Radiocarbon dating of Quaternary groundwater in the North China Plain and its implication to 14C correction
-
摘要:
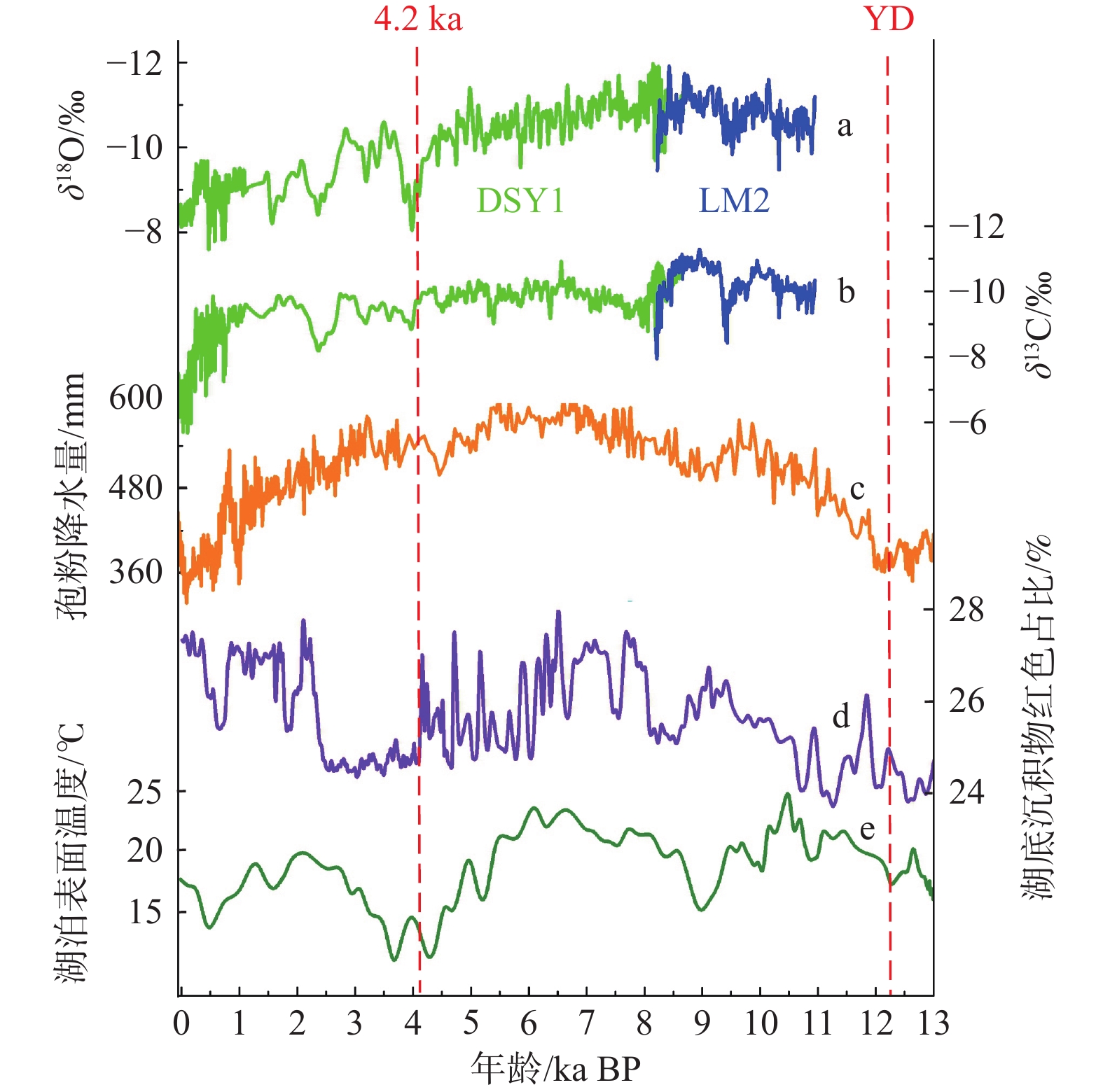
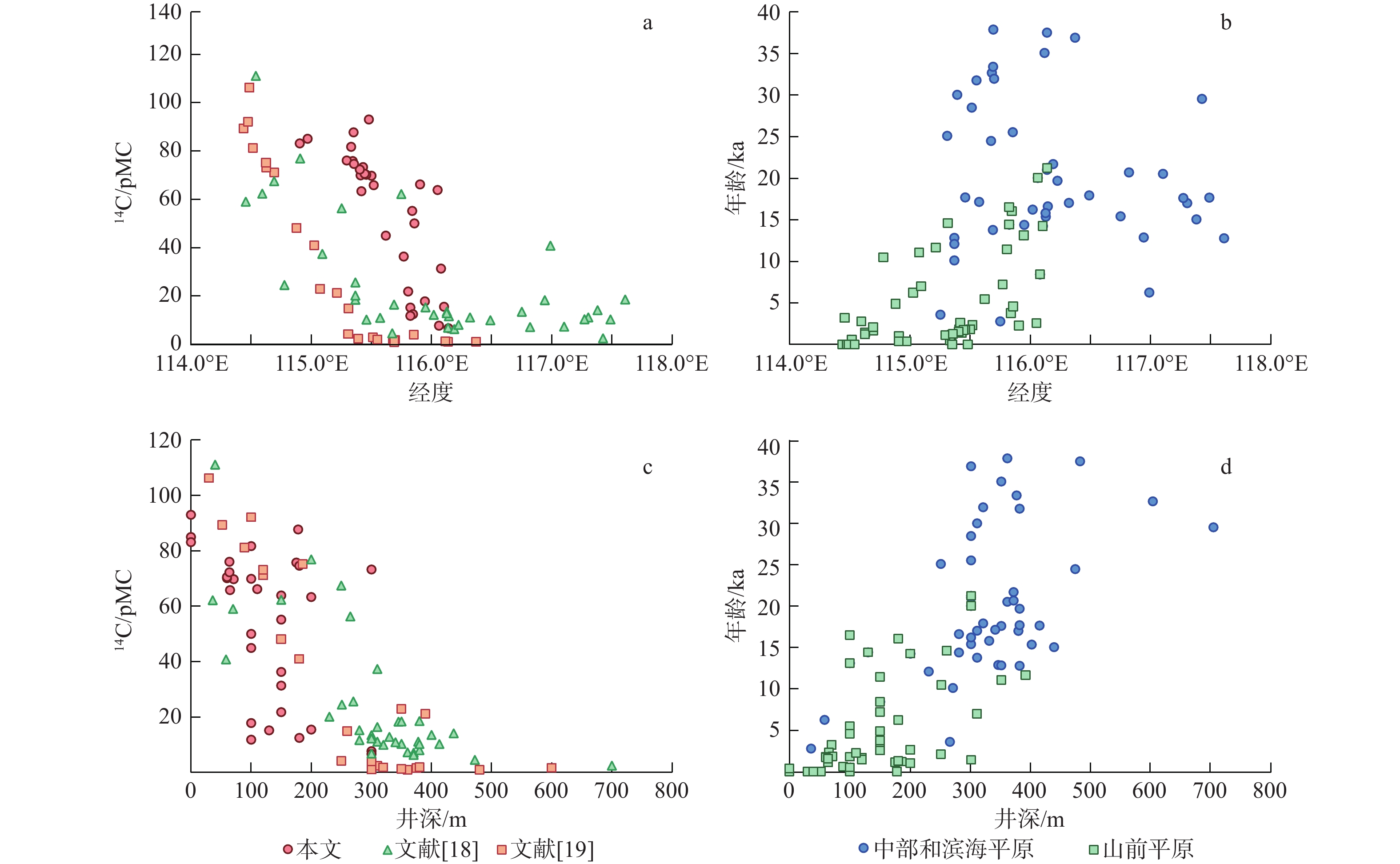
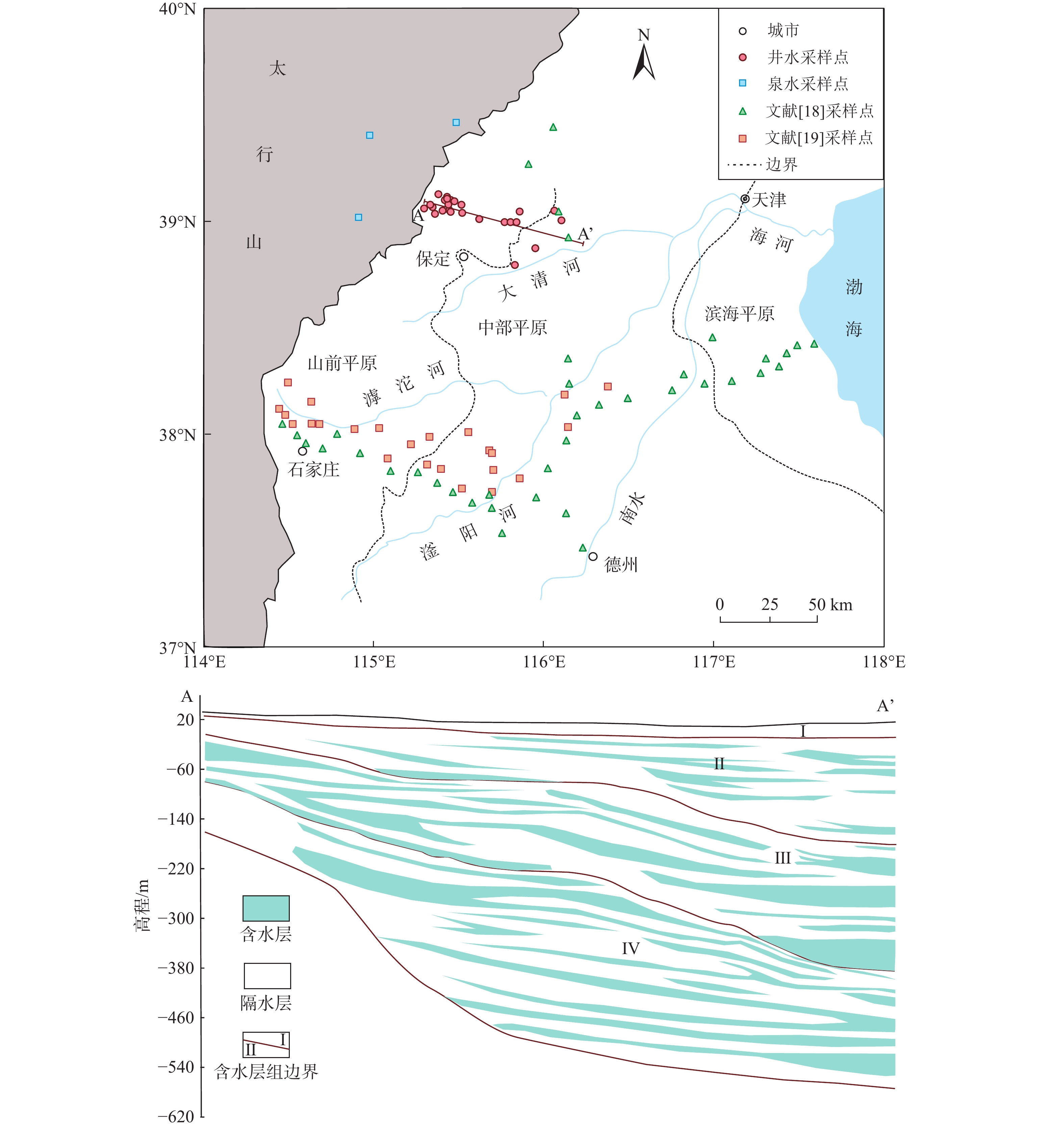
14C是确定地下水年龄的常用方法,但受14C定年模型中的初始14C含量不确定性及深部地球化学过程影响,地下水14C年龄仍存在较大争议。为确定华北平原第四系冷水14C年龄,在雄安新区及周边区域补充了27组地下水14C数据,结合前人在华北平原的文献数据65组,通过分析研究区水化学演化规律及构建地下含水层参数模型,确定了华北平原地下水14C校正模型的初始值,并尝试性提出了一种评估地下水14C年龄准确性的方法。结果表明:(1)研究区地下水14C校正模型的初始值是87.0 pMC,含水层死碳溶解可基本忽略;(2)地下水氧同位素变化通过4.2 ka的气候异常事件和新仙女木事件分割成三阶段;(3)华北平原第四系地下水14C含量沿地下水流向逐渐降低,中部和滨海平原地下水14C定年结果和4He/81Kr定年结果在300 m深度存在巨大差异,指示着14C定年方法极限的到来。以4.2 ka的气候异常事件和新仙女木事件作为拐点的地下水氧同位素变化是一种有效评估地下水14C年龄准确性的方法,但在深层含水层中建议慎重使用14C定年方法。
Abstract:14C is commonly used in groundwater dating. Due to the uncertainty of the initial 14C contents (A0) and the complex geochemical processes in the subsurface, the 14C ages were corrected but remain largely uncertain. To determine the groundwater age for the Quaternary aquifer in the North China Plain, 27 new 14C samples were collected from the Xiongan Area and its surroundings. Combined with 65 14C samples from published references, the initial 14C content (A0) was determined after analyzing the hydrochemical evolution and constructing a parameter model of the aquifer. A feasible method was proposed to evaluate the accuracy of 14C ages. The initial 14C content was expected to be 87.0 pMC, with the dissolution of dead carbon being neglected in the aquifer. Oxygen isotope in groundwater can be divided into three stages by two climatic anomalous of 4.2 ka and Younger Dryas (YD, approximately 12 ka). There is a significant divergence between 14C dating results and 4He/81Kr ages at the well depth of 300 m in the central and coastal plain, which indicates the arrival of the 14C dating limit. Therefore, the 14C ages can be evaluated by oxygen isotope in groundwater divided by two climatic anomalous of 4.2 ka and Younger Dryas. The 14C method should be used with caution in the deep aquifer.
-
Key words:
- 14C ages correction /
- groundwater /
- the North China Plain /
- climate anomalies /
- 4.2 ka /
- YD
-

-
表 1 华北平原地下水样品化学和同位素数据表
Table 1. Major ions and isotopic compositions of groundwater samples in the North China Plain
井号 井深/m 经度/
°E纬度/
°N14C/
pMCδ13C/
‰δ18O/
‰δD/
‰质量浓度(ρ)/ (mg·L−1) ρ(Sr)
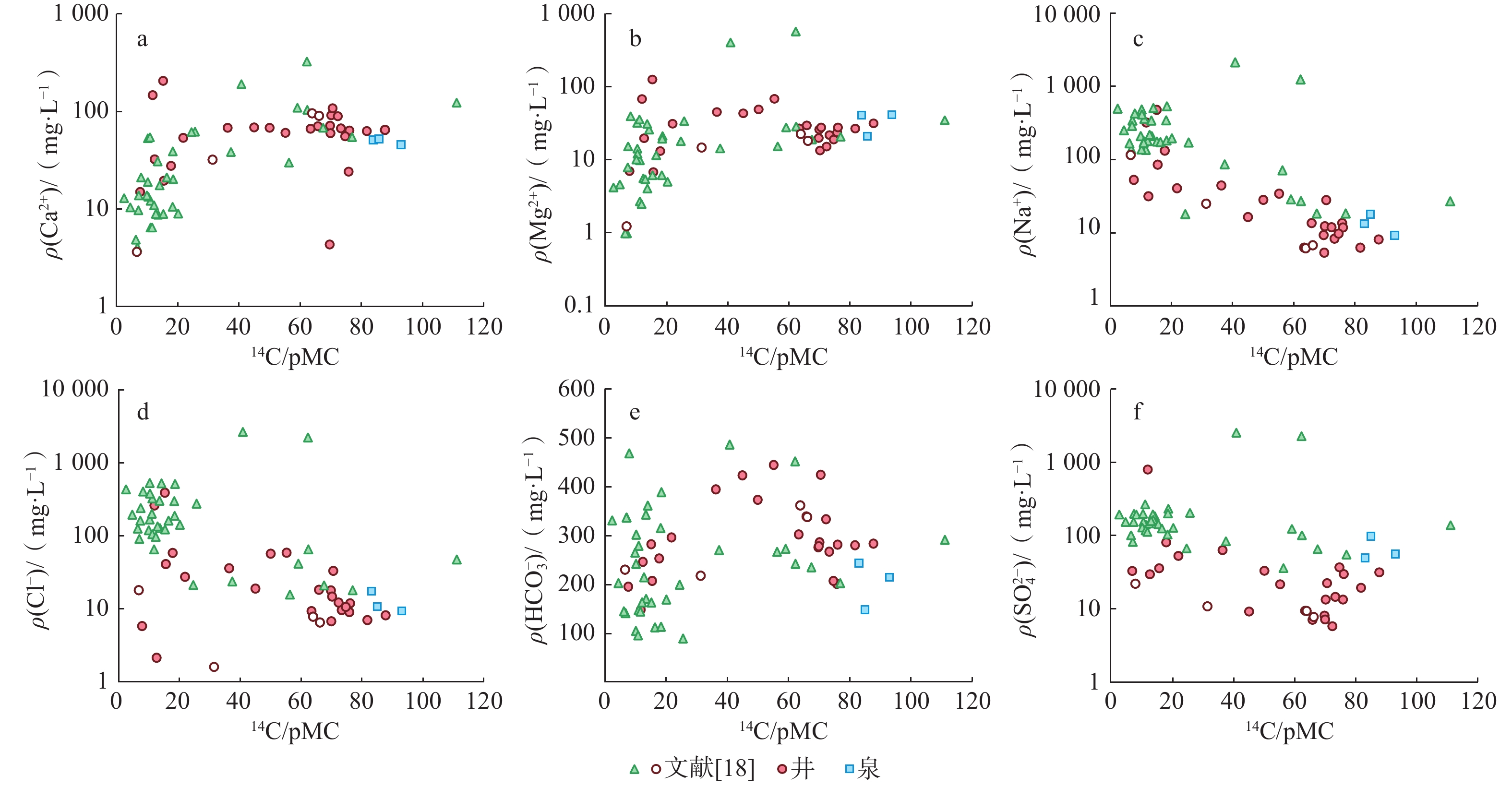
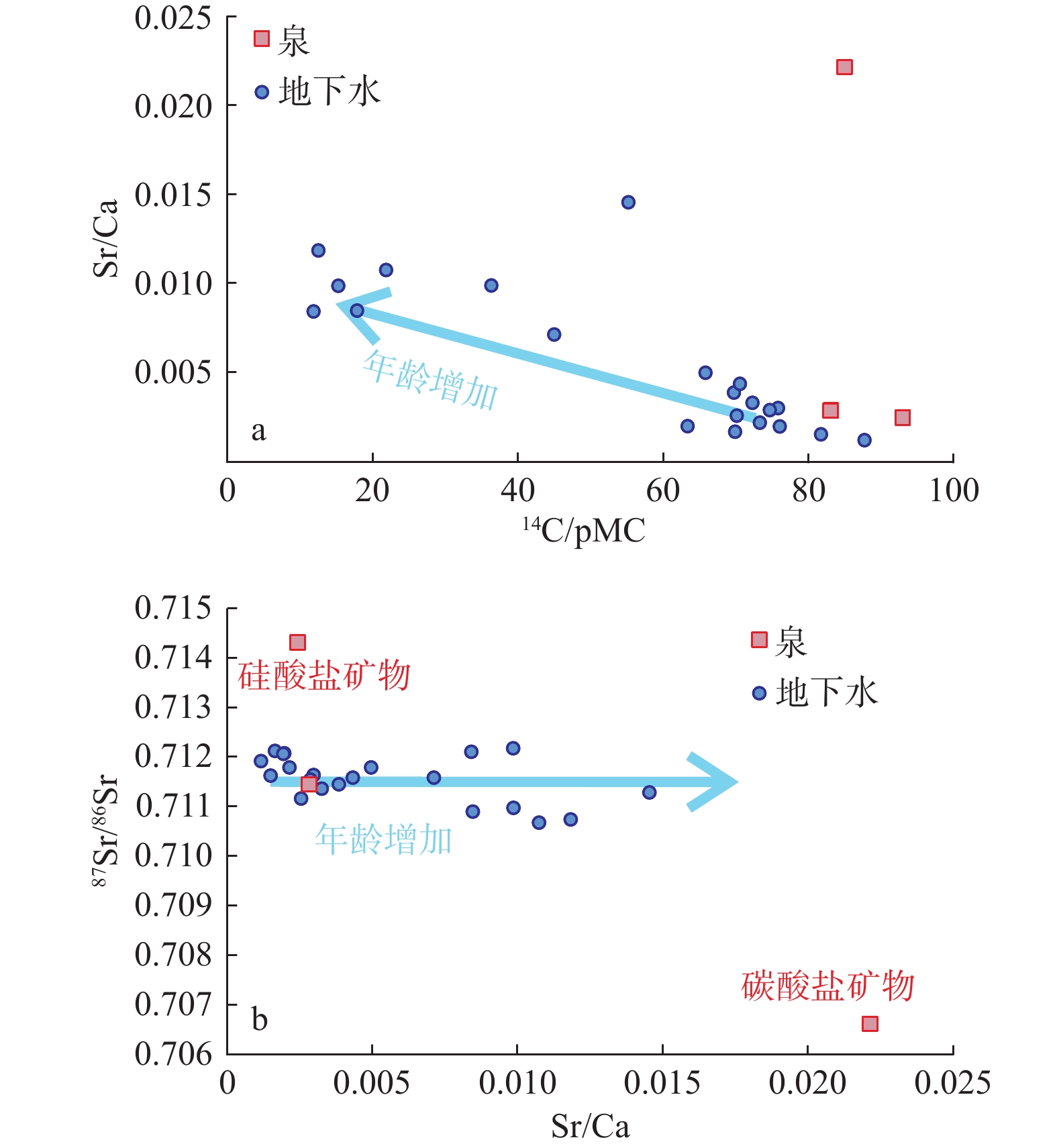
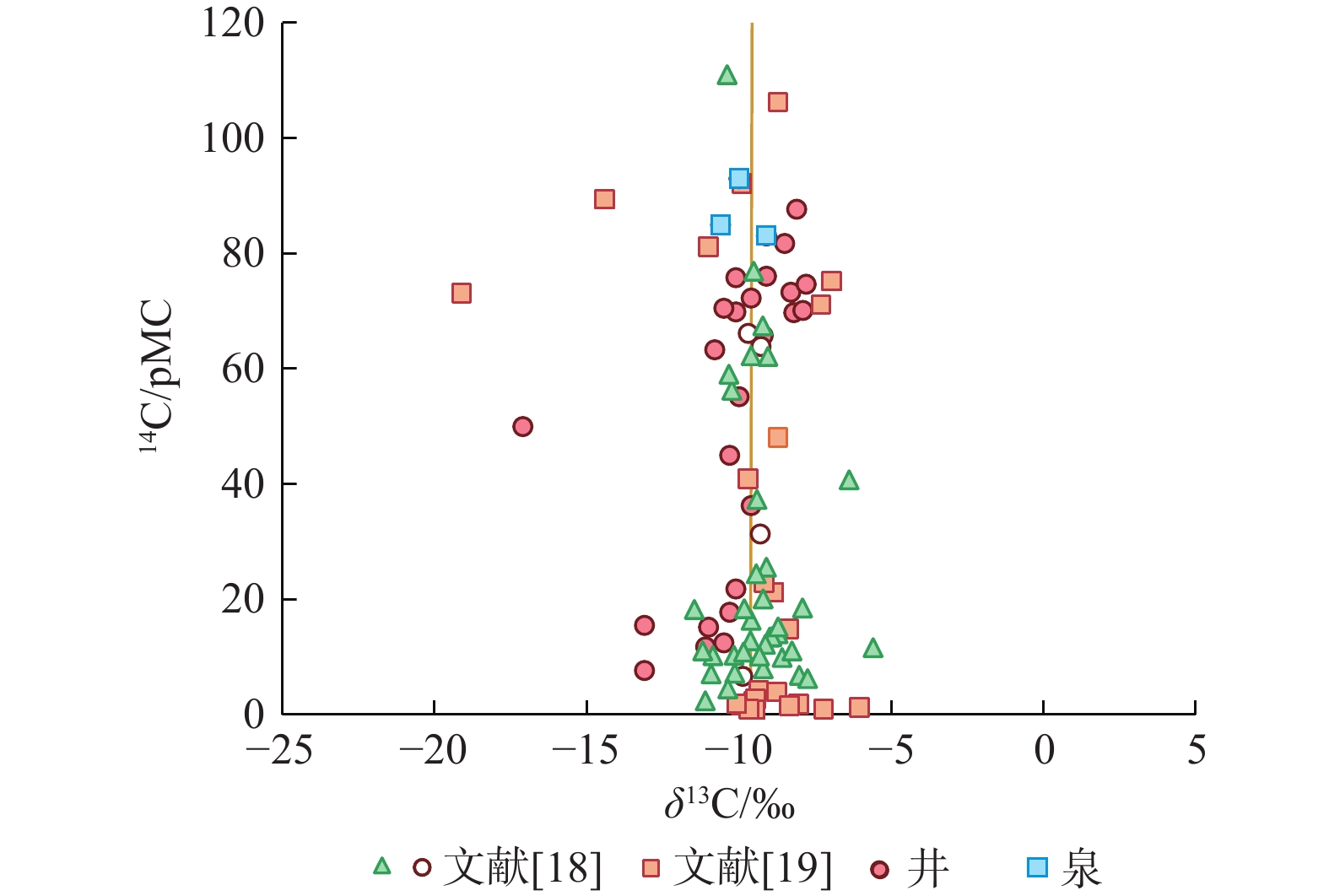
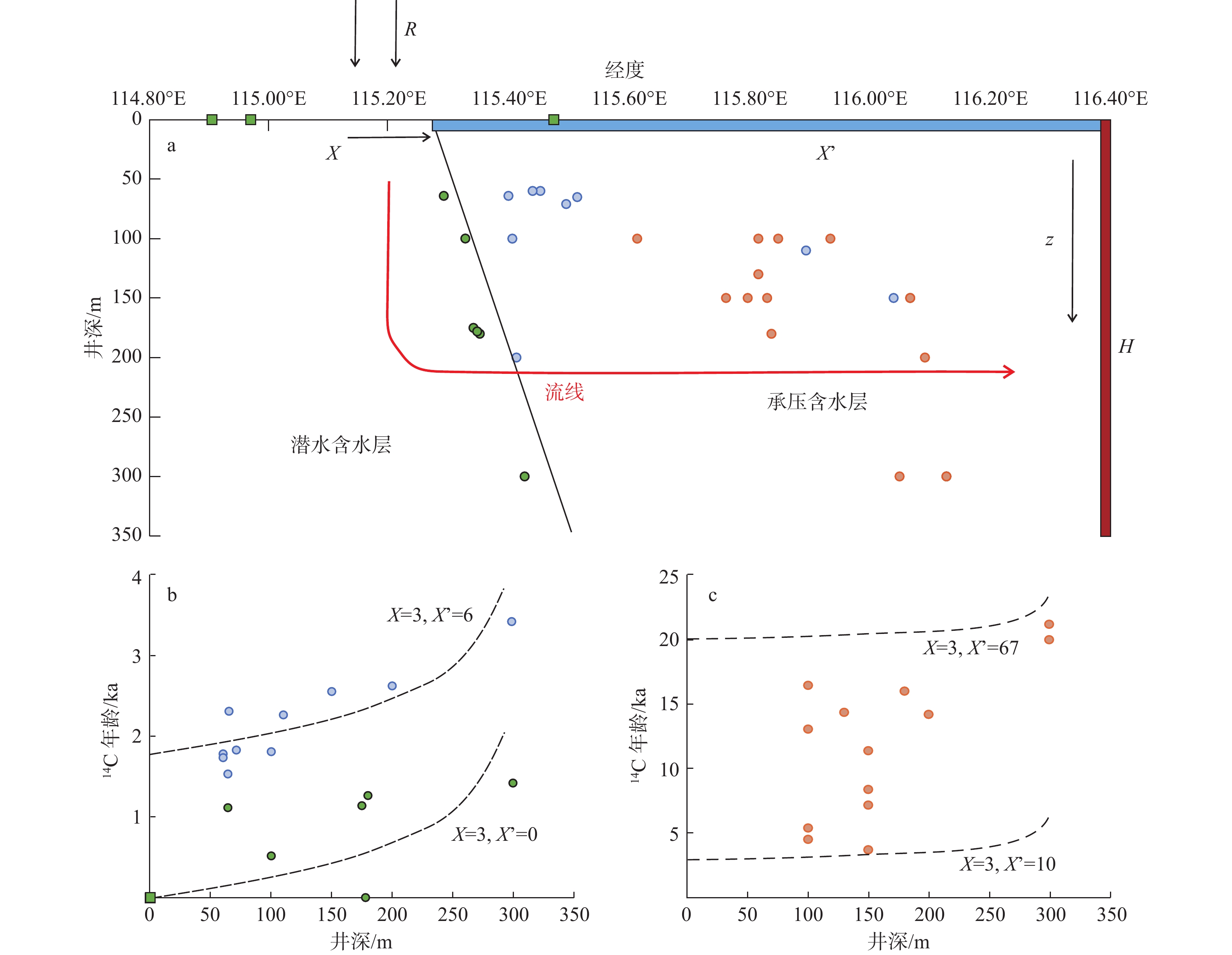
/ (μg·L−1)87Sr/86Sr Ca2+ Mg2+ Na+ K+ ${\mathrm{HCO}}_3^- $ ${\mathrm{CO}}_3^{2-}$ Cl− ${\mathrm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 1 130 115.824 38.796 15.2 −11.0 −10.9 −81.2 206.0 126.0 481.0 2.3 281.0 0 390.0 — 2026.0 0.7122 2 150 115.839 38.996 55.2 −10.0 −9.0 −65.5 60.5 68.7 34.4 0.5 443.0 0 58.6 21.5 879.0 0.7113 3 150 115.806 38.985 21.8 −10.1 −9.9 −70.9 53.7 31.3 40.8 1.8 295.0 0 27.4 52.6 576.0 0.7107 4 150 115.769 38.995 36.3 −9.6 −9.7 −70.0 68.0 45.3 44.7 1.3 393.0 0 35.9 63.1 670.0 0.7110 5 180 115.846 39.006 12.5 −10.5 −9.8 −69.9 32.4 19.8 31.8 1.9 245.0 0 2.1 29.5 383.0 0.7107 6 100 115.620 39.010 45.0 −10.3 −9.3 −65.8 68.8 43.3 16.5 1.1 422.0 0 18.9 9.1 489.0 0.7116 7 65 115.519 39.040 65.8 −9.2 −8.9 −64.5 70.5 29.7 13.7 0.9 338.0 0 18.3 7.0 349.0 0.7118 8 71 115.500 39.066 69.7 −8.2 −8.6 −62.2 71.6 19.9 9.4 0.8 275.0 0 17.9 8.0 275.0 0.7114 9 60 115.457 39.086 70.1 −7.9 −8.8 −63.3 91.6 13.4 12.4 0.3 285.0 0 14.7 13.3 233.0 0.7112 10 300 115.431 39.106 73.3 −8.3 −8.9 −63.7 67.1 21.8 8.4 0.3 266.0 0 9.6 14.5 144.0 0.7118 11 100 115.410 39.105 69.9 −10.1 −9.2 −64.8 59.9 26.0 5.4 0.5 277.0 0 6.8 7.1 98.2 0.7121 12 200 115.417 39.099 63.3 −10.8 −9.1 −65.2 66.4 27.0 6.3 0.6 301.0 0 9.3 9.4 130.0 0.7121 13 175 115.344 39.067 75.8 −10.1 −8.8 −63.4 24.2 23.7 13.7 31.8 200.0 10.4 9.0 13.3 72.0 0.7116 14 100 115.331 39.062 81.7 −8.5 −8.8 −63.3 63.0 26.8 6.3 0.4 279.0 0 7.0 19.3 94.1 0.7116 15 64 115.295 39.059 76.0 −9.1 −8.1 −59.2 63.8 27.8 11.9 1.0 280.0 0 11.9 29.7 123.0 0.7121 16 60 115.444 39.051 70.5 −10.5 −9.0 −64.1 108.0 27.7 28.2 0.4 423.0 0 33.1 22.3 467.0 0.7116 17 64 115.403 39.049 72.3 −9.6 −8.9 −64.8 89.4 15.2 12.0 0.4 332.0 0 12.2 5.8 291.0 0.7114 18 180 115.355 39.058 74.7 −7.8 −7.9 −55.0 55.6 19.0 9.8 0.6 206.0 0 10.6 36.9 159.0 0.7115 19 178 115.351 39.098 87.7 −8.1 −8.8 −62.3 64.7 31.6 8.2 0.5 282.0 0 8.2 31.4 75.3 0.7119 20 泉 115.480 39.468 93.0 −10.0 −8.4 −60.5 45.5 41.5 9.3 1.2 213.0 7.8 9.4 55.7 110.0 0.7143 21 泉 114.970 39.407 85.0 −10.6 −8.9 −65.7 52.2 21.0 17.9 1.6 147.0 6.9 10.7 97.4 1155.0 0.7066 22 泉 114.905 39.017 83.1 −9.1 −9.2 −67.2 51.1 41.0 13.4 2.0 242.0 8.9 17.4 49.2 144.0 0.7114 23 100 115.824 38.797 11.8 −11.1 −10.9 −83.0 147.0 68.3 323.0 1.9 147.0 15.9 261.0 799.0 1234.0 0.7121 24 100 115.945 38.874 17.8 −10.3 −9.5 −73.4 27.7 13.2 133.0 0.9 252.0 14.8 58.3 80.8 234.0 0.7109 25 100 115.857 39.046 50.0 −17.1 −8.5 −62.4 68.1 49.2 28.3 1.6 372.0 29.1 57.1 33.0 703.0 — 26 200 116.104 39.004 15.5 −13.1 −11.1 −82.7 19.5 6.8 85.9 0.6 206.0 0 41.0 35.6 318.0 — 27 300 116.061 39.048 7.7 −13.1 −11.3 −82.4 15.0 7.0 53.2 1.0 194.0 0 5.8 21.9 282.0 — -
[1] DE GRAAF I E M,GLEESON T,RENS VAN BEEK L P H,et al. Environmental flow limits to global groundwater pumping[J]. Nature,2019,574:90 − 94. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1594-4
[2] 林学钰. “地下水科学与工程”学科形成的历史沿革及其发展前景[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2007,37(2):209 − 215. [LIN Xueyu. Historical change and prospect of discipline development of “groundwater science and engineering”[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition),2007,37(2):209 − 215. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIN Xueyu. Historical change and prospect of discipline development of “groundwater science and engineering”[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 2007, 37(2): 209 − 215. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 中国科学院. 中国学科发展战略-地下水科学[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2018. [Chinese Academy of Sciences. China’s discipline development strategy-groundwater science[M]. Beijing:Science Press,2018. (in Chinese)]
Chinese Academy of Sciences. China’s discipline development strategy-groundwater science[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2018. (in Chinese)
[4] 汪集旸,陈建生,陆宝宏,等. 同位素水文学的若干回顾与展望[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版),2015,43(5):406 − 413. [WANG Jiyang,CHEN Jiansheng,LU Baohong,et al. Review and prospect of isotope hydrology[J]. Journal of Hohai University(Natural Sciences),2015,43(5):406 − 413. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3876/j.issn.1000-1980.2015.05.004
WANG Jiyang, CHEN Jiansheng, LU Baohong, et al. Review and prospect of isotope hydrology[J]. Journal of Hohai University(Natural Sciences), 2015, 43(5): 406 − 413. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3876/j.issn.1000-1980.2015.05.004
[5] KAZEMI G A,LEHR J H,PERROCHET P. Groundwater age[M]. Hoboken, N J:John Wiley & Sons,Inc,2006.
[6] HAN Liangfeng,PLUMMER L N,AGGARWAL P. A graphical method to evaluate predominant geochemical processes occurring in groundwater systems for radiocarbon dating[J]. Chemical Geology,2012,318/319:88 − 112. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.05.004
[7] LI Jie,PANG Zhonghe,FROEHLICH K,et al. Paleo-environment from isotopes and hydrochemistry of groundwater in East Junggar Basin,Northwest China[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2015,529:650 − 661.
[8] 顾慰祖. 同位素水文学[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2011. [GU Weizu. Isotope hydrology[M]. Beijing:Science Press,2011. (in Chinese)]
GU Weizu. Isotope hydrology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2011. (in Chinese)
[9] HAN Liangfeng,PLUMMER L N. A review of single-sample-based models and other approaches for radiocarbon dating of dissolved inorganic Carbon in groundwater[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2016,152:119 − 142. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.11.004
[10] CARTWRIGHT I,CURRELL M J,CENDÓN D I,et al. A review of the use of radiocarbon to estimate groundwater residence times in semi-arid and arid areas[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2020,580:124247. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124247
[11] 刘存富. 地下水14C年龄校正方法——以河北平原为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,1990,17(5):4 − 8. [LIU Cunfu. Correction methods of 14C ages of groundwater:With the Hebei Plain as example[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,1990,17(5):4 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Cunfu. Correction methods of 14C ages of groundwater: With the Hebei Plain as example[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 1990, 17(5): 4 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 陈茜茜,陈建生,王婷. 我国北方地下水年龄测定问题讨论[J]. 水资源保护,2014,30(2):1 − 5. [CHEN Xixi,CHEN Jiansheng,WANG Ting. A discussion of groundwater dating in northern China[J]. Water Resources Protection,2014,30(2):1 − 5. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHEN Xixi, CHEN Jiansheng, WANG Ting. A discussion of groundwater dating in northern China[J]. Water Resources Protection, 2014, 30(2): 1 − 5. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] WANG Tao,CHEN Jiansheng,ZHANG Chenming,et al. 14C‐dating model for groundwater affected by CO2 inputs from deep underground formations[J]. Water Resources Research,2020,56(3):e2019WR025155. doi: 10.1029/2019WR025155
[14] HUANG Tianming,PANG Zhonghe,LIU Jilai,et al. Groundwater recharge mechanism in an integrated tableland of the Loess Plateau,northern China:Insights from environmental tracers[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2017,25(7):2049 − 2065. doi: 10.1007/s10040-017-1599-8
[15] LI Zhenbin,HUANG Tianming,WANG Gang,et al. A conceptual model for correcting groundwater 14C age[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2022,143:105360. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2022.105360
[16] 李文鹏,王龙凤,杨会峰,等. 华北平原地下水超采状况与治理对策建议[J]. 中国水利,2020(13):26 − 30. [LI Wenpeng,WANG Longfeng,YANG Huifeng,et al. The groundwater overexploitation status and countermeasure suggestions of the North China Plain[J]. China Water Resources,2020(13):26 − 30. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1123.2020.13.017
LI Wenpeng, WANG Longfeng, YANG Huifeng, et al. The groundwater overexploitation status and countermeasure suggestions of the North China Plain[J]. China Water Resources, 2020(13): 26 − 30. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1123.2020.13.017
[17] 张之淦,张洪平,孙继朝,等. 河北平原第四系地下水年龄,水流系统及咸水成因初探——石家庄至渤海湾同位素水文地质剖面研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,1987,14(4):1 − 6. [ZHANG Zhigan,ZHANG Hongping,SUN Jichao,et al. Environmental isotope study related to groundwater age,flow system and saline water origin in Quaternary aquifer of Hebei Plain[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,1987,14(4):1 − 6. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Zhigan, ZHANG Hongping, SUN Jichao, et al. Environmental isotope study related to groundwater age, flow system and saline water origin in Quaternary aquifer of Hebei Plain[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 1987,14(4): 1 − 6. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] CHEN Zongyu,QI Jixiang,XU Jianming,et al. Paleoclimatic interpretation of the past 30 ka from isotopic studies of the deep confined aquifer of the North China plain[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2003,18(7):997 − 1009. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(02)00206-8
[19] KREUZER A M,VON ROHDEN C,FRIEDRICH R,et al. A record of temperature and monsoon intensity over the past 40 kyr from groundwater in the North China Plain[J]. Chemical Geology,2009,259(3/4):168 − 180.
[20] MATSUMOTO T,CHEN Zongyu,WEI Wen,et al. Application of combined 81Kr and 4He chronometers to the dating of old groundwater in a tectonically active region of the North China Plain[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2018,493:208 − 217. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2018.04.042
[21] WEI Wen,AESCHBACH-HERTIG W,CHEN Zongyu. Identification of he sources and estimation of he ages in groundwater of the North China Plain[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2015,63:182 − 189. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2015.08.010
[22] 刘存富,王佩仪,周炼,等. 河北平原第四系地下水36Cl年龄研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,1993,20(6):35 − 38. [LIU Cunfu,WANG Peiyi,ZHOU Lian,et al. Study on the 36Cl age of Quaternary groundwater in Hebei Plain[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,1993,20(6):35 − 38. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Cunfu, WANG Peiyi, ZHOU Lian, et al. Study on the 36Cl age of Quaternary groundwater in Hebei Plain[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 1993, 20(6): 35 − 38. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 张宗祜. 华北平原地下水环境演化[M]. 北京:地质出版社,2000. [ZHANG Zonghu. Evolution of groundwater environment in the North China Plain[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House,2000. (in Chinese)]
ZHANG Zonghu. Evolution of groundwater environment in the North China Plain[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2000. (in Chinese)
[24] VEIZER J,ALA D,AZMY K,et al. 87Sr/86Sr,δ13C and δ18O evolution of Phanerozoic seawater[J]. Chemical Geology,1999,161(1/2/3):59 − 88.
[25] 叶萍,金勤胜,周爱国,等. 河北平原地下水锶同位素形成机理[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报),2008,33(1):137 − 144. [YE Ping,JIN Qinsheng,ZHOU Aiguo,et al. Formation mechanism of Sr isotopes in groundwater of Hebei plain[J]. Earth Science,2008,33(1):137 − 144. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2008.019
YE Ping, JIN Qinsheng, ZHOU Aiguo, et al. Formation mechanism of Sr isotopes in groundwater of Hebei plain[J]. Earth Science, 2008, 33(1): 137 − 144. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2008.019
[26] LIN Dan,JIN Menggui,LIANG Xing,et al. Estimating groundwater recharge beneath irrigated farmland using environmental tracers fluoride,chloride and sulfate[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2013,21(7):1469 − 1480. doi: 10.1007/s10040-013-1015-y
[27] EDMUNDS W M,MA Jinzhu,AESCHBACH-HERTIG W,et al. Groundwater recharge history and hydrogeochemical evolution in the Minqin Basin,North West China[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2006,21(12):2148 − 2170. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2006.07.016
[28] AESCHBACH-HERTIG W,STUTE M,CLARK J F,et al. A paleotemperature record derived from dissolved noble gases in groundwater of the Aquia Aquifer (Maryland,USA)[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2002,66(5):797 − 817. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(01)00804-3
[29] STUTE M,CLARK J F,SCHLOSSER P,et al. A 30,000 yr continental paleotemperature record derived from noble gases dissolved in groundwater from the San Juan Basin,new Mexico[J]. Quaternary Research,1995,43(2):209 − 220. doi: 10.1006/qres.1995.1021
[30] ZHANG Na,YANG Yan,CHENG Hai,et al. Timing and duration of the East Asian summer monsoon maximum during the Holocene based on stalagmite data from North China[J]. The Holocene,2018,28(10):1631 − 1641. doi: 10.1177/0959683618782606
[31] CHEN Fahu,XU Qinghai,CHEN Jianhui,et al. East Asian summer monsoon precipitation variability since the last deglaciation[J]. Scientific Reports,2015,5:11186. doi: 10.1038/srep11186
[32] JI Junfeng,SHEN Ji,BALSAM W,et al. Asian monsoon oscillations in the northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau since the late glacial as interpreted from visible reflectance of Qinghai Lake sediments[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2005,233(1/2):61 − 70.
[33] HOU Juzhi,HUANG Yongsong,ZHAO Jiangtao,et al. Large Holocene summer temperature oscillations and impact on the peopling of the northeastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2016,43(3):1323 − 1330. doi: 10.1002/2015GL067317
[34] CHENG Zhongshuang,ZHANG Yongbo,SU Chen,et al. Chemical and isotopic response to intensive groundwater abstraction and its implications on aquifer sustainability in Shijiazhuang,China[J]. Journal of Earth Science,2017,28(3):523 − 534. doi: 10.1007/s12583-017-0729-5
[35] ZHANG Jun,WANG Xusheng,YIN Lihe,et al. Inflection points on groundwater age and geochemical profiles along wellbores light up hierarchically nested flow systems[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2021,48(16):e2020GL092337. doi: 10.1029/2020GL092337
[36] AGGARWAL P K,MATSUMOTO T,STURCHIO N C,et al. Continental degassing of 4He by surficial discharge of deep groundwater[J]. Nature Geoscience,2015,8(1):35 − 39. doi: 10.1038/ngeo2302
[37] YOKOCHI R,BERNIER R,PURTSCHERT R,et al. Field degassing as a new sampling method for 14C analyses in old groundwater[J]. Radiocarbon,2018,60(1):349 − 366. doi: 10.1017/RDC.2017.64
-



 下载:
下载: