Characteristics of Miocene Guangle carbonate platforms in the Xisha area and its evolution
-
摘要:
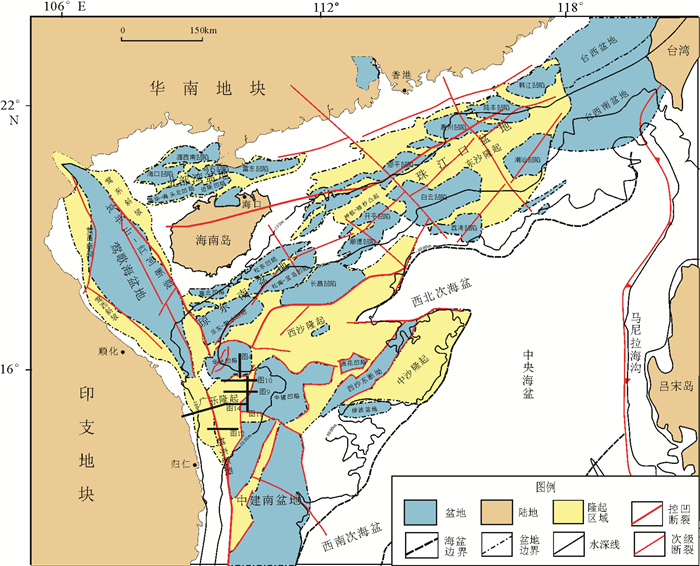
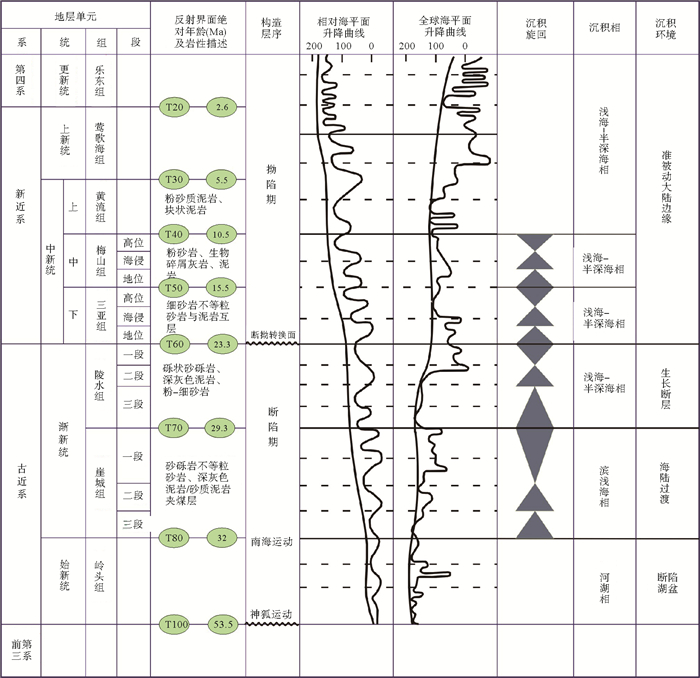
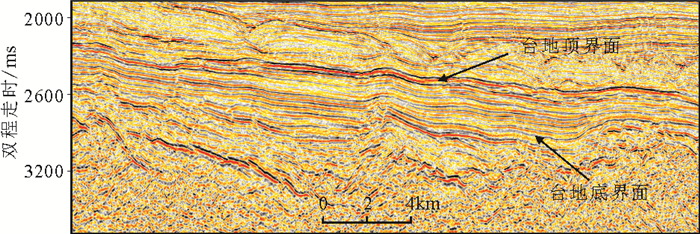
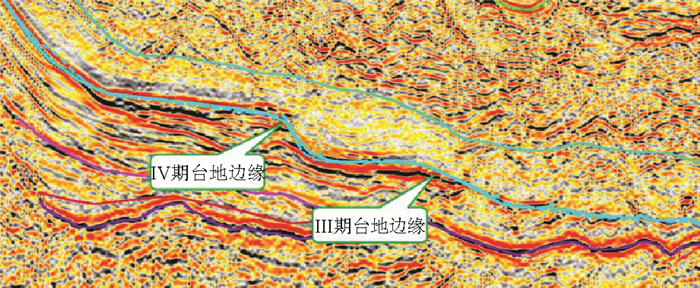
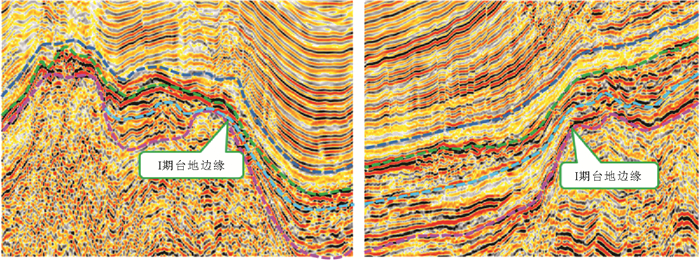
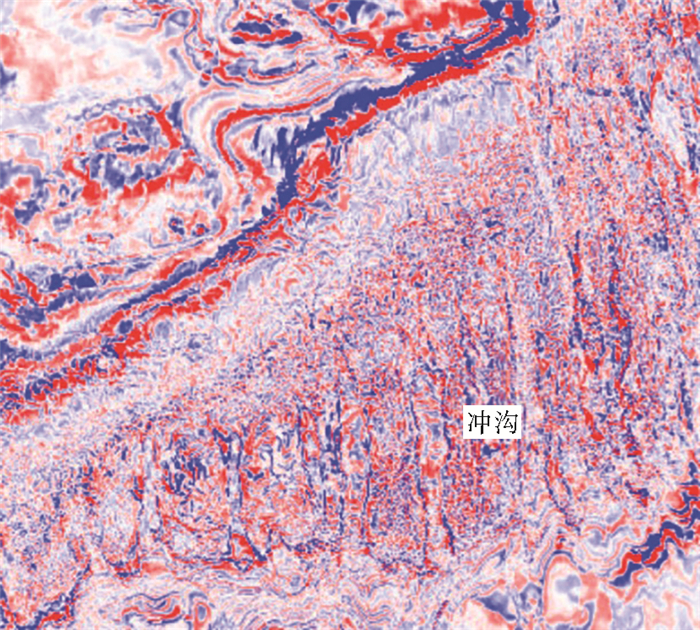
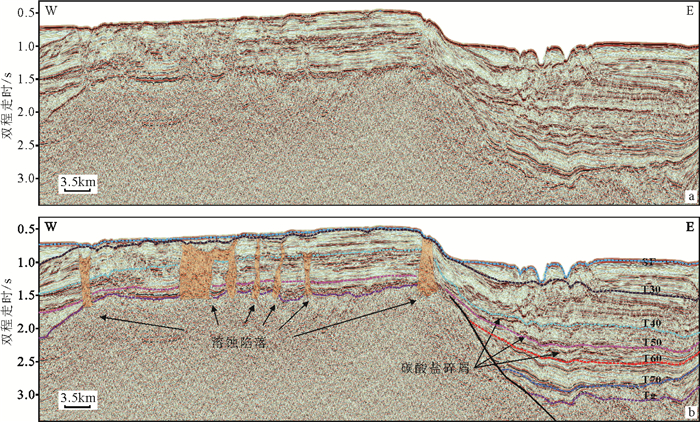
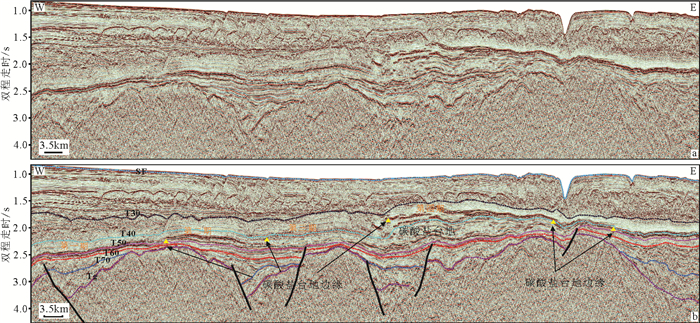
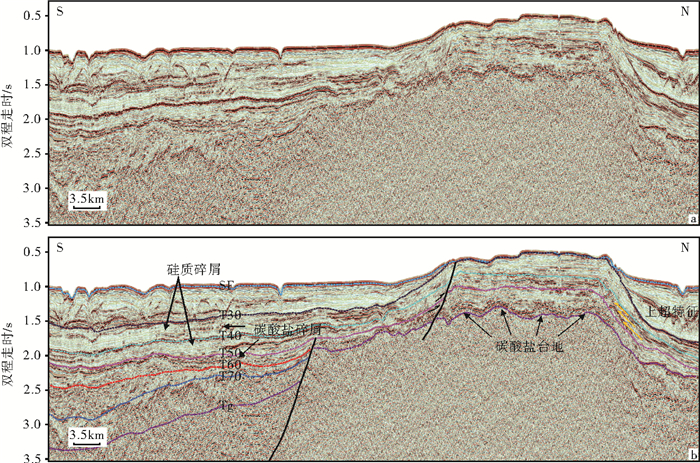
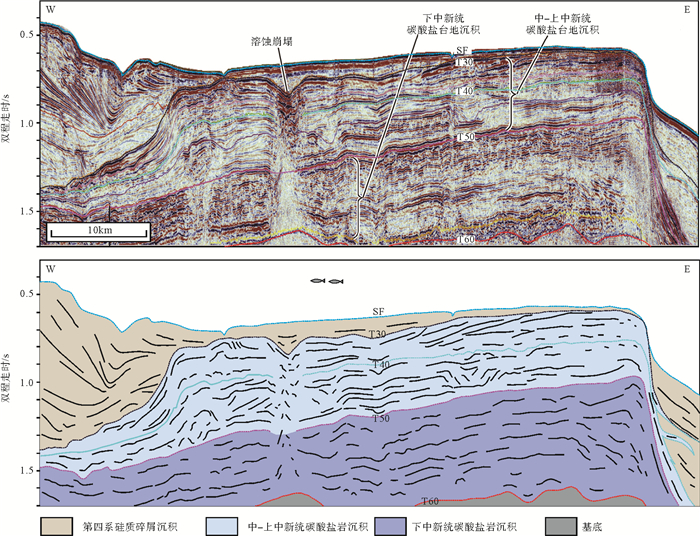
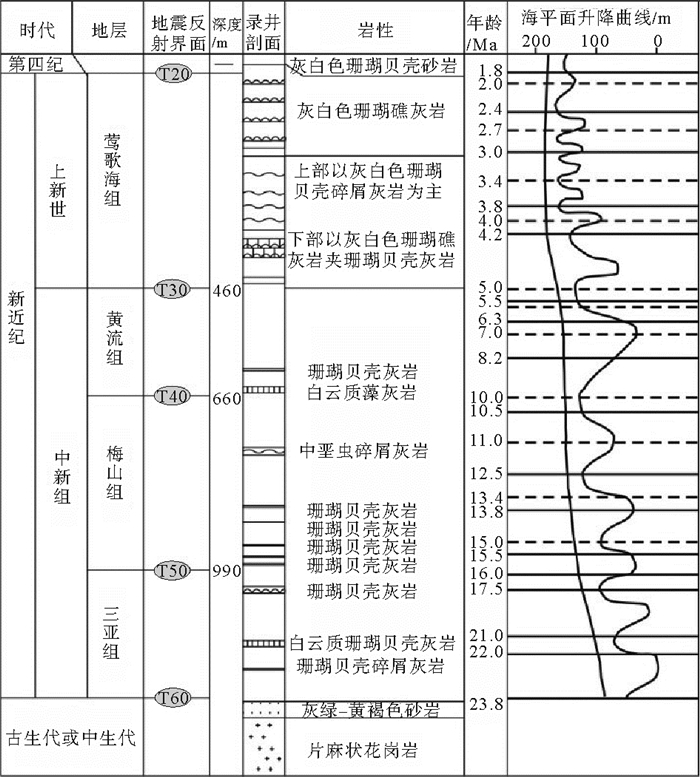
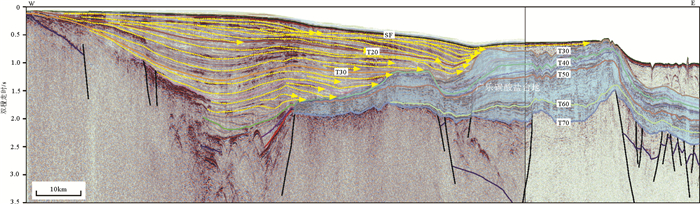
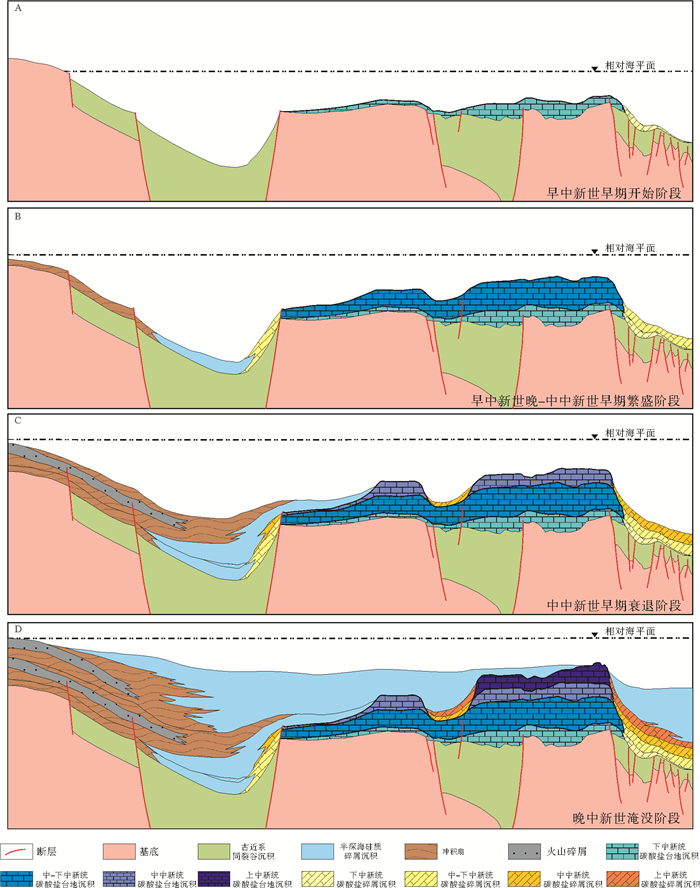
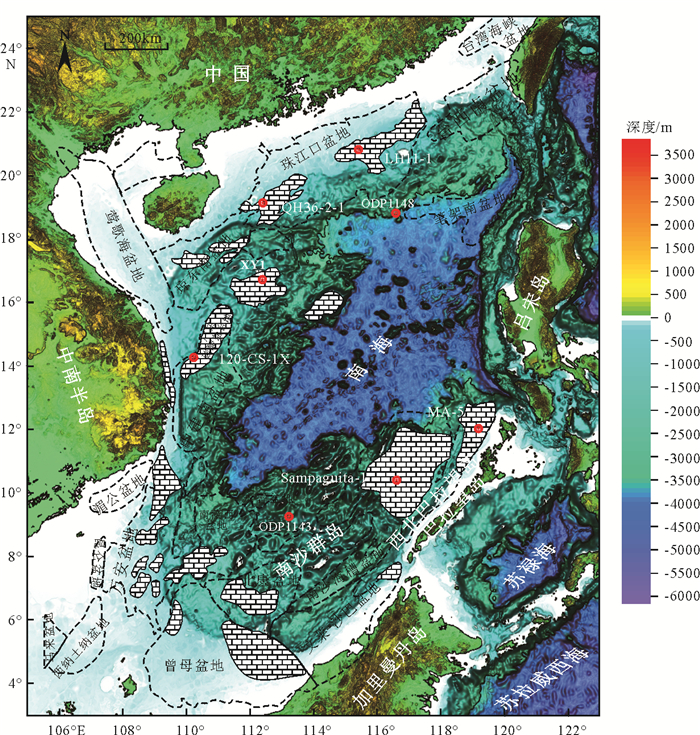
南海自海底扩张以来,在南北共轭大陆边缘发育了一系列的新生代碳酸盐台地,且碳酸盐台地分布面积广、厚度巨大。中新世时期,南海西北部陆缘发育有大量的生物礁碳酸盐台地,形成了重要的油气储层。在前期对南海西北部陆缘中新世碳酸盐台地与生物礁识别研究的基础上,结合对西沙海区地震资料与区域地质资料的分析,对广乐碳酸盐台地进行了深入研究。广乐碳酸盐台地位于西沙海区广乐隆起之上,地震反射特征具有分段性特点,自早中新世开始广泛发育,在构造作用控制下,一直持续发育至晚中新世,发育过程中表现出自西向东迁移的特点,最终由于构造沉降加速和西部中南半岛的陆缘碎屑物质注入导致水体环境改变,广乐碳酸盐台地在晚中新世被淹没。
Abstract:Cenozoic carbonate platforms of huge thickness are widely distributed on the conjugate continental margins of the South China Sea. A large number of Miocene reefs and carbonate platforms, which are potential reservoirs for hydrocarbon accumulation, have been found on the northwestern margin. The Guangle carbonate platforms are located on the Guangle Uplift of the Xisha region. Based on previous studies, the latest seismic data acquired are used by this paper for study of the seismic characteristics of the carbonate platforms. An evolutionary model is then proposed to reveal the history of the Guangle carbonate platforms. The platforms started growing in Early Miocene, built up and expanded towards east in early and middle Miocene, shrank by the end of Middle Miocene, and finally submerged under sea water due to tectonic subsidence and the environmental changes caused by the input of detrital sediments since late Miocene.
-
Key words:
- carbonate platform /
- platform evolution /
- tectonics /
- terrigenous detrital input /
- Xisha Islands
-

-
[1] 吴时国, 张新元.南海共轭陆缘新生代碳酸盐台地对海盆构造演化的响应[J].地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 2015, 40(2):234-248. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201502005
WU Shiguo, ZHANG Xinyuan. Response of Cenozoic carbonate platform on tectonic evolution in the conjugated margin of South China Sea [J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2015, 40(2):234-248. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201502005
[2] 马玉波, 吴时国, 谷明峰, 等.西沙海区碳酸盐台地地震反射特征及沉积模式[J].海洋学报(中文版), 2010, 32(4):118-128. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyxb201004012
MA Yubo, WU Shiguo, GU Mingfeng, et al. Seismic reflection characteristics and sedimentary model of carbonate platform in Xisha sea area [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2010, 32(4):118-128. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyxb201004012
[3] Fournier F, Borgomano J, Montaggioni L F. Development patterns and controlling factors of Tertiary carbonate buildups: Insights from high-resolution 3D seismic and well data in the Malampaya gas field (Offshore Palawan, Philippines)[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2005, 175(1-4):189-215. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2005.01.009
[4] 龚再升, 李思田.南海北部大陆边缘盆地分析与油气聚集[M].北京:科学出版社, 1997:510-515.
GONG Zaisheng, LI Sitian. Basin Analysis and Hydrocarbon Accumulation in the Northern Margin of the South China Sea [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1997: 510-515.
[5] 龚再升.生物礁是南海北部深水区的重要勘探领域[J].中国海上油气, 2009, 21(5):289-295. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2009.05.001
GONG Zaisheng. Reef is an important exploration area in the northern deepwater area of the South China Sea [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2009, 21(5):289-295. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2009.05.001
[6] 吴时国, 袁圣强.世界深水油气勘探进展与我国南海深水油气前景[J].天然气地球科学, 2005, 16(6):693-699. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1926.2005.06.002
WU Shiguo, YUAN Shengqiang. Progress of deepwater oil and gas exploration in the world and prospects for deepwater oil and gas in South China Sea [J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2005, 16(6):693-699. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1926.2005.06.002
[7] 吴时国, 袁圣强, 董冬冬, 等.南海北部深水区中新世生物礁发育特征[J].海洋与湖沼, 2009, 40(2): 117-121. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2009.02.002
WU Shiguo, YUAN Shengqiang, DONG Dongdong, et al. Development characteristics of Miocene reefs in the northern deepwater area of the South China Sea [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2009, 40(2): 117-121. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2009.02.002
[8] 张功成, 米立军, 吴时国, 等.深水区-南海北部大陆边缘盆地油气勘探新领域[J].石油学报, 2007, 28(2): 15-21. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/6414335
ZHANG Gongcheng, MI Lijun, WU Shiguo, et al. Deep water area- new field of oil and gas exploration in the continental margin basin of northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Petroleum, 2007, 28(2): 15-21. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/6414335
[9] 张功成.南海北部陆坡深水区构造演化及其特征[J].石油学报, 2010, 31(4):528-533. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syxb201004002
ZHANG Gongcheng. Ectonic evolution and characteristics of northern slope deep water area in the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Petroleum, 2010, 31(4):528-533. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syxb201004002
[10] Steuer S, Franke D, Meresse F, et al. Oligocene-Miocene carbonates and their role for constraining the rifting and collision history of the Dangerous Grounds, South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2014, 58:644-657. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2013.12.010
[11] Wu S, Yang Z, Wang D, et al. Architecture, development and geological control of the Xisha carbonate platforms, northwestern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 2014, 350:71-83. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2013.12.016
[12] 周小康, 汪瑞良, 曾驿, 等.珠江口盆地东沙隆起珠江组碳酸盐岩层序地层及沉积模式[J].石油天然气学报, 2011, 33(9): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2011.09.001
ZHOU Xiaokang, WANG Ruiliang, ZENG Yi, et al. Sequence stratigraphy and sedimentary model of carbonate rocks in the Zhujiang Formation, Dongsha uplift, Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. Journal of Petroleum and Natural Gas, 2011, 33(9): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2011.09.001
[13] Yu K, Zhao J. Coral Reefs[M]// In Wang P, Li Q eds. The South China Sea: Paleoceanography and Sedimentology. Springer, 2009: 229-255.
[14] 姚伯初, 万玲, 刘振湖.南海海域新生代沉积盆地构造演化的动力学特征及其油气资源[J].地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 2004, 29(5):543-549. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2004.05.007
YAO Bochu, WANG Ling, LIU Zhenghu. Dynamic characteristics of tectonic evolution and hydrocarbon resources of Cenozoic sedimentary basins in the South China Sea [J]. Geoscience Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2004, 29(5):543-549. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2004.05.007
[15] 高红芳.南海西缘断裂带走滑特征及其形成机理初步研究[J].中国地质, 2011, 3:537-543. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2011.03.003
GAO Hongfang. A preliminary study on the characteristics of the strike slip and its formation mechanism in the western margin fault of the South China Sea [J]. Geology of China, 2011, 3:537-543. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2011.03.003
[16] 马玉波, 吴时国, 张功成, 等.南海北部陆缘深水区礁相碳酸盐岩的地球物理特征[J].中国石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2009, 33(4):33-39. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sydxxb200904007
MA Yubo, WU Shiguo, ZHANG Gongcheng, et al. Geophysical characteristics of reef facies carbonate rocks in the deep continental margin of the northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Natural Science Edition), 2009, 33(4):33-39. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sydxxb200904007
[17] Fyhn M B W, Boldreel L O, Nielsen L H, et al. Carbonate platform growth and demise offshore Central Vietnam: Effects of Early Miocene transgression and subsequent onshore uplift[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 76:152-168. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.02.023
[18] Moldovanyi E P, Waal F M, Yan Z J. Regional Exposure Events and Platform Evolution of Zhuijang Formation Carbonates, Pearl River Mouth Basin: Evidence for Primary and Diagenetic Seismic Facies[M]. Unconformities and Porosity in Carbonate Strata, AAPG Memoir 63, 1995: 133-145.
[19] Bachtel S T, Kissling R D, Martono D, et al. Seismic Stratigraphic Evolution of the Miocene-Pliocene Segitiga Platform, East Natuna Sea, Indonesia: the Origin Growth and Demise of an Isolated Carbonate Platform[M]. Seismic Imaging of Carbonate Reservoirs and Systems, AAPG Memoir 81, 2004: 309-328.
[20] Heubeck C, Story K, Peng P, et al. An Integrated Reservoir Study of the Liuhua 11-1 Field Using a High-Resolution Three-Dimensional Seismic Data Set[M]. Seismic Imaging of Carbonate Reservoirs and Systems, AAPG Memoir 81, 2004: 149-168.
[21] Vahrenkamp V C, David F, Duijndam P, et al. Growth Architecture, Faulting and Karstification of a Middle Miocene Carbonate Platform, Luconia Province, Offshore Sarawak, Malaysia[M]. Seismic Imaging of Carbonate Reservoirs and Systems, AAPG Memoir 81, 2004: 329-350.
[22] Fyhn M B W, Boldreel L O, Nielsen L H. Tectonic and climatic control on growth and demise of the Phanh Rang Carbonate Platform offshore south Vietnam[J]. Basin Research, 2009, 21(2):225-251. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2117.2008.00380.x
[23] Carter A, Roques D, Bristow C. Denudation history of onshore central Vietnam: constraints on the Cenozoic evolution of the western margin of the South China Sea[J]. Tectonophysics, 2000, 322(3):265-277. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195100000913
[24] Wang D, Wu S, Qin Z, et al. Seismic characteristics of the Huaguang mass transport deposits in the Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea: Implications for regional tectonic activity[J]. Marine Geology, 2013, 346:165-182. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2013.09.003
[25] 张新元.南海西北部陆缘中新世碳酸盐台地发育演化与生物礁识别研究[D].中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所), 2016.
http://www.irgrid.ac.cn/handle/1471x/1102890?mode=full&submit_simple=Show+full+item+record ZHANG Xinyuan. The evolution and characteristics of Miocene carbonate platforms and reefs in the Xisha area, northwestern continental margin of the South China Sea [D]. Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of Oceanography), 2016.
-



 下载:
下载: