Study on the risk assessment of geological disasters in alpine valley area: A case study in Aba County, Sichuan Province
-
摘要:
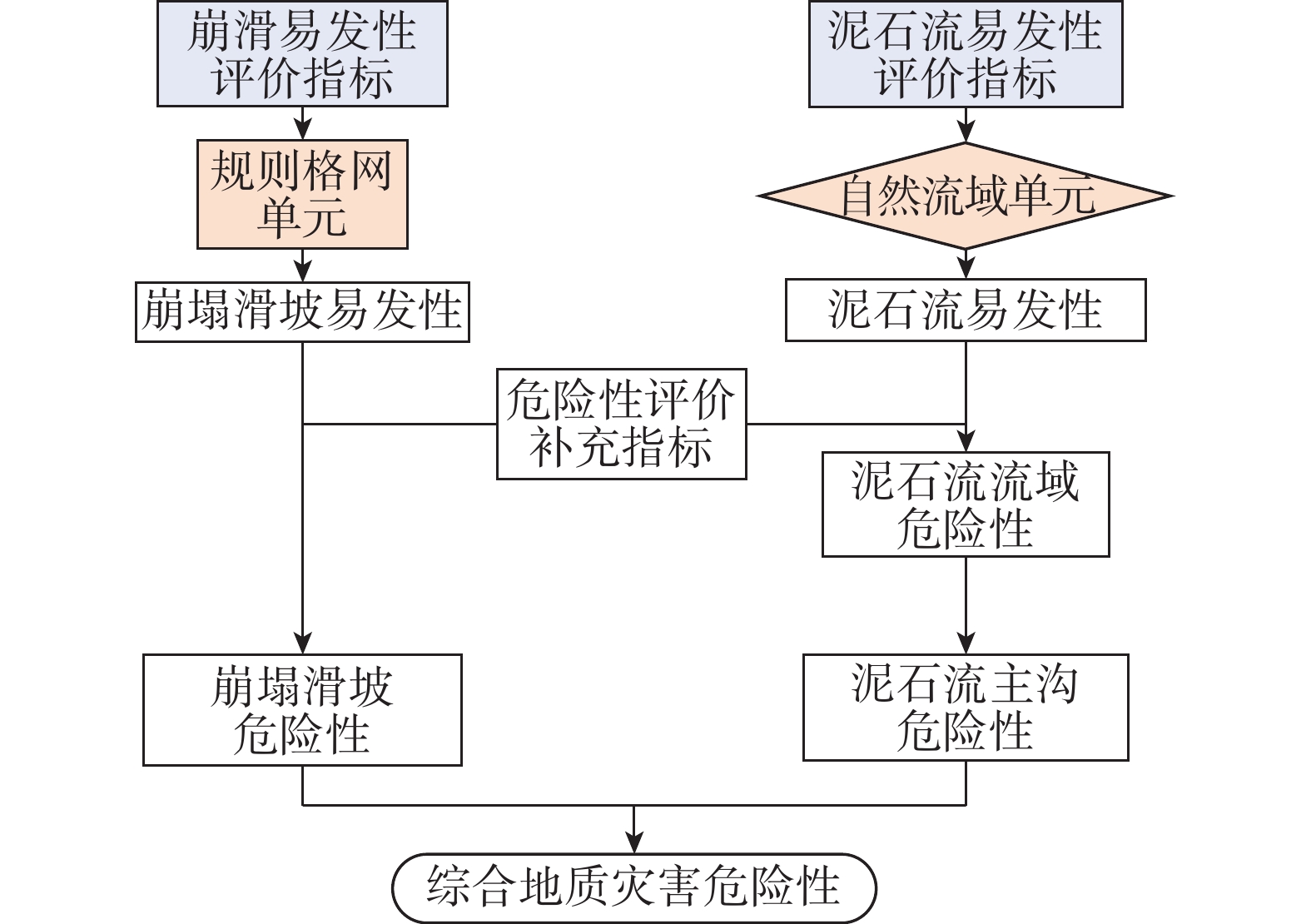
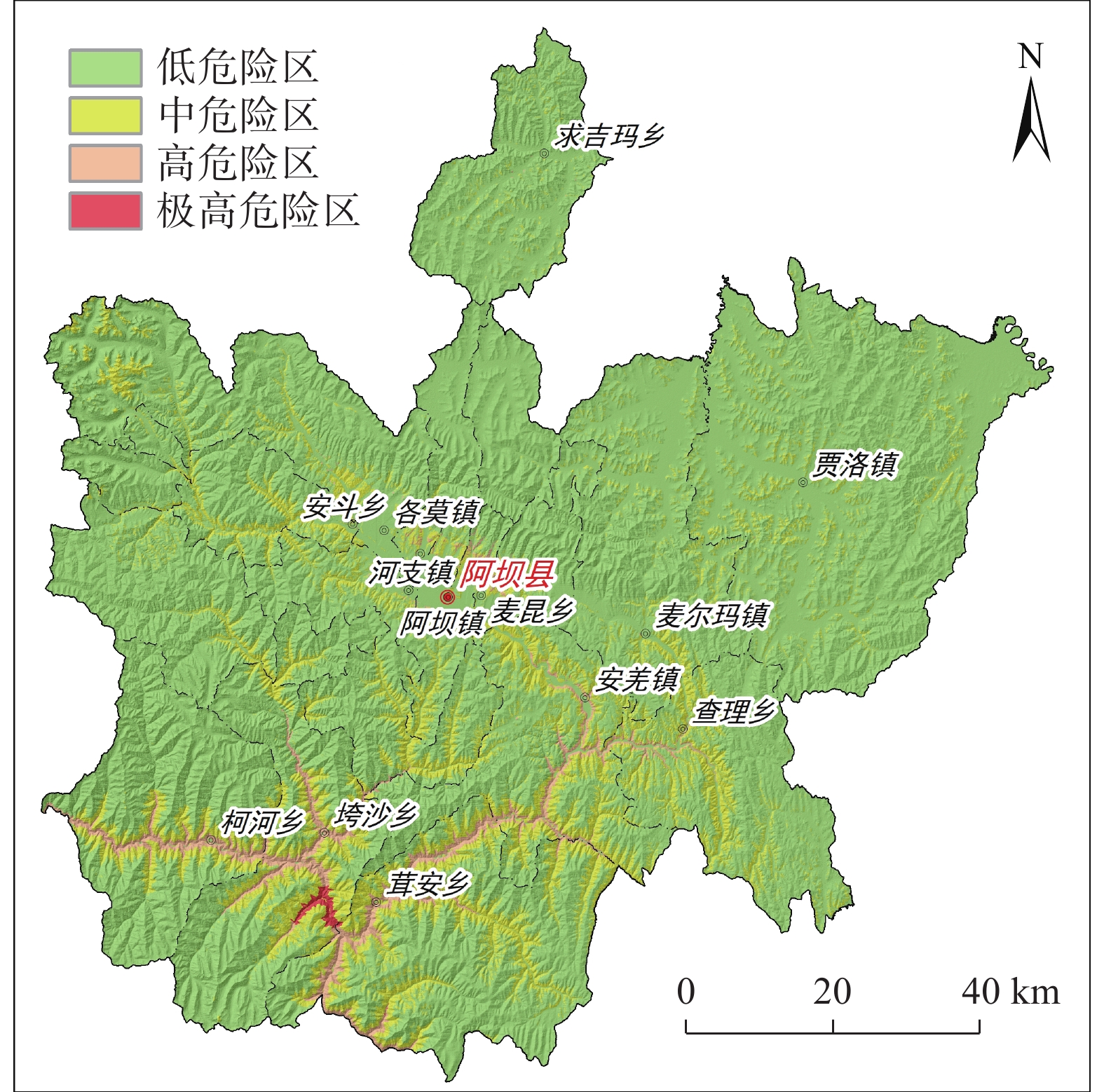
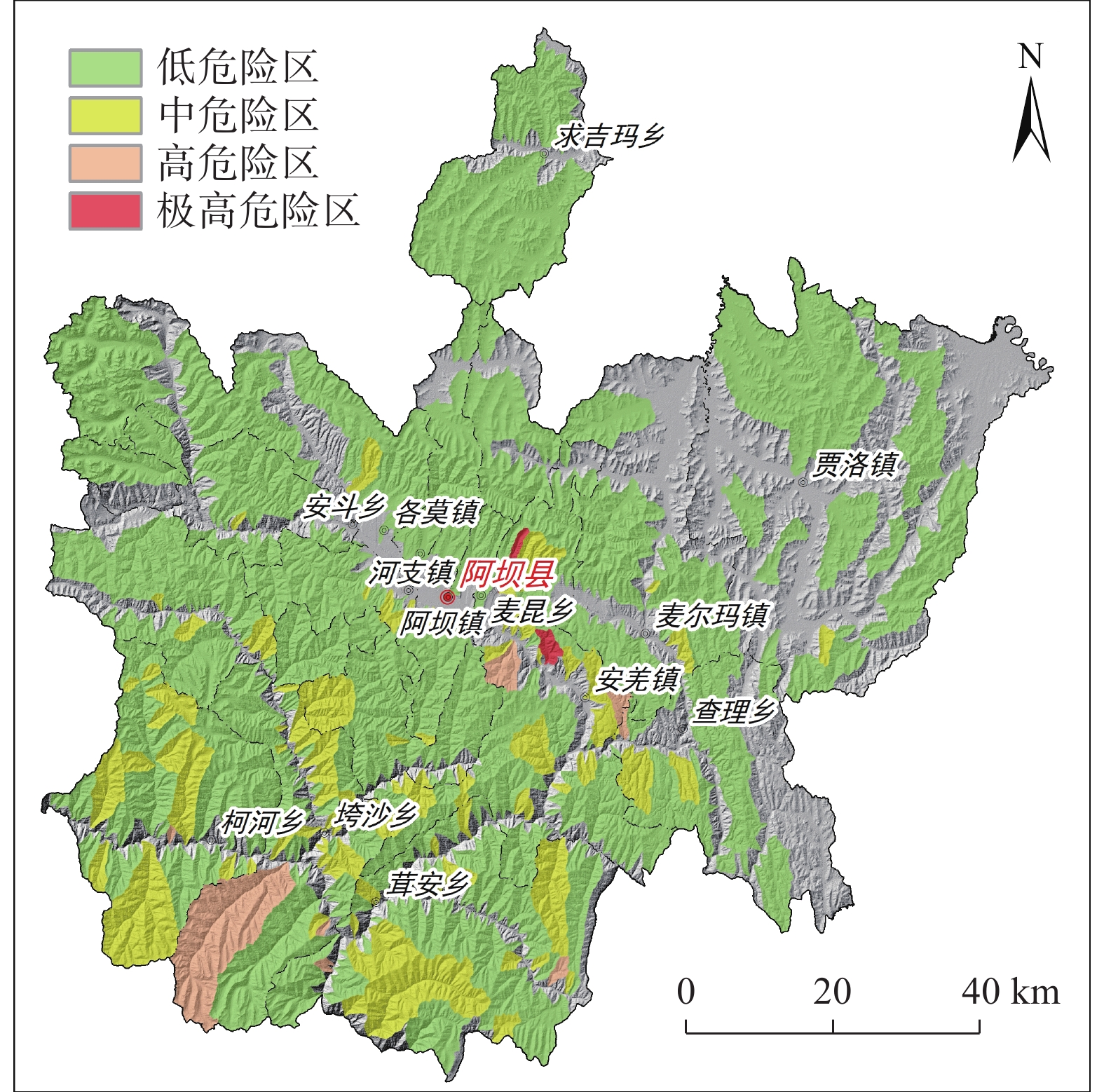
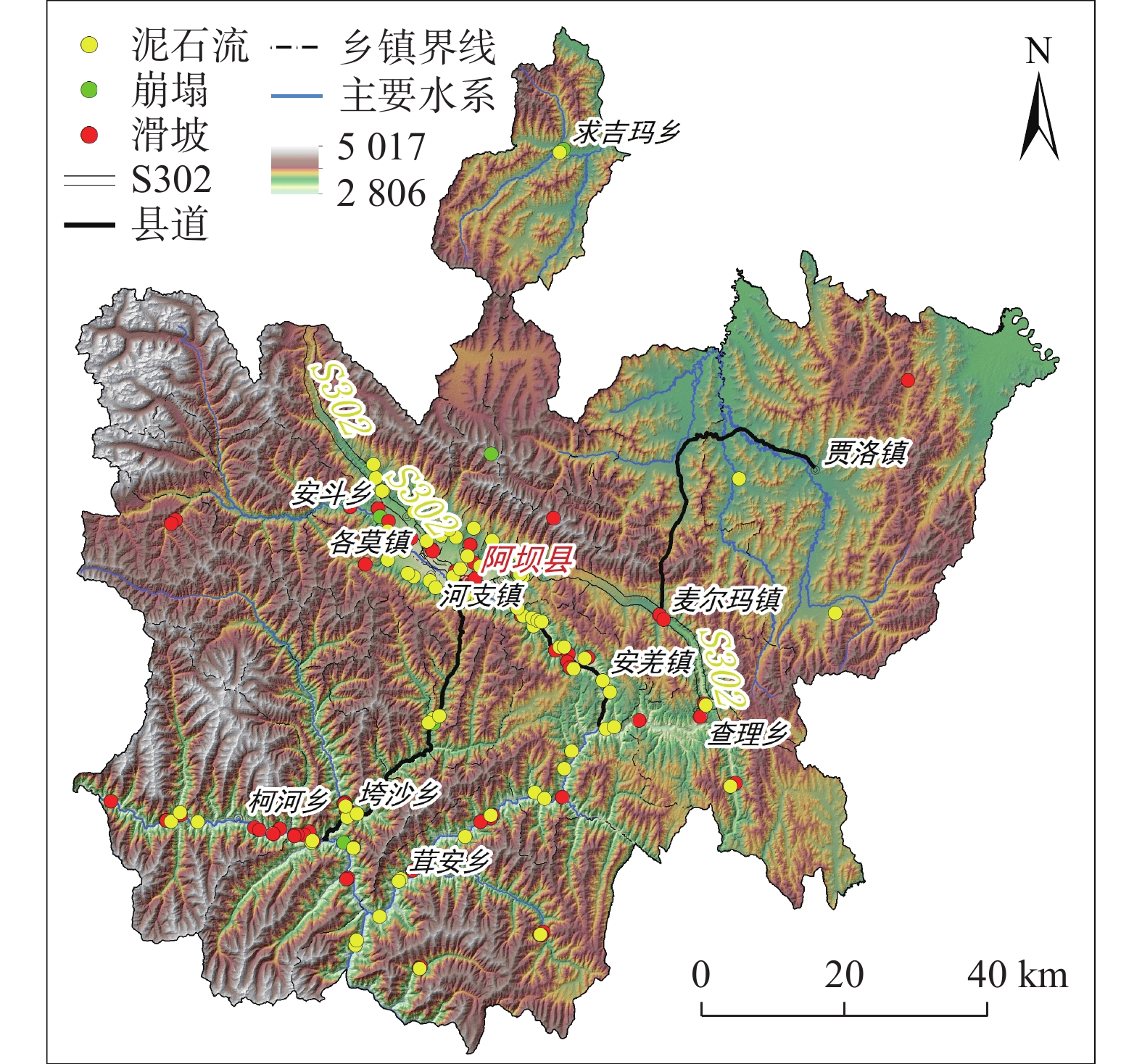
针对崩塌、滑坡和泥石流等灾种齐全的高山峡谷区,选取四川省阿坝县为研究区,采用多灾种耦合的评价思路,开展地质灾害危险性精细化评价。崩塌、滑坡等斜坡类灾害危险性评价以栅格为评价单元,泥石流灾害危险性评价以流域为评价单元。基于信息量模型和层次分析法,分别开展危险性评价,进而采用取大值的方法,获取研究区综合地质灾害危险性评价结果。研究表明,工作区综合地质灾害极高危险区、高危险区面积明显大于单灾种评价结果,极高危险区、高危险区主要位于崩塌、滑坡较发育的碎裂岩区域和极度易发的泥石流流域。针对高山峡谷区地质灾害危险性评价,多灾种耦合的评价思路能更合理的反映不同类型灾害在形态及空间上的差异,获取更精确的危险性评价结果。
Abstract:The geological hazard assessment was carried out by the evaluation train thought the study area of multiple disaster species coupling , which has a complete range of disasters such as collapse, landslide and debris flow. The evaluate unit of collapse, landslide and other slopes are grids and the debris flow disasters evaluate units are watershed, Based on the information model and analytic hierarchy process, the risk assessment is carried out respectively, then, the comprehensive geological disaster risk evaluation results of the study area were obtained by taking the method of large value. In the study area, the area of extremely high and high risk area of comprehensive geological disaster is obviously larger than that of the evaluation results of single hazard. The extremely high and high risk area is mainly located in the cataclastic rock area with relatively developed collapse and landslide and extremely prone debris flow basin. In view of the risk assessment of geological disasters in high mountains and valleys, the idea of dividing first and combining later can more reasonably reflect the morphological and spatial differences of different disaster types in the process of risk assessment, and obtain more accurate risk assessment results.
-

-
表 1 崩塌、滑坡评价指标信息量表
Table 1. The evaluation index information scale of collapse and landslide
因子 区间 信息量 坡度/(°) 0~10 −2.2697 10~20 −1.2429 20~30 0.7574 30~50 0.4213 >50 0.0812 高程/m <3300 2.6673 3300~3700 0.0276 3700~4100 −1.5253 4100~4500 −2.3652 工程地质岩组 第四系松散堆积层 1.0828 较软的千枚岩、板岩 0.0000 坚硬-半坚硬的石英砂岩、凝灰质粉砂岩 −0.2585 坚硬的花岗岩、石英闪长岩 −0.8895 斜坡结构类型 松散堆积层土质斜坡 1.0829 顺向坡 0.2555 斜交坡 -0.7319 横交坡 −0.2417 逆向坡 −0.6745 距构造距离/m 0~500 1.6921 500~1000 1.1808 1000~1500 0.9655 1500~2000 0.7052 >2000 −0.5296 距水系距离/m 0~200 2.4620 200~400 1.2733 400~600 1.0352 600~800 −0.7252 距道路距离/m 0~200 2.5407 200~400 2.4767 400~600 2.2700 600~800 1.8107 >800 −0.4365 24小时最大
降雨量/mm<20 −0.2619 20~25 −0.0582 25~30 0.1937 >30 0.2271 地震峰值
加速度/g0.20 0.6574 0.15 0.1816 0.10 0.1053 表 2 构建A-B层判断矩阵
Table 2. A-B layer judgment matrix
B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 B6 B7 权重W1 B1 1 1/2 3 3 1/5 3 5 0.413 B2 2 1 3 3 1/7 3 2 0.045 B3 1/3 1/3 1 1/3 1/7 1/2 3 0.576 B4 1/3 1/3 3 1 1/5 3 2 0.329 B5 5 7 7 5 1 5 1 0.105 B6 1/3 1/3 2 1/3 1/5 1 1 0.073 B7 1/5 1/2 1/3 1/2 1 1 1 0.259 表 3 崩塌、滑坡危易发性评价因子权重统计表
Table 3. weight statistics table of risk assessment factors of collapse and landslide
评价指标 B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 B6 B7 权重 0.413 0.045 0.576 0.329 0.105 0.073 0.259 表 4 泥石流灾害评价指标信息量统计表
Table 4. Statistical table of debris flow disaster assessment index information
因子 区间 信息量 流域面积/km2 <2 2.7745 2~5 1.7429 5~10 0.8964 10~20 0.2742 >20 −1.4672 坡度/(°) 0~10 −2.2250 10~20 0.1730 20~30 −0.4071 30~50 0.5887 >50 −1.3470 流域地形起伏度/m <600 1.2871 600~900 0.2749 900~1200 −0.5489 1200~1500 −0.6350 >1500 −2.2932 工程地质岩组 一般土松散岩类(1) 0.4190 碳酸盐岩半坚硬-坚硬岩类(3) −0.1305 碎屑岩半坚硬-坚硬岩类(4) −0.0440 流域断层密度
/(km·km−2)0 −0.0405 0~0.1 −0.3192 0.1~0.2 −0.0562 0.2~0.4 1.1638 >0.4 3.0451 流域滑坡、崩塌密度
/(个·km−2)0 −0.2771 0~0.02 −0.8640 0.02~0.04 0.2370 0.04~0.08 0.8731 >0.08 1.3365 水系密度/(km·km−2) 0~0.1 1.6277 0.1~0.3 −1.1610 0.3~0.5 −0.9105 0.5~0.7 −0.2938 >0.7 0.1380 道路密度/(km·km−2) 0 1.6539 0~0.4 −0.3312 0.4~0.7 −0.7134 0.7~1.0 0.1333 >1.0 1.1917 植被覆盖率/% <30 0.1748 30~44 0.8532 44~48 −0.0080 48~52 −0.7143 >52 0.9825 流域月累积
降雨量/mm<120 0.0571 120~150 0.0893 150~200 0.2741 >200 0.5109 表 5 泥石流易发性评价因子权重统计表
Table 5. The weight statistics table of debris flow evaluation factors
评价指标 B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 B6 B7 B8 B9 权重 0.207 0.165 0.13 0.093 0.108 0.126 0.085 0.049 0.037 表 6 各类灾害危险性评价结果统计表
Table 6. The Statistical table of all kinds of disaster risk assessment results
危险分级 极高危险区 高危险区 中危险区 低危险区 斜坡类灾害评价结果 23.68 362.19 2467.93 7581.2 泥石流灾害评价结果 38.38 250.12 1654.2 8492.3 综合评价结果 54.79 382.25 2902.16 7095.8 -
[1] 汪茜, 李广杰. 数量化理论在泥石流灾害预测预报中的应用—以吉林和龙市泥石流为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2006,17(2):85 − 88. [WANG Qian, LI Guangjie. Application of quantification theory in forecasting debris flows: An example of Helong City, Jilin Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2006,17(2):85 − 88. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2006.02.019
WANG Qian, LI Guangjie. Application of quantification theory in forecasting debris flows: An example of Helong City, Jilin Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2006, 17(2): 85-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2006.02.019
[2] 周国云, 陈光齐. 基于GIS和数量化理论Ⅱ的滑坡危险性预测[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2008,27(12):2494 − 2500. [ZHOU Guoyun, CHEN Guangqi. Landslide risk prediction based on coupling gis and second theory of quantification[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2008,27(12):2494 − 2500. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.12.015
ZHOU Guoyun, CHEN Guangqi. Landslide risk prediction based on coupling gis and second theory of quantification[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 27(12): 2494-2500. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.12.015
[3] 唐亚明, 张茂省, 李林, 等. 滑坡易发性危险性风险评价例析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2011,38(2):125 − 129. [TANG Yaming, ZHANG Maosheng, LI Lin, et al. Discrimination to the landslide susceptibility, hazard and risk assessment[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2011,38(2):125 − 129. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2011.02.022
TANG Yaming, ZHANG Maosheng, LI Lin, et al. Discrimination to the landslide susceptibility, hazard and risk assessment[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2011, 38(2): 125-129. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2011.02.022
[4] 乔建平, 王萌, 吴彩燕. 基于概率方法的区域地质灾害风险防御工程效益评估[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2017,28(2):131 − 136. [QIAO Jianping, WANG Meng, WU Caiyan. Preventing engineering benefit evaluation of regional geological disaster risk based on probability method[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2017,28(2):131 − 136. (in Chinese with English abstract)
QIAO Jianping, WANG Meng, WU Caiyan. Preventing engineering benefit evaluation of regional geological disaster risk based on probability method[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2017, 28(2): 131-136. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 范林峰, 胡瑞林, 曾逢春, 等. 加权信息量模型在滑坡易发性评价中的应用—以湖北省恩施市为例[J]. 工程地质学报,2012,20(4):508 − 513. [FAN Linfeng, HU Ruilin, ZENG Fengchun, et al. Application of weighted information value model to landslide susceptibility assessment: A case study of Enshi City, Hubei Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2012,20(4):508 − 513. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2012.04.005
FAN Linfeng, HU Ruilin, ZENG Fengchun, et al. Application of weighted information value model to landslide susceptibility assessment: A case study of Enshi City, Hubei Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2012, 20(4): 508-513. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2012.04.005
[6] 张春山, 张业成, 马寅生, 等. 区域地质灾害风险评价要素权值计算方法及应用—以黄河上游地区地质灾害风险评价为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2006,33(6):84 − 88. [ZHANG Chunshan, ZHANG Yecheng, MA Yinsheng, et al. Calculation method and application of the right-weighty value on geological hazards in region[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2006,33(6):84 − 88. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2006.06.021
ZHANG Chunshan, ZHANG Yecheng, MA Yinsheng, et al. Calculation method and application of the right-weighty value on geological hazards in region[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2006, 33(6): 84-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2006.06.021
[7] 牛瑞卿, 彭令, 叶润青, 等. 基于粗糙集的支持向量机滑坡易发性评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2012,42(2):430 − 439. [NIU Ruiqing, PENG Ling, YE Runqing, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on rough sets and support vector machine[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2012,42(2):430 − 439. (in Chinese with English abstract)
NIU Ruiqing, PENG Ling, YE Runqing, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on rough sets and support vector machine[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2012, 42(2): 430-439. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 叶潇潇, 钱德玲, 朱志鹏, 等. 基于组合赋权法的中巴公路奥依塔克至布伦口段泥石流危险性评价[J]. 水土保持通报,2018,38(1):246 − 251. [YE Xiaoxiao, QIAN Deling, ZHU Zhipeng, et al. Hazard assessment of debris flow at aoyitake-bulunkou section of China-Pakistan Highway based on combined weight method[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2018,38(1):246 − 251. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YE Xiaoxiao, QIAN Deling, ZHU Zhipeng, et al. Hazard assessment of debris flow at aoyitake-bulunkou section of China-Pakistan Highway based on combined weight method[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2018, 38(1): 246-251. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 陈亮胜, 韦秉旭, 廖欢, 等. 膨胀土边坡非饱和渗流及渐进性破坏耦合分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(4):132 − 140. [CHEN Liangsheng, WEI Bingxu, LIAO Huan, et al. A coupling analysis of unsaturated seepage and progressive failure of an expansive soil slope[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(4):132 − 140. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CHEN Liangsheng, WEI Bingxu, LIAO Huan, et al. A coupling analysis of unsaturated seepage and progressive failure of an expansive soil slope[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(4): 132-140. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 牛全福, 陆铭, 李月锋, 等. 基于灰色关联与粗糙依赖度的甘肃兰州市区泥石流危险性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(5):48 − 56. [NIU Quanfu, LU Ming, LI Yuefeng, et al. Hazard assessment of debris flow in Lanzhou City of Gansu Province based on methods of grey relation and rough dependence[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(5):48 − 56. (in Chinese with English abstract)
NIU Quanfu, LU Ming, LI Yuefeng, et al. Hazard assessment of debris flow in Lanzhou City of Gansu Province based on methods of grey relation and rough dependence[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2019, 30(5): 48-56. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 孟凡奇, 李广杰, 秦胜伍, 等. 基于证据权法的泥石流危险度区划[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2010,40(6):1380 − 1384. [MENG Fanqi, LI Guangjie, QIN Shengwu, et al. Zoning of debris flow hazard degree with weight-of-evidence method[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2010,40(6):1380 − 1384. (in Chinese with English abstract)
MENG Fanqi, LI Guangjie, QIN Shengwu, et al. Zoning of debris flow hazard degree with weight-of-evidence method[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2010, 40(6): 1380-1384. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 刘力维, 程传周. 基于GIS的滑坡泥石流风险评估及其应用[J]. 地理空间信息,2014,12(3):8 − 10. [LIU Liwei, CHENG Chuanzhou. Landslide and debris flow risk assessment based on GIS and its application[J]. Geospatial Information,2014,12(3):8 − 10. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11709/j.issn.1672-4623.2014.03.003
LIU Liwei, CHENG Chuanzhou. Landslide and debris flow risk assessment based on GIS and its application[J]. Geospatial Information, 2014, 12(3): 8-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11709/j.issn.1672-4623.2014.03.003
-



 下载:
下载: