Distribution of the gas vents at the seabed of the Mid-Okinawa Trough and their controlling factors
-
摘要:
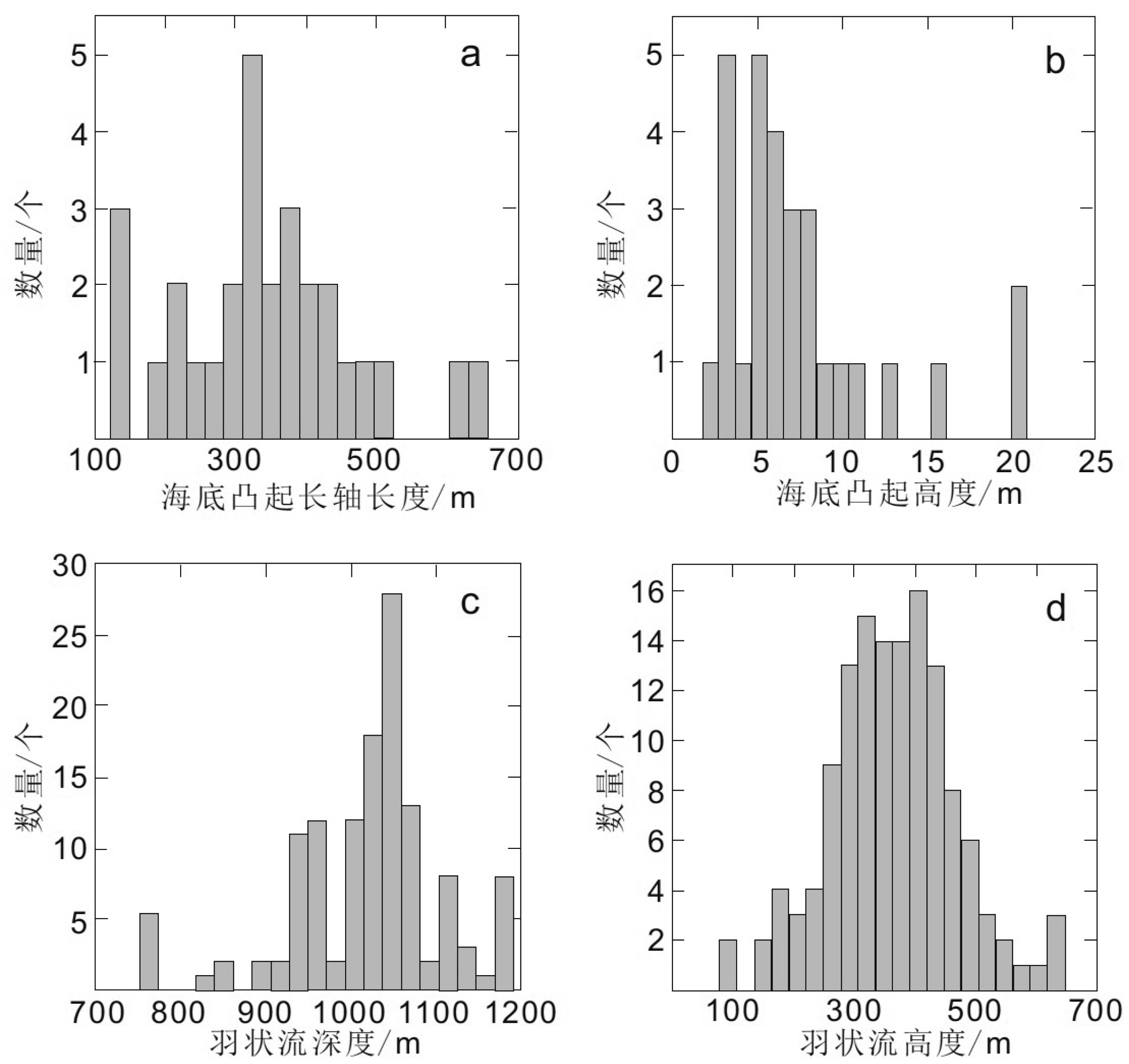
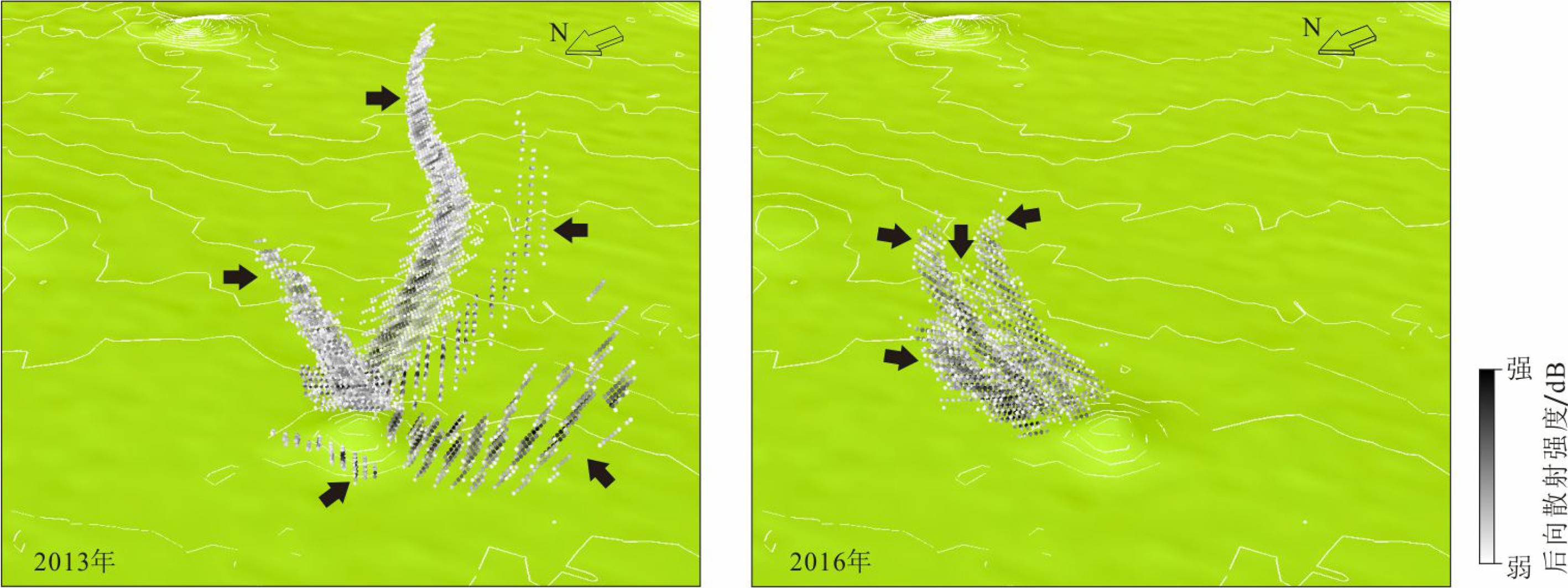
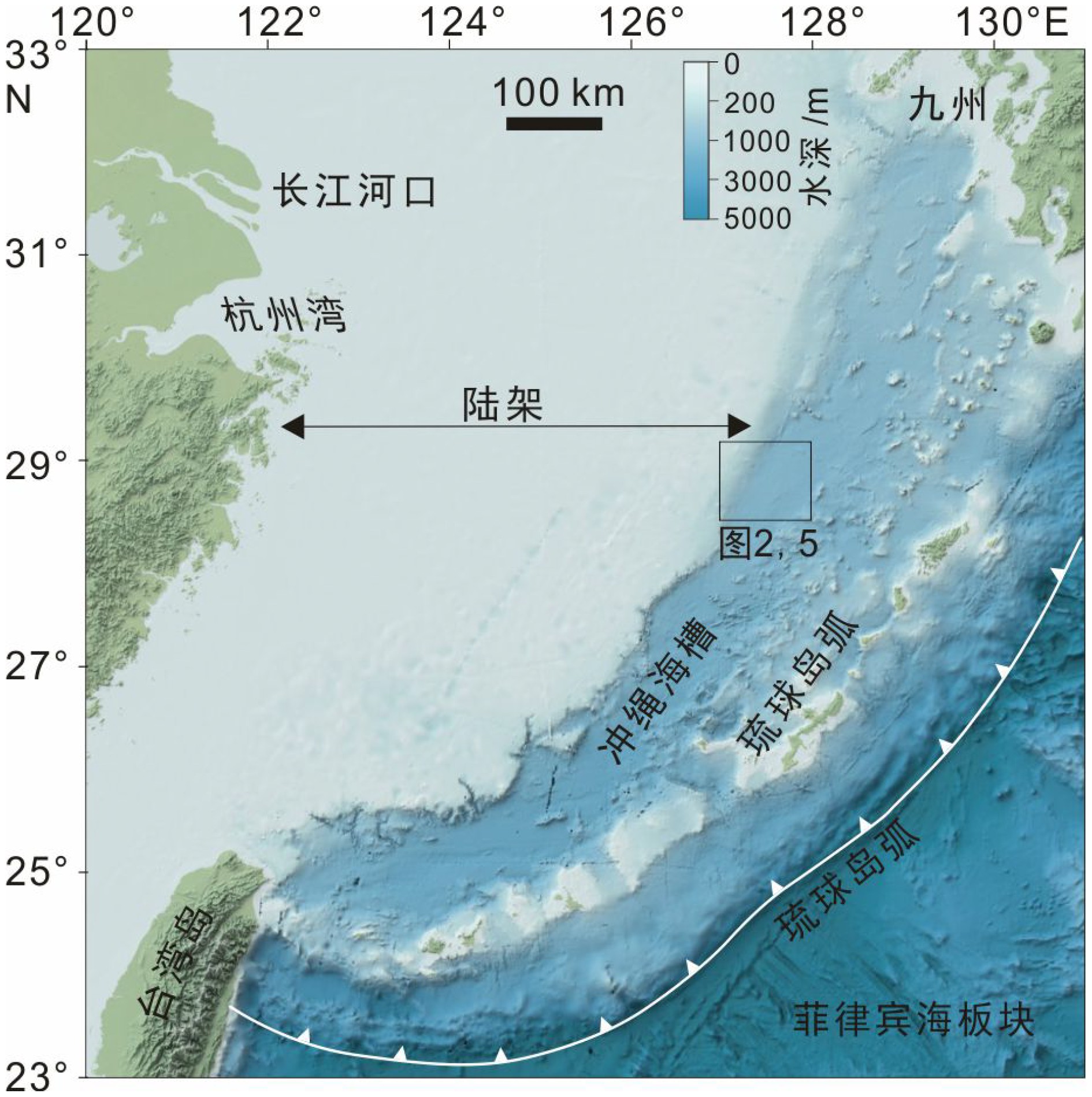
海底气体排放是海洋环境中碳物质从岩石圈进入到水圈中的重要地质过程,理解甲烷在该过程中的迁移方式和表征是定量评价海底甲烷排放在全球碳循环中环境效应的重要基础。本次研究使用2013—2016年采集的多波束回声测深以及二维多道地震数据,展示了与海底气体排放有关的地球物理特征,在水体、浅部地层中以及海底界面处分别识别出了束状羽状流、柱状裂隙气体疏导通道和下伏有碳酸盐岩的海床凸起,它们被解释为气体排放的地质表征,这些构成要素在空间上的叠置关系呈现了冲绳海槽中部气体排放特征,研究选取典型实例刻画了这一地质过程并总结了模型。经过分析断层与气体排放地质表征的空间位置关系,提出冲绳海槽研究区内海底气体排放的分布受到了盆地构造活动的控制,冲绳海槽发生的斜向裂谷作用导致了研究区张扭断层的形成,以拉张为主的断层为富甲烷流体提供了垂向运移通道,致使气体排放沿正断层分布。研究表明海底气体排放可以广泛发育在以拉张应力为主的地质环境中。
Abstract:Gas venting at the seabed is recognized as a key geological process for carbon transfer from the lithosphere to hydrosphere. Understanding how methane is transported and the geological expressions in this process is necessary for quantatively evaluating its climatic impact on global carbon cycle. In this study, multi-beam echo-sounder (MBES) and multi-channel seismic (MCS) data acquired between 2013 and 2016 from the Mid-Okinawa Trough are used to show the geophysical features associated with gas vents. We identified the bundle-shaped gas flares in water column, the migration pathways consisting of cylindrical cluster of fractures in the shallow subsurface and the seabed domes underlain by carbonate-cemented sediments. They are regarded hereby as the geological indicators of gas vents, indicating how gases are vented in the Mid-Okinawa Trough. An example has been selected for description to represent the gas vents in the study area. We proposed that the distribution of gas vents in the study area is controlled by basin-scale tectonic activities after analyzing their spatial relationship with the faults. The oblique rifting in the Mid-Okinawa Trough resulted in the formation of the transtensional faults. The faults that formed in the tensile regime provide vertical conduits for gas-rich pore fluids to migrate, which caused that the gas vents were elongated along the normal faults. This study suggests that gas vents on the seabed can occur extensively in the extension-dominated tectonic regime.
-
Key words:
- gas vent /
- tectonic control /
- gas flare /
- Okinawa Trough
-

-
[1] Riedel M, Scherwath M, Römer M, et al. Distributed natural gas venting offshore along the Cascadia margin [J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 3264. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05736-x
[2] Tryon M D, Brown K M, Torres M E, et al. Measurements of transience and downward fluid flow near episodic methane gas vents, Hydrate Ridge, Cascadia [J]. Geology, 1999, 27(12): 1075-1078. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1999)027<1075:MOTADF>2.3.CO;2
[3] Haacke R R, Hyndman R D, Park K P, et al. Migration and venting of deep gases into the ocean through hydrate-choked chimneys offshore Korea [J]. Geology, 2009, 37(6): 531-534. doi: 10.1130/G25681A.1
[4] Haese R R, Meile C, Van Cappellen P, et al. Carbon geochemistry of cold seeps: methane fluxes and transformation in sediments from Kazan mud volcano, eastern Mediterranean Sea [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2003, 212(3-4): 361-375. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(03)00226-7
[5] Reeburgh W S. Oceanic methane biogeochemistry [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2007, 107(2): 486-513. doi: 10.1021/cr050362v
[6] Dale A W, Regnier P, Knab N J, et al. Anaerobic oxidation of methane (AOM) in marine sediments from the Skagerrak (Denmark): Ⅱ. Reaction-transport modeling [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2008, 72(12): 2880-2894. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.11.039
[7] Xu W Y, Germanovich L N. Excess pore pressure resulting from methane hydrate dissociation in marine sediments: a theoretical approach [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2006, 111(B1): B01104.
[8] Biastoch A, Treude T, Rüpke L H, et al. Rising Arctic Ocean temperatures cause gas hydrate destabilization and ocean acidification [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2011, 38(8): L08602.
[9] Yamamoto A, Yamanaka Y, Oka A, et al. Ocean oxygen depletion due to decomposition of submarine methane hydrate [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2014, 41(14): 5075-5083. doi: 10.1002/2014GL060483
[10] Houghton J T, Callander B A, Varney S K. Climate change 1992: the supplementary report to the IPCC scientific assessment[R]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1992.
[11] Mazzini A, Etiope G. Mud volcanism: an updated review [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2017, 168: 81-112. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.03.001
[12] Roberts H H. Fluid and gas expulsion on the northern Gulf of Mexico continental slope: Mud-prone to mineral-prone responses[M]//Paull C K, Dillon W P. Natural Gas Hydrates: Occurrence, Distribution, and Detection: Occurrence, Distribution, and Detection, Volume 124. Washington, DC: American Geophysical Union, 2001: 145-161.
[13] Roberts H H, Hardage B A, Shedd W W, et al. Seafloor reflectivity-An important seismic property for interpreting fluid/gas expulsion geology and the presence of gas hydrate [J]. The Leading Edge, 2006, 25(5): 620-628. doi: 10.1190/1.2202667
[14] Li A, Davies R J, Mathias S A, et al. Gas venting that bypasses the feather edge of marine hydrate, offshore Mauritania [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2017, 88: 402-409. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.08.026
[15] Judd A G. The global importance and context of methane escape from the seabed [J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 2003, 23(3-4): 147-154. doi: 10.1007/s00367-003-0136-z
[16] Milkov A V, Sassen R, Apanasovich T V, et al. Global gas flux from mud volcanoes: a significant source of fossil methane in the atmosphere and the ocean [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2003, 30(2): 1037.
[17] Arntsen B, Wensaas L, Løseth H, et al. Seismic modeling of gas chimneys [J]. Geophysics, 2007, 72(5): SM251-SM259. doi: 10.1190/1.2749570
[18] Moss J L, Cartwright J. 3D seismic expression of km-scale fluid escape pipes from offshore Namibia [J]. Basin Research, 2010, 22(4): 481-501. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2117.2010.00461.x
[19] Løseth H, Wensaas L, Arntsen B, et al. 1000 m long gas blow-out pipes [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2011, 28(5): 1047-1060. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2010.10.001
[20] 业治铮, 张明书, 潘志良. 冲绳海槽晚更新世—全新世沉积物的初步研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1983, 3(2):1-14
YE Zhizheng, ZHANG Mingshu, PAN Zhiliang. A preliminary study of Late Pleistocene-Holocene sediments in the Okinawa trough [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1983, 3(2): 1-14.
[21] Sibuet J C, Deffontaines B, Hsu S K, et al. Okinawa trough backarc basin: early tectonic and magmatic evolution [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1998, 103(B12): 30245-30267. doi: 10.1029/98JB01823
[22] Lee C S, Shor Jr G G, Bibee L D, et al. Okinawa trough: origin of a back-arc basin [J]. Marine Geology, 1980, 35(1-3): 219-241. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(80)90032-8
[23] Kimura M. Back-arc rifting in the Okinawa Trough [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 1985, 2(3): 222-240. doi: 10.1016/0264-8172(85)90012-1
[24] Letouzey J, Kimura M. Okinawa Trough genesis: structure and evolution of a backarc basin developed in a continent [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 1985, 2(2): 111-130. doi: 10.1016/0264-8172(85)90002-9
[25] Gungor A, Lee G H, Kim H J, et al. Structural characteristics of the northern Okinawa Trough and adjacent areas from regional seismic reflection data: Geologic and tectonic implications [J]. Tectonophysics, 2012, 522-523: 198-207. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2011.11.027
[26] Xu J Y, Ben-Avraham Z, Kelty T, et al. Origin of marginal basins of the NW Pacific and their plate tectonic reconstructions [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2014, 130: 154-196. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.10.002
[27] 金翔龙, 喻普之. 冲绳海槽的构造特征与演化[J]. 中国科学 B辑, 1988, 31(5):614-623
JIN Xianglong, YU Puzhi. Structure and tectonic evolution of Okinawa trough [J]. Scientia Sinica (Series B), 1988, 31(5): 614-623.
[28] Fabbri O, Monié P, Fournier M, et al. Transtensional deformation at the junction between the Okinawa trough back-arc basin and the SW Japan island arc [J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 2004, 227(1): 297-312. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2004.227.01.15
[29] Lu R S, Pan J J, Lee T C. Heat flow in the southwestern Okinawa Trough [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1981, 55(2): 299-310. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(81)90109-6
[30] 栾锡武. 热液活动区数目和洋脊扩张速率的关系及其在冲绳海槽的应用[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2006, 26(2):55-64
LUAN Xiwu. Relationship between the number of hydrothermal activity fields and spreading rate and its application in the Okinawa Trough [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2006, 26(2): 55-64.
[31] 栾锡武. 琉球沟弧盆系的海底热流分布特征及冲绳海槽热演化的数值模拟[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1997, 28(1):44-48 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1997.01.008
LUAN Xiwu. Study of heatflow distribution of Ryukyu TA-B-A system and thermo dynamic modeling of Okinawa Trough [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1997, 28(1): 44-48. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1997.01.008
[32] Tsuji T, Takai K, Oiwane H, et al. Hydrothermal fluid flow system around the Iheya North Knoll in the mid-Okinawa trough based on seismic reflection data [J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2012, 213-214: 41-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2011.11.007
[33] 尚鲁宁, 张训华, 韩波. 重磁资料揭示的冲绳海槽及邻区断裂和岩浆岩分布[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(1):99-106
SHANG Luning, ZHANG Xunhua, HAN Bo. Fault belts and igneous rocks of the Okinawa Trough and adjacent areas: evidence from gravity and magnetic data [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2016, 36(1): 99-106.
[34] 栾锡武, 秦蕴珊. 冲绳海槽宫古段西部槽底海底气泉的发现[J]. 科学通报, 2005, 50(13):1358-1365 doi: 10.1360/04wd0257
LUAN Xiwu, QIN Yunshan. Gas seepage on the sea floor of Okinawa trough Miyako Section [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2005, 50(13): 1358-1365. doi: 10.1360/04wd0257
[35] Sakai H, Gamo T, Kim E S, et al. Venting of carbon dioxide-rich fluid and hydrate formation in mid-okinawa trough backarc basin [J]. Science, 1990, 248(4959): 1093-1096. doi: 10.1126/science.248.4959.1093
[36] Xu C L, Wu N Y, Sun Z L, et al. Methane seepage inferred from pore water geochemistry in shallow sediments in the western slope of the Mid-Okinawa Trough [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 98: 306-315. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.08.021
[37] 李清, 蔡峰, 梁杰, 等. 东海冲绳海槽西部陆坡甲烷渗漏发育的孔隙水地球化学证据[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2015, 58(6):986-995 doi: 10.1007/s11430-014-5034-x
LI Qing, CAI Feng, LIANG Jie, et al. Geochemical constraints on the methane seep activity in western slope of the middle Okinawa Trough, the East China Sea [J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2015, 58(6): 986-995. doi: 10.1007/s11430-014-5034-x
[38] Yin P, Berné S, Vagner P, et al. Mud volcanoes at the shelf margin of the East China Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 2003, 194(3-4): 135-149. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(02)00678-3
[39] Wan Z F, Yao Y J, Chen K W, et al. Characterization of mud volcanoes in the northern Zhongjiannan Basin, western South China Sea [J]. Geological Journal, 2019, 54(1): 177-189. doi: 10.1002/gj.3168
[40] Prior D B, Doyle E H, Kaluza M J. Evidence for sediment eruption on deep sea floor, gulf of Mexico [J]. Science, 1989, 243(4890): 517-519. doi: 10.1126/science.243.4890.517
[41] Serié C, Huuse M, Schødt N H, et al. Gas hydrate pingoes: deep seafloor evidence of focused fluid flow on continental margins [J]. Geology, 2012, 40(3): 207-210. doi: 10.1130/G32690.1
[42] Koch S, Berndt C, Bialas J, et al. Gas-controlled seafloor doming [J]. Geology, 2015, 43(7): 571-574. doi: 10.1130/G36596.1
[43] Mienis F, de Stigter H C, White M, et al. Hydrodynamic controls on cold-water coral growth and carbonate-mound development at the SW and SE Rockall Trough margin, NE Atlantic Ocean [J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2007, 54(9): 1655-1674. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2007.05.013
[44] Hovland M, Talbot M R, Qvale H, et al. Methane-related carbonate cements in pockmarks of the North Sea [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1987, 57(5): 881-892.
[45] 龚建明. 冲绳海槽天然气水合物成因及资源潜力评价[D]. 中国海洋大学博士学位论文, 2007.
GONG Jianming. Origin and resources assessment of gas hydrate in Okinawa Trough[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2007.
[46] Hornbach M J, Saffer D M, Holbrook W S. Critically pressured free-gas reservoirs below gas-hydrate provinces [J]. Nature, 2004, 427(6970): 142-144. doi: 10.1038/nature02172
[47] Cartwright J, Huuse M, Aplin A. Seal bypass systems [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2007, 91(8): 1141-1166. doi: 10.1306/04090705181
[48] McGinnis D F, Greinert J, Artemov Y, et al. Fate of rising methane bubbles in stratified waters: how much methane reaches the atmosphere? [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2006, 111(C9): C09007.
[49] Liu B, Li S Z, Suo Y H, et al. The geological nature and geodynamics of the Okinawa Trough, western Pacific [J]. Geological Journal, 2016, 51(S1): 416-428.
[50] Autin J, Bellahsen N, Leroy S, et al. The role of structural inheritance in oblique rifting: insights from analogue models and application to the Gulf of Aden [J]. Tectonophysics, 2013, 607: 51-64. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2013.05.041
[51] Mazzini A, Nermoen A, Krotkiewski M, et al. Strike-slip faulting as a trigger mechanism for overpressure release through piercement structures. Implications for the Lusi mud volcano, Indonesia [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2009, 26(9): 1751-1765. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2009.03.001
[52] Choi J H, Seol Y, Boswell R, et al. X‐ray computed‐tomography imaging of gas migration in water‐saturated sediments: from capillary invasion to conduit opening [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2011, 38(17): L17310.
[53] 姜振学, 庞雄奇, 曾溅辉, 等. 油气优势运移通道的类型及其物理模拟实验研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2005, 12(4):507-516 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2005.04.020
JIANG Zhenxue, PANG Xiongqi, ZENG Jianhui, et al. Research on types of the dominant migration pathways and their physical simulation experiments [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2005, 12(4): 507-516. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2005.04.020
[54] Plaza-Faverola A, Keiding M. Correlation between tectonic stress regimes and methane seepage on the western Svalbard margin [J]. Solid Earth, 2019, 10(1): 79-94. doi: 10.5194/se-10-79-2019
-



 下载:
下载: