THE INVERSION OF LATE QUATERNARY PALEO-WATER DEPTH IN SOUTHWESTERN OFFSHORE HAINAN ISLAND
-
摘要:
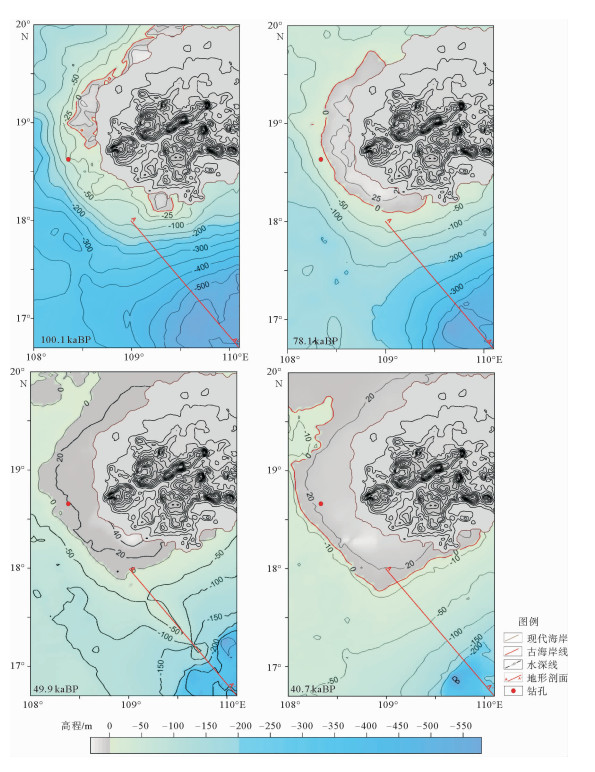
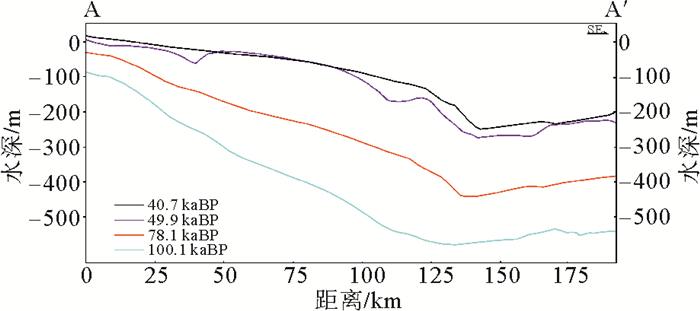
晚第四纪以来,因古气候和海平面发生多次变化,南海西北部经历了海岸线变迁和海陆演变多个过程。利用钻孔测年和高分辨率单道地震资料开展对比、划分了7个主要地震反射界面并确定其时代。同时基于现今水深数据,依据全球海平面变化曲线和地层厚度,对海南岛西南海域晚第四纪(100.1~40.7 kaBP)以来的古水深和海岸线进行反演。反演结果表明,100.1 kaBP时,海南岛西部、西北和南部局部地区海岸线向海方向移动, 陆域面积略微增加, 海域陆架较窄,最大水深超过550 m,海底地形以陆坡深水区为主。78.1 kaBP时,海南岛西部海岸线发生较大规模迁移,陆域面积增加,陆架变宽,海底地形平缓。大部分区域水深均小于200 m。49.9~40.7 kaBP,海南岛西部陆域面积进一步扩大,海底地形平坦,水深变浅,地形以陆架区浅水区为主。研究表明,100.1~40.7 kaBP以来研究区的水深变浅,地形变为平缓,海岸线向海迁移,区域古气候、海平面变化以及物源供应对塑造海底地形地貌具有重要的作用。
Abstract:There are several cycles of coastal line migration and water-land inversion in the northwestern South China Sea due to climate and sea level changes during late Quaternary. Seven seismic reflectors have been recognized and dated based on high resolution seismic profiles and drilling cores. The inversion of late Quaternary (100.1~40.7 kaBP) paleo-water depth and coastal line have been build based on modern water depth, global sea level change curves and thickness of sediment in the study area. The inversion results indicate that part of the coastal line in western, northwestern and southern Hainan Island migrated seawards 100.1 kaBP. The water depth was larger than 550 m with a narrow shelf in the study area then. The shelf area became larger with a flat sea floor at 78.1 kaBP. The western coastal line migrate to sea in large scale with more land area exposed.The water depth was less than 200m. Factors suggest that the paleo-water depth and coastal line was controlled by climate, sea level changes and sediment supply.
-
Key words:
- Hainan Island /
- Late Quaternary /
- paleo-water depth /
- inversion /
- sea level change
-

-
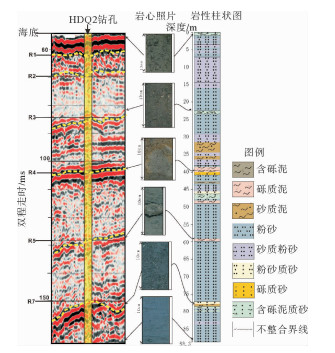
表 1 地震反射界面时间-深度
Table 1. The time-depth of seismic reflectors
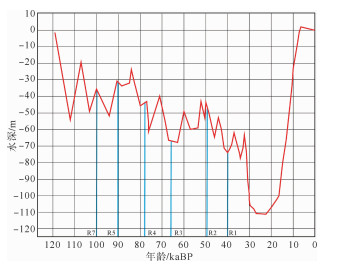
反射界面 双程走时/ms 深度/m 海底 55 0 R1 63 6.4 R2 69 11.2 R3 86 24.8 R4 103 38.4 R5 128 58.4 R7 150 76.0 表 2 HDQ2钻孔AMS-14C和光释光测年结果
Table 2. The AMS-14C and OSL age of Core HDQ2
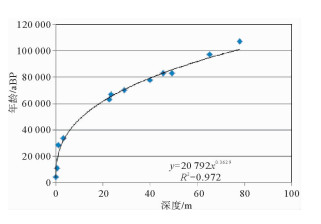
样品编号 深度/m 年代/ka 误差/a 校正年龄/cal. kaBP 标准偏差/a 测年方法 1 0.01 4.300 ±30 4.320~4.520 AMS-14C 2 0.63 9.740 ±38 11.220~11.169 AMS-14C 3 1.10 23.734 ±85 28.435 ±168 AMS-14C 4 3.40 28.620 ±113 34.014 ±185 AMS-14C 5 3.60 35.501 ±188 40.813 ±241 AMS-14C 6 7.00 33.405 ±166 38.796 ±221 AMS-14C 7 8.05 35.300 ±370 38.620~40.240 AMS-14C 8 9.50 25.268 ±143 30.421 ±209 AMS-14C 9 14.25 31.111 ±159 36.473 ±207 AMS-14C 10 19.99 43.180 ±920 44.400~48.050 AMS-14C 11 22.70 63.000 7 OSL 12 23.40 67.000 7 OSL 13 29.00 70.000 9 OSL 14 39.80 78.000 8 OSL 15 45.6 80 000 8 OSL 16 49.20 83.000 9 17 65.2 97.000 11 OSL 18 78.0 107.000 11 OSL 19 88.0 67.000 9 OSL 表 3 HDQ2孔地震反射界面深度、年龄、沉积速率和古水深
Table 3. The age, depth, sediment rate and water depth of seismic reflectors at Core HDQ2
反射界面 深度/mbsb 年代/kaBP 沉积速率/(m/ka) 古水深/m R1 6.4 40.7 0.16 -72 R2 11.2 49.9 0.52 -47 R3 24.8 66.7 0.93 -68 R4 38.4 78.1 1.20 -44 R5 58.4 90.9 1.57 -32 R7 76.0 100.1 1.91 -37 -
[1] 李平日, 黄镇国, 张仲英, 等.广东东部晚更新世以来的海平面变化[J].海洋学报, 1987, 9(2): 216-222. http://www.hyxb.org.cn/aos/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=19870211&journal_id=aos
LI Pinri, HUANG Zhenguo, ZHANG Zhongying, et al. Sea level changes since Late Pleistocene in eastern Guangdong[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1987, 9(2): 216-222. http://www.hyxb.org.cn/aos/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=19870211&journal_id=aos
[2] Kershaw S, Guo L. Marine notches in coastal cliffs: indicators of relative sea-level change, Perachora Peninsula, central Greece[J]. Marine Geology, 2001, 179(3-4): 213-228. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(01)00218-3
[3] 庄振业, 林振宏, 刘志杰, 等.海平面变化及其海岸响应[J].海洋地质动态, 2003, 19(7): 1-12, 37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2003.07.001
ZHUANG Zhenye, LIN Zhenhong, LIU Zhijie, et al. Sea level changes and coastal responses[J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2003, 19(7): 1-12, 37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2003.07.001
[4] 赵信文, 向薇, 肖尚斌, 等.末次冰消期以来海平面变化研究进展[J].华南地质与矿产, 2012, 28(3): 189-196. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3701.2012.03.001
ZHAO Xinwen, XIANG Wei, XIAO Shangbin, et al. Research progress in sea-level changes since the last deglaciation[J]. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 2012, 28(3): 189-196. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3701.2012.03.001
[5] 张虎男, 赵红梅.华南沿海晚更新世晚期-全新世海平面变化的初步探讨[J].海洋学报, 1990, 12(5): 620-630. http://www.hyxb.org.cn/aos/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=19900510&journal_id=aos
ZHANG Hunan, ZHAO Hongmei. The primary discussion of sea level changes during Late Pleistocene to Holocene in coastal Huanan[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1990, 12(5): 620-630. http://www.hyxb.org.cn/aos/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=19900510&journal_id=aos
[6] 时小军, 余克服, 陈特固.南海周边中全新世以来的海平面变化研究进展[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2007, 27(5): 121-132. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200705017
YE Xiaojun, YU Kefu, CHEN Tegu. Progress in researches on sea-level changes in South China Sea since mid-Holocene[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2007, 27(5): 121-132. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200705017
[7] Tanabe S, Hori K, Saito Y, et al. Song Hong (Red River) delta evolution related to millennium-scale Holocene sea-level changes[J]. Quaternary Science Review, 2003, 22(21-22): 2345-2361. doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(03)00138-0
[8] 姚衍桃, Harff J, Meyer M, 等.南海西北部末次盛冰期以来的古海岸线重建[J].中国科学(D辑:地球科学), 2009, 36(6): 753-762. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd200906007
YAO Yantao, Harff J, Meyer M, et al. Reconstruction of paleocoastlines for the northwestern South China Sea since the Last Glacial Maximum[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2009, 52(8): 1127-1136. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd200906007
[9] 周川, 范奉鑫, 栾振东, 等.南海北部陆架主要地貌特征及灾害地质因素[J].海洋地质前沿, 2013, 29(1): 51-60. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzdt201301007
ZHOU Chuan, FANG Fengxin, LUAN Zhendong, et al. Geomorphology and hazardous geological factors on the continental shelf of the northern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2013, 29(1): 51-60. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzdt201301007
[10] 汪品先.冰期时的中国海:研究现状与问题[J].第四纪研究, 1990, 10(2): 111-124. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1990.02.002
WANG Pinxian. The ice-age China sea-status and problems[J]. Quaternary Science, 1990, 10(2): 111-124. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1990.02.002
[11] 张虎男.南海北部地质灾害对油气勘探开发的影响[J].中国海上石油(地质), 1994, 8(4): 252-259. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199400608722
ZHANG Hunan. Geological disasters in the northern part of South China Sea influence on the oil and gas exploration and exploitation[J]. China offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 1994, 8(4): 252-259. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199400608722
[12] 鲍才旺.珠江口陆架区埋藏古河道与古三角洲[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1995, 15(2): 25-34. http://hydt.cbpt.cnki.net/WKA/WebPublication/index.aspx?mid=hydt
BAO Caiwang. Buried ancient channels and deltas in the Zhujiang River Mouth shelf area[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1995, 15(2): 25-34. http://hydt.cbpt.cnki.net/WKA/WebPublication/index.aspx?mid=hydt
[13] 张明书, 李绍全, 刘健.中国海岸带晚更新世风成沉积分区、序列特征及其气候-环境意义[J].第四纪研究, 1996, 16(1): 31-41. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1996.01.004
ZHANG Mingshu, LI Shaoquan, LIU Jian. Sedimentary zones, sequential features and climatic environmental significance of late Pleistocene eolian deposits along coastal areas of China[J]. Quaternary Science, 1996, 16(1): 31-41. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1996.01.004
[14] 黄镇国, 陈特固, 张伟强, 等.广东海平面变化及其影响与对策[M].广州:广东科技出版社, 2000: 33-60.
HUANG Zhenguo, CHEN Tegu, ZHANG Weiqiang, et al. Sea Level Changes, Influence and Countermeasure in Guangdong Province[M]. Guangzhou: Science and Technology of Guangdong Press, 2000: 33-60.
[15] 王树民, 陈泓君, 钟和贤.南海东北部晚第四纪地层不整合的发现及其地质意义[J].南海地质研究, 2001: 55-61. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000005399617
WANG Shuming, CHEN Hongjun, ZHONG Hexian. The foundation of late Quaternary strata unconformity and their geological significant in northeastern South China Sea[J]. Research of geological South China Sea, 2001: 55-61. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000005399617
[16] 寇养琦.南海北部大陆边缘海底滑坡的初步研究[J].南海地质研究, 1993(5): 43-56. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000005399617
KOU Yangqi. The primary research of submarine slide in the northern margin of South China Sea[J]. Geological of South China Sea, 1993(5): 43-56. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000005399617
[17] 蓝东兆, 张维林, 陈承惠, 等.晚更新世以来台湾海峡西部的海侵及海平面变化[J].海洋学报, 1993, 15(4): 77-84. doi: 10.1007/BF02677081
LAN Dongzhao, ZHANG Weilin, CHEN Chenhui, et al. Sea intrusion and sea level changes since late Pleistocene in western Taiwan strait[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1993, 15(4): 77-84. doi: 10.1007/BF02677081
[18] 常琳, 罗运利, 孙湘君.南海北部MD05-2904站位2万年以来孢粉记录的古环境演变[J].科学通报, 2013, 58(30): 3079-3087. doi: 10.1360/972012-786
CHANG Lin, LUO YunLi, SUN Xiangjun. Paleoenvironmental change base on a pollen record from deep sea core MD05-2904 from the northern South China Sea during the past 20000 years[J]. Chinese Science China, 2013, 58(30): 3079-3087. doi: 10.1360/972012-786
[19] Steinke S, Kienast M, Hanebuth T J J. On the significance of sea-level variations and shelf paleo-morphology in governing sedimentation in the southern South China Sea during the last deglaciation[J]. Marine Geology, 2003, 201(1-3): 179-206. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(03)00216-0
[20] 陈泓君, 李文成, 陈弘, 等.南海北部中更新世晚期以来古海岸变迁及其地质意义[J].南海地质研究, 2005(1): 57-66. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000005399617
CHEN Hongjun, LI Wencheng, CHEN Hong. Ancient coastline transfer since middle-Pleistocene in northern South China Sea and its geological significance[J] Geological South China Sea, 2005(1): 57-66. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000005399617
[21] Posamentier H W, Allen G P, James D P, et al. Forced regressions in a sequence stratigraphic framework: concepts, examples and exploration significant[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1992, 76(11): 1687-1709. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/279938254_Forced_regressions_in_a_sequence_stratigraphic_framework_Concepts_examples_and_exploration_significance
[22] 赵希涛, 杨达源.全球海面变化[M].北京:科学出版社, 1992.
ZHAO Xitao, YANG Dayuan. Global Sea Level Change[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1992.
[23] 陈欣树, 包呖彦, 陈俊仁, 等.珠江口外陆架晚第四纪最低海面的发现[J].热带海洋, 1990, 9(4): 73-77.
CHEN Xinshu, BAO Liyan, CHEN Junren, et al. Discovery of lowest at the continental sea level in late quaternary shelf off pearl river mouth [J]. Tropical Oceanology, 1990, 9(4): 73-77.
[24] 朱俊江, 詹文欢, 唐诚, 等, 红河断裂带活动性研究[J].华南地震, 2003, 23(2): 13-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8662.2003.02.002
ZHU Junjiang, ZHAN Wenhuan, TANG Chen, et al. Study on activity of Red River Fault Zone[J]. South China Journal of Seismology, 2003, 23(2): 13-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8662.2003.02.002
[25] 李思田, 林畅松, 张启明, 等.南海北部大陆边缘盆地幕式裂陷的动力过程及10Ma以来的构造事件[J].科学通报, 1998, 43(8): 797-810. doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7290029
LI Sitian, LIN Changsong, ZHANG Qiming, et al. Episodic rifting of continental marginal basins and tectonic events since 10 Ma in the South China Sea[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1999, 44(1): 10-23. doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7290029
[26] 孙珍, 钟志洪, 周蒂.莺歌海盆地构造演化与强烈沉降机制的分析和模拟[J].地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 2007, 32(3): 347-356. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2007.03.007
SUN Zhen, ZHONG Zhihong, ZHOU Di. The Analysis and Analogue Modeling of the Tectonic Evolution and Strong Subsidence in the Yinggehai Basin[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2007, 32(3): 347-356. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2007.03.007
[27] 李纯泉.莺歌海盆地流体底辟构造及其对天然气成藏的贡献[J].中国海上油气(地质), 2000, 14(4): 253-257. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zghsyq-dz200004006
LI Chunquan. Fluid diapirs and their contributions to hydrocarbon accumulation in Yinggehai Basin[J] China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 2000, 14(4): 253-257. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zghsyq-dz200004006
[28] 夏伦煜, 麦文, 赖霞红, 等.莺歌海-琼东南盆地第四系初步研究[J].中国海上油气(地质), 1989, 3(3): 21-28. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/85683X/198903/7916195.html
XIA Lunli, MAI Wen, LAI Xiahong, et al. The primary Quaternary research of Yingehai-Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. China offshore oil and gas (geology), 1989, 3(3): 21-28. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/85683X/198903/7916195.html
[29] 吕明.莺-琼盆地低位沉积模式的新探讨[J].中国海上油气(地质), 2002, 16(4): 221-230. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZHSD200204000.htm
LV Ming. A new discussion on lowstand deposition models in Ying-Qiong Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 2002, 16(4): 221-230. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZHSD200204000.htm
[30] 陈双喜, 赵信文, 黄长生, 等.现代珠江三角洲地区QZK4孔第四纪沉积年代[J].地质通报, 2014, 33(10): 1629-1634. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.10.022
CHEN Shuangxi, ZHAO Xinwen, HUANG Changsheng, et al. Chronology of Quaternary sediments from drill hole QZK4 in modern Pearl River Delta region[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2014, 33(10): 1629-1634. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.10.022
[31] 宋维宇.莺歌海盆地由沉积负载引起的裂后期快速沉降的耦合模式[J].海洋地质动态, 2010, 26(8): 8-14. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/HYDT201008004.htm
SONG Weiyu. A coupled model incorporating lower-crustal flow in response to post-rift sedimentary load of Yinggehai Basin's rapid subsidence[J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2010, 26(8): 8-14. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/HYDT201008004.htm
[32] Waelbroeck C, Labeyrie L, Michel E, et al. Sea-level and deep water temperature changes derived from benthic formainifera isotopic records[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2002, 21(1-3): 295-305. doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(01)00101-9
[33] 许冬, 龙江平, 钱江初, 等.海南岛近海海域7个沉积岩芯的现代沉积速率及其分布特征[J].海洋学研究, 2008, 26(3): 9-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2008.03.002
XU Dong, LONG Jiangpin, QIAN Jiangchu, et al. The modern sedimentation rate and the distribution character of 7 cores in Hainan Island offshore[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2008, 26(3): 9-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2008.03.002
[34] 王颖.海南岛海岸环境特征[J].海洋地质动态, 2002, 18(3): 1-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2002.03.001
WANG Ying. Features of Hainan island coastal environment[J]. Maine Geology Letters, 2002, 18(3): 1-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2002.03.001
[35] 张军强, 唐璐璐, 邹昊.晚更新世以来古气候与海平面变化在东海地区的响应[J].海洋湖沼通报, 2008(1): 25-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2008.01.004
ZHANG Junqiang, TANG Lulu, ZOU Hao. The response to the variety of Paleoclimate and sea level in the East China Sea after the Late Pleistocene[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2008(1): 25-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2008.01.004
-



 下载:
下载: