Controlling influence of the “perched water structure” on rainfall-induced landslide: A case study of the Yaogou landslide in Zhushan County, Hubei Province
-
摘要:
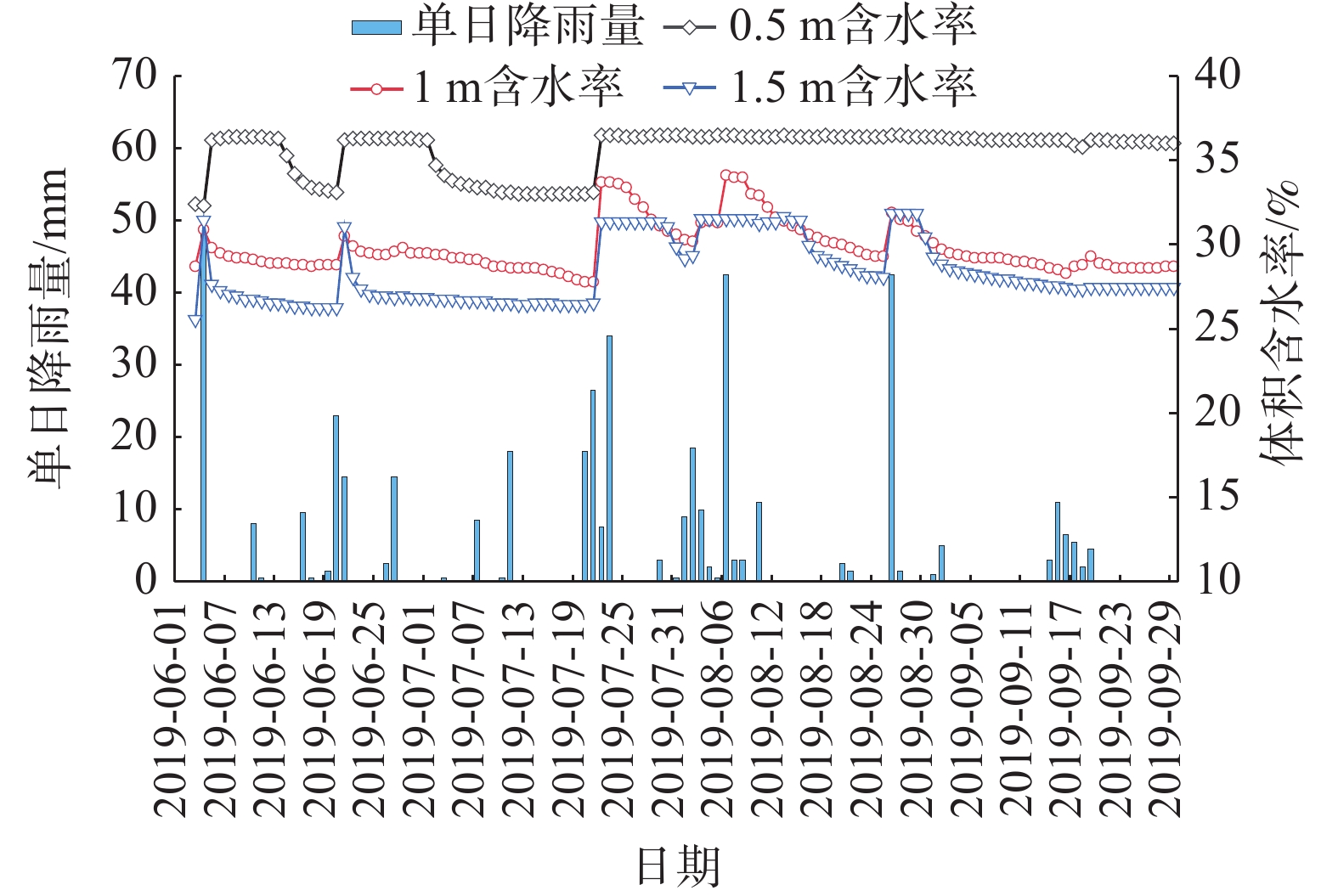
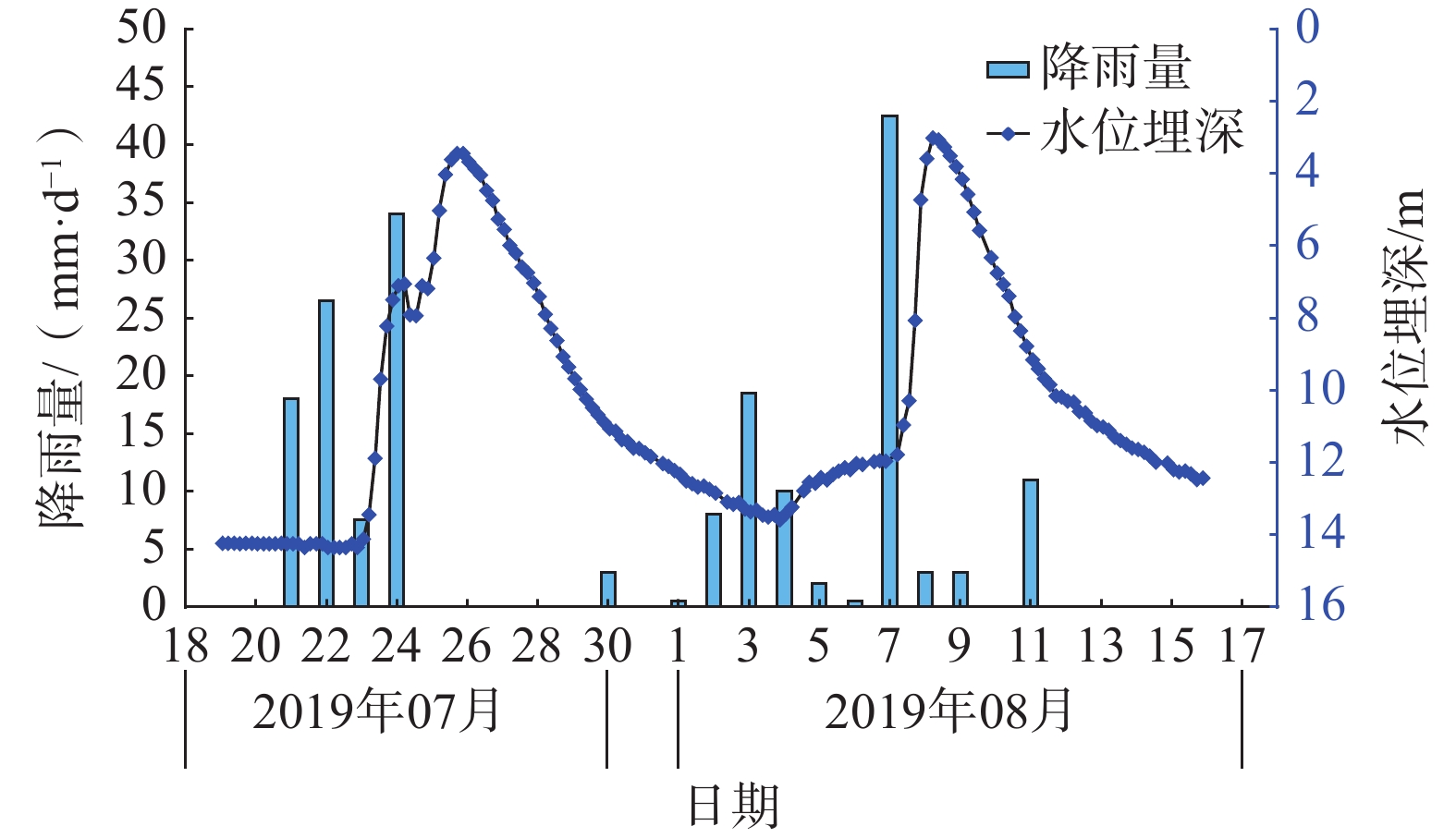
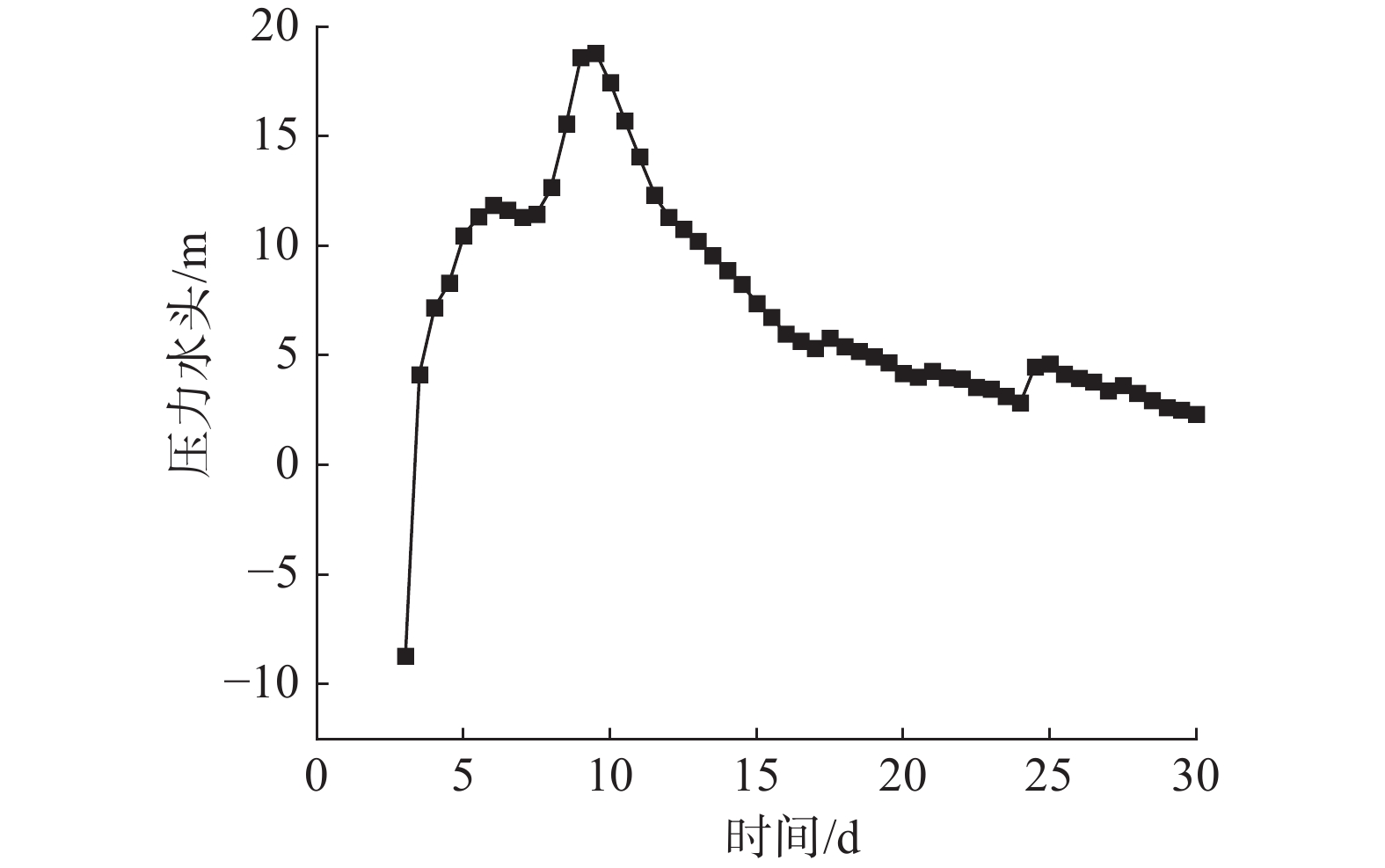
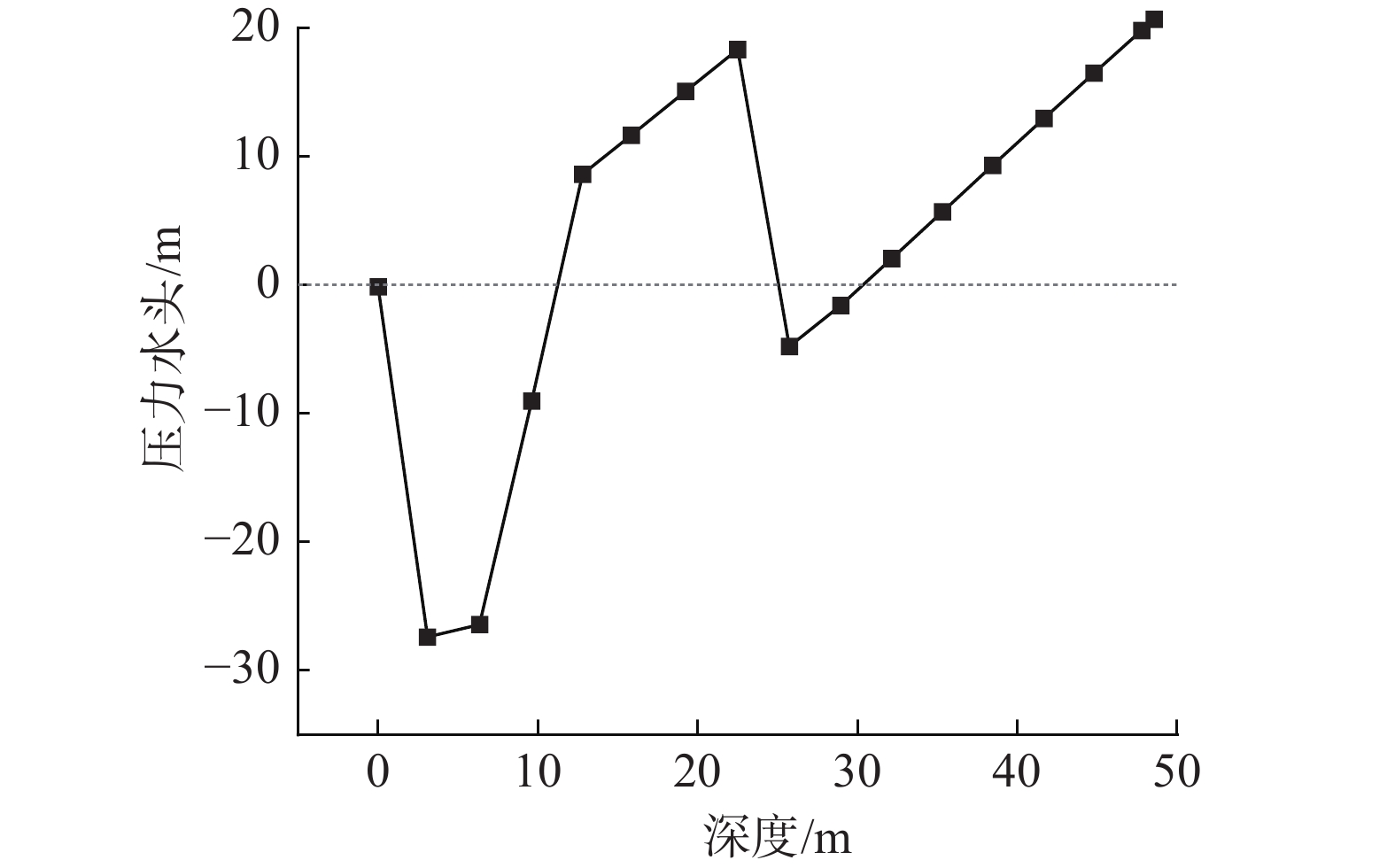
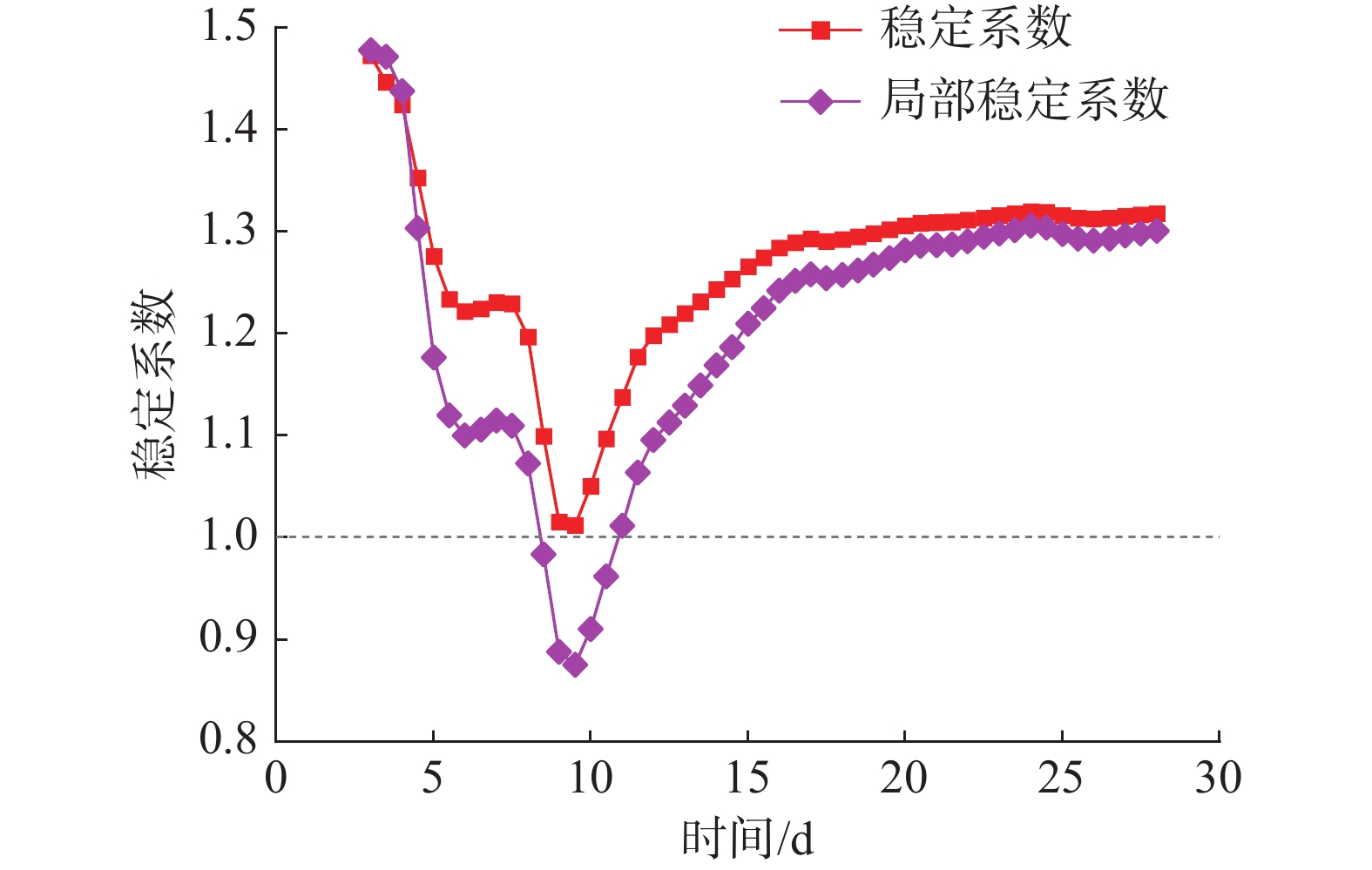
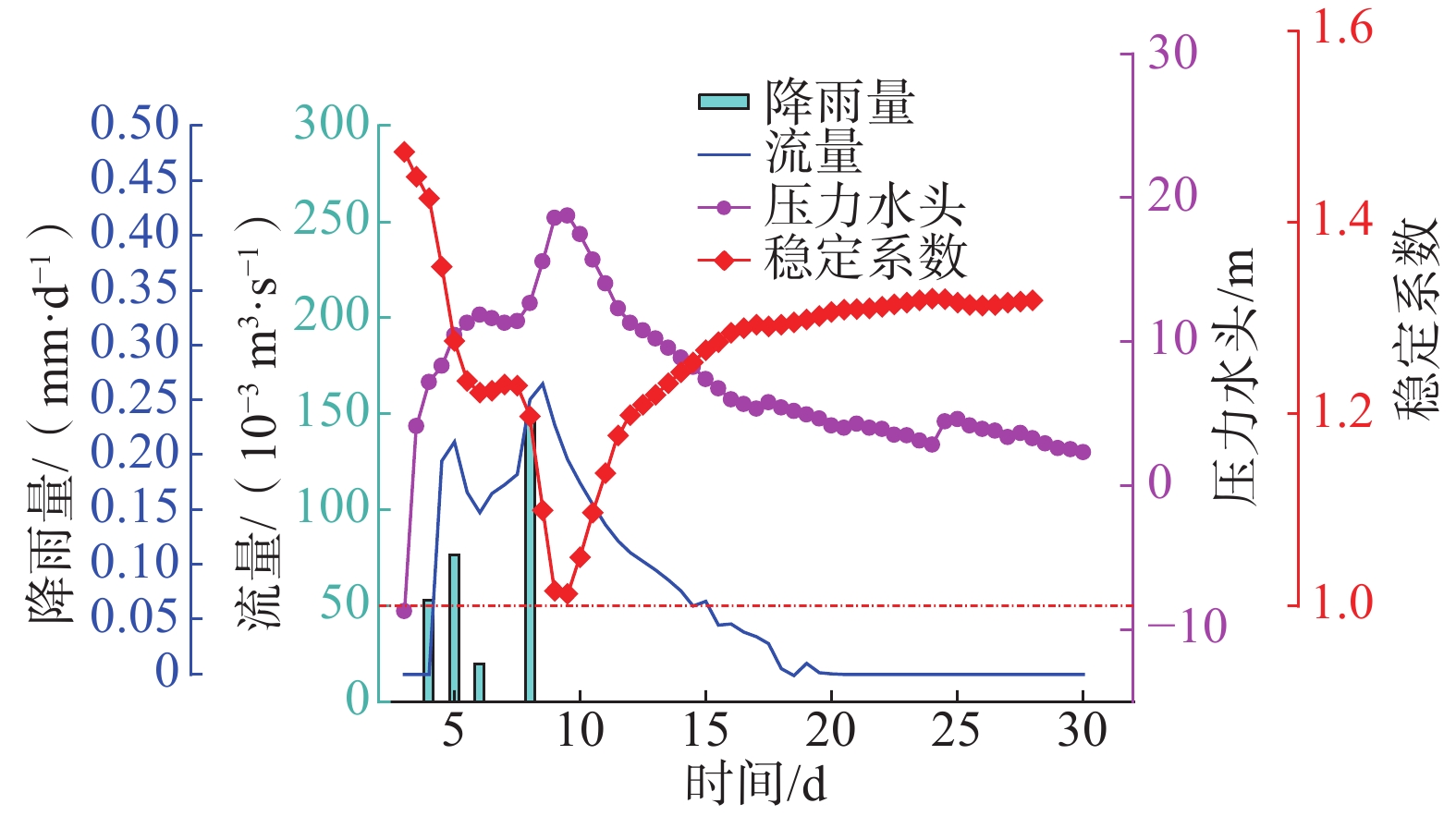
窑沟滑坡因其独特的含水层特征及差异性的渗透特征,强降雨后地下水在滑坡中排泄受阻形成短时承压水,此类下伏弱透水岩土体的滑坡含水层即为滞水构造。通过对窑沟滑坡2年的降雨量、地下水位、含水率、位移等数据进行监测,发现滑坡承压水头随降雨陡升缓降,具有明显的“滞水”特征。采用Geostudio软件模拟降雨入渗过程,验证了滑体承受承压水作用,且承压水的抬升幅度、作用位置与观测情况基本一致。滑坡稳定系数与压力水头呈现变化曲率基本一致的反向曲线。表明滑坡的“滞水构造”对滑坡的承压水头的形成及滑坡的稳定性具有明显的控制作用。
Abstract:The Yaogou landslide, located in Zhushan County, Hubei Province, exhibits distinctive aquifer characteristics and varying permeability, leading to the retention of groundwater within the landslide after rainfall, forming confined water. This kind of landslide aquifer underlying weakly permeable rock and soil mass is called a “stagnant water structure”. By monitoring a two-year dataset of rainfall, groundwater level, water content and displacement of the Yaogou landslide, it was found that the confined water head of the landslide fell slowly with the sharp rise of rainfall, which showed an obvious "stagnant water" pattern. Geostudio software was used to simulate the rainfall infiltration process, and it was verified that the sliding body was subjected to the action of confined water, and the lifting amplitude and acting position of confined water were basically consistent with the observed situation. The landslide stability coefficient and pressure head exhibited a reverse curve with a consistent curvature. It showed that the "water stagnation structure" of the landslide had a significant controlling effect on the formation of confined water head and the stability of landslide. This emphasizes the significant control exerted by the "water stagnation structure" on confined water head formation and landslide stability.
-
Key words:
- landslide /
- rainfall infiltration /
- confined water /
- stagnant water structure /
- stability
-

-
表 1 窑沟滑坡物理力学及水力学参数表
Table 1. Physical mechanics and hydraulics parameters of Yaogou landslide
材料 天然重度
/(kN·m−3)饱和重度
/(kN·m−3)天然黏聚力
/kPa天然内摩擦角
/(°)饱和黏聚力
/kPa饱和内摩擦角
/(°)渗透系数
/(cm·s−1)饱和含水率 粉质黏土 19.5 20.4 13.1 11.2 10.5 9.0 9.99×10−6 0.36 卵砾石 21.4 21.0 2.00×10−3 0.32 强风化片岩 25.5 27.0 2.50×10−4 0.06 -
[1] 魏鹏飞,李丽华,许程程,等. 鄂西北变质岩地区降雨型堆积层滑坡稳定性研究报告[R]. 湖北:湖北省地质局第八地质大队,2022. [WEI Pengfei,LI Lihua,XU Chengcheng,et al. Study on the stability of rainfall accumulation bed landslide in metamorphic rock area of northwest Hubei Province[R].Hubei:8th Geological Brigade of Hubei Geological Bureau,2022. (in Chinese)]
WEI Pengfei, LI Lihua, XU Chengcheng, et al. Study on the stability of rainfall accumulation bed landslide in metamorphic rock area of northwest Hubei Province[R].Hubei: 8th Geological Brigade of Hubei Geological Bureau, 2022. (in Chinese)
[2] 贺可强,阳吉宝,王思敬. 堆积层滑坡位移动力学理论及其应用:三峡库区典型堆积层滑坡例析[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2007. [HE Keqiang,YANG Jibao,WANG Sijing. Displacement dynamics theory on debris landslides & its application[M]. Beijing:Science Press,2007. (in Chinese)]
HE Keqiang, YANG Jibao, WANG Sijing. Displacement dynamics theory on debris landslides & its application[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2007. (in Chinese)
[3] 汪磊,尚岳全. 外部降雨条件和内部瞬态承压水作用对堆积层滑坡的影响分析和数值模拟[J]. 水土保持通报,2020,40(5):141 − 145. [WANG Lei,SHANG Yuequan. Analysis and numerical simulation on influence of external rainfall conditions and internal transient confined water on accumulation landslide[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2020,40(5):141 − 145.(in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Lei, SHANG Yuequan. Analysis and numerical simulation on influence of external rainfall conditions and internal transient confined water on accumulation landslide[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 40(5): 141 − 145.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 俞良晨,阎长虹,郭书兰,等. 受暂时性承压水影响的南京游子山滑动机制分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(1):133 − 141. [YU Liangchen,YAN Changhong,GUO Shulan,et al. An analysis of sliding mechanism of Youzi Mountain affected by temporary confined water in a confined quifer in Nanjing[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(1):133 − 141. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YU Liangchen, YAN Changhong, GUO Shulan, et al. An analysis of sliding mechanism of Youzi Mountain affected by temporary confined water in a confined quifer in Nanjing[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(1): 133 − 141. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 章校,阎长虹,郭书兰,等. 受暂时性承压水作用的山前缓坡稳定计算公式推求[J]. 工程地质学报,2021,29(5):1507 − 1514. [ZHANG Xiao,YAN Changhong,GUO Shulan,et al. Derivation of stability formula of gentle slope affected by temporary confined water[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2021,29(5):1507 − 1514.(in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Xiao, YAN Changhong, GUO Shulan, et al. Derivation of stability formula of gentle slope affected by temporary confined water[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2021, 29(5): 1507 − 1514.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 孟生勇,江兴元,杨义,等. 降雨诱发堆积体滑坡水土响应与稳定性时空演化试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(1):104 − 112. [MENG Shengyong,JIANG Xingyuan,YANG Yi,et al. An experimental study of spatial-temporal evolution of water-soil response and stability of a rainfall-induced accumulation landslide[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(1):104 − 112. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
MENG Shengyong, JIANG Xingyuan, YANG Yi, et al. An experimental study of spatial-temporal evolution of water-soil response and stability of a rainfall-induced accumulation landslide[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(1): 104 − 112. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 胡爱国,周伟. 地震与强降雨作用下堆积体滑坡变形破坏机理及防治方案分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(1):27 − 34. [HU Aiguo,ZHOU Wei. Deformation and failure mechanism and analysis on prevention measures of colluction landslide under earthquake and heavy rainfall[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(1):27 − 34. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HU Aiguo, ZHOU Wei. Deformation and failure mechanism and analysis on prevention measures of colluction landslide under earthquake and heavy rainfall[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(1): 27 − 34. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 尚敏,徐鑫,Dave CHAN,等. 基于降雨渗流场变化的三峡库区白水河滑坡变形机制与预测[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2016,27(2):26 − 32. [SHANG Min,XU Xin,CHAN D,et al. Deformation mechanism and prediction of Baishuihe landslide based on the analysis of rainfall seepage field in China Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2016,27(2):26 − 32. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
SHANG Min, XU Xin, CHAN D, et al. Deformation mechanism and prediction of Baishuihe landslide based on the analysis of rainfall seepage field in China Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2016, 27(2): 26 − 32. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 檀梦皎,殷坤龙,付智勇,等. 降雨及库水位影响下麻地湾滑坡地下水响应特征分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(1):45 − 57. [TAN Mengjiao,YIN Kunlong,FU Zhiyong,et al. Analysis on groundwater response characteristics of Madiwan landslide under the influence of rainfall and reservoir water[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(1):45 − 57. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
TAN Mengjiao, YIN Kunlong, FU Zhiyong, et al. Analysis on groundwater response characteristics of Madiwan landslide under the influence of rainfall and reservoir water[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(1): 45 − 57. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 魏占玺,谢东武,毋远召,等. 基于动态残余强度的不同含水率条件下滑坡稳定性研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(2):126 − 136. [WEI Zhanxi,XIE Dongwu,WU Yuanzhao,et al. Research on landslide stability under different water content conditions based on the dynamic residual strength[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(2):126 − 136. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WEI Zhanxi, XIE Dongwu, WU Yuanzhao, et al. Research on landslide stability under different water content conditions based on the dynamic residual strength[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(2): 126 − 136. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 李宁,许建聪,钦亚洲. 降雨诱发浅层滑坡稳定性的计算模型研究[J]. 岩土力学,2012,33(5):1485 − 1490. [LI Ning,XU Jiancong,QIN Yazhou. Research on calculation model for stability evaluation of rainfall-induced shallow landslides[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2012,33(5):1485 − 1490. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Ning, XU Jiancong, QIN Yazhou. Research on calculation model for stability evaluation of rainfall-induced shallow landslides[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2012, 33(5): 1485 − 1490. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 石爱红,李国庆,丁德民,等. 考虑非饱和土基质吸力的丁家坡滑坡变形机制及稳定性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(6):141 − 151. [SHI Aihong,LI Guoqing,DING Demin,et al. Deformation mechanism and stability evaluation of Dingjiapo landslide considering the matric suction of unsaturated soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(6):141 − 151. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
SHI Aihong, LI Guoqing, DING Demin, et al. Deformation mechanism and stability evaluation of Dingjiapo landslide considering the matric suction of unsaturated soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(6): 141 − 151. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 唐红梅,魏来,唐云辉,等. 重庆地区降雨型滑坡相关性分析及预报模型[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2013(4):7. [TANG Hongmei,WEI Lai,TANG Yunhui,et al. Correlation analysis and prediction model of rainfall-type landslide in Chongqing[J]. Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2013(4):7. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
TANG Hongmei, WEI Lai, TANG Yunhui, et al. Correlation analysis and prediction model of rainfall-type landslide in Chongqing[J]. Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2013(4): 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 林鸿州. 降雨诱发土质边坡失稳的试验与数值分析研究[D]. 北京:清华大学,2007. [LIN Hongzhou. The study on the mechanism and numerical analysis of rainfall-induced soil slope failure [D]. Beijing:Tsinghua University,2007. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIN Hongzhou. The study on the mechanism and numerical analysis of rainfall-induced soil slope failure [D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2007. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 李丽华,张磊,薛梅. 湖北省竹山县城关镇窑沟滑坡防治工程可行性研究报告[R]. 湖北: 湖北省地质局第八地质大队,2017. [LI Lihua,ZHANG Lei,XUE Mei. Feasibility study report of Yaogou landslide control project,Chengguan Town,Zhushan County,Hubei Province[R]. Hubei: The 8th Geological Brigade of Hubei Geology Bureau,2017. (in Chinese)]
LI Lihua, ZHANG Lei, XUE Mei. Feasibility study report of Yaogou landslide control project, Chengguan Town, Zhushan County, Hubei Province[R]. Hubei: The 8th Geological Brigade of Hubei Geology Bureau, 2017. (in Chinese)
[16] 李丽华, 镇方军.湖北省竹山县城关镇窑沟滑坡勘查报告[R]. 湖北:湖北省地质局第八地质大队, 2017. [LI Lihua, ZHEN Fangjun. Investigation report of Yaogou landslide, Chengguan Town, Zhushan County, Hubei Province[R]. Hubei:The 8th Geological Brigade of Hubei Geology Bureau, 2017. (in Chinese)]
LI Lihua, ZHEN Fangjun. Investigation report of Yaogou landslide, Chengguan Town, Zhushan County, Hubei Province[R]. Hubei: The 8th Geological Brigade of Hubei Geology Bureau, 2017. (in Chinese)
[17] 冉涛,徐如阁,周洪福,等. 雅砻江流域深切河谷区滑坡类型、成因及分布规律——以子拖西―麻郎错河段为例[J/OL]. 中国地质,2022:1 − 16. (2022-08-22)[2024-01-29]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20220822.1358.014.html. [RAN Tao,XU Ruge,ZHOU Hongfu,et al. Type, formation mechanism and distribution regularity of landslides in the deeply-incised valley area of Yalong River Basin:A case study of Zituoxi–Malangcuo River section[J/OL]. Geology in China,2022:1 − 16. (2022-08-22)[2024-01-29]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20220822.1358.014.html. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
RAN Tao, XU Ruge, ZHOU Hongfu, et al. Type, formation mechanism and distribution regularity of landslides in the deeply-incised valley area of Yalong River Basin: A case study of Zituoxi–Malangcuo River section[J/OL]. Geology in China, 2022: 1 − 16. (2022-08-22)[2024-01-29]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20220822.1358.014.html. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 刘帅,王涛,曹佳文,等. 基于优化随机森林模型的降雨群发滑坡易发性评价研究——以西秦岭极端降雨事件为例[J/OL]. 地质通报,2024:1 − 15. (2024-01-19)[2024-01-29]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.4648.P.20240118.1821.002.html. [LIU Shuai,WANG Tao,CAO Jiawen,et al. A case study on susceptibility assessment of precipitation-induced mass landslides based on optimal random forest model, West Qinling Mountains[J/OL]. Geological Bulletin of China,2024:1 − 15. (2024-01-19)[2024-01-29]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.4648.P.20240118.1821.002.html. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Shuai, WANG Tao, CAO Jiawen, et al. A case study on susceptibility assessment of precipitation-induced mass landslides based on optimal random forest model, West Qinling Mountains[J/OL]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2024: 1 − 15. (2024-01-19)[2024-01-29]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.4648.P.20240118.1821.002.html. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 罗阳华. 降雨作用下非饱和残积土坡渗流稳定分析[D]. 福州:福州大学,2016. [LUO Yanghua. Analysis of seepage and stability on unsaturated residual soil slope under rainfall[D]. Fuzhou:Fuzhou University,2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LUO Yanghua. Analysis of seepage and stability on unsaturated residual soil slope under rainfall[D]. Fuzhou: Fuzhou University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: