Preliminary research on characteristics, distribution patterns and origins of submarine slides in deepwater oil and gas exploration area of Baiyun Sag
-
摘要:
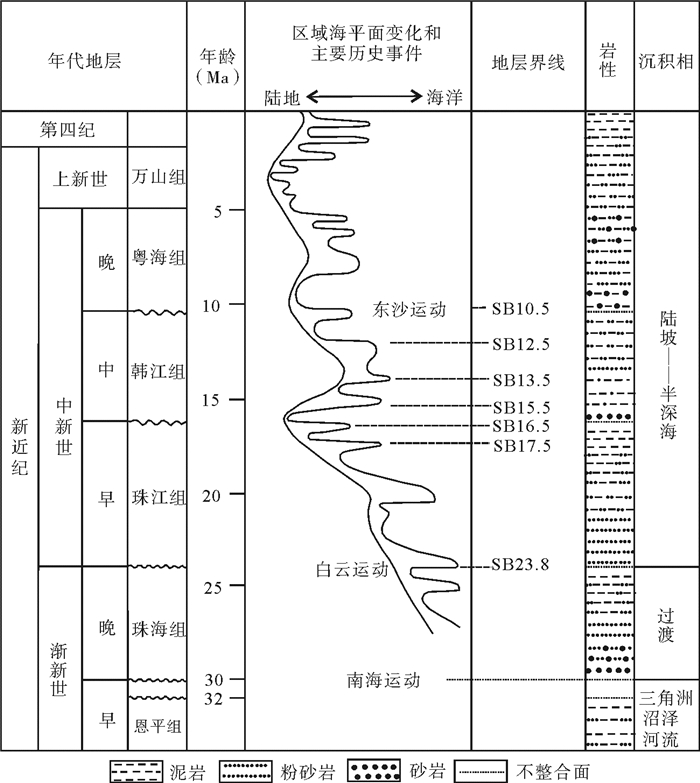
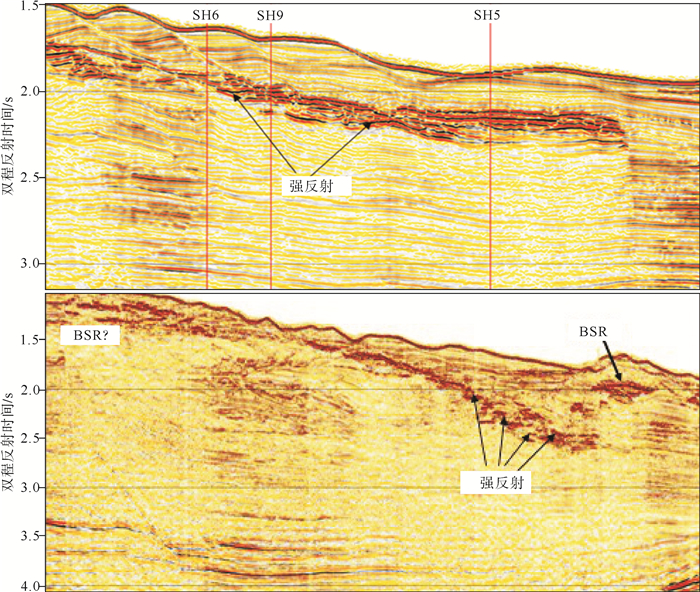
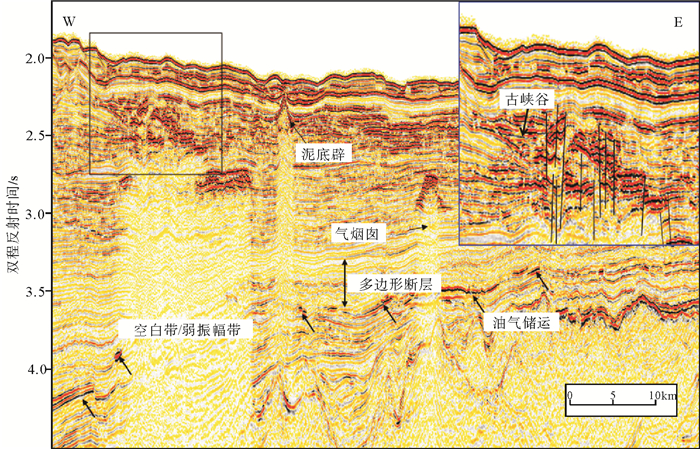
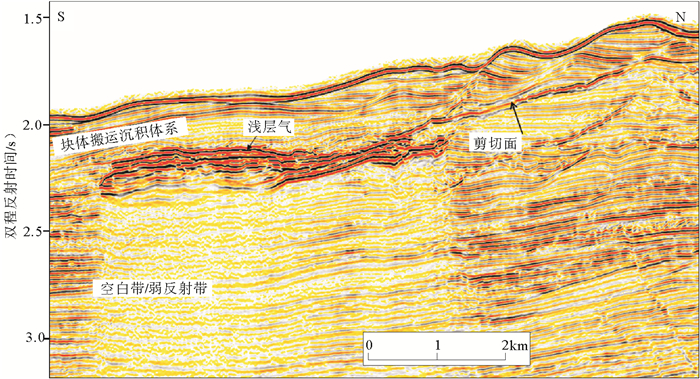
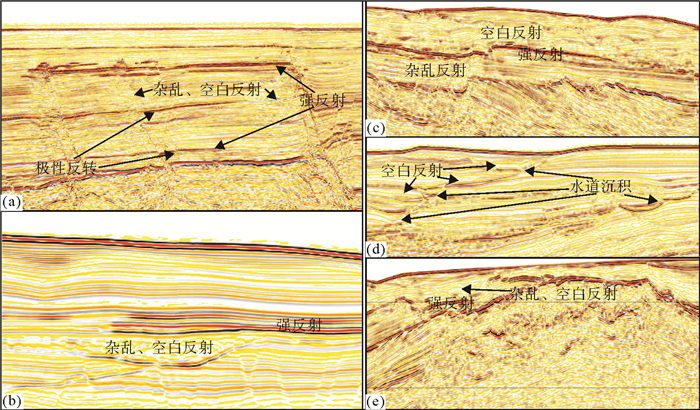
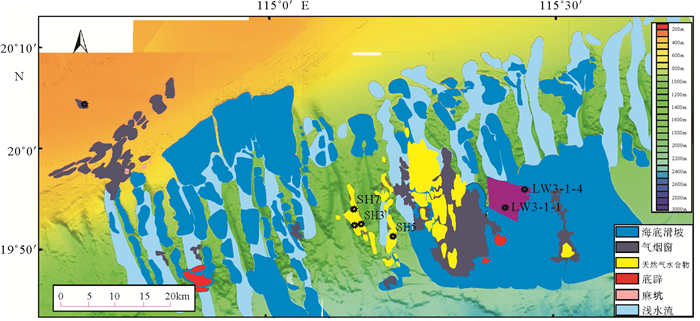
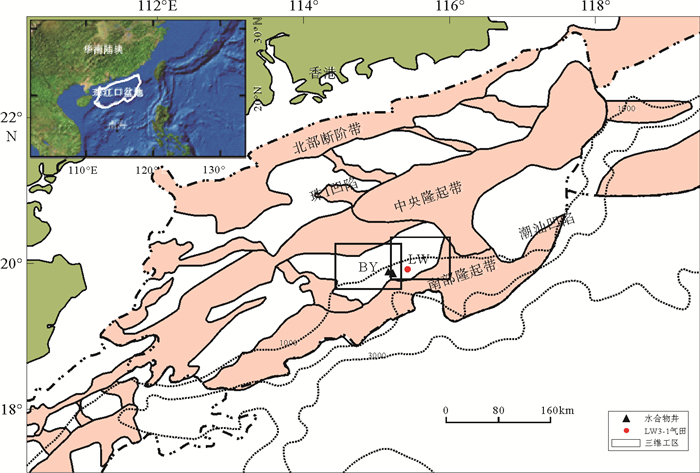
白云凹陷深水区是深水油气勘探开发的热点区域,深水地质灾害严重威胁深水油气开发的施工安全,通过研究其主要深水地质灾害海底滑坡的形成、分布,可对深水油气开发过程中不必要的风险和损失进行预测和预防。通过分析中海油高精度三维地震资料,识别了白云凹陷深水油气开发区的海底滑坡以及与之相关的天然气水合物、气烟囱、泥底辟、浅层气和浅水流等深水地质灾害现象。这些深水地质灾害现象与海底滑坡的发育密不可分,是识别海底滑坡的重要因素。利用地球物理属性识别并发现了白云凹陷规模巨大和分布广泛的海底滑坡,并认为超压流体释放、水合物分解、高沉积速率等主导了白云凹陷海底滑坡的发育,这些主要控制因素都是南海北部新构造活动的产物,新构造活动才是海底滑坡的主要成因。
Abstract:Deepwater geohazards, especially submarine slides, may seriously threaten the safe construction of deepwater facilities for oil and gas development. However, the risks and economic losses could be predicted and prevented if the formation mechanism and distribution pattern of submarine landslides are carefully studied. Based on the high-resolution 3D seismic data acquired by CNOOC in the Baiyun Sag, we identified the submarine slide and other deepwater geohazards, such as gas hydrate, gas chimneys, mud diapirs, shallow gas and shallow water, and found that they are closely related. In fact, the decomposition of gas hydrate, release of overpresured fluid and high rate of sedimentation are the main causes of submarine slide in the Baiyun Sag. These controlling factors are resulted from neotectonics in the northern South China Sea. Therefore, neotectonics is the main reason of submarine slides.
-
Key words:
- submarine slide /
- deepwater geohazard /
- neotectonics /
- Baiyun Sag
-

-
[1] Henry S P, Paul W. Worldwide deepwater exploration and production: Past, present, and future[J]. The Leading Edge, 2002, 21(4): 371-376. doi: 10.1190/1.1471600
[2] 张功成, 米立军, 吴时国, 等.深水区——南海北部大陆边缘盆地油气勘探新领域[J].石油学报, 2007, 28(2):15-21. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/6414335
ZHANG Gongcheng, MI Lijun, WU Shiguo, et al. Deepwater area——the new prospecting targets of northern continental margin of South China Sea[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2007, 28(2): 15-21. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/6414335
[3] 吴时国, 王大伟, 姚根顺, 等.南海深水沉积与储层的地球物理识别[M].科学出版社, 2014.
WU Shiguo, WANG Dawei, YAO Genshun, et al. Geophysical identification of deepwater deposition and reservoir in South China Sea[M]. Science Press, 2014.
[4] Dugan B, Flemings P B. Overpressure and fluid flow in the New Jersey continental slope: implications for slope failure and cold seeps[J]. Science, 2000, 289(5477): 288-291. doi: 10.1126/science.289.5477.288
[5] McConnell D R, Zhang Z, Boswell R. Review of progress in evaluating gas hydrate drilling hazards[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2012, 34(1): 209-223. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2012.02.010
[6] Sun Q, Wu S, Cartwright J, et al. Shallow gas and focused fluid flow systems in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 2012, 315: 1-14. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=6ab647482948e848eb254ec0452515a4
[7] 叶银灿.中国海洋灾害地质学[M].北京: 海洋出版社, 2015.
YE Yincan. Marine Disaster Geology in China[M]. Ocean Press, 2012.
[8] 吴时国, 谢杨冰, 秦芹, 等.深水油气浅层钻井的"三浅"地质灾害[J].探矿工程(岩土钻掘工程), 2014(9): 38-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7428.2014.09.008
WU Shiguo, XIE Yangbing, QIN Qin, et al. Shallow Drilling Geological Disasters of Oil nd Gas in Deepwater[J]. Exploration Engineering:Rock & Soil Drilling and Tunneling, 2014(9): 38-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7428.2014.09.008
[9] Dong D, Zhang G, Zhong K, et al. Tectonic evolution and dynamics of deepwater area of Pearl River Mouth basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2009, 20(1): 147-159. doi: 10.1007/s12583-009-0016-1
[10] Sun Q, Wu S, Cartwright J, et al. Neogene igneous intrusions in the northern South China Sea: Evidence from high-resolution three dimensional seismic data[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2014, 54: 83-95. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.02.014
[11] Ma B, Wu S, Sun Q, et al. The late Cenozoic deep-water channel system in the Baiyun Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin: Development and tectonic effects[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2015, 122: 226-239. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2015.06.015
[12] Pang X, Chen C, Peng D, et al. Sequence stratigraphy of deep-water fan system of Pearl River, South China Sea[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2007, 14: 220-229. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5791(07)60010-4
[13] Zhou D, Sun Z, Liao J, et al. Filling history and post-breakup acceleration of sedimentation in Baiyun Sag, deepwater northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2009, 20(1): 160-171. doi: 10.1007/s12583-009-0015-2
[14] Lüdmann T, Wong H K. Neotectonic regime on the passive continental margin of the northern South China Sea[J]. Tectonophysics, 1999, 311(1): 113-138. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=163340c2aff985b48ce69e4b3803398d
[15] Gong C, Wang Y, Zhu W, et al. Upper Miocene to Quaternary unidirectionally migrating deep-water channels in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2013, 97(2): 285-308. doi: 10.1306/07121211159
[16] 庞雄, 陈长民, 彭大钧.南海珠江深水扇系统及油气[M].科学出版社, 2007.
PANG Xiong, CHEN Changmin, PENG Dajun. Deepwater Fan System and Oil Gas of Pearl River, South China Sea[M]. Science Press, 2007.
[17] Chen D, Wang X, Völker D, et al. Three dimensional seismic studies of deep-water hazard-related features on the northern slope of South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology A, 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.08.012.
[18] 孙运宝.南海北部陆坡深水区地质灾害机理与钻前预测[D].中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所), 2011.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-80068-1011093909.htm SUN Yunbao. The mechanism and prediction of deepwater geohazard in the northern of South China Sea[D]. Chinese Academy of Sciences(Institute of Oceanology), 2011.
[19] 王磊, 吴时国, 李清平, 等.珠江口盆地陆架坡折带海底滑坡及其影响因素[J].海洋科学, 2016, 40(5):131-141. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hykx201605017
WANG Lei, WU Shiguo, LI Qingping, et al. Submarine slides and influencing factors in the continental shelf break area of the Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Marine Sciences, 2016, 40(5): 131-141. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hykx201605017
[20] 吴时国, 秦志亮, 王大伟, 等.南海北部陆坡块体搬运沉积体系的地震响应与成因机制[J].地球物理学报, 2011, 54(12):3184-3195. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.12.018
WU Shiguo, QIN Zhiliang, WANG Dawei, et al. Seismic characteristics and triggering mechanism analysis of mass transport deposits in the northern continental slope of the South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2011, 54(12): 3184-3195. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.12.018
[21] 刘锋, 吴时国, 孙运宝.南海北部陆坡水合物分解引起海底不稳定性的定量分析[J].地球物理学报, 2010, 53(4):946-953. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2010.04.019
LIU Feng, WU Shiguo, SUN Yunbao. A quantitative analysis for submarine slope instability of the northern South China Sea due to gas hydrate dissociation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2010, 53(4):946-953. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2010.04.019
[22] 吴时国, 孙运宝, 王秀娟, 等.南海北部深水盆地浅水流的地球物理特性及识别[J].地球物理学报, 2010, 53(7):1681-1690. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2010.07.019
WU Shiguo, SUN Yunbao, WANG Xiujuan, et al. Geophysical signature and detection of shallow water flow in the deepwater basin of the northern South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2010, 53(7): 1681-1690. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2010.07.019
[23] Wu S, Gao J, Zhao S, et al. Post-rift uplift and focused fluid flow in the passive margin of northern South China Sea[J]. Tectonophysics, 2014, 615: 27-39. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/9218936
-



 下载:
下载: