Characteristics of seismic data and its processing procedures in the areas of Reef Islands——a case from Yon-gle Atoll of Xisha Islands
-
摘要:
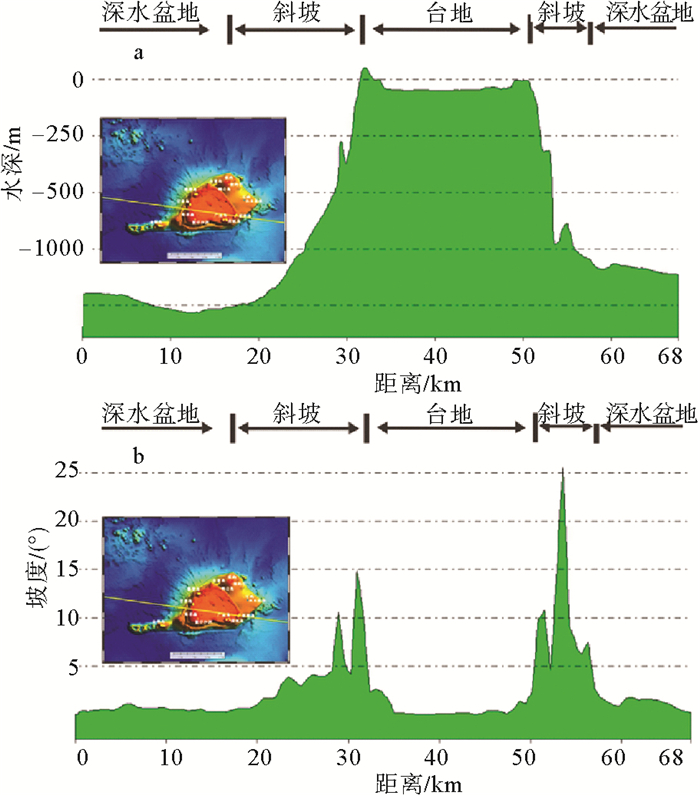
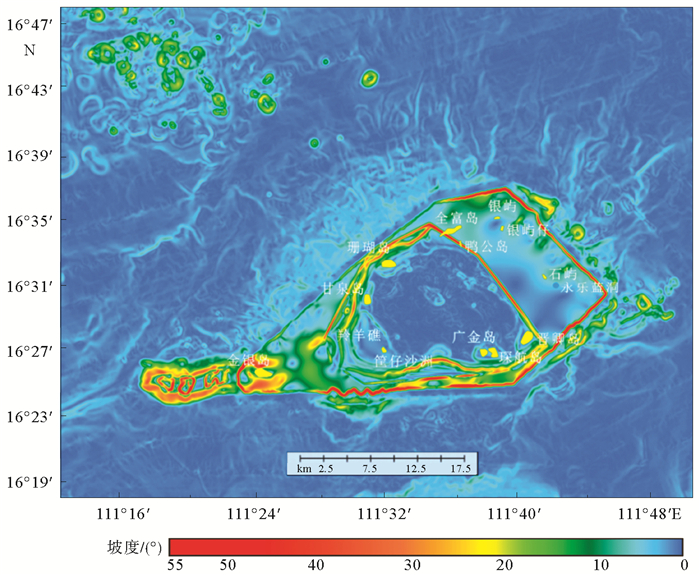
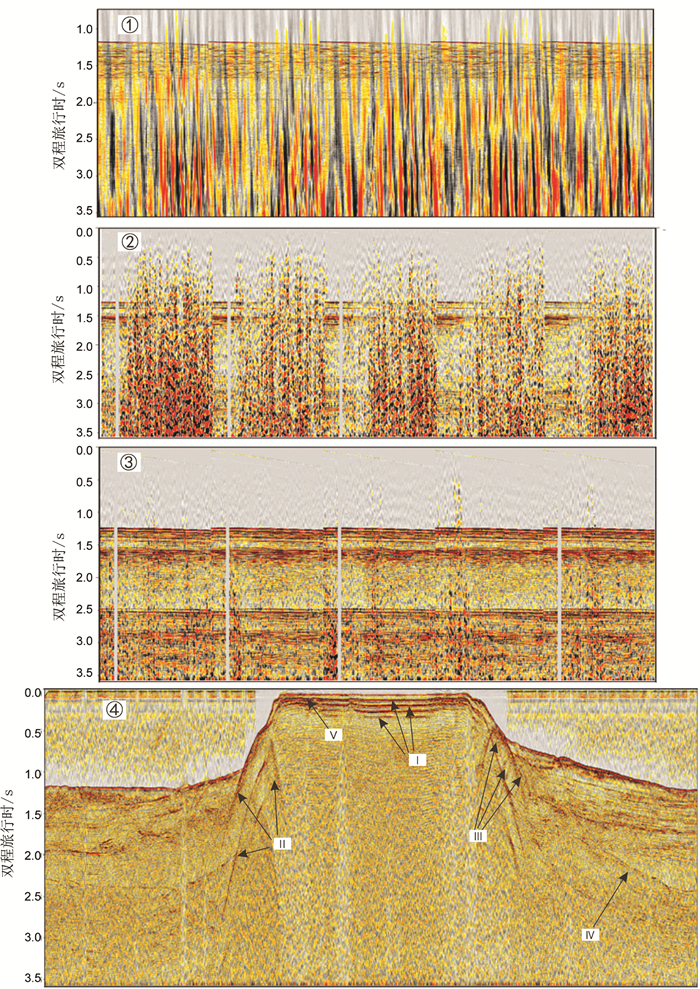
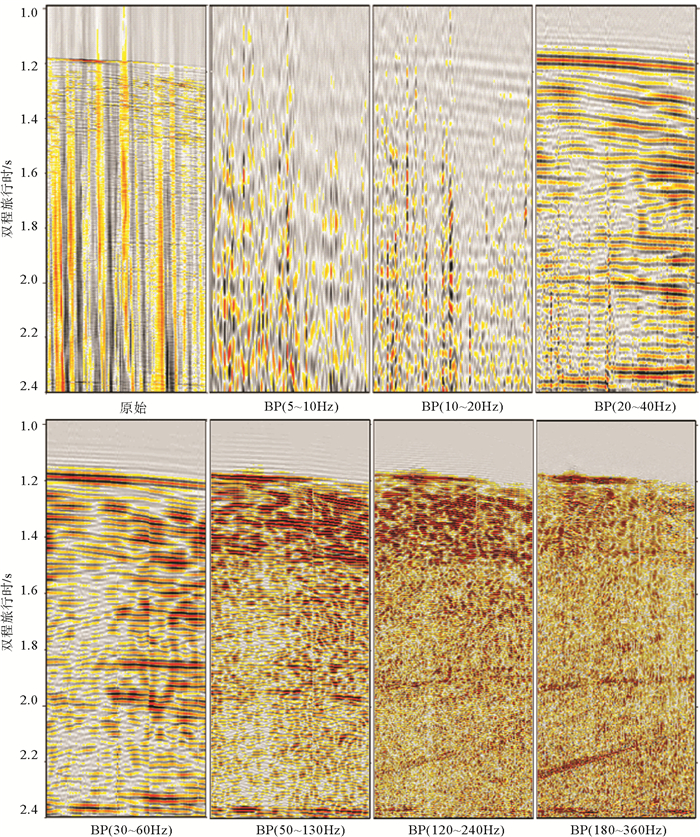
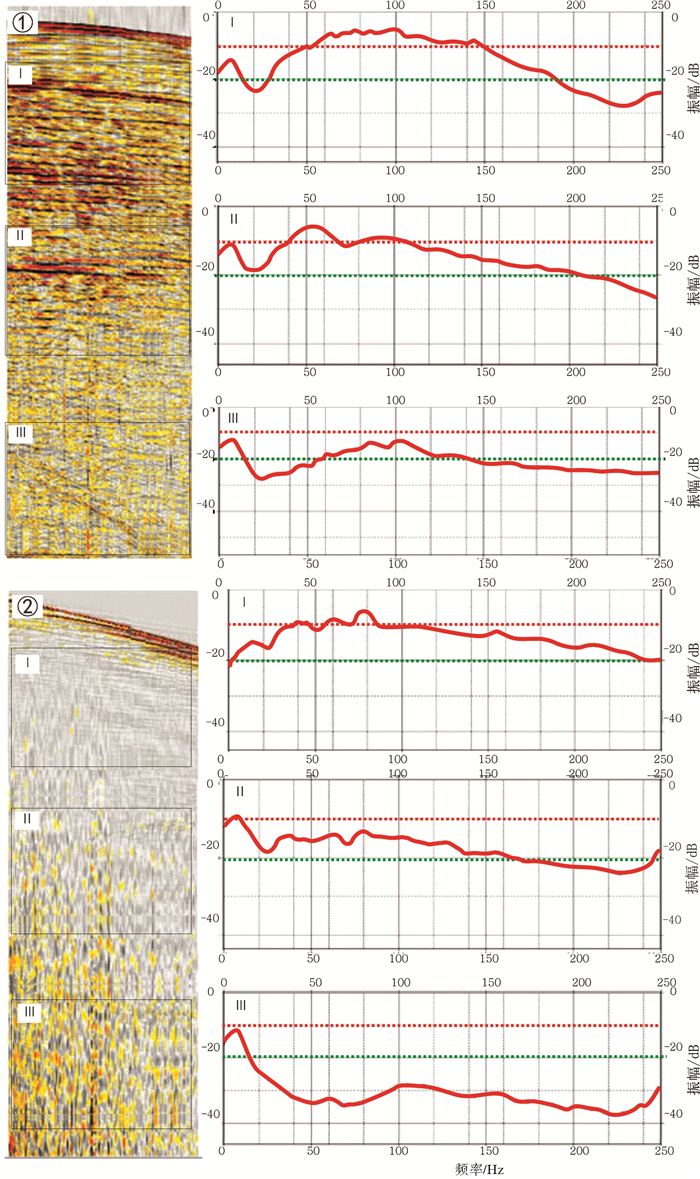
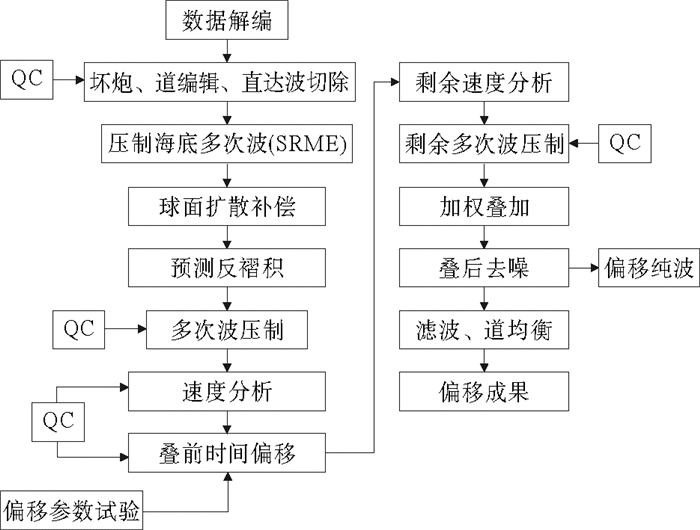
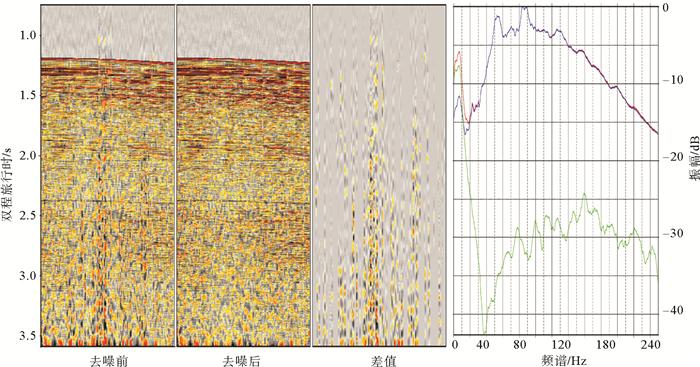
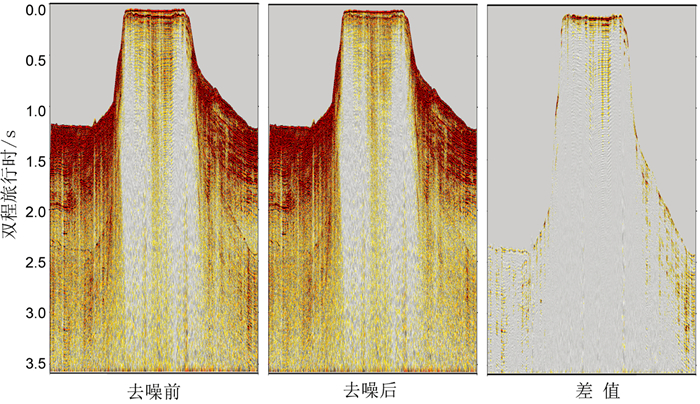
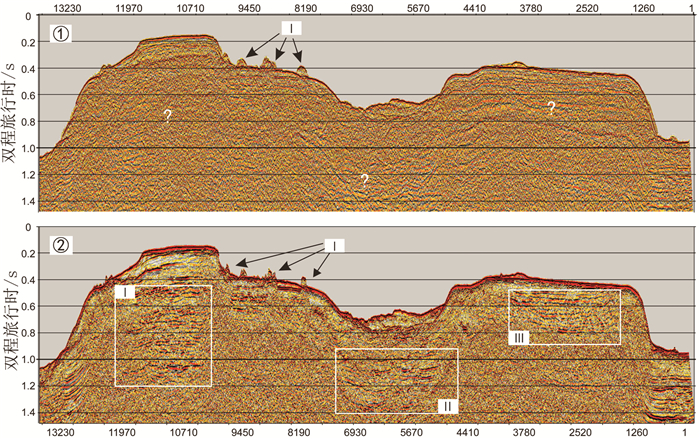
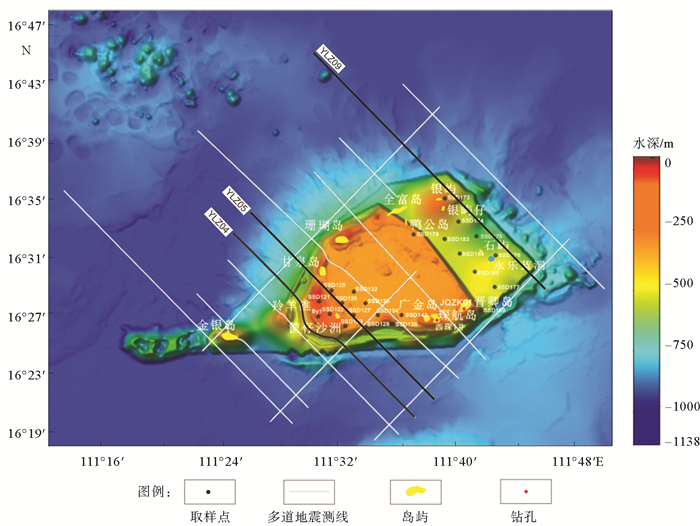
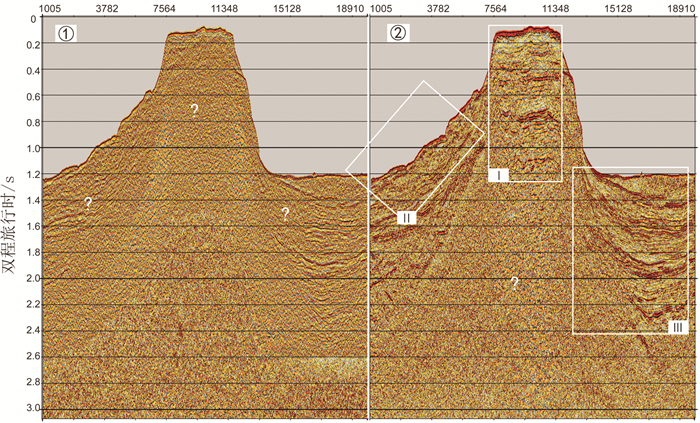
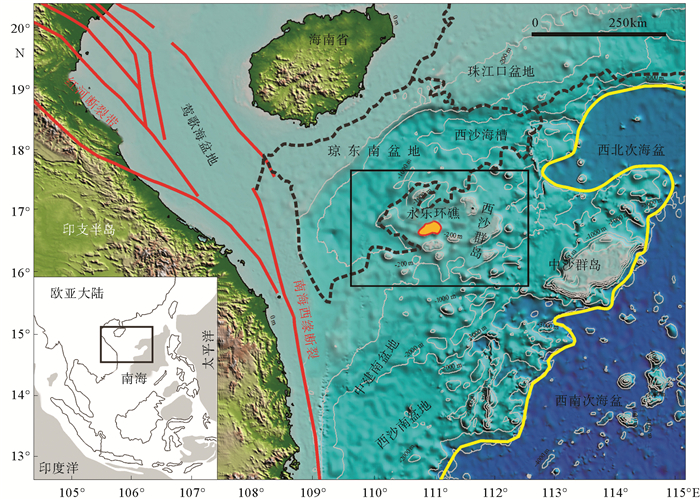
岛礁为国际科学研究前沿,其内部结构是揭示深海地质演变、古环境古气候变化等科学问题和解决岛礁建设、人造岛礁等工程问题的关键。西沙永乐环礁历经南海地质演变过程,发育了世界最深海洋蓝洞,为我国岛礁研究重点区域,但受限于探测手段和成像方法目前尚未窥得其内部结构。以西沙永乐环礁为例,利用3.125m道间距高分辨地震探测试验数据,开展岛礁地震资料特征分析,探索岛礁地震资料处理流程和岛礁地震处理方法,提升岛礁地震资料信噪比、分辨率和成像准确度,获取反映岛礁内部结构的高精度地震成像剖面。研究结果表明:本文提出的岛礁地震资料处理流程在海底珊瑚礁绕射波偏移归位、岛礁内部浅层结构和深水盆地区域地震同相轴刻画方面具有优势,将为我国下一步的南海岛礁地震资料采集和处理提供借鉴。
Abstract:Reef islands have recently become one of the hot interests in international geoscientific researches. Recent progress indicates that the internal structure of reef island is the key to some scientific issues, such as deep-sea geological evolution, paleo-environmental and paleo-climatic changes and to some engineering problems, for example, the construction of man-made reefs and islands. The Yongle Atoll in the Xisha Islands of the South China Sea, which has experienced the geological evolution as part of the South China Sea and become famous because of the deepest Blue Hole in the world, is a key area for marine scientific research in China. However, the internal structure of the islands is not clear at present due to lack of detecting facilities and imaging methods. Based on the collected high- resolution seismic data with 3.125m trace distance from the Yongle Atoll, this paper revealed for the first time the fine internal structure of the reef islands of the Yongle Atoll with high-precision seismic images by enhancing the signal-to-noise ratio, resolution and imaging accuracy of the seismic data via improvement of seismic data analysis, seismic data processing process and seismic imaging methods. The output indicates that the seismic data processing procedures promoted by this paper has advantages in the migration and reorientation of the seabed reef's diffraction wave, working out clearer shallow structures inside the reef, and acquiring the in-phase axis of seismic reflection from deep water. Our study proves that it is a suitable and effective method for seismic data acquisition and processing in the area of reef islands as such in the South China Sea of China.
-

-
表 1 岛礁地震探测航次采集参数对比
Table 1. Comparison of reef island seismic acquisition parameters
采集参数 2010年巴哈马Carambar航次 2007年马尔代夫M74/4航次 2017年永乐环礁高分辨地震探测航次 接收道数 96道 144道 128道 测线间距 斜坡区2.5km其他5~30km 不详 主测线2.5~5km联络测线10km 道间距 6.25m 6.25m 3.125m 最小偏移距 不详 不详 69.7m 炮间距 不详 25m 12.5m 震源容量 Mini-G I 24 in3 组合Mini-GI 105 in3 组合Mini-GI 520in3 信号频带 40~350Hz 主频100~120Hz 主频100~120Hz 公里数 1480km 1400km 413.41km -
[1] Austin J, Schlager W, Comet P, et al. Site 628: Little Bahama Bank. Proceedings of the Ocean drilling program[R]. part A: initial reports, College Station, TX (Ocean Drilling Program), 1986, 101: 213-270.
[2] WU Shiguo, ZHANG Xinyuan, YANG Zhen, et al. Spatial and temporal evolution of Cenozoic carbonate platforms on the continental margins of the South China Sea: Response to opening of the ocean basin[J]. Interpretation, 2016, 4(3): SP1-SP19. doi: 10.1190/INT-2015-0162.1
[3] McNeill L, Shillington D, Carter G. Expedition 381 Scientific Prospectus: Corinth Active Rift Development[R]. International Ocean Discovery Program, 2017.https://doi.org/10.14379/iodp.sp.381.
[4] 汪品先.追踪边缘海的生命史:"南海深部计划"的科学目标[J].科学通报, 2012, 57(20):1807-1826. doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5087-1
WANG Pingxian. Tracing the life history of a marginal Sea: On the "South China Sea Deep" Research Program [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57, doi:10.1007/s11434-012-5087-1
[5] 丁巍伟, 李家彪.南海南部陆缘构造变形特征及伸展作用:来自两条973多道地震测线的证据[J].地球物理学报, 2011, 54(12):3038-3056. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqwlxb201112006
DING Weiwei, LI Jiabiao. Seismic stratigraphy, tectonic structure and extension model across the Reed Bank Basin in the South China Sea: evidence from NH973-2 multi-channel seismic profile [J]. Geophysics, 2011, 36(5): 895-904. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqwlxb201112006
[6] 吴时国, 张新元.南海共轭陆缘新生代碳酸盐台地对海盆构造演化的响应[J].地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 2015, 40(2):234-248. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201502005
WU Shiguo, ZHANG Xinyuan. Response of Cenozoic Carbonate Platform on Tectonic Evolution in the Conjugated Margin of South China Sea [J]. Earth Science, 2015, 40(2):234-248. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201502005
[7] 卢树参, 许红, 陈勇, 等.巴哈马滩与西沙群岛台地生物礁地质特征对比[J].海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(3):57-63. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzdt201603008
LU Shuchen, XU Hong, CHEN Yong, et al. Comparative study of the reef Geology Between Bahama Banks and Xisha Islands[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2016, 32(3):57-63. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzdt201603008
[8] 杨振, 吴时国, 吕福亮, 等.西沙海区晚新生代碳酸盐台地的发育模式及控制因素[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2014, 34(5):47-55. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201405006
YANG Zhen, WU Shiguo, LV Fuliang, et al. Evolutionary model and control factors of late cenozoic carbonate platform in xisha area[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2014, 34(5):47-55. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201405006
[9] France R E. The Holocene Geology of the Pelsaert Reef Complex, Southern Houtman-Abrolhos, Western Australia[D]. Perth, Australia: University of Western Australia, doctoral thesis, 1985: 248.
[10] Willams T D, Kroon S, Spezzaferri. Middle-upper-Miocene cyclostratigraphy of downhole logs and short to long term astronomical cycles in carbonate production of Great Bahama Bank[J]. Marine Geology, 2002, 185:75-93. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(01)00291-2
[11] Wyrwoll K H, Zhu Z R, Collins L B, Hatcher B G. Origin of Blue Hole Structures in Coral Reefs: Houtman Abrolhos, Western Australia[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2006, 221: 202-208. doi: 10.2112/05A-0015.1
[12] MA Benjun, WU Shiguo, LV Fuliang, et al. Seismic characteristics and development of the Xisha carbonate platforms, northern margin of the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 40(3): 770-783. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.11.003
[13] Mulder T, Ducassou E, Eberli G. P, et al. New insights into the morphology and sedimentary processes along the western slope of Great Bahama Bank[J]. Geology, 2012, 40(7): 603-606. doi: 10.1130/G32972.1
[14] Mulder T, Ducassou E, Gillet H, et al. First Discovery of Channel-Level Complexes In A Modern Deep-Water Carbonate Slope Environment[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2014, 84(11): 1139-1146. doi: 10.2110/jsr.2014.90
[15] Read J F. Carbonate platforms of passive (extensional) continental Margins-types, characteristics and evolution[J]. Tectonophysics, 1982, 81:195-212. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(82)90129-9
[16] Read J F. Carbonate platform facies models[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1985, 69:1- 21. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cjxb201306003
[17] Saenger E H, Gold N, Shapiro S A. Modeling the propagation of elastic waves using a modified finite-difference grid[J]. Wave Motion, 2000, 33: 77-92. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=293408bd1b4da49b9dab0b67e3173d87
[18] Betzler C, John J G. Reijm, et al. Sedimentary patterns and geometries of the Bahamian outer carbonate ramp (Miocene ±Lower Pliocene, Great Bahama Bank)[J]. Sedimentology, 1999, 46: 1127-1143. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3091.1999.00268.x
[19] Betzler C, Lindhorst S, Eberl G P, et al. Periplatform drift: The combined result of contour current and off-bank transport along carbonate platforms[J]. Geology, 2014, 42: 871-874. doi: 10.1130/G35900.1
[20] Betzler C, Fürstenau J, Lüdmann T, et al. Sea-level and ocean-current control on carbonate-platform growth, Maldives, Indian Ocean[J]. Basin Research, 2013, 25(2): 172-196. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2117.2012.00554.x
[21] Betzler C, Hübscher C, Lindhorst S, et al. Lowstand wedges in carbonate platform slopes (Quaternary, Maldives, Indian Ocean)[J]. The Depositional Record, 2016, 2(2):196-207. doi: 10.1002/dep2.21
[22] Betzler C, Lüdmann T, Hübscher C, et al. Current and sea-level signals in periplatform ooze (Neogene, Maldives, Indian Ocean)[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2013, 290: 126-137. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2013.03.011
[23] Principaud M, Ponte J P, Mulder T, et al. Slope-to-basin stratigraphic evolution of the northwestern Great Bahama Bank (Bahamas) during the Neogene to Quaternary: interactions between downslope and bottom currents deposits[J]. Basin Research, 2017, 29(6): 699-724. doi: 10.1111/bre.12195
[24] Lüdmann T, Kalvelage C, Betzler C, et al. The Maldives, a giant isolated carbonate platform dominated by bottom currents[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2013, 43: 326-340. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2013.01.004
[25] 马玉波, 吴时国, 杜晓慧, 等.西沙碳酸盐岩建隆发育模式及其主控因素[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(4):59-67. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201104010
MA Yubo, WU Shiguo, DU Xiaohui, et al. Evolutionary Model and Control Factors of Xisha Carbonate Buildup[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2011, 31(4):59-68. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201104010
[26] 马玉波, 吴时国, 邢树文, 等.南海北部陆坡混合沉积地层模式及地震响应特征[J].吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2012, 42(S1):88-95. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7267278
MA Yubo, WU Shiguo, XING Shuwen, et al.Stratigraphic model and seismic characteristics of the mixed sedimentation in the slope area of north south china sea[J]. Journal of Jilin University, 2012, 42(S1): 88-95. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7267278
-



 下载:
下载: