-
摘要:
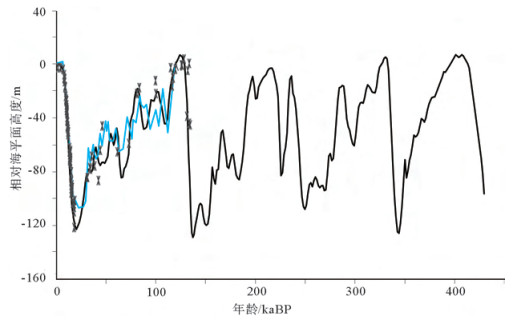
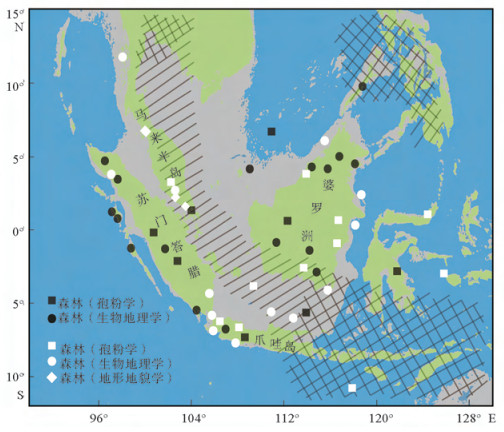
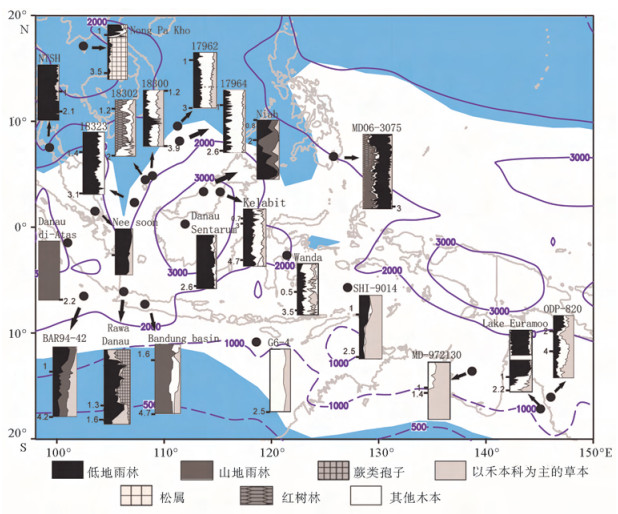
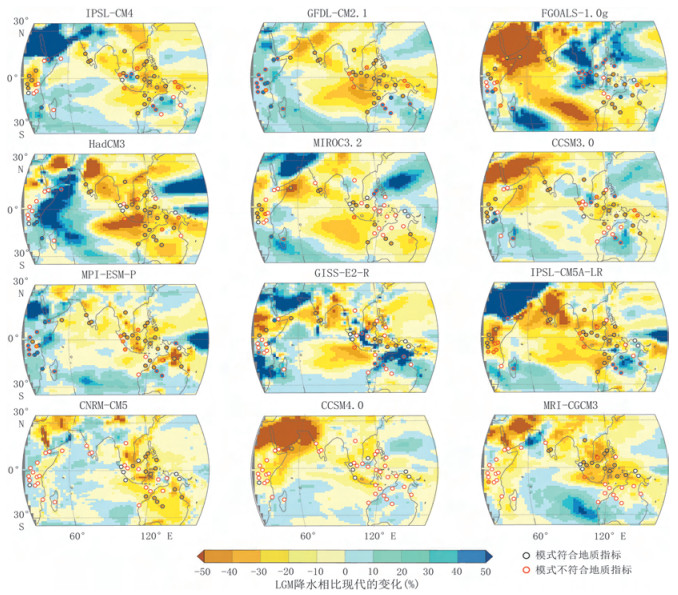
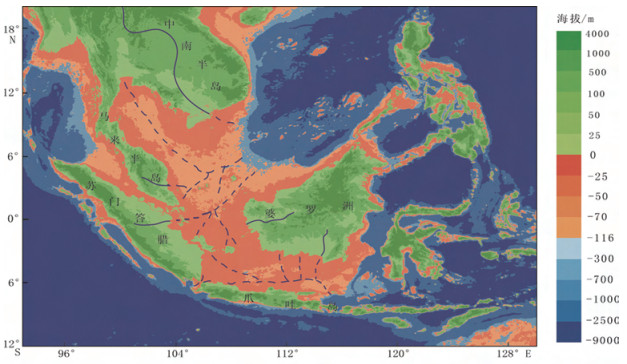
在约10万年的冰期-间冰期旋回中, 大气CO2浓度与温度存在几乎同步的周期性变化:间冰期的CO2浓度约为280×10-6, 冰期逐渐下降, 至盛冰期达到最低(约180×10-6), 冰消期又快速回升。关于冰期大气CO2的去向, 前人的许多研究表明, 冰期的海洋是个巨大的碳汇, 而陆地碳储量在冰期是下降的。从海洋和陆地碳库整体的变化来看, 似乎冰期大气CO2浓度的下降完全可以用海洋碳库的增加来解释, 甚至陆地碳库还是大气的源。但通过分析各种地质证据与数值模拟结果, 发现末次冰期南海南部暴露的巽他陆架上分布着广阔的热带森林, 这意味着, 末次冰期暴露的巽他陆架可能具有较强的储碳能力, 与冰期陆地的碳源角色相反。因此, 为更准确了解碳循环与气候变化, 未来的研究需要对陆地碳库进行有效细分, 定量描述各区域在碳循环中的角色。
Abstract:So far, the ice cores from Antarctica have provided a high-resolution record of atmospheric CO2concentration levels over the past 800000 years.A significant fact is that the atmospheric CO2concentration variation with respect to change in temperature is almost synchronous throughout these eight glacial-interglacial cycles, ranging from about 180×10-6 to 280×10-6.While the terrestrial carbon pool is the source of atmospheric CO2, the deep ocean acts as the sink of the atmospheric CO2)which could explain the reduction of atmospheric CO2concentration during the glacial period.However, lots of palynological and numerical simulated evidences reveal that tropical forest must have dominated the emerged Sunda Shelf in the South China Sea during the last glacial period (LGP), suggesting that the Sunda shelf may have played a role as an atmospheric carbon sink in the LGP.In order to better understand the carbon cycle and climate change, future research needs to subdivide the terrestrial carbon pool effectively with quantitative calculation.
-
Key words:
- terrestrial carbon pool /
- tropical forest /
- carbon cycle /
- Sunda shelf /
- Last glacial period
-

-
[1] Lüthi D, Le F M, Bereiter B, et al.High-resolution carbon dioxide concentration record 650000~800000years before present[J].Nature, 2008, 453 (7193) :379-82. doi: 10.1038/nature06949
[2] Jouzel J, Massondelmotte V, Cattani O, et al.Orbital and Millennial Antarctic Climate Variability over the Past 800000Years[J].Science, 2007, 317 (5839) :793-796. doi: 10.1126/science.1141038
[3] Zeebe R E.History of Seawater Carbonate Chemistry, Atmospheric CO2, and Ocean Acidification[J].Annual Review of Earth & Planetary Sciences, 2012, 40 (1) :141-165. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=948aea5ee81f84edf960ee574dcbba97
[4] Ciais P, Tagliabue A, Cuntz M, et al.Large inert carbon pool in the terrestrial biosphere during the Last Glacial Maximum[J].Nature Geoscience, 2011, 5 (1) :74-79. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1324
[5] Prentice K C, Fung I Y.The sensitivity of terrestrial carbon storage to climate change[J].Nature, 1990, 346 (6279) :48-51. doi: 10.1038/346048a0
[6] Adams J M, Faure H, Fauredenard L, et al.Increases in terrestrial carbon storage from the Last Glacial Maximum to the present[J].Nature, 1990, 348 (6303) :711-714. doi: 10.1038/348711a0
[7] Houghton R A.Balancing the Global Carbon Budget[J].Annual Review of Earth & Planetary Sciences, 2007, 35 (1) :313-347. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-S0277-3791(03)00135-5/
[8] Bird M I, Lloyd J, Farquhar G D.Terrestrial carbon storage at the LGM[J].Nature, 1994, 371 (6498) :566-566. doi: 10.1038/371566a0
[9] François L M, Goddéris Y, Warnant P, et al.Carbon stocks and isotopic budgets of the terrestrial biosphere at mid-Holocene and last glacial maximum times[J].Chemical Geology, 1999, 159 (1-4) :163-189. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00039-X
[10] Otto D, Rasse D, Kaplan J, et al.Biospheric carbon stocks reconstructed at the Last Glacial Maximum:comparison between general circulation models using prescribed and computed sea surface temperatures[J].Global & Planetary Change, 2002, 33 (1-2) :117-138. doi: 10.1016/S0921-8181(02)00066-8
[11] Hanebuth T, Stattegger K, Grootes P M.Rapid flooding of the sunda shelf:A late-glacial sea-level record[J].Science, 2000, 288 (5468) :1033. doi: 10.1126/science.288.5468.1033
[12] Sathiamurthy E, Voris H K.Maps of Holocene Sea level transgression and submerged lakes on the Sunda Shelf[J].2006, 2: 1-44.
[13] Page S E, Rieley J O, Banks C J.Global and regional importance of the tropical peatland carbon pool[J].Global Change Biology, 2011, 17 (2) :798-818. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2010.02279.x
[14] Schimel D S, House J I, Hibbard K A, et al.Recent patterns and mechanisms of carbon recent patterns and mechanisms of carbon exchange by terrestrial ecosystems[J].Nature, 2001, 414 (6860) :169-72. doi: 10.1038/35102500
[15] Stephens B B, Gurney K R, Tans P P, et al.Weak northern and strong tropical land carbon uptake from vertical profiles of atmospheric CO2[J].Science, 2007, 316 (5832) :1732-1735. doi: 10.1126/science.1137004
[16] Pan Y, Birdsey R A, Phillips O L, et al.The Structure, Distribution, and Biomass of the World's Forests[J].Annual Review of Ecology Evolution & Systematics, 2013, 44 (44) :593. doi: 10.1146/annurev-ecolsys-110512-135914
[17] Beer C, Reichstein M, Tomelleri E, et al.Terrestrial gross carbon dioxide uptake:global distribution and covariation with climate[J].Science, 2010, 329 (5993) :834. doi: 10.1126/science.1184984
[18] Saatchi S S, Morel A.Benchmark map of forest carbon stocks in tropical regions across three continents[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2011, 108 (24) :9899-9904. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1019576108
[19] Scharlemann J P, Tanner E V, Hiederer R, et al.Global soil carbon:understanding and managing the largest terrestrial carbon pool[J].Carbon Management, 2014, 5 (1) :81-91. doi: 10.4155/cmt.13.77
[20] Prentice I C, Harrison S P, Bartlein P J.Global vegetation and terrestrial carbon cycle changes after the last ice age[J].New Phytologist, 2011, 189 (4) :988-998. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03620.x
[21] Tjia H D.The Sunda Shelf, Southeast Asia[J].Zeitschrift Fur Geomorphologie, 1980, 24:405-427. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_pubmedcentral.nih.gov_3145692
[22] Hanebuth T J J, Voris H K, Yokoyama Y, et al.Formation and fate of sedimentary depocentres on Southeast Asia's Sunda Shelf over the past sea-level cycle and biogeographic implications[J].Earth-Science Reviews, 2011, 104 (1-3) :92-110. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2010.09.006
[23] Heaney L R.A synopsis of climatic and vegetational change in Southeast Asia[J].Climatic Change, 1991, 19 (1-2) :53-61. doi: 10.1007/BF00142213
[24] Molengraaff G A F, Weber M.On the relation between the pleistocene glacial period and the origin of the Sunda sea (Java and South China-sea), and its influence on the distribution of coralreefs and on the land-and freshwater fauna[J].Koninklijke Nederlandse Akademie Van Wetenschappen Proceedings, 1921, 23:395-439. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=d88aeb7497011bcb95e4709bf89eb762&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[25] Waelbroeck C, Labeyrie L, Michel E, et al.Sea-level and deep water temperature changes derived from benthic foraminifera isotopic records[J].Quaternary Science Reviews, 2002, 21 (1) :295-305. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ029910042/
[26] 汪品先.巽他陆架——淹没的亚马逊河盆地?[J].地球科学进展, 2017, 32 (11) :1119-1125. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2017.11.1119
WANG Pinxian.The Sunda Shelf—A Submerged Amazon Basin?[J].Advances in Earth Science, 2017, 32 (11) :1119-1125. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2017.11.1119
[27] Deckker P D, Tapper N J, Kaars S V D.The status of the Indo-Pacific Warm Pool and adjacent land at the Last Glacial Maximum[J].Global & Planetary Change, 2003, 35 (1) :25-35. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-S0921-8181(02)00089-9/
[28] 杨昕, 王明星.末次冰期极盛时陆地生态系统碳库的模式研究[J].自然科学进展:国家重点实验室通讯, 2001, 11 (10) :1074-1080. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zrkxjz200110011
YANG Xin, WANG Mingxing.The modelling of terrestrial carbon pool during the last glacial maximum[J].Progress in natural science:state key laboratory of communications, 2001, 11 (10) :1074-1080. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zrkxjz200110011
[29] Anderegg W R, Ballantyne A P, Smith W K, et al.Tropical nighttime warming as a dominant driver of variability in the terrestrial carbon sink[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112 (51) :15591. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=99963bc7edc0a54536a3e06a933d8751
[30] Bird M I, Taylor D, Hunt C.Palaeoenvironments of insular Southeast Asia during the Last Glacial Period:a savanna corridor in Sundaland?[J].Quaternary Science Reviews, 2005, 24 (20) :2228-2242. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2005.04.004
[31] Slik J W, Aiba S, Bastian M, et al.Soils on exposed Sunda shelf shaped biogeographic patterns in the equatorial forests of Southeast Asia[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2011, 108 (30) :12343-12350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1103353108
[32] Situmorang M, Kuntoro A, Ilahude D, et al.Distribution and characteristics of Quaternary peat deposits in the eastern Jawa Sea (abstract).Bulletin of the Marine Geological Institute of Indonesia, 1993, 8: 9-20.
[33] Meijaard E.Mammals of South-East Asian Islands and Their Late Pleistocene Environments[J].Journal of Biogeography, 2003, 30 (8) :1245-1257. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2699.2003.00890.x
[34] Wurster C M, Bird M I, Bull I D, et al.Forest contraction in north equatorial Southeast Asia during the Last Glacial Period[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107 (35) :15508-15511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1005507107
[35] Penny D.A 40000year palynological record from north-east Thailand; implications for biogeography and palaeo-environmental reconstruction[J].Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2001, 171 (3-4) :97-128. doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(01)00242-5
[36] White J C, Penny D, Kealhofer L, et al.Vegetation changes from the late Pleistocene through the Holocene from three areas of archaeological significance in Thailand[J].Quaternary International, 2004, 113 (1) :111-132. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2003.09.001
[37] Stuijts Ⅰ, Newsome J C, Flenley J R.Evidence for late quaternary vegetational change in the Sumatran and Javan highlands[J].Review of Palaeobotany & Palynology, 1988, 55 (1) :207-216. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-0034-6667(88)90086-3/
[38] Taylor D, Yen O H, Sanderson P G, et al.Late Quaternary peat formation and vegetation dynamics in a lowland tropical swamp; Nee Soon, Singapore[J].Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology, 2001, 171 (3) :269-287. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-S0031-0182(01)00249-8/
[39] Sun X, Li X, Luo Y, et al.The vegetation and climate at the last glaciation on the emerged continental shelf of the South China Sea[J].Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2000, 160 (3-4) :301-316. doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(00)00078-X
[40] Wang X M, Sun X J, Wang P X, et al.Vegetation on the Sunda Shelf, South China Sea, during the Last Glacial Maximum[J].Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2009, 278 (1-4) :88-97. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2009.04.008
[41] Sun X, Li X, Luo Y.Vegetation and climate on the sunda shelf of the South China Sea during the last Glactiation--Pollen results from station 17962[J].Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2002, 44 (6) :746-752. doi: 10.1093/emboj/21.11.2833
[42] Hunt C O, Gilbertson D D, Rushworth G.A 50, 000-year record of late Pleistocene tropical vegetation and human impact in lowland Borneo[J].Quaternary Science Reviews, 2012, 37 (2) :61-80. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2012.01.014
[43] Jones S E, Hunt C O, Reimer P J.A Late Pleistocene record of climate and environmental change from the northern and southern Kelabit Highlands of Sarawak, Malaysian Borneo[J].Journal of Quaternary Science, 2014, 29 (2) :105-122. doi: 10.1002/jqs.2682
[44] 边叶萍, 翦知湣, 翁成郁, 等.末次盛冰期以来菲律宾南部气候变化的孢粉记录[J].科学通报, 2011, 56, 1554-1561. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201119008
BIAN Yeping, JIAN Zhimin, WENG Chengyu, et al.A palynological and palaeoclimatological record from the southern Philippines since the Last Glacial Maximum[J].Chinese Sci Bull, 2011, 56, 1554-1561. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201119008
[45] Maloney BK., McCORMAC.A 30, 000-year pollen and radiocarbon record from highland Sumatra as evidence for climatic change[J].Radiocarbon, 1995, 37, 181-190. doi: 10.1017/S0033822200030629
[46] Anshari G, Kershaw A P, Kaars S V D, et al.Environmental change and peatland forest dynamics in the Lake Sentarum area, West Kalimantan, Indonesia[J].Journal of Quaternary Science, 2004, 19 (7) :637-655. doi: 10.1002/jqs.879
[47] Hope G.Environmental change in the Late Pleistocene and later Holocene at Wanda Site, Soroako, South Sulawesi, Indonesia[J].Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2001, 171 (3) :129-145.
[48] Kaars S V D, Bassinot F, Deckker P D, et al.Changes in monsoon and ocean circulation and the vegetation cover of southwest Sumatra through the last 83, 000years:the record from marine core BAR94-42[J].Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2010, 296 (1) :52-78.
[49] Kaars S V D, Dan P, Tibby J, et al.Late Quaternary palaeoecology, palynology and palaeolimnology of a tropical lowland swamp:Rawa Danau, West-Java, Indonesia[J].Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2001, 171 (3-4) :185-212. doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(01)00245-0
[50] Kaars S V D, Dam R.Vegetation and climate change in West-Java, Indonesia during the last 135, 000years[J].Quaternary International, 1997, 37 (2) :67-71.
[51] Wang X, Kaars S V D, Kershaw P.A record of fire, vegetation and climate through the last three glacial cycles from Lombok Ridge core G6-4, eastern Indian Ocean, Indonesia[J].Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1999, 147 (3-4) :241-256. doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(98)00169-2
[52] Kaars S V D, Kershaw P, Wang X, et al.A Late Quaternary palaeoecological record from the Banda Sea, Indonesia:pattern of vegetation, climate and biomass burning in Indonesia and Northern Australia[J].Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2000, 155 (1) :135, 147-143, 153. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-S0031-0182(99)00098-X/
[53] Chivas A R, GarcíA A, Kaars S V D, et al.Sea-level and environmental changes since the last interglacial in the Gulf of Carpentaria, Australia:an overview[J].Quaternary International, 2001, s83-85 (1) :19-46.
[54] Haberle S G.A 23000-yr Pollen Record from Lake Euramoo, Wet Tropics of NE Queensland, Australia[J].Quaternary Research, 2005, 64 (3) :343-356. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2005.08.013
[55] Moss P T, Kershaw A P.A late Quaternary marine palynological record (oxygen isotope stages 1to 7) for the humid tropics of northeastern Australia based on ODP Site 820[J].Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology, 2007, 251 (1) :4-22. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2007.02.014
[56] 戴璐, Yeok F S.末次冰期时暴露的巽他大陆架可能被热带稀树草原覆盖吗?[J].地球科学进展, 2017, 32 (11) :1147-1156. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2017.11.1147
DAI Lu, Foong Swee Yeok.Was there savanna corridor on the exposed Sunda Shelf during the last glacial period?[J].Advances in Earth Science, 2017, 32 (11) :1147-1156. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2017.11.1147
[57] Cannon C H, Morley R J, Bush A B.The current refugial rainforests of Sundaland are unrepresentative of their biogeographic past and highly vulnerable to disturbance[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2009, 106 (27) :11188-11193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0809865106
[58] Raes N, Cannon CH, Hijmans RJ, et al.Historical distribution of Sundaland's Dipterocarp rainforests at Quaternary glacial maxima[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2014, 111 (47) :16790. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1403053111
[59] Members C P.The surface of the ice-age Earth[J].Science, 1976, 191 (4232) :1131-1137. doi: 10.1126/science.191.4232.1131
[60] 宋长青, 孙湘君.中国第四纪孢粉学研究进展[J].地球科学进展, 1999, 14 (4) :401-406. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.1999.04.015
SONG Changqing, SUN Xiangjun.Advances in studies of quaternary palynology in china[J].Advances in Earth Science, 1999, 14 (4) :401-406. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.1999.04.015
[61] Dinezio P N, Tierney J E.The effect of sea level on glacial Indo-Pacific climate[J].Nature Geoscience, 2013, 6 (6) :485-491. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1823
[62] Sarmiento G, Monasterio M.A Critical Consideration of the Environmental Conditions Associated with the Occurrence of Savanna Ecosystems in Tropical America[J].1975.
[63] Lehmann C E R, Archibald S A, Hoffmann W A, et al.Deciphering the distribution of the savanna biome[J].New Phytologist, 2011, 191 (1) :197-209. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03689.x
[64] Bush M B.Climate science:The resilience of Amazonian forests[J].Nature, 2017, 541 (7636) :167-168. doi: 10.1038/541167a
[65] Wang X, Edwards R L, Auler A S, et al.Hydroclimate changes across the Amazon lowlands over the past 45000years[J].Nature, 2017, 541 (7636) :204. doi: 10.1038/nature20787
[66] Breukelen M R V, Vonhof H B, Hellstrom J C, et al.Fossil dripwater in stalagmites reveals Holocene temperature and rainfall variation in Amazonia[J].Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 2014, 275 (1) :54-60. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e7d1fd4a7936eb447ab79516925c0f23
[67] Cheng H, Sinha A, Cruz F W, et al.Climate change patterns in Amazonia and biodiversity[J].Nature Communications, 2013, 4 (1) :1411. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2415
[68] 赵艳, 刘耀亮, 郭正堂, 等.全新世气候渐变导致中亚地区植被突变[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2017, 60:1317-1327. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201708005
ZHAO Yan, LIU Yaoliang, GUO Zhengtang, et al.Abrupt vegetation shifts caused by gradual climate changes in central Asia during the Holocene[J].Science China (Earth Sciences), 2017, 60:1317-1327. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201708005
-

| 引用本文: | 李金澜, 田军. 末次冰期南海南部暴露的巽他陆架是大气碳汇?[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(4): 155-163. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2018.04.013 |
| Citation: | LI Jinlan, TIAN Jun. The Sunda Shelf—A carbon sink during the last glacial period?[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(4): 155-163. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2018.04.013 |


 下载:
下载: