A PRELIMINARY STUDY ON STATIC STRESS TRIGGERING EFFECTS ON MANILA SUBDUCTION ZONE BY THE PHILIPPINE Mw 7.7 EARTHQUAKE 1990
-
摘要:
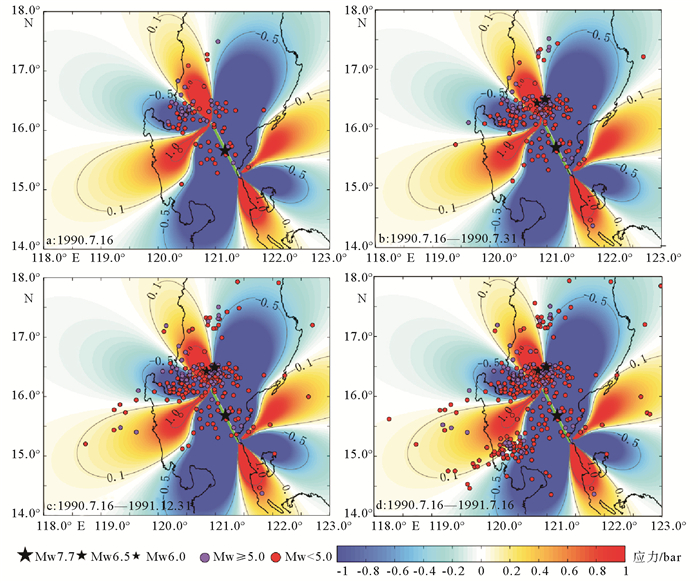
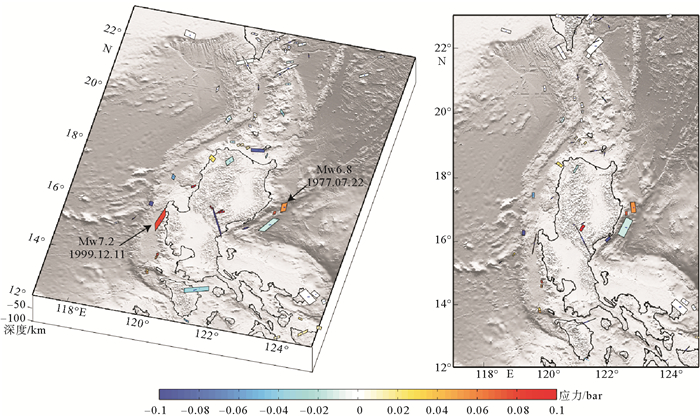
基于震源机制解模型和弹性半空间模型,计算了1990年7月16日Mw 7.7级地震所产生的静态库伦应力变化,研究结果表明Mw 7.7级地震触发了其后Mw 6.0级和Mw 6.5级2次强余震的发生,应力加载值分别达到了21.63 bars和9.15 bars。依据地震重复原则和构造外推原则,以马尼拉俯冲带及其附近区域Mw 6.0级以上地震震源机制解中的一个节面作为接收断层面,计算了Mw 7.7级地震对马尼拉俯冲带区域静态库伦应力的影响,结果表明其对马尼拉俯冲带的影响主要集中在西吕宋海槽的部分断层上,但变化量值很小,对马尼拉俯冲带北部区域基本不产生影响。
Abstract:Based on the solutions of earthquake focal mechanism and the half space homogeneous elastic model, we calculated the variation in stress fields after the Mw 7.7 earthquake. Our results show that the two subsequent strong aftershocks were triggered by the Mw 7.7 earthquake of 16 July 1990, and the static Coulomb stress increased by 21.63 bars and 9.15 bars, respectively. Based on the principles of earthquake recurrence and the structural extrapolation, we used the earthquake focal mechanism solutions for the events greater than Mw 6.0 along the Manila Trench and its adjacent region, one of the nodal plane of the focal mechanism was taken as the receive fault plane in the static stress triggering calculation. The results show that the effect of static Coulomb stress on the Manila subduction zone caused by the Mw 7.7 is mainly concentrated in some faults of the West Luzon Trough, but the variation in Coulomb stress is very small, which has little effect on the northern area of the Manila subduction zone.
-
Key words:
- stress triggering /
- focal mechanism /
- Manila subduction zone
-

-
表 1 1990年Mw7.7级地震震源机制解
Table 1. Focal mechanism solutions for the 1990 Philippine Mw7.7 earthquake
-
[1] Harris R A. Introduction to special section: Stress triggers, stress shadows, and implications for seismic hazard[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1998, 103(B10): 24347-24358. doi: 10.1029/98JB01576
[2] Stein R S, Barka A A, Dieterich J H. Progressive failure on the North Anatolian fault since 1939 by earthquake stress triggering[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 1997, 128(3): 594-604. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.1997.tb05321.x
[3] Toda S, Lin J, Meghraoui M, et al. 12 May 2008 M=7.9 Wenchuang, China, earthquake calculated to increase failure stress and seismicity rate on three major fault systems[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2008, 35(17): L17305, doi: 10.1029/2008GL034903
[4] 张洪由. 1990年7月16日菲律宾强烈地震概况[J].国际地震动态, 1991(1): 16-19. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000000646590
ZHANG Hongyou. Strong earthquake in Philippines in July 16, 1990[J]. Recent Developments in World Seismology, 1991(1): 16-19. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000000646590
[5] Tsutsumi H, Perez J S. Large-scale active fault map of the Philippine fault based on aerial photograph interpretation[J]. Active Fault Research, 2013, 39: 29-37. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=J-STAGE_1512703
[6] Seno T, Stein S, Gripp A E. A model for the motion of the Philippine Sea Plate consistent with NUVEL-1 and geological data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1993, 98(B10): 17941-17948. doi: 10.1029/93JB00782
[7] Yu S B, Hsu Y J, Bacolcol T, et al. Present-day crustal deformation along the Philippine fault in Luzon, Philippines[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 65: 64-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.12.007
[8] Hsu Y J, Yu S B, Song T R A, et al. Plate coupling along the Manila subduction zone between Taiwan and northern Luzon[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 51: 98-108. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.01.005
[9] Hayes D E, Lewis S D. A geophysical study of the manila trench, luzon, philippines 1. Crustal structure, gravity, and regional tectonic evolution[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1984, 89(B11): 9171-9195. doi: 10.1029/JB089iB11p09171
[10] Pautot G, Rangin C. Subduction of the south China sea axial ridge below Luzon (Philippine)[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1989, 92(1): 57-69. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(89)90020-4
[11] 尾池和夫, 沈耀龙, 张维德. 1990年菲律宾地震前后菲律宾海板块俯冲带地区地震活动的变化[J].世界地震译丛, 1994(1): 5-9. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199400057862
WEI Chihefu, SHEN Yaolong, ZHANG Weide. Changes of seismic activity in the Philippines Sea plate subduction zone before and after the Philippines earthquake in 1990[J]. Translated World Seismology, 1994(1): 5-9. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199400057862
[12] 魏柏林, 康英, 陈玉桃, 等.南海地震与海啸[J].华南地震, 2006, 26(1): 47-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8662.2006.01.007
WEI Bolin, KANG Ying, CHEN Yutao, et al. Earthquake and tsunami of the South China Sea[J]. South China Journal of Seismology, 2006, 26(1): 47-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8662.2006.01.007
[13] Doo W B, Hsu S K, Armada L. Philippine island arc system tectonic features inferred from magnetic data analysis[J]. Terrestrial Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, 2015, 26(6): 679-686. doi: 10.3319/TAO.2015.05.11.04(TC)
[14] King G C P, Stein R S, Lin J. Static stress changes and the triggering of earthquakes[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 1994, 84(3): 935-953. doi:10.1029/94JB00611
[15] Okada Y. Internal deformation due to shear and tensile faults in a half-space[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 1992, 82(2): 1018-1040. doi: 10.1016/0148-9062(86)90674-1
[16] Toda S, Stein R S. Response of the San Andreas fault to the 1983 Coalinga-Nuez earthquake: An application of interaction-based probabilities for Parkfield[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2002, 107(B6): ESE 6-1-ESE 6-16. doi: 10.1029/2001JB000172
[17] Lin J, Stein R S. Stress triggering in thrust and subduction earthquakes and stress interaction between the southern San Andreas and nearby thrust and strike-slip faults[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2004, 109(B2): B02303, doi: 10.1029/2003JB002607.
[18] Toda, S, Stein R S, Richards-Dinger K, et al. Forecasting the evolution of seismicity in southern California: Animations built on earthquake stress transfer[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2005, 110(B5): B05S16, doi: 10.1029/2004JB003415.
[19] Bautista M L P, Oike K. Estimation of the magnitudes and epicenters of Philippine historical earthquakes[J]. Tectonophysics, 2000, 317(1-2): 137-169. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(99)00272-3
[20] Dziewonski A M, EkstrÖm G, Woodhouse J H, et al. Centroid-moment tensor solutions for July-September, 1990[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 1991, 67(3-4): 211-220. doi: 10.1016/0031-9201(91)90018-D
[21] Yoshida Y, Abe K. Source mechanism of the Luzon, Philippine earthquake of July 16, 1990[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1992, 19(6): 545-548. doi: 10.1029/91GL02467
[22] Velasco A A, Ammon C J, Lay T, et al. Rupture process of the 1990 Luzon, Philippines (Mw=7.7), earthquake[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1996, 101(B10): 22419-22434. doi: 10.1029/96JB02290
[23] Nakata T, Tsutsumi H, Punongbayan R S, et al. Surface faulting associated with the Philippine earthquake of 1990[J]. Journal of Geography, 1990, 99(5): 515-532. doi: 10.5026/jgeography.99.515
[24] 李保昆, 刁桂苓, Shapira A, 等.唐山与通海两大地震的强余震的差别及其原因探讨[J].西北地震学报, 2009, 31(2): 161-166. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2009.02.012
LI Baokun, DIAO Guiling, Shapira A, et al. Differences between the strong aftershock of Tonghai and Tangshan earthquakes and disscussion on its mechanism[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 2009, 31(2): 161-166. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2009.02.012
[25] 袁一凡, 田启文.工程地震学[M].北京:地震出版社, 2012: 221-222.
YUAN Yifan, TIAN Qiwen. Engineering Seismology[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press, 2012: 221-222.
[26] 盛书中, 万永革, 蒋长胜, 等. 2015年尼泊尔Ms 8.1级强震对中国大陆静态应力触发影响的初探[J].地球物理学报, 2015, 58(5): 1834-1842. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqwlxb201505034
SHENG Shuzhong, WAN Yongge, JIANG Changsheng, et al. Preliminary study on the static stress triggering effects on China mainland with the 2015 Nepal Ms 8.1 earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(5): 1834-1842. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqwlxb201505034
[27] Wells D L, Coppersmith K J. New empirical relationships among magnitude, rupture length, rupture width, rupture area, and surface displacement[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 1994, 84(4): 974-1002.
[28] Harris R A, Simpson R W, Reasenberg P A. Influence of static stress changes on earthquake locations in south California[J]. Nature, 1995, 375(6528): 221-224. doi: 10.1038/375221a0
[29] 缪淼, 朱守彪.俯冲带上特大地震静态库伦应力变化对后续余震触发效果的研究[J].地球物理学报, 2012, 55(9): 2982-2993. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.09.017
MIAO Miao, ZHU Shoubiao. A study of the impact of static Coulomb stress changes of megathrust earthquakes along subduction zone on the following aftershocks[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2012, 55(9): 2982-2993. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.09.017
[30] 单斌, 李佳航, 韩立波, 等. 2010年Ms 7.1级玉树地震同震库仑应力变化以及对2011年Ms 5.2级囊谦地震的影响[J].地球物理学报, 2012, 55(9): 3028-3042. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.09.021
SHAN Bin, LI Jiahang, HAN Libo, et al. Coseismic Coulomb stress change caused by 2010 Ms =7.1 Yushu earthquake and its influence to 2011 Ms =5.2 Nangqen earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2012, 55(9): 3028-3042. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.09.021
-




 下载:
下载: