Experimental study on physical simulation of reactivation mechanism of ancient landslides under rainfall condition
-
摘要:
水是导致古滑坡复活的重要因素,而经历长久固结的土石混杂滑坡体通常渗透性较低,降雨形成的地表水如何入渗并诱发古滑坡复活的机理尚未明晰。文章在古滑坡复活案例调查和分析的基础上,采用滑坡物理模拟试验研究了降雨与裂缝共同作用下古滑坡复活机理。结果表明:(1)裂缝影响降雨渗透速率和渗透深度,当坡体表面无裂缝时,滑体渗透系数较小,降雨只能引起浅表层滑动;当坡体表面发育裂缝时,雨水沿裂缝快速渗入至深部滑带位置,诱发古滑坡复活。(2)裂缝的位置影响古滑坡的复活模式,无裂缝时,古滑坡表现为渐进式的溯源侵蚀复活;有裂缝时,首先出现溯源侵蚀复活变形,并沿前缘预设裂缝处逐渐扩张滑动,然后沿后缘预设裂缝发生拉张变形并出现向前推挤现象,最终在前部牵引和后缘推挤作用下发生整体复活滑动。(3)滑坡在临滑前,深部孔隙水压力和土压力均急速上升,而在滑动后快速释放,故可将孔隙水压力和土压力值的骤变作为古滑坡复活失稳的临界判据。
Abstract:Water is a crucial factor leading to the reactivation of ancient landslides. However, soil‒rock mixed landslides that have undergone long-term consolidation typically exhibit low permeability. The mechanism by which surface water generated by rainfall infiltrates and triggers landslide reactivation remains unclear. Based on the investigation of reactivation cases, this study explores the reactivation mechanism under the coupling effect of rainfall and cracks using landslide physical model tests. The results show the following: (1) Cracks can affect the seepage rate and depth of the landslide body. Without surface cracks, the landslide body has a low permeability coefficient, and rainfall can only cause shallow landslide. When surface cracks develop, rainwater can quickly infiltrate along the cracks to the deep sliding zone, triggering the reactivation of ancient landslides. (2) The location of the cracks can affect the reactivation mode of ancient landslides. Without cracks, ancient landslides exhibit a gradual retrogressive erosion reactivation. With cracks, reactivation deformation initially appears as retrogressive erosion, and gradually expanding to sliding along the preset cracks at the front edge, followed by tensile deformation and forward pushing at the rear edge, ultimately leading to overall reactivation sliding due to the combined effects of front traction and rear pushing. (3) Before sliding, both deep pore water pressure and soil pressure rapidly increased and then quickly release after sliding. Therefore, abrupt change in pore water pressure and soil pressure can be taken as the critical criterion for the reactivation of ancient landslides.
-

-
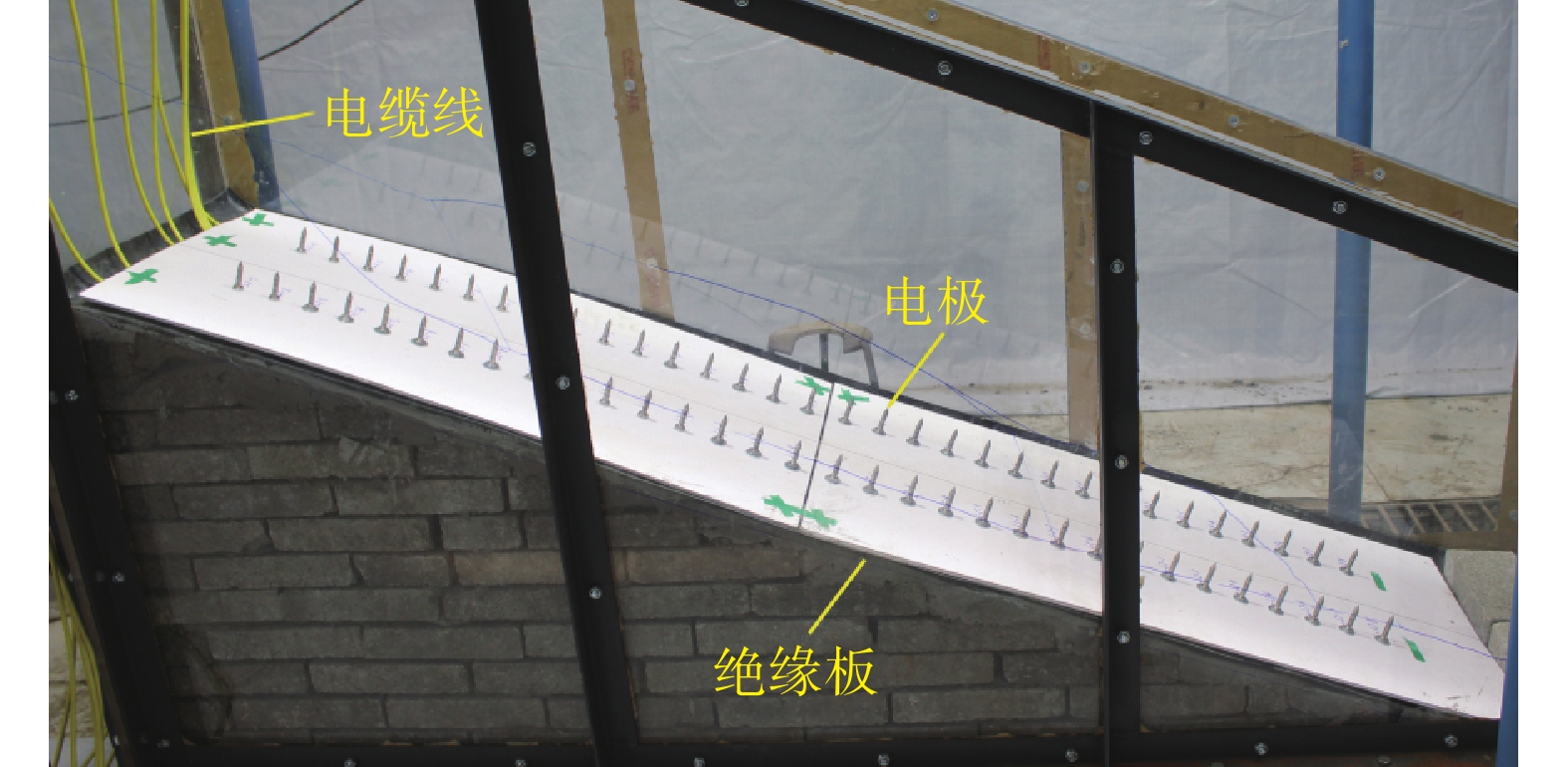
图 12 古滑坡复活作用力的综合示意图(据Lacroix et al, 2020修改)[16]
Figure 12.
-
[1] YIN Yueping,ZHENG Wamo,LIU Yuping,et al. Integration of GPS with InSAR to monitoring of the Jiaju landslide in Sichuan,China[J]. Landslides,2010,7(3):359 − 365. doi: 10.1007/s10346-010-0225-9
[2] 张永双,吴瑞安,郭长宝,等. 古滑坡复活问题研究进展与展望[J]. 地球科学进展,2018,33(7):728 − 740. [ZHANG Yongshuang,WU Ruian,GUO Changbao,et al. Research progress and prospect on reactivation of ancient landslides[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2018,33(7):728 − 740. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Yongshuang, WU Ruian, GUO Changbao, et al. Research progress and prospect on reactivation of ancient landslides[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2018, 33(7): 728 − 740. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] GARCÍA-DELGADO H. The San Eduardo Landslide (Eastern Cordillera of Colombia):Reactivation of a deep-seated gravitational slope deformation[J]. Landslides,2020,17(8):1951 − 1964. doi: 10.1007/s10346-020-01403-9
[4] TU Guoxiang,HUANG Da,DENG Hui. Reactivation of a huge ancient landslide by surface water infiltration[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2019,16(4):806 − 820. doi: 10.1007/s11629-018-5315-5
[5] GUO Changbao,ZHANG Yongshuang,LI Xue,et al. Reactivation of giant Jiangdingya ancient landslide in Zhouqu County,Gansu Province,China[J]. Landslides,2020,17(1):179 − 190. doi: 10.1007/s10346-019-01266-9
[6] MA Shuyue,QIU Haijun,HU Sheng,et al. Characteristics and geomorphology change detection analysis of the Jiangdingya landslide on July 12,2018,China[J]. Landslides,2021,18(1):383 − 396. doi: 10.1007/s10346-020-01530-3
[7] HE Kun,MA Guotao,HU Xiewen. Formation mechanisms and evolution model of the tectonic-related ancient giant basalt landslide in Yanyuan County,China[J]. Natural Hazards,2021,106(3):2575 − 2597. doi: 10.1007/s11069-021-04555-6
[8] BOOTH A M,MCCARLEY J,HINKLE J,et al. Transient reactivation of a deep-seated landslide by undrained loading captured with repeat airborne and terrestrial lidar[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2018,45(10):4841 − 4850. doi: 10.1029/2018GL077812
[9] IVERSON R M,GEORGE D L,ALLSTADT K,et al. Landslide mobility and hazards:Implications of the 2014 Oso disaster[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2015,412:197 − 208. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2014.12.020
[10] NOTTI D,WRZESNIAK A,DEMATTEIS N,et al. A multidisciplinary investigation of deep-seated landslide reactivation triggered by an extreme rainfall event:A case study of the Monesi di Mendatica landslide,Ligurian Alps[J]. Landslides,2021,18(7):2341 − 2365. doi: 10.1007/s10346-021-01651-3
[11] MACCIOTTA R,HENDRY M,MARTIN C D. Developing an early warning system for a very slow landslide based on displacement monitoring[J]. Natural Hazards,2016,81(2):887 − 907. doi: 10.1007/s11069-015-2110-2
[12] 杨校辉,朱鹏,窦晓东,等. 甘肃舟曲江顶崖古滑坡复活变形特征与稳定性分析[J]. 地质通报,2024,43(6):947 − 957. [YANG Xiaohui,ZHU Peng,DOU Xiaodong,et al. Resurrection deformation characteristics and stability of Jiangdingya ancient landslide in Zhouqu,Gansu Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2024,43(6):947 − 957. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YANG Xiaohui, ZHU Peng, DOU Xiaodong, et al. Resurrection deformation characteristics and stability of Jiangdingya ancient landslide in Zhouqu, Gansu Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2024, 43(6): 947 − 957. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 齐畅,吴瑞安,马海善,等. 西藏庞村古滑坡发育特征与危险性评价[J/OL]. 地质通报,(2023-11-27)[2024-06-08]. [QI Chang,WU Ruian,MA Haishan,et al. Development characteristics and hazard assessment of the Pangcun landslide,Xizang[J/OL]. Geological Bulletin of China,(2023-11-27)[2024-06-08]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.4648.P.20231124.1820.002.html. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
QI Chang, WU Ruian, MA Haishan, et al. Development characteristics and hazard assessment of the Pangcun landslide, Xizang[J/OL]. Geological Bulletin of China, (2023-11-27)[2024-06-08]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.4648.P.20231124.1820.002.html. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 杨志华,吴瑞安,郭长宝,等. 融合斜坡形变特征的复杂山区区域滑坡评价研究现状与展望[J/OL]. 中国地质,(2023-10-10)[2024-06-08]. [YANG Zhihua,WU Rui’an,GUO Changbao,WU Yuming,et al. Research status and prospect of regional landslide assessment integrating slope deformation characteristics in the complex mountainous area[J/OL]. Geology in China,(2023-10-10)[2024-06-08]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20231009.1724.016.html. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YANG Zhihua, WU Rui’an, GUO Changbao, WU Yuming, et al. Research status and prospect of regional landslide assessment integrating slope deformation characteristics in the complex mountainous area[J/OL]. Geology in China, (2023-10-10)[2024-06-08]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20231009.1724.016.html. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 胡瑞林,李晓,王宇,等. 土石混合体工程地质力学特性及其结构效应研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(2):255 − 281. [HU Ruilin,LI Xiao,WANG Yu,et al. Research on engineering geomechanics and structural effect of soil-rock mixture[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(2):255 − 281. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HU Ruilin, LI Xiao, WANG Yu, et al. Research on engineering geomechanics and structural effect of soil-rock mixture[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(2): 255 − 281. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] LACROIX P,HANDWERGER A L,BIÈVRE G. Life and death of slow-moving landslides[J]. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment,2020,1:404 − 419.
[17] KRZEMINSKA D M,BOGAARD T A,MALET J P,et al. A model of hydrological and mechanical feedbacks of preferential fissure flow in a slow-moving landslide[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences,2013,17(3):947 − 959. doi: 10.5194/hess-17-947-2013
[18] 李同录,习羽,侯晓坤. 水致黄土深层滑坡灾变机理[J]. 工程地质学报,2018,26(5):1113 − 1120. [LI Tonglu,XI Yu,HOU Xiaokun. Mechanism of surface water infiltration induced deep loess landslide[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2018,26(5):1113 − 1120. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Tonglu, XI Yu, HOU Xiaokun. Mechanism of surface water infiltration induced deep loess landslide[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2018, 26(5): 1113 − 1120. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 张永双,郭长宝,李向全,等. 川藏铁路廊道关键水工环地质问题:现状与发展方向[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(5):1 − 12. [ZHANG Yongshuang,GUO Changbao,LI Xiangquan,et al. Key problems on hydro-engineering-environmental geology along the Sichuan-Tibet Railway corridor:Krent status and development direction[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(5):1 − 12. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Yongshuang, GUO Changbao, LI Xiangquan, et al. Key problems on hydro-engineering-environmental geology along the Sichuan-Tibet Railway corridor: Krent status and development direction[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(5): 1 − 12. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] ZHOU Zhou,SHEN Junhui,LI Ying,et al. Mechanism of colluvial landslide induction by rainfall and slope construction:A case study[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2021,18(4):1013 − 1033. doi: 10.1007/s11629-020-6048-9
[21] 许强,汤明高,徐开祥,等. 滑坡时空演化规律及预警预报研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2008,27(6):1104 − 1112. [XU Qiang,TANG Minggao,XU Kaixiang,et al. Research on space-time evolution laws and early warning-prediction of landslides[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2008,27(6):1104 − 1112. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
XU Qiang, TANG Minggao, XU Kaixiang, et al. Research on space-time evolution laws and early warning-prediction of landslides[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 27(6): 1104 − 1112. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 杜飞,任光明,夏敏,等. 地震作用诱发老滑坡复活机制的数值模拟[J]. 山地学报,2015,33(2):233 − 239. [DU Fei,REN Guangming,XIA Min,et al. Numerical simulation of ecurrence mechanism of old landslide under earthquake loading[J]. Mountain Research,2015,33(2):233 − 239. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
DU Fei, REN Guangming, XIA Min, et al. Numerical simulation of ecurrence mechanism of old landslide under earthquake loading[J]. Mountain Research, 2015, 33(2): 233 − 239. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 吴瑞安,张永双,郭长宝,等. 川西松潘上窑沟古滑坡复活特征及危险性预测研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2018,40(9):1659 − 1667. [WU Ruian,ZHANG Yongshuang,GUO Changbao,et al. Reactivation characteristics and hazard prediction of Shangyaogou ancient landslide in Songpan County of Sichuan Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2018,40(9):1659 − 1667. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WU Ruian, ZHANG Yongshuang, GUO Changbao, et al. Reactivation characteristics and hazard prediction of Shangyaogou ancient landslide in Songpan County of Sichuan Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2018, 40(9): 1659 − 1667. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 任三绍,张永双,徐能雄,等. 含砾滑带土复活启动强度研究[J]. 岩土力学,2021,42(3):863 − 873. [REN Sanshao,ZHANG Yongshuang,XU Nengxiong,et al. Mobilized strength of sliding zone soils with gravels in reactivated landslides[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2021,42(3):863 − 873. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
REN Sanshao, ZHANG Yongshuang, XU Nengxiong, et al. Mobilized strength of sliding zone soils with gravels in reactivated landslides[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2021, 42(3): 863 − 873. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 任三绍,郭长宝,张永双,等. 川西巴塘茶树山滑坡发育特征及形成机理[J]. 现代地质,2017,31(5):978 − 989. [REN Sanshao,GUO Changbao,ZHANG Yongshuang,et al. Development characteristics and formation mechanism of Chashushan landslide in Batang,western Sichuan[J]. Geoscience,2017,31(5):978 − 989. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
REN Sanshao, GUO Changbao, ZHANG Yongshuang, et al. Development characteristics and formation mechanism of Chashushan landslide in Batang, western Sichuan[J]. Geoscience, 2017, 31(5): 978 − 989. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] ZHANG Yongshuang,REN Sanshao,LIU Xiaoyi,et al. Reactivation mechanism of old landslide triggered by coupling of fault creep and water infiltration:A case study from the East Tibetan Plateau[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2023,82(8):291. doi: 10.1007/s10064-023-03290-5
[27] 闫亚景,闫永帅,赵贵章,等. 基于高密度电法的天然边坡水分运移规律研究[J]. 岩土力学,2019,40(7):2807 − 2814. [YAN Yajing,YAN Yongshuai,ZHAO Guizhang,et al. Study on moisture migration in natural slope using high-density electrical resistivity tomography method[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2019,40(7):2807 − 2814. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YAN Yajing, YAN Yongshuai, ZHAO Guizhang, et al. Study on moisture migration in natural slope using high-density electrical resistivity tomography method[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2019, 40(7): 2807 − 2814. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 赵宽耀,许强,刘方洲,等. 黄土中优势通道渗流特征研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2020,42(5):941 − 950. [ZHAO Kuanyao,XU Qiang,LIU Fangzhou,et al. Seepage characteristics of preferential flow in loess[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2020,42(5):941 − 950. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHAO Kuanyao, XU Qiang, LIU Fangzhou, et al. Seepage characteristics of preferential flow in loess[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2020, 42(5): 941 − 950. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] IVANOV V,AROSIO D,TRESOLDI G,et al. Investigation on the role of water for the stability of shallow landslides—insights from experimental tests[J]. Water,2020,12(4):1203. doi: 10.3390/w12041203
[30] 肖捷夫,李云安,蔡浚明. 水位涨落作用下藕塘滑坡响应特征模型试验研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(5):1049 − 1056. [XIAO Jiefu,LI Yun’an,CAI Junming. Model test research on response characteristics of outang landslide under water level fluctuation[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(5):1049 − 1056. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
XIAO Jiefu, LI Yun’an, CAI Junming. Model test research on response characteristics of outang landslide under water level fluctuation[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(5): 1049 − 1056. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] SHUZUI Haruo. Process of slip-surface development and formation of slip-surface clay in landslides in Tertiary volcanic rocks,Japan[J]. Engineering Geology,2001,61(4):199 − 220. doi: 10.1016/S0013-7952(01)00025-4
[32] NERESON A L,DAVILA OLIVERA S,FINNEGAN N J. Field and remote-sensing evidence for hydro-mechanical isolation of a long-lived earthflow in central California[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2018,45(18):9672 − 9680. doi: 10.1029/2018GL079430
[33] 党杰,杨亮,段方情,等. 贵州晴隆红寨大型古滑坡复活变形特征及成因分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2024,35(4):25 − 35. [DANG Jie,YANG Liang,DUAN Fangqing,et al. Reactivation characteristics and genesis analysis of the large ancient landslide in Hongzhai, Qinglong County, Guizhou Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2024,35(4):25 − 35. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
DANG Jie, YANG Liang, DUAN Fangqing, et al. Reactivation characteristics and genesis analysis of the large ancient landslide in Hongzhai, Qinglong County, Guizhou Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2024, 35(4): 25 − 35. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[34] 胡卸文,黄润秋,朱海勇,等. 唐家山堰塞湖库区马铃岩滑坡地震复活效应及其稳定性研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2009,28(6):1270 − 1278. [HU Xiewen,HUANG Runqiu,ZHU Haiyong,et al. Earthquake reactivation effects and stability study of malingyan landslide in Tangjiashan dammed lake[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2009,28(6):1270 − 1278. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HU Xiewen, HUANG Runqiu, ZHU Haiyong, et al. Earthquake reactivation effects and stability study of malingyan landslide in Tangjiashan dammed lake[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2009, 28(6): 1270 − 1278. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[35] BONTEMPS N,LACROIX P,LAROSE E,et al. Rain and small earthquakes maintain a slow-moving landslide in a persistent critical state[J]. Nature Communications,2020,11(1):780. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-14445-3
[36] 张永双,吴瑞安,任三绍. 降雨优势入渗通道对古滑坡复活的影响[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2021,40(4):777 − 789. [ZHANG Yongshuang,WU Ruian,REN Sanshao. Influence of rainfall preponderance infiltration path on reactivation of ancient landslides[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2021,40(4):777 − 789. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Yongshuang, WU Ruian, REN Sanshao. Influence of rainfall preponderance infiltration path on reactivation of ancient landslides[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(4): 777 − 789. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[37] REN Sanshao,ZHANG Yongshuang,LI Jinqiu,et al. Deformation behavior and reactivation mechanism of the dandu ancient landslide triggered by seasonal rainfall:A case study from the East Tibetan Plateau,China[J]. Remote Sensing,2023,15(23):5538. doi: 10.3390/rs15235538
[38] 王立朝,侯圣山,董英,等. 甘肃积石山Ms 6.2级地震的同震地质灾害基本特征及风险防控建议[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2024,35(3):108 − 118. [WANG Lichao,HOU Shengshan,DONG Ying,et al. Basic characteristics of co-seismic geological hazards induced by Jishishan Ms 6.2 earthquake and[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2024,35(3):108 − 118. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Lichao, HOU Shengshan, DONG Ying, et al. Basic characteristics of co-seismic geological hazards induced by Jishishan Ms 6.2 earthquake and[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2024, 35(3): 108 − 118. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[39] 黄达,高溢康,黄文波. 基于CT扫描的渗流作用下碎石土孔隙结构变化规律研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2024,51(2):123 − 131. [HUANG Da,GAO Yikang,HUANG Wenbo. Research on pore structural change of gravel soil under seepage erosion based on CT scanning[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2024,51(2):123 − 131. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HUANG Da, GAO Yikang, HUANG Wenbo. Research on pore structural change of gravel soil under seepage erosion based on CT scanning[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2024, 51(2): 123 − 131. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: