GEOCHEMISTRY OF THE SEDIMENTS IN SHENHU HYDRATE DRILLING AREA, NORTHERN SOUTH CHINA SEA
-
摘要:
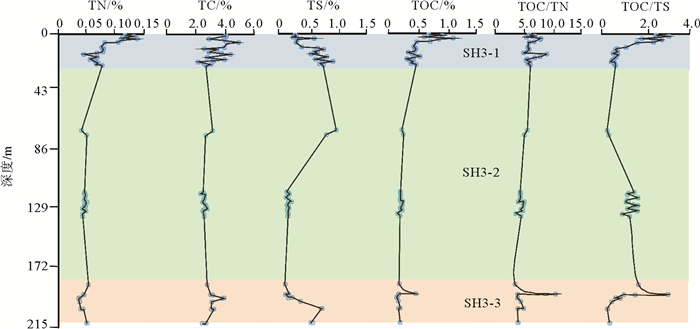
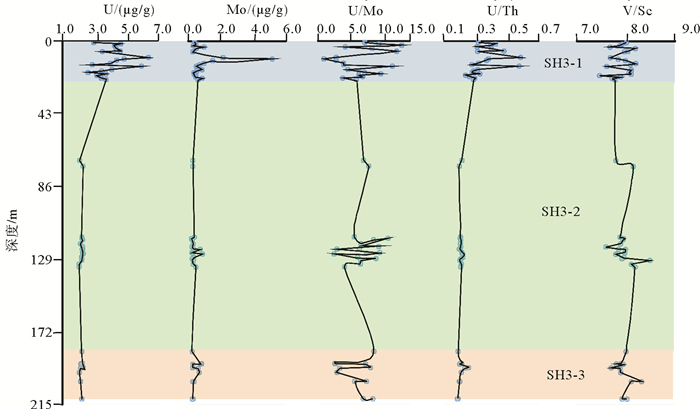
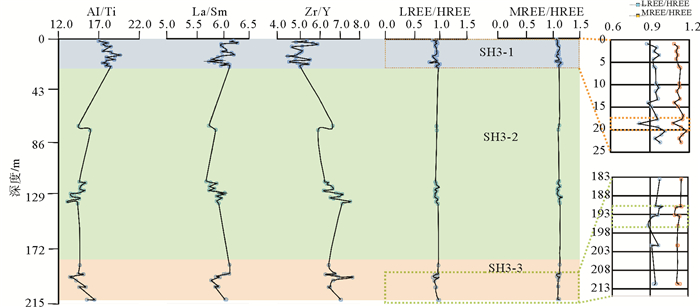
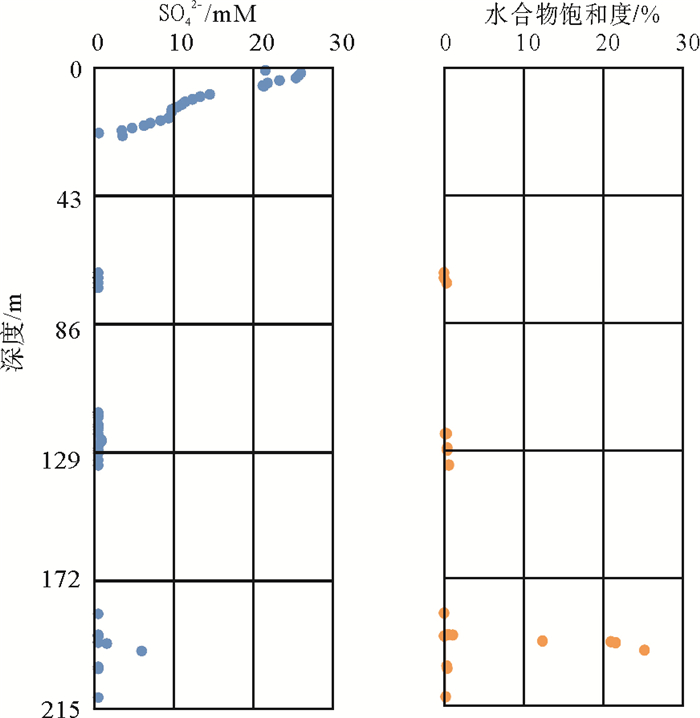
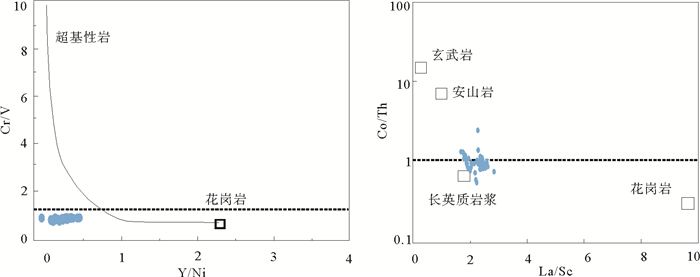
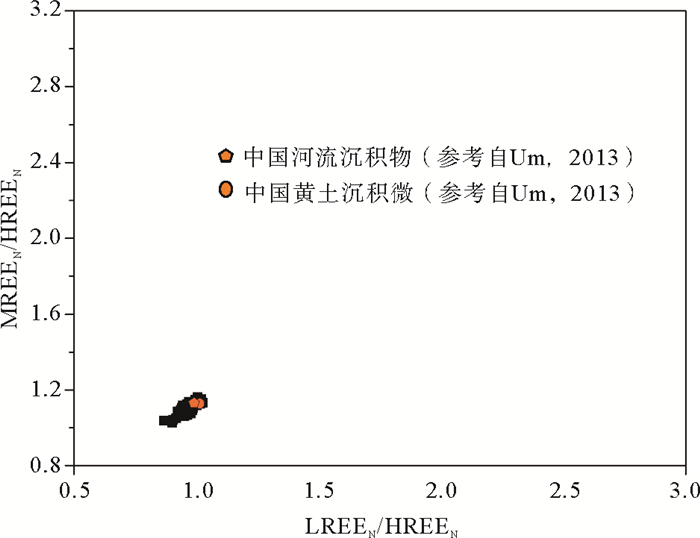
海底水合物形成分解/甲烷渗漏的甲烷以及相关的生物地球化学过程可能对海底的沉积环境产生影响,因此识别水合物的形成分解/甲烷渗漏对海洋沉积环境改造有助于了解水合物成藏特征及其形成分解过程。选取南海北部神狐海域2007年水合物钻探区的SH3钻孔沉积物为研究对象,对SH3钻孔岩心的碳硫数据、主微量元素,尤其是氧化还原敏感元素(U、Mo、U/Mo、V/Sr)进行分析测试,同时结合SH3钻孔孔隙水数据和前人对神狐水合物钻探区的研究成果等进行对比研究。结果表明南海北部神狐海域沉积物来源除河流沉积物以外,同时还有少量中国黄土以及大陆岛弧的长英质岩浆岩沉积物;通过对U、Mo、U/Mo以及碳硫数据分析,发现SH3钻孔在10~25 mbsf(meter below the seafloor)层位为硫酸盐驱动的甲烷厌氧氧化作用(Anaerobic oxidation of methane, AOM)造成的还原沉积环境,AOM作用导致了在这一层位发生了LREE/HREE、MREE/HREE的分馏;SH3钻孔沉积物在约180~215 mbsf的含水合物层位出现了浊流沉积的次氧化的沉积环境,同时其赋存的细粒沉积环境也导致了轻重稀土元素的分馏,与水合物饱和度存在一定的相关性。
Abstract:The formation and decomposition of gas hydrate as well as the methane leakage caused by associated biogeochemical processes may change the depositional environment of the seabed. To identify the decomposition of hydrate as well as the change in marine environment caused by the seeping methane will contribute to the understanding of the processes of hydrate formation and decomposition. In this paper, we selected the Core SH3 as a case from the Shenhu hydrate drilling area in the northern part of South China Sea to study the formation and deterioration of hydrate. Carbon and sulfur contents, main and trace elements, especially redox sensitive elements are measured. Data from pore water and previous researches are also studied. The study suggests that the sediments of the Shenhu area are mainly sourced from a fluvial origin with a little of loess and felsic igneous materials. From the data of U, Mo contents and U/Mo ratio, as well as carbon and sulfur contents, it is inferred that the layers at 10~25 mbsf in the core of SH3 is mainly formed in a reduced depositional environment, resulted from sulfate reduction by the anaerobic oxidation of methane. The change in redox condition of depositional environment may lead to the fractionation of LREE/HREE and MREE/HREE in the layers. In the SH3 core sediment, there is a sub-oxidized depositional environment at the level of about 180~215 mbsf. It is supposed to be caused by the deposition of turbidites. The depositional environment of fine-grained sediments, at the same time, also leads to the fractionation of light and heavy rare earth elements. To sum up, we have succeeded in revealing material source, environment change in the Shenhu area and the specific role of hydrate-sedimentary environment in this paper and the results are very useful for understanding of the origin of gas hydrate.
-
Key words:
- the Shenhu area /
- hydrate drilling area /
- gas hydrate /
- sedimentary environment
-

-
表 1 SH3钻孔主要稀土元素特征与主要构造环境对比
Table 1. Major provenance types and corresponding elemental characteristics used to define the tectonic setting of the SH3
-
[1] Wu S, Zhang G, Huang Y, et al. Gas hydrate occurrence on the continental slope of the northern South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2005, 22(3): 403-412. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2004.11.006
[2] 吴能友, 张光学, 梁金强, 等.南海北部陆坡天然气水合物研究进展(英文)[J].新能源进展, 2013, 1(1): 80-94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-560X.2013.01.008
WU Nengyou, ZHANG Guangxue, LIANG Jingqiang, et al. Progress of gas hydrate research in northern South China Sea[J]Progress of Gas Hydrate Research in Northern South China Sea, 2013, 1 (1): 80-94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-560X.2013.01.008
[3] Zhang H Q, Yang S X, Wu N Y, et al. Successful and surprising results for China's first gas hydrate drilling expedition[C]//Fire in the Ice: Methane Hydrate Newsletter. Washington D C: Natl. Energy Technol. Lab., U.S. Dep. of Energy, 2007.
[4] Zhang G X, Yang S X, Zhang M, et al. Melanie Holland, Peter Schultheiss, and the GMGS2 Science Team, GMGS2 expedition investigates rich and complex gas hydrate environment in the South China Sea[J]. Fire in the Ice, Methane Hydrate Newsletter, 2014, 14(1): 1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.05.004
[5] Yang S X, Zhang M, Liang J Q, et al. Preliminary results of China's third gas hydrate drilling expedition: A critical step from discovery to development in the South China Sea[J]. Fire in the Ice, Methane Hydrate Newsletter, 2015, 15(12): 1-5.
[6] Yang S X, Liang J Q, Lei Y, et al. GMGS4 gas hydrate drilling expedition in the South China Sea[J]. Fire in the Ice, Methane Hydrate Newsletter, 2017, 17(1): 7-11.
[7] Zhong G F, Liang J, Guo Y, et al. Integrated core-log facies analysis and depositional model of the gas hydrate-bearing sediments in the northeastern continental slope, South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2017, 86: 1159-1172. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.07.012
[8] Li D L, Li R X, Zhu Z W, et al. Origin of organic matter and paleo-sedimentary environment reconstruction of the Triassic oil shale in Tongchuan City, southern Ordos Basin (China)[J]. Fuel, 2017, 208: 223-235. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.07.008
[9] Chen H T, Wang M C, Chang K M, et al. Phase transformation and morphology of calcium phosphate prepared by electrochemical deposition process through alkali treatment and calcination[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2014, 45(4): 2260-2269. doi: 10.1007/s11661-013-2115-y
[10] Li N, Feng D, Chen L Y, et al. Compositions of foraminifera-rich turbidite sediments from the Shenhu area on the northern slope of the South China Sea: Implication for the presence of deep water bottom currents[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2017, 138: 148-160. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.02.010
[11] Song H B, Osamu M, Yang S X, et al. Physical property models of gas hydrate-bearing sediments and AVA character of bottom simulating reflector[J]. Chinese Journal Of Geophysics, 2002, 45(4): 569-579. doi: 10.1002/cjg2.270
[12] Lu Z Q, Zhu Y H, Zhang Y Q, et al. Estimation method of gas hydrate resources in the Qilian Mountain permafrost area, Qinghai, China-A case of the drilling area[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2010, 29(9): 1310-1318. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1231.2010.06586
[13] Um I K, Choi M S, Bahk J J, et al. Discrimination of sediment provenance using rare earth elements in the Ulleung Basin, East/Japan Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 2002, 346: 208-219. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2013.09.007
[14] Zhu L Q, Liu D, Hu J, et al. "GSK-3β Inhibits presynaptic vesicle exocytosis by phosphorylating P/Q-type calcium channel and interrupting SNARE complex formation[J] Journal of Neuroscience, 2010, 30(10): 3624-3633. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5223-09.2010
[15] 吴能友, 张海啟, 杨胜雄, 等.南海神狐海域天然气水合物成藏系统初探[J].天然气工业, 2007, 27(9): 1-6. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2007.09.001
WU Nengyou, ZHANG Haiqi, YANG Shengxiong, et al. Preliminary discussion on natural gas hydrate (ngh) reservoir system of shenhu area, north slope of South China sea[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2007, 27(9): 1-6. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2007.09.001
[16] Chen H, Savage P S, Teng F Z, et al. Zinc isotope fractionation during magmatic differentiation and the isotopic composition of the bulk Earth[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2013, 369-370: 34-42. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2013.02.037
[17] 吴能友, 杨胜雄, 王宏斌, 等.南海北部陆坡神狐海域天然气水合物成藏的流体运移体系[J].地球物理学报, 2009, 52(6): 1641-1650. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.06.027
WU Nengyou, YANG Shengxiong, WANG Hongbing, et al. Gas-bearing fluid influx sub-system for gas hydrate geological system in Shenhu Area, Northern South China Sea[J] Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2009, 52(6): 1641-1650. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.06.027
[18] Bordovskiy O K. Accumulation of organic matter in bottom sediments[J]. Marine Geology, 1965, 3(1-2): 33-82. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(65)90004-6
[19] Bordovskiy O K. Sources of organic matter in marine basins[J]. Marine Geology, 1965, 3(1-2): 5-31. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(65)90003-4
[20] 吴自军.沉积物甲烷厌氧氧化—从珠江河口至南海[D].广州: 中国科学院研究生院(广州地球化学研究所), 2006.
WU Zijun. Anaerobic oxidation of methane in sediments from the Pearl River estusry to South China sea [D]. Guangzhou: Graduate School of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry), 2006.
[21] Berner R A. Burial of organic carbon and pyrite sulfur in the modern ocean: its geochemical and environmental significance[J]. American Journal of Science, 1982, 282(4): 451-473.
[22] Chen F, Feng D, Zhang X, et al. Evidence of intense methane seepages from molybdenum enrichments in gas hydrate-bearing sediments of the northern South China Sea[J]. Chemical Geology, 2016, 443: 173-181. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2016.09.029
[23] 苏丕波, 梁金强, 沙志彬, 等.神狐深水海域天然气水合物成藏的气源条件[J].西南石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2014, 36(2): 1-8. doi: 10.11885/j.issn.1674-5086.2013.10.16.01
SU Peibo, LIANG Jingqiang, SHA Zhibing, et al. Gas sources condition of gas hydrate formation in shenhu deep water sea zone[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University: Natural Science Edition, 2014, 36(2): 1-8. doi: 10.11885/j.issn.1674-5086.2013.10.16.01
[24] 邬黛黛, 吴能友, 张美, 等.东沙海域SMI与甲烷通量的关系及对水合物的指示[J].地球科学—中国地质大学学报, 2013, 38(6): 1309-1320. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2013.128
WU Daidai, WU Nengyou, ZHANG Mei, et al. Relationship of sulfate-methane interface (SMI), methane flux and the underlying gas hydrate in Dongsha area, northern South China Sea[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2013, 38(6): 1309-1320. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2013.128
[25] 张辉, 卢海龙, 梁金强, 等.南海北部神狐海域沉积物颗粒对天然气水合物聚集的主要影响[J].科学通报, 2016, 61(3): 388-397. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201603014
ZHANG Hui, LU Hailong, LIANG Jinqiang, et al. The methane hydrate accumulation controlled compellingly by sediment grain at Shenhu, Northern South China Sea[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2016, 61(3): 388-397. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201603014
[26] Shao L, Meng A H, Li Q Y, et al. Detrital zircon ages and elemental characteristics of the Eocene sequence in IODP Hole U1435A: Implications for rifting and environmental changes before the opening of the South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 2017, doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2017.08.002.In Press.
[27] 苏明, 杨睿, 吴能友, 等.南海北部陆坡区神狐海域构造特征及对水合物的控制[J].地质学报, 2014, 88(3): 318-326. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2014.03.002
SU Ming, YANG Rui, WU Nengyou, et al. Structural characteristics in the Shenhu area, northern continental slope of South China Sea, and their influences on gas hydrate[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(3): 318-326. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2014.03.002
[28] 苏明, 沙志彬, 乔少华, 等.南海北部神狐海域天然气水合物钻探区第四纪以来的沉积演化特征[J].地球物理学报, 2005, 58(8): 2975-2985. doi: 10.6038/cjg20150829
SU Ming, SHA Zhibing, QIAO Shaohua, et al. Sedimentary evolution since Quaternary in the Shenhu hydrate drilling area, northern South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2005, 58(8): 2975-2985. doi: 10.6038/cjg20150829
[29] 李云, 郑荣才, 杨宝泉, 等.珠江口盆地白云凹陷中新统珠江组物源及其研究意义[J].地质评论, 2013, 59(1): 41-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0371-5736.2013.01.005
LI Yun, ZHENG Rongcai, YANG Baoquan, et al. Source of the miocene Zhujiang formation in baiyun depression, pearl river mouth basin and its significance[J]. Geological Review, 2013, 59(1): 41-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0371-5736.2013.01.005
[30] Bhatia M R, Crook K A W. Trace element characteristics of graywackes and tectonic setting discrimination of sedimentary basins[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1986, 92(2): 181-193. doi: 10.1007/BF00375292
-




 下载:
下载: