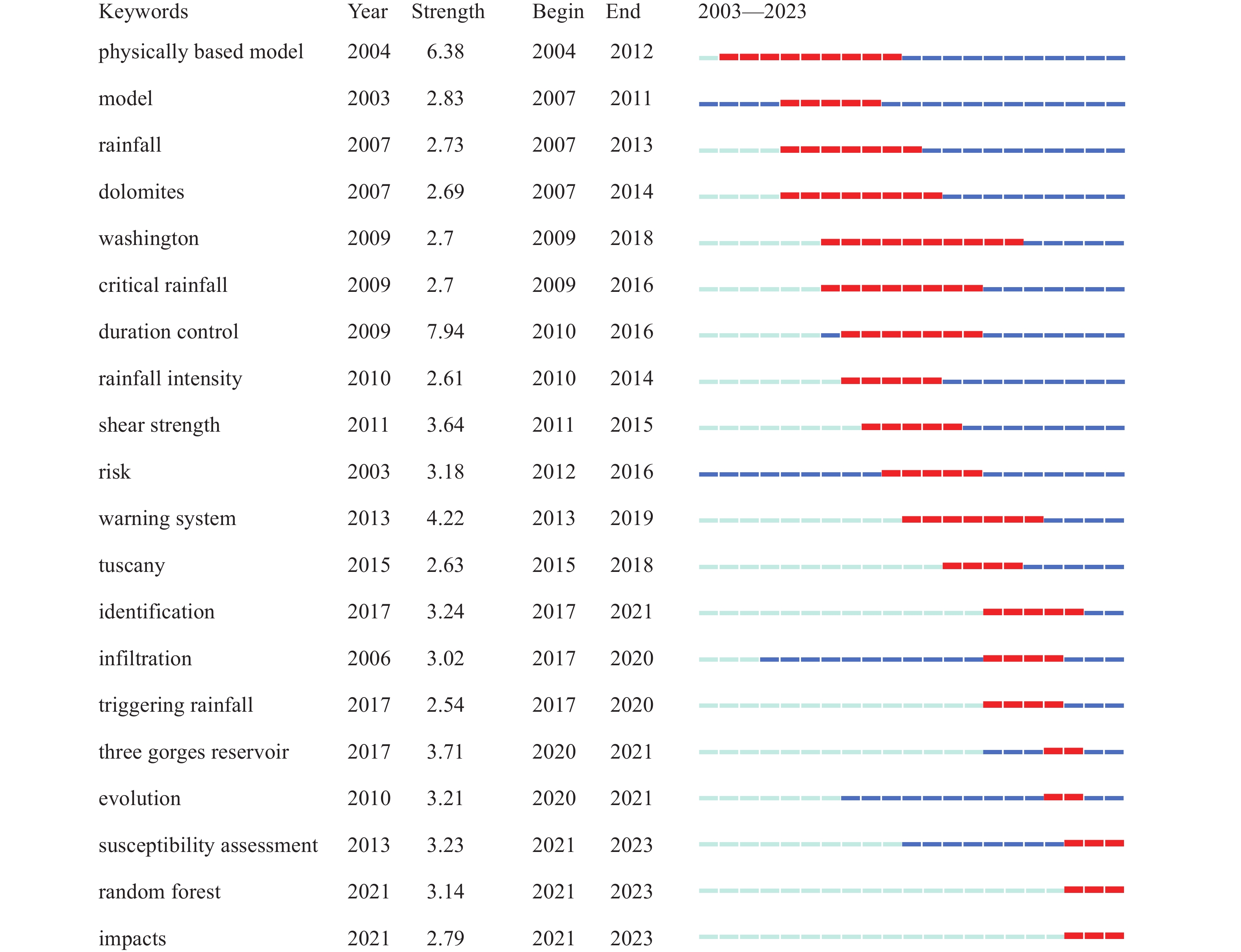
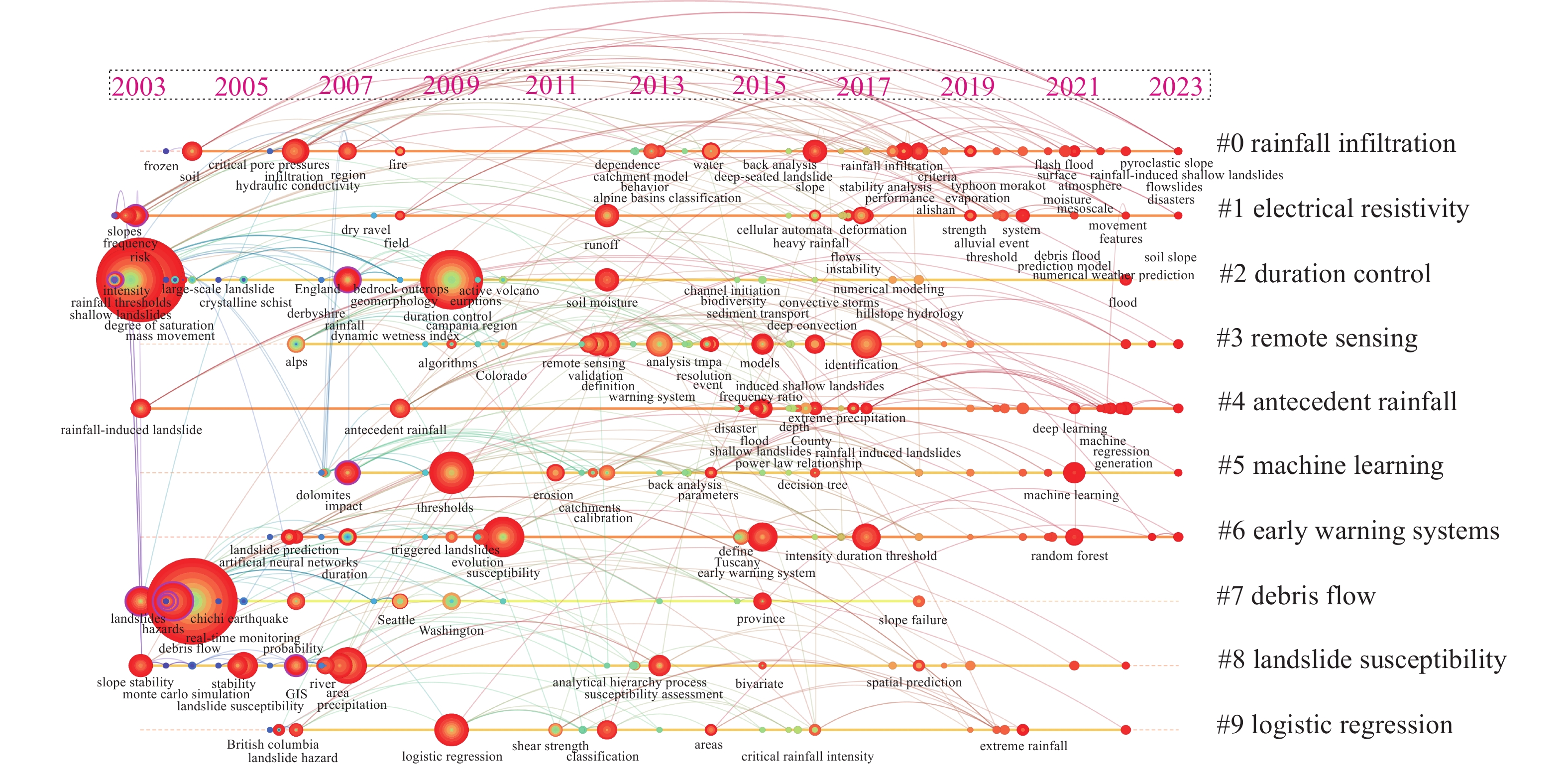
Visualization analysis of research literature on early warning of geo-hazards based on meteorological factors in the past 20 years
-
摘要:
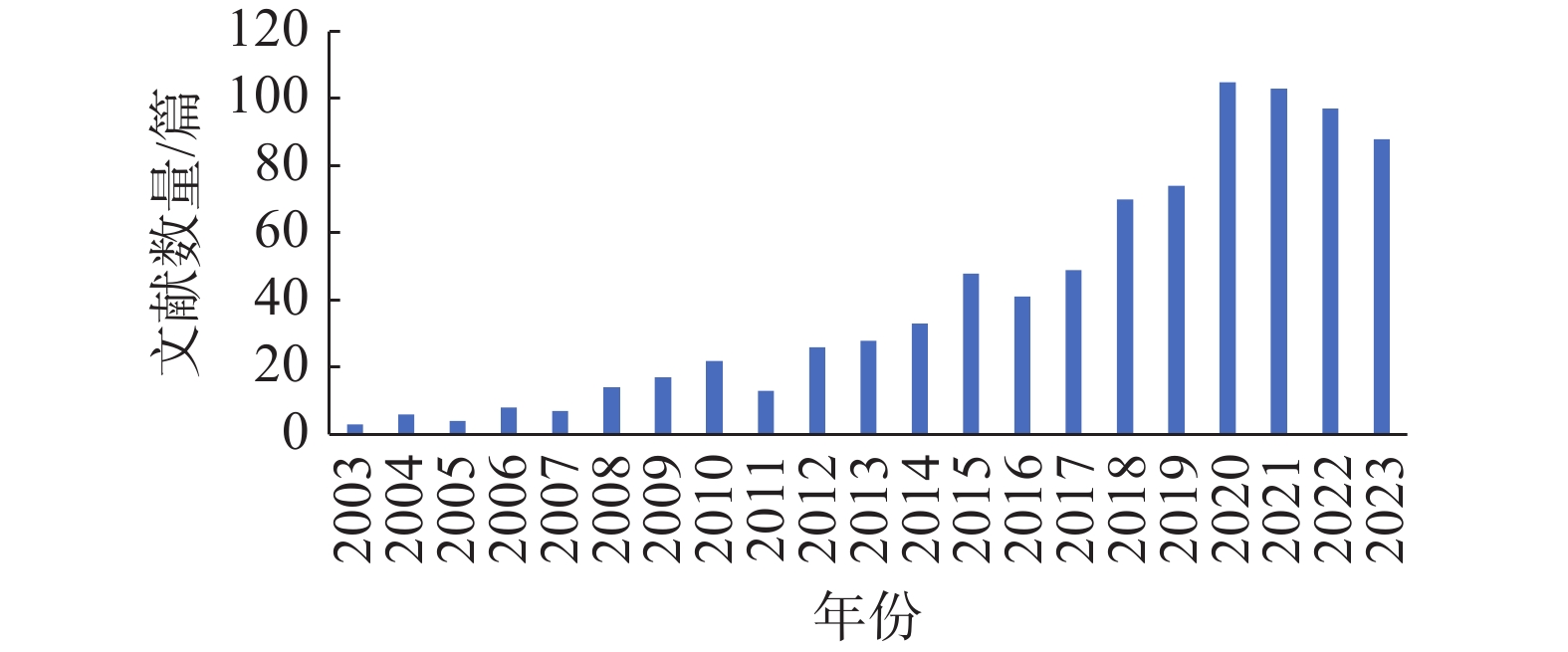
中国地质灾害气象预警始于 2003 年,每年汛期向公众发布预警信息,警示群众注意防范降雨引发的崩塌滑坡泥石流等地质灾害。为了更深入了解地质灾害气象风险预警研究的现状和未来趋势,以中国知网及SCI-Expanded国内外数据库作为数据来源,采用可视化工具CiteSpace,梳理了2003—2023年发表的国内外地质灾害气象风险预警文献,绘制科学知识图谱,分别从研究主题、演进趋势和研究热点进行多维度分析。结果表明:(1)基于历史降雨及灾害关系的临界降雨阈值研究在地质灾害气象风险预警研究中处于主导地位,与降雨相关阈值研究在未来仍将是研究热点;(2)关键词聚类分析显示不同地质灾害形成条件、气象条件下,不同类型、成因模式的地质灾害发生的预警预报模型、临界阈值研究文献占比较高,表明精细化是地质灾害气象风险预警发展的重要方向;(3)在国际上,中国学者发文量占总发文量的39%,我国在地质灾害气象风险预警研究中有绝对优势。研究结果较客观地展示了中国地质灾害气象风险预警研究的发展脉络和国内外研究热点及趋势,以期有助于我国地质灾害研究与预警预报业务进步。
Abstract:Early warning of geo-hazards based on meteorological factors in China began in 2003, and early warning informations are issued to the public every year during the flood season to alert the public to guard against geo-hazards such as landslides, debris flows, and mudslides caused by rainfall. To better understand the current situation and future trends of research for early warning of geo-hazards based on meteorological factors, the visualization tool CiteSpace was utilized to review the domestic and foreign literature on geo-hazards meteorological risk warning published from 2003 to 2023 and construct the scientific knowledge map. The CNKI database and SCI-Expanded databases were used as data sources. The result show that: (1) The study of critical rainfall thresholds based on the relationship between historical rainfall and disaster is in the leading position in research on early warning of geo-hazards based on meteorological factors, and the study of rainfall-related thresholds will continue to be a research hotspot in the future. (2) Keyword cluster analysis shows that a large number of studies have conducted research on early warning and prediction models and critical thresholds of geo-hazards under different formation conditions, meteorological conditions, different types, and genetic models, indicating that refinement is an important direction for the development of early warning of geo-hazards based on meteorological factors. (3) In the international research, Chinese scholars account for 39% of the total number of publications, showing an absolute advantage in research on geo-hazards meteorological risk early warning. The research results objectively demonstrate the development context, domestic and foreign research hotspots, and trends of research on geo-hazards meteorological risk warning in China, aiming to contribute to the progress of geo-hazards research and early warning forcast business in China.
-
Key words:
- geo-hazards /
- early warning /
- bibliometrics /
- visual analysis /
- CiteSpace
-

-
表 1 数据来源
Table 1. Data sources
数据库 CNKI SCI-E 检索词汇 地质灾害、滑坡、泥石流、崩塌、降水阈值、降雨阈值、临界降水、临界雨量、有效雨量、降水、气象、预测、预警、预报 geologic* hazard*、geologic* disast*、geologic* calamit*、landslid* 、debrisflow*、collaps*、rockfall* 、avalanch*、warning*、threshold*、rainfall 、predict* 、forecast* 、warn* 时间范围 2003—2023 2003—2023 来源类别 EI 来源期刊、核心期刊、
CSCD、学位论文期刊 文献检索数量 1040 856 表 2 CNKI 数据库地质灾害气象风险预警研究高频关键词
Table 2. High-frequency keywords in research on early warning of geo-hazards based on meteorological factors in CNKI database
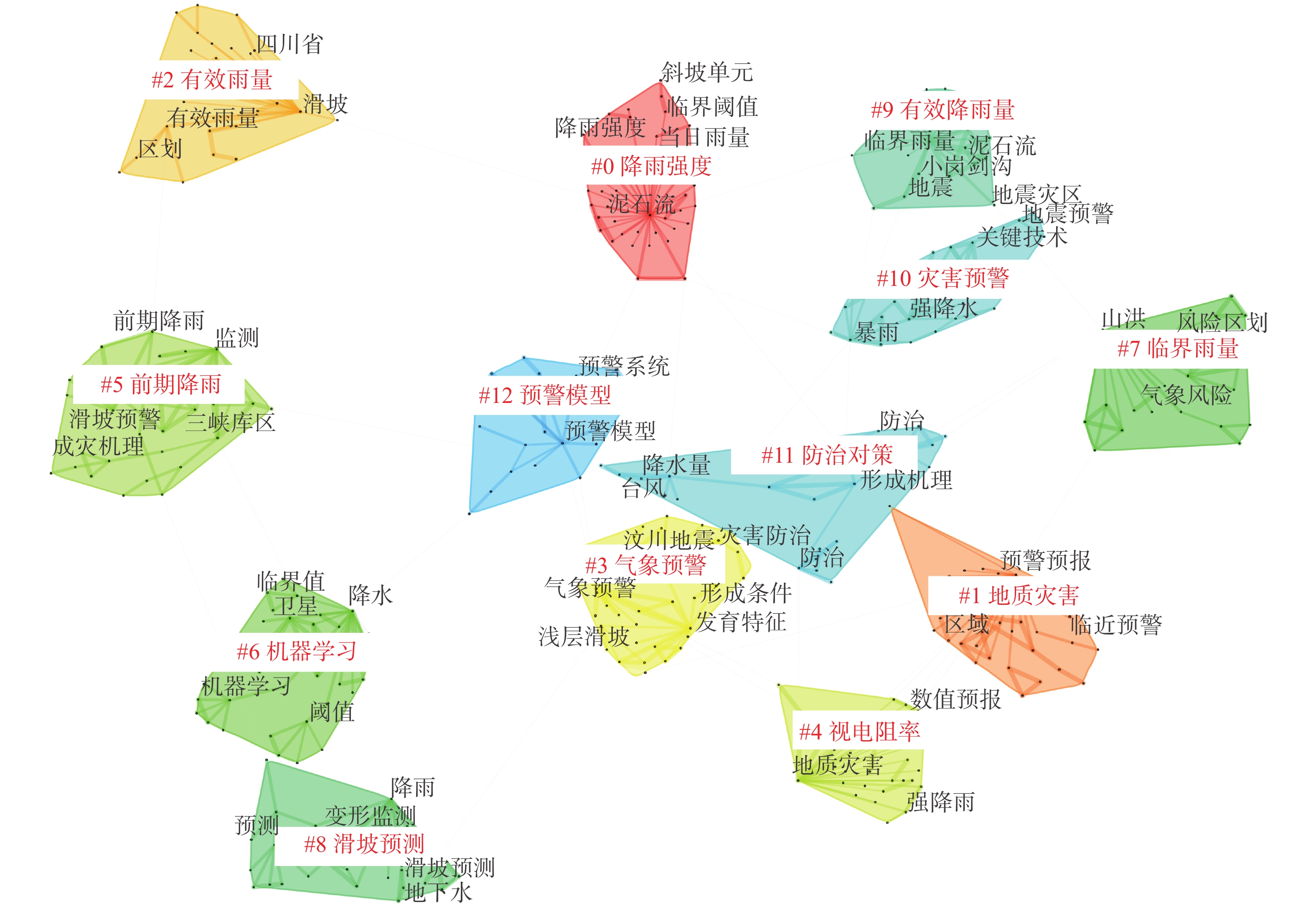
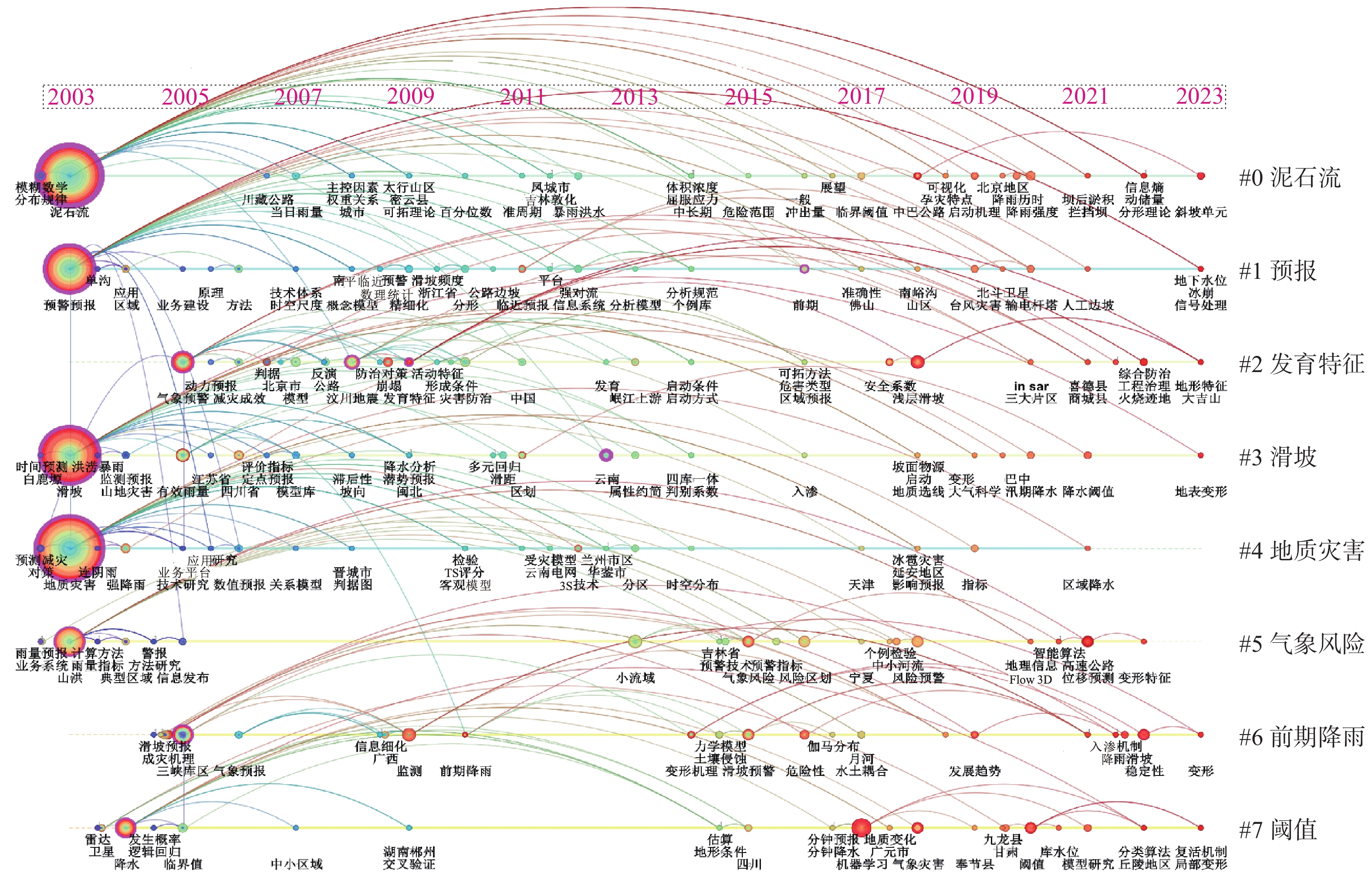
序号 高频关键词 频次 1 地质灾害 200 2 泥石流 168 3 滑坡 154 4 预警预报 118 5 临界雨量 92 6 降雨阈值 71 7 山洪 54 8 降雨 42 9 预警模型 30 10 暴雨 25 11 监测预警 25 12 气象预警 24 13 降水 22 14 机器学习 15 15 有效雨量 14 16 发育特征 12 17 汶川地震 12 18 数值模拟 11 19 前期降雨 10 20 气象条件 10 表 3 地质灾害气象风险预警领域英文发文量排名前20国家(地区)分布
Table 3. Distribution of top 20 countries (regions) in English publications in early warning of geo-hazards based on meteorological factors research
序号 国家(地区) 发文量/篇 占比/% 1 中国 274 32.01 2 意大利 194 22.66 3 美国 124 14.49 4 中国台湾省 60 7.01 5 印度 57 6.66 6 韩国 43 5.02 7 日本 40 4.67 8 英国 38 4.44 9 澳大利亚 29 3.39 10 荷兰 29 3.39 11 西班牙 22 2.57 12 瑞士 22 2.57 13 法国 21 2.45 14 德国 17 1.99 15 挪威 17 1.99 16 马来西亚 16 1.87 17 奥地利 15 1.75 18 巴西 13 1.52 19 加拿大 12 1.40 20 尼泊尔 12 1.40 表 4 SCI-Expend数据库地质灾害气象风险预警研究高频关键词
Table 4. High-frequency keywords in research on early warning of geo-hazards based on meteorological factors in SCI-E database
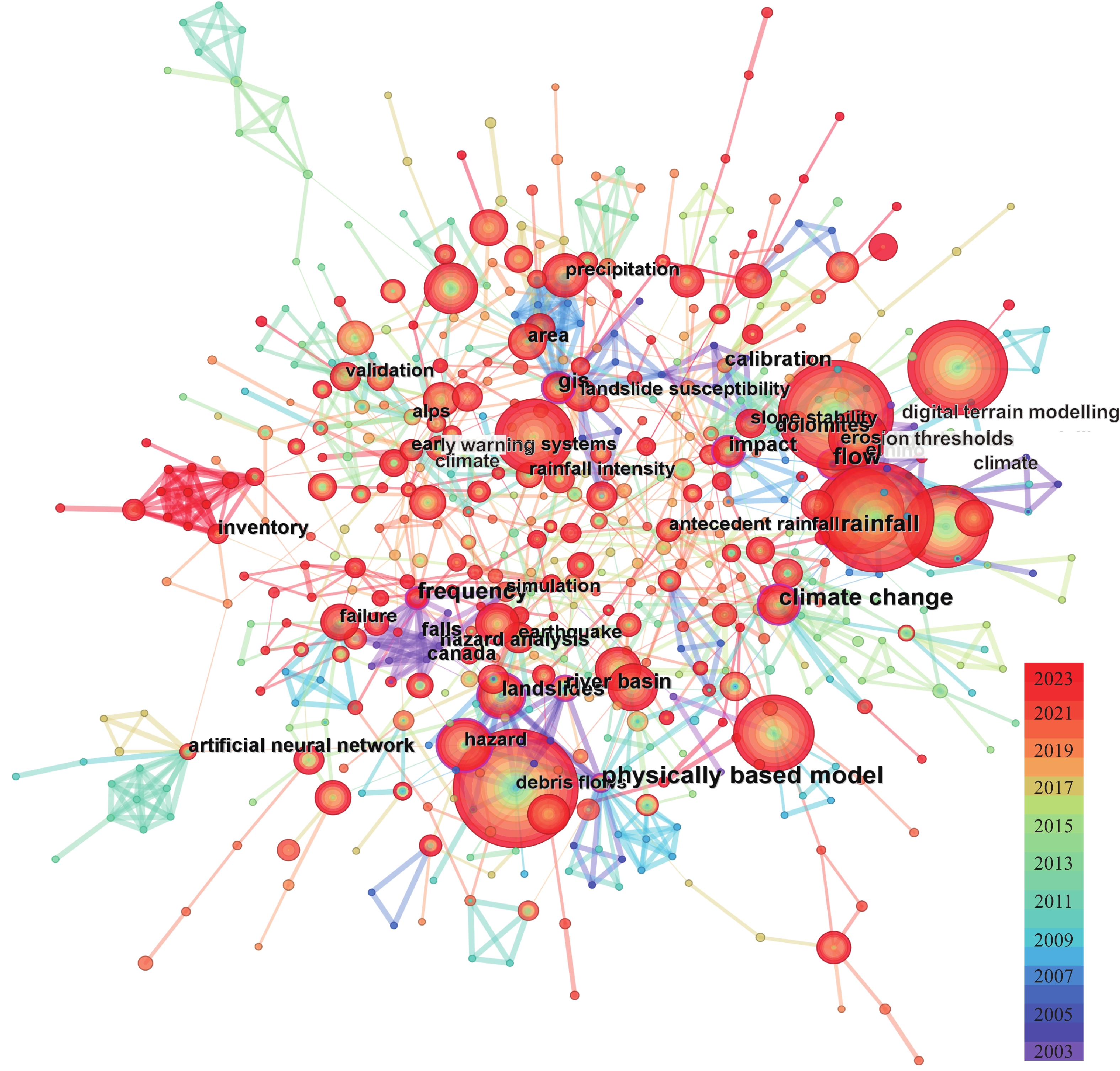
序号 高频关键词 频次 1 debris flows 324 2 shallow landslides 290 3 rainfall thresholds 284 4 initiation 204 5 intensity 185 6 duration control 172 7 model 171 8 prediction 153 9 thresholds 91 10 hazard 84 11 susceptibility 76 12 logistic regression 66 13 precipitation 65 14 system 64 15 landslides 58 16 rainfall 47 17 area 45 18 climate change 44 19 early warning system 43 20 definition 43 -
[1] LIU Chuanzheng,LIU Yanhui,WEN Mingsheng,et al. Early warning for geo-hazards based on the weather condition in China[J]. Global Geology,2006,9(2):131 − 137.
[2] 刘传正. 地质灾害防治研究的认识论与方法论[J]. 工程地质学报,2015,23(5):809 − 820. [LIU Chuanzheng. Epistemology and methodology on geo-hazard research[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2015,23(5):809 − 820. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Chuanzheng. Epistemology and methodology on geo-hazard research[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2015, 23(5): 809 − 820. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 许强. 对滑坡监测预警相关问题的认识与思考[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(2):360 − 374. [XU Qiang. Understanding the landslide monitoring and early warning:Consideration to practical issues[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(2):360 − 374. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
XU Qiang. Understanding the landslide monitoring and early warning: Consideration to practical issues[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(2): 360 − 374. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 自然资源部地质灾害应急技术指导中心,中国气象局公共气象服务中心. 中国地质灾害气象预警预报十年工作总结(2003—2012)[R]. 2013. [Technical Center for Geo-Hazards Emergency of MLR,Public Weather Service Center,CMA. A decade summary to early warning for regional geo-hazards,China(2003-2012) [R]. 2013. (in Chinese)]
Technical Center for Geo-Hazards Emergency of MLR, Public Weather Service Center, CMA. A decade summary to early warning for regional geo-hazards, China(2003-2012) [R]. 2013. (in Chinese)
[5] 自然资源部地质灾害应急技术指导中心,中国气象局公共气象服务中心. 中国地质灾害气象预警预报十五年工作总结(2003—2017)[R]. 2017. [Technical Center for Geo-Hazards Emergency of MLR,Public Weather Service Center,CMA. A fifteen years summary to early warning for regional geo-hazards,China(2003-2017) [R]. 2013. (in Chinese)]
Technical Center for Geo-Hazards Emergency of MLR, Public Weather Service Center, CMA. A fifteen years summary to early warning for regional geo-hazards, China(2003-2017) [R]. 2013. (in Chinese)
[6] 王圣洁,周永青,张兆代,等. 我国海洋地质论文的科学计量分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2012,32(6):94. [WANG Shengjie,ZHOU Yongqing,ZHANG Zhaodai,et al. A quantitative analysis of Chinese papers on marine geology[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2012,32(6):94. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Shengjie, ZHOU Yongqing, ZHANG Zhaodai, et al. A quantitative analysis of Chinese papers on marine geology[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(6): 94. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 王圣洁,周立君,孙萍. 科学计量:中国海洋地质40年发展历程与研究热点分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2021,41(6):1 − 14. [WANG Shengjie,ZHOU Lijun,SUN Ping. Forty years development of marine geology in China:Evidence from scientometrics[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2021,41(6):1 − 14. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Shengjie, ZHOU Lijun, SUN Ping. Forty years development of marine geology in China: Evidence from scientometrics[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2021, 41(6): 1 − 14. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 高云峰,徐友宁,祝雅轩,等. 矿山生态环境修复研究热点与前沿分析——基于VOSviewer和CiteSpace的大数据可视化研究[J]. 地质通报,2018,37(12):2144 − 2153. [GAO Yunfeng,XU Youning,ZHU Yaxuan,et al. An analysis of the hotspot and frontier of mine eco-environment restoration based on big data visualization of VOSviewer and CiteSpace[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2018,37(12):2144 − 2153. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
GAO Yunfeng, XU Youning, ZHU Yaxuan, et al. An analysis of the hotspot and frontier of mine eco-environment restoration based on big data visualization of VOSviewer and CiteSpace[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2018, 37(12): 2144 − 2153. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 李伟,石超. 水文地质的研究进展与研究趋势——基于CiteSpace的可视化分析[J]. 甘肃地质,2022,31(3):39 − 45. [LI Wei,SHI Chao. Analysis of hydrogeology research progress and trend based on Citespace software[J]. Gansu Geology,2022,31(3):39 − 45. (in Chines with English abstract)]
LI Wei, SHI Chao. Analysis of hydrogeology research progress and trend based on Citespace software[J]. Gansu Geology, 2022, 31(3): 39 − 45. (in Chines with English abstract)
[10] 汪美华,赵慧,倪天翔,等. 近30年滑坡研究文献图谱可视化分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(4):75 − 85. [WANG Meihua,ZHAO Hui,NI Tianxiang,et al. Visualization analysis of research literature map on landslides in the past 30 years[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(4):75 − 85. (in Chines with English abstract)]
WANG Meihua, ZHAO Hui, NI Tianxiang, et al. Visualization analysis of research literature map on landslides in the past 30 years[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2023, 34(4): 75 − 85. (in Chines with English abstract)
[11] 李彬彬,许明祥,巩晨,等. 国际土壤质量研究热点与趋势——基于大数据的Citespace可视化分析[J]. 自然资源学报,2017,32(11):1983 − 1998. [LI Binbin,XU Mingxiang,GONG Chen,et al. Hotspots and trends in international soil quality research[J]. Journal of Natural Resources,2017,32(11):1983 − 1998. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Binbin, XU Mingxiang, GONG Chen, et al. Hotspots and trends in international soil quality research[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2017, 32(11): 1983 − 1998. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 程刚,王振雪,李刚强,等. 我国滑坡监测文献计量研究的可视化分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报,2022,32(7):172 − 179. [CHENG Gang,WANG Zhenxue,LI Gangqiang,et al. Visual analysis of bibliometric research on landslide monitoring in China[J]. China Safety Science Journal,2022,32(7):172 − 179. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHENG Gang, WANG Zhenxue, LI Gangqiang, et al. Visual analysis of bibliometric research on landslide monitoring in China[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(7): 172 − 179. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] CHEN Chaomei. CiteSpace II:Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature[J]. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2006,57(3):359 − 377. doi: 10.1002/asi.20317
[14] 王若佳,李颖. 基于知识图谱的国际和国内竞争情报对比研究[J]. 情报杂志,2016,35(1):74 − 80. [WANG Ruojia,LI Ying. Comparative study on competitive intelligence based on mapping knowledge domains at home and abroad[J]. Journal of Intelligence,2016,35(1):74 − 80. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Ruojia, LI Ying. Comparative study on competitive intelligence based on mapping knowledge domains at home and abroad[J]. Journal of Intelligence, 2016, 35(1): 74 − 80. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 崔鹏,邹强. 山洪泥石流风险评估与风险管理理论与方法[J]. 地理科学进展,2016,35(2):137 − 147. [CUI Peng,ZOU Qiang. Theory and method of risk assessment and risk management of debris flows and flash floods[J]. Progress in Geography,2016,35(2):137 − 147. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2016.02.001
CUI Peng, ZOU Qiang. Theory and method of risk assessment and risk management of debris flows and flash floods[J]. Progress in Geography, 2016, 35(2): 137 − 147. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2016.02.001
[16] OLAWUMI T O,CHAN D W M. A scientometric review of global research on sustainability and sustainable development[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2018,183:231 − 250. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.162
[17] 韦方强,胡凯衡,陈杰. 泥石流预报中前期有效降水量的确定[J]. 山地学报,2005,23(4):4453 − 4457. [WEI Fangqiang,HU Kaiheng,CHEN Jie. Determination of effective antecedent rainfall for debris flow forecast[J]. Journal of Mountain Research,2005,23(4):4453 − 4457. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WEI Fangqiang, HU Kaiheng, CHEN Jie. Determination of effective antecedent rainfall for debris flow forecast[J]. Journal of Mountain Research, 2005, 23(4): 4453 − 4457. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 张桂荣,殷坤龙,刘礼领,等. 基于WEBGIS和实时降雨信息的区域地质灾害预警预报系统[J]. 岩土力学,2005,26(8):1312 − 1317. [ZHANG Guirong,YIN Kunlong,LIU Liling,et al. A real-time regional geological hazard warning system in terms of WEBGIS and rainfall[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2005,26(8):1312 − 1317. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Guirong, YIN Kunlong, LIU Liling, et al. A real-time regional geological hazard warning system in terms of WEBGIS and rainfall[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2005, 26(8): 1312 − 1317. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 张永双,姚鑫,郭长宝,等. 龙门山地区震后泥石流灾害区域预警研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(5):1014 − 1023. [ZHANG Yongshuang,YAO Xin,GUO Changbao,et al. Regional warning of debris flow hazards after Wenchuan earthquake in Longmenshan Region[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University,2016,51(5):1014 − 1023. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Yongshuang, YAO Xin, GUO Changbao, et al. Regional warning of debris flow hazards after Wenchuan earthquake in Longmenshan Region[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(5): 1014 − 1023. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 刘艳辉,温铭生,苏永超,等. 台风暴雨型地质灾害时空特征及预警效果分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(5):119 − 126. [LIU Yanhui,WEN Mingsheng,SU Yongchao,et al. Characteristics of geo-hazards induced by typhoon rainstorm and evaluation of geo-hazards early warning[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016,43(5):119 − 126. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Yanhui, WEN Mingsheng, SU Yongchao, et al. Characteristics of geo-hazards induced by typhoon rainstorm and evaluation of geo-hazards early warning[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2016, 43(5): 119 − 126. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 孟凡奇,李广杰,王庆兵,等. 基于功效系数法的泥石流灾害预警研究[J]. 岩土力学,2012,33(3):835 − 840. [MENG Fanqi,LI Guangjie,WANG Qingbing,et al. Research on early warning of debris flow based on efficacy coefficient method[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2012,33(3):835 − 840. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
MENG Fanqi, LI Guangjie, WANG Qingbing, et al. Research on early warning of debris flow based on efficacy coefficient method[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2012, 33(3): 835 − 840. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 刘佳意,陈春利,付昱凯等. 降雨诱发的浅表堆积层滑坡成因机理与稳定性预测模型[J/OL]. 水文地质工程地质,(2023-10-24)[2024-01-21]. [LIU Jiayi,CHEN Chunli,FU Yukai et al. Mechanism of rainfall-induced shallow landslide and stabilityprediction model[J/OL]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,(2023-10-24)[2024-01-21]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=smPsKIJgVaCeB4_GWsYbHgp39-xbu8sxy0R-whhyrBTPDjnnzyLxi8t4RmLS9DO4r1GAFUlE2Tv2YV4ORBwXTebQcJeLOj4opoRl49oUpi1VLIYJ8Wtf3w==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=gb. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Jiayi, CHEN Chunli, FU Yukai et al. Mechanism of rainfall-induced shallow landslide and stabilityprediction model[J/OL]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, (2023-10-24)[2024-01-21]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=smPsKIJgVaCeB4_GWsYbHgp39-xbu8sxy0R-whhyrBTPDjnnzyLxi8t4RmLS9DO4r1GAFUlE2Tv2YV4ORBwXTebQcJeLOj4opoRl49oUpi1VLIYJ8Wtf3w==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=gb. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 赵放,王东法,杨军,等. 突发暴雨型滑坡泥石流地质灾害格点化预警方法[J]. 浙江气象,2011,32(3):8 − 12. [ZHAO Fang,WANG Dongfa,YANG Jun,et al. Lattice early warning method for geological disasters of landslide and debris flow caused by sudden rainstorm[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Meteorology,2011,32(3):8 − 12. (in Chinese)]
ZHAO Fang, WANG Dongfa, YANG Jun, et al. Lattice early warning method for geological disasters of landslide and debris flow caused by sudden rainstorm[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Meteorology, 2011, 32(3): 8 − 12. (in Chinese)
-




 下载:
下载: