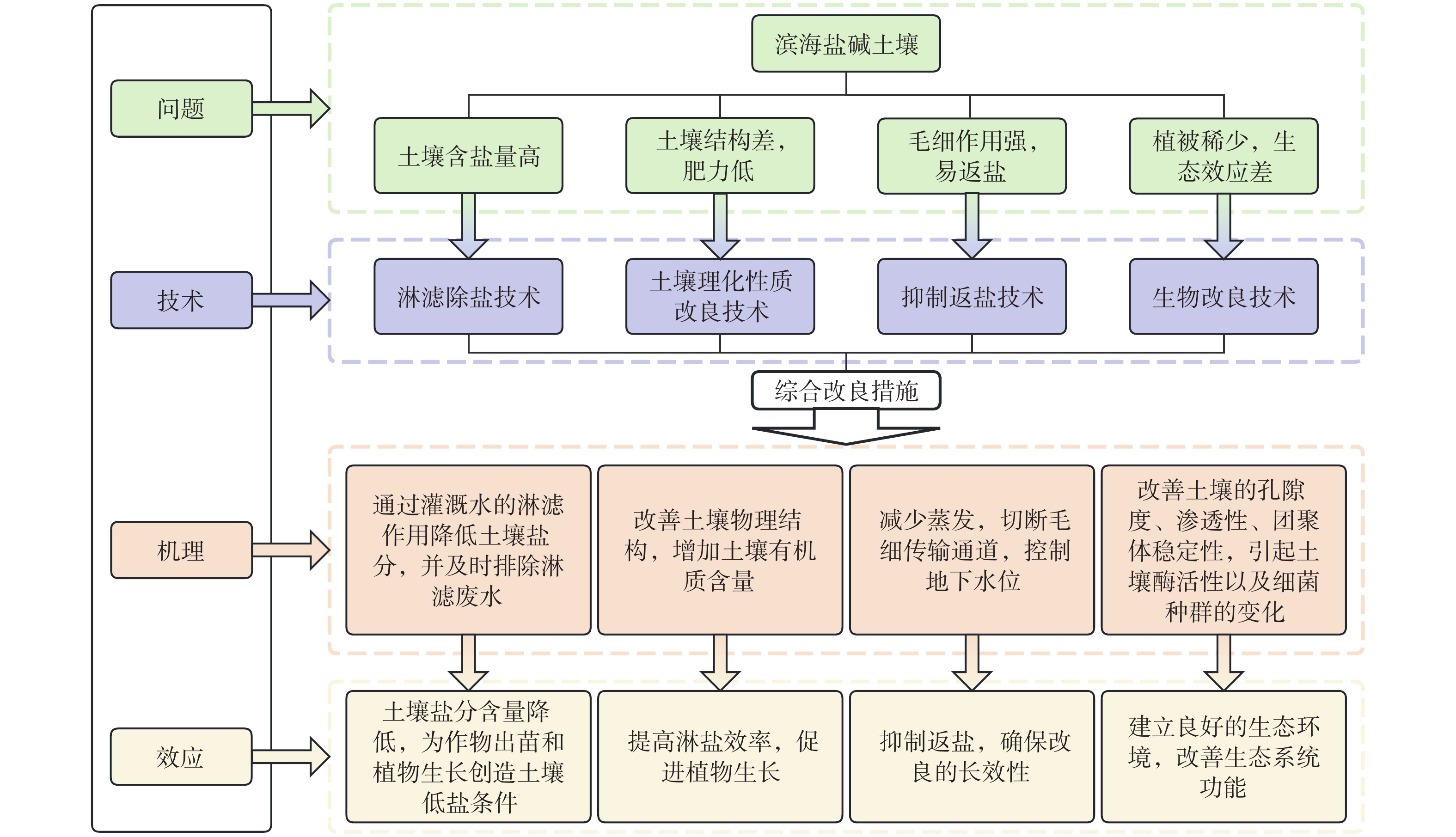
土壤盐碱化是农业生产和生态环境建设面临的重大问题之一。随着我国滨海地区的快速发展,土地资源愈发紧缺,改良利用滨海盐碱地的需求日益迫切,相关研究成果不断丰富。然而,现有针对滨海盐碱地改良技术的综述研究多以物理、化学等基于学科的分类方式划分改良技术,难以指导实际工程中改良技术的选择和应用。因此,文章旨在系统梳理现有滨海盐碱地改良技术,总结更易于实践的技术分类方式,以指导实际工程应用。文章通过系统收集和筛选我国滨海盐碱地改良相关研究文献,综合对比和总结不同改良技术的优劣性及适用范围,依据其调控改良目标进行技术分类,并选取不同条件下高效改良方案进行案例分析。研究结果表明:(1)滨海盐碱地主要成因为成土盐分高、土壤理化性质差、毛细返盐作用强;(2)滨海盐碱地改良技术可根据调控改良目标划分为淋滤除盐技术、土壤理化性质改良技术、抑制返盐技术、生物改良技术四类;(3)淋滤除盐与土壤理化性质改良技术在滨海地区应用最广泛,抑制返盐技术多用于高盐地区,生物改良技术应根据盐分水平的不同选择适宜的植物品种,在轻度盐碱化土壤中,适宜种植耐盐作物从而兼顾生态与经济效益。基于对改良技术的总结分析,文章提出了滨海盐碱地针对性改良技术体系构建、滨海盐碱土改良过程中水资源的高效与安全利用、加强多学科交叉的滨海盐碱地改良技术方法研究及滨海盐碱地改良的长效性管理等研究方向,以期为滨海盐碱地的高效治理及可持续利用提供参考。
Abstract:Soil salinization is one of the major challenges in agricultural production and ecological development. With the rapid development of China’s coastal areas, land resources are becoming increasingly scarce, creating an urgent need for the improvement and utilization of coastal saline-alkali land. Research findings in this area are continually expanding. However, most existing reviews of coastal saline-alkali land improvement technologies are classified based on disciplines such as physics and chemistry, which limits their guidance on technology selection and application in practical engineering. Therefore, this paper aims to systematically review current coastal saline-alkali land improvement technologies and summarize classification methods that are more practical for guiding real-world engineering applications. This paper systematically collected and screened relevant literature on the improvement of coastal saline-alkali land in China, comprehensively compared and summarized the advantages, disadvantages, and application scopes of various improvement technologies, categorized these technologies according to their regulatory and improvement objectives, and selected efficient improvement schemes under different conditions for case analysis. The findings indicate that: (1) The primary causes of coastal saline-alkali land are high soil salinity, poor physical and chemical properties of the soil, and strong capillary rise of salts. (2) Coastal saline-alkali land improvement technologies can be divided into four categories based on regulatory and improvement objectives: leaching and desalination technology, soil physical and chemical properties improvement technology, salt rise inhibition technology, and biological improvement technology. (3) Leaching and desalination, as well as soil physical and chemical properties improvement, are the most widely applied technologies in coastal areas. Salt rise inhibition technology is mainly used in areas with high salinity, while biological improvement technology involves selecting suitable plant varieties according to different salt levels. In mildly salinized soil, planting salt-tolerant crops can balance ecological and economic benefits. Based on the summary and analysis of improvement technologies, this paper proposes research directions for constructing targeted improvement technology systems for coastal saline-alkali land, ensuring efficient and safe utilization of water resources during the amelioration process, strengthening interdisciplinary research on improvement techniques, and establishing long-term management practices. These insights aim to provide basic information for efficient management and sustainable use of coastal saline-alkali land.
-

-
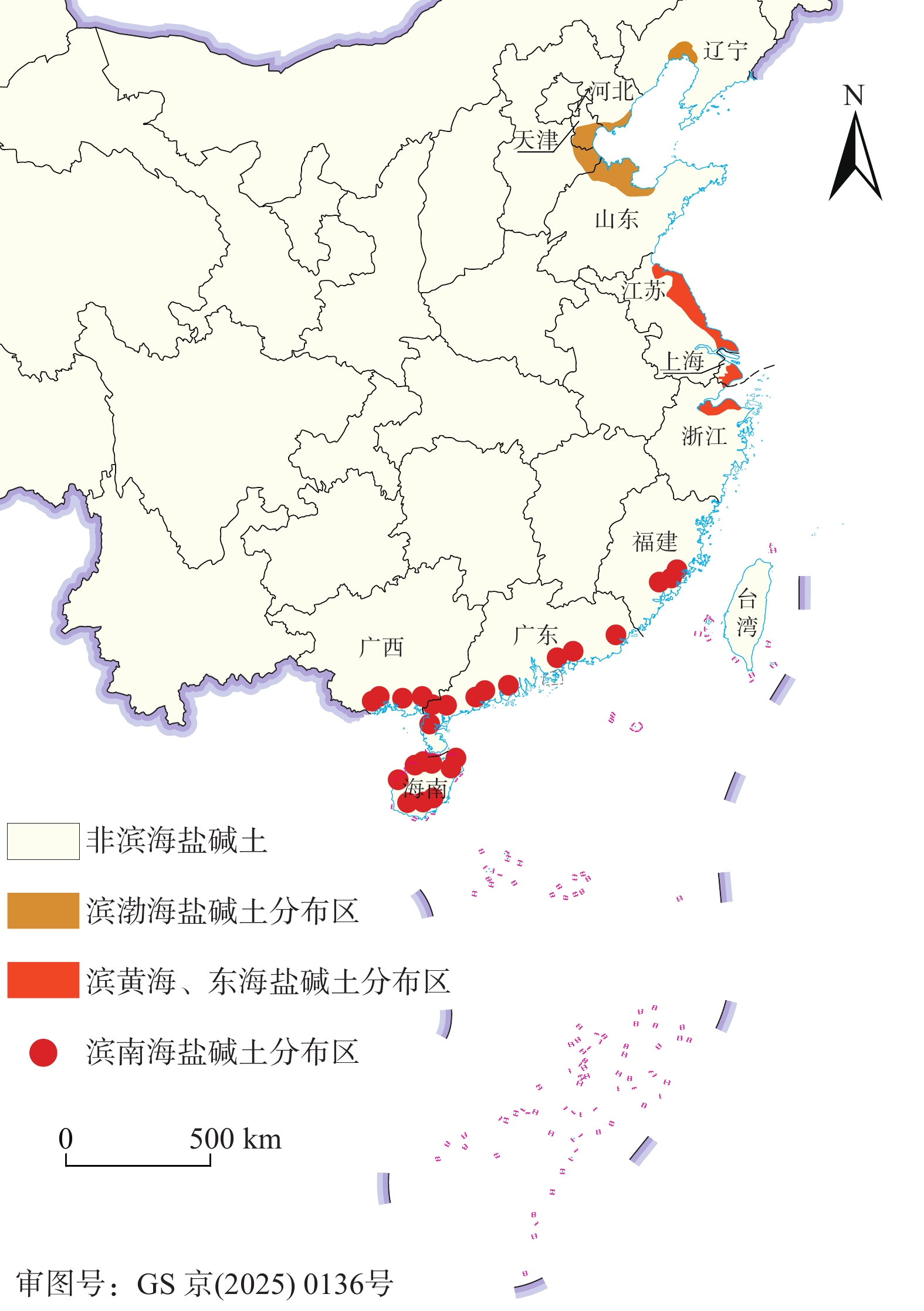
图 1 我国滨海盐碱土分布图(据王遵亲等[14],作者进行了重绘)
Figure 1.
表 1 我国滨海盐碱地改良案例
Table 1. Case studies on the amelioration of coastal saline-alkali land in China
文献 分布区 研究区 前期条件 改良技术类别 改良具体方案 改良效果 [107] 滨渤海盐碱土分布区 辽宁省
盘锦市土壤体积电导率5.32 dS/m,
生物多样性低生物改良技术 建设防护林 土壤体积电导率1.29~2.20 dS/m,
生物多样性显著提升[108] 天津市
宁河区土壤含盐量2.27 g/kg,
pH值8.87淋滤除盐技术,土壤理化性质改良技术 灌溉淋洗,添加土壤改良剂 土壤含盐量1.42 g/kg,
pH值8.47[109] 天津市
滨海新区土壤含盐量13.04~14.32 g/kg 淋滤除盐技术,抑制返盐技术 灌溉淋洗,地下排水暗管 土壤含盐量0.94~8.65 g/kg [110] 河北省
唐山市土壤容重平均
1.73 g/cm3,
土壤饱和电导率25 dS/m,
水位埋深0.5~3.0 m淋滤除盐技术,土壤理化性质改良技术,抑制返盐技术,生物改良技术 滴灌,土壤旋耕,铺设隔盐,建设防护林 土壤容重平均1.45 g/cm3,
土壤饱和电导率0.81 dS/m,
植被覆盖度显著增加[110] 河北省
海兴县土壤含盐量7.74 g/kg,
水位埋深0.9~1.5 m淋滤除盐技术,抑制返盐技术 咸水结冰灌溉,地膜覆盖 土壤含盐量约2 g/kg,
土壤细菌丰度显著增加[111] 山东省
垦利县土壤浸提液电导率
约0.8 dS/m土壤理化性质改良技术,抑制返盐技术 土壤旋耕,地膜覆盖 土壤浸提液电导率约0.3 dS/m [112] 黄河三角洲 耕层含盐量大于0.5%,
土壤有机质含量13 g/kg土壤理化性质改良技术,生物改良技术 生态种养循环:耐盐牧草种植-养殖-生物有机肥生产-盐碱地改良和肥力提升 耕层含盐量小于0.2%,
土壤有机质含量16 g/kg[113] 滨黄海、东海盐碱土分布区 江苏省
连云港市土壤含盐量32.3 g/kg,
水位埋深0.56~150.00 cm淋滤除盐技术,土壤理化性质改良技术,抑制返盐技术 灌溉淋洗,地下排水暗管,基质改良,铺设隔盐层,数值模拟预测 土壤含盐量2.3 g/kg,
有效抑制返盐[114] 江苏省
南通市土壤含盐量2.6%~4.2%,
有机质含量不足0.1%,
水位埋深1 m左右淋滤除盐技术,土壤理化性质改良技术,抑制返盐技术,生物改良技术 灌溉淋洗,地表深排沟,地下秸秆排水,秸秆覆盖,添加土壤改良剂,植物栽种 土壤含盐量0.1%~0.5%,
有机质含量1.9%,
耐盐作物长势良好[115] 浙江省
慈溪市土壤含盐量超10 g/kg,
有机质含量不足6 g/kg土壤理化性质改良技术,抑制返盐技术,生物改良技术 地形整平,排盐沟渠,植物地被覆盖,铺设棉花秸秆隔盐层 土壤含盐量小于2 g/kg,
有机质含量超10 g/kg[116] 滨南海盐碱土分布区 福建省
平潭县土壤含水量较低,
孔隙度不足45%,
pH值8.89土壤理化性质改良技术 添加土壤改良剂 土壤含水量提高24.8%,
孔隙度超50%,
pH值7.65[117] 广东省
湛江市滨海酸性盐碱化土壤
(土壤含盐量0.2%~0.6%)生物改良技术 种植海水稻 海水稻正常生长
微生物丰度及活性显著提升[118] 海南省
文昌市土壤含盐量3.36 g/kg,
pH值6.35,
有机质含量、微生物丰度低淋滤除盐技术,土壤理化性质改良技术 灌溉淋洗,添加土壤改良剂 土壤含盐量2.86~3.13 g/kg,
pH值7.43~7.51,
有机质含量、微生物丰度提高表 2 滨海盐碱地改良技术优缺点及适用范围
Table 2. Advantages and disadvantages of coastal saline-alkali land improvement technology and its application scope
改良技术类别 优点 缺点 适用范围 淋滤除盐技术 原理简单,效果显著 消耗水资源,存在引发次生盐碱化
及环境污染的风险适用范围广泛,需根据水资源状况确定合理的盐分淋洗策略 土壤理化性质改良技术 快速生效,材料多样 改良的长效性不足,可能污染环境 适用范围广泛,可依据改良地区水文地质条件
及资源状况选择适宜的改良剂抑制返盐技术 机理明确,操作性强 成本高昂,参数需评估 主要应用于地下水埋深浅的高盐地区 生物改良技术 生态良好,经济高效 存在生态风险,耐盐品种有限 可根据改良区盐分含量确定植被类型 -
[1] LIU Feng,WU Huayong,ZHAO Yuguo,et al. Mapping high resolution National Soil Information Grids of China[J]. Science Bulletin,2022,67(3):328 − 340. doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2021.10.013
[2] PRĂVĂLIE R,PATRICHE C,BORRELLI P,et al. Arable lands under the pressure of multiple land degradation processes: A global perspective[J]. Environmental Research,2021,194:110697. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.110697
[3] HOPMANS J W,QURESHI A S,KISEKKA I,et al. Critical knowledge gaps and research priorities in global soil salinity[J]. Advances in Agronomy,2021,169:1 − 191.
[4] 王高祥,苏小四,张岩,等. 连云港徐圩新区盐渍土盐分时空分布特征及其主要影响因素分析[J]. 安全与环境工程,2021,28(3):16 − 24. [WANG Gaoxiang,SU Xiaosi,ZHANG Yan,et al. Characteristics of temporal and spatial distribution of salinity in saline soil and its main influencing factors in Xuwei New District of Lianyungang[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering,2021,28(3):16 − 24. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Gaoxiang, SU Xiaosi, ZHANG Yan, et al. Characteristics of temporal and spatial distribution of salinity in saline soil and its main influencing factors in Xuwei New District of Lianyungang[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2021, 28(3): 16 − 24. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] ONDRASEK G,RENGEL Z. Environmental salinization processes:Detection,implications & solutions[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2021,754:142432. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142432
[6] 习近平. 切实加强耕地保护抓好盐碱地综合改造利用[EB/OL]. 北京:中国政府网,(2023-11-30)[2024-09-10]. https://www.gov.cn/yaowen/liebiao/202311/content_6917806.htm.
[7] 霍小光,李凤双. 总书记强调做好盐碱地特色农业大文章[EB/OL]. (2023-05-13)[2024-09-10]. http://www.news.cn/2023-05/13/c_1129610964.htm.
[8] 胥伟华,王建林,刘小京,等. 建设“滨海草带”的科技缘由、内容与对策[J]. 中国科学院院刊,2022,37(2):238 − 245. [XU Weihua,WANG Jianlin,LIU Xiaojing,et al. Scientific and technological reasons,contents and corresponding policies of constructing “coastal grass belt”[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences,2022,37(2):238 − 245. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
XU Weihua, WANG Jianlin, LIU Xiaojing, et al. Scientific and technological reasons, contents and corresponding policies of constructing “coastal grass belt”[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2022, 37(2): 238 − 245. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 孙盛楠,严学兵,尹飞虎. 我国沿海滩涂盐碱地改良与综合利用现状与展望[J]. 中国草地学报,2024,46(2):1 − 13. [SUN Shengnan,YAN Xuebing,YIN Feihu. Current situation and prospect of improvement and comprehensive utilization for saline-alkali land of coastal tidal flats in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland,2024,46(2):1 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
SUN Shengnan, YAN Xuebing, YIN Feihu. Current situation and prospect of improvement and comprehensive utilization for saline-alkali land of coastal tidal flats in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2024, 46(2): 1 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 赵英,王丽,赵惠丽,等. 滨海盐碱地改良研究现状及展望[J]. 中国农学通报,2022,38(3):67 − 74. [ZHAO Ying,WANG Li,ZHAO Huili,et al. Research status and prospects of saline-alkali land amelioration in the coastal region of China[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2022,38(3):67 − 74. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2021-0255
ZHAO Ying, WANG Li, ZHAO Huili, et al. Research status and prospects of saline-alkali land amelioration in the coastal region of China[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2022, 38(3): 67 − 74. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2021-0255
[11] 郑栅洁. 扎实推进盐碱地综合利用 做好盐碱地特色农业大文章[EB/OL]. (2023-10-14)[2024-09-10]. https://www.gov.cn/lianbo/bumen/202310/content_6909201.htm.
[12] 魏文杰,程知言,胡建,等. 滨海盐碱地形成及离子附着形态综述[J]. 土壤通报,2017,48(4):1003 − 1007. [WEI Wenjie,CHENG Zhiyan,HU Jian,et al. A review on formation and ion attached form of coastal saline-alkali soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science,2017,48(4):1003 − 1007. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WEI Wenjie, CHENG Zhiyan, HU Jian, et al. A review on formation and ion attached form of coastal saline-alkali soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2017, 48(4): 1003 − 1007. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] LONG Xiaohua,LIU Liping,SHAO Tianyun,et al. Developing and sustainably utilize the coastal mudflat areas in China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2016,569/570:1077 − 1086. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.170
[14] 王遵亲. 中国盐渍土[M]. 北京:科学出版社,1993. [WANG Zunqin. Saline soil in China[M]. Beijing:Science Press,1993. (in Chinese)]
WANG Zunqin. Saline soil in China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1993. (in Chinese)
[15] 魏丹,李艳,秦程程,等. 环渤海地区设施蔬菜土壤障碍与治理措施[J]. 中国土壤与肥料,2021(5):303 − 309. [WEI Dan,LI Yan,QIN Chengcheng,et al. Soil barrier and countermeasure of protected vegetable in the Bohai Rim[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China,2021(5):303 − 309. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.11838/sfsc.1673-6257.20390
WEI Dan, LI Yan, QIN Chengcheng, et al. Soil barrier and countermeasure of protected vegetable in the Bohai Rim[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2021(5): 303 − 309. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11838/sfsc.1673-6257.20390
[16] 钞锦龙,张化,李颖,等. 渤海湾滨海盐渍土地区农业灌溉用水可能途径探究[J]. 灌溉排水学报,2014,33(3):141 − 144. [CHAO Jinlong,ZHANG Hua,LI Ying,et al. The possible avenues of agricultural irrigation water in Bohai Bay coastal saline land area[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage,2014,33(3):141 − 144. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHAO Jinlong, ZHANG Hua, LI Ying, et al. The possible avenues of agricultural irrigation water in Bohai Bay coastal saline land area[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2014, 33(3): 141 − 144. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 祝瑜,褚琳琳,朱文东,等. 客土造林后滨海盐碱地土壤盐分分布及影响因素分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2023,39(6):149 − 157. [ZHU Yu,CHU Linlin,ZHU Wendong,et al. Spatial distribution pattern and influencing factors of soil salt in coastal saline-alkali land after afforestation with foreign soil[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2023,39(6):149 − 157. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.202210190
ZHU Yu, CHU Linlin, ZHU Wendong, et al. Spatial distribution pattern and influencing factors of soil salt in coastal saline-alkali land after afforestation with foreign soil[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2023, 39(6): 149 − 157. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.202210190
[18] 陆宏,厉仁安. 杭州湾南岸土壤演变及其开发利用研究[J]. 土壤通报,2009,40(2):218 − 220. [LU Hong,LI Ren’an. Soil evolution on the South of Hangzhou Gulf and its exploiting and utilization[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science,2009,40(2):218 − 220. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LU Hong, LI Ren’an. Soil evolution on the South of Hangzhou Gulf and its exploiting and utilization[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2009, 40(2): 218 − 220. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 赵秀芳,杨劲松,姚荣江. 基于典范对应分析的苏北滩涂土壤春季盐渍化特征研究[J]. 土壤学报,2010,47(3):422 − 428. [ZHAO Xiufang,YANG Jinsong,YAO Rongjiang. Characteristics of soil salinization in mudflat of North Jiangsu Province based on canonical correspondence analysis[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica,2010,47(3):422 − 428. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.11766/trxb2010470306
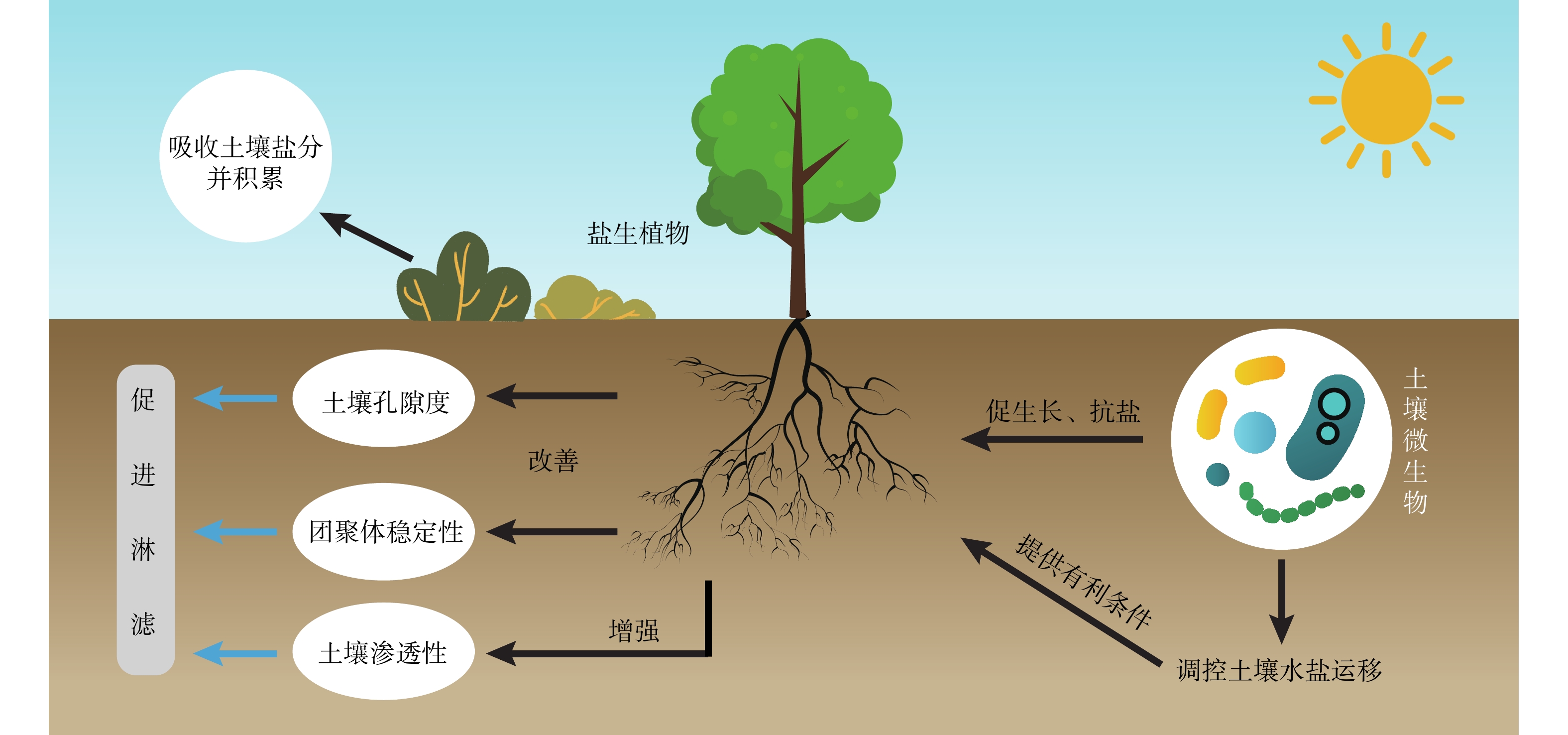
ZHAO Xiufang, YANG Jinsong, YAO Rongjiang. Characteristics of soil salinization in mudflat of North Jiangsu Province based on canonical correspondence analysis[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2010, 47(3): 422 − 428. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11766/trxb2010470306
[20] ARULMATHI C,PORKODI G. Characteristics of coastal saline soil and their management:A review[J]. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences,2020,9(10):1726 − 1734.
[21] 韩笑晨,张贵芹,王亚辉,等. 土壤调理剂对滨海盐碱地土壤盐分含量及夏玉米产量的影响[J]. 作物学报,2024,50(7):1776 − 1786. [HAN Xiaochen,ZHANG Guiqin,WANG Yahui,et al. Effects of soil conditioners on soil salinity content and maize yield in coastal saline-alkali land[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica,2024,50(7):1776 − 1786. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HAN Xiaochen, ZHANG Guiqin, WANG Yahui, et al. Effects of soil conditioners on soil salinity content and maize yield in coastal saline-alkali land[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2024, 50(7): 1776 − 1786. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] YAO Rongjiang,YANG Jingsong,ZHANG Tongjuan,et al. Studies on soil water and salt balances and scenarios simulation using SaltMod in a coastal reclaimed farming area of eastern China[J]. Agricultural Water Management,2014,131:115 − 123. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2013.09.014
[23] 李晓彬,康跃虎. 滨海重度盐碱地微咸水滴灌水盐调控及月季根系生长响应研究[J]. 农业工程学报,2019,35(11):112 − 121. [LI Xiaobin,KANG Yuehu. Water-salt control and response of Chinese rose (Rosa chinensis) root on coastal saline soil using drip irrigation with brackish water[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2019,35(11):112 − 121. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.11.013
LI Xiaobin, KANG Yuehu. Water-salt control and response of Chinese rose (Rosa chinensis) root on coastal saline soil using drip irrigation with brackish water[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2019, 35(11): 112 − 121. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.11.013
[24] MOHANAVELU A,NAGANNA S R,AL-ANSARI N. Irrigation induced salinity and sodicity hazards on soil and groundwater:An overview of its causes,impacts and mitigation strategies[J]. Agriculture,2021,11(10):983. doi: 10.3390/agriculture11100983
[25] AKTER S,AHMED K R,MARANDI A,et al. Possible factors for increasing water salinity in an embanked coastal island in the southwest Bengal Delta of Bangladesh[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,713:136668. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136668
[26] 章家恩. 酸性硫酸盐土的酸害暴发机制及其环境影响[J]. 热带地理,1999,19(2):137 − 141. [ZHANG Jiaen. The process of acid hazards in acid sulfate soils and its environmental effects[J]. Tropical Geography,1999,19(2):137 − 141. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5221.1999.02.007
ZHANG Jiaen. The process of acid hazards in acid sulfate soils and its environmental effects[J]. Tropical Geography, 1999, 19(2): 137 − 141. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5221.1999.02.007
[27] 赵君涵,佘冬立,姚怀柱,等. 地下水埋深及矿化度变化对番茄产量及品质的影响[J]. 灌溉排水学报,2022,41(5):90 − 96. [ZHAO Junhan,SHE Dongli,YAO Huaizhu,et al. The change in yield and fruit quality of tomato as affected by groundwater depth and salinity in coastal regions[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage,2022,41(5):90 − 96. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHAO Junhan, SHE Dongli, YAO Huaizhu, et al. The change in yield and fruit quality of tomato as affected by groundwater depth and salinity in coastal regions[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2022, 41(5): 90 − 96. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 张凤荣. 分区分类因地制宜综合改造利用盐碱地[J]. 中国土地,2023(8):30 − 32. [ZHANG Fengrong. Zoning and classification for comprehensive improvement and utilization of saline-alkali land according to local conditions[J]. China Land,2023(8):30 − 32. (in Chinese)]
ZHANG Fengrong. Zoning and classification for comprehensive improvement and utilization of saline-alkali land according to local conditions[J]. China Land, 2023(8): 30 − 32. (in Chinese)
[29] YU Xiayang,DAN Hancheng,XIN Pei. Method for improving leaching efficiency of coastal subsurface drainage systems[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering,2018,144(8):04018019. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)IR.1943-4774.0001330
[30] ZHENG Wenjuan,YANG Zhenlei,WANG Xiaoxuan,et al. Impacts of evaporation and inundation on near-surface salinity at a coastal wetland park[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2022,185(Pt B):114373.
[31] 王鹏山. 不同淋洗方式下滨海盐渍土改良效果研究[D]. 北京:北京林业大学,2012. [WANG Pengshan. The effect of different leaching way on improvement of coastal saline soil[D]. Beijing:Beijing Forestry University,2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Pengshan. The effect of different leaching way on improvement of coastal saline soil[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] CHU Linlin,ZHU Yu,XIONG Ling,et al. Approach of water-salt regulation using micro-sprinkler irrigation in two coastal saline soils[J]. Water Science and Engineering,2023,16(1):106 − 112. doi: 10.1016/j.wse.2022.10.002
[33] LI Xiaobin,ZHANG Chen. Effect of natural and artificial afforestation reclamation on soil properties and vegetation in coastal saline silt soils[J]. Catena,2021,198:105066. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2020.105066
[34] ZHANG Chen,LI Xiaobin. Using saline water drip irrigation and soil matric potential control for tree establishment in coastal saline soil[J]. Ecological Engineering,2021,170:106337. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2021.106337
[35] LIU Bingxia,WANG Shiqin,LIU Xiaojing,et al. Evaluating soil water and salt transport in response to varied rainfall events and hydrological years under brackish water irrigation in the North China Plain[J]. Geoderma,2022,422:115954. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2022.115954
[36] 李俊杰,屈忠义,杨威,等. 咸水结冰灌溉下盐碱地土壤水热盐动态迁移特征分析[J]. 水土保持学报,2023,37(2):377 − 384. [LI Junjie,QU Zhongyi,YANG Wei,et al. Analysis of dynamic migration characteristics of Soil water,heat,and salt in saline-alkali soils under saline water freezing irrigation[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2023,37(2):377 − 384. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Junjie, QU Zhongyi, YANG Wei, et al. Analysis of dynamic migration characteristics of Soil water, heat, and salt in saline-alkali soils under saline water freezing irrigation[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2023, 37(2): 377 − 384. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[37] WANG Xiaogai,WANG Luming,YU Zhenhua,et al. Differential responses of bacterial communities in rhizosphere and bulk soils of cotton to long-term amelioration practices based on freezing saline water irrigation and plastic mulching in a coastal saline soil[J]. Agronomy,2024,14(1):103. doi: 10.3390/agronomy14010103
[38] 高会,赵亮,刘斌,等. 河北滨海盐碱地浅层轻度咸水资源冬小麦灌溉安全利用研究[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文),2023,31(7):1102 − 1109. [GAO Hui,ZHAO Liang,LIU Bin,et al. Study on shallow mild saline groundwater use safety in winter wheat irrigation based on the subsurface drainage system in the coastal area of Hebei Province in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture,2023,31(7):1102 − 1109. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
GAO Hui, ZHAO Liang, LIU Bin, et al. Study on shallow mild saline groundwater use safety in winter wheat irrigation based on the subsurface drainage system in the coastal area of Hebei Province in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2023, 31(7): 1102 − 1109. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[39] SHOKRI‐KUEHNI S M S,RAAIJMAKERS B,KURZ T,et al. Water table depth and soil salinization:From pore-scale processes to field-scale responses[J]. Water Resources Research,2020,56(2):e2019WR026707. doi: 10.1029/2019WR026707
[40] GAO Hui,FU Tonggang,TANG Shoupu,et al. Effects of saline water irrigation on winter wheat and its safe utilization under a subsurface drainage system in coastal saline-alkali land of Hebei Province,China[J]. Irrigation Science,2023,41(2):251 − 260. doi: 10.1007/s00271-023-00849-8
[41] 陆海明,孙金华,邹鹰,等. 农田排水沟渠的环境效应与生态功能综述[J]. 水科学进展,2010,21(5):719 − 725. [LU Haiming,SUN Jinhua,ZOU Ying,et al. Review of environmental impact and ecological function of agricultural drainage ditches[J]. Advances in Water Science,2010,21(5):719 − 725. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LU Haiming, SUN Jinhua, ZOU Ying, et al. Review of environmental impact and ecological function of agricultural drainage ditches[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2010, 21(5): 719 − 725. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[42] AFRUZI A,NAZEMI A H,SADRADDINI A A. Steady-state subsurface drainage of ponded fields by rectangular ditch drains:Subsurface drainage of ponded fields by ditch drains[J]. Irrigation and Drainage,2014,63(5):668 − 681. doi: 10.1002/ird.1857
[43] TAO Yuan,WANG Shaoli,XU Di,et al. Experiment and analysis on flow rate of improved subsurface drainage with ponded water[J]. Agricultural Water Management,2016,177:1 − 9. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2016.05.016
[44] 杨鹏年,孙珍珍,汪昌树,等. 绿洲灌区春灌效应及定额研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2015,42(5):29 − 33. [YANG Pengnian,SUN Zhenzhen,WANG Changshu,et al. A study of the effect and quota of spring irrigation on oasis irrigation areas[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2015,42(5):29 − 33. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YANG Pengnian, SUN Zhenzhen, WANG Changshu, et al. A study of the effect and quota of spring irrigation on oasis irrigation areas[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2015, 42(5): 29 − 33. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[45] SHAYGAN M,READING L P,BAUMGARTL T. Effect of physical amendments on salt leaching characteristics for reclamation[J]. Geoderma,2017,292:96 − 110. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.01.007
[46] NAVEED M,DITTA A,AHMAD M,et al. Processed animal manure improves morpho-physiological and biochemical characteristics of Brassica napus L. under Nickel and salinity stress[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International,2021,28(33):45629 − 45645. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-14004-3
[47] WU Linjian,XIANG Zhouyu,JIANG Han,et al. A review of durability issues of reinforced concrete structures due to coastal soda residue soil in China[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering,2022,10(11):1740. doi: 10.3390/jmse10111740
[48] 李品芳,杨永利,兰天,等. 天津滨海盐渍土客土改良后的土壤理化性质与持水特性[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(7):149 − 156. [LI Pinfang,YANG Yongli,LAN Tian,et al. Physicochemical properties and water holding characteristics of Tianjin coastal saline soil improved by foreign soil[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2017,33(7):149 − 156. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.07.019
LI Pinfang, YANG Yongli, LAN Tian, et al. Physicochemical properties and water holding characteristics of Tianjin coastal saline soil improved by foreign soil[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2017, 33(7): 149 − 156. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.07.019
[49] 刘洪光,李智杰,李玲,等. 粉垄深松深耕改善南疆重度盐碱土理化性质和棉花产量及其后效[J]. 农业工程学报,2024,40(13):45 − 57. [LIU Hongguang,LI Zhijie,LI Ling,et al. Effects of deep vertical rotary tillage depth on the improvement of soil physicochemical properties and cotton yield in the current year and the following year in severe saline land in Southern Xinjiang of China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2024,40(13):45 − 57. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.202309085
LIU Hongguang, LI Zhijie, LI Ling, et al. Effects of deep vertical rotary tillage depth on the improvement of soil physicochemical properties and cotton yield in the current year and the following year in severe saline land in Southern Xinjiang of China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2024, 40(13): 45 − 57. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.202309085
[50] SCHWARTZ R C,BAUMHARDT R L,EVETT S R. Tillage effects on soil water redistribution and bare soil evaporation throughout a season[J]. Soil and Tillage Research,2010,110(2):221 − 229. doi: 10.1016/j.still.2010.07.015
[51] ZHENG Xu,CHEN Chaoqun,LI Luhua,et al. Ridge tillage increased halophyte fine root production and turnover rates by altering soil properties in an abandoned farmland in northwest China[J]. Rhizosphere,2023,27:100742. doi: 10.1016/j.rhisph.2023.100742
[52] LI Wenxiu,YANG Jingsong,TANG Chong,et al. The temporal–spatial dynamic distributions of soil water and salt under deep vertical rotary tillage on coastal saline soil[J]. Water,2022,14(21):3370. doi: 10.3390/w14213370
[53] 杨劲松,姚荣江,王相平,等. 中国盐渍土研究:历程、现状与展望[J]. 土壤学报,2022,59(1):10 − 27. [YANG Jinsong,YAO Rongjiang,WANG Xiangping,et al. Research on salt-affected soils in China:History,status quo and prospect[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica,2022,59(1):10 − 27. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.11766/trxb202110270578
YANG Jinsong, YAO Rongjiang, WANG Xiangping, et al. Research on salt-affected soils in China: History, status quo and prospect[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2022, 59(1): 10 − 27. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11766/trxb202110270578
[54] LI Kesheng,KONG Weihang,XU Wenshuo,et al. Impacts of application patterns and incorporation rates of dredged Yellow River sediment on structure and infiltration of saline-alkali soil[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering,2022,15(4):139 − 146. doi: 10.25165/j.ijabe.20221504.6556
[55] MAO Yumei,LI Xiaoping. Desalting effect of flue gas desulfurization gypsum (FGDG) on coastal saline-sodic soil with different textures[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments,2023,23(2):765 − 776. doi: 10.1007/s11368-022-03344-3
[56] WANG Jinman,YANG Peiling. Potential flue gas desulfurization gypsum utilization in agriculture:A comprehensive review[J]. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews,2018,82:1969 − 1978.
[57] YAO Rongjiang,LI Hongqiang,ZHU Wei,et al. Biochar and potassium humate shift the migration,transformation and redistribution of urea-N in salt-affected soil under drip fertigation:Soil column and incubation experiments[J]. Irrigation Science,2022,40(2):267 − 282. doi: 10.1007/s00271-021-00763-x
[58] MAHDY A M. Soil properties and wheat growth and nutrients as affected by compost amendment under saline water irrigation[J]. Pedosphere,2011,21(6):773 − 781. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0160(11)60181-1
[59] HUANG Ruirui. The effect of humic acid on the desalinization of coastal clayey saline soil[J]. Water Supply,2022,22(9):7242 − 7255. doi: 10.2166/ws.2022.311
[60] BAI Yanchao,XUE Weijie,YAN Yiyun,et al. The challenge of improving coastal mudflat soil:Formation and stability of organo-mineral complexes[J]. Land Degradation & Development,2018,29(4):1074 − 1080.
[61] LI Shan,YAO Yuanyuan,YANG Mingchuan,et al. Effects of different amendments on aggregate stability and microbial communities of coastal saline–alkali soil in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Land Degradation & Development,2023,34(6):1694 − 1707.
[62] NAN Jiangkuan,CHEN Xiaomin,WANG Xiaoyang,et al. Effects of applying flue gas desulfurization gypsum and humic acid on soil physicochemical properties and rapeseed yield of a saline-sodic cropland in the eastern coastal area of China[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments,2016,16(1):38 − 50. doi: 10.1007/s11368-015-1186-3
[63] CHEN Jiancheng,HU Guoqing,WANG Hui,et al. Leaching and migration characteristics of nitrogen during coastal saline soil remediation by combining humic acid with gypsum and bentonite[J]. Annals of Agricultural Sciences,2023,68(1):1 − 11. doi: 10.1016/j.aoas.2023.02.001
[64] LIANG Jiaping,LI Yi,SI Bingcheng,et al. Optimizing biochar application to improve soil physical and hydraulic properties in saline-alkali soils[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2021,771:144802. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144802
[65] WANG Xiao,DING Jianli,HAN Lijing,et al. Biochar addition reduces salinity in salt-affected soils with no impact on soil pH:A meta-analysis[J]. Geoderma,2024,443:116845. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2024.116845
[66] CUI Qian,XIA Jiangbao,YANG Hongjun,et al. Biochar and effective microorganisms promote sesbania cannabina growth and soil quality in the coastal saline-alkali soil of the Yellow River Delta,China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2021,756:143801. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143801
[67] 刘强,袁延飞,刘一帆,等. 生物炭对盐渍化土壤改良的研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展,2022,37(10):1005 − 1024. [LIU Qiang,YUAN Yanfei,LIU Yifan,et al. Research progress:The application of biochar in the remediation of salt-affected soils[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2022,37(10):1005 − 1024. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2022.050
LIU Qiang, YUAN Yanfei, LIU Yifan, et al. Research progress: The application of biochar in the remediation of salt-affected soils[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2022, 37(10): 1005 − 1024. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2022.050
[68] 朱建峰,崔振荣,吴春红,等. 我国盐碱地绿化研究进展与展望[J]. 世界林业研究,2018,31(4):70 − 75. [ZHU Jianfeng,CUI Zhenrong,WU Chunhong,et al. Research advances and prospect of saline and alkali land greening in China[J]. World Forestry Research,2018,31(4):70 − 75. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHU Jianfeng, CUI Zhenrong, WU Chunhong, et al. Research advances and prospect of saline and alkali land greening in China[J]. World Forestry Research, 2018, 31(4): 70 − 75. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[69] ZHENG Hao,WANG Xiao,CHEN Lei,et al. Enhanced growth of halophyte plants in biochar-amended coastal soil:Roles of nutrient availability and rhizosphere microbial modulation[J]. Plant,Cell & Environment,2018,41(3):517 − 532.
[70] LI Xiaoqian,XIA Jiangbao,ZHAO Ximei,et al. Effects of planting Tamarix chinensis on shallow soil water and salt content under different groundwater depths in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Geoderma,2019,335:104 − 111. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2018.08.017
[71] WANG Juan,CHEN Anquan,LI Yan,et al. Buried straw layer coupling film mulching regulates soil salinity of coastal tidal soil and improves maize(Zea mays L.)growth[J]. Water,2022,14(24):4119. doi: 10.3390/w14244119
[72] ZHANG Yifu,WANG Wancheng,YUAN Wei,et al. Cattle manure application and combined straw mulching enhance maize (Zea mays L.) growth and water use for rain-fed cropping system of coastal saline soils[J]. Agriculture,2021,11(8):745. doi: 10.3390/agriculture11080745
[73] HUO Long,PANG Huancheng,ZHAO Yonggan,et al. Buried straw layer plus plastic mulching improves soil organic carbon fractions in an arid saline soil from Northwest China[J]. Soil and Tillage Research,2017,165:286 − 293. doi: 10.1016/j.still.2016.09.006
[74] ZHANG Hongyuan,PANG Huancheng,LU Chuang,et al. Subsurface organic amendment plus plastic mulching promotes salt leaching and yield of sunflower[J]. Agronomy Journal,2019,111(1):457 − 466. doi: 10.2134/agronj2018.02.0097
[75] 孟德臣,宗宪春,郗登宝,等. 地膜覆盖对重度盐碱地土壤水盐状况及羊草移栽效果的影响[J]. 吉林农业大学学报,2018,40(6):722 − 726. [MENG Dechen,ZONG Xianchun,XI Dengbao,et al. Effects of plastic film mulching on soil water and salt status and transplanting effect of leymus chinensis in heavy saline-alkali land[J]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University,2018,40(6):722 − 726. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
MENG Dechen, ZONG Xianchun, XI Dengbao, et al. Effects of plastic film mulching on soil water and salt status and transplanting effect of leymus chinensis in heavy saline-alkali land[J]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 2018, 40(6): 722 − 726. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[76] 李小牛,苏沛兰. 中度盐碱地不同秸秆覆盖量对土壤含盐量的影响[J]. 灌溉排水学报,2017,36(增刊1):66 − 70. [LI Xiaoniu,SU Peilan. Effect of different straw mulch quantities on soil salinity of moderate saline-alkali soil[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage,2017,36(Sup 1):66 − 70. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Xiaoniu, SU Peilan. Effect of different straw mulch quantities on soil salinity of moderate saline-alkali soil[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2017, 36(Sup 1): 66 − 70. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[77] HULIN C,MERCURY L. Regeneration of capillary water in unsaturated zones[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2019,265:279 − 291. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2019.07.058
[78] 陶彦臻,苏春利,谢先军,等. 基于碎石屏障的土壤盐渍化改良技术及机理研究[J]. 地球科学,2021,46(11):4118 − 4126. [TAO Yanzhen,SU Chunli,XIE Xianjun,et al. Technology and mechanism of soil salinization using gravel barrier[J]. Earth Science,2021,46(11):4118 − 4126. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2020.377
TAO Yanzhen, SU Chunli, XIE Xianjun, et al. Technology and mechanism of soil salinization using gravel barrier[J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(11): 4118 − 4126. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2020.377
[79] ZHAO Li,HENG Tong,YANG Lili,et al. Study on the farmland improvement effect of drainage measures under film mulch with drip irrigation in saline–alkali land in arid areas[J]. Sustainability,2021,13(8):4159. doi: 10.3390/su13084159
[80] HAN Danni,CHEN Chao,WANG Fan,et al. Effects of subsurface pipe drainage spacing on soil salinity movement in Jiangsu coastal reclamation area[J]. Sustainability,2023,15(18):13932. doi: 10.3390/su151813932
[81] 张万钧,龙怀玉,郭育文,等. 天津滨海园林绿化中盐土治理的理论及工艺[J]. 北京林业大学学报,2000,22(5):40 − 44. [ZHANG Wanjun,LONG Huaiyu,GUO Yuwen,et al . The theory and techniques about the improvement of saline soil in Tianjin seashore region under landscape greening[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University,2000,22(5):40 − 44. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1522.2000.05.008
ZHANG Wanjun, LONG Huaiyu, GUO Yuwen, et al . The theory and techniques about the improvement of saline soil in Tianjin seashore region under landscape greening[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2000, 22(5): 40 − 44. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1522.2000.05.008
[82] LU Peirong,ZHANG Zhanyu,SHENG Zhuping,et al. Assess effectiveness of salt removal by a subsurface drainage with bundled crop straws in coastal saline soil using HYDRUS-3D[J]. Water,2019,11(5):943. doi: 10.3390/w11050943
[83] 刘鹏飞,张光辉,崔尚进,等. 旱区湿地周边盐渍化农田生态水位阈值与“水位-水量”双控技术[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(5):42 − 51. [LIU Pengfei,ZHANG Guanghui,CUI Shangjin,et al. Threshold value of ecological water table and dual control technology of the water table and its quantity in the salinized farmland around wetland in arid areas[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(5):42 − 51. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Pengfei, ZHANG Guanghui, CUI Shangjin, et al. Threshold value of ecological water table and dual control technology of the water table and its quantity in the salinized farmland around wetland in arid areas[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(5): 42 − 51. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[84] 何锦. 水平井开采条件下浅层地下咸水水盐运移规律与开发利用研究——以河北沧州地区为例[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2021. [HE Jin. Utilization and water-salt migration characteristic in the shallow saline water under horizontal well mining conditions:A case study of Cangzhou region of Heibei[D]. Changchun:Jilin University,2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HE Jin. Utilization and water-salt migration characteristic in the shallow saline water under horizontal well mining conditions: A case study of Cangzhou region of Heibei[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[85] 邹荣松,陈军华,邓丞,等. 盐渍化土壤隔盐脱盐材料及技术研究进展[J]. 世界林业研究,2023,36(2):20 − 25. [ZOU Rongsong,CHEN Junhua,DENG Cheng,et al. Research progress of materials and technologies for salt isolation and desalination of salinized soil[J]. World Forestry Research,2023,36(2):20 − 25. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZOU Rongsong, CHEN Junhua, DENG Cheng, et al. Research progress of materials and technologies for salt isolation and desalination of salinized soil[J]. World Forestry Research, 2023, 36(2): 20 − 25. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[86] CHÁVEZ-GARCÍA E,SIEBE C. Rehabilitation of a highly saline-sodic soil using a rubble barrier and organic amendments[J]. Soil and Tillage Research,2019,189:176 − 188. doi: 10.1016/j.still.2019.01.003
[87] LI Jingsong,CHEN Huanyu,GUO Kai,et al. Changes in soil properties induced by pioneer vegetation patches in coastal ecosystem[J]. Catena,2021,204:105393. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2021.105393
[88] KOEVOETS I T,VENEMA J H,ELZENGA J T M,et al. Roots withstanding their environment:Exploiting root system architecture responses to abiotic stress to improve crop tolerance[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science,2016,7:1335.
[89] BALASUBRAMANIAM T,SHEN Guoxin,ESMAEILI N,et al. Plants’ response mechanisms to salinity stress[J]. Plants,2023,12(12):2253.
[90] MANOUSAKI E,KALOGERAKIS N. Halophytes—an emerging trend in phytoremediation[J]. International Journal of Phytoremediation,2011,13(10):959 − 969. doi: 10.1080/15226514.2010.532241
[91] LI Jingsong,YANG Ce,HUSSAIN T,et al. Long-term effect of tamarisk plantation on soil physical properties and soil salt distribution in coastal saline land[J]. Agronomy,2022,12(8):1947.
[92] FANG Dong,GUO Kai,AMEEN A,et al. A root density tradeoff in an okra-assisted subsurface pipe drainage system for amelioration of saline soil[J]. Agronomy,2022,12(4):866. doi: 10.3390/agronomy12040866
[93] GUO Longmei,CAO Banghua,MAO Peili,et al. Fine root vertical-seasonal distribution of Robinia pseudoacacia in relation to abiotic factors in a chronosequence in coastal saline alkali land of the Yellow River Delta,China[J]. Turkish Journal of Agriculture and Forestry,2021,45(6):750 − 765. doi: 10.3906/tar-2105-100
[94] RATHORE A P,CHAUDHARY D R,JHA B. Seasonal patterns of microbial community structure and enzyme activities in coastal saline soils of perennial halophytes[J]. Land Degradation & Development,2017,28(5):1779 − 1790.
[95] JING Changliang,XU Zongchang,ZOU Ping,et al. Coastal halophytes alter properties and microbial community structure of the saline soils in the Yellow River Delta,China[J]. Applied Soil Ecology,2019,134:1 − 7. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2018.10.009
[96] GU Chen,HUANG Weibin,SHAO Qing,et al. Effects of different growth patterns of Tamarix chinensis on saline-alkali soil:Implications for coastal restoration and management[J]. Biotechnology Letters,2022,44(12):1519 − 1526. doi: 10.1007/s10529-022-03317-z
[97] TEO H M,A A,A W A,et al. Setting a plausible route for saline soil-based crop cultivations by application of beneficial halophyte-associated bacteria:A review[J]. Microorganisms,2022,10(3):657. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10030657
[98] 崔丽洋,谢茜,毛青,等. 土壤微藻对盐胁迫的响应及其对盐渍化土壤的改良作用[J]. 地球科学,2023,48(11):4270 − 4278. [CUI Liyang,XIE Qian,MAO Qing,et al. Response of soil microalgae to salt stress and its improvement effect on salinized soil[J]. Earth Science,2023,48(11):4270 − 4278. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CUI Liyang, XIE Qian, MAO Qing, et al. Response of soil microalgae to salt stress and its improvement effect on salinized soil[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(11): 4270 − 4278. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[99] ZHOU Lixiu,LIU Wei,DUAN Huijie,et al. Improved effects of combined application of nitrogen-fixing bacteria Azotobacter beijerinckii and microalgae Chlorella pyrenoidosa on wheat growth and saline-alkali soil quality[J]. Chemosphere,2023,313:137409. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.137409
[100] ZHOU Di,YU Junbao,GUAN Bo,et al. A comparison of the development of wetland restoration techniques in China and other nations[J]. Wetlands,2020,40(6):2755 − 2764. doi: 10.1007/s13157-020-01305-5
[101] SUN Ruibo,WANG Xiaogai,TIAN Yinping,et al. Long-term amelioration practices reshape the soil microbiome in a coastal saline soil and alter the richness and vertical distribution differently among bacterial,archaeal,and fungal communities[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2022,12:768203. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.768203
[102] YANG Hongjun,XIA Jiangbao,CUI Qian,et al. Effects of different Tamarix chinensis-grass patterns on the soil quality of coastal saline soil in the Yellow River Delta,China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2021,772:145501. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145501
[103] XIE Wei,ZHANG Kai,WANG Xiaoying,et al. Peanut and cotton intercropping increases productivity and economic returns through regulating plant nutrient accumulation and soil microbial communities[J]. BMC Plant Biology,2022,22(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03506-y
[104] ATTA K,MONDAL S,GORAI S,et al. Impacts of salinity stress on crop plants:Improving salt tolerance through genetic and molecular dissection[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science,2023,14:1241736. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1241736
[105] NGUYEN H L,TRAN D H. Saline soils and crop production in coastal zones of Vietnam:Features,strategies for amelioration and management[J]. Pakistan Journal of Botany,2020,52(4):1327 − 1333.
[106] SHAYGAN M,BAUMGARTL T. Reclamation of salt-affected land:A review[J]. Soil Systems,2022,6(3):61. doi: 10.3390/soilsystems6030061
[107] 陈罡,邢献予,潘文利,等. 辽河三角洲杨树防护林对盐碱地改良效应研究[J]. 北方园艺,2017(5):156 − 160. [CHEN Gang,XING Xianyu,PAN Wenli,et al. Improvement effect of poplar shelterbelts on saline-alkalized soil of Liaohe River delta[J]. Northern Horticulture,2017(5):156 − 160. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHEN Gang, XING Xianyu, PAN Wenli, et al. Improvement effect of poplar shelterbelts on saline-alkalized soil of Liaohe River delta[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2017(5): 156 − 160. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[108] XIAO Meng,LIU Guangming,JIANG Shengguo,et al. Bio-organic fertilizer combined with different amendments improves nutrient enhancement and salt leaching in saline soil:A soil column experiment[J]. Water,2022,14(24):4084. doi: 10.3390/w14244084
[109] 张金龙,闻铁,王鹏山,等. 暗管排水控制区土壤盐分淋洗研究[J]. 水土保持学报,2014,28(5):242 − 246. [ZHANG Jinlong,WEN Tie,WANG Pengshan,et al. Studies on salt-leaching of soil in the region between subsurface drains[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2014,28(5):242 − 246. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Jinlong, WEN Tie, WANG Pengshan, et al. Studies on salt-leaching of soil in the region between subsurface drains[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2014, 28(5): 242 − 246. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[110] LI Xiaoguang,GUO Kai,FENG Xiaohui,et al. Soil respiration response to long-term freezing saline water irrigation with plastic mulching in coastal saline plain[J]. Sustainability,2017,9(4):621. doi: 10.3390/su9040621
[111] ZHANG Jishi,BIAN Qianqian,MIAO Qi,et al. Maize productivity response to combined tillage and mulching in coastal saline zones[J]. Agronomy Journal,2022,114(1):784 − 794. doi: 10.1002/agj2.20941
[112] 欧阳竹,王竑晟,来剑斌,等. 黄河三角洲农业高质量发展新模式[J]. 中国科学院院刊,2020,35(2):145 − 153. [OUYANG Zhu,WANG Hongsheng,LAI Jianbin,et al. New approach of high-quality agricultural development in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences,2020,35(2):145 − 153. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
OUYANG Zhu, WANG Hongsheng, LAI Jianbin, et al. New approach of high-quality agricultural development in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020, 35(2): 145 − 153. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[113] SU Xiaosi,WANG Yongqi,WANG Gaoxiang,et al. Assessment and prediction of coastal saline soil improvement effects combining substrate amendments and salt barrier materials in typical region of the Yangtze River Delta[J]. Soil and Tillage Research,2022,223:105483. doi: 10.1016/j.still.2022.105483
[114] 姜月华,倪化勇,周权平,等. 长江经济带生态修复示范关键技术及其应用[J]. 中国地质,2021,48(5):1305 − 1333. [JIANG Yuehua,NI Huayong,ZHOU Quanping,et al. Key technology of ecological restoration demonstration in the Yangtze River Economic Zone and its application[J]. Geology in China,2021,48(5):1305 − 1333. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.12029/gc20210501
JIANG Yuehua, NI Huayong, ZHOU Quanping, et al. Key technology of ecological restoration demonstration in the Yangtze River Economic Zone and its application[J]. Geology in China, 2021, 48(5): 1305 − 1333. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12029/gc20210501
[115] 崔心红,朱义,张群,等. 棉花秸秆隔离层对滨海滩涂土壤及绿化植物的影响[J]. 林业科学,2009,45(1):31 − 35. [CUI Xinhong,ZHU Yi,ZHANG Qun,et al. Effect of cotton stalk isolator layer in soil on garden plants and soil characters of coastal saline soils[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae,2009,45(1):31 − 35. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7488.2009.01.007
CUI Xinhong, ZHU Yi, ZHANG Qun, et al. Effect of cotton stalk isolator layer in soil on garden plants and soil characters of coastal saline soils[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2009, 45(1): 31 − 35. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7488.2009.01.007
[116] WANG Peijun,LIN Xiaolan,LIU Qi,et al. Interactions between flue gas desulfurization gypsum and biochar on water infiltration characteristics and physicochemical properties of saline-alkaline soil[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment,2023,195(11):1273. doi: 10.1007/s10661-023-11894-3
[117] 李高洋,黄永相,吴伟健,等. 海水稻根际效应对滨海盐碱地土壤氨氧化微生物的影响[J]. 土壤学报,2023,60(2):587 − 598. [LI Gaoyang,HUANG Yongxiang,WU Weijian,et al. Effects of seawater rice rhizosphere effect on soil ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in coastal saline-alkali soil[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica,2023,60(2):587 − 598. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Gaoyang, HUANG Yongxiang, WU Weijian, et al. Effects of seawater rice rhizosphere effect on soil ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in coastal saline-alkali soil[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2023, 60(2): 587 − 598. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[118] 邓晓,武春媛,杨桂生,等. 椰壳生物炭对海南滨海土壤的改良效果[J]. 生态环境学报,2022,31(4):723 − 731. [DENG Xiao,WU Chunyuan,YANG Guisheng,et al. Improvement effect of coconut-shell biochar on coastal soil in Hainan[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences,2022,31(4):723 − 731. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
DENG Xiao, WU Chunyuan, YANG Guisheng, et al. Improvement effect of coconut-shell biochar on coastal soil in Hainan[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2022, 31(4): 723 − 731. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[119] 陆宝金,田生昌,左忠,等. 盐渍化土地可持续利用研究综述及展望[J]. 宁夏大学学报(自然科学版),2023,44(1):79 − 88. [LU Baojin,TIAN Shengchang,ZUO Zhong, et al. Review and prospect on sustainableutilization of salinized land[J]. Journal of NingxiaUniversity(Natural Science Edition),2023,44(1):79 − 88. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LU Baojin, TIAN Shengchang, ZUO Zhong, et al. Review and prospect on sustainableutilization of salinized land[J]. Journal of NingxiaUniversity(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 44(1): 79 − 88. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[120] WICKE B,SMEETS E,DORNBURG V,et al. The global technical and economic potential of bioenergy from salt-affected soils[J]. Energy & Environmental Science,2011,4(8):2669 − 2681.
-



 下载:
下载: