Changes of evolution models of China's large river deltas since Holocene and their responses to anthropogenic activities
-
摘要:
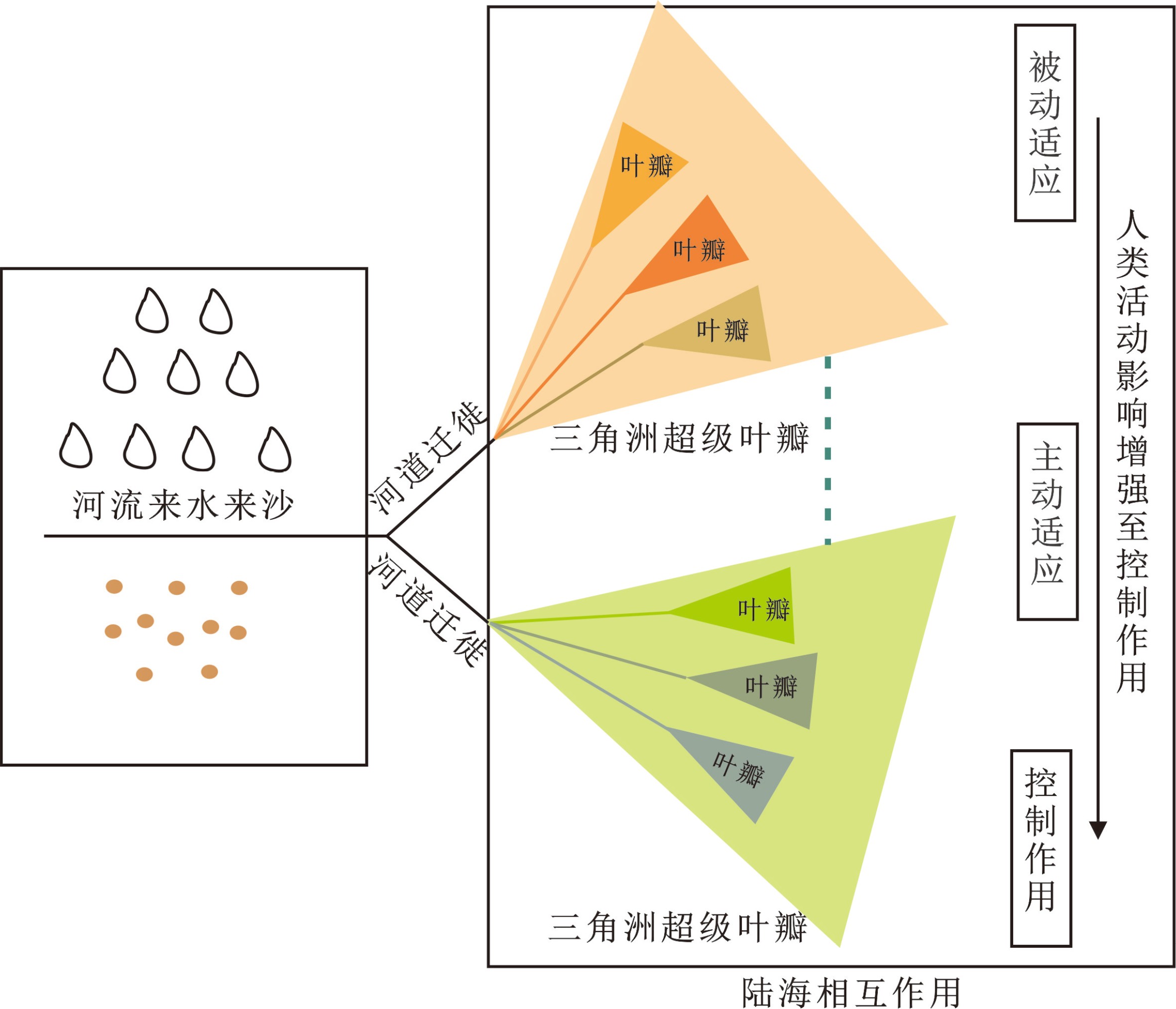
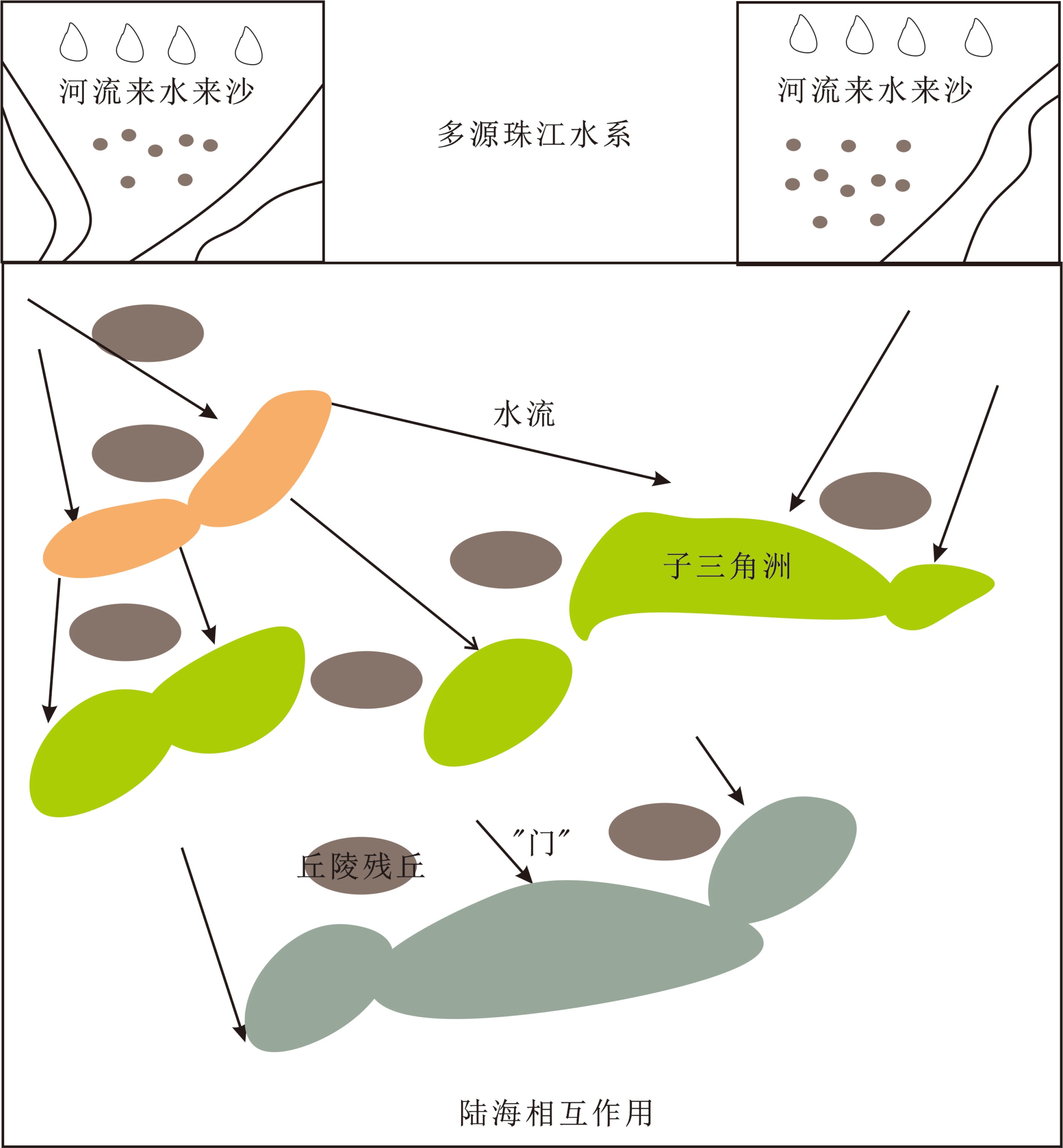
中国三大河口三角洲包括黄河三角洲、长江三角洲和珠江三角洲,在国民经济发展和全球海陆相互作用研究中均扮演着非常重要的角色。因此,全面揭示河口三角洲演化进程,总结河口三角洲演化模式,对指导河口三角洲可持续开发利用具有重要意义。本文结合前人研究进展及近年来海洋区域地质调查资料,系统总结了全新世以来我国三大河口三角洲“三个阶段,三个尺度,各具特色”的演化模式,揭示了全新世初期、两千年前和工业革命后三个阶段千年-百年-年代际时间尺度下河口三角洲演变模式转化的主控因素,认为河口三角洲的演化模式正在由自然演变向人为控制转型,人类活动正剧烈地影响着河口三角洲的自然演化进程。三大河口三角洲沉积演化模式各具特色,黄河三角洲具有超级叶瓣与叶瓣发育演替特色,长江三角洲具有北岸沙岛并岸、南岸不断推展特色,珠江三角洲则表现为河网发育充填、逐级分汊延伸特色。随着河口三角洲演化受人类活动影响的加剧,正确认识河口三角洲演化规律及其主控因素,不仅有助于提升三角洲地区陆海相互作用研究水平,而且将为三角洲可持续开发利用提供科学依据。
Abstract:As a key component of the global environmental system, deltas are located in the specific areas suffering strong land-sea interaction. Generally, the deltaic regions are rich in natural resources, densely populated, highly urbanized and active in human activities, but they are fragile in terms of ecological conditions. The China’s large deltas, i.e the Yellow River Delta, the Yangtze River Delta and the Pearl River Deltas, have played important roles in the economic development of the country and contributed much to global environmental changes. Therefore, it is significant to reveal the deltas’ evolution processes and depositional models to ensure the sustainable development of the deltas and utilization of their resources. In this paper, we summarized synthetically the evolutionary models of these deltas based on the data from regional marine geological surveys and their precious results. Since Holocene, the evolution of China’s large river deltas has suffered three stages of evolution in three time-scales with their exclusive features. By these models, the factors influencing the delta evolution are discussed on millennium, centennial, interannual time scales respectively. The evolutionary models have changed from the natural factor dominated to human factor dominated owing to the stronger anthropogenic activities. It is an urgent need to strengthen the study of estuary delta evolution under the influence of human activities, so as to provide more scientific support for the sustainable development and full use of deltaic resources in these regions.
-
Key words:
- river delta /
- the evolution model /
- land and ocean interaction /
- anthropogenic activities /
- the Holocene
-

-
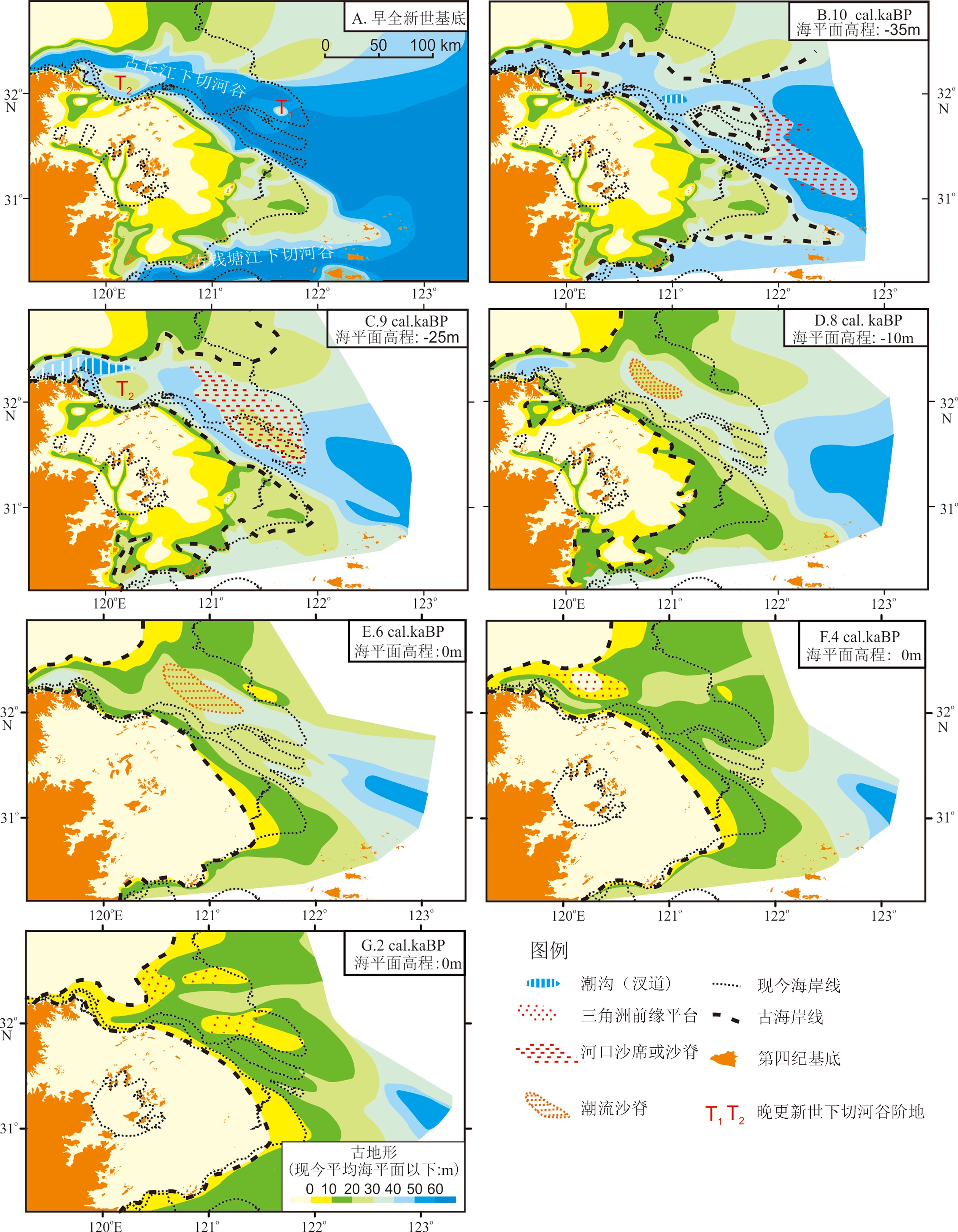
图 2 基于钻孔资料重建全新世以来长江河口地貌变化[22]
Figure 2.
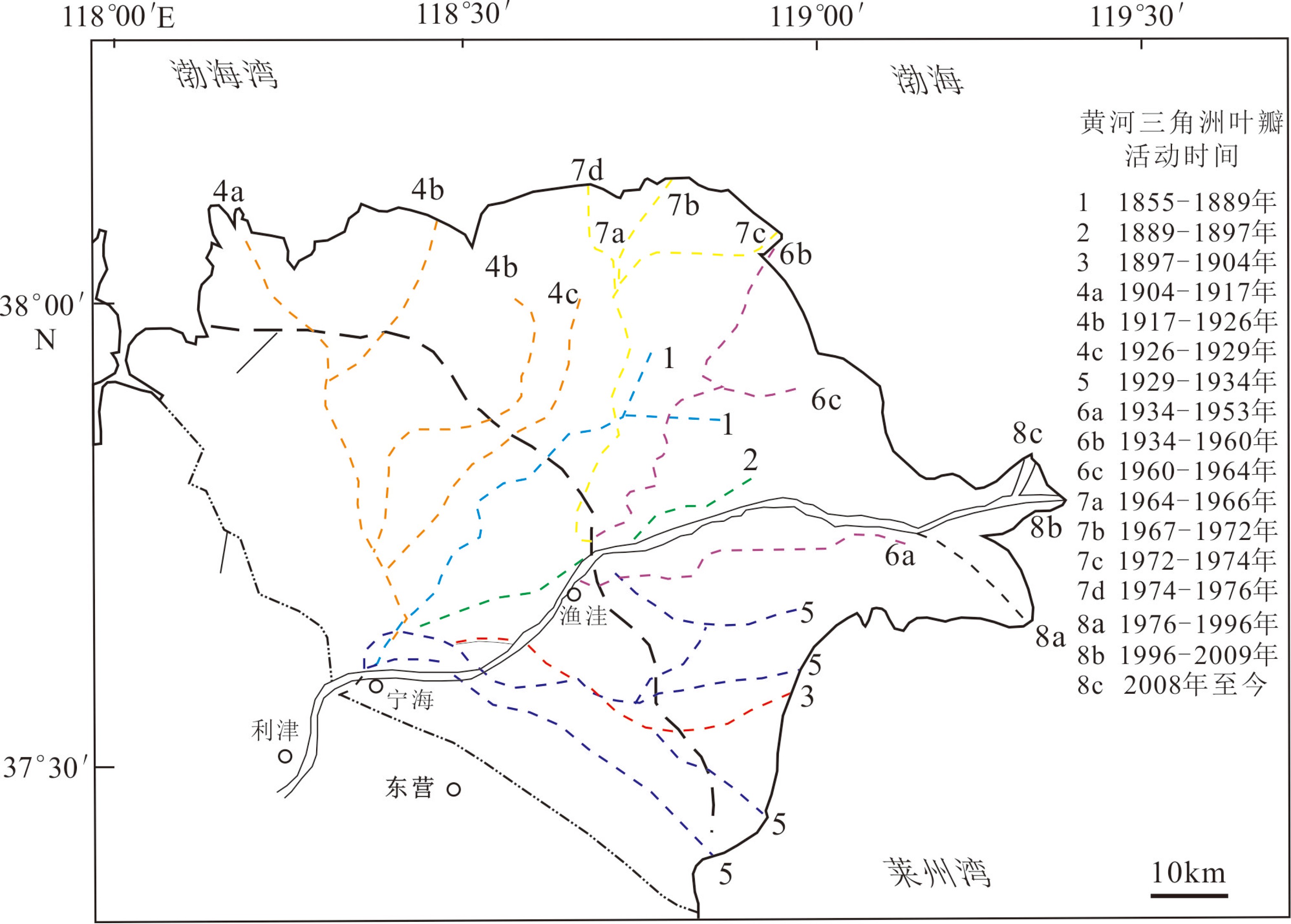
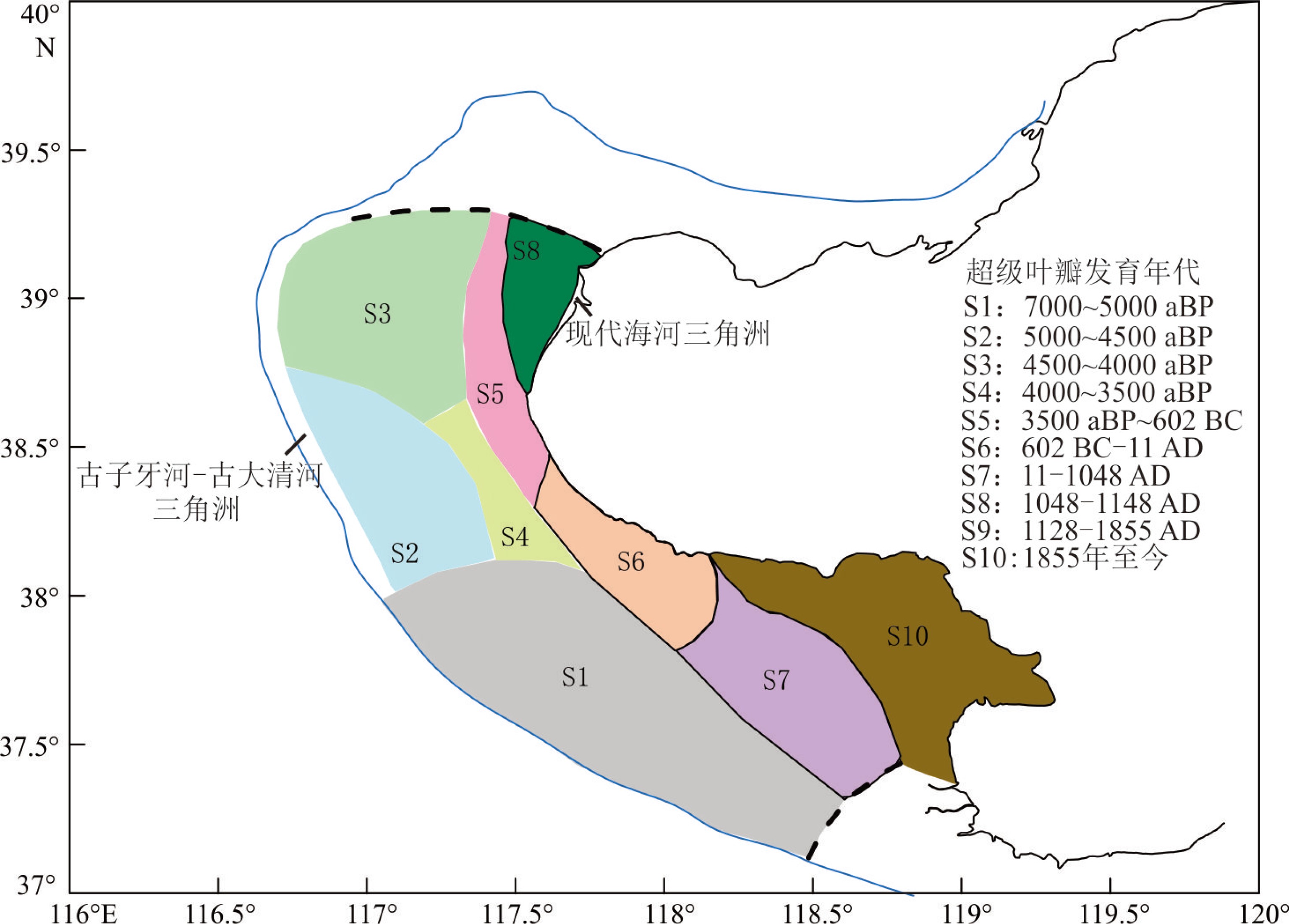
图 3 1855年以来黄河大规模尾闾改道信息[7]
Figure 3.
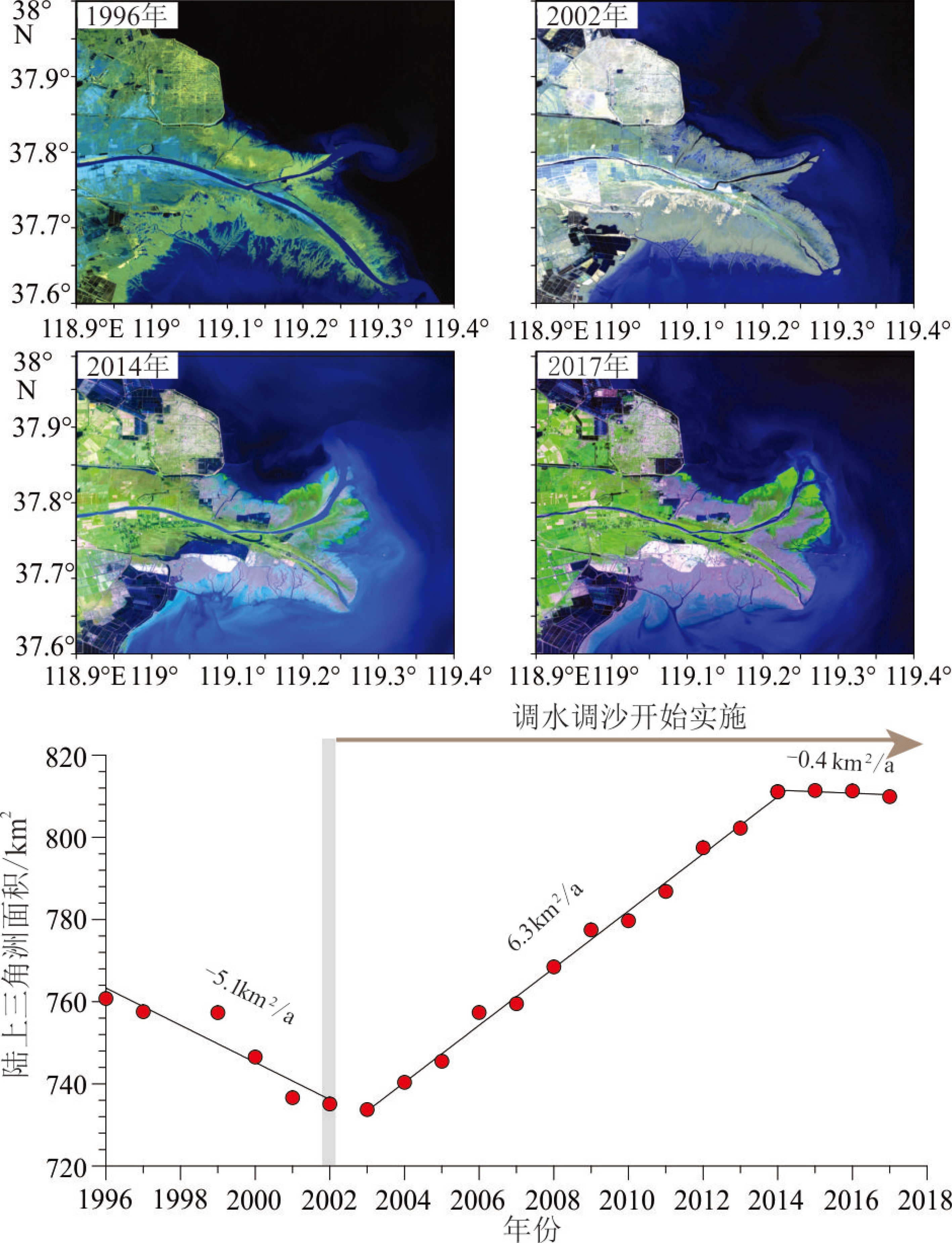
图 4 1976—2013年现行黄河三角洲叶瓣陆地面积变化[53]
Figure 4.
表 1 全新世以来黄河年均入海泥沙量[44]
Table 1. Annual average sediment discharge of the Yellow River since Holocene[44]
面积/km2 厚度/m 体积/km3 年淤积量 /108t 发育时间/a 年输沙量/108t S1 6739.0 1.55 10.45 0.08 2000 0.33 S2 2544.0 2.02 5.09 0.15 500 0.64 S3 3546.6 1.50 5.32 0.16 500 0.67 S4 821.5 3.00 2.46 0.07 500 0.31 S5 1291.3 5.88 7.59 0.12 950 0.50 S6 1567.5 5.36 8.40 0.21 613 0.86 S7 2834.6 13.00 36.85 0.54 1037 2.24 S8 987.2 6.45 6.37 1.20 80 5.01 S9 7160.0 14.03 100.45 2.09 727 8.69 S10 3939.0 10.50 31.81 2.40 160 10.01 表 2 不同时间尺度长江水下三角洲沉积通量估算[22]
Table 2. Estimation of sediment flux in the Yangtze River estuary on different time scale
阶段 时间/aBP 总沉积体积/km3 年沉积体积/ (106 m3/a) 年平均沉积量/ (106 t/a) 年最大沉积量/ (106 t/a) 年最小沉积量/ (106 t/a) Ⅰ 11.7~10 300.95 150.5 224 302 154 Ⅱ 10~8 217.29 108.7 137 186 95 Ⅲ 8~6 239.09 119.6 151 205 104 Ⅳ 6~4 156.55 78.3 99 134 68 Ⅴ 4~2 179.56 89.8 113 154 78 Ⅵ 2~0 256.75 128.9 162 220 112 Ⅶ 1958—1979 3.97 189.2 212 278 165 Ⅷ 1979—2002 1.92 83.3 93 122 72 Ⅸ 2002—2011 0.4 43.9 49 65 38 Ⅹ 2011—2013 −1.14 −570.0 −638 −838 −496 表 3 历史时期珠江三角洲伸展速度估算[28]
Table 3. Estimation of the expansion velocity of the Pearl River Delta in historical periods [28]
时代 年数 西、北江 北江 东江 伸展长度/km 伸展速度/ (m/a) 伸展长度/km 伸展速度/ (m/a) 伸展长度/km 伸展速度/ (m/a) 秦汉 837 8.0 9.6 8.5 10.2 7.0 8.4 唐 342 8.5 24.9 6.4 18.7 5.0 14.6 宋 408 13.6 33.3 8.0 19.6 8.0 19.6 明 276 11.0 39.9 7.2 26.9 4.2 15.2 清 316 9.8 31.8 13.6 43.0 2.6 8.2 -
[1] Liu J P, Milliman J D, Gao S, et al. Holocene development of the Yellow River’s subaqueous delta, North Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 2004, 209(1-4): 45-67. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2004.06.009
[2] Liu J, Saito Y, Wang H, et al. Sedimentary evolution of the Holocene subaqueous clinoform off the Shandong Peninsula in the Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 2007, 236(3-4): 165-187. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2006.10.031
[3] Liu J, Saito Y, Wang H, et al. Stratigraphic development during the Late Pleistocene and Holocene offshore of the Yellow River delta, Bohai Sea [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Science, 2009, 36(4-5): 318-331. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2009.06.007
[4] 薛春汀, 周永青, 朱雄华. 晚更新世末至公元前7世纪的黄河流向和黄河三角洲[J]. 海洋学报, 2004, 26(1):48-61
XUE Chunting, ZHOU Yongqing, ZHU Xionghua. The Huanghe River course and delta from end of Late Pleistocene to the 7th century BC [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2004, 26(1): 48-61.
[5] 杨子赓. 南黄海陆架晚更新世以来的沉积及环境[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1985, 5(4):1-19
Yang Zigeng. Sedimentology and environment in South Huanghai Sea shelf since Late Pleistocene [J]. Marine Geology&Quaternary Geology, 1985, 5(4): 1-19.
[6] 李凡, 张秀荣, 李永植, 等. 南黄海埋藏古三角洲[J]. 地理学报, 1998, 53(3):238-244 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1998.03.006
LI Fan, ZHANG Xiurong, LI Yongzhi, et al. Buried paleo delta in the South Yellow Sea [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1998, 53(3): 238-244. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1998.03.006
[7] Xue C T. Historical changes in the Yellow River delta, China [J]. Marine Geology, 1993, 113(3-4): 321-330. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(93)90025-Q
[8] Mosseman S. Delta of the Yangtze delta [J]. Geography Magazine, 1877, 1(1): 25-35.
[9] 李从先, 王靖泰, 李萍. 长江三角洲沉积相的初步研究[J]. 同济大学学报, 1979(2):1-14
LI Congxian, WANG Jingtai, LI Ping. Preliminary study on sedimentary facies and sequence of the Yangtze Delta [J]. Journal of Tongji University, 1979(2): 1-14.
[10] 李从先, 汪品先. 长江晚第四纪河口地层学研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1998.
LI Congxian, WANG Pinxian. Stratigraphy of the Yangtze River Estuary in the late Quaternary[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1998.
[11] 陈吉余, 恽才兴, 徐海根, 等. 两千年来长江河口发育的模式[J]. 海洋学报, 1979, 1(1):103-111
CHEN Jiyu, YUN Caixing, XU Haigen, et al. The developmental model of the Chang Jiang River Estuary during last 2000 years [J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 1979, 1(1): 103-111.
[12] 陈吉余, 沈焕庭, 恽才兴. 长江河口动力过程和地貌演变[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 1988.
CHEN Jiyu, SHEN Huanting, YUN Caixing. Dynamic Process and Geomorphic Evolution of the Yangtze River Estuary[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 1988.
[13] Stanley D J, Chen Z Y. Yangtze delta, eastern China: 1. geometry and subsidence of Holocene depocenter [J]. Marine Geology, 1993, 112(1-4): 1-11. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(93)90157-Q
[14] Stanley D J, Warne A G. Worldwide initiation of Holocene marine deltas by deceleration of sea-level rise [J]. Science, 1994, 265(5169): 228-231. doi: 10.1126/science.265.5169.228
[15] Chen Z Y, Song B P, Wang Z H, et al. Late Quaternary evolution of the sub-aqueous Yangtze Delta, China: sedimentation, stratigraphy, palynology, and deformation [J]. Marine Geology, 2000, 162(2-4): 423-441. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(99)00064-X
[16] Chen Z Y, Saito Y, Hori K, et al. Early Holocene mud-ridge formation in the Yangtze offshore, China: a tidal-controlled estuarine pattern and sea-level implications [J]. Marine Geology, 2003, 198(3-4): 245-257. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(03)00119-1
[17] Saito Y, Yang Z S, Hori K. The Huanghe (Yellow River) and Changjiang (Yangtze River) deltas: a review on their characteristics, evolution and sediment discharge during the Holocene [J]. Geomorphology, 2001, 41(2-3): 219-231. doi: 10.1016/S0169-555X(01)00118-0
[18] Hori K, Saito Y, Zhao Q H, et al. Sedimentary facies and Holocene progradation rates of the Changjiang (Yangtze) delta, China [J]. Geomorphology, 2001, 41(2-3): 233-248. doi: 10.1016/S0169-555X(01)00119-2
[19] Hori K, Saito Y, Zhao Q H, et al. Sedimentary facies of the tide-dominated paleo-Changjiang (Yangtze) estuary during the last transgression [J]. Marine Geology, 2001, 177(3-4): 331-351. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(01)00165-7
[20] Hori K, Saito Y, Zhao Q H, et al. Architecture and evolution of the tide-dominated Changjiang (Yangtze) River delta, China [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2002, 146(3-4): 249-264. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(01)00122-1
[21] Wang Z H, Chen Z Y, Chen J, et al. Seismic framework and the Holocene morphological evolution of the Changjiang River mouth, China [J]. Geomorphology, 2007, 85(3-4): 237-248. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.03.022
[22] Wang Z H, Saito Y, Zhan Q, et al. Three-dimensional evolution of the Yangtze River mouth, China during the Holocene: impacts of sea level, climate and human activity [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2018, 185: 938-955. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.08.012
[23] 陈国达. 广州三角洲问题[J]. 科学, 1934, 18(3):356-364
CHEN Guoda. Guangzhou delta problem [J]. Science, 1934, 18(3): 356-364.
[24] 吴超羽, 包芸, 任杰, 等. 珠江三角洲及河网形成演变的数值模拟和地貌动力学分析: 距今6000~2500a[J]. 海洋学报, 2006, 28(4):64-80
WU Chaoyu, BAO Yun, REN Jie, et al. A numerical simulation and mophodynamic analysis on the evolution of the Zhujiang River Delta in China: 6000~2500 a BP [J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2006, 28(4): 64-80.
[25] Heim A. Fragmentary observations in the region of Hong Kong, compared with Canton [J]. Annual Report of Geological Survey, 1929, 2: 1-32.
[26] Hubbard G D. The Pearl River delta [J]. 岭南学报, 1929, 7: 23-34.
[27] 吴尚时, 曾昭璇. 珠江三角洲[J]. 岭南学报, 1947, 8(1):105-122
WU Shangshi, ZENG Zhaoxuan. Pearl river delta [J]. Acta Lingnan, 1947, 8(1): 105-122.
[28] 黄镇国, 李平日, 张仲英, 等. 珠江三角洲形成发育演变[M]. 广州: 科学普及出版社广州分社, 1982: 1-274.
HUANG Zhenguo, LI Pingri, ZHANG Zhongying, et al. The Formation and Evolution of the Pearl River Delta[M]. Guangzhou: Science Popularization press, Guangzhou Branch, 1982: 1-274.
[29] 李平日, 乔彭年, 郑洪汉, 等. 珠江三角洲一万年来环境演变[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1991: 1-154.
LI pingri, QIAO Pengnian, ZHENG Honghan, et al. The Environment Evolution of The Zhujiang Delta in The Last 10000 Years[M]. Beijing: Ocean Press, 1991: 1-154.
[30] 赵焕庭. 珠江河口演变[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1990: 1-357.
ZHAO Huanting. Evolution of the Pearl River Estuary[M]. Beijing: Ocean Press, 1990: 1-357.
[31] 龙云作. 珠江三角洲沉积地质学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1997: 1-165.
LONG Yunzuo. Sedimentary Geology of the Pearl River Delta[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1997: 1-165.
[32] 吴超羽, 何志刚, 任杰, 等. 珠江三角洲中部子平原形成演变机理研究: 以大鳌平原为例[J]. 第四纪研究, 2007, 27(5):814-827 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2007.05.023
WU Chaoyu, HE Zhigang, REN Jie, et al. A physical study on the evolution of the sub-deltaic plains in the mid Zhujiang River Delta: a case study of DA’AO sub-delta [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2007, 27(5): 814-827. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2007.05.023
[33] 曾昭璇, 黄少敏. 珠江三角洲历史地貌学研究[M]. 广州: 广东高等教育出版社, 1987: 1-201.
ZENG Zhaoxuan, HUANG Shaomin. Historical Geomorphology of the Pearl River Delta[M]. Guangzhou: Guangdong Higher Education Press, 1987: 1-201.
[34] Zong Y, Yim W W S, Yu F, et al. Late Quaternary environmental changes in the Pearl River mouth region, China [J]. Quaternary International, 2009, 206(1-2): 35-45. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2008.10.012
[35] Zong Y, Yu F, Huang G, et al. Sedimentary evidence of Late Holocene human activity in the Pearl River delta, China [J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2010, 35(9): 1095-1102. doi: 10.1002/esp.1970
[36] Lu X X, Zhang S R, Xie S P, et al. Rapid channel incision of the lower Pearl River (China) since the 1990s as a consequence of sediment depletion [J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2007, 11(6): 1897-1906. doi: 10.5194/hess-11-1897-2007
[37] Zhang S R, Lu X X, Higgitt D L, et al. Recent changes of water discharge and sediment load in the Zhujiang (Pearl River) Basin, China [J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2008, 60(3-4): 365-380. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2007.04.003
[38] Zhang Q, Xu C Y, Chen Y D, et al. Abrupt behaviors of the streamflow of the Pearl River basin and implications for hydrological alterations across the Pearl River Delta, China [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2009, 377(3-4): 274-283. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.08.026
[39] Zhang W, Wei X Y, Zheng J H, et al. Estimating suspended sediment loads in the Pearl River Delta region using sediment rating curves [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2012, 38: 35-46. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2012.02.017
[40] Liu F, Yuan L R, Yang Q S, et al. Hydrological responses to the combined influence of diverse human activities in the Pearl River delta, China [J]. CATENA, 2014, 113: 41-55. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2013.09.003
[41] Wu C S, Yang S L, Lei Y P. Quantifying the anthropogenic and climatic impacts on water discharge and sediment load in the Pearl River (Zhujiang), China (1954-2009) [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2012(452-453): 190-204.
[42] 吴晓. 不同时间尺度黄河三角洲的演化及人类活动的影响: 从全新世到人类世[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2016.
WU Xiao. Evolution of the Yellow River Delta at different time scales and the influence of human activities: from Holocene to Anthropocene[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2016.
[43] 李小强, 安芷生, 周杰, 等. 全新世黄土高原塬区植被特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2003, 23(3):109-114
LI Xiaoqiang, AN Zhisheng, ZHOU Jie, et al. Characteristics of vegetation in the Loess Plateau area since Holocene [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2003, 23(3): 109-114.
[44] Wu X, Wang H J, Bi N S, et al. Climate and human battle for dominance over the Yellow River's sediment discharge: from the Mid-Holocene to the Anthropocene [J]. Marine Geology, 2020, 425: 106188. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2020.106188
[45] Dykoski C A, Edwards R L, Cheng H, et al. A high-resolution, absolute-dated Holocene and deglacial Asian monsoon record from Dongge Cave, China [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 233(1-2): 71-86. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2005.01.036
[46] Jian Z M, Wang P X, Saito Y, et al. Holocene variability of the Kuroshio current in the Okinawa trough, northwestern Pacific Ocean [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2000, 184(1): 305-319. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(00)00321-6
[47] Song B, Li Z, Saito Y, et al. Initiation of the Changjiang (Yangtze) delta and its response to the mid-Holocene sea level change [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2013, 388: 81-97. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2013.07.026
[48] 陈欣树, 包砺彦, 陈俊仁, 等. 珠江口外陆架晚第四纪最低海面的发现[J]. 热带海洋, 1990, 9(4):73-77
CHEN Xinshu, BAO Liyan, CHEN Junren, et al. Discovery of lowest sea level in late Quaternary at the continental shelf off Pearl river mouth [J]. Tropic Oceanology, 1990, 9(4): 73-77.
[49] 陈志清. 历史时期黄河下游的淤积、决口改道及其与人类活动的关系[J]. 地理科学进展, 2001, 20(1):44-50 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6301.2001.01.006
CHEN Zhiqing. The deposition, breach, and diversion in the lower Yellow River and their relationships with human activities during the historical period [J]. Progress in Geography, 2001, 20(1): 44-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6301.2001.01.006
[50] Wang Z H, Li M T, Zhang R H, et al. Impacts of human activity on the late-Holocene development of the subaqueous Yangtze delta, China, as shown by magnetic properties and sediment accumulation rates [J]. The Holocene, 2011, 21(3): 393-407. doi: 10.1177/0959683610378885
[51] Wang H J, Yang Z S, Saito Y, et al. Stepwise decreases of the Huanghe (Yellow River) sediment load (1950–2005): Impacts of climate change and human activities [J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2007, 57(3-4): 331-354. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2007.01.003
[52] Wu X, Bi N S, Xu J P, et al. Stepwise morphological evolution of the active Yellow River (Huanghe) delta lobe (1976–2013): Dominant roles of riverine discharge and sediment grain size [J]. Geomorphology, 2017, 292: 115-127. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2017.04.042
[53] Wu X, Bi N S, Syvitski J, et al. Can reservoir regulation along the Yellow River be a sustainable way to save a sinking delta? [J]. Earth’s Future, 2020, 8(11): e2020EF001587. doi: 10.1029/2020EF001587
[54] 吴晓, 范勇勇, 王厚杰, 等. 黄河下游与河口对2015-2017年调水调沙中断的沉积响应[J]. 科学通报, 2021, 66:1-12
Wu Xiao, Fan Yongyong, Wang Houjie, et al. Geomorphological responses of the lower river channel and delta to interruption of reservoir regulation in the Yellow River, 2015–2017 [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2021, 66: 1-12.
[55] 黎兵, 严学新, 何中发, 等. 长江口水下地形演变对三峡水库蓄水的响应[J]. 科学通报, 2015, 60(18):1735-1744 doi: 10.1360/N972014-01074
LI Bing, YAN Xuexin, HE Zhongfa, et al. Impacts of the Three Gorges Dam on the bathymetric evolution of the Yangtze River Estuary [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2015, 60(18): 1735-1744. doi: 10.1360/N972014-01074
[56] Yang S L, Milliman J D, Li P, et al. 50, 000 dams later: erosion of the Yangtze River and its delta [J]. Global and Planetary Chang, 2011, 75(1-2): 14-20. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2010.09.006
[57] Yang S L, Milliman J D, Xu K H, et al. Downstream sedimentary and geomorphic impacts of the Three Gorges Dam on the Yangtze River [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2014, 138: 469-486. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.07.006
[58] Lu X X, Higgitt D L. Recent changes of sediment yield in the upper Yangtze, China [J]. Environmental Management, 1998, 22(5): 697-709. doi: 10.1007/s002679900140
[59] Dai Z J, Liu J T, Wei W, et al. Detection of the Three Gorges Dam influence on the Changjiang (Yangtze River) submerged delta [J]. Scientific Report, 2014, 4(1): 6600.
[60] Du J L, Yang S L, Feng H. Recent human impacts on the morphological evolution of the Yangtze River delta foreland: a review and new perspectives [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2016, 181: 160-169. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2016.08.025
[61] 胡刚, 沈焕庭, 庄克琳, 等. 长江河口岸滩侵蚀演变模式[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2007, 27(1):13-21
HU Gang, SHEN Huanting, ZHUANG Kelin, et al. Evolution pattern of coastal erosion in the Yangtze River estuary [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2007, 27(1): 13-21.
-



 下载:
下载: