Types and genesis of the mixed deposits in the Pearl River Mouth Basin of South China Sea
-
摘要:
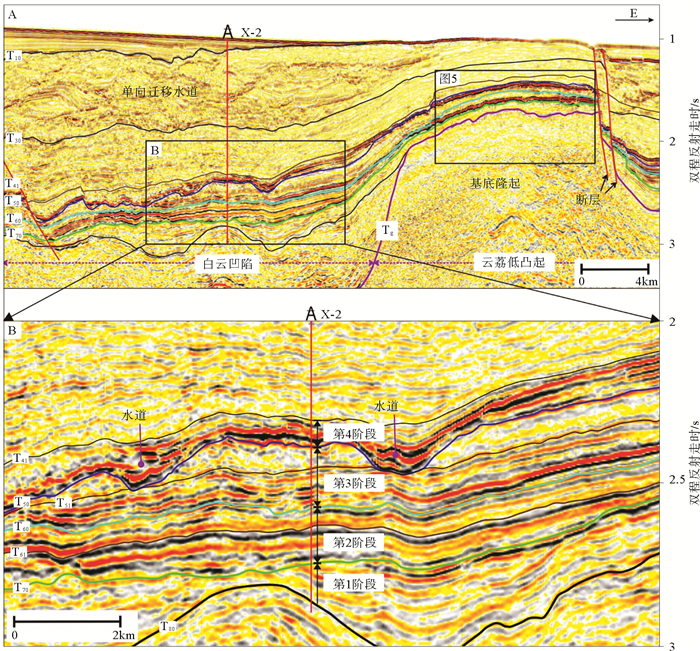
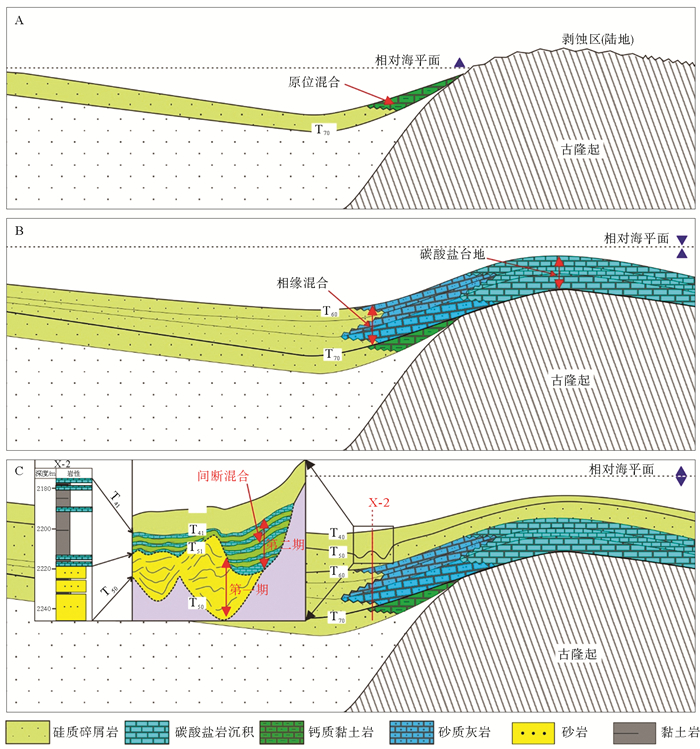
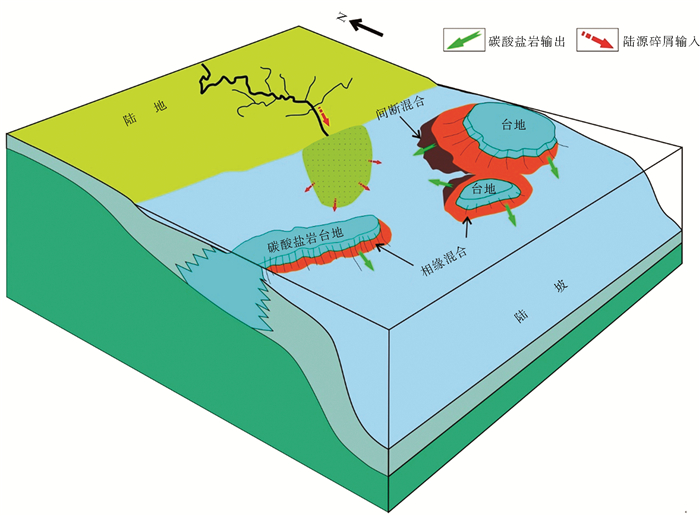
珠江口盆地是研究深水沉积过程和南海油气勘探的热点区域。利用地震、测井和钻井岩屑等资料,发现珠江口盆地深水区晚渐新世至中中新世期间,发育混合沉积体系。该混合沉积体系岩相主要表现为碳酸盐岩与硅质碎屑以不同比例的混合堆积,垂向岩相变化存在突变式、渐变式和交互式三种递变类型。根据地震反射以及岩相特征,混合沉积体系可划分为4个沉积阶段:第1阶段主要为原位混合沉积,形成渐变式或突变式混合沉积;第2阶段为相缘混合,产生渐变式混合沉积层系;第3、4阶段为间断混合,形成交互式混合沉积。在硅质碎屑沉积为主的背景下,混合沉积由于碳酸盐碎屑的加入,可能会形成潜在的油气储层,对今后深水油气勘探有一定的启示意义。
Abstract:The Pearl River Mouth Basin is a hotspot to the study of deep-water sedimentation and petroleum exploration in the South China Sea. This study is contributed to the mixed depositional system developed from late Oligocene to Middle Miocene, based on seismic, logging and cuttings data. This mixed depositional system is characterized by the mixtures of different proportions of carbonate and siliciclastic debris. In the vertical sequence, there are three types of lithofacies, i.e. mutational, tapered and alternated types. Based on seismic reflections and lithofacies characteristics, the formation of the mixed depositional system may be further divided into four stages and three mixing processes: the stage 1 of in-situ mixing; the stage 2 of mixing at facies border; and the stage 3 and 4 of punctuated mixing. It is proposed in this paper that these mixed depositional sequences developed in a siliciclastic-dominated environment, may be significant to the formation of potential petroleum reservoirs and has implications for deep-water petroleum exploration in the South China Sea
-

-
[1] Dolan J F. Eustatic and tectonic controls on deposition of hybrid siliciclastic/carbonate basinal cycles: discussion with examples[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1989, 73(10): 1233-1246.
[2] Mount T J F. Mixing of siliciclastic and carbonate sediments in shallow shelf environments[J]. Geology, 1984, 12(7): 432-435. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1984)12<432:MOSACS>2.0.CO;2
[3] Tcherepanov E N, Droxler A W, Lapointe P, et al. Siliciclastic influx and burial of the Cenozoic carbonate system in the Gulf of Papua[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2010, 27(2): 533-554. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2009.09.002
[4] Francis J M, Dunbar G B, Dickens G R, et al. Siliciclastic Sediment Across the North Queensland Margin (Australia): A Holocene Perspective on Reciprocal Versus Coeval Deposition in Tropical Mixed Siliciclastic-Carbonate Systems[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2007, 77(7): 572-586. doi: 10.2110/jsr.2007.057
[5] 董桂玉, 陈洪德, 何幼斌, 等.陆源碎屑与碳酸盐混合沉积研究中的几点思考[J].地球科学进展, 2007, 22(9): 931-938. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2007.09.007
DONG Guiyu, CHEN Hongde, HE Youbin, et al. Some problems on the study of the mixed siliciclastic-carbonate sediments [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2007, 22(9):931-938. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2007.09.007
[6] 沙庆安.混合沉积和混积岩的讨论[J].古地理学报, 2004, 3(3): 63-66. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gdlxb200103008
SHA Qingan. Discussion on mixed deposit and hunji rock [J]. Journal of Plaeogeography, 2004, 3(3): 63-66. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gdlxb200103008
[7] 郭福生, 严兆彬, 杜杨松.混合沉积, 混积岩和混积层系的讨论[J].地学前缘, 2003, 10(3): 312-314. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy200303030
GUO Fusheng, YAN Zhaobin, DU Yangsong. Discussion on mixed deposit, Hunji rock and mixed sequence [J]. Earth Science frontiers, 2003, 10(3): 312-314. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy200303030
[8] Tucker M E. Mixed clastic-carbonate cycles and sequences: Quaternary of Egypt and Carboniferous of England[J]. Geologia Croatica, 2003, 56(1): 19-37. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/27189580_Mixed_Clastic-Carbonate_Cycles_and_Sequences_Quaternary_of_Egypt_and_Carboniferous_of_England
[9] John C M, Karner G D, Browning E, et al. Timing and magnitude of Miocene eustasy derived from the mixed siliciclastic-carbonate stratigraphic record of the northeastern Australian margin[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2011, 304(3-4): 455-467. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2011.02.013
[10] Valladare M I. Siliciclastic-carbonate slope apron in an immature tensional margin (Upper Precambrian-Lower Cambrian), Central Iberian Zone, Salamanca, Spain[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1995, 94(1): 65-86. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/248232961_Siliciclastic-carbonate_slope_apron_in_an_immature_tensional_margin_Upper_Precambrian-Lower_Cambrian_Central_Iberian_Zone_Salamanca_Spain
[11] Zeller M, Verwer K, Eberli G P, et al. Depositional controls on mixed carbonate-siliciclastic cycles and sequences on gently inclined shelf profiles[J]. Sedimentology, 2015, 62:2009-2037. doi: 10.1111/sed.12215
[12] 董桂玉, 陈洪德, 李君文, 等.环渤海湾盆地寒武系混合沉积研究[J].地质学报, 2009, 83(6): 800-811. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2009.06.006
DONG Guiyu, CHEN Hongde, LI Junwen, et al. The Cambrian Mixed Sedimentation around Bohai Sea Bay Basin [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2009, 83(6): 800-811. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2009.06.006
[13] Brandano M, Roncas. Depositional processes of the mixed carbonate-siliciclastic rhodolith beds of the Miocene Saint-Florent Basin, northern Corsica[J]. Facies, 2014, 60(1): 73-90. doi: 10.1007/s10347-013-0367-z
[14] Pugaobernab U á, Webster J M, Beaman R J, et al. Morphology and controls on the evolution of a mixed carbonate-siliciclastic submarine canyon system, Great Barrier Reef margin, north-eastern Australia[J]. Marine Geology, 2011, 289(1-4): 100-116. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2011.09.013
[15] Milliman J, Droxler A. Neritic and pelagic carbonate sedimentation in the marine environment: ignorance is not bliss[J]. Geologische Rundschau, 1996, 85(3): 496-504. doi: 10.1007/BF02369004
[16] Bostock H C, Opdyke B N, Gagan M K, et al. Late Quaternary siliciclastic/carbonate sedimentation model for the Capricorn Channel, southern Great Barrier Reef province, Australia[J]. Marine Geology, 2009, 257(1-4): 107-123. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2008.11.003
[17] Wilson J L. Cyclic and reciprocal sedimentation in Virgilian strata of southern New Mexico[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1967, 78(7): 805-818. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1967)78[805:CARSIV]2.0.CO;2
[18] Pang X, Chen C, Peng D, et al. Sequence Stratigraphy of Deep-water Fan System of PeaRiver, South China Sea[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2007, 14(1): 220-229. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5791(07)60010-4
[19] Pang X, Chen C, Zhu M, et al. Baiyun movement: A significant tectonic event on Oligocene/Miocene boundary in the northern South China Sea and its regional implications[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2009, 20(1): 49-56. doi: 10.1007/s12583-009-0005-4
[20] Sattler U, Immenhauser A, Schlager W, et al. Drowning history of a Miocene carbonate platform (Zhujiang Formation, South China Sea)[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2009, 219(1-4): 318-331. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2009.06.001
[21] Sattler U, Zampetti V, Schlager W, et al. Late leaching under deep burial conditions: a case study from the Miocene Zhujiang Carbonate Reservoir, South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2004, 21(8): 977-992. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2004.05.005
[22] Turner N. The Lower Miocene Liuhua Carbonate Reservoir, Pearl River Mouth Basin, Offshore Peoples Republic of China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1996, 74(6): 1006-1007.
[23] Xie H, Zhou D, Li Y, et al. Cenozoic tectonic subsidence in deepwater sags in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Tectonophysics, 2014, 615-616(4):182-198. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/260028249_Cenozoic_Tectonic_Subsidence_in_Deepwater_Sags_in_the_Pearl_River_Mouth_Basin_Northern_South_China_Sea
[24] Zhu J, Shi H, Pang X, et al. Oil filling phases and timing analyze based on fluid inclusion in LW3-1-1 Well, Baiyun Sag[J]. Explor. Tech., 2010, 1: 52-66.
[25] Feng Z, Zheng W. Tectonic evolution of Zhujiangkou (Pearl-river-mouth) basin and origin of South China Sea[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1982, 56(3): 212-222.
[26] Guong Z, Jin Q, Qiu Z, et al. Geology, tectonics and evolution of the Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Chinese Sedimentary Basins Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1989: 181-196.
[27] Su N, He Z. The characteristics of fault activities in the Pearl River Mouth Basin and their control of hydrocarbons[C]//Proceedings of the Collection of Papers from the International Petroleum Geological Convention, Northern South China Sea Continental Shelf, China Oil Magazine (Hong Kong), F, 1987.
[28] Sun Q, Wu S, Cartwright J, et al. Neogene igneous intrusions in the northern South China Sea: Evidence from high-resolution three dimensional seismic data[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2014, 54(1):83-95. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/260911773_Neogene_igneous_intrusions_in_the_northern_South_China_Sea_Evidence_from_high-resolution_three_dimensional_seismic_data
[29] Zhou D, Sun Z, Chen H Z, et al. Mesozoic paleogeography and tectonic evolution of South China Sea and adjacent areas in the context of Tethyan and Paleo-Pacific interconnections[J]. Island Arc, 2008, 17(2): 186-207. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1738.2008.00611.x
[30] Ma B, Wu S., Mi L., et al. Mixed Carbonate-Siliciclastic Deposits in a Channel Complex in the Northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences, 2018, 29(3):707-720. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx-e201803021
[31] Sattler A, Dharmasamadhi N W. Controls on the development of valleys, canyons, and unconfined channel-levee complexes on the Pleistocene Slope of East Kalimantan, Indonesia[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2012, 29(1): 15-34. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.09.002
[32] 汪瑞良, 周小康, 曾驿, 等.珠江口盆地东部东沙隆起中新世碳酸盐岩与生物礁地震响应特征及其识别[J].石油天然气学报(江汉石油学院院报), 2011, 33(8): 63-69.
http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jhsyxyxb201108014 WANG Ruiling, ZHOU Xiaokang, ZENG Yi, et al. The seismic characteristics of Miocene carbonate platform and bigenic reefs in the earthern Dongsha Uplift of Pearl River Mouth Basin, 2011, 33(8): 63-69.
[33] 王国忠.南海北部大陆架现代礁源碳酸盐与陆源碎屑的混合沉积作用[J].古地理学报, 2004, 3(2): 47-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2001.02.007
WANG Guozhong. Mixed sedimentation of recent reefoid carbonates and terrigenous clastics in the north continental shelf of the south china sea[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2001, 3(2): 47-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2001.02.007
[34] 董桂玉, 何幼斌, 陈洪德, 等.惠民凹陷沙-中湖相碳酸盐与陆源碎屑混合沉积[J].沉积学报, 2007, 25(3): 343-350. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2007.03.003
DONG Guiyu, HE Youbin, CHEN Hongde, et al. Mixed sedimentation of carbonates of lagoonal facies and terrigenous clastics of the Middle submember of Member 1 of Shahejie Formation[J]. Acta sedimentologica Sinica 2007, 25(3): 343-350. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2007.03.003
[35] 张宁生, 任晓娟, 魏金星, 等.柴达木盆地南翼山混积岩储层岩石类型及其与油气分布的关系[J].石油学报, 2006, 27(1): 42-46. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2006.01.009
ZHANG Ningsheng, REN Xiaojuan, WEI Jinxing, et al. Rock types of mixosedimentite reservoirs and oil-gas distributionin Nanyishan of Qaidam Basin [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2006, 27(1): 42-46. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2006.01.009
[36] 冯进来, 胡凯, 曹剑, 等.陆源碎屑与碳酸盐混积岩及其油气地质意义[J].高校地质学报, 2011, 17(2): 297-307. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2011.02.015
FENG Jinlai, HU Kai, CAO Jian, et al. A review on mixed rocks of terrigenous clastics and carbonates and their petroleum-gas geological significance [J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2011, 17(2): 297-307. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2011.02.015
[37] 朱政源, 董凌峰, 于航, 等.海绿石的成因与应用[J].科技创新与应用, 2015(33):16-18. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=666275310
ZHU Zhengyuan, DONG Llingfeng, YU Hang, et al. The genesis and application of glauconite [J]. Technological Innovation and Application, 2015(33):16-18. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=666275310
-



 下载:
下载: