Hydrological characteristics and suspended sediment transport mechanism in spring at the Mulan Estuary and its adjacent seas
-
摘要:
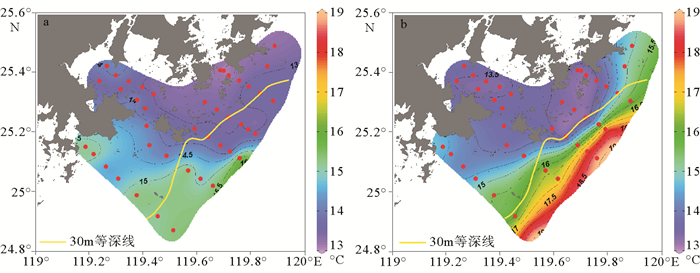
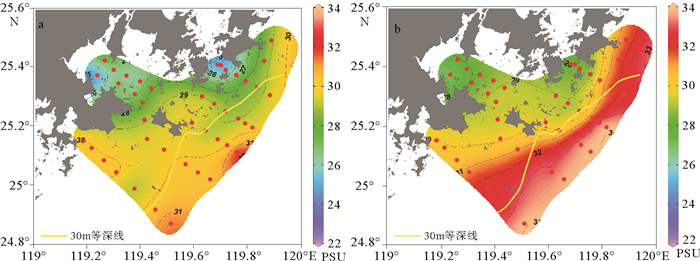
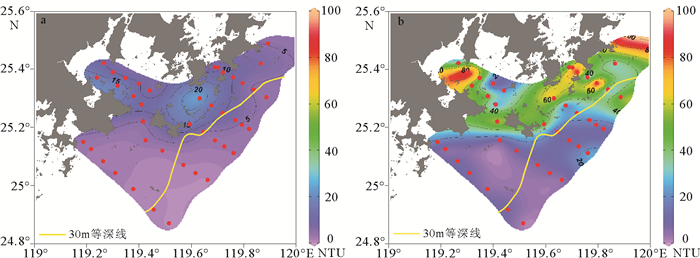
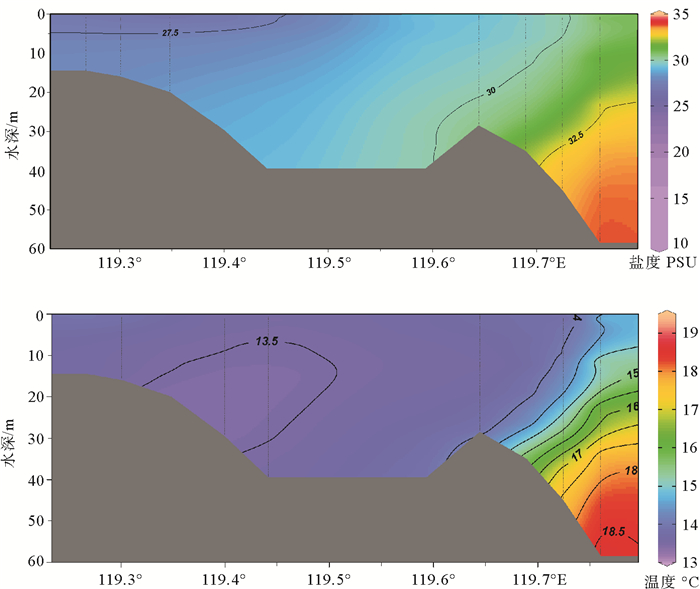
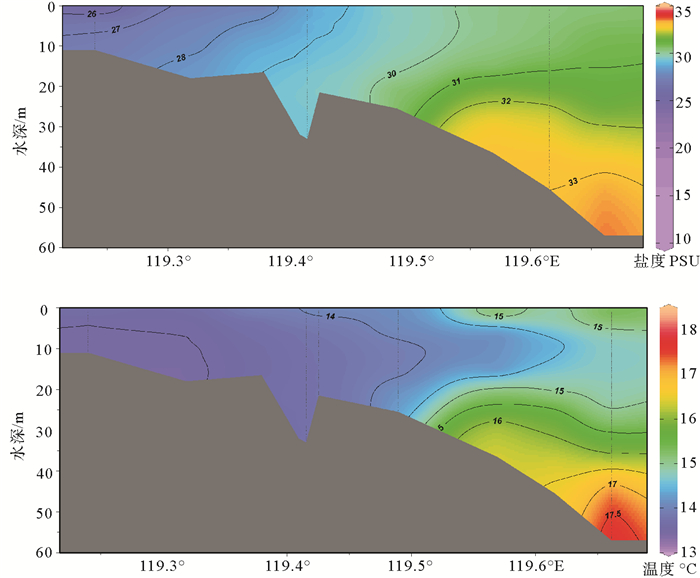
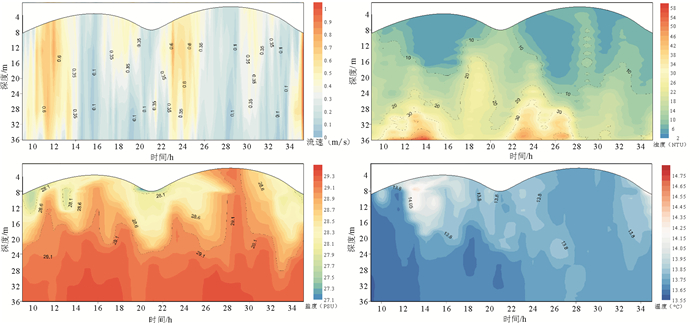
基于2016年春季航次观测数据,分析了木兰溪河口及邻近海域温度、盐度及浊度等水文环境要素特征;并运用通量机制分解法分析该区兴化湾南日水道连续观测站位资料,以揭示该海域悬沙输移的控制机制。结果表明,春季兴化湾及邻近海域温盐变化受木兰溪径流、浙闽沿岸流和台湾暖流共同控制,湾外东南侧海域受高温高盐台湾暖流控制,西北侧近岸海域受低温低盐的浙闽沿岸流显著影响。调查海域悬沙浓度总体较低,外海泥沙通过南日水道向兴化湾内输移,但净输运量非常有限,仅为0.32×10-4kg/(m·s)。平流输沙与潮泵输沙是南日水道泥沙净输运的主要机制,底沙再悬浮作用较显著,且剪切扩散效应也不容忽视。
Abstract:Based on the field observation data in spring of 2016 in the Mulan Estuary and its adjacent seas, hydrological environment factors, such as temperature, salinity and turbidity were analyzed. And the characteristics and mechanism of suspended sediment transport in the Nanri waterway were studied using the mechanism decomposition method. Results show that the changes in temperature and salinity in the Xinghua Bay and its adjacent seas in spring are jointly controlled by the Mulan River runoff, the Zhejiang-Fujian Coastal Current and the Taiwan Warm Current. The offshore water in southeast Xinghua Bay is dominated by Taiwan Warm Current characterized by high temperature and high salinity, while the nearshore water in the northwest of the bay is significantly affected by the Zhejiang-Fujian Coastal Current featured by low temperature and low salinity. Suspended sediment concentration in Xinghua Bay and its adjacent seas is relatively low. Offshore sediments can be transported into Xinghua Bay through the Nanri waterway, but the net sediment flux is quite limited, only 0.32×10-4 kg/(m·s). The advection and tidal pumping are the major mechanisms for net sediment transport in the waterway, the resuspension of bottom sediment is significant, and the shear diffusion effect cannot be ignored.
-

-
表 1 观测方法及仪器参数设置
Table 1. Method of observation and instrumental parameters
仪器/布放方式 观测参数 采样方式 Campbell OBS 3A/绞车 浊度 1Hz,表中底或六点法观测,每层位观测2min左右 CTD/绞车 温、盐、深 同OBS Flowquest ADCP 600k/船舷固定,探头朝下 流速 2Hz,连续观测,bin:0.5m,ping:120 双频测深仪/船舷固定,探头距水面约30cm 水位变化 连续测量 表 2 各项悬沙输沙量及其所占百分比
Table 2. Distribution of suspended sediment transport influenced by different factors in Xinghua Bay
T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 T7 T8 T 输沙量(10-4kg/(m·s)) 1 -0.065 0.016 -1.1 0.11 -0.0025 -0.64 0.35×10-4 -0.32 占总输沙量之比(%) 40.5 2.22 1.37 37.64 3.84 0.08 15.62 0.0014 -
[1] Tian T, Merico A, Su J, et al. Importance of resuspended sediment dynamics for the phytoplankton spring bloom in a coastal marine ecosystem[J]. Journal of Sea Research, 2009, 62(4):214-228. doi: 10.1016/j.seares.2009.04.001
[2] Liu J T, Hsu R T, Hung J J, et al. From the highest to the deepest: The Gaoping River-Gaoping Submarine Canyon dispersal system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2016, 153:274-300. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.10.012
[3] Milliman J D, Farnsworth K L. River Discharge to the Coastal Ocean——A Global Synthesis[M]// River discharge to the coastal ocean: a global synthesis. 2011.
[4] Liu J P, Liu C S, Xu K H, et al. Flux and fate of small mountainous rivers derived sediments into the Taiwan Strait[J]. Marine Geology, 2008, 256(1): 65-76. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dc54df5d21a0280d8807d0991ae92ed1
[5] 高建华, 高抒, 董礼先, 等.鸭绿江河口地区沉积物特征及悬沙输送[J].海洋通报, 2003, 22(5):26-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2003.05.005
GAO Jianhua, GAO Shu, DONG Lixian, et al. Sediment distribution and suspended sediment transport in Yalu River Estuary[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2003, 22(5):26-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2003.05.005
[6] 陈斌, 印萍, 高飞, 等.滦河口水文环境要素季节性变化特征及动力响应关系[J].海洋环境科学, 2015, 34(5):729-735.
http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HYHJ201505015.htm CHEN Bin, YIN Ping, GAO Fei, LIU Jinqing, et al. Seasonal variation characteristics of hydrological environment factors and dynamic response relationship in Luanhe Estuary[J].Marine Environment Science, 2015, 34(5):729-735.
[7] 赵建春, 戴志军, 李九发, 等.强潮海湾近岸表层沉积物时空分布特征及水动力响应——以杭州湾北岸为例[J].沉积学报, 2008, 26(6): 1043-1051.
http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-CJXB200806020.htm ZHAO Jianchun. Study on the characteristics of temporal and spatial changes in properties of surface sediment on near-shore seabed of strong-tide Bay: a case from the north bank of Hangzhou Bay in Shanghai[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2008, 26(6): 1043-1051.
[8] 陈小英, 刘金庆, 郭磊, 等.胶州湾大沽河河口近岸海域短时间尺度沉积动力过程[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(6):45-50. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201606006
CHEN Xiaoying, LIU Jinqing, GUO Lei, et al. Short term depositional dynamic processes at Duge River Mouth of Jiaozhou Bay[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2016, 36(6):45-50. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201606006
[9] 郭琳, 陈植华.椒江口-台州湾悬浮泥沙分布特征遥感研究[J].武汉理工大学学报, 2007, 29(5):49-52. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-4431.2007.05.015
GUOLin, CHEN Zhihua.Remote sensing research on the distributed characteristics of suspended matter in Jiaojiang Estuary and Taizhou Gulf[J].Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2007, 29(5):49-52. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-4431.2007.05.015
[10] Rao V P, Shynu R, Kessarkar P M, et al. Suspended sediment dynamics on a seasonal scale in the Mandovi and Zuari estuaries, central west coast of India[J]. Estuarine Coastal & Shelf Science, 2011, 91(1):78-86. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0272771410003495
[11] Priya K L, Jegathambal P, James E J. On the factors affecting the settling velocity of fine suspended sediments in a shallow estuary[J]. Journal of Oceanography, 2015, 71(2):1-13. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=a69f85b24b9a6f2fb81ba4c48bc14907
[12] 李孟国.兴化湾水文泥沙特征分析[J].水道港口, 2001, 22(4):156-159. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8443.2001.04.002
LI Mengguo. Hydrographic and sediment analyses of Xinghua Bay[J]. Journal of Waterway & Harbor, 2001, 22(4):156-159. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8443.2001.04.002
[13] 高劲松, 周良明.兴化湾的潮流研究[J].海岸工程, 2009, 28(4):1-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3682.2009.04.001
GAO Jinsong, ZHOU Liangming. Study on tide current of the Xinghua Bay[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2009, 28(4):1-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3682.2009.04.001
[14] 童朝锋, 王俊杰, 张青.兴化湾潮汐潮流特性及工程影响分析[J].水利水运工程学报, 2015(1):53-60. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/slsykxyj201501008
TONG Chaofeng, WANG Junjie, ZHANG Qing. Tidal regime and impacts of works in Xinghua bay on hydrodynamics[J].Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2015(1): 53-60. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/slsykxyj201501008
[15] 童朝锋, 郑联枭, 孟艳秋, 等.兴化湾悬沙输移机理分析[J].水利水运工程学报, 2016(2):1-10. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/slsykxyj201602001
TONG Chaofeng, ZHENG Lianxiao, MENG Yanqiu, et al.Mechanism of suspended sediment transport in Xinghua bay[J].Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2016(2):1-10. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/slsykxyj201602001
[16] 万新宁, 李九发, 何青, 等.国内外河口悬沙通量研究进展[J].地球科学进展, 2002, 17(6):864-870. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2002.06.010
WAN Xinning, LI Jiufa, HE Qing, et al. Review of suspended sediment flux in the world[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 2002, 17(6):864-870. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2002.06.010
[17] Hansen D V. Currents and Mixing in the Columbia River Estuary[J]. Ocean Science and Ocean Engineering, 1965, 2:943-955.
[18] Fisher H B.Mixing and dispersion in estuaries[J].Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 1976, 8:107-133. doi: 10.1146/annurev.fl.08.010176.000543
[19] Jay D A, Uncles R J, Largeir J, et al. A review of recent developments in estuarine scalar flux estimation[J]. Estuaries, 1997, 20(2):262-280. doi: 10.2307/1352342
[20] Uncles R J, Easton A E, Griffiths M L, et al. Seasonality of the Turbidity Maximum in the Humber-Ouse Estuary, UK[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 1999, 37(3-7):206-215. doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(98)90157-6
[21] 王康墡, 苏纪兰.长江口南港环流及悬移物质输运的计算分析[J].海洋学报, 1987, 9(5):627-637. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SEAC198705013.htm
WANG Kangshan, SU Jilan. Analysis and calculation of circulation and suspended sediment transportation in the Yangtze Estuary[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1987, 9(5):627-637. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SEAC198705013.htm
[22] 万新宁, 李九发, 沈焕庭.长江口外海滨典型断面悬沙通量计算[J].泥沙研究, 2004(6):64-70. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2004.06.012
WAN Xinning, LI Jiufa, SHEN Huanting. Suspended sediment flux at the typical cross sections in the offshore area of Changjiang Estuary[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2004(6):64-70. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2004.06.012
[23] Yu Q, Wang Y P, Flemming B, et al. Tide-induced suspended sediment transport: Depth-averaged concentrations and horizontal residual fluxes[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2012, 34(1):53-63. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0278434311003694
[24] Becherer J, Flöser G, Umlauf L, et al. Estuarine circulation vs tidal pumping: Sediment transport in a well-mixed tidal inlet[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Oceans, 2016, DOI: 10.1002/2016JCO∥640.
[25] 中国海湾志编纂委员会.中国海湾志(第七分册)[M].海洋出版社, 1994.
Compilation Committee of China Bays. China Bay in Seventh Volumes (north of Fujian Bay)[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1994.
[26] 闫新兴, 刘国亭.福建兴化湾近岸地貌特征与泥沙来源分析[J].水道港口, 2012, 33(6):469-474. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8443.2012.06.002
YAN Xinxing, LIU Guoting. Analysis of geomorphic characteristics and sediment source of near-shore area in Xinghua Bay[J]. Journal of Waterway & Harbor, 2012, 33(6):469-474. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8443.2012.06.002
[27] Dyer K R. The salt balance in stratified estuaries[J]. Estuarine & Coastal Marine Science, 1974, 2(3):273-281. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/0302352474900176
[28] 沈健, 沈焕庭, 潘定安, 等.长江河口最大浑浊带水沙输运机制分析[J].地理学报, 1995(5):411-420. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1995.05.004
SHEN Jian, SHEN Huanting, PAN Dingan, et al. Analysis of transport mechenism of water and suspended sediment in the turbidity maximum of the Changjiang Estuary [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1995(5):411-420. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1995.05.004
[29] Dyer K R. Fine Sediment Particle Transport in Estuaries[M]// Physical Processes in Estuaries. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 1988: 295-310.
https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007%2F978-3-642-73691-9_16 [30] Uncles R J, Elliott R C A, Weston S A, et al. Synoptic Observations of Salinity, Suspended Sediment and Vertical Current Structure in a Partly Mixed Estuary[M]// Physics of Shallow Estuaries and Bays. Springer-Verlag, 1986: 58-70.
https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1029/LN016p0058 [31] 万小芳, 潘爱军, 郭小钢, 等.台湾海峡西侧水动力环境的季节变化特征[J].应用海洋学学报, 2013, 32(2):156-163. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2013.02.002
WAN Xiaofang, PAN Aijun, GUO Xiaogang, et al. Seasonal variation features of the hydrodynamic environment in the western Taiwan Strait[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2013, 32(2):156-163. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2013.02.002
[32] Gao S, Wang D, Yang Y, et al. Holocene sedimentary systems on a broad continental shelf with abundant river input: Process-product relationships[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 2015:1-37. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/281629535_Holocene_sedimentary_systems_on_a_broad_continental_shelf_with_abundant_river_input_Process-product_relationships
[33] Su Y S, Weng X C. Water Masses in China Seas[M]// Oceanology of China Seas. Springer Netherlands, 1994: 3-16.
[34] 唐晓晖, 王凡.长江口邻近海域夏、冬季水文特征分析[J].海洋科学集刊, 2004:46-70.
TANG Xiaohun, WANG Fan. Analyses on hydrographic structure in the Changjiang River Estuary adjacent waters in summer and winter[J]. Studia Marina Sinica, 2004:46-70.
-




 下载:
下载: