IMPACT OF SEAFLOOR TOPOGRAPHY ON DISTRIBUTION OF CLAY MINERALS IN THE EAST PHILIPPINES SEA
-
摘要:
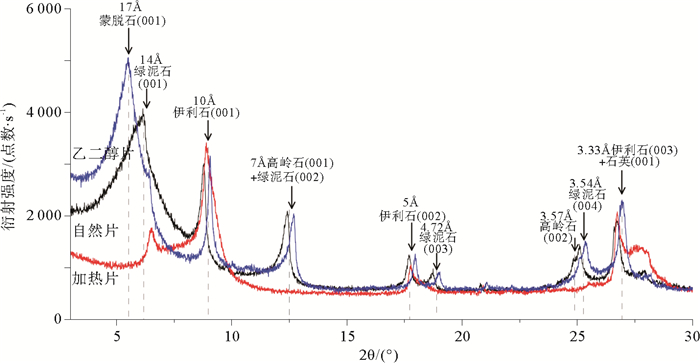
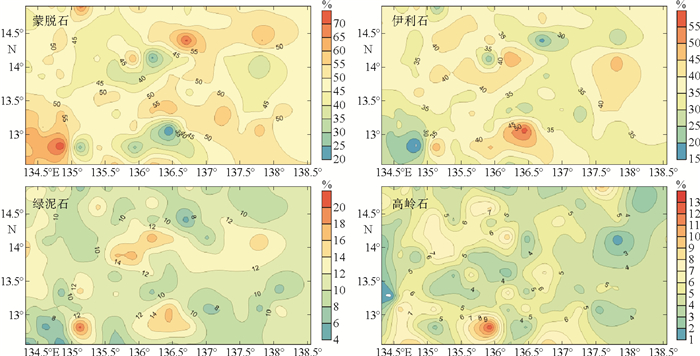
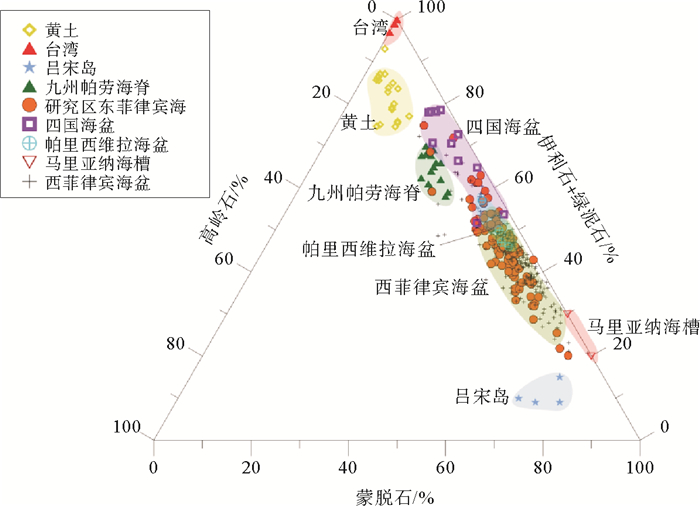
对东菲律宾海帕里西维拉海盆南部的125个表层沉积物样品的黏土矿物组成、含量及其矿物学特征进行了分析。研究结果表明,研究区黏土矿物组成以蒙脱石为主,平均含量为49%;其次是伊利石,平均含量为35%;绿泥石平均含量为11%;高岭石含量最少,平均含量为5%。通过将研究区黏土矿物组合特征与潜在物源区进行对比,并结合主要黏土矿物的结晶学特征,认为蒙脱石主要来源于帕里西维拉海盆周边的海山或海脊物质的风化和蚀变,其分布可能主要受控于底层洋流;伊利石和绿泥石主要来自于亚洲大陆,风力吹扬为其主要输运方式。黏土矿物表层分布显示伊利石主要富集于地势较低处,蒙脱石在靠近帕劳海脊和雅浦海脊等地势较高处呈现高值。由于较少受到周边海山或海脊物质稀释和底层洋流侵蚀作用的影响,东菲律宾海深水区沉积物中风尘组分通量最能代表亚洲大陆风尘对研究区的实际贡献量,这一研究将对从东菲律宾海沉积物中提取亚洲大陆风尘物质输入信号进而追溯亚洲大陆的古气候演化历史具有重要意义。
Abstract:We analyzed the clay mineral assemblages, contents and mineralogical characteristics for the 125 surface sediments recovered from the Parece Vela Basin. It is found that the clay minerals are mainly composed of smectite (average 49%), illite (average 35%) and chlorite (average 11%) with minor kaolinite(average 5%).Comparing the clay mineral assemblages and their crystallographic characters with the potential provenances, we suggest that smectite is mainly from the volcanic arc materials around the Parece Vela Basin and its distribution pattern may be mainly controlled by deep currents. Illite and chlorite are mainly derived from the Asian eolian deposits transported by wind. The spatial distribution of clay minerals indicates that illite dominates the lower terrain, while smectite is concentrated in the higher places near the Palau ridge and the Yap ridge. With the minimal effects of the volcanic material dilution and the influence of deep current erosion, the eolian flux in the deep East Philippine Sea can represent the actual contribution of Asian wind dust to the study area. It will be of great significance to extract the wind dust from the East Philippine Sea sediments for the further study of the paleoclimate evolution in the Asian continent.
-
Key words:
- clay mineralsl /
- provenance /
- seafloor topography /
- East Philippines Sea /
- Parece Vela basin
-

-
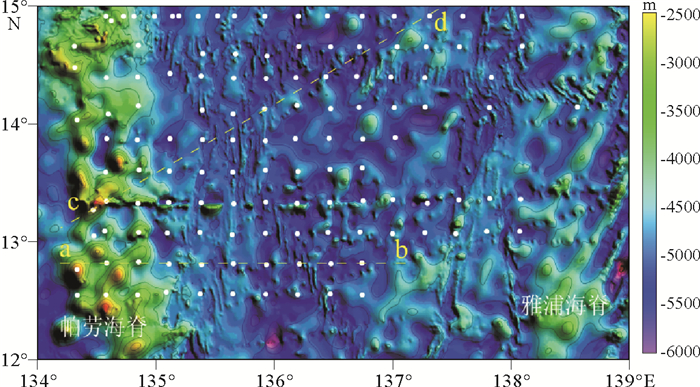
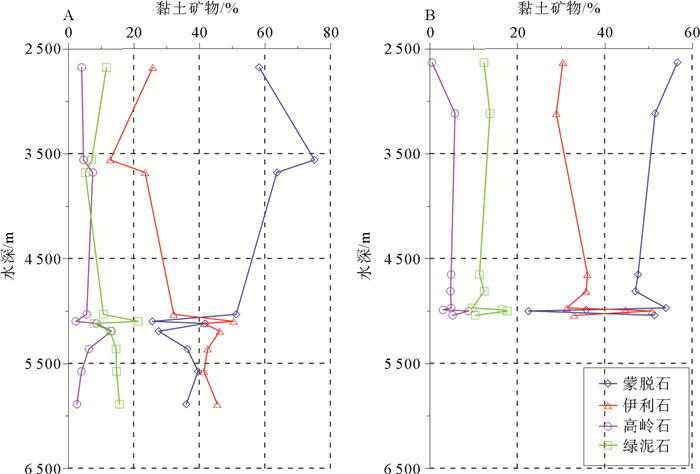
图 6 黏土矿物沿水深横断面分布图(A: ab横断面,B: cd横断面,横断面位置在图 2中显示)
Figure 6.
-
[1] 石学法, 陈丽蓉, 李坤业, 等.西菲律宾海西部海域黏土沉积物的成因矿物学研究[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1995, 15(2): 61-71. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HYDZ502.007.htm
SHI Xuefa, CHEN Lirong, LI Kunye, et al. Study on mineralogy of the clay sediment in the west of Philippine Sea[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology. 1995, 15(2): 61-71. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HYDZ502.007.htm
[2] 池野, 李安春, 蒋富清, 等.吕宋岛东部海域黏土矿物组合特征及物源分析[J].海洋科学, 2009, 33: 80-88. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hykx200909016
CHI Ye, LI Anchun, JIANG Fuqing, et al. Assemblage and provenance of clay minerals of the east of Luzon Island[J]. Marine Science, 2009, 33: 80-88. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hykx200909016
[3] Wan S M, Yu Z J, Clift P D, et al. History of Asian eolian input to the West Philippine Sea over the last one million years[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2012, 326: 152-159. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/8574156
[4] Jiang F Q, Frank M, Li T G, et al. Asian dust input in the western Philippine Sea: Evidence from radiogenic Sr and Nd isotopes[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2013, 14(5): 1538-1551. doi: 10.1002/ggge.20116
[5] Seo I, Lee Y I, Yoo C M, et al. Sr-Nd isotope composition and clay mineral assemblages in eolian dust from the central Philippine Sea over the last 600 kyr: Implications for the transport mechanism of Asian dust[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2014, 119(19): 11, 492-11, 504. doi: 10.1002/2014JD022025
[6] Xu Z K, Li T G, Clift P D, et al. Quantitative estimates of Asian dust input to the western Philippine Sea in the mid-late Quaternary and its potential significance for paleoenvironment[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2015, 16(9): 3182-3196. doi: 10.1002/2015GC005929
[7] Yu Z J, Wan S M, Colin C, et al. Co-evolution of monsoonal precipitation in East Asia and the tropical Pacific ENSO system since 2.36 Ma: New insights from high-resolution clay mineral records in the West Philippine Sea[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2016, 446: 45-55. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2016.04.022
[8] 靳宁, 李安春, 刘海志, 等.帕里西维拉海盆西北部表层沉积物中黏土矿物的分布特征及物源分析[J].海洋与湖沼, 2007, 38(6): 504-511. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814x.2007.06.004
JIN Ning, LI Anchun, LIU Haizhi, et al. Clay minerals in surface sediment of the northwest Parece Vela basin: distribution and provenance[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2007, 38: 504-511. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814x.2007.06.004
[9] 徐兆凯, 李安春, 蒋富清, 等.东菲律宾海深水铁锰结壳发育站位沉积物的粒度及黏土矿物学特征[J].海洋学报, 2007, 29(2): 150-155. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2007.02.019
XU Zhaokai, LI Anchun, JIANG Fuqing, et al. Grain-size and clay mineral characteristics of sediments under deep water ferromanganese crusts in the eastern Philippine Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2007, 29(2): 150-155. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2007.02.019
[10] 徐兆凯, 李安春, 蒋富清, 等.东菲律宾海沉积物的地球化学特征与物质来源[J].科学通报, 2008, 53(6): 695-702. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2008.06.013
XU Zhaokai, LI Anchun, JIANG Fuqing, et al. The geochemical characteristics and material sources in the eastern Philippine Sea[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2008, 53(6): 695-702. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2008.06.013
[11] 孟庆勇, 李安春, 蒋富清, 等.近2 Ma来东菲律宾海地球磁场相对强度变化的沉积记录[J].海洋与湖沼, 2010, 41(4): 606-613. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyyhz201004021
MENG Qingyong, LI Anchun, JIANG Fuqing, et al. A geomagnetic paleointensity record over the last 2Ma from the east Philippine Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2010, 41(4): 606-613. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyyhz201004021
[12] 熊志方, 李铁刚, 翟滨, 等.低纬度西太平洋末次冰期Ethmodiscus rex硅藻席黏土矿物特征及形成机制启示[J].地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2010 (4): 551-562.
XIONG Zhifang, LI Tiegang, ZHAI Bin, et al. Clay Mineral Characteristics of Ethmodiscus rex Diatom Mats from Low-Latitude Western Pacific during the Last Glacial and Implications for Their Formation[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2010 (4): 551-562.
[13] 明洁, 李安春, 孟庆勇, 等.东菲律宾海帕里西维拉海盆第四纪黏土矿物组合特征及物源分析[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(4): 139-148. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201204017
MING Jie, LI Anchun, MENG Qingyong, et al. Quaternary assemblage characteristic and provenance of clay minerals in the Parecevela Basin of the east Philippine Sea[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(4): 139-148. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201204017
[14] 徐兆凯, 李铁刚, 李安春.东菲律宾海表层沉积物来源的稀土证据[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2013, 33(2): 1-7. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201302001
XU Zhaokai, LI Tiegang, LI Anchun. Provenance of surficial sediments of the east Philippine Sea: evidence from rare earth elements[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2013, 33(2): 1-7. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201302001
[15] Xiong Z F, Li T G, Crosta X, et al. Potential role of giant marine diatoms in sequestration of atmospheric CO2 during the Last Glacial Maximum: δ13C evidence from laminated Ethmodiscus rex mats in tropical West Pacific[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2013, 108: 1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2013.06.003
[16] Xiong Z F, Li T G, Algeo T, et al. The silicon isotope composition of Ethmodiscus rex laminated diatom mats from the tropical West Pacific: Implications for silicate cycling during the Last Glacial Maximum[J]. Paleoceanography, 2015, 30(7): 803-823. doi: 10.1002/2015PA002793
[17] Asahara Y, Tanaka T, Kamioka H, et al. Asian continental nature of 87Sr/86Sr ratios in north central Pacific sediments[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1995, 133(1): 105-116.
[18] 秦蕴珊, 陈丽蓉, 石学法.西菲律宾海风成沉积物的研究[J].科学通报, 1995, 40(17): 1595-1597. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1995.17.017
QIN Yunshan, CHEN Lirong, SHI Xuefa. Research on the eolian sediment in the West Philippine Sea[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1995, 40(17): 1595-1597. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1995.17.017
[19] Asahara Y, Tanaka T, Kamioka H, et al. Provenance of the north Pacific sediments and process of source material transport as derived from Rb-Sr isotopic systematic[J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 158(3): 271-291. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs11430-007-0052-6
[20] Rebesco M, Camerlenghi A, Van Loon A J. Contourite research: a field in full development[M]. In: Rebesco M, Camerlenghi A. (Eds.), Contourites. Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2008:3-10.
[21] 田纪伟, 曲堂栋.南海深海环流研究进展[J].科学通报, 2012, 57(20): 1827-1832. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201220002
TIAN Jiwei, QU Tangdong. Advances in research on the deep South China Sea circulation[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(20): 1827-1832. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201220002
[22] Nagel U, Muller G, Schumann D. Mineralogy of sediments cored during Deep Sea Project Leg 58-60 in the North and South Philippine Sea: results of x-ray diffraction analyses[C]// In: Hussong D M, Uyeda S, Blanchet R, et al. eds. Initial Reports of the Deep Sea Drilling Project. 1981, 60: 415-435.
[23] Qiu B. Kuroshio and Oyashio currents[M]. Academic Press, New York, 2001: 1413-1425.
[24] Kawabe M, Fujio S. Pacific Ocean circulation based on observation[J]. Journal of Oceanography, 2010, 66(3): 389-403. doi: 10.1007/s10872-010-0034-8
[25] Biscaye P E. Mineralogy and sedimentation of recent deep-sea clay in the Atlantic Ocean and adjacent seas and oceans[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1965, 76(7): 803-832. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1965)76[803:MASORD]2.0.CO;2
[26] Ehrmann W. Implications of late Eocene to early Miocene clay mineral assemblages in McMurdo Sound (Ross Sea, Antarctica) on paleoclimate and ice dynamics[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1998, 139(3): 213-231. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-S0031-0182(97)00138-7/
[27] Chamley H. Clay Sedimentology[M]. New York: Springer-Verlag. 1989.
[28] Petschick R, Kuhn G, Gingele F. Clay mineral distribution in surface sediments of the South Atlantic: sources, transport, and relation to oceanography[J]. Marine Geology, 1996, 130(3): 203-229. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-0025-3227(95)00148-4/
[29] 杨雅秀, 张乃娴, 苏昭冰, 等.中国黏土矿物[M].北京:地质出版社, 1994: 143-150.
YANG Yaxiu, ZHANG Naixian, SU Zhaobing, et al. Clay Minerals in China[M]. Beijing: Geological Press, 1994: 143-150.
[30] Liu Z, Colin C, Li X, et al. Clay mineral distribution in surface sediments of the northeastern South China Sea and surrounding fluvial drainage basins: Source and transport[J]. Marine Geology, 2010, 277(1): 48-60. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=51e3ac19a036ceb401b4c0030fb95262&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[31] Wan S, Li A, Clift P D, et al. Development of the East Asian monsoon: mineralogical and sedimentologic records in the northern South China Sea since 20 Ma[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2007, 254(3): 561-582. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=69b0d1afbfe10b3f9b0ca393b5a6a5cb&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[32] Yang S, Jung H S, Lim D I, et al. A review on the provenance discrimination of sediments in the Yellow Sea[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2003, 63(1): 93-120. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=9692c64055ede8f886a2a97ba93984b3&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[33] Lu J, Li A, Huang P, et al. Mineral distributions in surface sediments of the western South Yellow Sea: implications for sediment provenance and transportation[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2015, 33(2):510-524. doi: 10.1007/s00343-015-4106-x
[34] Liu Z, Zhao Y, Colin C, et al. Chemical weathering in Luzon, Philippines from clay mineralogy and major-element geochemistry of river sediments[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2009, 24(11): 2195-2205. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2009.09.025
[35] 于兆杰.近百万年以来西菲律宾海风尘沉积研究[D].中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所), 2013.
YU Zhaojie. Research on Asian eolian input to the West Philippine Sea over the last one million years[D]. Qingdao: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of Oceanology), 2013.
[36] 刘华华, 蒋富清, 周烨, 等.晚更新世以来奄美三角盆地黏土矿物的来源及其对古气候的指示[J].地球科学进展, 2016, 31(3): 286-297. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkxjz201603007
LIU Huahua, JIANG Fuqing, ZHOU Ye, et al. Provenance of clay minerals in the Amami Sankaku Basin and their paleoclimate implications since late Pleistocene[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2016, 31(3): 286-297. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkxjz201603007
[37] Honza E, Fujioka K. Formation of arcs and backarc basins inferred from the tectonic evolution of Southeast Asia since the Late Cretaceous[J]. Tectonophysics, 2004, 384(1): 23-53. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c3488168eb8f7fc8f8ab68f379f6695f
[38] Ji J, Chen J, Lu H. Origin of illite in the loess from the Luochuan area, Loess Plateau, Central China[J]. Clay Minerals, 1999, 34(4): 525-525. doi: 10.1180/000985599546398
[39] Li C S, Shi X F, Kao S J, et al. Clay mineral composition and their sources for the fluvial sediments of Taiwanese rivers[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(6): 673-681. doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4824-1
[40] Liu Z, Tuo S, Colin C, et al. Detrital fine-grained sediment contribution from Taiwan to the northern South China Sea and its relation to regional ocean circulation[J]. Marine Geology, 2008, 255(3): 149-155. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=3c70f15b2d54be4783aa8b6db264f74b
[41] Dadson S J, Hovius N, Chen H, et al. Links between erosion, runoff variability and seismicity in the Taiwan orogen[J]. Nature, 2003, 426: 648-651. doi: 10.1038/nature02150
[42] Divins D L, Total Sediment Thickness of the World's Oceans and Marginal Seas[J], NOAA National Geophysical Data Center, Boulder, CO, 2003.
[43] Wan S, Li A, Clift P D, et al. Development of the East Asian monsoon: mineralogical and sedimentologic records in the northern South China Sea since 20 Ma[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2007, 254(3): 561-582. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=69b0d1afbfe10b3f9b0ca393b5a6a5cb&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[44] 师育新, 戴雪荣, 李节通, 等.末次间冰期兰州黄土记录中的黏土矿物及其环境意义探讨[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1997, 17(1): 87-94. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HYDZ701.012.htm
SHI Yuxin, DAI Xuerong, LI Jietong. Origin and significance of clay minerals in the Last Interglacial loess in Lanzhou area, North Central China[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 1997, 17(1): 87-94. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HYDZ701.012.htm
[45] 师育新, 戴雪荣, 宋之光, 等.我国不同气候带黄土中黏土矿物组合特性分析[J].沉积学报, 2005, 23(4): 690-695. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2005.04.019
SHI Yuxin, DAI Xuerong, SONG Zhiguang, et al. Characteristics of Clay Mineral Assemblages and Their Spatial Distribution of Chinese Loess in Different Clmiatic Zones[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2005, 23(4): 690-695. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2005.04.019
[46] 郑洪汉, 顾雄飞, 韩家懋, 等.中国黄土中的黏土矿物及其在地层剖面中的变化趋势——洛川和陇西黄土剖面的初步研究[J].第四纪研究, 1985(1): 158-165. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DSJJ198501019.htm
ZHENG Honghan, GU Xiongfei, HAN Jiamao, et al. Clay Minerals in Loess of China and Their Tendency in Loess Section[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1985(1): 158-165. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DSJJ198501019.htm
[47] 唐诵六, 顾新运, 罗家贤.豫北第四纪沉积物的矿物特征[J].土壤学报, 1979, 16(2): 157-163. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-TRXB197902006.htm
TANG Songliu, GU Xinyun, LUO Jiaxian. Mineralogical Prooerties of the Quaternary Sedients in Northern Henan[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 1979, 16(2): 157-163. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-TRXB197902006.htm
[48] 张德玉.马里亚纳海槽区黏土矿物组成及分布特征[J].黄渤海海洋, 1994, 12(2): 32-39. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HBHH402.004.htm
ZHANG Deyu. Clay Mineral Composition and Distribution in the Mariana Trough[J]. Journal of Oceanography of Huanghai and Bohai Seas, 1994, 12(2): 32-39. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HBHH402.004.htm
-




 下载:
下载: