-
摘要:
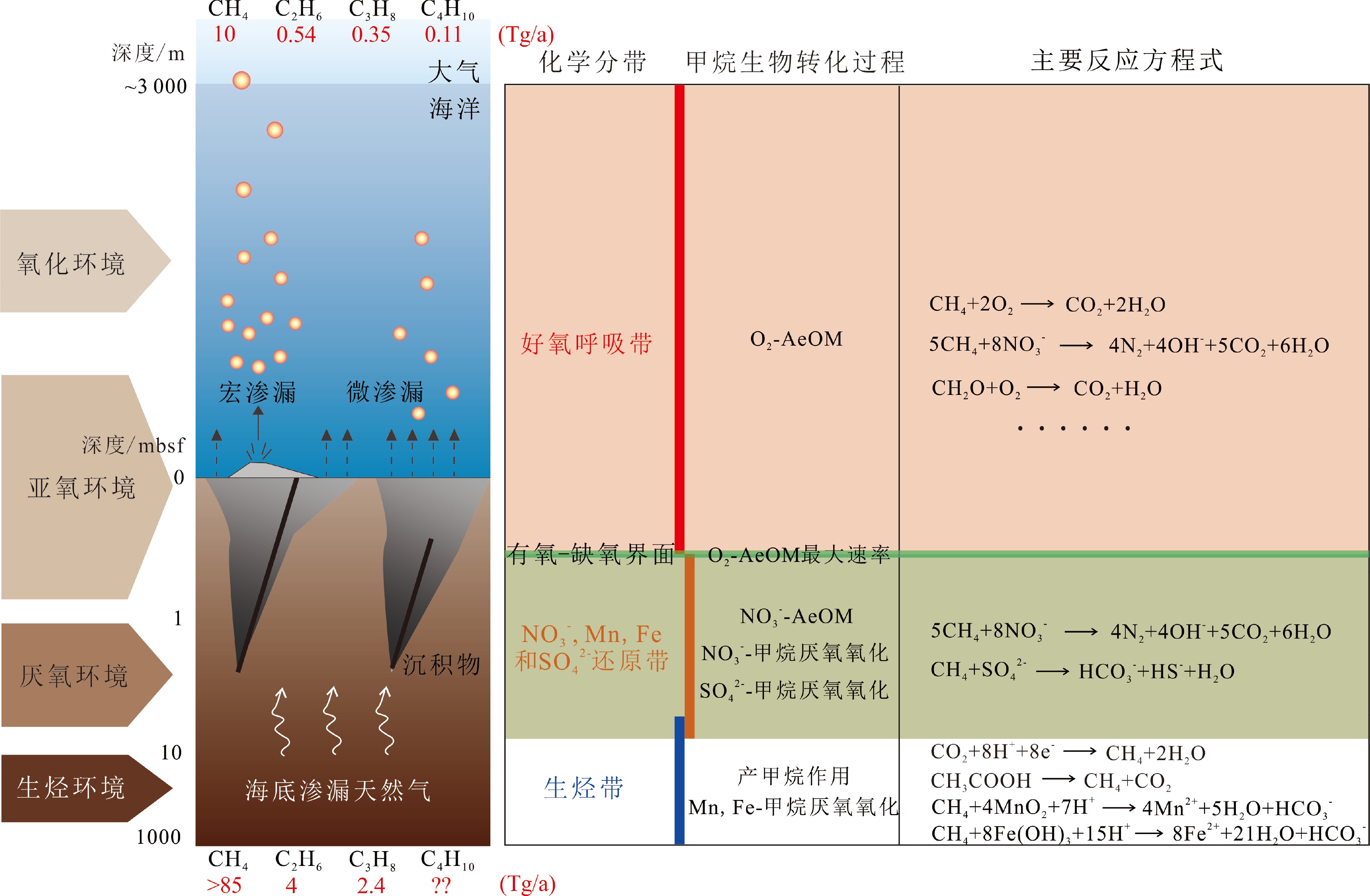
海洋环境中微生物驱动的甲烷好氧氧化作用是甲烷迁移转化过程的关键环节之一,在降解甲烷方面的贡献不容忽视,能够有效降低甲烷大气通量、影响海洋碳循环。本文系统调研了国内外文献资料,认识到海洋环境中甲烷好氧氧化的赋存范围十分广泛,可赋存于超过3 000 m水深的深海环境、热液喷口等极端环境,其中海底高压、渗漏甲烷的动态运移等是甲烷好氧氧化所面临的特殊环境,在该赋存环境下,好氧甲烷氧化菌主要以I型氧化菌为主。I型与II型氧化菌对甲烷、微量金属元素等环境条件具有一定偏向性,并且在水体和沉积物两种赋存环境下氧化菌的类型也不尽相同。同时,在该赋存环境下甲烷好氧氧化强度存在时间或空间上的差异,受温度、甲烷浓度、氧浓度、微量金属元素等环境因子影响显著,但目前对压力以及甲烷渗漏运移状态对好氧氧化过程的影响规律认识不清。随着深海科研探索不断发展,甲烷氧化菌菌群多样性研究将更加丰富。此外,还需进一步针对海底高压渗漏状态下的好氧氧化过程开展精细研究工作,进一步理解海洋环境中甲烷的好氧氧化规律,这对深刻揭示甲烷迁移转化机制、科学评估甲烷生态环境效应具有重要意义。
Abstract:The aerobic oxidation of methane driven by methanotrophs is a key process for methane migration and transformation in marine environment. Its contribution to the degradation of methane should not be ignored because it may effectively reduce methane flux to the atmosphere and affect the carbon cycle in the sea. In this paper, a large number of domestic and foreign literatures are systematically investigated, from which it is found that the aerobic oxidation of methane occurs widely in marine environment. It may even occur in some extreme environments with very high pressure and dynamic migration of methane seepage, such as the deep sea and hydrothermal vents at depths of more than 3 000 m. In these environments, methanotrophs are mainly predominated by the type I of oxidizing bacteria. Meanwhile, the type I and type II of oxidizing bacteria have a certain bias to environmental conditions such as methane and trace metal elements, and the types of oxidizing bacteria are also different in water and sediment. At the same time, temporal and spatial differences occur in the aerobic oxidation intensity of methane, which is significantly affected by such environmental factors as temperature, methane concentration, oxygen concentration and trace metal elements. However, the influence of pressure and methane seepage on aerobic oxidation is not so clear up to date. Further research and exploration are required so as to enrich the knowledge on diversity of methane-oxidizing bacteria and improve the understanding of their physiological and ecological characteristics. In addition, it is a need to carry out detailed research on the aerobic oxidation process under the condition of submarine high-pressure leakage, in order to better understand the oxidation process of the environment. It would be of great significance to the revealing of the mechanism of methane migration and transformation and evaluation of its ecological and environmental effects.
-

-
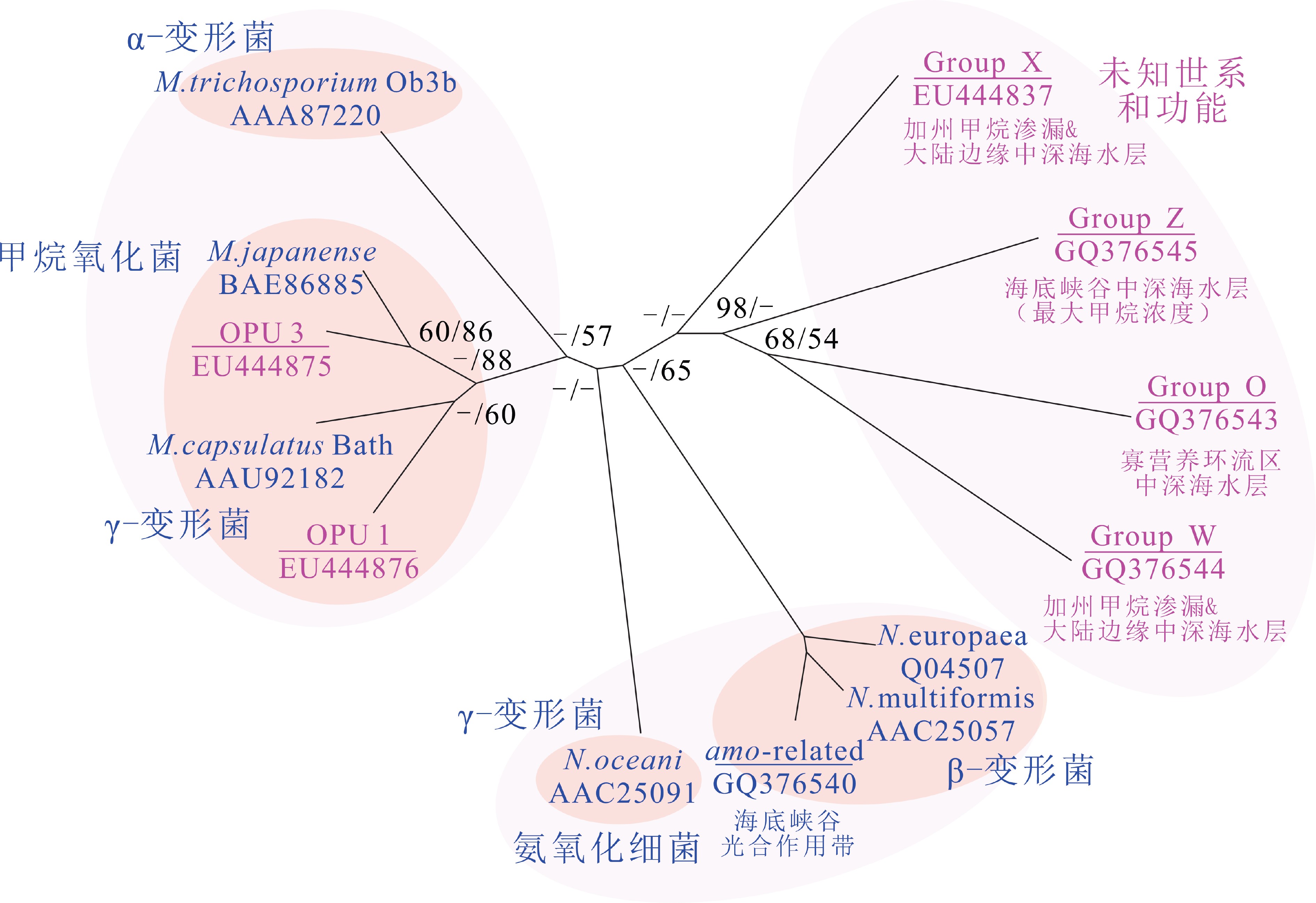
图 2 海洋水体中的MOB新菌种OPU1、OPU3和Group-X菌群系统发育树[47]
Figure 2.
表 1 由野外监测及室内培养方式获取的海洋甲烷好氧氧化速率数据统计
Table 1. Statistics of marine aerobic methane oxidation rates obtained by field investigation and laboratory culture experiment
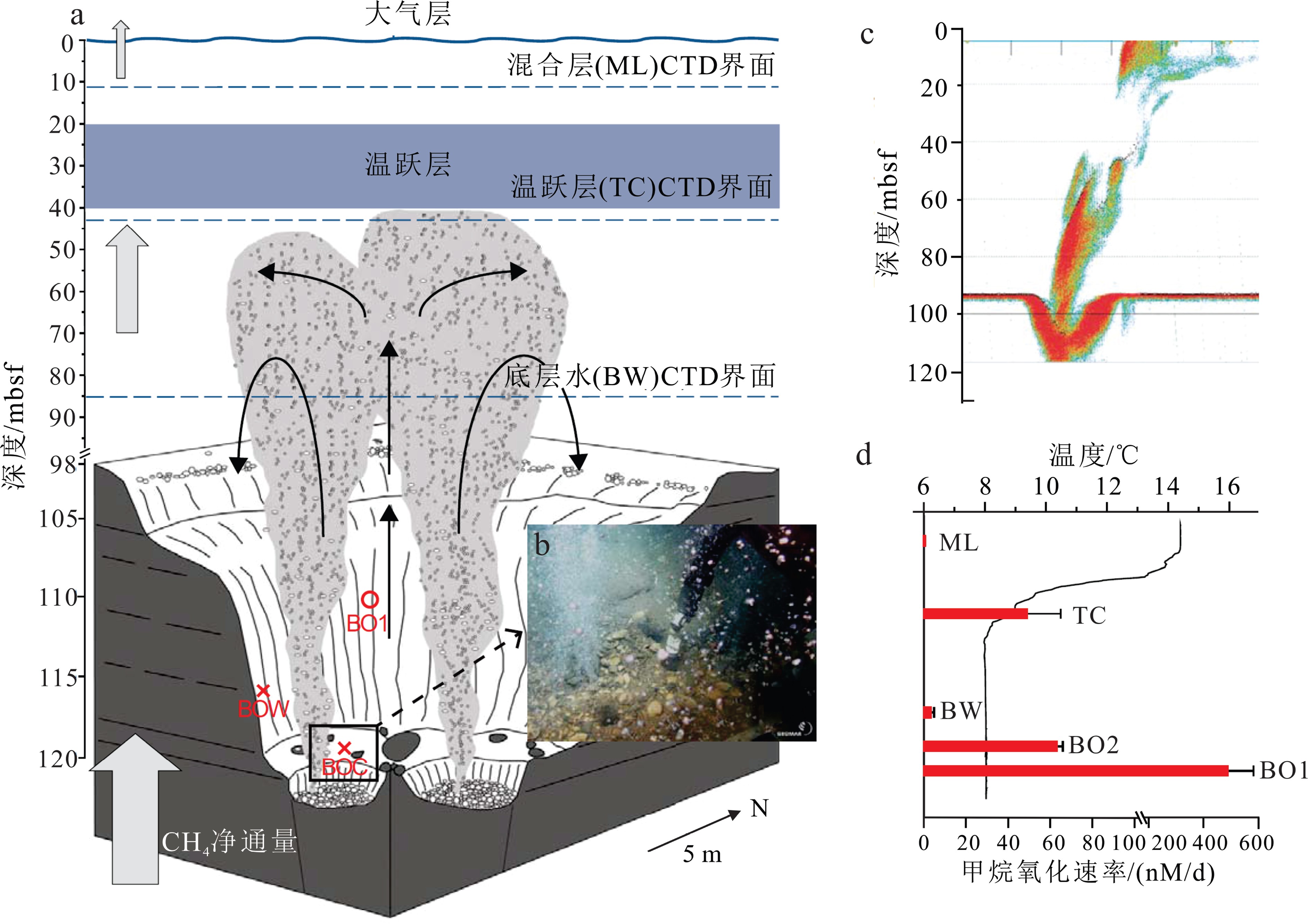
位置 水深/m CH4浓度/nM 好氧氧化速率/(nM/d) 文献来源 野外监测数据 正常海水背景 − 0.5~5 0.0001~0.1 [49, 57] Håkon Mosby泥火山 1250 >104 22×103~36×103 [58] 墨西哥湾GC185 50~530 2.4~274 0.0028~0.7 [47] REGAB麻坑 3160 200~3 600 6×103~289×103 [9] Amon泥火山 1120 2×106 13×103~30×103 [27] 墨西哥湾Macondo油井 0~2 000 0~1.8×105 0.014~5 900 [49] 斯瓦尔巴特大陆边缘 0~380 9~100 <3.2 [59] 北海北部某井喷 98 5~42 097 0.03~498 [32] 哈德逊峡谷 350~532 5.72~96.6 22.8±17 [11] 实验测试数据 墨西哥湾Macondo油井 ~1 000 570~18 300 0~820 [60] 圣芭芭拉盆地 530~2 600 4~242 0.6~491 [57] 圣芭芭拉海峡煤油富集区 5~70 <1 900 0.01~100 [61] 斯图尔峡湾 0~160 20~72.3 <2.3 [62] 北海 − 300 20 [52] -
[1] Emerson S, Hedges J. Chemical oceanography and the marine carbon cycle [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2008, 131(6): 2417-2418.
[2] Knittel K, Boetius A. Anaerobic oxidation of methane: progress with an unknown process [J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 2009, 63(1): 311-334. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.61.080706.093130
[3] Judd A G, Hovland M, Dimitrov L I, et al. The geological methane budget at continental margins and its influence on climate change [J]. Geofluids, 2002, 2(2): 109-126. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-8123.2002.00027.x
[4] Wang Y Z, Wegener G, Hou J L, et al. Expanding anaerobic alkane metabolism in the domain of Archaea [J]. Nature Microbiology, 2019, 4(4): 595-602. doi: 10.1038/s41564-019-0364-2
[5] 冯东, 陈多福, 苏正, 等. 海底天然气渗漏系统微生物作用及冷泉碳酸盐岩的特征[J]. 现代地质, 2005, 19(1):26-32 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2005.01.004
FENG Dong, CHEN Duofu, SU Zheng, et al. Characteristics of cold seep carbonates and microbial processes in gas seep system [J]. Geoscience, 2005, 19(1): 26-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2005.01.004
[6] 王风平, 陈云如. 深部生物圈研究进展与展望[J]. 地球科学进展, 2017, 32(12):1277-1286 doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2017.12.1277
WANG Fengping, CHEN Yunru. Progress and prospect in deep biosphere investigation [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2017, 32(12): 1277-1286. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2017.12.1277
[7] Boetius A, Wenzhöfer F. Seafloor oxygen consumption fuelled by methane from cold seeps [J]. Nature Geoscience, 2013, 6(9): 725-734. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1926
[8] Okita N, Hoaki T, Suzuki S, et al. Characteristics of microbial community structure at the seafloor surface of the nankai trough [J]. Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology, 2019, 13(4): 1917-1928. doi: 10.22207/JPAM.13.4.04
[9] Ristova P P, Wenzhöfer F, Ramette A, et al. Bacterial diversity and biogeochemistry of different chemosynthetic habitats of the REGAB cold seep (West African margin, 3160 m water depth) [J]. Biogeosciences, 2012, 9(12): 5031-5048. doi: 10.5194/bg-9-5031-2012
[10] Carere C R, McDonald B, Peach H A, et al. Hydrogen oxidation influences glycogen accumulation in a verrucomicrobial methanotroph [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2019, 10: 1873. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01873
[11] Leonte M, Kessler J D, Kellermann M Y, et al. Rapid rates of aerobic methane oxidation at the feather edge of gas hydrate stability in the waters of Hudson Canyon, US Atlantic Margin [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2017, 204: 375-387. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2017.01.009
[12] Tavormina P L, Hatzenpichler R, McGlynn S, et al. Methyloprofundus sedimenti gen. nov., sp. nov., an obligate methanotroph from ocean sediment belonging to the 'deep sea-1' clade of marine methanotrophs [J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2015, 65(1): 251-259.
[13] Ketzer M, Praeg D, Pivel M A G, et al. Gas seeps at the edge of the gas hydrate stability zone on Brazil's continental margin [J]. Geosciences, 2019, 9(5): 193. doi: 10.3390/geosciences9050193
[14] 薛明, 翁艺斌, 刘光全, 等. 石油与天然气生产过程甲烷逃逸排放检测与核算研究现状及建议[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15(2):187-196 doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2018.118
XUE Ming, WENG Yibin, LIU Guangquan, et al. Current status on fugitive methane emission measurements and inventory during oil and gas production [J]. Climate Change Research, 2019, 15(2): 187-196. doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2018.118
[15] Jørgensen B B, Kasten S. Sulfur cycling and methane oxidation[M]//Schulz H D, Zabel M. Marine Geochemistry. Berlin-Heidelberg: Springer, 2006: 271-309.
[16] Etiope G. Natural gas Seepage[M]. Cham: Springer, 2015.
[17] Mendes S D. Microbial oxidation of marine hydrocarbons: quantifying rates of methane, ethane, propane, and butane consumption[D]. Doctor Dissertation of University of California, 2015.
[18] Padilla C C, Bristow L A, Sarode N, et al. NC10 bacteria in marine oxygen minimum zones [J]. The ISME Journal, 2016, 10(8): 2067-2071. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2015.262
[19] 段晓勇, 印萍, 刘金庆, 等. 中国东部近海现代沉积环境[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2019, 39(2):14-20
DUAN Xiaoyong, YIN Ping, LIU Jinqing, et al. Modern sedimentation environments in the coastal zone of East China [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2019, 39(2): 14-20.
[20] Svensen H, Planke S, Malthe-Sørenssen A, et al. Release of methane from a volcanic basin as a mechanism for initial Eocene global warming [J]. Nature, 2004, 429(6991): 542-545. doi: 10.1038/nature02566
[21] 吴能友, 黄丽, 胡高伟, 等. 海域天然气水合物开采的地质控制因素和科学挑战[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(5):1-11
WU Nengyou, HUANG Li, HU Gaowei, et al. Geological controlling factors and scientific challenges for offshore gas hydrate exploitation [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(5): 1-11.
[22] Feng D, Qiu J W, Hu Y, et al. Cold seep systems in the South China Sea: An overview [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 168: 3-16. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.09.021
[23] 曾志刚, 陈祖兴, 张玉祥, 等. 海底热液活动的环境与产物[J]. 海洋科学, 2020, 44(7):143-155 doi: 10.11759/hykx20200316001
ZENG Zhigang, CHEN Zuxing, ZHANG Yuxiang, et al. Seafloor hydrothermal activities and their geological envi-ronments and products [J]. Marine Sciences, 2020, 44(7): 143-155. doi: 10.11759/hykx20200316001
[24] 贺行良, 谭丽菊, 段晓勇, 等. 杭州湾沉积物中硫酸盐-甲烷转换带内的碳循环[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(3):51-60
HE Xinglianig, TAN Liju, DUAN Xiaoyong, et al. Carbon cycle within the sulfate-methane transition zone in the marine sediments of Hangzhou Bay [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(3): 51-60.
[25] Giovannelli D, D'errico G, Fiorentino F, et al. Diversity and distribution of prokaryotes within a shallow-water pockmark field [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2016, 7: 941.
[26] Grünke S, Felden J, Lichtschlag A, et al. Niche differentiation among mat-forming, sulfide-oxidizing bacteria at cold seeps of the Nile Deep Sea Fan (Eastern Mediterranean Sea) [J]. Geobiology, 2011, 9(4): 330-348. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-4669.2011.00281.x
[27] Felden J, Lichtschlag A, Wenzhöfer F, et al. Limitations of microbial hydrocarbon degradation at the Amon mud volcano (Nile deep-sea fan) [J]. Biogeosciences, 2013, 10(5): 3269-3283. doi: 10.5194/bg-10-3269-2013
[28] Meng L, Jain S, Baker B J, et al. Novel hydrocarbon monooxygenase genes in the metatranscriptome of a natural deep-sea hydrocarbon plume [J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2014, 16(1): 60-71. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.12182
[29] Talbot H M, Handley L, Spencer-Jones C L, et al. Variability in aerobic methane oxidation over the past 1.2 Myrs recorded in microbial biomarker signatures from Congo fan sediments [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2014, 133: 387-401. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2014.02.035
[30] Røy H, Kallmeyer J, Adhikari R R, et al. Aerobic microbial respiration in 86-million-year-old deep-sea red clay [J]. Science, 2012, 336(6083): 922-925. doi: 10.1126/science.1219424
[31] Wasmund K, Kurtböke D I, Burns K A, et al. Microbial diversity in sediments associated with a shallow methane seep in the tropical Timor Sea of Australia reveals a novel aerobic methanotroph diversity [J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2009, 68(2): 142-151. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2009.00667.x
[32] Steinle L, Schmidt M, Bryant L, et al. Linked sediment and water-column methanotrophy at a man-made gas blowout in the North Sea: Implications for methane budgeting in seasonally stratified shallow seas [J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2016, 61(S1): S367-S386. doi: 10.1002/lno.10388
[33] 吴能友, 孙治雷, 卢建国, 等. 冲绳海槽海底冷泉-热液系统相互作用[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2019, 39(5):23-35
WU Nengyou, SUN Zhilei, LU Jianguo, et al. Interaction between seafloor cold seeps and adjacent hydrothermal activities in the Okinawa Trough [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2019, 39(5): 23-35.
[34] Skennerton C T, Ward L M, Michel A, et al. Genomic reconstruction of an uncultured hydrothermal vent gammaproteobacterial methanotroph (family methylothermaceae) indicates multiple adaptations to oxygen limitation [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2015, 6: 1425.
[35] 郭莹莹, 陈坚, 尹希杰, 等. 九龙江河口表层水体及沉积物中甲烷的分布和环境控制因素研究[J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(2):558-564
GUO Yingying, CHEN Jian, YIN Xijie, et al. Spatial distribution of methane in surface water and sediment of Jiulongjiang estuary and the effect environment factors of it [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Science, 2012, 33(2): 558-564.
[36] Horita J, Berndt M E, et al. Abiogenic methane formation and isotopic fractionation under hydrothermal conditions [J]. Science, 1999, 285(5430): 1055-1057. doi: 10.1126/science.285.5430.1055
[37] 赵广涛, 徐翠玲, 张晓东, 等. 海底沉积物-水界面溶解甲烷渗漏通量原位观测研究进展[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2014, 44(12):73-81
ZHAO Guangtao, XU Cuiling, ZHANG Xiaodong, et al. Research progress in in-situ observations of dissolved methane seepage fluxed across the water-sediment interface [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2014, 44(12): 73-81.
[38] Sommer S, Pfannkuche O, Linke P, et al. Efficiency of the benthic filter: biological control of the emission of dissolved methane from sediments containing shallow gas hydrates at Hydrate Ridge [J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2006, 20(2): GB2019.
[39] 陈多福, 冯东, 陈光谦, 等. 海底天然气渗漏系统演化特征及对形成水合物的影响[J]. 沉积学报, 2005, 23(2):323-328 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2005.02.020
CHEN Duofu, FENG Dong, CHEN Guangqian, et al. Evolution of marine gas venting system and impact on gas hydrate crystallization [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2005, 23(2): 323-328. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2005.02.020
[40] Roberts H H. Fluid and gas expulsion on the northern gulf of mexico continental slope: mud-prone to mineral-prone responses[M]//Paull C K, Dillon W P. Natural Gas Hydrates: Occurrence, Distribution, and Detection: Occurrence, Distribution, and Detection. Washington, DC, USA: American Geophysical Union, 2013.
[41] Bowman J P. The methanotrophs-the families methylococcaceae and methylocystaceae[M]//Dworkin M, Falkow S, Rosenberg E, et al. The Prokaryotes. New York: Springer, 2006: 266-289.
[42] Yu W J, Lee J W, Nguyen N L, et al. The characteristics and comparative analysis of methanotrophs reveal genomic insights into Methylomicrobium sp. enriched from marine sediments [J]. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 2018, 41(5): 415-426. doi: 10.1016/j.syapm.2018.05.004
[43] Ruff S E, Felden J, Gruber-Vodicka H R, et al. In situ development of a methanotrophic microbiome in deep-sea sediments [J]. The ISME Journal, 2019, 13(1): 197-213. doi: 10.1038/s41396-018-0263-1
[44] Vekeman B, Kerckhof F M, Cremers G, et al. New Methyloceanibacter diversity from North Sea sediments includes methanotroph containing solely the soluble methane monooxygenase [J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2016, 18(12): 4523-4536. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.13485
[45] Hakobyan A, Liesack W. Unexpected metabolic versatility among type II methanotrophs in the Alphaproteobacteria [J]. Biological Chemistry, 2020, 401(12): 1469-1477. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2020-0200
[46] Martins P D, Jong A D, Lenstra W K, et al. Enrichment of novel Verrucomicrobia, Bacteroidetes and Krumholzibacteria in an oxygen-limited, methane- and iron-fed bioreactor inoculated with Bothnian Sea sediments[Z]. 2020, doi: 10.1101/2020.09.22.307553.
[47] Tavormina P L, Ussler W, Joye S B, et al. Distributions of putative aerobic methanotrophs in diverse pelagic marine environments [J]. The ISME Journal, 2010, 4(5): 700-710. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2009.155
[48] Takeuchi M, Katayama T, Yamagishi T, et al. Methyloceanibacter caenitepidi gen. nov., sp. nov., a facultatively methylotrophic bacterium isolated from marine sediments near a hydrothermal vent [J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2014, 64(2): 462-468.
[49] Crespo-Medina M, Meile C D, Hunter K S, et al. The rise and fall of methanotrophy following a deepwater oil-well blowout [J]. Nature Geoscience, 2014, 7(6): 423-427. doi: 10.1038/ngeo2156
[50] Kessler J D, Valentine D L, Redmond M C, et al. A persistent oxygen anomaly reveals the fate of spilled methane in the deep gulf of Mexico [J]. Science, 2011, 331(6015): 312-315. doi: 10.1126/science.1199697
[51] Zhang Y, Maignien L, Zhao X X, et al. Enrichment of a microbial community performing anaerobic oxidation of methane in a continuous high-pressure bioreactor [J]. BMC Microbiology, 2011, 11: 137. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-11-137
[52] Bussmann I, Matousu A, Osudar R, et al. Assessment of the radio 3H-CH4 tracer technique to measure aerobic methane oxidation in the water column [J]. Limnology and Oceanography: Methods, 2015, 13(6): 312-327. doi: 10.1002/lom3.10027
[53] Li J, Liu C L, He X L, et al. Aerobic microbial oxidation of hydrocarbon gases: Implications for oil and gas exploration [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 103: 76-86. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.02.013
[54] Lopes F, Viollier E, Thiam A, et al. Biogeochemical modelling of anaerobic vs. aerobic methane oxidation in a meromictic crater lake (Lake Pavin, France) [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2011, 26(12): 1919-1932. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2011.06.021
[55] Yao Y J, Su Y, Wu Y, et al. An analytical model for estimating the reduction of methane emission through landfill cover soils by methane oxidation [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 283: 871-879. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.10.035
[56] Reeburgh W S. Oceanic methane biogeochemistry [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2007, 107(2): 486-513. doi: 10.1021/cr050362v
[57] Heintz M B, Mau S, Valentine D L. Physical control on methanotrophic potential in waters of the Santa Monica Basin, Southern California [J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2012, 57(2): 420-432. doi: 10.4319/lo.2012.57.2.0420
[58] Felden J, Wenzhöfer F, Feseker T, et al. Transport and consumption of oxygen and methane in different habitats of the Håkon Mosby Mud Volcano (HMMV) [J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2010, 55(6): 2366-2380. doi: 10.4319/lo.2010.55.6.2366
[59] Graves C A, Steinle L, Rehder G, et al. Fluxes and fate of dissolved methane released at the seafloor at the landward limit of the gas hydrate stability zone offshore western Svalbard [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2015, 120(9): 6185-6201. doi: 10.1002/2015JC011084
[60] Valentine D L, Kessler J D, Redmond M C, et al. Propane respiration jump-starts microbial response to a deep oil spill [J]. Science, 2010, 330(6001): 208-211. doi: 10.1126/science.1196830
[61] Mau S, Heintz M B, Valentine D L. Quantification of CH4 loss and transport in dissolved plumes of the Santa Barbara Channel, California [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2012, 32: 110-120. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2011.10.016
[62] Mau S, Blees J, Helmke E, et al. Vertical distribution of methane oxidation and methanotrophic response to elevated methane concentrations in stratified waters of the Arctic fjord Storfjorden (Svalbard, Norway) [J]. Biogeosciences, 2013, 10(10): 6267-6278. doi: 10.5194/bg-10-6267-2013
[63] 张瑞林, 任学清. 不同压力及氧环境条件下微生物降解煤层瓦斯实验研究[J]. 煤矿安全, 2014, 45(11):1-4
ZHANG Ruilin, REN Xueqing. Experimental study on coal seam gas degradation by microorganism under different pressure and oxygen environment conditions [J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2014, 45(11): 1-4.
[64] Case D H, Ijiri A, Morono Y, et al. Aerobic and anaerobic methanotrophic communities associated with methane hydrates exposed on the seafloor: a high-pressure sampling and stable isotope-incubation experiment [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2017, 8: 2569. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02569
[65] 张鑫. 深海环境及深海沉积物拉曼光谱原位定量探测技术研究: 深海沉积物孔隙水及天然气水合物原位定量探测新方法[D]. 中国海洋大学博士学位论文, 2009.
ZHANG Xin. Quantitative applications of Raman technique for deep-sea environment and sediment detection: New tecinque for deep-sea sediment pore water and methane hydrates in situ detection[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2009.
[66] 马立杰, 崔迎春. 南海中部和北部上层海水中溶存甲烷浓度及海气交换通量[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2013, 32(2):94-101
MA Lijie, CUI Yingchun. Dissolved methane concentration and sea-to-air transfer flux of dissolved methane in the upper seawater of the central and northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2013, 32(2): 94-101.
[67] Zhang Y, Henriet J P, Bursens J, et al. Stimulation of in vitro anaerobic oxidation of methane rate in a continuous high-pressure bioreactor [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101(9): 3132-3138. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.11.103
[68] Wegener G, Boetius A. An experimental study on short-term changes in the anaerobic oxidation of methane in response to varying methane and sulfate fluxes [J]. Biogeosciences, 2009, 6(5): 867-876. doi: 10.5194/bg-6-867-2009
[69] Valentine D L. Emerging topics in marine methane biogeochemistry [J]. Annual Review of Marine Science, 2011, 3: 147-171. doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-120709-142734
[70] Chan E W, Shiller A M, Joung D J, et al. Investigations of aerobic methane oxidation in two marine seep environments: Part 2—isotopic kinetics [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2019, 124(11): 8392-8399. doi: 10.1029/2019JC015603
[71] Kim I T, Lee Y E, Yoo Y S, et al. Development of a combined aerobic–anoxic and methane oxidation bioreactor system using mixed methanotrophs and biogas for wastewater denitrification [J]. Water, 2019, 11(7): 1377. doi: 10.3390/w11071377
-

| 引用本文: | 李晶, 刘昌岭, 吴能友, 贺行良, 孟庆国, 许晓晴, 陈烨. 海洋环境中甲烷好氧氧化过程的研究进展[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2021, 41(5): 67-76. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2020112302 |
| Citation: | LI Jing, LIU Changling, WU Nengyou, HE Xingliang, MENG Qingguo, XU Xiaoqing, CHEN Ye. A review on microbial aerobic methane oxidation in marine environment[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2021, 41(5): 67-76. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2020112302 |


 下载:
下载: