Analysis on characteristics and reactivation mechanism of secondary landslides in the front part of the Xijitan giant landslide, Guide Basin
-
摘要:
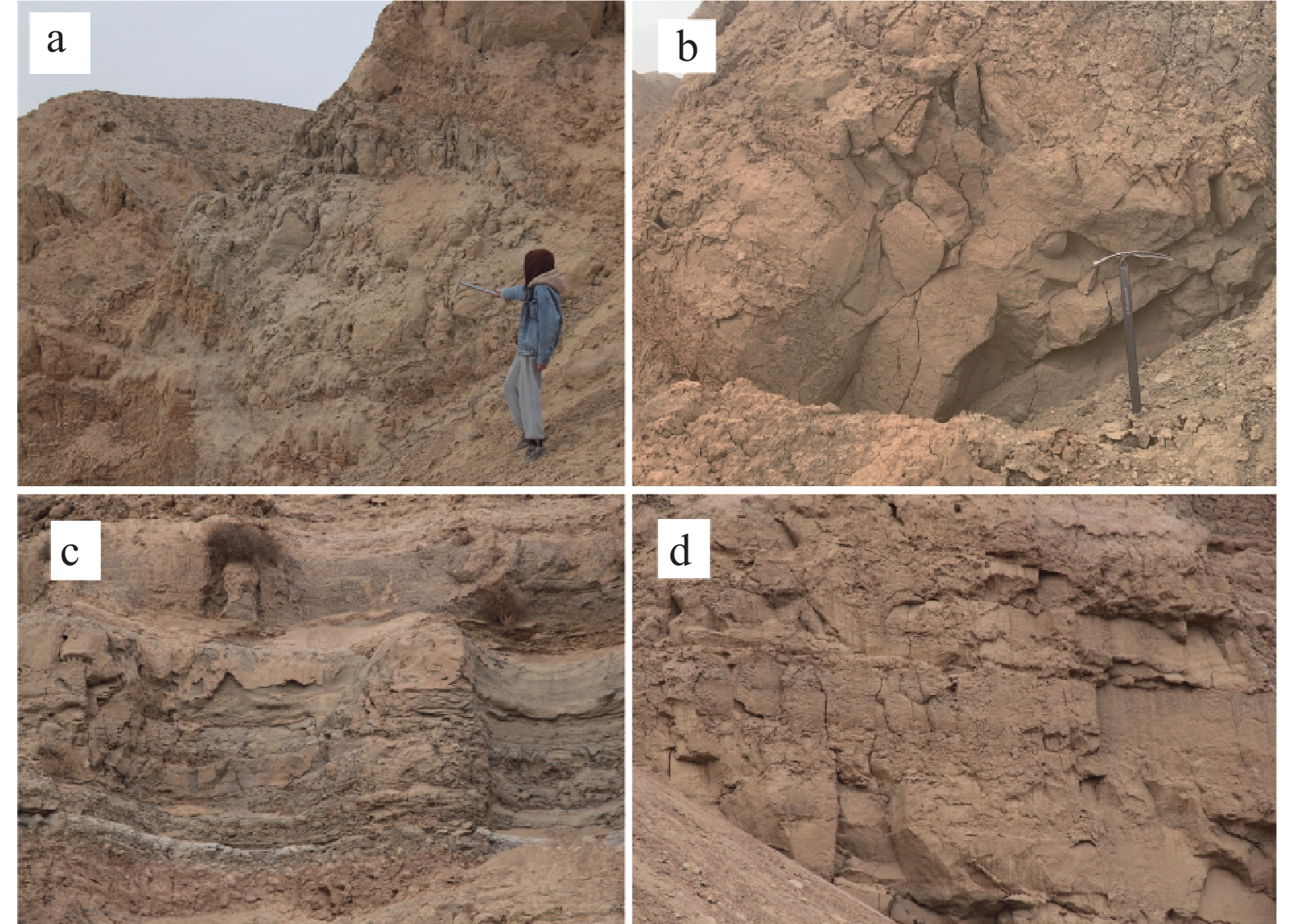
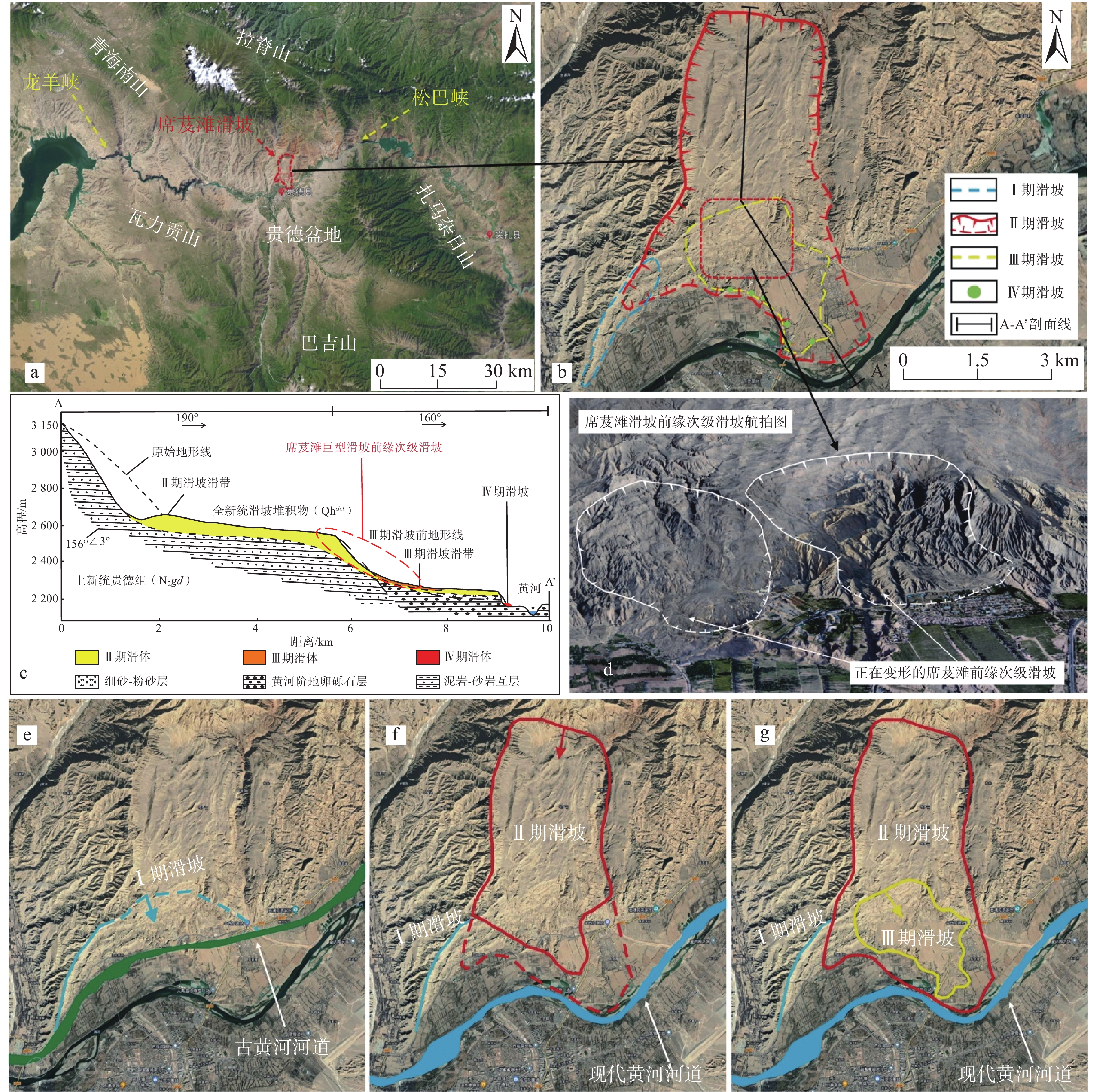
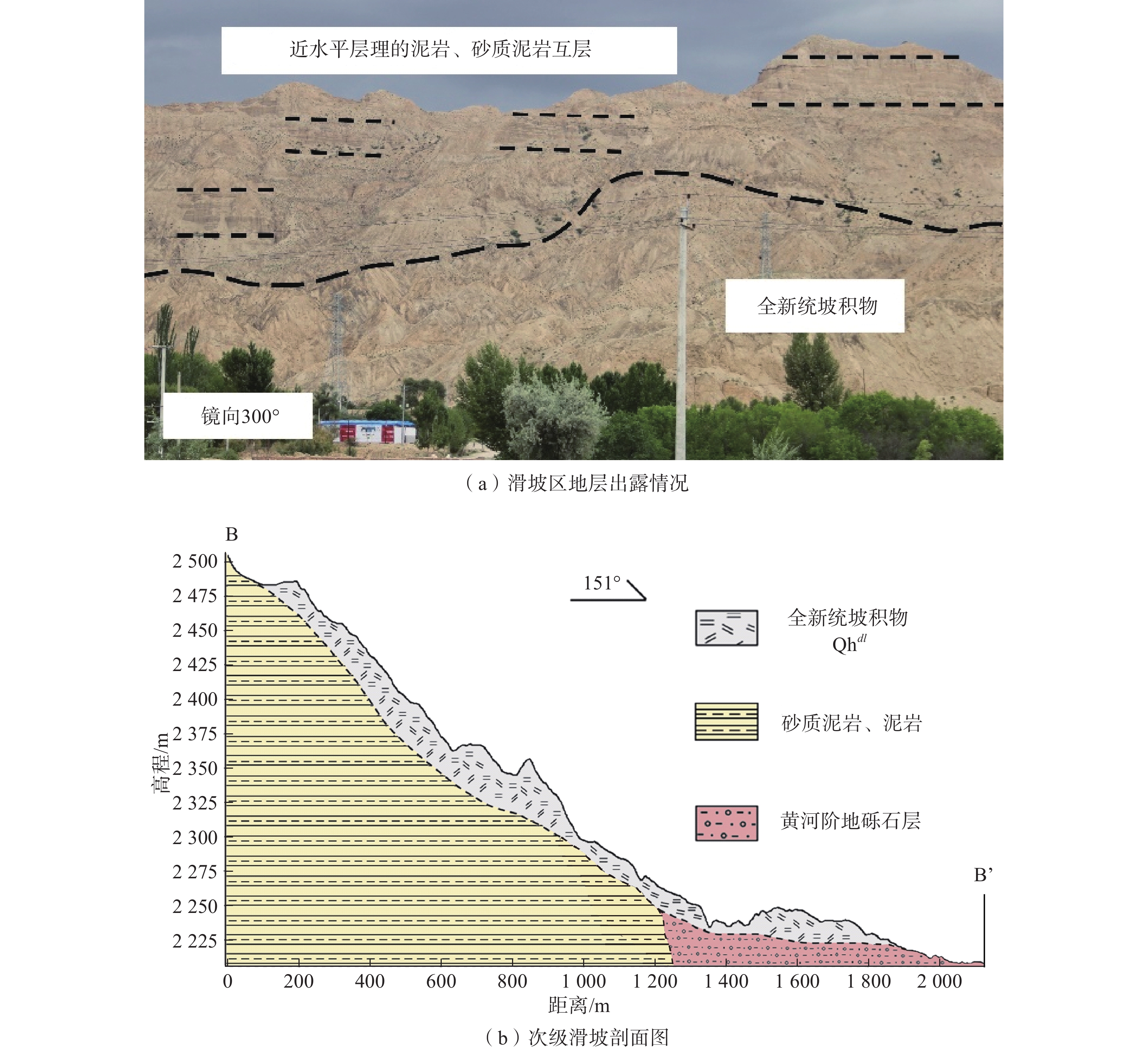
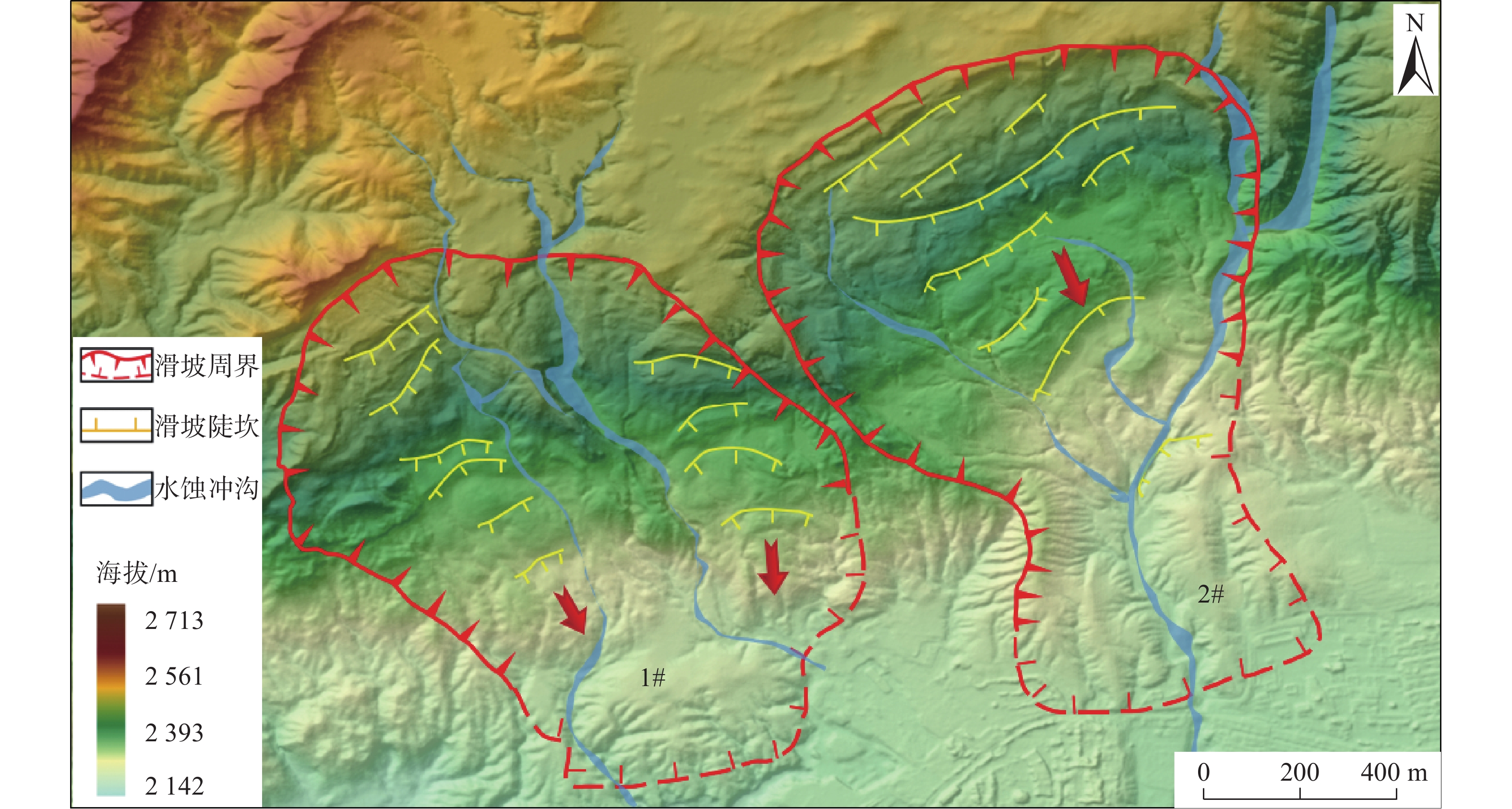
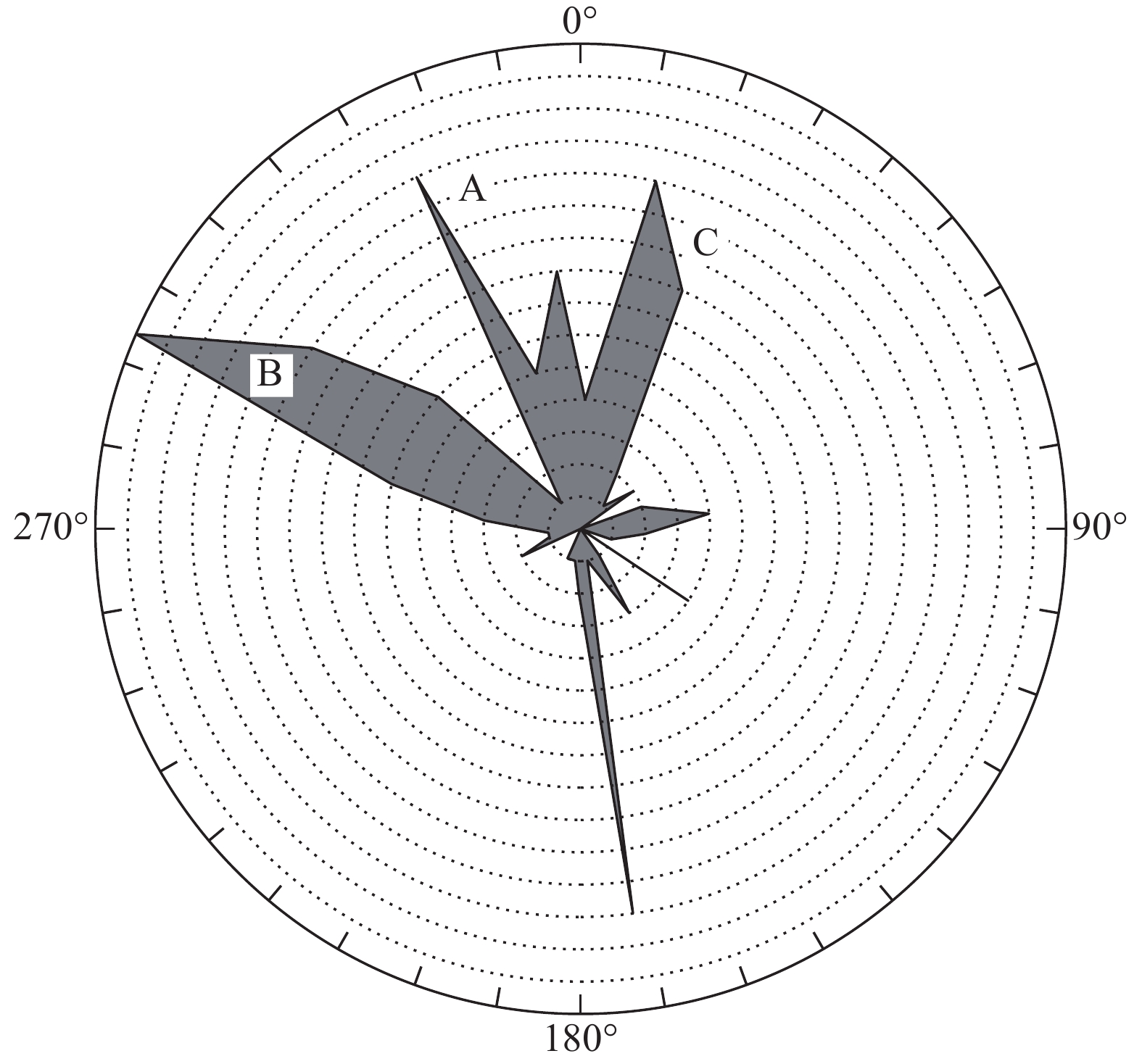
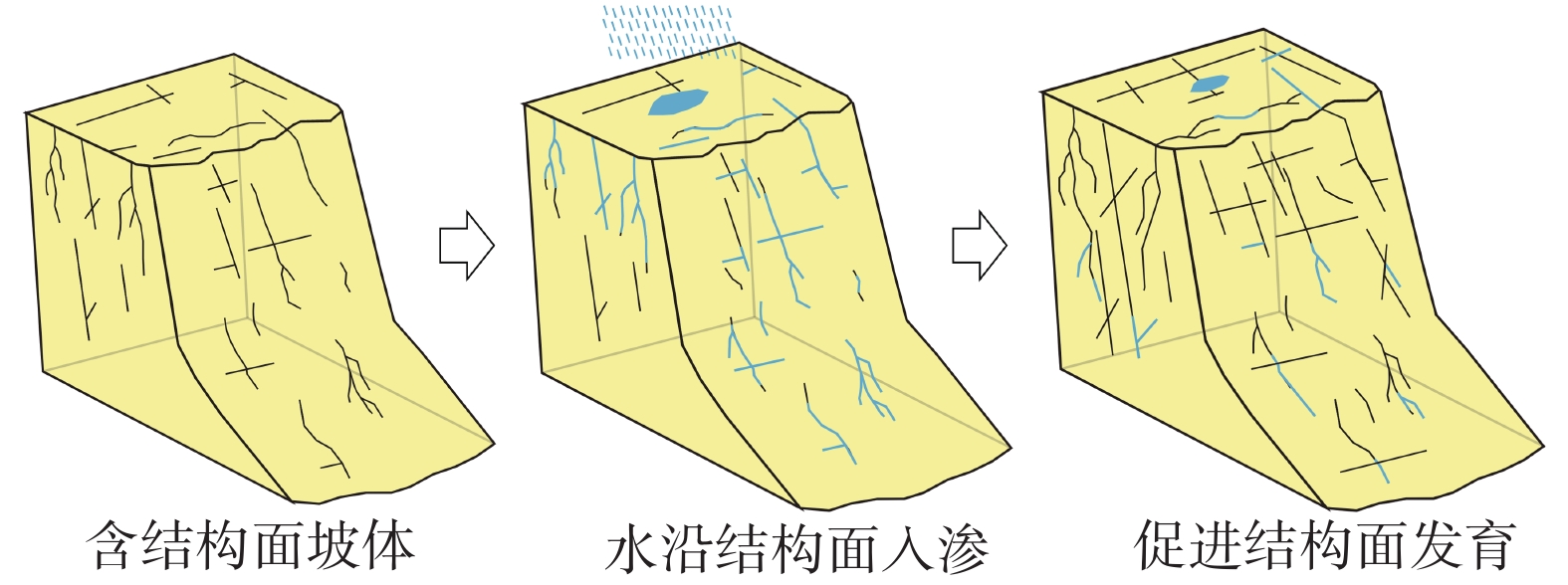
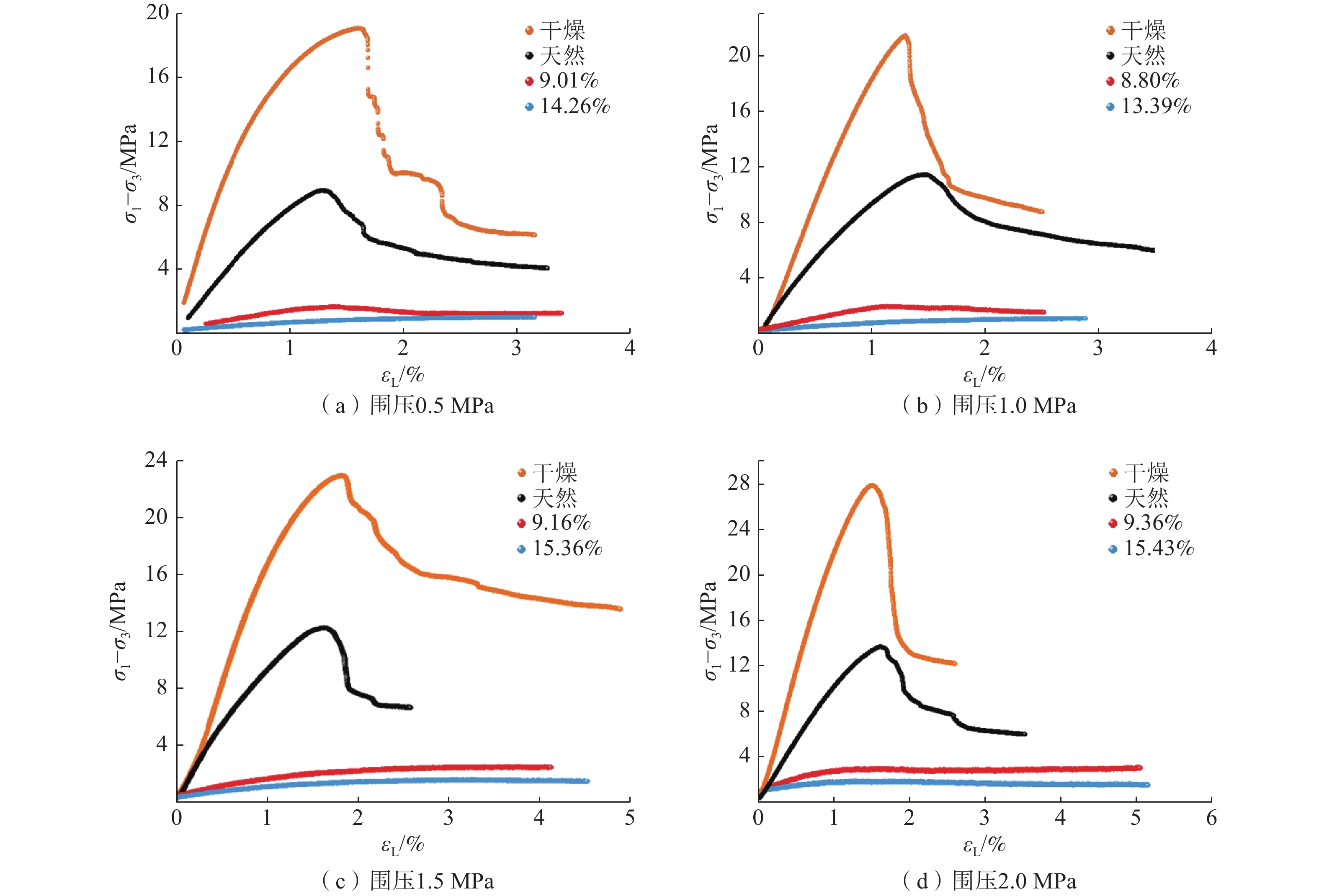
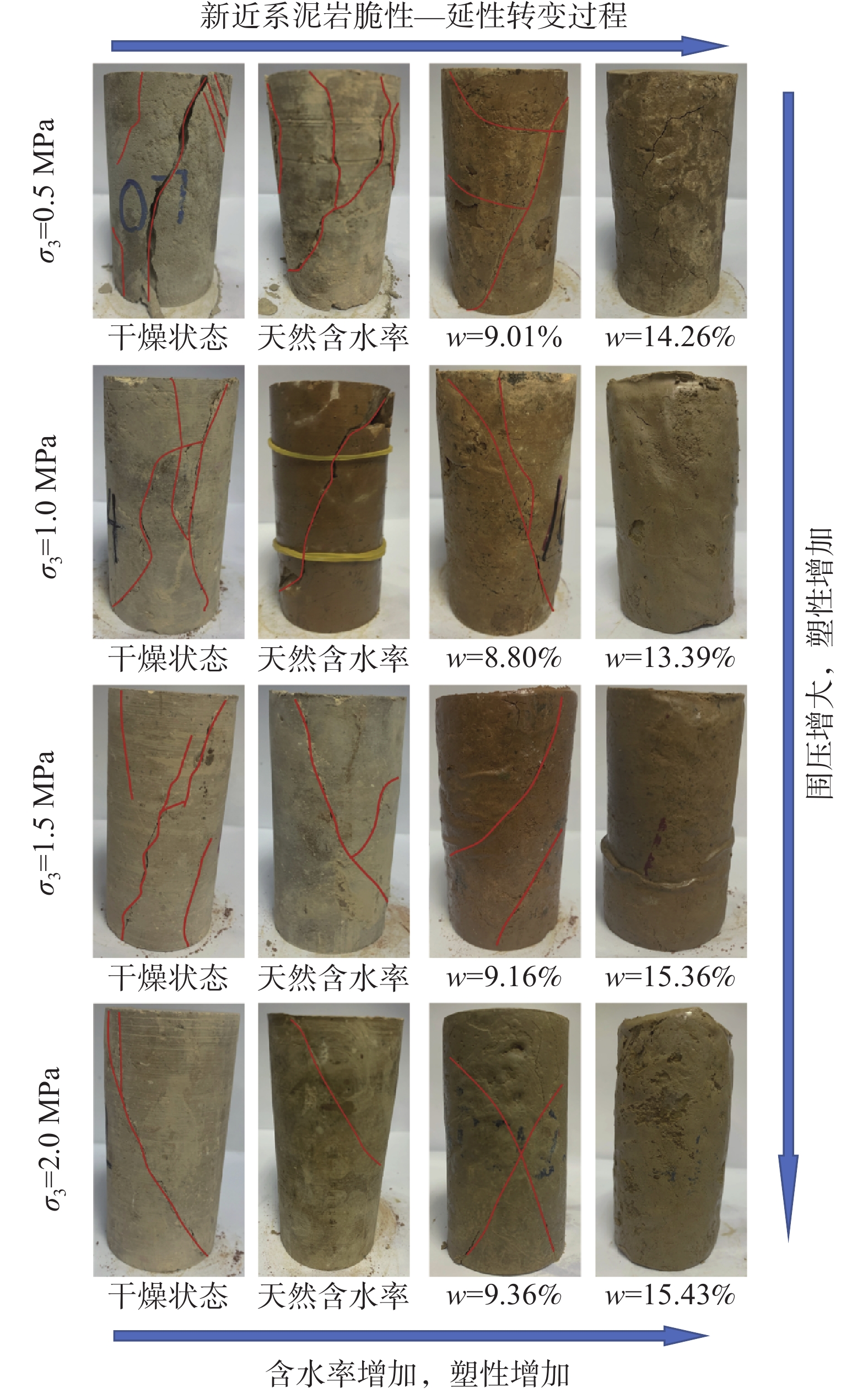
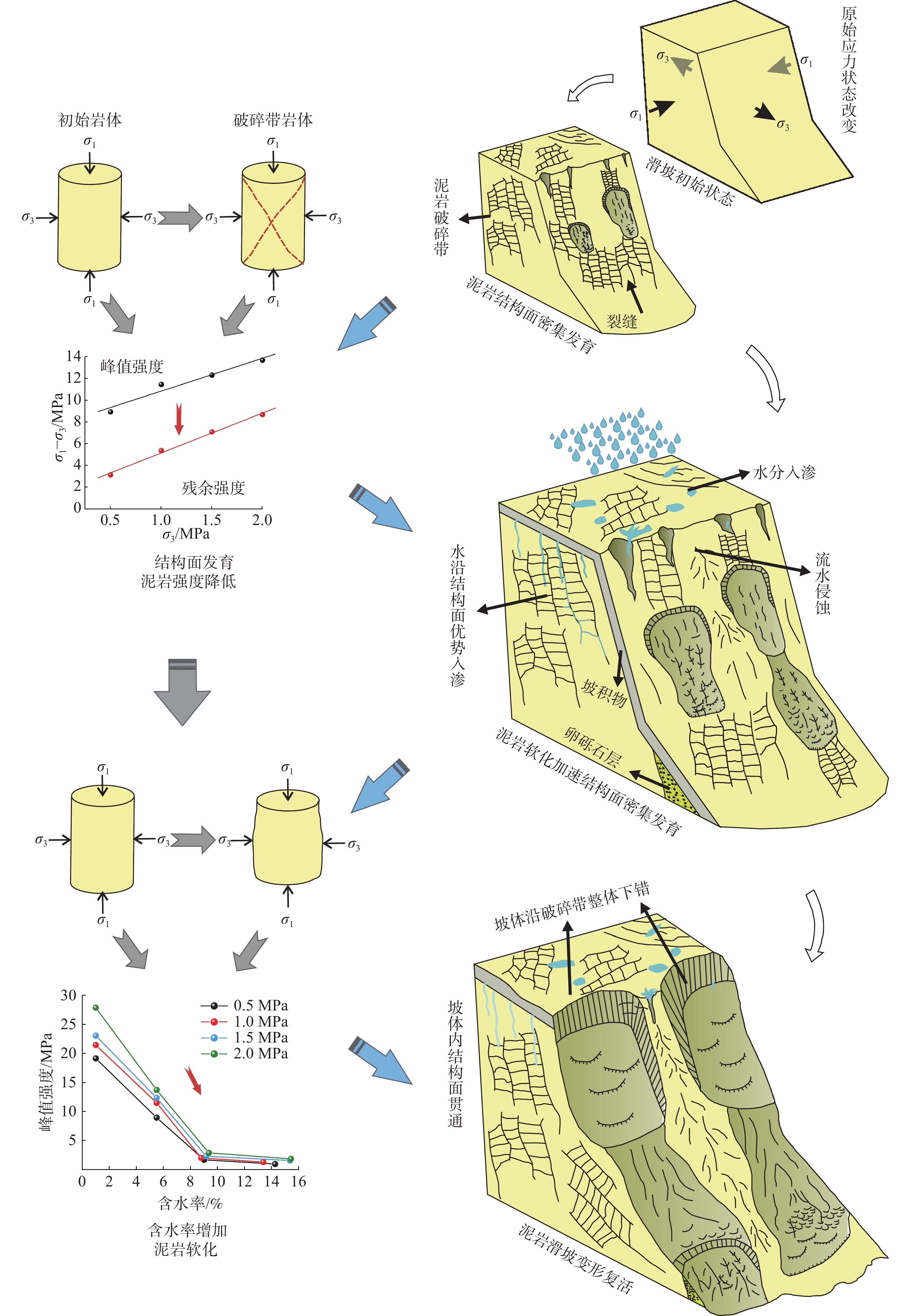
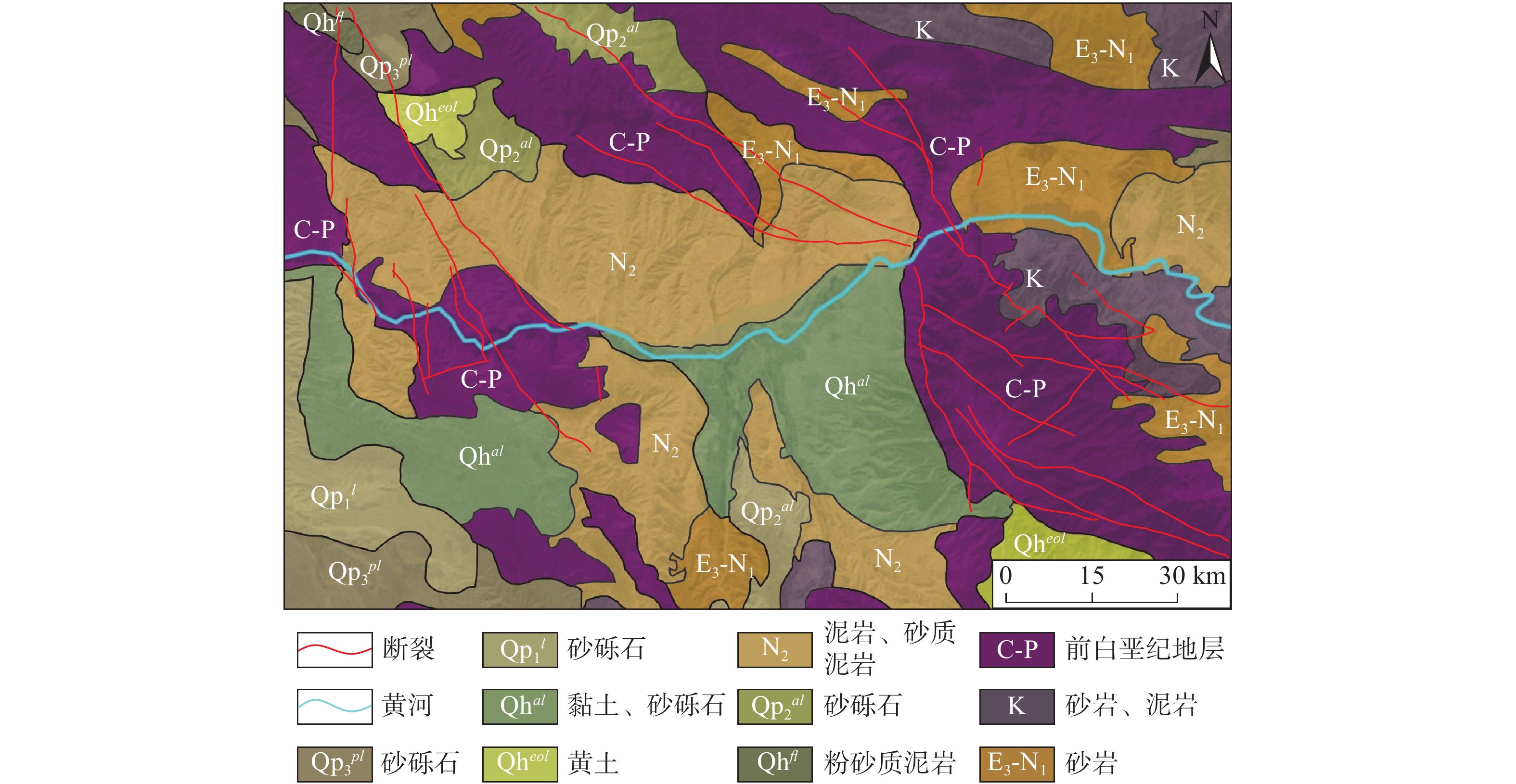
黄河上游地区位于构造活动剧烈的青藏高原东北缘,其复杂的地质条件孕育了大量的滑坡、崩塌等地质灾害。文章以青海省贵德县尕让乡江拉新村北席芨滩巨型滑坡前缘次级滑坡为研究对象,采用无人机航测、InSAR地表位移监测、现场调查和室内力学试验等手段,详细分析了滑坡的地质背景、发育特征和复活机制。现场调查发现:滑坡区岩体结构破碎疏松,主要出露地层岩性为新近系泥岩和全新统坡积物;次级滑坡后缘发育多条大型裂缝和张拉带,地表变形明显,处于蠕滑变形阶段;密集发育的结构面对次级滑坡的复活起到控制作用,集中降雨导致的泥岩软化是诱发滑坡复活的关键因素,二者的互馈作用会持续降低滑坡区岩体的完整度和强度,导致次级滑坡的变形复活。研究结果可为黄河上游地区防灾减灾工作提供理论基础。
Abstract:The upper reaches of the Yellow River, located on the northeastern edge of the tectonically active Qinghai Xizang Plateau, are characterized by complex geological conditions that have led to a high incidence of geological disasters such as landslides and collapses. This study focuses on the secondary landslide at the front part of the Xijitan landslide on the north side in Jiangla Village, Garang Township, Guide County, Qinghai Province. Using methods including unmanned aerial vehicle surveying, InSAR surface displacement monitoring, and on-site investigation methods, a detailed analysis of the geological environmental conditions, development characteristics, and reactivation mechanism of the landslide are conducted. On-site investigation results indicate that the rock mass structure in the landslide area is fragmented, with concentrated rainfall. The main exposed strata are Neogene mudstone and Holocene slope deposits. Multiple large cracks and tension bands are developed at the rear edge of the landslide, and the surface deformation is obvious, in the stage of creep deformation. Analysis of the mechanism of landslide reactivation reveals that densely developed structures play a controlling role in the reactivation of secondary landslides, and the softening of mudstone caused by concentrated rainfall is a key factor in inducing landslide reactivation. The interaction between two factors continuously reduce the integrity and strength of the rock mass, leading to the deformation and reactivation of secondary landslides. The research results aim to provide a theoretical basis for disaster prevention and reduction work in the upper reaches of the Yellow River.
-

-
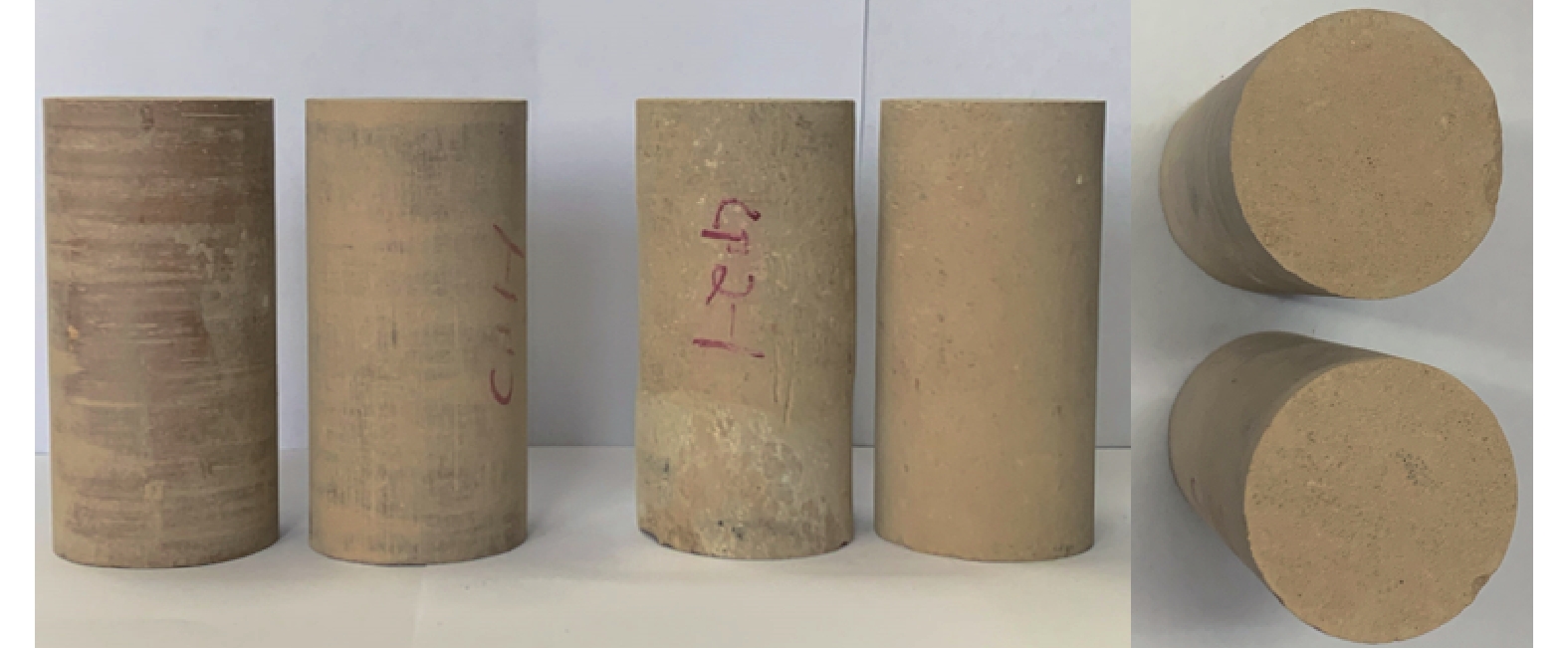
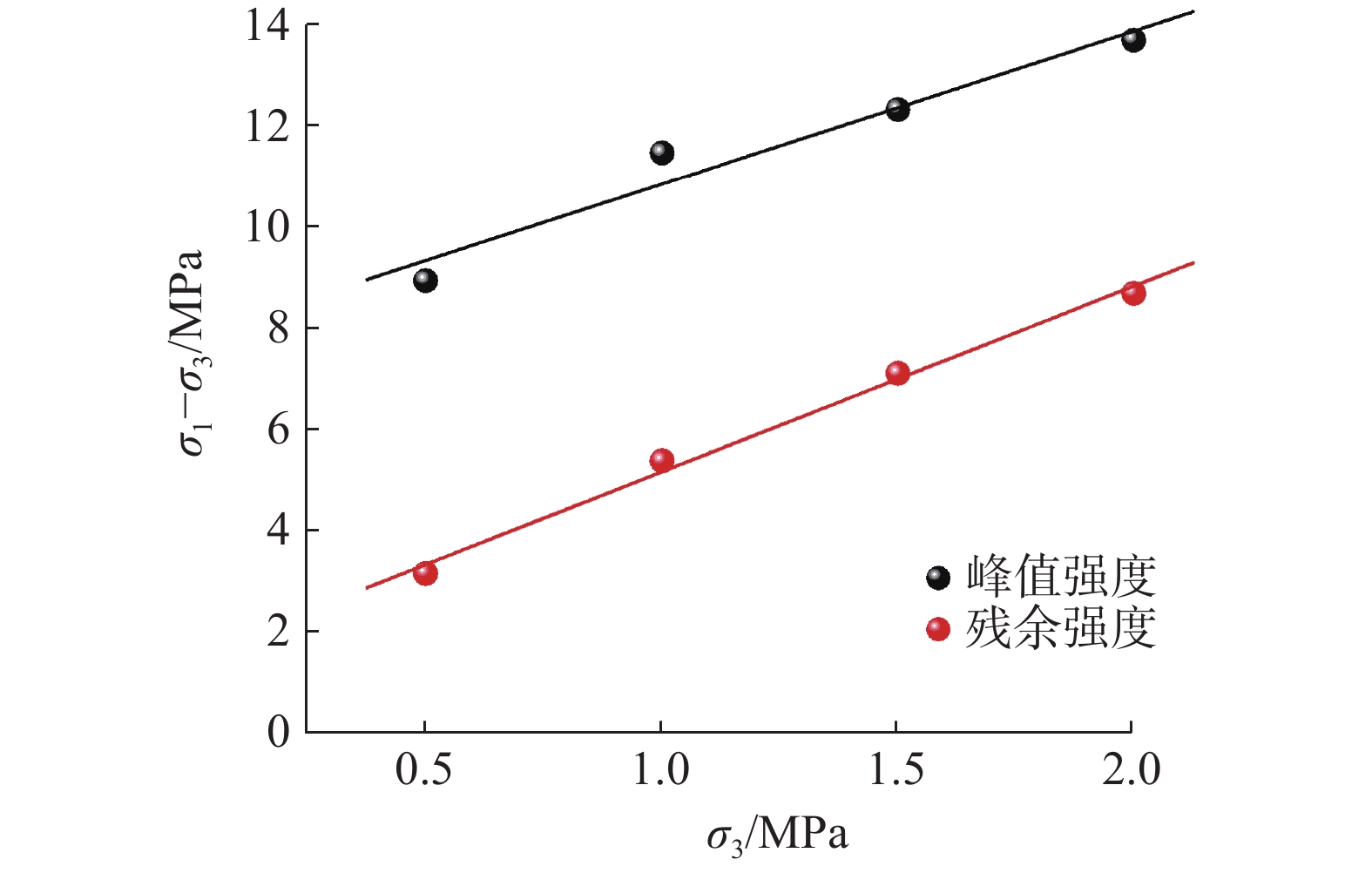
表 1 泥岩峰值强度和残余强度拟合参数
Table 1. Fitting parameters for peak strength and residual strength of mudstone
a b R2 峰值强度 3.028 ± 0.479 7.835 ± 0.656 0.9523 残余强度 3.663 ± 0.209 1.517 ± 0.287 0.9935 -
[1] 殷跃平, 高少华. 高位远程地质灾害研究: 回顾与展望[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2024,35(1):1 − 18. [YIN Yueping, GAO Shaohua. Research on high-altitude and long-runout rockslides: review and prospects[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2024,35(1):1 − 18. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YIN Yueping, GAO Shaohua. Research on high-altitude and long-runout rockslides: review and prospects[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2024, 35(1): 1 − 18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 兰恒星,彭建兵,祝艳波,等. 黄河流域地质地表过程与重大灾害效应研究与展望[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,2022,52(2):199 − 221. [LAN Hengxing,PENG Jianbing,ZHU Yanbo,et al. Research and prospect of geological surface processes and major disaster effects in the Yellow River Basin[J]. Science Chinese:Earth Science,2022,52(2):199 − 221. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LAN Hengxing, PENG Jianbing, ZHU Yanbo, et al. Research and prospect of geological surface processes and major disaster effects in the Yellow River Basin[J]. Science Chinese: Earth Science, 2022, 52(2): 199 − 221. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] YIN Z,QIN X,YIN Y,et al. Landslide developmental characteristics and response to climate change since the last glacial in the upper reaches of the Yellow River,NE Xizang Plateau[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica‐English Edition,2014,88(2):635 − 646. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12219
[4] 胡贵寿. 青海省特大型滑坡发育分布规律[D]. 北京:中国地质大学,2013. [HU Guishou. Development and distribution patterns of large-scale landslides in Qinghai Province [D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences,2013 (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HU Guishou. Development and distribution patterns of large-scale landslides in Qinghai Province [D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2013 (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 崔之久,伍永秋,刘耕年,等. 关于“昆仑-黄河运动”[J]. 中国科学(D辑),1998,28(1):53 − 59. [CUI Zhijiu,WU Yongqiu,LIU Gengnian,et al. On the Kunlun Yellow River Movement[J]. Science In Chinese (Series D),1998,28(1):53 − 59. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CUI Zhijiu, WU Yongqiu, LIU Gengnian, et al. On the Kunlun Yellow River Movement[J]. Science In Chinese (Series D), 1998, 28(1): 53 − 59. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 张春山. 黄河上游地区地质灾害形成条件与风险评价研究[D]. 北京:中国地质科学院,2003. [ZHANG Chunshan. Study on the formation conditions and risk assessment about geological hazards in the upper reaches of the Yellow River [D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences,2003. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Chunshan. Study on the formation conditions and risk assessment about geological hazards in the upper reaches of the Yellow River [D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2003. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 贾润幸,方维萱,张建国,等. 山西清徐——太谷地区地裂缝形成机理[J]. 地质通报,2022,41(7):1282 − 1290. [JIA Runxing,FANG Weixuan,ZHANG Jianguo,et al. The formation mechanism of ground fissures in the Qingxu Taigu area of Shanxi Province[J]. Geolgical Bulletin of China,2022,41(7):1282 − 1290. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
JIA Runxing, FANG Weixuan, ZHANG Jianguo, et al. The formation mechanism of ground fissures in the Qingxu Taigu area of Shanxi Province[J]. Geolgical Bulletin of China, 2022, 41(7): 1282 − 1290. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 范宣梅,方成勇,戴岚欣,等. 地震诱发滑坡空间分布概率近实时预测研究——以2022年6月1日四川芦山地震为例[J]. 工程地质学报,2022,30(3):729 − 739. [FAN Xuanmei,FANG Chengyong,DAI Lanxin,et al. Near real time prediction of spatial distribution probability of earthquake-induced landslides: Take the Lushan Earthquake on June 1,2022 as an example[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2022,30(3):729 − 739. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
FAN Xuanmei, FANG Chengyong, DAI Lanxin, et al. Near real time prediction of spatial distribution probability of earthquake-induced landslides: Take the Lushan Earthquake on June 1, 2022 as an example[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2022, 30(3): 729 − 739. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 殷跃平,王文沛,张楠,等. 强震区高位滑坡远程灾害特征研究——以四川茂县新磨滑坡为例[J]. 中国地质,2017,44(5):827 − 841. [YIN Yueping,WANG Wenpei,ZHANG Nan,et al. Long runout geological disaster initiated by the ridge-top rockslide in a strong earthquake area:A case study of the Xinmo landslide in Maoxian County,Sichuan Province[J] Geology in China,2017,44(5):827 − 841. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YIN Yueping, WANG Wenpei, ZHANG Nan, et al. Long runout geological disaster initiated by the ridge-top rockslide in a strong earthquake area: A case study of the Xinmo landslide in Maoxian County, Sichuan Province[J] Geology in China, 2017, 44(5): 827 − 841. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 杨琴,范宣梅,许强,等. 北川唐家湾滑坡变形历史与形成机制研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(2):136 − 141. [YANG Qin,FAN Xuanmei,XU Qiang,et al. A study of the deformation history and mechanism of the Tangjiawan landslide[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(5):827 − 841. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YANG Qin, FAN Xuanmei, XU Qiang, et al. A study of the deformation history and mechanism of the Tangjiawan landslide[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2017, 44(5): 827 − 841. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] CHEN G,JIN JC,MENG X,et al. Influence of tectonic effects on the formation and characteristics of landslide dams on the NE Xizang Plateau:A case study in the Bailong River Basin,China[J]. Landslides,2024:1 − 19.
[12] YU H,LI A,et al. "Present-day crustal deformation and strain transfer in northeastern Xizang Plateau[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,487(2018):179 − 189.
[13] 周保,马涛,魏正发,等. 黄河上游曲哇加萨滑坡“9•20”动力学过程模拟与分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(2):9 − 15. [ZHOU Bao,MA Tao,WEI Zhengfai,et al. Dynamic simulation and analysis of “9•20” sliding process of Quwajiasa landslide in the upper reaches of Yellow River[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(2):9 − 15. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHOU Bao, MA Tao, WEI Zhengfai, et al. Dynamic simulation and analysis of “9•20” sliding process of Quwajiasa landslide in the upper reaches of Yellow River[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(2): 9 − 15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 魏刚,殷志强,马吉福,等. 黄河上游阿什贡滑坡群发育期次及演化过程分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(6):133 − 140. [WEI Gang,YIN Zhiqiang,MA Jifu,et al. An analysis of forming stages and evolution process of the Ashigong landslide cluster in the upper reaches of the Yellow River[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016,43(6):133 − 140. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WEI Gang, YIN Zhiqiang, MA Jifu, et al. An analysis of forming stages and evolution process of the Ashigong landslide cluster in the upper reaches of the Yellow River[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2016, 43(6): 133 − 140. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 李小林,郭小花,李万花. 黄河上游龙羊峡—刘家峡河段巨型滑坡形成机理分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2011,19(4):516 − 529. [LI Xiaolin,GUO Xiaohua,LI Wanhua. Mechanism of giant landslides from Longyangxia Vally to Liujiaxia Vally along upper Yellow River[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2011,19(4):516 − 529. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2011.04.013
LI Xiaolin, GUO Xiaohua, LI Wanhua. Mechanism of giant landslides from Longyangxia Vally to Liujiaxia Vally along upper Yellow River[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2011, 19(4): 516 − 529. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2011.04.013
[16] 张永双,杜国梁,姚鑫,等. 塔吉克斯坦MS7.2级地震滑坡危险性快速评估及其对中国西部边疆山区巨灾风险防控的启示[J]. 地质学报,2023,97(5):1371 − 1382. [ZHANG Yongshuang,DU Guoliang,YAO Xin,et al. Rapid assessment of landslide risk during the MS7.2 earthquake in Tajikistan inspiration on disaster risk prevention and control in the mountainous regions of western China's border regions[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2023,97(5):1371 − 1382. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2023.05.001
ZHANG Yongshuang, DU Guoliang, YAO Xin, et al. Rapid assessment of landslide risk during the MS7.2 earthquake in Tajikistan inspiration on disaster risk prevention and control in the mountainous regions of western China's border regions[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2023, 97(5): 1371 − 1382. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2023.05.001
[17] 邓威,肖世国. 含裂隙近水平红层软岩边坡渗透稳定性模型试验[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2024,51(1):57 − 68. [DENG Wei,XIAO Shiguo. Model test on stability of soft rock slopes composed of nearly horizontal redbeds with cracks[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2024,51(1):57 − 68. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
DENG Wei, XIAO Shiguo. Model test on stability of soft rock slopes composed of nearly horizontal redbeds with cracks[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2024, 51(1): 57 − 68. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 刘建强,许强,郑光,等. 贵州省鸡场滑坡地下水化学特征反映的水-岩(土)作用[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(2):132 − 140. [LIU Jianqiang,XU Qiang,ZHENG Guang,et al. Water-rock /soil interaction reflected by the chemical characteristics of groundwater of Jichang landslide in Guizhou Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(2):132 − 140. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Jianqiang, XU Qiang, ZHENG Guang, et al. Water-rock /soil interaction reflected by the chemical characteristics of groundwater of Jichang landslide in Guizhou Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(2): 132 − 140. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] KONG Lingwei,ZENG Zhixiong,BAI Wei,et al. Engineering geological properties of weathered swelling mudstones and their effects on the landslides occurrence in the Yanji section of the Jilin-Hunchun high-speed railway[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2018,77(4):1491 − 1503. doi: 10.1007/s10064-017-1096-2
[20] ZHOU Zhe,CHEN Shanxiong,WANG Yinhui,et al. Crack evolution characteristics and cracking mechanism of red beds in central Sichuan during seepage and swelling[J]. Geofluids,2021,Article ID 9981046:1 − 19.
[21] WANG H J,SUN P,ZHANG S,et al. Rainfall-induced landslide in loess area,Northwest China:A case study of the Changhe landslide on September 14,2019,in Gansu Province[J]. Landslides,2020,17(9):2145 − 2160 doi: 10.1007/s10346-020-01460-0
[22] LIU Y J,CHIU Y Y,TSAI F T C,et al. Analysis of landslide occurrence time via rainfall intensity and soil water index ternary diagram[J]. Landslides,2022,19(12):2823 − 2837. doi: 10.1007/s10346-022-01944-1
[23] 魏刚,殷志强,罗银飞,等. 黄河上游康杨滑坡堆积体特征及形成机理分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(2):1 − 8. [WEI Gang,YIN Zhiqiang,LUO Yinfei,et al. Analysis on the accumulation deposits characteristics and formation mechanism of Kangyang landslide in the upper reaches of Yellow River[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(2):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WEI Gang, YIN Zhiqiang, LUO Yinfei, et al. Analysis on the accumulation deposits characteristics and formation mechanism of Kangyang landslide in the upper reaches of Yellow River[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(2): 1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] CHEN L,YANG H,SONG K,et al. Failure mechanisms and characteristics of the Zhongbao landslide at Liujing Village,Wulong,China[J]. Landslides,2021,18(4):1445 − 1457. doi: 10.1007/s10346-020-01594-1
[25] 万飞鹏,杨为民,邱占林,等. 甘肃岷县纳古呢沟滑坡-泥石流灾害链成灾机制及其演化[J]. 中国地质,2023,50(3):911 − 925. [WAN Feipeng,YANG Weimin,QIU Zhanlin,et al. Disaster mechanism and evolution of Nagune Gully landslide-debris flow disaster chain in Minxian County,Gansu Province[J]. Geology in China,2023,50(3):911 − 925. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WAN Feipeng, YANG Weimin, QIU Zhanlin, et al. Disaster mechanism and evolution of Nagune Gully landslide-debris flow disaster chain in Minxian County, Gansu Province[J]. Geology in China, 2023, 50(3): 911 − 925. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] GRABER A,SANTI P,MEZA Arestegui P. Constraining the critical groundwater conditions for initiation of large,irrigation-induced landslides,Siguas River Valley,Peru[J]. Landslides,2021,18(12):3753 − 3767. doi: 10.1007/s10346-021-01767-6
[27] 史立群,魏刚,殷志强,等. 青海尖扎盆地寺门村滑坡发育特征及成因分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(5):15 − 21. [SHI Liqun,WEI Gang,YIN Zhiqiang,et al. Characteristics and formation of Simencun landslides in Jianzha Basin of Qinghai Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(5):15 − 21. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
SHI Liqun, WEI Gang, YIN Zhiqiang, et al. Characteristics and formation of Simencun landslides in Jianzha Basin of Qinghai Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(5): 15 − 21. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 冉林,马鹏辉,彭建兵,等. 甘肃黑方台“10•5”黄土滑坡启动及运动特征分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(6):1 − 9. [RAN Lin,MA Penghui,PENG Jianbing,et al. The initiation and motion characteristics of the “10•5” loess landslide in the Heifangtai platform,Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(6):1 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
RAN Lin, MA Penghui, PENG Jianbing, et al. The initiation and motion characteristics of the “10•5” loess landslide in the Heifangtai platform, Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(6): 1 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 潘保田. 贵德盆地地貌演化与黄河上游发育研究[J]. 干旱区地理,1994(3):43 − 50. [PAN Baotian. Study on the landform evolution of the Guide Basin and the development of the upper Yellow River[J]. Arid Area Geography,1994(3):43 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.13826/j.cnki.cn65-1103/x.1994.03.006.
PAN Baotian. Study on the landform evolution of the Guide Basin and the development of the upper Yellow River[J]. Arid Area Geography, 1994(3): 43 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13826/j.cnki.cn65-1103/x.1994.03.006.
[30] 赵无忌,殷志强,马吉福,等. 黄河上游贵德盆地席芨滩巨型滑坡发育特征及地貌演化[J]. 地质论评,2016,62(3):709 − 721. [ZHAO Wuji,YIN Zhiqiang,MA Jifu,et al. Development characteristics and geomorphological evolution of the Xijitan giant landslide in the Guide Basin of the Upper Yellow River[J]. Geological Review,2016,62(3):709 − 721. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2016.03.013.
ZHAO Wuji, YIN Zhiqiang, MA Jifu, et al. Development characteristics and geomorphological evolution of the Xijitan giant landslide in the Guide Basin of the Upper Yellow River[J]. Geological Review, 2016, 62(3): 709 − 721. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2016.03.013.
[31] 赵无忌. 黄河上游贵德盆地滑坡泥石流扇发育特征及地貌演化过程[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2015. [ZHAO Wuji. The formation characteristics and geomorphical evolution of the landslides and debris flow fans in Guide Basin,the upper Yellow River [D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing),2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHAO Wuji. The formation characteristics and geomorphical evolution of the landslides and debris flow fans in Guide Basin, the upper Yellow River [D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] CRADDOCK W H, KIRBY E, HARKINS N W, et al. Rapid fluvial incision along the Yellow River during headward basin integration[J]. Nature Geoscience,2010(3):209 − 213.
[33] ZHANG H, ZHANG P, CHAMPAGNAC J D, et al. Pleistocene drainage reorganization driven by the isostatic response to deep incision into the northeastern Xizang Plateau[J]. Geology, 2014, 42(4): 303-306.
[34] 周保. 黄河上游(拉干峡—寺沟峡段)特大型滑坡发育特征与群发机理研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2010. [ZHOU Bao. Study on the development characteristics and mass mechanism of super-large landslide in the upper reaches of the Yellow River (Laganxia-Sigouxia section)[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHOU Bao. Study on the development characteristics and mass mechanism of super-large landslide in the upper reaches of the Yellow River (Laganxia-Sigouxia section)[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[35] National Earth System Science Data Center,National Science & Technology Infrastructure of China (http://www.geodata.cn).
[36] 刘佑荣,唐辉明. 岩体力学[M]. 北京:化学工业出版社,2009. [LIU Yourong,TANG Huiming. Rock mass mechanics[M]. Beijing:Chemical Industry Press,2009. (in Chinese)]
LIU Yourong, TANG Huiming. Rock mass mechanics[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2009. (in Chinese)
-



 下载:
下载: