Analysis of Yuqiupo landslide motion process based on PFC3D
-
摘要:
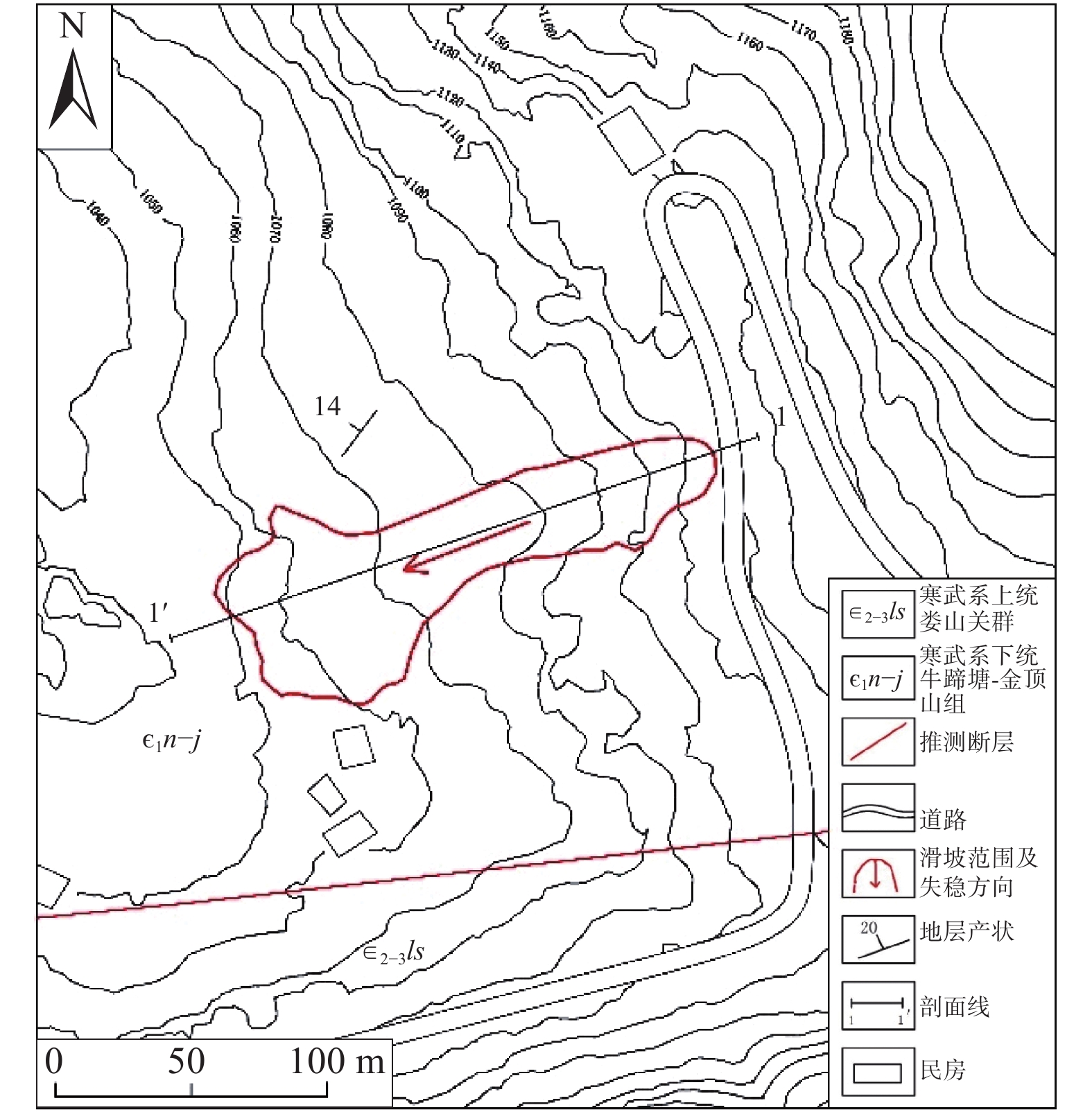
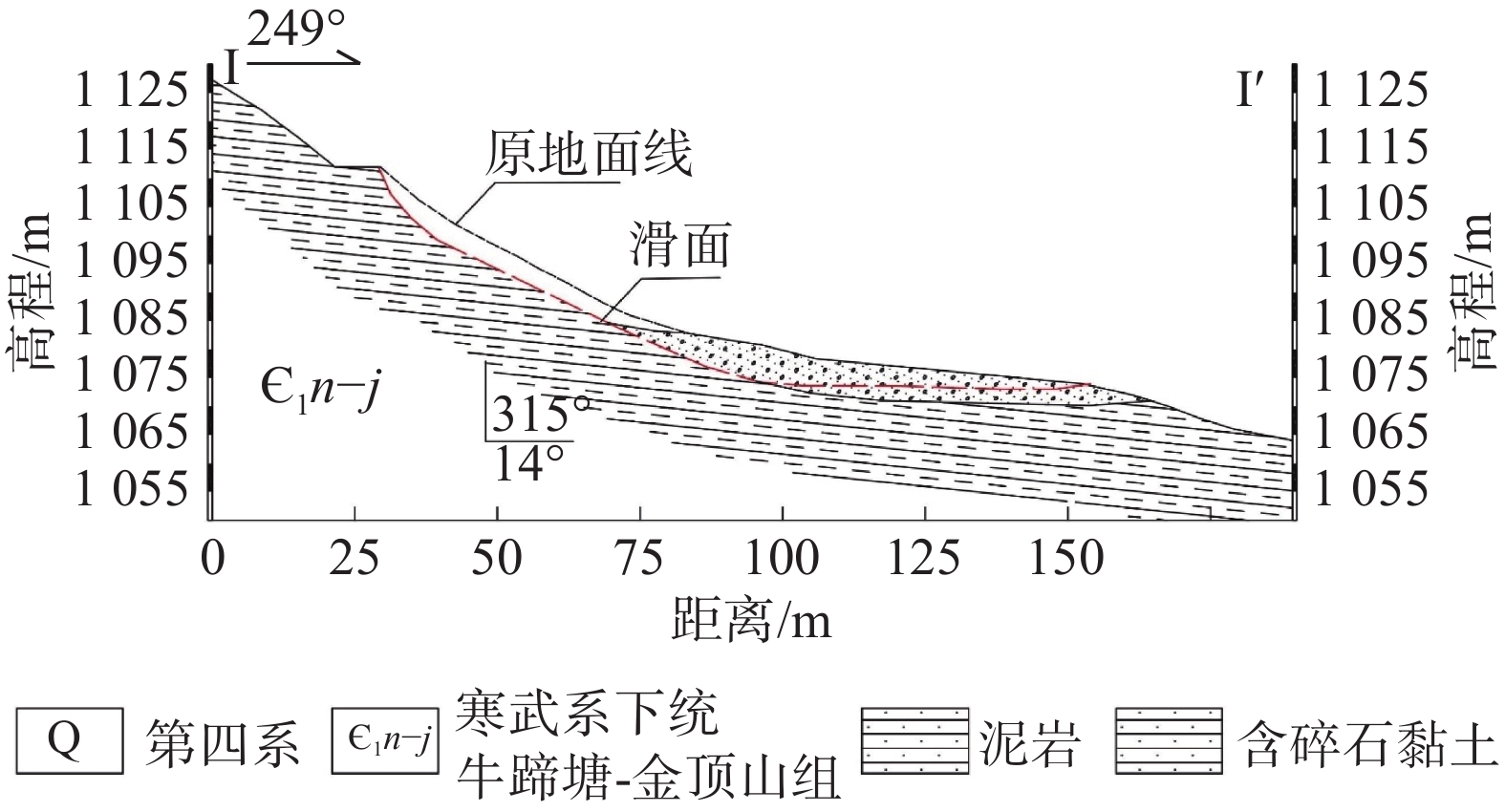
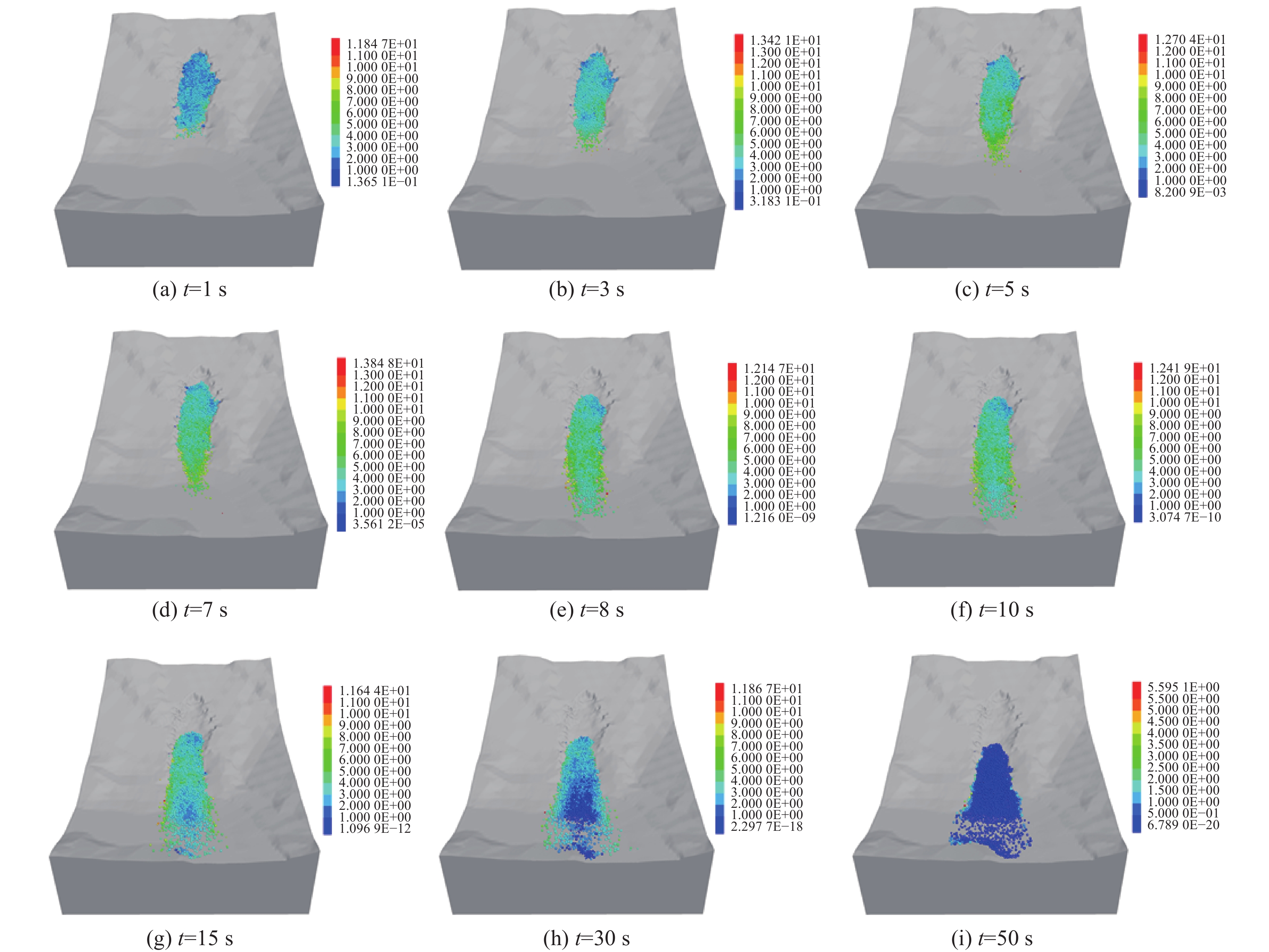
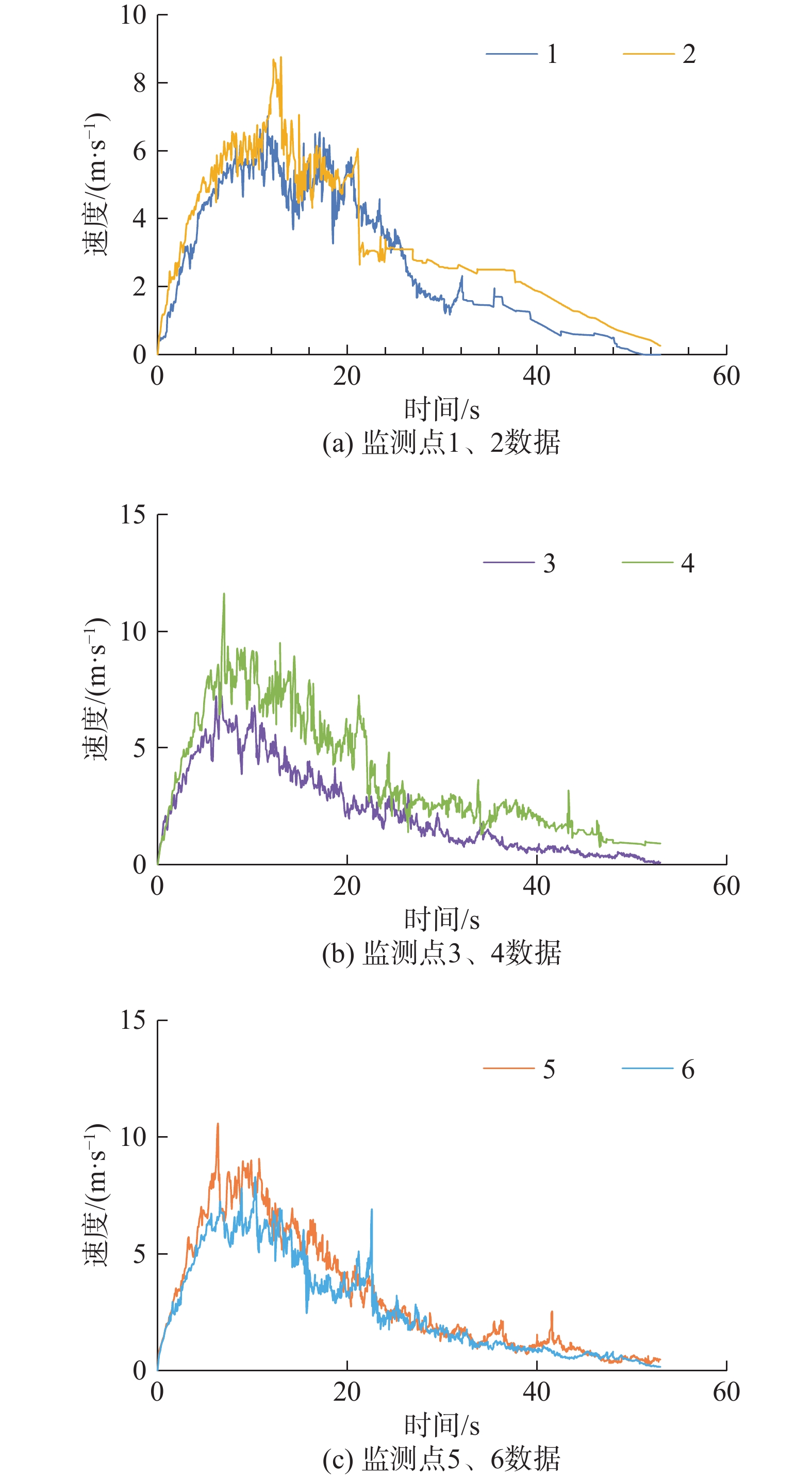
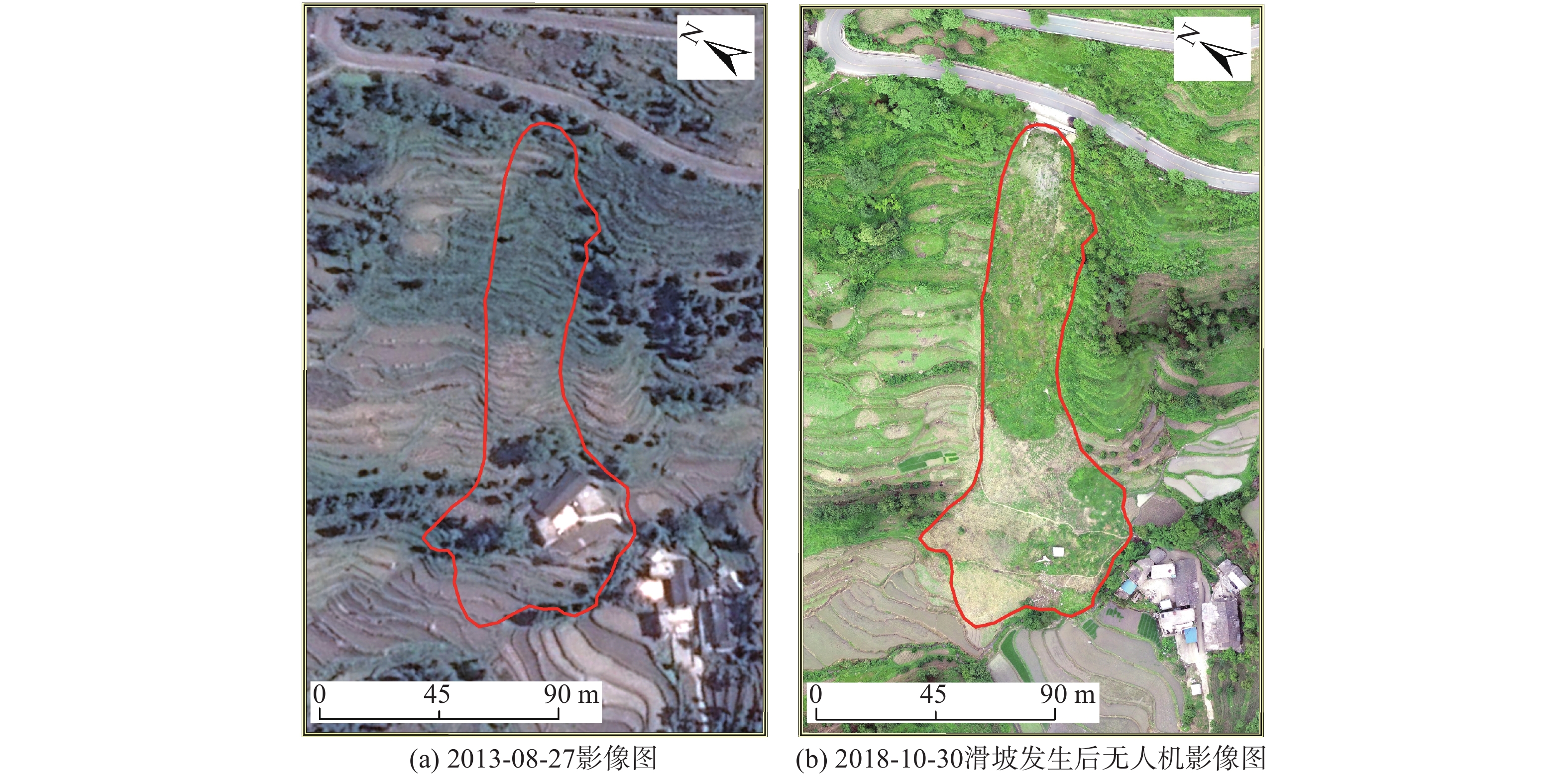
以贵州省开阳县鱼鳅坡滑坡为研究对象,采用颗粒流离散元(PFC3D)对其破坏运动过程进行数值模拟。采用Ball-Wall建模方法建立滑坡模型,对滑坡不同关键部位颗粒进行位移、速度监测,阐明其破坏运动特征。结果表明,降雨为鱼鳅坡滑坡的直接诱发因素。该滑坡在破坏初始阶段以蠕滑变形为主,随着变形量的增加,滑坡体不断挤压坡脚,滑坡岩土体到达应力平衡极限,坡脚产生剪切破坏,并向上牵引发展,滑坡发生整体滑动,斜坡变形破坏模式为蠕滑-拉裂,按照力学条件为牵引式破坏。滑坡滑动最高时速12.4 m/s,最大滑移80 m,滑动阶段持续50 s。研究成果可为对该类滑坡影响范围预测,以及工程措施的制定具有一定的参考意义。
Abstract:A case study of the Yuqiupo landslide in Kaiyang County, Guizhou Province, the particle flow discrete element (PFC3D) was used to simulate the failure process of the landslide. The landslide model was built through the Ball-Wall method, and the characteristics of their destructive movement was described through the monitoring of the displacement and velocity of the particles at different key parts of the landslide. The results show that the rainfall is the direct inducing factor of the Yuqiupo landslide. In the initial stage of failure, the landslide is mainly creep deformation. The landslide continuously squeezes the slope toe with the increase of the deformation. The landslide rock-soil mass reaches the stress equilibrium limit, leading to shear failure at the slope foot, and the landslide happens with upward traction development, the failure mode is creep-crack, and it is traction failure according to the mechanical conditions. The maximum sliding speed of the landslide is 12.4 m/s, the maximum sliding slip is 80 m, and the sliding stage lasts for 50 s. The results have a good applicability to simulate the process of landslide destruction, which can provide a reference for engineering construction.
-
Key words:
- landslide /
- motion process /
- grain flow /
- the numerical simulation
-

-
表 1 滑坡岩土体颗粒细观参数
Table 1. Mesoscopic parameters of rock and soil particles in landslide
细观参数 碎石土 颗粒密度/(kg·m−3) 2000 颗粒半径/m 0.25~0.5 法向接触刚度/MPa 28 切向接触刚度/MPa 28 摩擦系数 0.3 法向黏结刚度/(MPa·m−1) 10 切向黏结刚度/(MPa·m−1) 10 黏结抗拉强度/MPa 0.1 黏结抗剪强度/MPa 0.75 -
[1] 郭振春. 贵州地质灾害的主要类型和诱因及其预防建议[J]. 贵州地质,2003,20(2):103 − 105. [GUO Zhenchun. Major types of geological hazards and predisposition in Guizhou and its preventive suggestion[J]. Guizhou Geology,2003,20(2):103 − 105. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2003.02.010
[2] 阳岳龙, 龙万学, 杨禹华, 等. 贵州省主要地质灾害危险度区划研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报,2008,18(5):5 − 10. [YANG Yuelong, LONG Wanxue, YANG Yuhua, et al. Study on risk region division of main geological hazards in Guizhou Province[J]. China Safety Science Journal (CSSJ)[J]. Chinese Journal of Safety Science,2008,18(5):5 − 10. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2008.05.001
[3] 彭小平, 陈开圣, 王成华, 等. 贵州省公路地质灾害基本特征及危险性分区[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2009,20(2):46 − 51. [PENG Xiaoping, CHEN Kaisheng, WANG Chenghua, et al. Basic characteristics and risk zoning of highway geological hazard in Guizhou Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological hazard and Control,2009,20(2):46 − 51. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2009.02.011
[4] 黄润秋. 20世纪以来中国的大型滑坡及其发生机制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2007,26(3):433 − 454. [HUANG Runqiu. Large scale landslides and their sliding mechanism in China since the 20th century[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2007,26(3):433 − 454. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.03.001
[5] 李世海, 刘天萍, 刘晓宇. 论滑坡稳定性分析方法[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2009,28(增刊2):3309 − 3324. [LI Shihai, LIU Tianping, LIU Xiaoyu. Analysis method for landslide stability[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2009,28(Sup2):3309 − 3324. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 赵洲, 魏江波. 基于颗粒流方法的滑坡破坏机理与强度分析[J]. 西安科技大学学报,2018,38(4):611 − 619. [ZHAO Zhou, WEI Jiangbo. Failure mechanism and strength analysis of landslide based on particle flow method[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Science and Technology,2018,38(4):611 − 619. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 吴剑. 滑带剪切过程的离散元模拟研究[D]. 武汉: 中国科学院研究生院(武汉岩土力学研究所), 2007.
WU Jian. Dem element simulation of shearing process of sliding zone[D]. Wuhan: Graduate School of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Wuhan Institute of Geotechnical Mechanics), 2007. (in Chinese)
[8] 张龙, 唐辉明, 熊承仁, 等. 鸡尾山高速远程滑坡运动过程PFC3D模拟[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2012,31(增刊1):2601 − 2611. [ZHANG Long, TANG Huiming, XIONG Chengren, et al. Movement process simulation of high-speed long-distance Jiweishan landslide with PFC3D[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2012,31(Sup1):2601 − 2611. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 施凤根. 基于PFC3D的文家沟滑坡高速远程运动学特征研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014.
SHI Fenggen. The study of rapid and long-runout characteristics of Wenjiagou landslide based on PFC3D[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 李冬冬. 文家沟滑坡碎屑流动力特性分析[D]. 郑州: 华北水利水电大学, 2016.
LI Dongdong. Dynamic characteristics analysis of the Wenjiagou rock avalanche[D]. Zhengzhou: North China University of Water Resources and Hydropower, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 王畯才. 滑坡—碎屑流堆积分布规律及其运动过程研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2018.
WANG Chuancai. Study of deposit position and motion process of landslide-debris avalanches[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 杜永彬. 太大公路徐家寨滑坡运动的数值模拟[J]. 重庆交通大学学报(自然科学版),2008,27(6):1099 − 1102. [DU Yongbin. Numerical simulation of the landslide movement in Xujiazhai in the highway from Taiyuan to Dalian[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University (Natural Science Edition),2008,27(6):1099 − 1102. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 王宇, 李晓, 王声星, 等. 滑坡渐进破坏运动过程的颗粒流仿真模拟[J]. 长江科学院院报,2012,29(12):46 − 52. [WANG Yu, LI Xiao, WANG Shengxing, et al. PFC simulation of progressive failure process of landslide[J]. Journal of the Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2012,29(12):46 − 52. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5485.2012.12.010
[14] 胡江春, 杨成林, 徐晓晨, 等. 颗粒流法及其在库岸滑坡稳定分析中的应用[J]. 中原工学院学报,2016,27(4):61 − 64. [HU Jiangchun, YANG Chenglin, XU Xiaochen, et al. Particle flow method and its application in stability analysis of landslide on reservoir bank[J]. Journal of Zhongyuan University of Technology,2016,27(4):61 − 64. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6906.2016.04.013
[15] 赵洲, 魏江波. 基于颗粒流方法的堆积层滑坡运动过程模拟[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2017,45(6):111 − 116. [ZHAO Zhou, WEI Jiangbo. Simulation on the movement process of accumulated layer landslide based on PFC2D[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2017,45(6):111 − 116. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2017.06.018
[16] 陈达, 薛喜成, 魏江波. 基于PFC2D的刘涧滑坡破坏运动过程模拟[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2018,46(4):115 − 121. [CHEN Da, XUE Xicheng, WEI Jiangbo. Simulation of failure process of Liujian landslide based on PFC2D[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2018,46(4):115 − 121. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2018.04.019
[17] 闫晓娟, 赵洲. 金泉寺滑坡破坏机理及冲击强度定量分析[J]. 科学技术与工程,2019,19(22):76 − 84. [YAN Xiaojuan, ZHAO Zhou. Deformation mechanism and impact intensity for the landslide in Jinquan temple, Mian County[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2019,19(22):76 − 84. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.22.010
[18] 汪华安, 焦春茂, 陈晓. 基于颗粒流方法的滑坡机理数值分析[J]. 三峡大学学报(自然科学版),2020,42(1):47 − 51. [WANG Hua'an, JIAO Chunmao, CHEN Xiao. Numerical analysis of landslide mechanism based on PEC2D[J]. Journal of China Three Gorges University (Natural Science Edition),2020,42(1):47 − 51. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 郭延辉, 杨溢, 杨志全, 等. 国产GB-InSAR在特大型水库滑坡变形监测中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(2):66 − 72. [GUO Yanhui, YANG Yi, YANG Zhiquan, et al. Application of GB-InSAR in deformation monitoring of huge landslide in reservoir area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(2):66 − 72. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 易连兴. 西南岩溶山区复合水动力场滑坡影响模式—以关岭县大寨滑坡为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(4):43 − 50. [YI Lianxing. Impact model of landslide with complex hydrodynamic field in karst mountain areas of southwest China: A case study of the Dazhai landslide in Guanling County[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(4):43 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 高杨, 贺凯, 李壮, 等. 西南岩溶山区特大滑坡成灾类型及动力学分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(4):14 − 23. [GAO Yang, HE Kai, LI Zhuang, et al. An analysis of disaster types and dynamics of landslides in the southwest karst mountain areas[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(4):14 − 23. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: