Application of X-ray computed tomography to porosity analysis of the along-shelf clinoform deposit in the East China Sea
-
摘要:
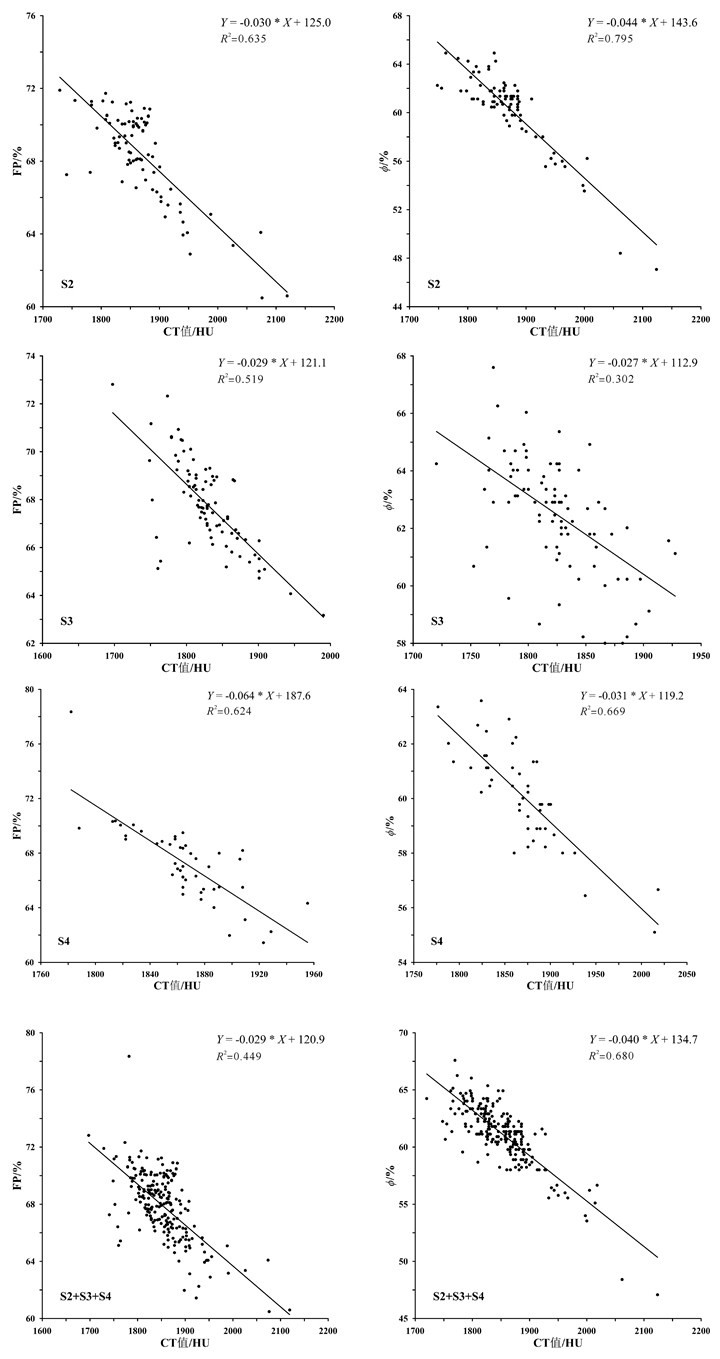
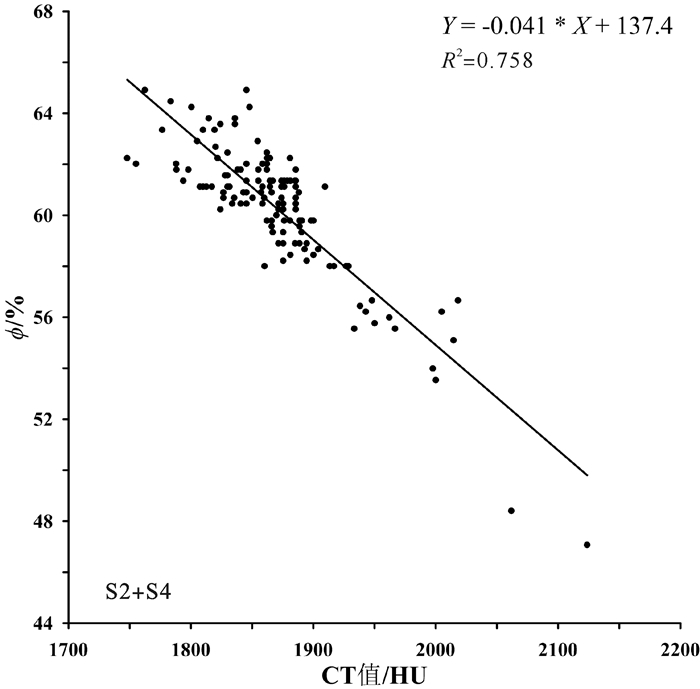
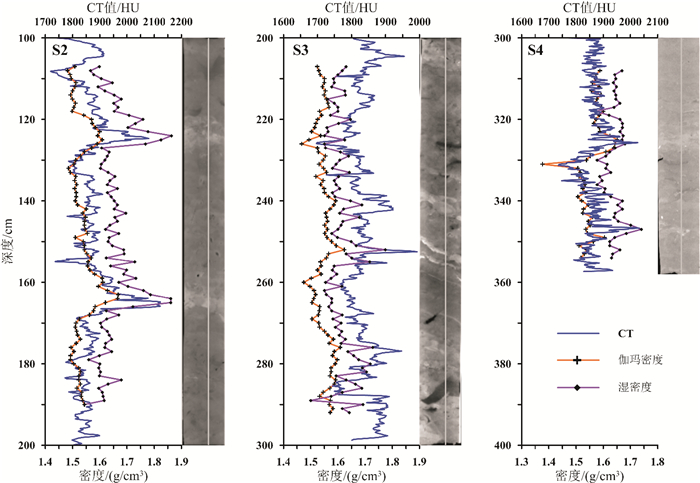
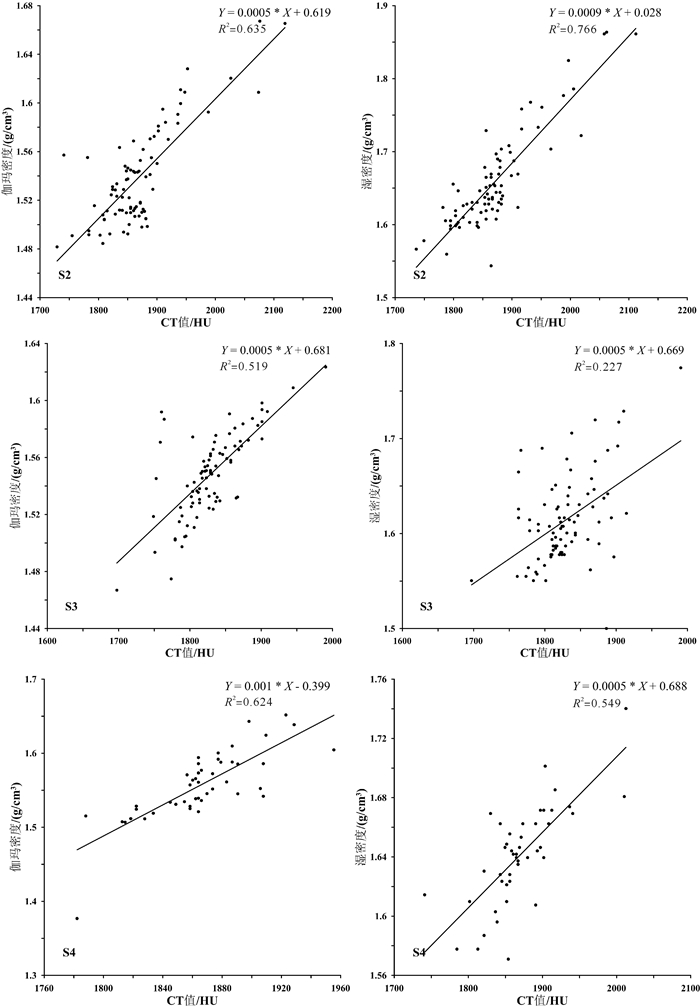
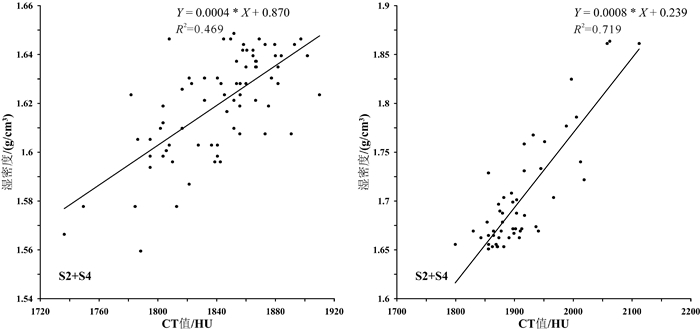
孔隙度作为海底沉积物的一项重要物理参数,其传统获取方法存在着一定的不足。本研究利用医学CT扫描技术对采自东海内陆架泥质沉积区的一沉积物岩心SS4进行了测试,提取了垂直方向上沉积物的CT值。通过CT值与部分孔隙度及环刀实验获得的孔隙度之间相关性的比较,建立了东海泥质区沉积物CT值与孔隙度之间的经验公式。同时,研究还发现CT扫描对于沉积物垂向上结构不均一的岩心,CT值与孔隙度之间的相关性较差,这并非方法和精度的问题,而是由于取样点结构不一致造成的,因此根据相关性好的层段拟合的经验公式具有更高的可靠性。作为一种快速、无损的测试和观测手段,CT扫描在沉积物岩心研究中将提供更多有用的帮助。
Abstract:Porosity is an important physical parameter of seabed sediments. However, the traditional method for porosity acquisition remains insufficient. In this study, we measured the porosity of the sediment core SS4 taken from the along-shelf clinoform deposit in the East China Sea with a medical CT-Scanner, and extracted the CT numbers one by one in vertical direction. By comparison of the CT numbers with the porosities obtained from the tube method, an empirical formula is derived between CT number and porosity for the clinoform deposit in the East China Sea. It is found that the CT number is poorly correlated with the porosity acquired from the tube method, when the vertical composition of the core was inhomogeneous, owing to the texture inconsistency of samples. However, the empirical formula acquired from the core sections where occur high correlations between CT numbers and porosities should have higher reliability. Thus we recommend the CT scanning method as a fast and nondestructive method for measurement and observation of sediment porosities.
-
Key words:
- porosity /
- X-ray computed tomography(CT) /
- mud area /
- East China Sea
-

-
图 1 沉积物岩心采样站位分布(阴影部分代表泥质沉积区,修改自文献[17])
Figure 1.
-
[1] Bennett R H, Lambert D N. Rapid and reliable technique for determining unit weight and porosity of deep-sea sediments[J]. Marine Geology, 1971, 11(3): 201-207. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(71)90007-7
[2] Brown K M, Ransom B. Porosity corrections for smectite-rich sediments: impact on studies of compaction, fluid generation, and tectonic history[J]. Geology, 1996, 24(9): 843-846. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1996)024<0843:PCFSRS>2.3.CO;2
[3] Xu S Y, White R E. A new velocity model for clay-sand mixtures[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 1995, 43(1): 91-118. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2478.1995.tb00126.x
[4] Marion D, Nur A, Yin H, et al. Compressional velocity and porosity in sand-clay mixtures[J]. Geophysics, 1992, 57(4): 554-563. doi: 10.1190/1.1443269
[5] Erickson S N, Jarrard R D. Velocity-porosity relationships for water-saturated siliciclastic sediments[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1998, 103(B12): 30385-30406. doi: 10.1029/98JB02128
[6] Tudge J, Tobin H J. Velocity-porosity relationships in smectite-rich sediments: Shikoku Basin, Japan[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2013, 14(12): 5194-5207. doi: 10.1002/2013GC004974
[7] Cnudde V, Masschaele B, Dierick M, et al. Recent progress in X-ray CT as a geosciences tool[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2006, 21(5): 826-832. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2006.02.010
[8] Ketcham R A, Carlson W D. Acquisition, optimization and interpretation of X-ray computed tomographic imagery: applications to the geosciences[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2001, 27(4): 381-400. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0098300400001163
[9] Cnudde V, Boone M N. High-resolution X-ray computed tomography in geosciences: A review of the current technology and applications[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2013, 123: 1-17. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.04.003
[10] Baker D R, Mancini L, Polacci M, et al. An introduction to the application of X-ray microtomography to the three-dimensional study of igneous rocks[J]. Lithos, 2012, 148: 262-276. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.06.008
[11] Mayo S, Josh M, Nesterets Y, et al. Quantitative micro-porosity characterization using synchrotron micro-CT and xenon K-edge subtraction in sandstones, carbonates, shales and coal[J]. Fuel, 2015, 154: 167-173. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2015.03.046
[12] Shigeki J, Jiro N, Satoshi T, et al. Structural investigation of methane hydrate sediments by microfocus X-ray computed tomography technique under high-pressure conditions[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2006, 45(7L): L714-L716. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=455c6cbdc64a50f8846c3d4741ce6e9c
[13] 李承峰, 胡高伟, 刘昌岭, 等. X射线计算机断层扫描在天然气水合物研究中的应用[J].热带海洋学报, 2012, 31(5): 93-99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2012.05.014
LI Chengfeng, HU Gaowei, LIU Changling, et al. Application of X-ray computed tomography in natural gas hydrate research[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2012, 31(5): 93-99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2012.05.014
[14] Milliman J D, Meade R H. World-wide delivery of river sediment to the oceans[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1983, 91(1): 1-21. https://www.jstor.org/stable/30060512
[15] 肖尚斌, 李安春.东海内陆架泥区沉积物的环境敏感粒度组分[J].沉积学报, 2005, 23(1): 122-129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2005.01.016
XIAO Shangbin, LI Anchun. A study on environmentally sensitive grain-size population in inner shelf of the East China Sea[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2005, 23(1): 122-129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2005.01.016
[16] Liu J P, Xu K H, Li A C, et al. Flux and fate of Yangtze River sediment delivered to the East China Sea[J]. Geomorphology, 2007, 85(3-4): 208-224. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.03.023
[17] Liu J P, Li A C, Xu K H, et al. Sedimentary features of the Yangtze River-derived along-shelf clinoform deposit in the East China Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2006, 26(17-18): 2141-2156. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2006.07.013
[18] Xu K H, Li A C, Liu J P, et al. Provenance, structure, and formation of the mud wedge along inner continental shelf of the East China Sea: a synthesis of the Yangtze dispersal system[J]. Marine Geology, 2012, 291-294: 176-191. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2011.06.003
[19] Best A I, Gunn D E. Calibration of marine sediment core loggers for quantitative acoustic impedance studies[J]. Marine Geology, 1999, 160(1-2): 137-146. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(99)00017-1
[20] Boespflug X, Long B F N, Occhietti S. CAT-scan in marine stratigraphy: a quantitative approach[J]. Marine Geology, 1995, 122(4): 281-301. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(94)00129-9
[21] St-Onge G, Mulder T, Francus P, et al. Chapter two continuous physical properties of cored marine sediments[J]. Developments in Marine Geology, 2007, 1: 63-98. doi: 10.1016/S1572-5480(07)01007-X
[22] Fortin D, Francus P, Gebhardt A C, et al. Destructive and non-destructive density determination: method comparison and evaluation from the Laguna Potrok Aike sedimentary record[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2013, 71: 147-153. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2012.08.024
[23] Orsi T H, Edwards C M, Anderson A L. X-ray computed tomography: a nondestructive method for quantitative analysis of sediment cores[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1994, 64(3): 690-693.
[24] Orsi T H, Anderson A L. Bulk density calibration for X-ray tomographic analyses of marine sediments[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 1999, 19(4): 270-274. doi: 10.1007/s003670050118
[25] Tanaka A, Nakano T, Ikehara K. X-ray computerized tomography analysis and density estimation using a sediment core from the Challenger Mound area in the Porcupine Seabight, off Western Ireland[J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 2011, 63(2): 103-110. doi: 10.5047/eps.2010.12.006
[26] Coles M E, Muegge E L, Sprunt E S. Applications of CAT scanning for oil and gas production[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 1991, 38(2): 510-515. doi: 10.1109/23.289350
[27] Lu J, Li A C, Huang P, et al. Mineral distributions in surface sediments of the western South Yellow Sea: implications for sediment provenance and transportation[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2015, 33(2): 510-524. doi: 10.1007/s00343-015-4106-x
-




 下载:
下载: