A deep learning recognition model for landslide terrain based on multi-source data fusion
-
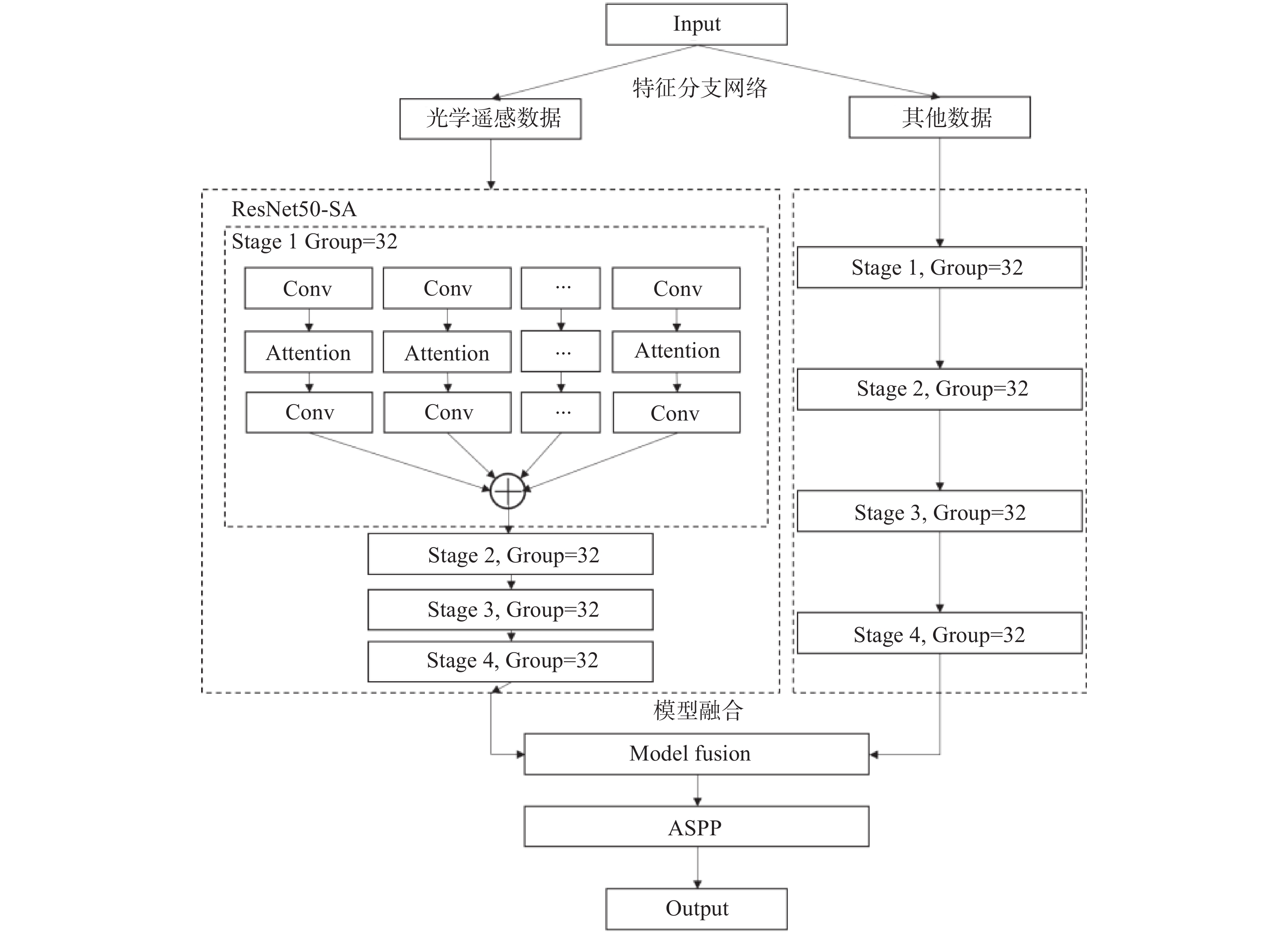
摘要:
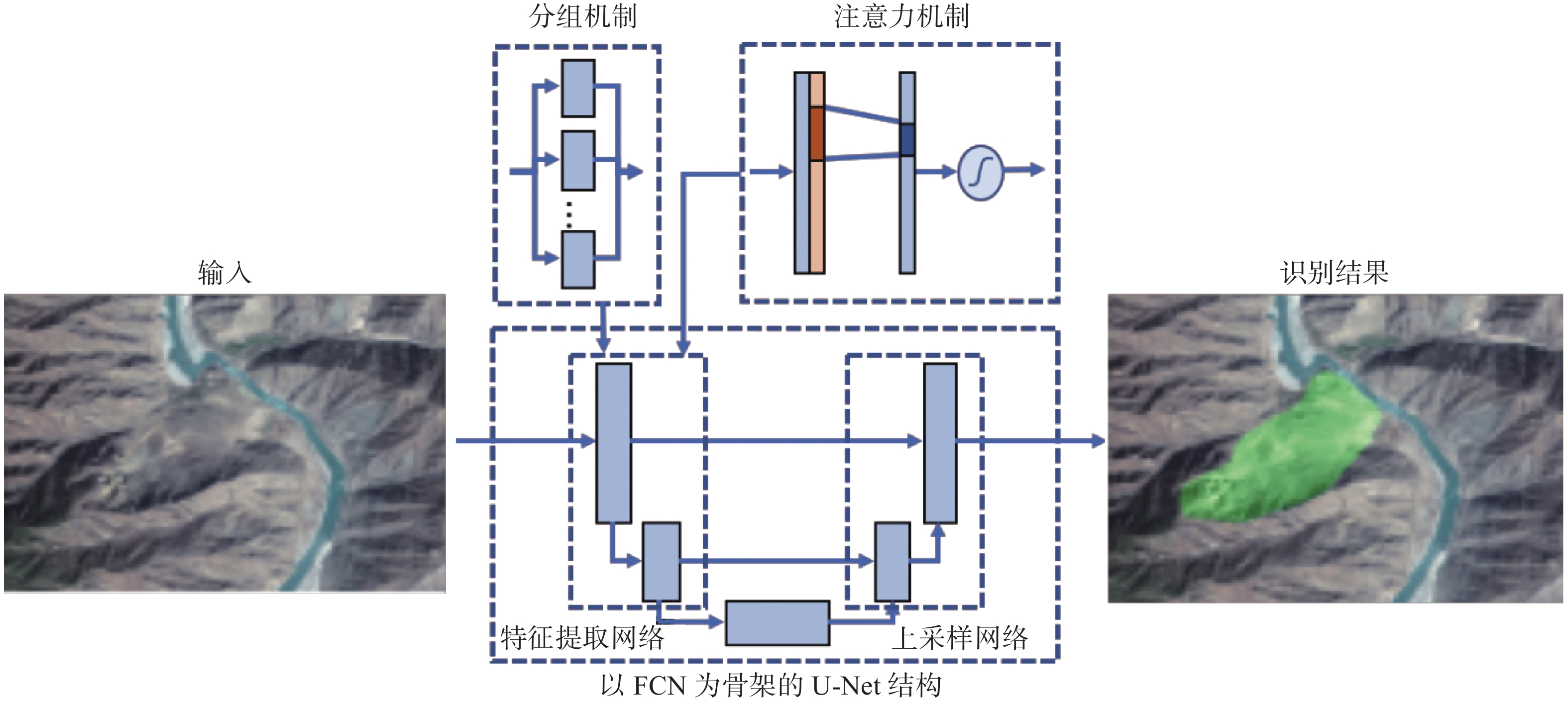
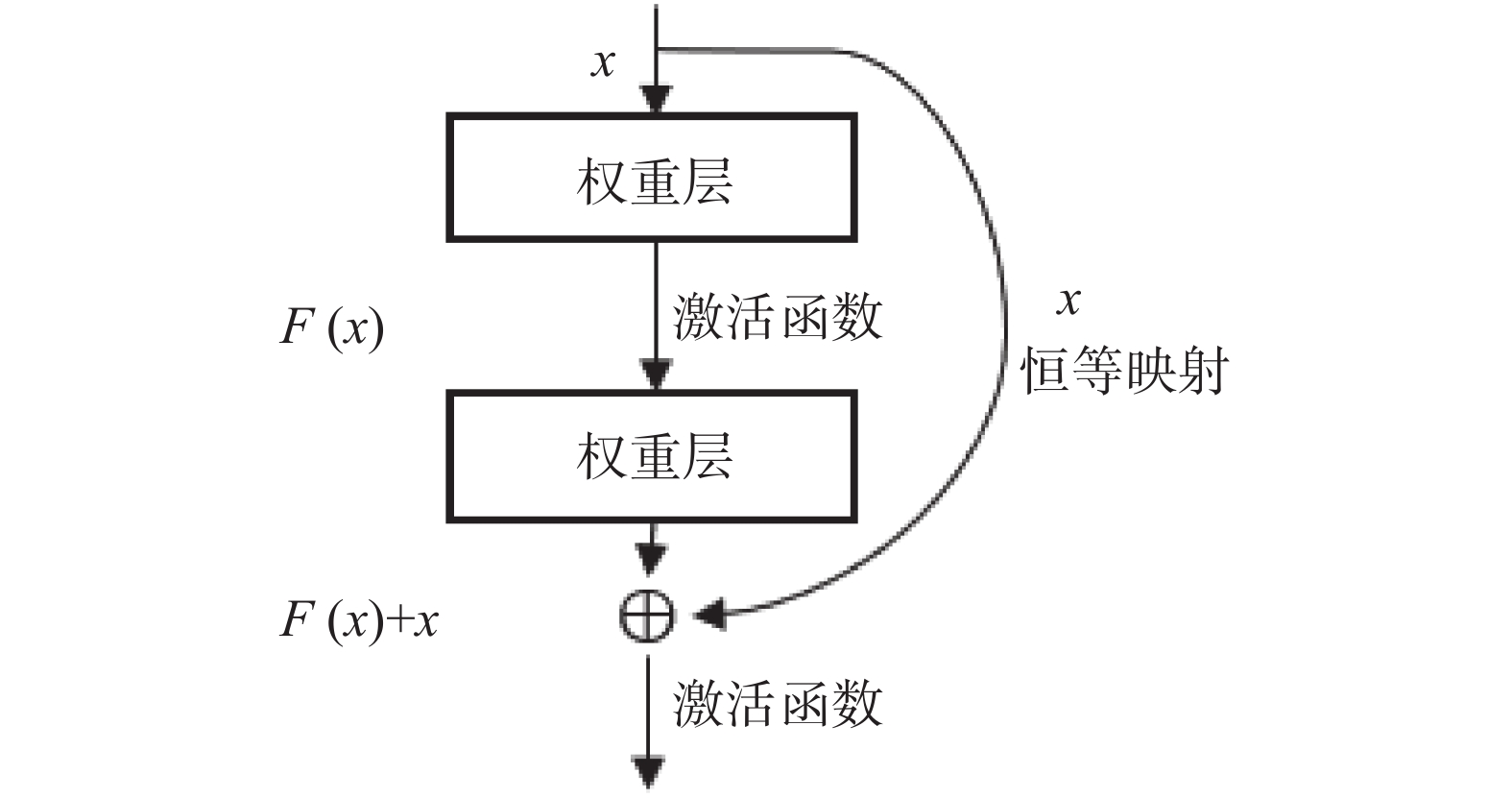
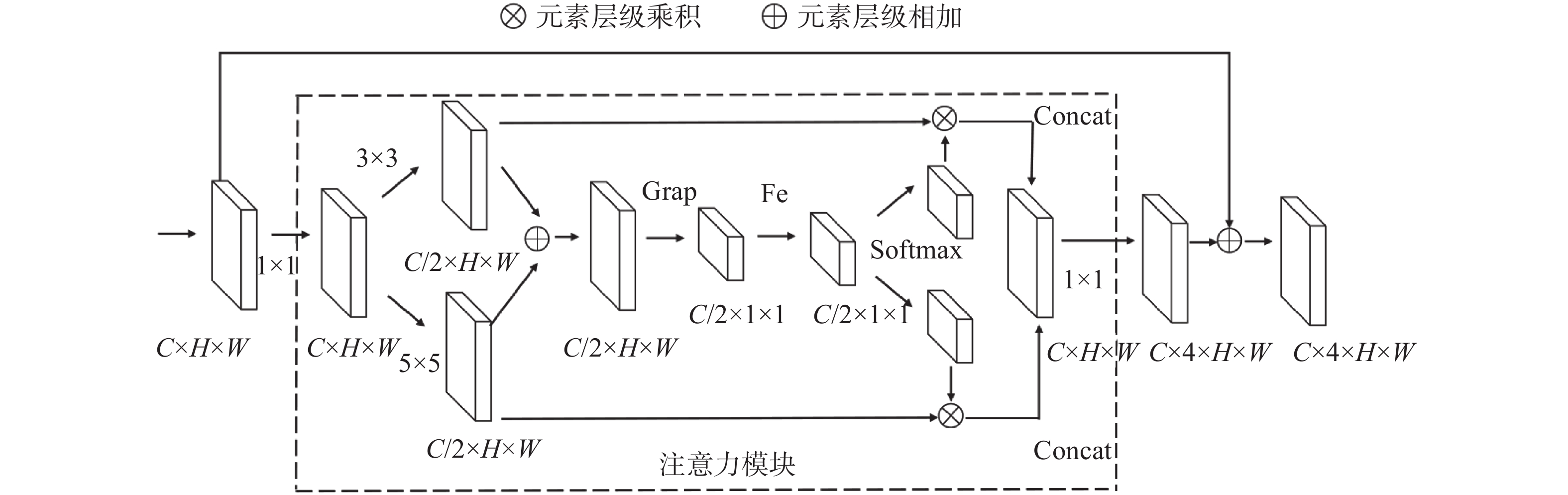
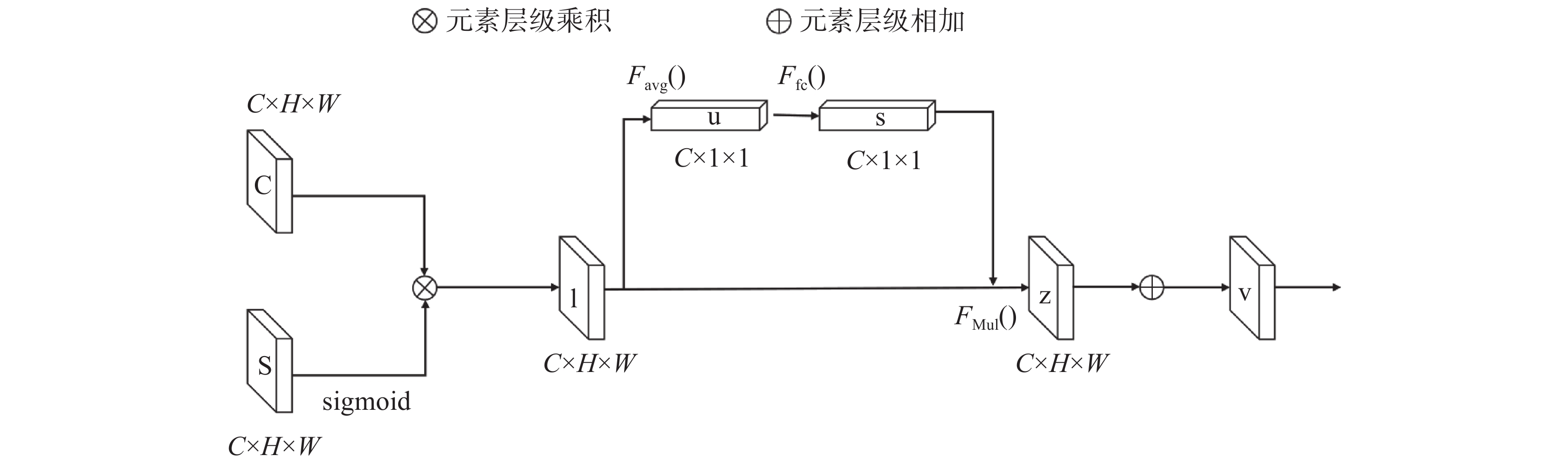
传统高位远程滑坡识别依赖地质专家人工判别,识别效率较低。研究实现一种基于深度学习的滑坡地形自动识别模型,以提高大范围区域潜在滑坡隐患点筛查工作的效率。该模型以目标区域的遥感图像、DEM数据、地质分区、河流水系等地质观测数据为输入,针对不同类型观测数据差异巨大的问题,设计构建特征分支网络,精确提取对应的滑坡特征。对光学影像数据采用深层网络架构提取复杂特征,对海拔、地质构成、河流和断裂带分布等结构化数据采用浅层网络架构提取特征。随后设计特征融合模块,融合两个网络的提取结果获得全面的滑坡灾害特征。模型基于提取的滑坡特征进行滑坡区域语义分割,实现精准的像素级别滑坡地形分类和定位。通过实验验证,该模型对滑坡区域的识别准确率(ACC)达到了0.85,可为滑坡自动识别提供技术支撑。
Abstract:The traditional high-level remote landslide recognition efficiency which relies on the artificial discrimination of geological experts is low. In this paper, an automatic landslide terrain recognition model based on deep learning is developed to improve the efficiency of the screening of potential landslide hazard in a large area. The model takes remote sensing images, DEM data, geological zones, river system and other geological observation data of the target area as input. For the huge difference of different types of observation data, a feature branch network is designed and constructed to accurately extract the corresponding landslide features: Among them, deep network architecture is used to extract complex features from optical image data, and shallow network architecture is used to extract features from structured data such as altitude, geological composition, river and fault zone distribution. Subsequently, a feature fusion module was designed to fuse the extraction results of the two networks to obtain a comprehensive landslide hazard feature. The model performs semantic segmentation of the landslide area based on the extracted landslide features, and achieves accurate pixel-level landslide terrain classification and positioning. The experimental results show that the recognition accuracy(ACC) of the model reaches 0.85, which can provide technical support for automatic landslide identification.
-

-
表 1 二分类问题中预测结果与真实标签的组合关系
Table 1. The combination between predicted results and real labels in dichotomous problems
预测值 Positive Negative 真实值 Positive True Positive(TP) False Negative(FN) Negative False Positive(FP) True Negative(TN) 表 2 基于光学遥感图像的识别结果
Table 2. Recognition result based on optical remote sensing image
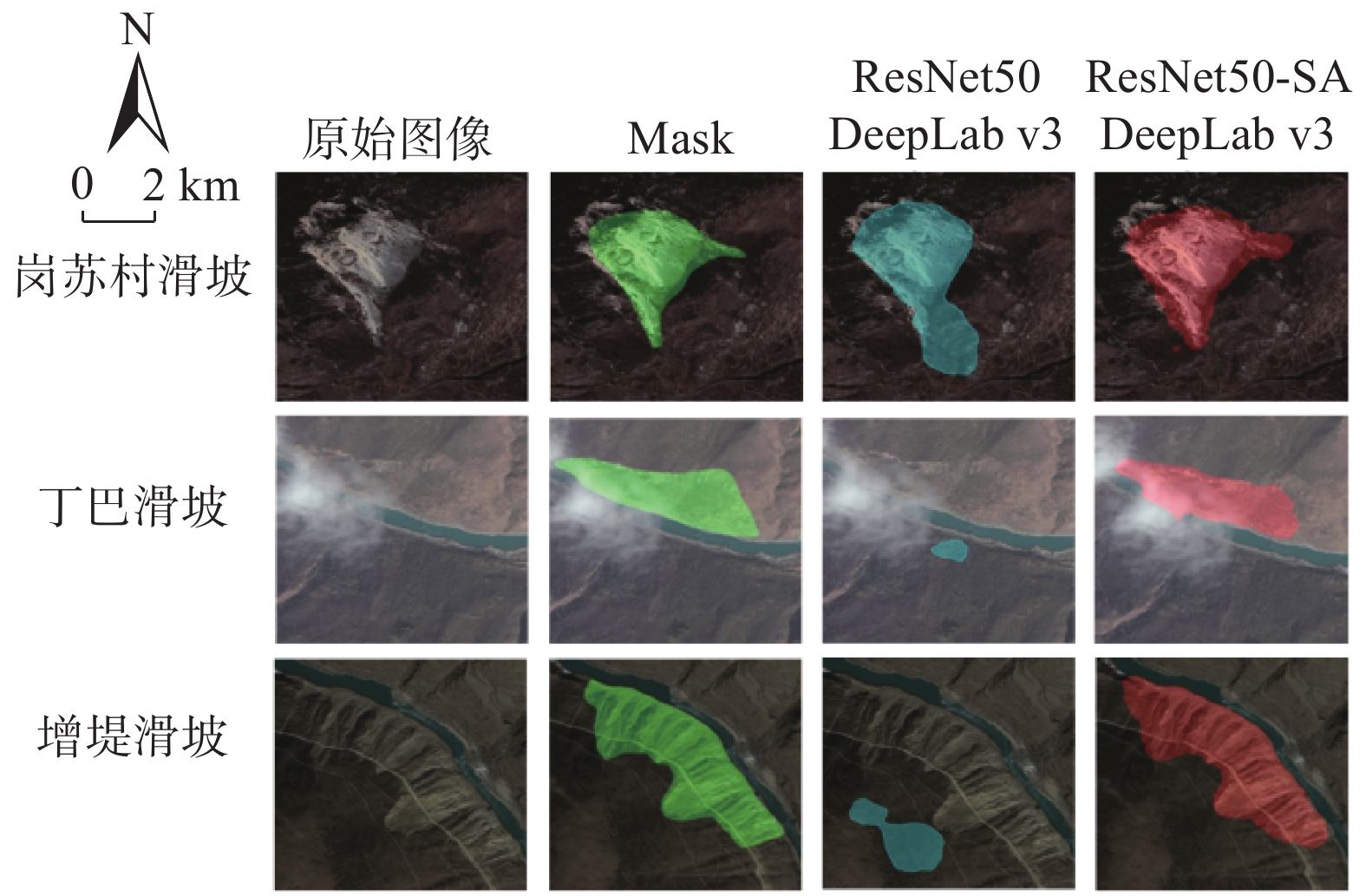
模型名称 评价指标 IOU ACC F1-Score U-Net 0.4365 0.5923 0.3428 PSPNet 0.4367 0.5769 0.398 DeepLab v3 0.5635 0.7154 0.5219 DeepLab v3+ 0.4263 0.6308 0.3685 基于 ResNet50-SA 的 DeepLab v3 (ours) 0.6582 0.7430 0.5844 表 3 基于多源数据融合的识别结果
Table 3. Recognition results based on multi-source data fusion
模型名称 评价指标 IOU ACC F1-Score 基于 ResNet50-SA 的 DeepLab v3 (ours) 0.6582 0.7430 0.5844 仅融合了地形数据的DeepLab-MFNet (ours) 0.714 0.809 0.673 采用数据融合思想的DeepLab-MFNet (ours) 0.755 0.850 0.742 -
[1] 解明礼, 巨能攀, 刘蕴琨, 等. 崩塌滑坡地质灾害风险排序方法研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(5):184 − 192. [XIE Mingli, JU Nengpan, LIU Yunkun, et al. A study of the risk ranking method of landslides and collapses[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(5):184 − 192. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 韩旭东, 付杰, 李严严, 等. 舟曲江顶崖滑坡的早期判识及风险评估研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(6):180 − 186. [HAN Xudong, FU Jie, LI Yanyan, et al. A study of the early identification and risk assessment of the Jiangdingya landslide in Zhouqu County[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(6):180 − 186. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 朱真, 江思义, 刘小明, 等. 基于广播RTK边缘计算的北斗高精度地质灾害监测系统及应用分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(5):176 − 183. [ZHU Zhen, JIANG Siyi, LIU Xiaoming, et al. The Beidou high precision geological disaster monitoring system based on RTK edge calculation and its application analysis[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(5):176 − 183. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 张倩荧, 王俊英, 雷冬冬. 基于深度学习目标检测算法的滑坡检测研究[J]. 信息通信,2019,193(1):15 − 18. [ZHANG Qianying, WANG Junying, LEI Dongdong. Research on landslide detection based on deep learning target detection algorithm[J]. Information and Communication,2019,193(1):15 − 18. (in Chinese)
[5] 何思明, 白秀强, 欧阳朝军, 等. 四川省茂县叠溪镇新磨村特大滑坡应急科学调查[J]. 山地学报,2017,35(4):598 − 603. [HE Siming, BAI Xiuqiang, OUYANG Chaojun, et al. On the survey of giant landslide at Xinmo village of Diexi town, Maoxian Country, Sichuan Province, China[J]. Mountain Research,2017,35(4):598 − 603. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 刘超云, 尹小波, 张彬. 基于Kalman滤波数据融合技术的滑坡变形分析与预测[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2015,26(4):30 − 35. [LIU Chaoyun, YIN Xiaobo, ZHANG Bin. Analysis and prediction of landslide deformations based on data fusion technology of Kalman-filter[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2015,26(4):30 − 35. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 徐俊峰, 张保明, 郭海涛, 等. 一种多特征融合的面向对象多源遥感影像变化检测方法[J]. 测绘科学技术学报,2015,32(5):505 − 509. [XU Junfeng, ZHANG Baoming, GUO Haitao, et al. Object-oriented change detection for multi-source images using multi-feature fusion[J]. Journal of Geomatics Science and Technology,2015,32(5):505 − 509. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6338.2015.05.014
[8] PRADHAN B, JEBUR M N, SHAFRI H Z M, et al. Data fusion technique using wavelet transform and taguchi methods for automatic landslide detection from airborne laser scanning data and QuickBird satellite imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2016,54(3):1610 − 1622. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2484325
[9] MA H R, CHENG X W, CHEN L J, et al. Automatic identification of shallow landslides based on Worldview2 remote sensing images[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing,2016,10:01600801 − 1600812.
[10] CHEN X, LI J, ZHANG Y F, et al. Evidential fusion based technique for detecting landslide barrier lakes from cloud-covered remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing,2017,10(5):1742 − 1757. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2665529
[11] 邱丹丹. 基于多源数据融合的滑坡风险分析研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2017
QIU Dandan. Landslide risk analysis based on multi-source data fusion[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, BROX T. U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]//Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2015, 2015: 234 − 241.
[13] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. June 27−30, 2016, Las Vegas, NV, USA. IEEE, 2016: 770 − 778.
[14] YANG M K, YU K, ZHANG C, et al. DenseASPP for semantic segmentation in street scenes[C]//2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. June 18−23, 2018, Salt Lake City, UT, USA. IEEE, 2018: 3684 − 3692.
[15] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM,2017,60(6):84 − 90. doi: 10.1145/3065386
[16] ZHAO H S, SHI J P, QI X J, et al. Pyramid scene parsing network[C]//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. July 21-26, 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA. IEEE, 2017: 6230-6239.
[17] CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, SCHROFF F, et al. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation[EB/OL]. 2017: arXiv: 1706.05587. https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.05587.
[18] CHEN L C, ZHU Y K, PAPANDREOU G, et al. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation[C]//Computer Vision – ECCV 2018, 2018: 801-818.
-




 下载:
下载: