Heinrich-5Event revealed by high-resolution grain-size and magnetic susceptibility records and its significance of climate evolution in the last glacial at Hongtong, Shanxi, China
-
摘要:
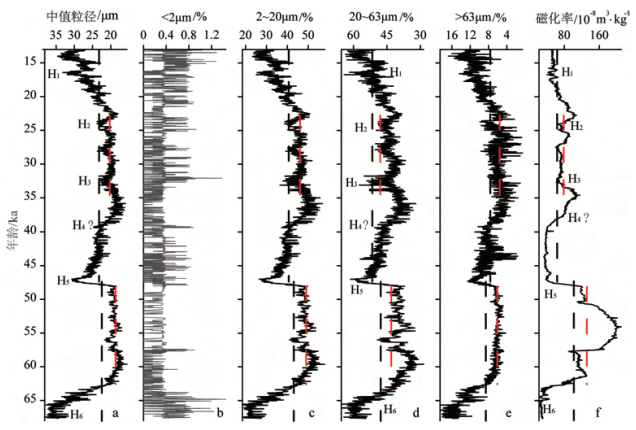
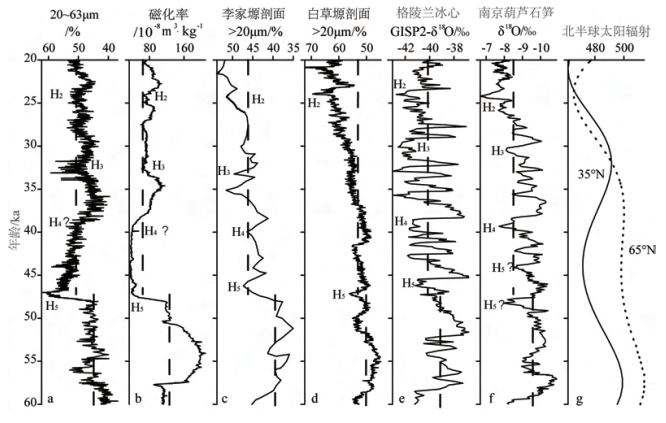
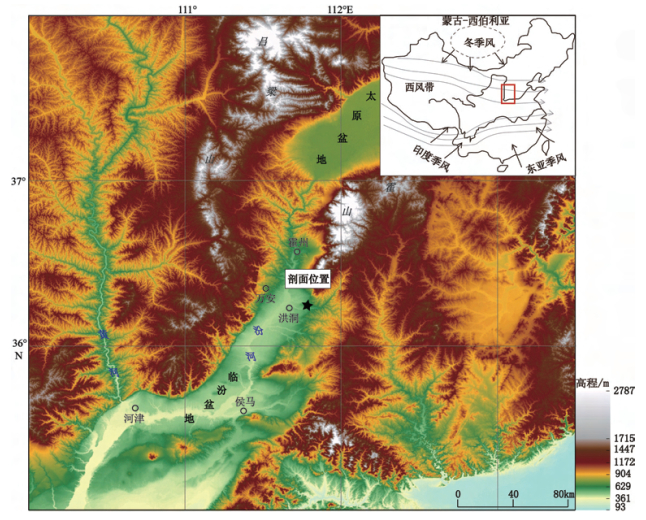
源于北大西洋的末次冰期千年尺度波动的Heinrich事件在东亚地区不同气候记录中得到较为广泛的识别。但是, 哪一次事件对东亚乃至北半球影响最显著还不清楚。山西临汾盆地作为中国东部的山间盆地保存了较为广泛的黄土沉积。本次研究对山西洪洞县洞峪沟剖面末次冰期厚10.5m的黄土进行光释光测年, 0.5cm间距的粒度测量、磁化率测量。结果显示, 该剖面跨越67.7~13.0ka, 粒度和磁化率记录所反映的气候特征可以以H5事件(47.3ka)为分界点分为前后两个时期。其中, 早期(67.7~47.3ka)粗粉砂(20~63μm)和砂含量(> 63μm)整体较低而磁化率较高, 反映该时期亚洲冬季风较弱而夏季风较强; 晚期(47.3~13.0ka)粗粉砂含量和砂含量整体较高而磁化率较低, 反映该时期亚洲冬季风明显增强而夏季风明显减弱。山西洪洞以H5事件(约47.3ka)为分界点的末次冰期气候演化模式在东亚、东地中海乃至北美均可以对比, 可能是北极地区冰量在这一时期得到显著发展, 导致东亚乃至北半球气候向寒冷方向发生显著变化。这一认识对理解东亚MIS3气候演化趋势具有一定意义。
Abstract:The millennial-scale fluctuations of Heinrich events during the last glacial stage initiated from the North Atlantic have been widely discovered in East Asia.However, which event has the most remarkable impact on East Asia or even the Northern Hemisphere remains unclear.There are widely distributed loess deposits, the best climate proxies, in the Linfen Basin, Shanxi province.In this study, we collected OSL dating samples and powder samples at a 0.5 cm intervals to analyze grain size and magnetic susceptibility for a 10.5 m thick loess sequence at Dongyugou of Hongtong, Shanxi.Dating results show that the section is in an age range from67.7~13.0 ka.Grain size and susceptibility data suggest an obvious H5 climate event of the last glacial at the depth of 47.3 ka.Therefore, this cores could be divided into two parts.In the early time (67.7~47.3 ka), the content of coarse silt (20~63μm) and sand fraction (> 63μm) was overall low, but magnetic susceptibility was relatively high.On the contrary, in the later time (47.3~13.0 ka), the content of coarse silt and sand fractions increases, while magnetic susceptibility is low.This implies that Asian winter monsoon was weak and summer monsoon was strong in the early time, while in the later period, Asian winter monsoon substantially enhanced and summer monsoon significantly weakened.The evolution models of last glacial climate demarcated by H5 (~ 47.0 ka) are comparable in East Asia, Eastern Mediterranean and even North America.It is supposed that ice accumulation in the Arctic in this period led to climate changed colder in East Asia and the Northern Hemisphere.This cognition plays an important role in deep understanding of the evolution trend of MIS3 climate in East Asia.
-
Key words:
- grain-size /
- magnetic susceptibility /
- OSL /
- loess /
- H5 event /
- Linfen Basin
-

-
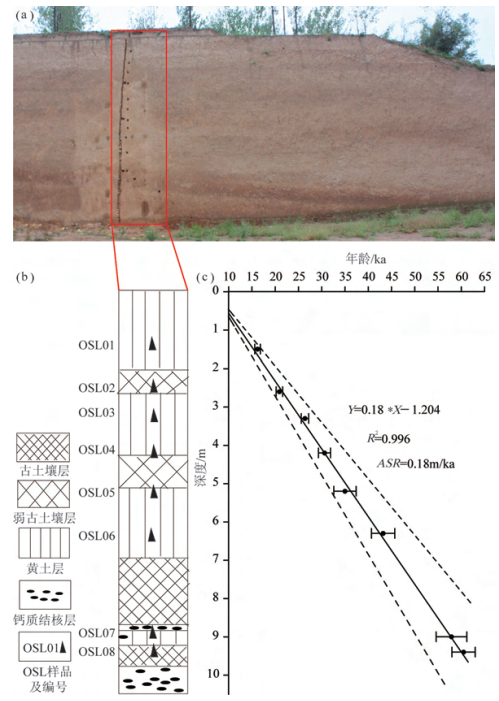
表 1 山西洪洞县洞峪沟剖面光释光年龄
Table 1. OSL ages at Dongyugou section in Hongtong, Shanxi
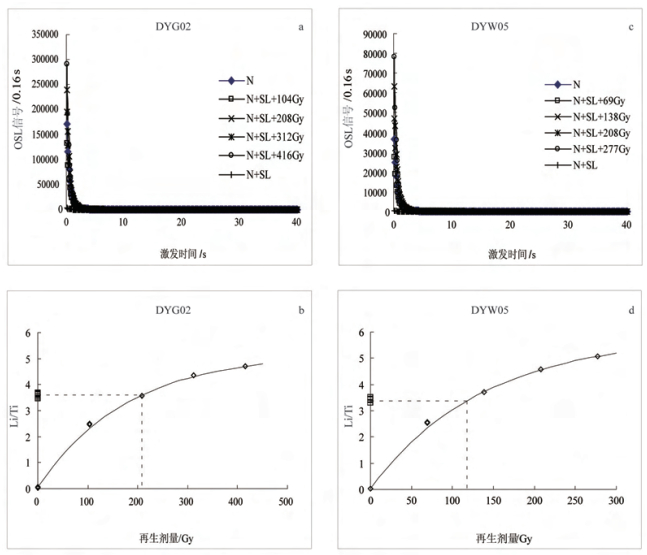
样品编号 埋深/m α计数率/Counts • ks-1 K2O/% 实测含水量/% 环境剂量率/Gy • ka-1 等效剂量/Gy 年龄/ka OSL01 1.5 93±0.3 2.06 1.6 3.4±0.2 54.3±1. 16.2±0.6 OSL02 2.6 10.4±0.3 2.41 1.2 3.8±0.2 78.6±18 20.9±0.7 OSL03 3.3 10.6±0.3 2.18 1.1 3.5±0.2 92.0±2.1 26.4±0.8 OSL04 4.2 10.8±0.3 2.44 1.8 3.8±0.2 117.4±4.2 30.6±1.3 OSL05 5.2 11.4±0.4 2.32 1.5 3.8±0.2 131.4± 8. 35.0±2.4 OSL06 6.3 10.8±0.4 2.36 1.0 3.6±0.2 157.5±8.6 43.2±2.5 OSL07 9 11.1±0.3 2.62 1.6 3.9±0.2 223.2±12.3 57.9±3.3 OSL08 9.4 9.5±0.3 2.37 2.2 3.4±0.2 208.4±7.8 60.5±2.5 -
[1] Johnsen S J, Clausen H B, Dansgaard W, et al.Irregular glacial interstadials recorded in a new Greenland ice core[J].Nature, 1992, 359(6393) :311-313. doi: 10.1038/359311a0
[2] Dansgaard W, Johnsen S J, Clausen H B, et al.Evidence for general instability of past climate from a 250-kyr ice-core record[J].Nature, 1993, 364(6434) :218-220. doi: 10.1038/364218a0
[3] Taylor K C, Lamorey G W, Doyle G A, et al.The"flickering switch"of late Pleistocene climate change[J].Nature, 1993, 361(6411) :432-436. doi: 10.1038/361432a0
[4] Bond G, Heinrich H, Broecker W, et al.Evidence for massive discharges of icebergs into the North Atlantic ocean during the last glacial period[J].Nature, 1992, 360(6401) :245-249. doi: 10.1038/360245a0
[5] Broecker W, Bond G, Klas M, et al.Origin of the northern Atlantic's Heinrich events[J].Climate Dynamics, 1992, 6(3-4) :265-273. doi: 10.1007/BF00193540
[6] Heinrich H.Origin and consequences of cyclic ice rafting in the northeast Atlantic Ocean during the past 130000years[J].Quaternary Research, 1988, 29(2) :142-152. doi: 10.1016/0033-5894(88)90057-9
[7] Wang Y J, Cheng H, Edwards R L, et al.A high-resolution absolute-dated late Pleistocene monsoon record from Hulu Cave, China[J].Science, 2001, 294(5550) :2345-2348. doi: 10.1126/science.1064618
[8] Lu H Y, Wu N Q, Liu K B, et al.Phytoliths as quantitative indicators for the reconstruction of past environmental conditions in China Ⅱ:palaeoenvironmental reconstruction in the Loess Plateau[J].Quaternary Science Reviews, 2007, 26(5-6) :759-772. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2006.10.006
[9] Guo Z, Liu T, Guiot J, et al.High frequency pulses of East Asian monsoon climate in the last two glaciations:link with the North Atlantic[J].Climate Dynamics, 1996, 12(10) :701-709. doi: 10.1007/s003820050137
[10] Porter S C, An Z S.Correlation between climate events in the North Atlantic and China during the last glaciation[J].Nature, 1995, 375(6529) :305-308. doi: 10.1038/375305a0
[11] Lu H Y, Li L, Huang X P, et al.East Asia winter monsoon oscillation and its correlation with the North Atlantic Heinrich events during the last glaciation[J].Progress in Natural Science, 1996, 6(6) :711-717. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=be86d4ce96dbcc4b7875db1d04662d39&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[12] Ding Z L, Liu D S.Forcing mechanisms for East-Asia monsoonal variations during the Late Pleistocene[J].Chinese Science Bulletin, 1998, 43(18) :1497-1510. doi: 10.1007/BF02883437
[13] Gwiazda R H, Hemming, S R, Broecker W S.Tracking the sources of icebergs with lead isotopes:the provenance of icerafted debris in Heinrich layer 2[J].Paleoceanography, 1996, 11(1) :77-93. doi: 10.1029/95PA03135
[14] McManus J F, Anderson R F, Broecker W S, et al.Radiometrically determined sedimentary fluxes in the sub-polar North Atlantic during the last 140, 000years[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1998, 155(1-2) :29-43. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(97)00201-X
[15] Hemming S R, Broecker W S, Sharp W D, et al.Provenance of the Heinrich layers in core Ⅴ28-82, northeastern Atlantic:40 Ar-39 Ar ages of ice-rafted hornblende, Pb isotopes in feldspar grains, and Nd-Sr-Pb isotopes in the fine sediment fraction[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1998, 164(1-2) :317-333. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(98)00224-6
[16] Gwiazda R H, Hemming S R, Broecker W S.Provenance of icebergs during Heinrich event 3and the contrast to their sources during other Heinrich episodes[J].Paleoceanography, 1996, 11(4) :371-378. doi: 10.1029/96PA01022
[17] Hemming S R.Heinrich events:Massive late Pleistocene detritus layers of the North Atlantic and their global climate imprint[J].Review of Geophysics, 2004, 42(1) :RG1005, doi:10.1029/2003RG000128.
[18] Igarashi Y, Murayama M, Igarashi T, et al.History of Larixforest in Hokkaido and Sakhalin, northeast Asia since the last glacial[J].Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 2002, 41(4) :524-533. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-GSWX200204006.htm
[19] Takemura K, Hayashida A, Okamura M, et al.Stratigraphy of multiple piston-core sediments for the last 30000years from Lake Biwa, Japan[J].Journal of Paleolimnology, 2000, 23(2) :185-199. doi: 10.1023/A:1008079418715
[20] Hayashida A, Ali M, Kuniko Y, et al.Environmental magnetic record and paleosecular variation data for the last 40kyrs from the Lake Biwa sediments, Central Japan[J].Earth, Planets and Space, 2007, 59(7) :807-814. doi: 10.1186/BF03352743
[21] Jia N, Wang Y H, Sun L G.Desiccation cracks in Zhoushan Archipelago, East China Sea, developed during Heinrich event 3[J].Quaternary Research, 2012, 77(2) :258-263. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2011.12.004
[22] Liew P M, Huang S Y, Kuo C M.Pollen stratigraphy, vegetation and environment of the last glacial and Holocene—a record from Toushe Basin, central Taiwan[J].Quaternary International, 2006, 147(1) :16-33. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2005.09.003
[23] Zheng H B, Huang X T, Ji J L, et al.Ultra-high rates of loess sedimentation at Zhengzhou since Stage 7:implication for the Yellow River erosion of the Sanmen Gorge[J].Geomorphology, 2007, 85(3-4) :131-142. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.03.014
[24] 胡小猛, 王杜涛, 陈美君, 等.山西临汾盆地末次冰期时段湖相沉积中的H、D/O事件记录[J].第四纪研究, 2014, 34(2) :354-363. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2014.02.09
HU Xiaomeng, WANG Dutao, CHEN Meijun, et al.The study on the records of H and D/O paleoclimatic events during the last glacial period from the lacustrine sediment in Linfen basin, Shanxi graben[J].Quaternary Sciences, 2014, 34(2) :354-363. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2014.02.09
[25] 邓起东, 苏宗正, 王挺梅, 等.临汾盆地地震构造基本特征和潜在震源区的划分[M]//马宗晋.山西临汾地震研究与系统减灾.北京:地震出版社, 1993:67-95.
DENG Qidong, SU Zongzheng, WANG Tingmei, et al.The basic characteristic of the seismogenic structure and the zonation of the potential seismic zone in the Linfen basin[M]//MA Zongjin, ed.Earthquake Research and Systematical Disaster Reduction in Linfen, Shanxi.Beijing:Seismological Press, 1993:67-95.
[26] Hu X M, Li Y L, Yang J C, Quaternary paleolake development in the Fen River basin, North China[J].Geomorphology, 2005, 65(1-2) :1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2004.06.008
[27] 徐岳仁.山西霍山山前断裂带晚第四纪活动特征研究[D].中国地震局地质研究所博士学位论文, 2013.
http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GJZT201406008.htm XU Yueren.A study on the late quaternary faulting of the Huoshan piedmont faultzone in the central Shanxi faulted basin belt[D].Doctor Dissertation of Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration, 2013.
[28] 王克鲁, 盛学斌, 严富华, 等.山西临汾盆地黄土及其形成古环境[J].地震地质, 1996, 18(4) :339-348. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199600061850
WANG Kelu, SHENG Xuebin, YAN Fuhua, et al.The loess and the paleoenvironment for its formation in the Linfen basin of Shanxi Province[J].Seismology and Geology, 1996, 18(4) :339-348. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199600061850
[29] Lu Y C, Wang X L, Wintle A G.A new OSL chronology for dust accumulation in the last 130000yr for the Chinese Loess Plateau[J].Quaternary Research, 2007, 67(1) :152-160. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2006.08.003
[30] Wang X L, Lu Y C, Zhao H.On the performances of the single-aliquot regenerative-dose (SAR) protocol for Chinese loess:fine quartz and polymineral grains[J].Radiation Measurements, 2006, 41(1) :1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2005.02.010
[31] Aitken M J.Thermoluminescence Dating[M].London:Academic Press, 1985:359.
[32] Prescott J R, Hutton J T.Cosmic ray contributions to dose rates for luminescence and ESR dating:Large depths and long-term time variations[J].Radiation Measurements, 1994, 23(2-3) :497-500. doi: 10.1016/1350-4487(94)90086-8
[33] Naafs B D A, Hefter J, Stein R.Millennial-scale ice rafting events and Hudson Strait Heinrich (-like) Events during the late Pliocene and Pleistocene:a review[J].Quaternary Science Reviews, 2013, 80:1-28. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2013.08.014
[34] An Z S, Kukla G J, Porter S C, et al.Magnetic susceptibility evidence of monsoon variation on the Loess Plateau of central China during the last 130, 000 years[J].Quaternary Research, 1991, 36(1) :29-36. doi: 10.1016/0033-5894(91)90015-W
[35] Xiao J L, Porter S C, An Z S, et al.Grain size of Quartz as an indicator of winter monsoon strength on the Loess Plateau of Central China during the last 130000yr[J].Quaternary Research, 1995, 43(1) :22-29. doi: 10.1006/qres.1995.1003
[36] Ding Z L, Sun J M, Liu D S.A sedimentological proxy indicator linking changes in loess and deserts in the Quaternary[J].Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences, 1999, 42(2) :146-152. doi: 10.1007/BF02878513
[37] Sun D H, Bloemendal J, Rea D K, et al.Bimodal grain-size distribution of Chinese loess, and its palaeoclimatic implications[J].Catena, 2004, 55(3) :325-340. doi: 10.1016/S0341-8162(03)00109-7
[38] Vandenberghe J.Grain size of fine-grained windblown sediment:A powerful proxy for process identification[J].EarthScience Reviews, 2013, 121:18-30. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=5698ebd0d007408c1e9c9d0b8a1b0cc6&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[39] Sun J M, Huang X G.Half-precessional cycles recorded in Chinese loess:response to low-latitude insolation forcing during the Last Interglaciation[J].Quaternary Science Reviews, 2006, 25(9-10) :1065-1072. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2005.08.004
[40] Jiang H C, Wang P, Thompson J, et al.Last glacial climate instability documented by coarse-grained sediments within the loess sequence, at Fanjiaping, Lanzhou, China[J].Quaternary Research, 2009, 72(1) :91-102. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2009.04.005
[41] Jiang H C, Mao X, Xu H Y, et al.Last glacial pollen record from Lanzhou (Northwestern China) and possible forcing mechanisms for the MIS 3climate change in Middle to East Asia[J].Quaternary Science Reviews, 2011, 30(5-6) :769-781. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2010.12.024
[42] Stuiver M, Grootes P M.GISP2 oxygen isotope ratios[J].Quaternary Research, 2000, 53(3) :277-284. doi: 10.1006/qres.2000.2127
[43] Laskar J, Robutel P, Joutel F, et al.A long-term numerical solution for the insolation quantities of the Earth[J].Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2004, 428(1) :261-285. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f7fe7701a325d340af795aabd1c336b6
[44] Cai Y J, An Z S, Cheng H, et al.High-resolution absolutedated Indian Monsoon record between 53and 36ka from Xiaobailong Cave, southwestern China[J].Geology, 2006, 34(8) :621-624. doi: 10.1130/G22567.1
[45] Bar-Matthews M, Ayalon A, Kaufman A, et al.The eastern Mediterranean paleoclimate as a reflection of regional events:Soreq cave, Israel[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1999, 166(1-2) :85-95. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(98)00275-1
[46] Asmerom Y, Polyak V J, Burns S J.Variable winter moisture in the southwestern United States linked to rapid glacial climate shifts[J].Nature Geoscience, 2010, 3(2) :114-117. doi: 10.1038/ngeo754
[47] Hodell D A, Anselmetti F S, Ariztegui D, et al.An 85-ka record of climate change in lowland Central America[J].Quaternary Science Reviews, 2008, 27(11-12) :1152-1165. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2008.02.008
[48] Grootes P M, Stuiver M, White J W C, et al.Comparison of oxygen isotope records from the GISP2and GRIP Greenland ice cores[J].Nature, 1993, 366(6455) :552-554. doi: 10.1038/366552a0
[49] Bard E, Rostek F, Turon J L, et al.Hydrological impact of Heinrich events in the subtropical Northeast Atlantic[J].Science, 2000, 289(5483) :1321-1324. doi: 10.1126/science.289.5483.1321
[50] Haug G H, Hughen K A, Sigman D M, et al.Southward migration of the Intertropical Convergence Zone through the Holocene[J].Science, 2001, 293(5533) :1304-1308. doi: 10.1126/science.1059725
[51] Wang X F, Auler A S, Edwards R L, et al.Wet periods in northeastern Brazil over the past 210kyr linked to distant climate anomalies[J].Nature, 2004, 432(7018) :740-743. doi: 10.1038/nature03067
[52] Oppo DW, Lehman S J.Suborbital timescale variability of North Atlantic Deep Water during the past 200000years[J].Paleoceanography, 1995, 10(5) :901-910. doi: 10.1029/95PA02089
[53] Siddall M, Rohling E J, Thompson W G, et al.Marine isotope stage 3sea level fluctuations:data synthesis and new outlook[J].Reviews of Geophysics, 2008, 46(4) :RG4003, doi:10.1029/2007RG000226.
-



 下载:
下载: