Igneous rocks in Jinghai Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin and their geological significance
-
摘要:
利用三维地震对靖海凹陷的火成岩体进行了识别,火山岩沉积后上覆地层会直接超覆在火山岩体上,而侵入岩体形成的地层上拱和超覆现象发生在上覆地层之内的不整合面上。研究区岩浆活动时间可分为4期:自老到新依次为晚白垩世内部Tm18不整合形成期,晚中新世T35不整合形成期(10.5Ma),上新世末T20不整合形成期(2.6Ma)和第四纪,且以第四纪火山活动最为强烈。火山口和侵入体主要沿北东向朝南大断裂分布,具小规模中心式分散分布特点,其分布趋势与古地温梯度朝南部洋壳区方向增大似乎没有关系。从绝大多数火山活动发生在第四纪且局部分布来看,它们对油气藏主要起有限的改造和破坏作用。
Abstract:Igneous rocks in the Jinghai sag are identified through 3D seismic interpretation by the contact relationship between the rocks and the overlying deposits. Four magmatic stages are recognized in the study area, separated by three unconformity reflections, i.e the late Cretaceous Tm18, the late Miocene T35 (10.5Ma), the late Pliocene T20 (2.6Ma) and the overlying Quaternary. Among them the Quaternary eruption is the strongest. Volcanic and intrusive bodies are mainly distributed along the NE trending Chaoshannan fault, in a form of scatter small scale central volcanoes. The distribution trend of the volcanoes seems irrelevant to the increase in paleogeothermal gradient toward the oceanic crust in the south. Limited impact is expected to the oil gas accumulations in the sag.
-
Key words:
- Jinghai sag /
- magma action /
- piercing /
- volcano /
- seismic reflection
-

-
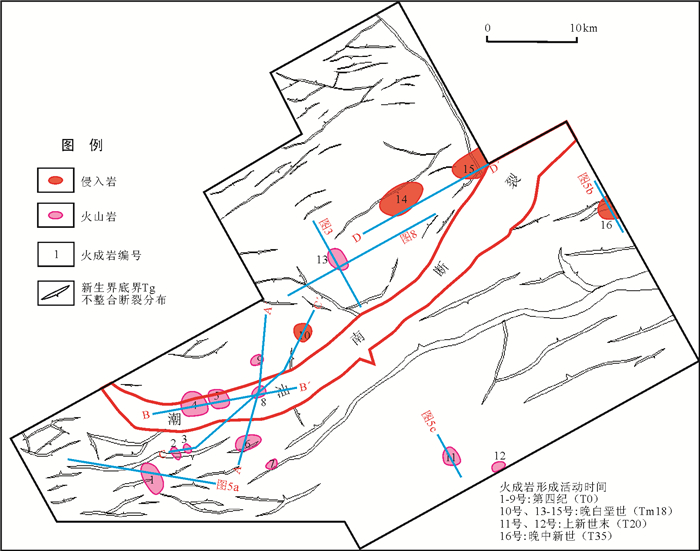
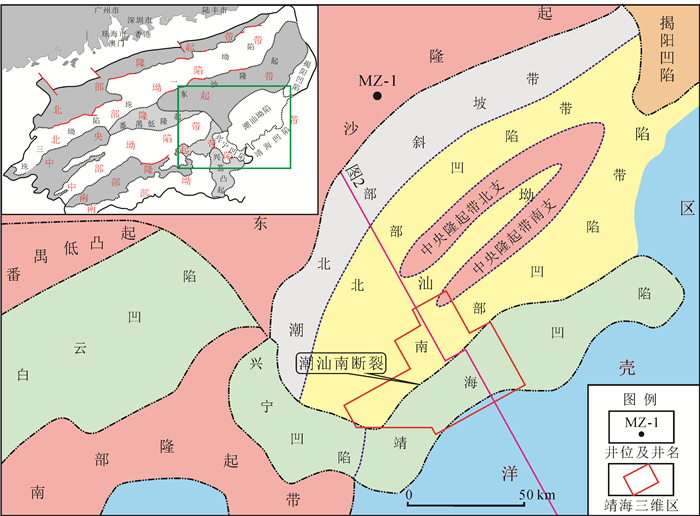
图 1 研究区位置图(修改自文献[22])
Figure 1.
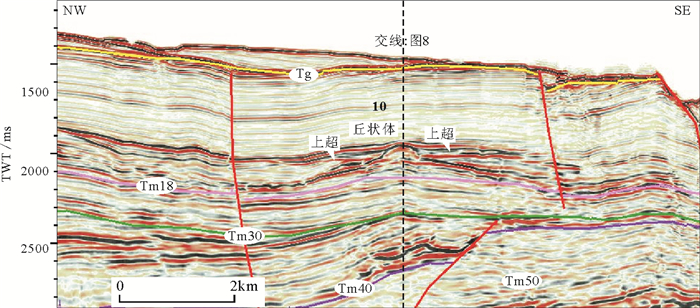
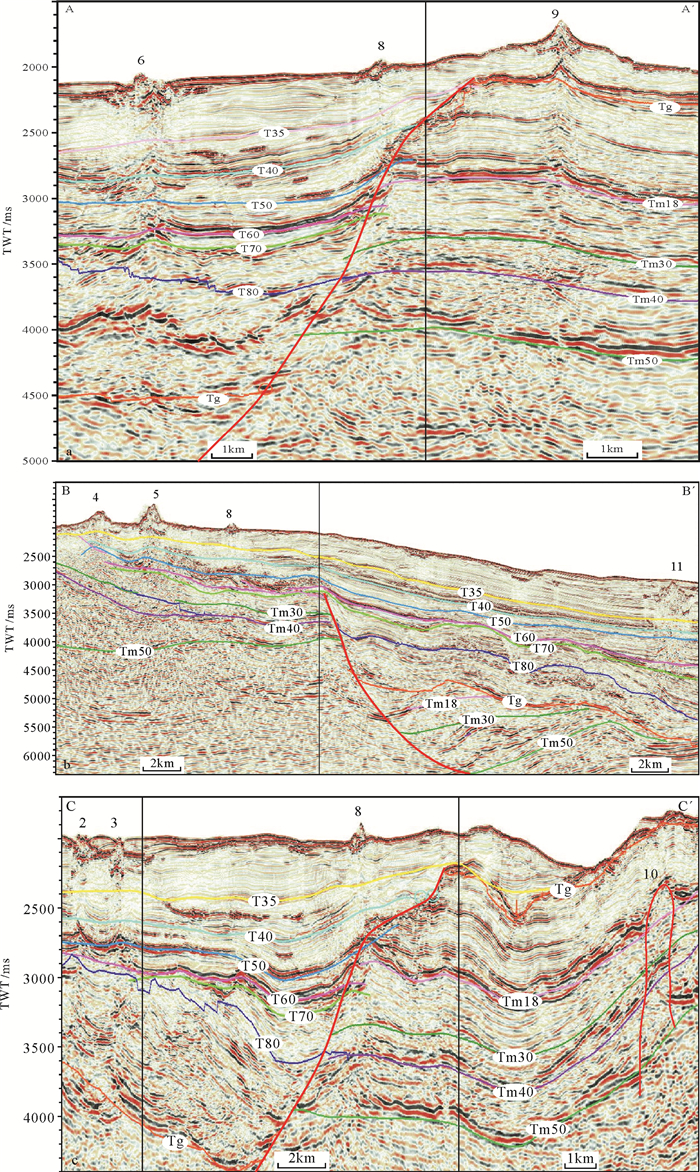
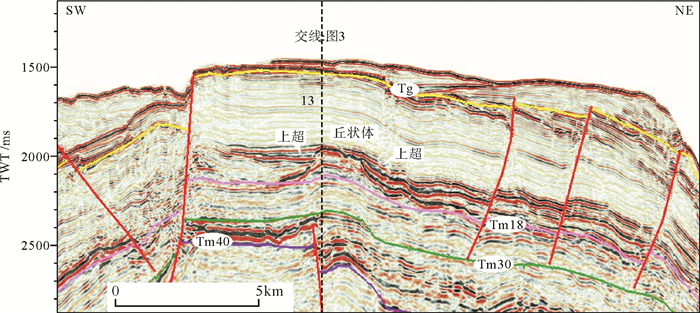
图 3 Tm18界面上部火山岩地震反射(剖面位置见图 4)
Figure 3.
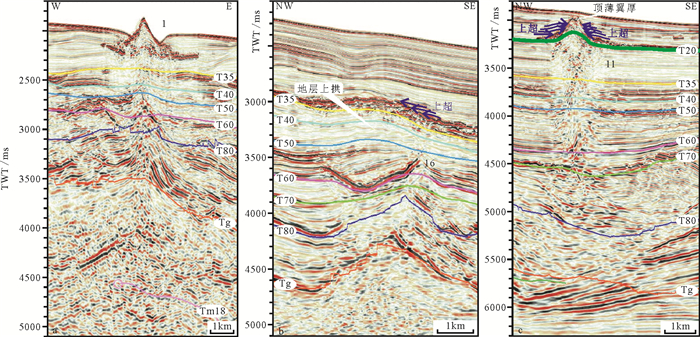
图 5 火成岩活动期次判别(剖面位置见图 4)
Figure 5.
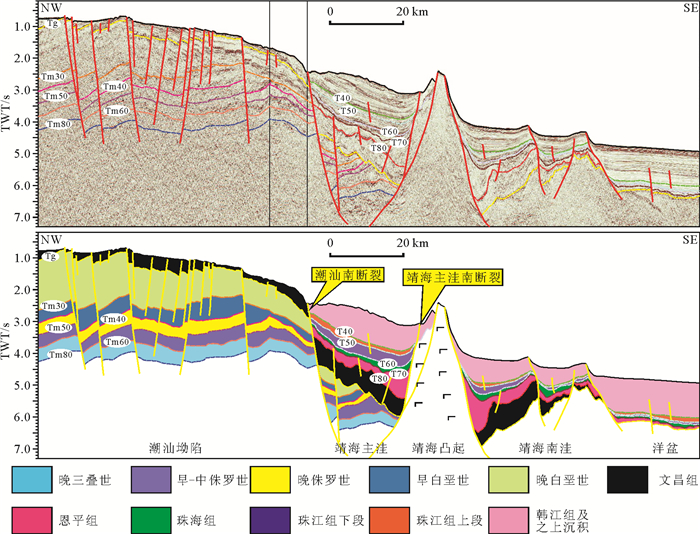
图 6 靖海三维区火山岩剖面(剖面位置见图 4)
Figure 6.
图 7 靖海三维区14和15号侵入岩剖面(剖面位置见图 4中DD′)
Figure 7.
-
[1] Ernst W C, Liou J G. Constrasting plate-tectonic styles of the Qinling-Dabie-Sulu and Fransiscan metamorphic belts[J]. Geology, 1995, 23(4): 353-356. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1995)023<0353:CPTSOT>2.3.CO;2
[2] Oh C W, Sajeev K, Kim S W, et al. Tectonic evolution of Korean Peninsula and adjacent crustal fragments in Asia:introduction[J]. Gondwana Research, 2006, 9(1-2): 19-20. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2005.07.001
[3] Rogers J J W, Santosh M. The Sino-Korea Craton and supercontinent history: Problems and perspectives[J]. Gondwana Research, 2006, 9(1-2): 21-23. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2005.04.001
[4] 万天丰.中朝与扬子板块的鉴别特征[J].地质论评, 2001, 47(1): 57-63. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2001.01.009
WAN Tianfeng. Distinctive characteristics of Sino-Korean and Yangtze Plates[J]. Geological Review, 2001, 47(1): 57-63. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2001.01.009
[5] Oh C W, Choi S G, Song S W, et al. Metamorphic evolution of the Baekdong metabasite in the Hongseong area, South Korea and its relationship with Sulu collision belt in China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2004, 7(3): 809-816. doi: 10.1016/S1342-937X(05)71065-0
[6] Kim S W, Oh C W, Williams I S, et al. Phanerozoic high-pressure eclogite and intermediate-pressure granulite facies metamorphism in the Gyeonggi Massif, South Korea: Implications for the eastward extension of the Dabie-Sulu continental collision zone[J]. Lithos, 2006, 92(3-4): 357-377. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2006.03.050
[7] 唐贤君, 於文辉, 单蕊.中国东部-朝鲜半岛中生代板块结合带划分研究现状与问题[J].地质学报, 2010, 84(5): 606-617. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201005002
TANG Xianjun, YU Wenhui, SHAN Rui. The mesozoic plate boundary in the Eastern China and Korean Peninsula: Present studies and problems[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2010, 84(5): 606-617. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201005002
[8] Yin A, Nie S Y. An indentation model for the North and South China collision and the development of the Tan-Lu and Honam fault systems: eastern Asia[J]. Tectonics, 1993, 12(4): 801-813. doi: 10.1029/93TC00313
[9] Lee S R, Cho M. Metamorphic and tectonic evolution of the Hwacheon granulite complex, Central Korea: composite P-T path resulting from two district crustal-thickening events[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2003, 44(2): 197-226. doi: 10.1093/petrology/44.2.197
[10] Oh C W, Krishnan S, Kim S W, et al. Mangerite magmatism associated with a probable Late-Permian to Triassic Hongseong-Odesan collision belt in South Korea[J]. Gondwana Research, 9(1-2): 95-105.
[11] Zhang K J. North and South China collision along the eastern and southern North China margins[J]. Tectonophysics, 2006, 270(1-2): 145-156. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-S0040-1951(96)00208-9/
[12] Zhai M G, Guo J H, Li Z, et al. Linking the Sulu UHP belt to the Korean Peninsula: Evidence from eclogite, Precambrian basement, and Paleozoic sedimentary basins[J]. Gondwana Research, 2007, 12(4): 388-403. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2007.02.003
[13] Chang K H, Park S O. Paleozoic Yellow Sea Transform Fault: its role in the tectonic history of Korea and adjacent regions[J]. Gondwana Research, 2001, 4(4): 588-589. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-S1342-937X(05)70393-2/
[14] Ishiwatari A, Tsujimoori T. Late Paleozoic high-pressure metamorphic belts in Japan and Sikhote-Alin: possible oceanic extension of the Chinese Dabie-Sulu suture detouring Korea[J]. Gondwana Research, 2001, 4(4): 636-638. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2001GondR...4R.636I
[15] Zhai M G, Guo J H, Peng P. U-Pb zircon age dating of a rapakivi granite batholith in Rangnim massif, North Korea[J]. Geological Magazine, 2007, 144(3): 547-552. doi: 10.1017/S0016756807003287
[16] Paek R J, Rim D S. On the Rimjinang belt[C]//Gondwana to Asia Symposium of 2005.Beijing: Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2005.
[17] Paek R J. Lower Proterozoic era stratigraphy[C]//Geological Institute, Academy of Sciences, North Korea, ed. Geology of Korea. Pyongyang: Foreign Languages Books Publishing House, 1993: 41-52.
[18] Jeong H, Lee Y I. Nd isotopic study of Upper Cambrian conodonts from Korea and implications for early Paleozoic paleogeography[J]. Paleogeography, Paleoclimatology, Paleoecology, 2004, 212(1-2): 77-94. doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(04)00305-0
[19] Kim S W, Oh C W, Choi S, et al. Ridge subduction-related Jurassic plutonism in and around the Okcheon metamorphic belt, South Korea, and implication for northeast Asian tectonics[J]. International Geological Review, 2005, 47(3): 248-269. doi: 10.2747/0020-6814.47.3.248
[20] Kwon Y K, Chough S K, Choi D K, et al. Sequence stratigraphy of the Taebaek Group(Cambrian-Ordovician), mideast Korea[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2006, 192(1-2): 19-55. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2006.03.024
[21] 翟明国, 郭敬辉, 李忠, 等.苏鲁造山带在朝鲜半岛的延伸:造山带、前寒武纪基底以及古生代沉积盆地的证据与制约[J].高校地质学报, 2007, 13(3): 415-428. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2007.03.011
ZHAI Mingguo, GUO Jinghui, LI Zhong, et al. Extension of the Sulu UHP Belt to the Korean peninsula: evidence from Orogenic Belts, precambrian basements, and paleozoic sedimentary basins[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2007, 13(3): 415-428. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2007.03.011
[22] Cluzel D. Ordovician bimodal magmatism in the Ogcheon belt (South Korea): intracontinental rift-related volcanic activity[J]. Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Sciences, 1992, 7(2-3): 195-209. doi: 10.1016/0743-9547(92)90054-F
[23] Cho K H, Takagi H, Suzuki K. CHIME monazite age of granitic rocks in the Sunchang shear zone, Korea: timing of dextral ductile shear[J]. Geoscience Journal, 1999, 3(1): 1-15. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF02910229
[24] Cheong C S, Kee W S, Jeong Y J, et al. Multiple deformations along the Honam shear zone in southwestern Korea constrained by Rb-Sr dating of synkinematic fabrics: Implications for the Mesozoic tectonic evolution of northeastern Asia[J]. Lithos, 2006, 87(3-4): 289-299. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2005.06.015
[25] 王小凤, 李中坚, 陈柏林, 等.郯庐断裂带[M].北京:地质出版社, 2000.
WANG Xiaofen, LI Zhongjian, CHNEG Bolin, et al. The Tanlu Fault Zone[M]. Beijing: Geological Press, 2000.
[26] 朱光, 刘国生, 牛漫兰, 等.郯庐断裂带的平移运动与成因[J].地质通报, 2003, 22(3): 200-207. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2003.03.009
ZHU Guang, LIU Guosheng, NIU Manlan, et al. Transcurrent movement and genesis of the Tan-Lu fault zone[J]. Geology Bulletin of China, 2003, 22(3): 200-207. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2003.03.009
[27] 徐嘉炜.郯城-庐江平移断裂系统[J].构造地质论丛, 1984, 3: 18-33.
XU Jiawei. Tancheng-Lujiang fault system[J]. Tectonic Geology Review, 1984, 3: 18-33.
[28] 张用夏, 李卢玲.郯庐断裂带的平移及其对邻区构造的影响[J].构造地质论丛, 1984, 3: 1-8.
ZHANG Yongxia, LI Luling. The translation of the Tanlu fault zone and its influence on the structure of adjacent area[J]. Tectonic Geology Review, 1984, 3: 1-8.
[29] 万天丰, 朱鸿.郯庐断裂带的最大左行走滑断距及其形成时期[J].高校地质学报, 1996, 2(1): 14-27. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199600146085
WAN Tianfeng, ZHU Hong. The maximum sinistral strike-slip and its forming age Tancheng-Lujiang fault zone[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 1996, 2(1): 14-27. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199600146085
[30] 朱光, 宋传中, 牛漫兰, 等.郯庐断裂带的岩石圈结构及其成因分析[J].高校地质学报, 2002, 8(3): 248-256. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2002.03.002
ZHU Guang, SONG Chuanzhong, NIU Manlan, et al. Lithospheric textures of the Tan-Lu Fault zone and their genetic analysis[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2002, 8(3): 248-256. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2002.03.002
[31] 朱光, 王道轩, 刘国生, 等.郯庐断裂带的演化及其对西太平洋板块运动的响应[J].地质科学, 2004, 39(1): 36-49. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2004.01.005
ZHU Guang, WANG Daoxuan, LIU Guosheng, et al. Evolution of the Tan-Lu fault zone and its responses to plate movements in west pacific basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2004, 39(1): 36-49. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2004.01.005
[32] 朱光, 王勇生, 王道轩, 等.前陆沉积与变形对郯庐断裂带同造山运动的制约[J].地质科学, 2006, 41(1): 102-121. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2006.01.009
ZHU Guang, WANG Yongsheng, WANG Daoxuan, et al. Constraints of foreland sedimentation and deformation on synorogenic motion of the Tan-Lu Fault Zone[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2006, 41(1): 102-121. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2006.01.009
[33] 杨文采, 徐纪人, 陈振炎, 等.苏鲁大别造山带地球物理与壳幔作用[M].北京:地质出版社, 2004.
YANG Wencai, XU Jiren, CHEN Zhenyan, et al. Regional Geophysics and Crust-Mantle Interaction in Sulu-Dabie Orogenic Belt[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2004.
[34] 翟明国, 郭敬辉, 王清晨, 等.苏鲁变质带北部的岩石构造单元及结晶块体推覆构造[J].地质科学, 2000, 35(1): 16-26. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2000.01.002
ZHAI Mingguo, GUO Jinghui, WANG Qingchen, et al. Division of petrological-tectonic units in the northern Sulu Ultra-High Pressure Zone: an example of thick-skin thrust of crystalline units[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2000, 35(1): 16-26. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2000.01.002
[35] Chio S C, Oh C W, Luehr H. Tectonic relation between northeastern China and the Korean peninsula revealed by interpretation of GRACE satellite gravity data[J]. Gondwana Research, 2006, 9(1-2): 62-67. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2005.06.002
[36] 金峰男, 杜劲松, 陈超.中朝与扬子地块结合带东部的卫星重力异常特征研究[J].地球物理学进展, 2010, 25(4): 1219-1232. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2010.04.010
Kim B N, DU Jinsong, CHEN Chao. Characteristic of satellite gravity anomalies in the eastern boundary belt between Sino-Korean and Yangtze blocks[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2010, 25(4): 1219-1232. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2010.04.010
[37] 郝天珧, Suh M, 刘建华, 等.黄海深部结构与中朝-扬子块体结合带在海区位置的地球物理研究[J].地学前缘, 2004, 11(3): 51-61. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.03.007
HAO Tianyao, SUH M, LIU Jianhua, et al. Deep structure and boundary belt position between Sino-Korean and Yangtze blocks in Yellow Sea[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2004, 11(3): 51-61. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.03.007
[38] 胥颐, 李志伟, Kim K, 等.黄海的地壳速度结构与中朝-扬子块体拼合边界[J].地球物理学报, 2009, 52(3): 646-652. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqwlxb200903007
XU Yi, LI Zhiwei, KIM K, et al. Crustal velocity structure and collision boundary between the Sino-Korea and Yangtze blocks in Yellow Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2009, 52(3): 646-652. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqwlxb200903007
[39] 李春峰, 陈冰, 周祖翼.中国东部及邻近海域磁异常数据所揭示的深部构造[J].中国科学D辑:地球科学, 2009, 39(12): 1770-1779. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JDXK200912013.htm
LI Chunfeng, CHEN Bing, ZHOU Zhuyi. Deep crustal structures of eastern China and adjacent seas revealed by magnetic data[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2009, 52(7): 984-993. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JDXK200912013.htm
[40] 郑永飞.超高压变质与大陆碰撞研究进展:以大别-苏鲁造山带为例[J].科学通报, 2008, 53(18): 2129-2152. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-j.fgb.2010.02.001/
ZHENG Yongfei. A perspective view on ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism and continental collision in the Dabie-Sulu orogenic belt[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2008, 53(20): 3081-3104. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-j.fgb.2010.02.001/
[41] 邢历生, 李中坚, 王小凤, 等.郯庐断裂带东侧华南地块部分的逆时针转动——古地磁新证据[J].地质力学学报, 1995, 1(3): 31-37. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZLX503.004.htm
XING Lisheng, LI Zhongjian, WANG Xiaofeng, et al. Counterclockwise rotation of South China Block, east of the Tan-Lu Fault Zone[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 1995, 1(3): 31-37. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZLX503.004.htm
[42] 陈沪生, 张永鸿.下扬子及邻区岩石圈结构构造特征与油气资源评价[M].北京:地质出版社, 1999.
CHEN Hushing, ZHANG Yonghong. The Lithospheric Textural and Structural Features as Well as Oil and Gas Evaluation in the Lower Yangtze Area and Its Adjacent Region, China[M]. Beijing: Geological Press, 1999.
[43] 葛肖虹.论宁镇山脉推覆构造的特征与形成[J].长春地质学院学报, 1987, 17(2): 143-154. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-CCDZ198702002.htm
GE Xiaohong. On the characteristic and formation of the Nanjing-Zhenjiang Mountain Nappe structure[J]. Journal of Changchun College of Geology, 1987, 17(2): 143-154. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-CCDZ198702002.htm
[44] Chwae U, Choi S J. On the possible extension of the Sulu belt toward the east through the Korean peninsula[J]. Gondwana Research, 1999, 2(4): 540-542. doi: 10.1016/S1342-937X(05)70188-X
-



 下载:
下载: