DISTRIBUTION PATTERN AND CONTROL FACTORS OF SAND WAVES IN SOUTHEAST BEIBU GULF
-
摘要:
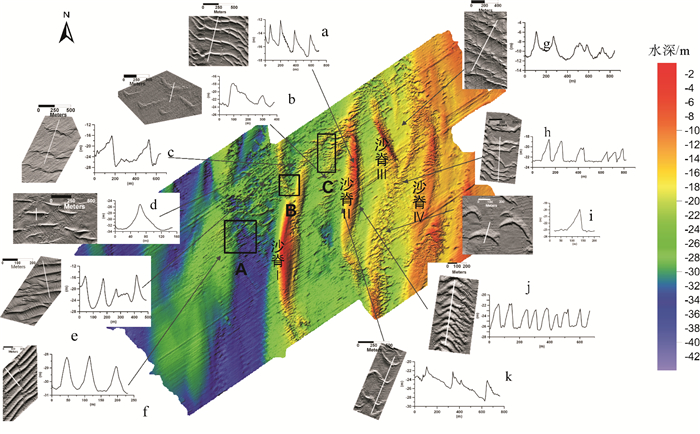
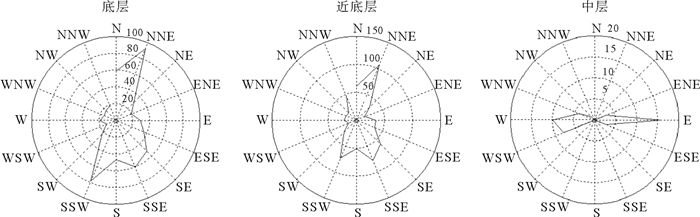
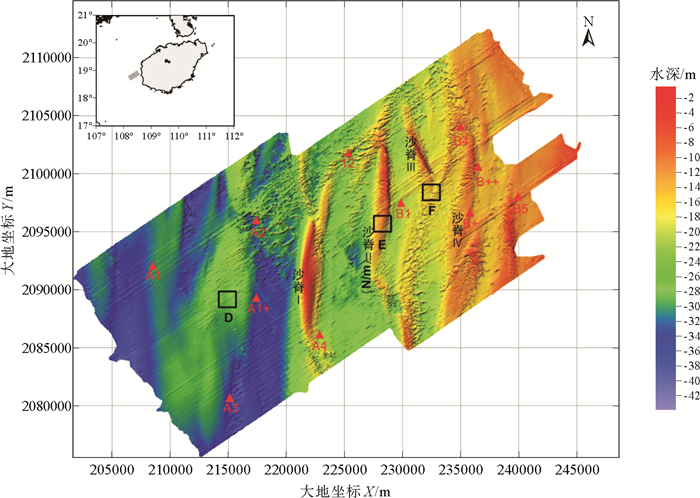
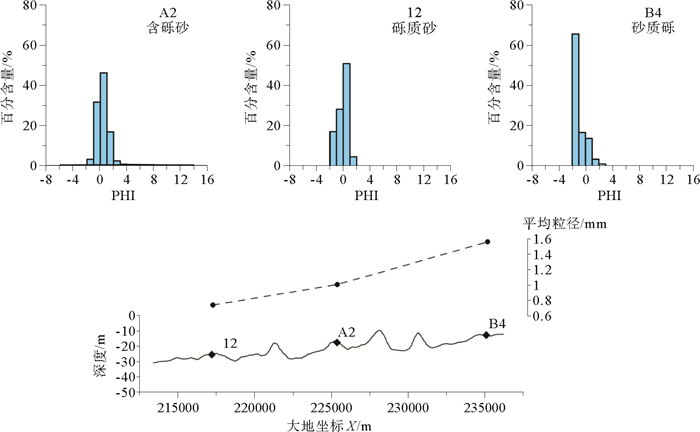
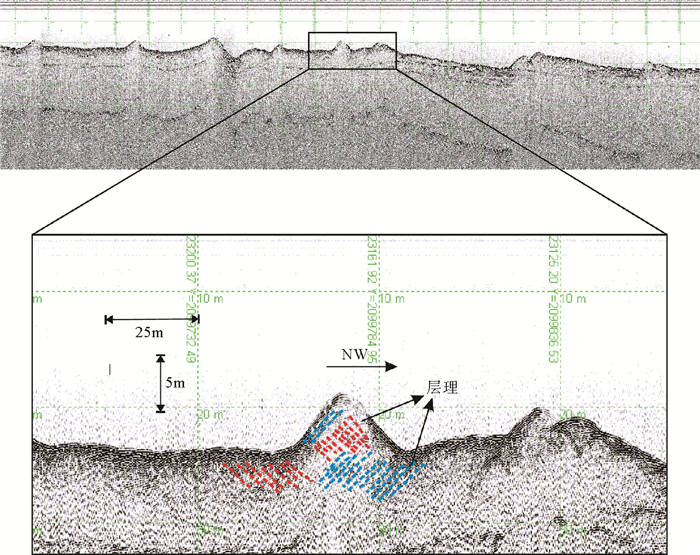
北部湾东南海域海底发育大量沙波,利用最新获得的多波束测深、沉积物和水动力数据对沙波形态和分布特征进行综合分析,探讨沉积物特征、水动力条件,海平面变化等不同控制因素对海底沙波发育及分布的影响。结果表明研究区沙波广泛分布于沙脊顶部、沙脊槽中线附近及沙脊槽北端,沙波呈现远岸区尺度较小、对称性较好,近岸区尺度较大、多不对称的分布特征。海底沙波的发育和分布受现代潮流作用和沉积物特征的共同控制。潮流通道及流速的分布情况与沙波形态、规模的差异性分布一致。表层沉积物具有“远岸细、近岸粗”的特点,与沙波远岸尺度小、近岸尺度大的分布规律有较好的对应关系。此外,研究区出现有近对称形态的沙波,可能为海平面变化期间多期潮流共同作用形成的残余沙波。
Abstract:To access the main factors influencing development and distribution of sand waves, analyses have been undertaken on the characteristics of sediment, hydrodynamics and sea level changes using the latest high-resolution multibeam, surface sediment and hydrodynamic data collected in the southeast of Beibu Gulf, where sand waves are abundantly developed. Results suggest that sand waves in this area are widespread, mostly developed on the sand ridges and in the troughs between sand ridges. Sand waves are smaller in scale in the offshore area but larger in the area nearshore. The development and distribution features of sand waves depend upon modern hydrodynamics and sediment supply. Geometric features and dimension of sand waves depend upon tidal inlet and flow velocity. Surface sediments are usually "finer offshore and coarser nearshore", corresponding to the distribution of sand waves referred above. Besides, some of the symmetrical sand waves are found in certain areas with residual properties, perhaps as the result of different hydrodynamics while sea level changes in different periods.
-
Key words:
- sand waves /
- distribution characteristics /
- control factors /
- Beibu Gulf
-

-
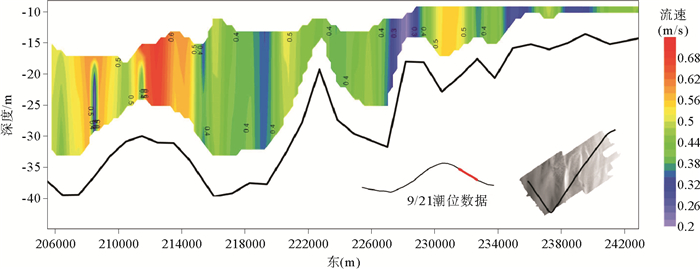
图 4 落潮中期流速剖面[24]
Figure 4.
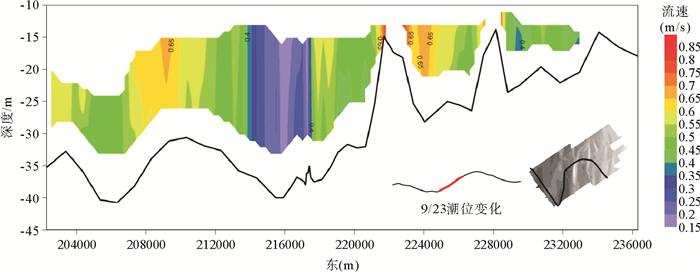
图 5 涨潮初期和中期流速剖面[24]
Figure 5.
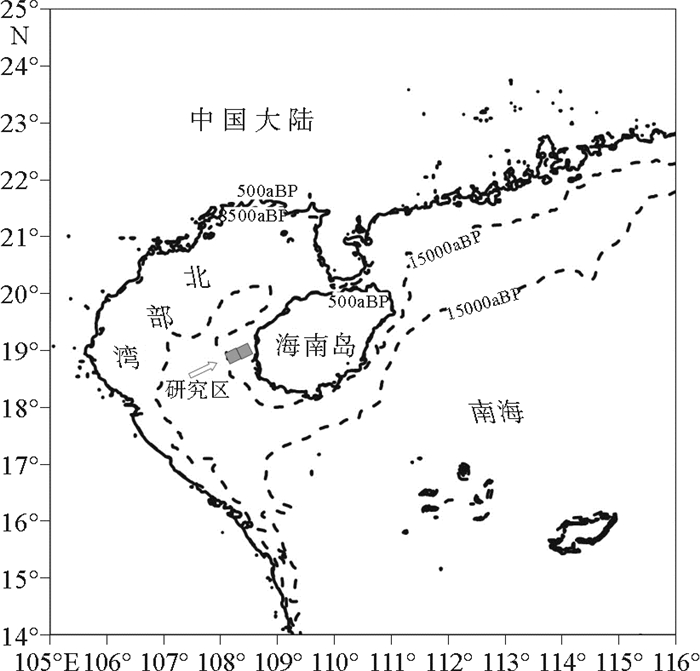
图 10 北部湾古海岸线变迁图(改编自文献[27])
Figure 10.
表 1 D、E、F区沙波和沉积物基本参数
Table 1. The basic parameters of sand waves and sediments in district D、E、F
区域 D E F 平均波高/m 1.8 2.63 3.79 平均波长/m 54 80.27 112.9 平均水深/m 31 19 17 平均粒径/mm 0.2 0.511 0.693 -
[1] Landeghem K J J V, Wheeler A J, Mitchell N C, et al. Variations in sediment wave dimensions across the tidally dominated Irish sea, NW Europe [J]. Marine Geology, 2009, 263(1-4): 108-119. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2009.04.003
[2] 夏东兴, 吴桑云, 刘振夏, 等.海南东方岸外海底沙波活动性研究[J].黄渤海海洋, 2001, 19(1): 17-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2001.01.003
XIA Dongxing, WU Sangyun, LIU Zhenxia, et al. Research on the activity of submarine sand waves off Dongfang, Hainan Island[J]. Journal of Oceanography of Huanghai and Bohai Seas, 2001, 19(1):17-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2001.01.003
[3] Allen J R L. Simple models for the shape and symmetry of tidal sand waves: (2)Dynamically stable symmetrieal equilibrium forms[J]. Marine Geology, 1982, 48(82): 51-73. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=07c8da730883e9bee24cdfa43965a996&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[4] Flemming B. Zur klassifikation subaquatischer, strömungstransversaler Transportkörper[J]. Bochumer Geologische und Geotechnische Arbeiten, 1988, 29(93-97):44-47.
[5] Huthnance J M. On one mechanism forming linear sand banks[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 1982, 14(1): 79-99. doi: 10.1016/S0302-3524(82)80068-6
[6] Hulscher S J, de Swart H E, de Vriend H J. The generation of offshore tidal sand banks and sand waves [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 1993, 13(11): 1183-1204. doi: 10.1016/0278-4343(93)90048-3
[7] Komarova N L, Newell A C. Nonlinear dynamics of sand banks and sand waves [J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2000, 415(5): 285-321. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=S0022112000008855
[8] Németh A A, Hulscher S J, de Vriend H J. Modelling sand wave migration in shallow shelf seas [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2002, 22(18): 2795-2806. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=212495f96039f2588719500fc75a9c5b&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[9] Duffy G P, Hughes-Clarke J E. Application of spatial cross correlation to detection of migration of submarine sand dunes [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface (2003-2012), 2005, 110(F4): 1-11. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=ed25bceb04309238e8b62b8b5fb8ac90&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[10] Buijsman M C, Ridderinkhof H. Long-term evolution of sandwaves in the Marsdiep inlet. Ⅰ: High-resolution observations [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2008, 28(9): 1190-1201. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2007.10.011
[11] Jim B, Ray K. An experimental study of turbulent flow over a low-angle dune [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Oceans, 2002, 107(C9): 18-1-18-19. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.1177/0309133308089500
[12] Whitmeyer S J, Fitzgerald D M. Episodic dynamics of a sand wave field [J]. Marine Geology, 2008, 252(1): 24-37. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f5beef0e84bc33a912dc8429ac4c2499
[13] 高抒, 方国洪, 于克俊, 等.沉积物输运对砂质海底稳定性影响的评估方法及应用实例[J].海洋科学集刊, 2001(43): 25-37. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFD2001-HKJK200100003.htm
GAO Shu, FANG Guohong, YU Kejun, et al. Methodology for evaluting the stability of sandy seabed controlled by sediment movement, with an example of application[J]. Studia Marina Sinica, 2001(43):25-37. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFD2001-HKJK200100003.htm
[14] Berné S, Vagner P, Guichard F, et al. Pleistocene forced regressions and tidal sand ridges in the East China Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 2002, 188(2): 293-315. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=4770fe4fb7c232b9cb92ae8455456ae3
[15] 罗深荣.侧扫声纳和多波束测深系统在海洋调查中的综合应用[J].海洋测绘, 2003, 23(1): 22-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2003.01.006
LUO Shenrong. Comprehensive utilization of side scan sonar and multi-beam sounding system in oceanographic research[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2003, 23(1):22-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2003.01.006
[16] 曹立华, 徐继尚, 李广雪, 等.海南岛西部岸外沙波的高分辨率形态特征[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2006, 26(4): 15-22. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200604003
CAO Lihua, XU Jishang, LI Guangxue, et al. High-resolution morphological characterisitics of sand waves off the west Hainan Island[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2006, 26(4): 15-22. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200604003
[17] 奉仰崇.面对北部湾的思考——关于环北部湾海岸的开发与保护[J].海洋开发与管理, 1999(2): 14-17. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199900274627
FENG Yangchong. In the face of the Gulf of Tonkin thinking: Central Gulf of Tonkin on the development and protection [J]. Ocean Development and Management, 1999(2): 14-17. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199900274627
[18] Li Z, Zhang Y, Li Y, et al. Palynological records of Holocene monsoon change from the Gulf of Tonkin (Beibuwan), northwestern South China Sea [J]. Quaternary Research, 2010, 74(1): 8-14. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2010.04.012
[19] Yao Y T, Harff J, Meyer M, et al. Reconstruction of paleocoastlines for the northwestern South China Sea since the Last Glacial Maximum [J]. Science in China, 2009, 52(8): 1127-1136. doi: 10.1007/s11430-009-0098-8
[20] 徐方建, 陈世悦, 操应长, 等.近4400年来南海北部陆架沉积地球化学记录及其地质意义[J].沉积学报, 2010, 28(6): 1198-1205. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb201006018
XU Fangjian, CHEN Shiyue, CAO Yingchang. Geochemical records and geological significance of the continental shelf sediments in the northern South China Sea since 4400a[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2010, 28(6): 1198-1205. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb201006018
[21] 刘振夏, 夏东兴, 王揆洋.中国陆架潮流沉积体系和模式[J].海洋与湖沼, 1998, 29(2): 141-147. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HYFZ199802004.htm
LIU Zhenxia, XIA Dongxing, WANG Kuiyang. Tidal depositional systems and patterns of China's continental shelf [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1993, 29(2): 141-147. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HYFZ199802004.htm
[22] 王文介.南海北部的潮波传播与海底沙脊和沙波发育[J].热带海洋, 2000, 19(1): 1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2000.01.001
WANG Wenjie. Propagation of tidal waves and development of sea-bottom sand ridges and sand ripples in northern South China Sea [J]. Tropic Oceanology, 2000, 19(1):1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2000.01.001
[23] 夏东兴, 刘振夏.潮流脊的形成机制和发育条件[J].海洋学报, 1984, 6(3): 361-367. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SEAC198403008.htm
XIA Dongxing, LIU Zhenxia. The formation mechanism and development conditons of tidal ridgs [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1984, 6(3): 361-367. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SEAC198403008.htm
[24] 马小川.海南岛西南海域海底沙波沙脊形成演化及其工程意义[D].青岛: 中国科学院海洋研究所, 2013.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-80068-1013299947.htm MA Xiaochuan. Formation, evolution and engineering significance of submarine sand waves and sand ridges, southeast of Hainan Island[D]. Institute of Oceanology, Qingdao: Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2013.
[25] 庄振业, 林振宏, 周江, 等.陆架沙丘(波)形成发育的环境条件[J].海洋地质动态, 2004, 20(4): 5-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2004.04.002
ZHUANG Zhenye, LIN Zhenhong, ZHOU Jiang, et al. Environmental conditions for the formation and development of sand dunes (waves) in the continental shelf[J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2004, 20(4): 5-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2004.04.002
[26] 吴自银, 金翔龙, 李家彪, 等.东海外陆架线状沙脊群[J].科学通报, 2006, 51(1): 93-103. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2006.01.018
WU Ziyin, JIN Xianglong, LI Jiabiao, et al. The linear sand ridges on continental shelf of East China Sea[J]. Chinese SCI Bull, 2006, 1(1): 93-103. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2006.01.018
[27] Kubo Y S, Soh W, Machiyama H, et al. Bedforms produced by the Kuroshio Current passing over the northern Izu Ridge [J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 2004, 24(1): 1-7. doi: 10.1007/s00367-003-0134-1
[28] 王伟伟, 范奉鑫, 李成钢, 等.海南岛西南海底沙波活动及底床冲淤变化[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2007, 27(4): 23-28. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200704004
WANG Weiwei, FAN Fengxin, LI Chenggang, et al. Activity of submarine sand waves and seafloor erosion and deposition in the sea area to the southwest of Hainan Island[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2007, 27(4): 23-28. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200704004
[29] 董志华.台风对东方岸外沙波沙脊和海底地貌的影响[D].青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2004.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10423-2004131706.htm DONG Zhihua. The influence on current ridge, sand wave and topography of Dongfang off shore by typhoon[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2004.
[30] 姚衍桃, Harff J, Meyer M, 等.南海西北部末次盛冰期以来的古海岸线重建[J].中国科学(D辑:地球科学), 2009, 39(6): 753-762. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd200906007
YAO Yantao, Harff J, Meyer M, et al. Reconstruction of paleocoastlines for the northwestern South China Sea since the Last Glacial Maximum[J]. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 2009, 39(6): 753-762. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd200906007
[31] 赵焕庭, 王丽荣, 袁家义.琼州海峡成因与时代[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2007, 27(2): 33-40. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200702005
ZHAO Huanting, WANG Lirong, YUAN Jiayi. Origin and time of Qiongzhou Strait[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2007, 27(2): 33-40. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200702005
[32] 时小军, 余克服, 陈特固.南海周边中全新世以来的海平面变化研究进展[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2007, 27(5): 121-132. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200705017
SHI Xiaojun, YU Kefu, CHEN Tegu. Progress in researches on sea-level changes in south china sea since mid-holocene[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2007, 27(5): 121-132. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200705017
[33] 吴自银, 金翔龙, 曹振轶, 等.东海陆架沙脊分布及其形成演化[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2010, 40(2): 188-198. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK201000351456
WU Ziyin, JIN Xianglong, CAO Zhenyi, et al. Distribution, formation and evolution of sand ridges on the East China Sea shelf[J]. Sci China Earth Sci, 2010, 40(2): 188-198. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK201000351456
[34] 贾建军, 闾国年, 宋志尧, 等.中国东部边缘海潮波系统形成机制的模拟研究[J].海洋与湖沼, 2000, 31(2): 159-167. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2000.02.008
JIA Jianjun, LV Guonian, SONG Zhiyao, et al. Simulation of mechanisms for the tidal wave system in marginal seas, eastern China[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2000, 31(2): 159-167. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2000.02.008
-



 下载:
下载: