HIGH-RESOLUTION PALEOCLIMATIC RECORDS OF MIS9 IN NORTHEASTERN SICHUAN, CENTRAL CHINA
-
摘要:
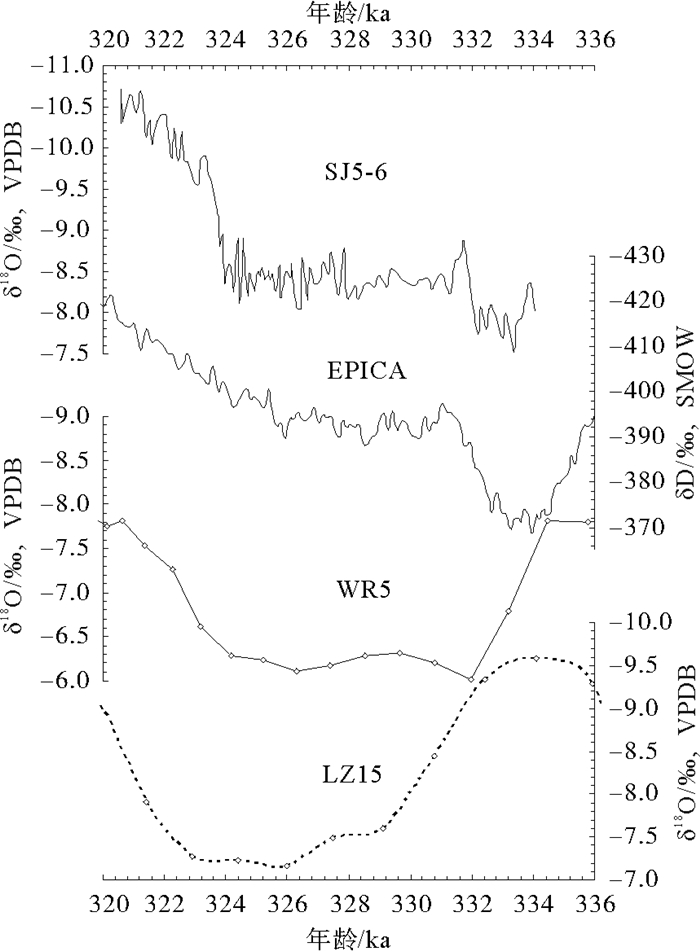
间冰期气候是古气候研究中重点关注的内容之一。通过对川东北宋家洞石笋SJ5-6高精度230Th定年和高分辨率氧同位素分析,重建了该地区334~320 ka(MIS9)时期高分辨率夏季风气候变化历史。结果发现,SJ5-6记录的夏季风变化趋势总体上与亚洲季风区其他石笋记录相似,也与南极冰芯记录的温度变化基本一致,反映了在MIS9间冰期南半球高纬度地区温度变化可能对川东北地区的夏季风气候变化产生了重要影响。
Abstract:Interglacial climate is one of the major concerns in paleoclimate investigations. The stable oxygen isotope of a stalagmite (SJ5-6) from the Songjia Cave in northeastern Sichuan, central China, which is precisely dated with 230Th dating method, show prominent paleoenvironmental changes during the MIS (marine oxygen isotope stage) 9. The stalagmite of SJ5-6 developed from 334 ka to 320 ka, a part of MIS9. The variations in δ18O of the stalagmite are interpreted as the responses to the millennial-scale fluctuations of the Asian summer monsoon intensity during 334~320 ka. The δ18O record studied is roughly parallel with the other speleothem δ18O records recovered from the Asian summer monsoon region. In particular, there is a high similarity of temperature pattern between the stalagmite SJ5-6 and the Antarctic ice core. This suggests that temperature changes over the Antarctica may play an important role in the evolution of the Asian summer monsoon during the past interglacial.
-
Key words:
- speleothem δ18O /
- summer monsoon /
- MIS9 /
- Central China /
- Antarctic influence
-

-
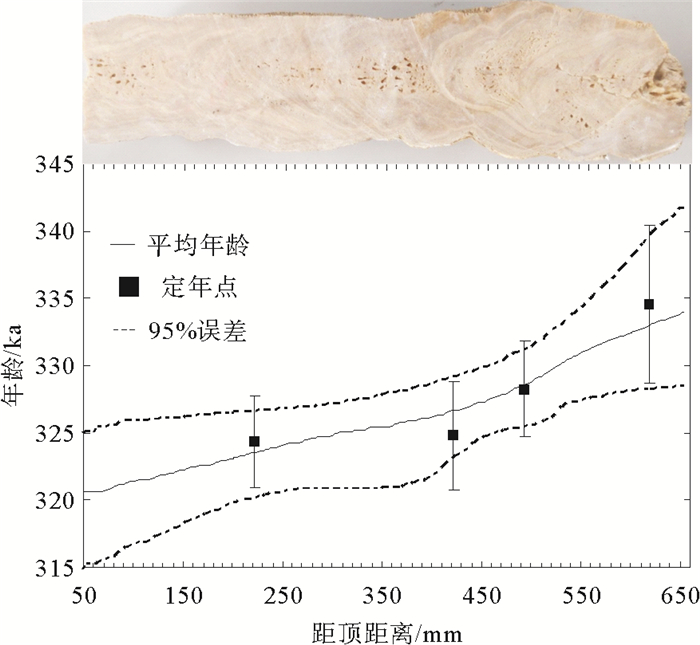
表 1 石笋SJ5-6的230Th测年结果
Table 1. 230Th dating results for stalagmite SJ5-6
样号 深度/mm 年龄/ka 误差±2σ SJ5-6-2 125 330 4.14 SJ5-6-3 218 324 3.42 SJ5-6-4 328 331 3.39 SJ5-6-5 416 325 4.06 SJ5-6-6 486 328 3.58 SJ5-6-7 610 335 5.83 -
[1] Ding Z, Liu T, Rutter N W, et al. Ice-volume forcing of East Asian winter monsoon variations in the past 800 000 years[J]. Quaternary Research, 1995, 44(2):149-159. doi: 10.1006/qres.1995.1059
[2] Wang Y J, Cheng H, Edwards R L, et al. A high-resolution absolute-dated late Pleistocene Monsoon record from Hulu Cave, China[J]. Science, 2001, 294 (5550):2345-2348. doi: 10.1126/science.1064618
[3] Cai Y, An Z, Cheng H, et al. High-resolution absolute-dated Indian Monsoon record between 53 and 36 ka from Xiaobailong Cave, southwestern China[J]. Geology, 2006, 34(8):621. doi: 10.1130/G22567.1
[4] Zhang P, Johnson K R. Test of climate, sun, and culture relationships from an 1810-year Chinese cave record [J]. Science, 2008, 322 (5903):940-942. doi: 10.1126/science.1163965
[5] Cheng H, Edwards R L, Broecker W S.Ice age terminations[J]. Science, 2009, 326 (5950):248-252. doi: 10.1126/science.1177840
[6] Zhou H, Zhao J, Wang Q, et al. Speleothem-derived Asian summer monsoon variations in Central China, 54~46?ka [J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2011, 26(8):781-790. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e1ece5adfa569a771c28d2383fbdeaa4
[7] An Z, Clemens S C, Shen J, et al. Glacial-Interglacial Indian summer monsoon dynamics [J]. Science, 2011, 333(6043):719-23. doi: 10.1126/science.1203752
[8] Xue F, Wang H, He J. Interannual variability of Mascarene High and Australian High and their influences on East Asian summer monsoon [J]. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan, 2004, 82(4):1173-1186. doi: 10.2151/jmsj.2004.1173
[9] Zhou H, Zhao J X, Feng Y, et al. Heinrich event 4 and Dansgaard/Oeschger events 5-10 recorded by high-resolution speleothem oxygen isotope data from central China[J]. Quaternary Research, 2014, 82(2):394-404. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2014.07.006
[10] Zhou H, Zhao J, Zhang P, et al. Decoupling of stalagmite-derived Asian summer monsoon records from North Atlantic temperature change during marine oxygen isotope stage 5d[J]. Quaternary Research, 2008, 70(2):315-321. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2008.04.007
[11] 陈琼, 刘淑华, 米小建, 等.川东北石笋记录的GIS4-5夏季风气候变化及与高纬气候的联系[J].第四纪研究, 2014, 34(6):1264-1269. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dsjyj201406015
CHEN Qiong, LIU Shuhua, MI Xiaojian, et al. Speleothem-derived Asian summer monsoon variations during Greenland interstadials 4 to 5 in NE Sichuan, central chian and teleconnections with high latitude climates [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2014, 34(6): 1264-1269. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dsjyj201406015
[12] Scholz D, Hoffmann D L. StalAge-An algorithm designed for construction of speleothem age models [J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2011, 6(3): 369-382. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=55e5ad95cfa7494bb324e83078a713f5
[13] Yuan D, Cheng H, Edwards R L, et al. Timing, duration, and transitions of the last interglacial Asian monsoon[J]. Science, 2004, 304(5670):575-578. doi: 10.1126/science.1091220
[14] Maher B A, Thompson R. Oxygen isotopes from Chinese caves: records not of monsoon rainfall but of circulation regime [J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2012, 27(6):615-624. doi: 10.1002/jqs.2553
[15] Dorale J A, Liu Z. Limitations of hendy test criteria in judging the paleoclimatic suitability of speleothems and the need for replication [J]. Journal of Cave & Karst Studies the National Speleological Society Bulletin, 2009, 71(1):73-80. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=Open J-Gate000001400941
[16] Meckler A N, Clarkson M O, Cobb K M, et al. Interglacial hydroclimate in the tropical West Pacific through the Late Pleistocene[J]. Science, 2012, 336(6086): 1301-1304. doi: 10.1126/science.1218340
[17] Jouzel J, Masson-Delmotte V, Cattani O, et al. Orbital and millennial Antarctic climate variability over the past 800 000 years [J]. Science, 2007, 317(5839):793-796. doi: 10.1126/science.1141038
[18] Zhao K, Wang Y, Edwards R L, et al. High-resolution stalagmite δ18O records of Asian monsoon changes in central and southern China spanning the MIS 3/2 transition[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 2010, 298(1-2):191-198. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e2220bf1e22983da2ced55c543fd3cc0
[19] Duan F, Liu D, Cheng H, et al. A high-resolution monsoon record of millennial-scale oscillations during Late MIS 3 from Wulu Cave, south-west China[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2014, 29(1):83-90. doi: 10.1002/jqs.2681
[20] Rohling E J, Liu Q S, Roberts A P, et al. Controls on the East Asian monsoon during the last glacial cycle, based on comparison between Hulu Cave and polar ice-core records[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2009, 28(27): 3291-3302. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=a417e96afd2a5b99b73c4f71d400a7bb
[21] EPICA community members. Eight glacial cycles from an Antarctic ice core [J]. Nature, 2004, 429:623-628. doi: 10.1038/nature02599
[22] Cheng H, Edwards R L, Sinha A, et al. The Asian monsoon over the past 640 000 years and ice age terminations [J]. Nature, 2016, 534: 640-646. doi: 10.1038/nature18591
-




 下载:
下载: