FINE-GRAINED TURBIDITES IN GMGS01 OF THE SHENHU AREA, NORTHERN SOUTH CHINA SEA AND ITS SIGNIFICANCE
-
摘要:
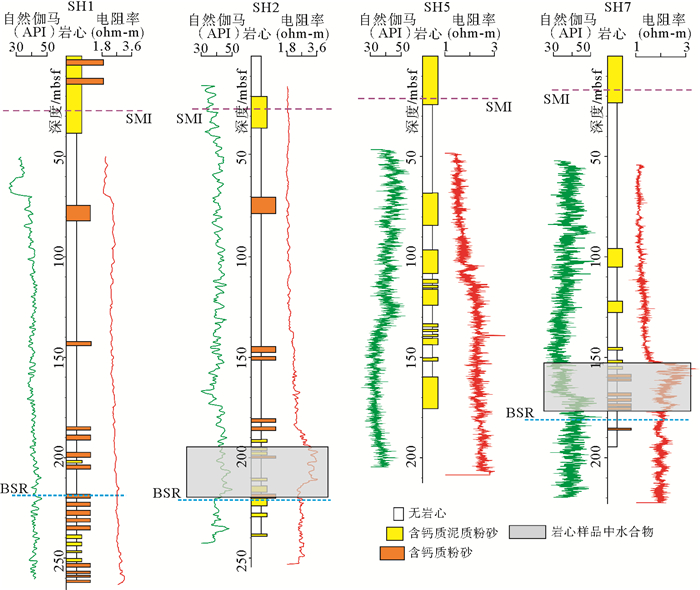
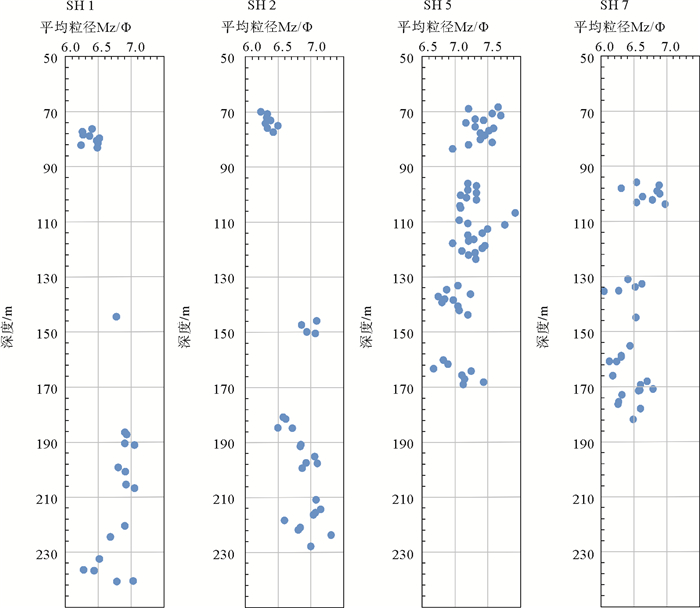
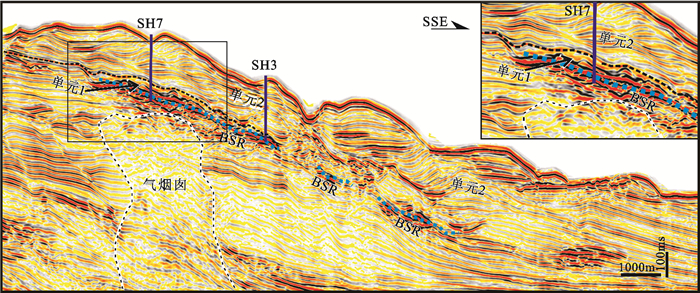
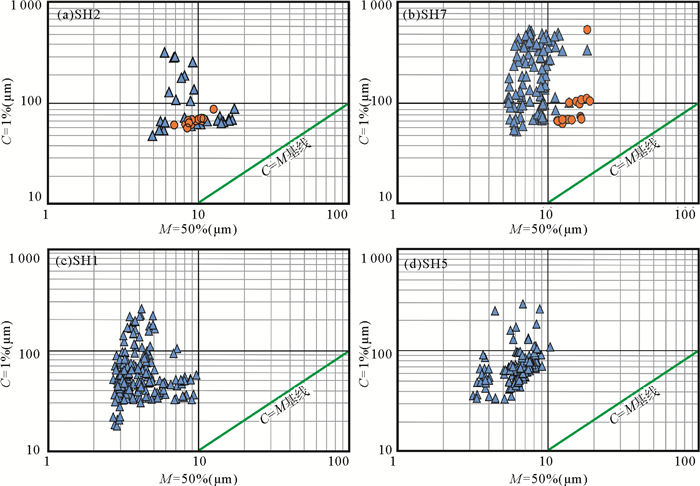
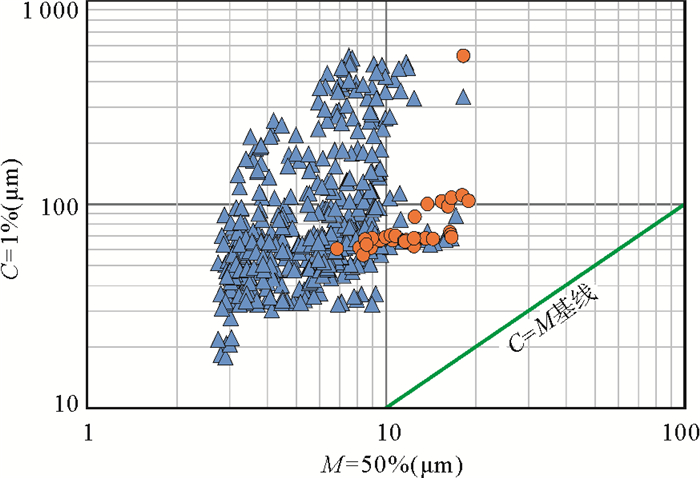
利用广州海洋地质调查局在神狐海域采集的高分辨率地震数据,结合2007年第一次水合物钻探航次(GMGS01)获取的岩心资料,从地震反射结构和岩心粒度特征两个方面对GMGS01区块内残留在峡谷群脊部的细粒浊积体进行了识别和特征刻画。过水合物钻探站位的准3D地震剖面显示,GMGS01区块似海底反射(bottom simulating reflectors,BSR)之上的沉积体表现为2套特征迥异的反射单元:位于下部的薄层透镜状的杂乱反射单元,位于上部的厚层波状起伏形态的连续性中—强振幅反射单元。实际钻获岩心的粒度分析结果表明,沉积物的粒度为4~63 μm,为细粒的粉砂或粉砂质泥。自下而上,沉积物的岩性和粒度特征没有发生大的变化,较为相似。但通过粒度CM图,可以发现,含水合物层段与不含水合物层段的沉积物表现为不同的特征,含水合物层段沉积物的结果近似与C=M基线平行,暗示了细粒浊积体的存在。结合神狐海域区域性覆盖的2D地震资料,研究认为发育在神狐海域北部的一系列小型水道,将会侵蚀下部地层的沉积物,使其沿着陆坡坡降的方向发生自北向南的再次搬运,在中—下陆坡的位置以细粒浊积体的形式再次沉积下来。神狐海域细粒浊积体的识别,将为从深水沉积的角度探讨GMGS01区块内水合物的不均匀性分布提供依据,从而有助于进一步揭示该区域水合物的成藏机制和富集规律。
Abstract:Based upon the high-resolution seismic data acquired by the Guangzhou Marine Geological Survey and the cores collected by the First Hydrate Drilling Expedition (GMGS01), a kind of fine-grained turbidite is identified in the Shenhu Area of the northern South China Sea. According to the seismic profiles crossing hydrate drilling sites, two seismic units are recognized above the BSR (bottom simulating reflectors): the Unit 1 at the bottom consisting of thin-bedded lenticular chaotic seismic reflectors and the Unit 2 at the top consisting of thick continuous moderate-amplitude seismic reflectors with wavy structures. Grain size analysis illustrates that the deposits are composed of fine-grained silt or silty clay ranging 4-63 μm in grain size. Both the lithological features and grain size parameters are consistent from bottom to top without significant changes. It implies that all the deposits should be the results of a similar depositional process. Moreover, on the C-M diagram, the samples from the hydrate bearing sediments show a distribution pattern parallel to the C=M baseline, indicating an origin of fine-grained turbidites. Regional survey suggests that these fine-grained turbidites might be associated with some small-scale channels in the north of the Shenhu Area. The sediments provided by these small channels move downslopewards and re-deposited in the middle to lower slope as fine-grained turbidites. Based upon the above interpretation, a model is proposed to reveal the relationships between fine-grained tuebidites and hydrates, It says that the heterogeneous distributions of gas hydrates in GMGS01 of the Shenhu Area, northern South China Sea probably owes its origin to the uneven distribution of fine grained turbidites.
-

-
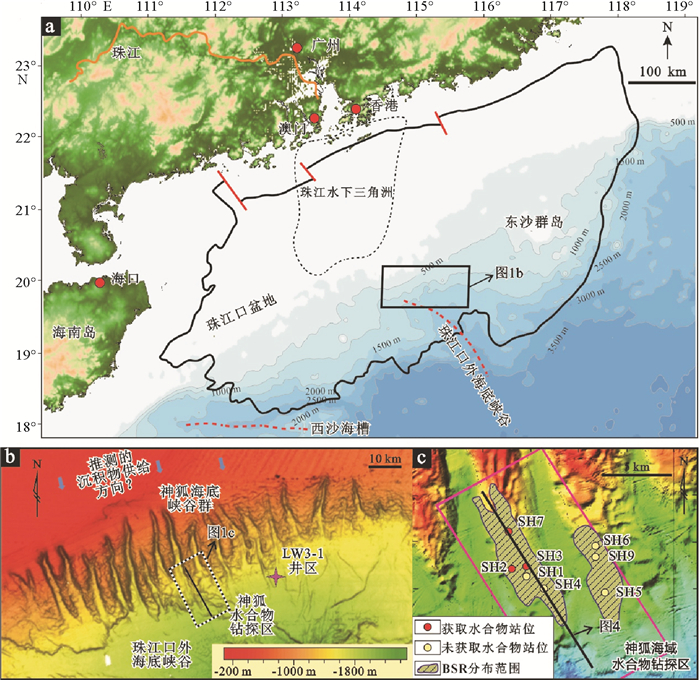
图 1 南海北部陆坡神狐海域区域位置图(a)、海底地貌特征图(b)及GMGS01区块内的钻井分布(c) [28]
Figure 1.
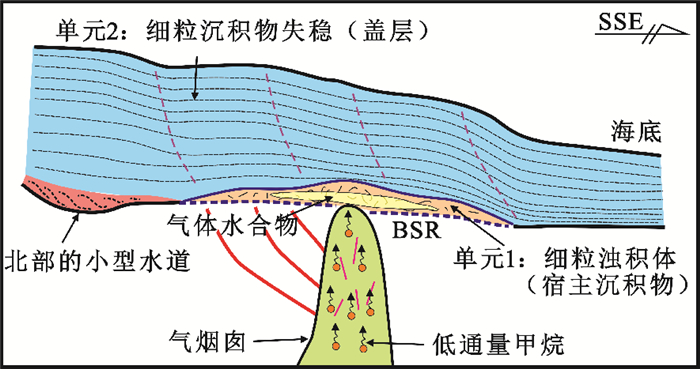
图 7 神狐海域GMGS01水合物的成藏模式图(据文献[27])
Figure 7.
-
[1] Wu Nengyou, Yang Shengxiong, Zhang Haiqi, et al. Preliminary discussion on natural gas hydrate reservoir system of Shenhu area, North Slope of South China Sea[C]//6th International Conference on Gas Hydrates (ICGH 2008), 7 pp, World oils, Vancouver B C, Canada, 6-10 Jul, 2008.
[2] Yang Shengxiong, Zhang Haiqi, Wu Nengyou, et al. High concentration hydrate in disseminated forms obtained in Shenhu area, North Slope of South China Sea[C]//6th International Conference on Gas Hydrates (ICGH 2008), 10 pp, World oils, Vancouver B C, Canada, 6-10 Jul, 2008.
[3] 陈芳, 周洋, 苏新, 等.南海神狐海域含水合物层粒度变化及与水合物饱和度的关系[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(5): 95-100. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201105014
CHEN Fang, ZHOU Yang, SU Xin, et al. Gas hydrate saturation and its relation with grain size of the hydrate-bearing sediments in the Shenhu Area of northern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2011, 31(5): 95-100. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201105014
[4] Liu C L, Ye Y G, Meng Q G, et al. The characteristics of gas hydrates recovered from Shenhu area in the South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 2012, 307-310: 22-27. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2012.03.004
[5] 张辉, 卢海龙, 梁金强, 等.南海北部神狐海域沉积物颗粒对天然气水合物聚集的主要影响[J].科学通报, 2016, 61(3): 388-397. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201603014
ZHANG Hui, LU Hailong, LIANG Jinqiang, et al. The methane hydrate accumulation controlled compellingly by sediment grain at Shenhu, northern South China Sea[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2016, 61(3): 388-397. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201603014
[6] 陈芳, 苏新, 周洋, 等.南海北部陆坡神狐海域晚中新世以来沉积物中生物组分变化及意义[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, 29(2): 1-8. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz200902001
CHEN Fang, SU Xin, ZHOU Yang, et al. Variations in biogenic components of Late Miocene-Holocene sediments from Shenhu Area in the northern South China Sea and their geological implication[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2009, 29(2): 1-8. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz200902001
[7] 陈芳, 周洋, 苏新, 等.南海神狐海域含水合物层底栖有孔虫群落结构与同位素组成[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2010, 30(2): 1-8. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201002001
CHEN Fang, ZHOU Yang, SU Xin, et al. Benthic foraminifera and stable isotopic composition of gas hydrate-bearing sediments from Shenhu Area in the northern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2010, 30(2): 1-8. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201002001
[8] 陈芳, 苏新, 周洋.南海神狐海域水合物钻探区钙质超微化石生物地层与沉积速率[J].地球科学--中国地质大学学报, 2013, 38(1): 1-9. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201301001
CHEN Fang, SU Xin, ZHOU Yang. Late Miocene-Pleistocene calcareous nannofossil biostratigraphy of Shenhu gas hydrate drilling area in the South China Sea and variations in sedimentation rates[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2013, 38(1): 1-9. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201301001
[9] 陈芳, 苏新, 陆红锋, 等.南海神狐海域有孔虫与高饱和度水合物的储存关系[J].地球科学--中国地质大学学报, 2013, 38(5): 907-915. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201305001
CHEN Fang, SU Xin, LU Hongfeng, et al. Relations between biogenic component (foraminifera) and highly saturated gas hydrates distribution from Shenhu Area, northern South China Sea[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2013, 38(5): 907-915. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201305001
[10] 李承峰, 胡高伟, 张巍, 等.有孔虫对南海神狐海域细粒沉积层中天然气水合物形成及赋存特征的影响[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2016, 46(9): 1223-1230. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201609007
LI Chengfeng, HU Gaowei, ZHANG Wei, et al. Influence of foraminifera on formation and occurrence characteristics of natural gas hydrates in fine-grained sediments from Shenhu area, South China Sea[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2016, 59(11): 2223-2230. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201609007
[11] 苏丕波, 雷怀彦, 梁金强, 等.神狐海域气源特征及其对天然气水合物成藏的指示意义[J].天然气工业, 2010, 30(10): 103-108. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trqgy201010025
SU Pibo, LEI Huaiyan, LIANG Jinqiang, et al. Characteristics of gas source in the waters of Shenhu and their significance to gas hydrate accumulation[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2010, 30(10): 103-108. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trqgy201010025
[12] Wu N Y, Zhang H Q, Yang S X, et al. Gas hydrate system of Shenhu Area, northern South China Sea: geochemical results[J]. Journal of Geological Research, 2011, 2011: Article ID 370298.
[13] ZHU Youhai, HUANG Xia, FU Shaoying, et al. Gas sources of natural gas hydrates in the Shenhu Drilling Area, South China Sea: Geochemical evidence and geological analysis[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 2013, 87(3): 767-776. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12088
[14] 吴时国, 董冬冬, 杨胜雄, 等.南海北部陆坡细粒沉积物天然气水合物系统的形成模式初探[J].地球物理学报, 2009, 52(7): 1849-1857. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.07.019
WU Shiguo, DONG Dongdong, YANG Shengxiong, et al. Genetic model of the hydrate system in the fine grain sediments in the northern continental slope of South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2009, 52(7): 1849-1857. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.07.019
[15] 马俊明, 薛林福, 付少英, 等.南海神狐海域地震-沉积相分析与沉积环境演化[J].世界地质, 2013, 32(2): 359-365. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2013.02.021
MA Junming, XUE Linfu, FU Shaoying, et al. Seismic-sedimentary facies analysis and evolution of sedimentary environment in Shenhu Area, South China Sea[J]. Global Geology, 2013, 32(2): 359-365. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2013.02.021
[16] Yu X H, Wang J Z, Liang J Q, et al. Depositional characteristics and accumulation model of gas hydrates in northern South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2014, 56: 74-86. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.03.011
[17] 陆敬安, 杨胜雄, 吴能友, 等.南海神狐海域天然气水合物地球物理测井评价[J].现代地质, 2008, 22(3): 447-451. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2008.03.015
LU Jing'an, YANG Shengxiong, WU Nengyou, et al. Well logging evaluation of gas hydrates in Shenhu Area, South China Sea[J]. Geoscience, 2008, 22(3): 447-451. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2008.03.015
[18] Wang X J, Lee M W, Collett T S, et al. Gas hydrate identified in sand-rich inferred sedimentary section using downhole logging and seismic data in Shenhu area, South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2014, 51: 298-306. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.01.002
[19] 吴能友, 杨胜雄, 王宏斌, 等.南海北部陆坡神狐海域天然气水合物成藏的流体运移体系[J].地球物理学报, 2009, 52(6): 1641-1650. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.06.027
WU Nengyou, YANG Shengxiong, WANG Hongbin, et al. Gas-bearing fluid influx sub-system for gas hydrate geological system in Shenhu Area, northern South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2009, 52(6): 1641-1650. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.06.027
[20] 王力峰, 沙志彬, 梁金强, 等.晚期泥底辟控制作用导致神狐海域SH5钻位未获水合物的分析[J].现代地质, 2010, 24(3): 450-456. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2010.03.005
WANG Lifeng, SHA Zhibin, LIANG Jinqiang, et al. Analysis of gas hydrate absence induced by the late-stage diapir domination in the Borehole SH5 of Shenhu Area[J]. Geoscience, 2010, 24(3): 450-456. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2010.03.005
[21] Sun Y B, Wu S G, Dong D D, et al. Gas hydrates associated with gas chimneys in fine-grained sediments of the northern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 2012, 311-314: 32-40. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2012.04.003
[22] 苏正, 曹运诚, 杨睿, 等.南海北部神狐海域天然气水合物成藏演化分析研究[J].地球物理学报, 2012, 55(5): 1764-1774. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqwlxb201205034
SU Zheng, CAO Yuncheng, YANG Rui, et al. Analytical research on evolution of methane hydrate deposits at Shenhu Area, northern South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2012, 55(5): 1764-1774. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqwlxb201205034
[23] Wang H B, Yang S X, Wu N Y, et al. Controlling factors for gas hydrate occurrence in Shenhu area on the northern slope of the South China Sea[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2013, 56(4): 513-520. doi: 10.1007/s11430-013-4596-3
[24] 梁金强, 王宏斌, 苏新, 等.南海北部陆坡天然气水合物成藏条件及其控制因素[J].天然气工业, 2014, 34(7): 128-135. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trqgy201407022
LIANG Jinqiang, WANG Hongbin, SU Xin, et al. Natural gas hydrate formation conditions and the associated controlling factors in the northern slope of the South China Sea[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(7): 128-135. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trqgy201407022
[25] Wang X J, Collett T S, Lee M W, et al. Geological controls on the occurrence of gas hydrate from core, downhole log, and seismic data in the Shenhu area, South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 2014, 357: 272-292. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.09.040
[26] 苏明, 沙志彬, 乔少华, 等.南海北部神狐海域天然气水合物钻探区第四纪以来的沉积演化特征[J].地球物理学报, 2015, 58(8): 2975-2985. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqwlxb201508030
SU Ming, SHA Zhibin, QIAO Shaohua, et al. Sedimentary evolution since Quaternary in the Shenhu hydrate drilling area, northern South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(8): 2975-2985. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqwlxb201508030
[27] Su M, Yang R, Wang H B, et al. Gas hydrates distribution in the Shenhu Area, northern South China Sea: comparisons between the eight drilling sites with gas-hydrate petroleum system[J]. Geologica Acta, 2016, 14(2): 79-100. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1a6f4cd9f6a5787218823d0f9bfc6ea5&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[28] Ding W W, Li J B, Li J, et al. Morphotectonics and evolutionary controls on the Pearl River Canyon System, South China Sea[J]. Marine Geophysical Research, 2013, 34(3-4): 221-238. doi: 10.1007/s11001-013-9173-9
[29] Li X S, Zhou Q J, Su T Y, et al. Slope-confined submarine canyons in the Baiyun deep-water area, northern South China Sea: variation in their modern morphology[J]. Marine Geophysical Research, 2016, 37(2): 95-112. doi: 10.1007/s11001-016-9269-0
[30] 刘杰, 苏明, 乔少华, 等.珠江口盆地白云凹陷陆坡限制型海底峡谷群成因机制探讨[J].沉积学报, 2016, 34(5): 940-950. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cjxb201605013
LIU Jie, SU Ming, QIAO Shaohua, et al. Forming Mechanism of the Slope-confined Submarine Canyons in the Baiyun Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2016, 34(5): 940-950. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cjxb201605013
[31] He Y, Zhang G F, Wang L L, et al. Characteristics and occurrence of submarine canyon-associated landslides in the middle of the northern continental slope, South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2014, 57: 546-560. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.07.003
[32] Chen D X, Wang X J, Volker D, et al. Three dimensional seismic studies of deep-water hazard-related features on the northern slope of South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 77: 1125-1139. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.08.012
[33] 李刚.我国可燃冰试采圆满结束[N].人民日报, 2017-07-30(001).
LI Gang. China's production of combustible ice ended[N]. People's Daily, 2017-07-30(001).
[34] 张树林, 陈多福, 黄君权.白云凹陷天然气水合物成藏条件[J].天然气工业, 2007, 27(9): 7-10. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2007.09.002
ZHANG Shulin, CHEN Duofu, HUANG Junquan. Conditions of accumulation of gas hydrate in Baiyun Sag[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2007, 27(9): 7-10. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2007.09.002
[35] 苏明, 杨睿, 吴能友, 等.南海北部陆坡区神狐海域构造特征及对水合物的控制[J].地质学报, 2014, 88(3): 318-326. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201403002
SU Ming, YANG Rui, WU Nengyou, et al. Structural characteristics in the Shenhu Area, northern continental slope of South China Sea, and their influences on gas hydrate[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(3): 318-326. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201403002
[36] Passega R. Grain size representation by Cm Patterns as a geological tool[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 1964, 34: 830-847. doi: 10.1306/74D711A4-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D
[37] Lüdmann T, Wong H K, Wang P X. Plio-Quaternary sedimentation processes and neotectonics of the northern continental margin of the South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 2001, 172(3-4): 331-358. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(00)00129-8
[38] Zhou W, Wang Y M, Gao X Z, et al. Architecture, evolution history and controlling factors of the Baiyun submarine canyon system from the middle Miocene to Quaternary in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2015, 67: 389-407. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.05.015
[39] Torres M E, Tréhu A M, Cespedes N, et al. Methane hydrate formation in turbidite sediments of northern Cascadia, IODP Expedition 311[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2008, 271(1-4): 170-180. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2008.03.061
[40] Riedel M, Collett T S, Shankar U. Documenting channel features associated with gas hydrates in the Krishna-Godavari Basin, Offshore India[J]. Marine Geology, 2011, 279(1-4): 1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2010.10.008
[41] Boswell R, Frye M, Shelander D, et al. Architecture of gas-hydrate-bearing sands from Walker Ridge 313, Green canyon 955, and Alaminos canyon 21: northern deepwater Gulf of Mexico[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2012, 34(1): 134-149. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.08.010
[42] Boswell R, Collett T S, Frye M, et al. Subsurface gas hydrates in the northern Gulf of Mexico[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2012, 34(1): 4-30. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.10.003
[43] Noguchi S, Shimoda N, Takano O, et al. 3-D internal architecture of methane hydrate-bearing turbidite channels in the eastern Nankai Trough, Japan[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2011, 28(10): 1817-1828. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.02.004
[44] Ito T, Komatsu Y, Fujii T, et al. Lithological features of hydrate-bearing sediments and their relationship with gas hydrate saturation in the eastern Nankai Trough, Japan[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2015, 66: 368-378. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.02.022
[45] Riedel M, Bahk J J, Kim H S, et al. Seismic facies analyses as aid in regional gas hydrate assessments. Part-II: prediction of reservoir properties, gas hydrate petroleum system analysis, and Monte Carlo simulation[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2013, 47: 269-290. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2013.04.012
[46] Riedel M, Collett T S, Kim H S, et al. Large-scale depositional characteristics of the Ulleung Basin and its impact on electrical resistivity and Archie-parameters for gas hydrate saturation estimates[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2013, 47: 222-235. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2013.03.014
[47] Mills P C. Genesis and diagnostic value of soft-sediment deformation structures-a review[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1983, 35(2): 83-104. doi: 10.1016/0037-0738(83)90046-5
[48] Hüneke H, Mulder T. Deep-Sea Sediments[M]//Developments in Sedimentology. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2011: 1-849.
[49] Normark W R, Gutmacher C E, Chase T E, et al. Monterey fan, pacific ocean[C]//Bouma A H, Normark W R, Barnes N E. Submarine Fans and Related Turbidite Systems. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1985: 79-86.
-



 下载:
下载: