Variations in water discharge and sediment load in the Yalu River catchment induced by human activities and climate changes
-
摘要:
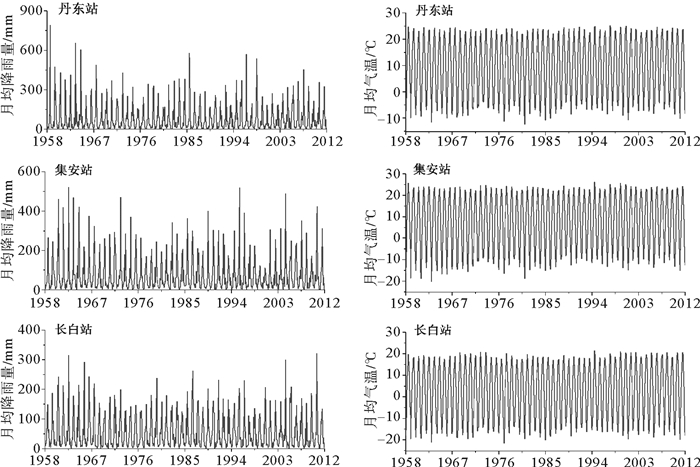
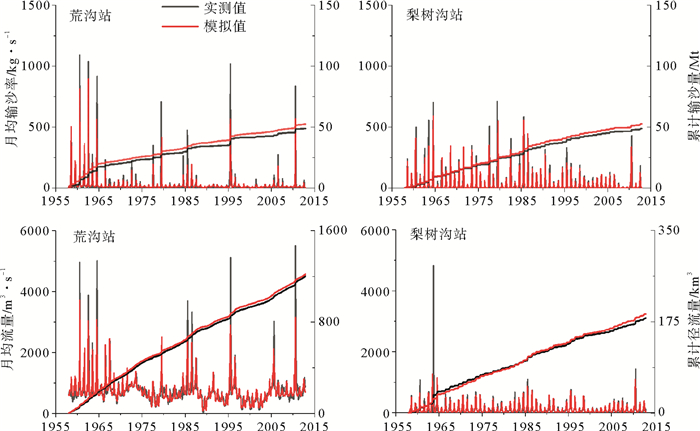
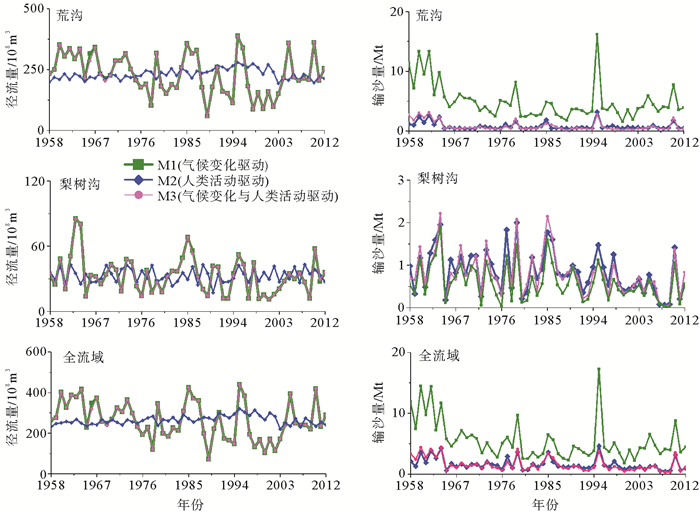
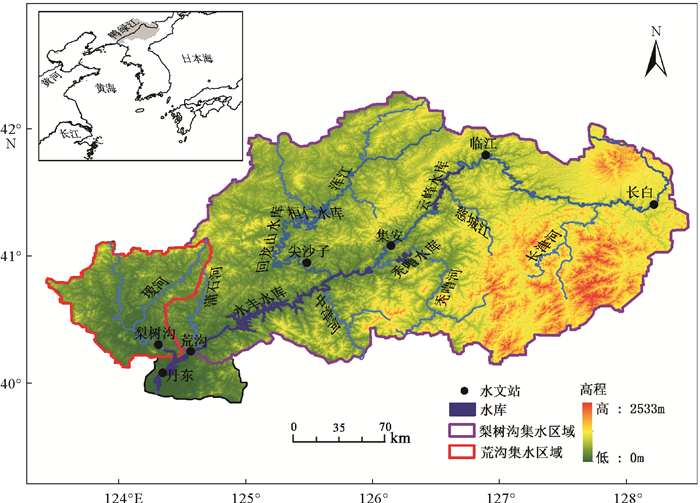
为探讨气候变化、人类活动(植被变化和水库修建活动)对入海水沙变化的影响,运用HydroTrend3.0.4水文模型,对1958—2012年,3种情景模式(气候变化、人类活动以及气候变化和人类活动共同驱动下)鸭绿江流域的入海水沙进行模拟,定量估算出流域气候变化和人类活动对入海水沙通量的影响。研究表明1958—2012年间气候变化驱动、人类活动驱动以及两者共同作用的流域年入海径流量分别为264.5×108、264.3×108和263.7×108m3/a,年入海输沙量达到5.53、1.62和1.59Mt/a,而流域多年实测入海径流量与输沙量分别为259.2×108m3/a和1.48Mt/a。气候变化驱动下,不同年际间的降雨量变化(即暴雨和干旱的频率和强度)是导致鸭绿江流域年均入海径流量变化的最主要原因,而频发的山洪是年均入海输沙量变化的主导因素。气候与人类活动共同作用下,流域不断加剧的人类活动成为鸭绿江流域年入海输沙量变化的主导因素。流域人类活动对入海输沙量变化的贡献量为3.94Mt/a,其中流域植被变化导致水土流失量增加1.20Mt/a, 而流域大坝拦截了5.14Mt/a的入海沉积物,76.4%的入海沉积物被鸭绿江流域的梯级水库所拦截。因此,估算1940年鸭绿江流域修建水库前,其入海输沙量达到6.73Mt/a,约为现在鸭绿江入海输沙量的5倍。
Abstract:In order to reveal the influence factors dominating the water input and sediment discharge into the sea from the Yalu River catchment, the numerical model of HydroTrend3.0.4 with three scenarios, i.e. the climate change-driven, Human activities-driven, and combined climate change and human activities-driven senarios, is adopted to simulate water and sediment fluxes into coastal coastal ocean during the period of 1958-2012 at two river gauging stations. Results indicate that, during the period, water discharge of climate change-driven, Human activities-driven, and combined climate change and human activities-driven scenarios were 264.5×108 m3/a, 264.3×108 m3/a and 263.7×108 m3/a, and sediment load was 5.53Mt/a, 1.62Mt/a and 1.59Mt/a, respectively. The observed water discharge and sediment load were 259.2×108m3/a and 1.48Mt/a. Under the scenario driven by climate change, the main factor dominating the variation of water discharge is precipitation, and the sediment flux variation under natural condition is mainly controlled by frequent flood events during the wet season. However, under the scenario of the combined climate change and human activities-driven, the intensifying human activities have caused dramatic change in sediment load into the sea: the anthropogenic impact can totally decrease the sediment flux of the Yalu River by 3.94Mt/a, including an increase in 1.2Mt/a sediment yielding by water and soil erosion, and a larger decrease in 5.14Mt/a by the dam interception effect. We also found that the sediment load entering the sea of the Yalu River before 1940 (pre-dams) was about 6.67Mt/a, 5 times of the present sediment load into the sea.
-
Key words:
- climate change /
- human activities /
- water discharge /
- Yalu River
-

-
表 1 不同模式下流域年均入海水沙通量变化(气候变化驱动M1、人类活动驱动M2、气候与人类共同影响驱动M3只考虑水土流失、气候与人类共同影响驱动M3综合考虑水土流失+水库拦截)
Table 1. Comparison of annual water discharge and sediment load variations forced with different scenarios (climate change-driven M1, human activities-driven M2, combined climate change and human activities-driven M3 soil erosion, combined climate change and human activities-driven M3-soil erosion and dams)
流域 年均径流量(108m3/a) 年均输沙量(Mt/a) M1 M2 M3 M1 M2 M3 M3(水土流失) M3(水土流失+水库拦截) 瑷河梨树沟 32.9 33.1 32.9 0.59 0.83 0.80 0.80 鸭绿江荒沟 231.6 231.2 230.8 4.94 0.79 5.93 0.79 全流域 264.5 264.3 263.7 5.53 1.62 6.73 1.59 表 2 不同模式下(气候变化驱动、气候与人类共同影响驱动)流域丰、枯水期年均水沙通量变化
Table 2. Comparison of annual water discharge and sediment load variations forced with different scenarios (climate change-driven, combined climate change and human activities-driven) in high precipitation year to that in low precipitation year
水文站 降雨丰、枯期 时间 降雨(mm) 年径流量(108m3/a) 年输沙量(Mt/a) M1 M3 M1 M3 瑷河 丰水期 1958-1974 1058.7 39.7 39.8 0.77 0.96 枯水期 1975-1982 854.5 25.6 23.3 0.52 0.85 梨树沟 丰水期 1983-1998 978.8 35.6 35.2 0.62 0.88 枯水期 1999-2012 779.3 25.8 26.0 0.37 0.48 鸭绿江 丰水期 1958-1964 917.1 301.2 300.9 10.08 2.36 枯水期 1965-1979 800.0 240.2 242.8 4.81 0.57 荒沟 枯水期 1980-2002 820.5 203.3 198.0 3.65 0.55 丰水期 2003-2012 910.3 239.0 239.3 4.45 0.59 -
[1] Walling D E, Fang D. Recent trends in the suspended sediment loads of the world's rivers[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2003, 39(1): 111-126
[2] Zhang Q, Xu C, Becker S, et al. Sediment and runoff changes in the Yangtze River basin during past 50 years[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2006, 331(3): 511-523. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=59e41a47b6b087412d631dd7e33807bb
[3] 徐夏楠, 高建华, 贾建军, 等.气候变化和人类活动对鄱阳湖流域入湖输沙量影响的定量估算[J].地理研究, 2015, 34(5): 838-850. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dlyj201505004
XU Xianan, GAO Jianhua, JIA Jianjun, et al. The quantitative estimation of sediment load changes entering Poyang Lake Basin induced by climate change and anthropogenic impacts[J]. Geographical Research, 2015, 34(5): 838-850. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dlyj201505004
[4] 刘成, 王兆印, 隋觉义.我国主要入海河流水沙变化分析[J].水利学报, 2007, 38(12): 1444-1452. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2007.12.006
LIU Cheng, WANG Zhaoyin, SUI Jueyi. Analysis on variation of seagoing water and sediment load in main rivers of China[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2007, 38(12): 1444-1452. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2007.12.006
[5] 高抒.长江三角洲对流域输沙变化的响应:进展与问题[J].地球科学进展, 2010, 25(3): 233-241. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkxjz201003001
GAO Shu. Changjiang delta sedimentation in response to catchment discharge changes: Progress and problems[J]. Advance in Earth Science, 2010, 25(3):233-241 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkxjz201003001
[6] Syvitski J P M, Milliman J D. Geology, geography, and humans battle for dominance over the delivery of fluvial sediment to the coastal ocean[J]. The Journal of Geology, 2007, 115(1): 1-19. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=7d390d9651dc16c1194438ba671c452c
[7] Syvitski J P M, Morehead M D, Nicholson M. HYDROTREND: A climate-driven hydrologic-transport model for predicting discharge and sediment load to lakes or oceans. Computers & Geosciences, 1998, 24(1): 51-68. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ027594125/
[8] Kettner A J, Syvitski J P M. HydroTrendv. 3. 0: A climate-driven hydrological transport model that simulates discharge and sediment load leaving a river system. Computers & Geosciences, 2008, 34(10): 1170-1183. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/222992421_HydroTrend_v30_A_climate-driven_hydrological_transport_model_that_simulates_discharge_and_sediment_load_leaving_a_river_system
[9] 符文侠, 贾锡钧, 魏成凯, 等.河流泥沙对辽东半岛海岸的填充作用[J].黄渤海海洋, 1984, 2(2): 53-59. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HBHH198402011.htm
FU Wenxia, JIA Xijun WEI Chengkai, et al. Filling effect of discharge silt on the coast in the Liaodong peninsula[J]. Journal of Oceanography of Huanghai & Bohai Seas, 1984, 2(2): 53-59. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HBHH198402011.htm
[10] 高建华, 高抒, 董礼先, 等.鸭绿江河口地区沉积物特征及悬沙输送[J].海洋通报, 2003, 22(5): 26-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2003.05.005
GAO Jianhua, GAO Shu, DONG Lixian, et al. Sediment distribution and suspended sediment transport in Yalu River estuary[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2003, 22(5):26-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2003.05.005
[11] 李光天, 符文侠, 贾锡钧.辽东潮间浅滩的综合特征[J].地理学报, 1986(3):262-273. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1986.03.008
LI Guangtian, FU Wenxia, JIA Xijun. The comprehensive characteristic of the Liaodong peninsular tidal flat[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1986, 41(3):262-273 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1986.03.008
[12] Ren M. Sediment discharge of the Yellow River, China: Past, present and future——A synthesis[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2015, 34(2): 1-8. doi: 10.1007/s13131-015-0619-6
[13] Warrick J A. Eel River margin source-to-sink sediment budgets: Revisited[J]. Marine Geology, 2014, 351: 25-37. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.03.008
[14] Gao J H, Xu X, Jia J, et al. A numerical investigation of freshwater and sediment discharge variations of Poyang Lake catchment, China over the last 1000 years[J]. The Holocene, 2015, 25(9): 1470-1482. doi: 10.1177/0959683615585843
[15] Kettner A J, Restrepo J D, Syvitski J P M. A spatial simulation experiment to replicate fluvial sediment fluxes within the Magdalena River Basin, Colombia[J]. The Journal of Geology, 2010, 118(4): 363-379. doi: 10.1086/652659
[16] 中国海湾志编纂委员会.中国海湾志(第十四分册): 重要河口[M].海洋出版社, 1998: 386-432
State Oceanic Administration. Chinese Harbours and Embayments (Volume 14): Important Estuaries[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1998: 386-432
[17] Gao J H, Jun L I, Harry W, et al. Rapid changes of sediment dynamic processes in Yalu River Estuary under anthropogenic impacts[J]. International Journal of Sediment Research, 2012, 27(1): 37-49. doi: 10.1016/S1001-6279(12)60014-6
[18] Milliman J D, Farnsworth K L. River discharge to the coastal ocean: a global synthesis[M]. Cambridge University Press, 2013.
[19] 郭芬芬, 范建容, 严冬, 等.基于像元二分模型的昌都县植被盖度遥感估算[J].中国水土保持, 2010, 2010(5):65-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0941.2010.05.024
GUO Fenfen, FAN Jianrong, YAN Dong, et al. Remote Sensing Estimation on Vegetation Coverage of Changdu County Based on Dimidiate Pixel Model[J]. Soil and Water Conservation in China, 2010, 2010(5):65-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0941.2010.05.024
[20] 尹学军, 中国水利部, 全国水资源调查报告, 辽河流域片[M]. 1981.
YIN Xuejun, Ministry of water resources of China, National Water Resources Survey Report, Liaohe river regions[M]. 1981.
[21] McCarney-Castle K, Voulgaris G, Kettner A J, et al. Simulating fluvial fluxes in the Danube watershed: The 'Little Ice Age'versus modern day[J]. The Holocene, 2012, 22(1): 91-105. doi: 10.1177/0959683611409778
[22] Syvitski J P M, Kettner A J, Peckham S D, et al. Predicting the Flux of Sediment to the Coastal Zone: Application to the Lanyang Watershed, Northern Taiwan[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2005, 21(3):580-497. https://www.jstor.org/stable/4299444
[23] 王铁锋, 俞宏, 马雪梅.鸭绿江2010年大洪水及梯级水库的防洪作用分析[J].东北水利水电, 2010, 28(12): 51-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0624.2010.12.026
WANG Tiefeng, YU Hong, MA Xuemei. Analysis on flood in 2010 and flood control effect of cascade reservoir in Yalu river[J]. Water Resources & Hydropower of Northeast China, 2010, 28(12):51-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0624.2010.12.026
-



 下载:
下载: