Stratigraphic classification and sedimentary evolution of the late Neogene to Quaternary sequence on the Central Uplift of the South Yellow Sea
-
摘要:
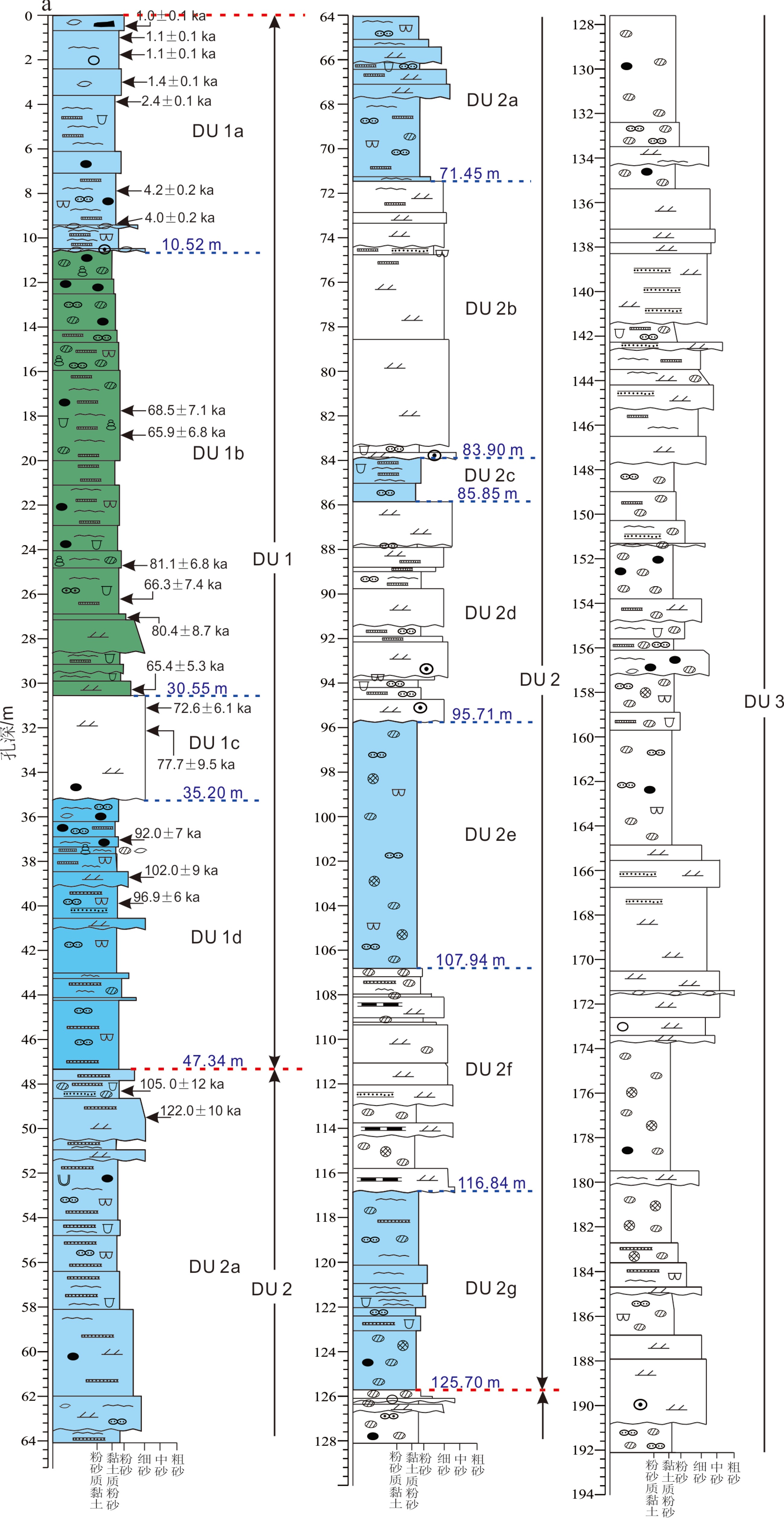
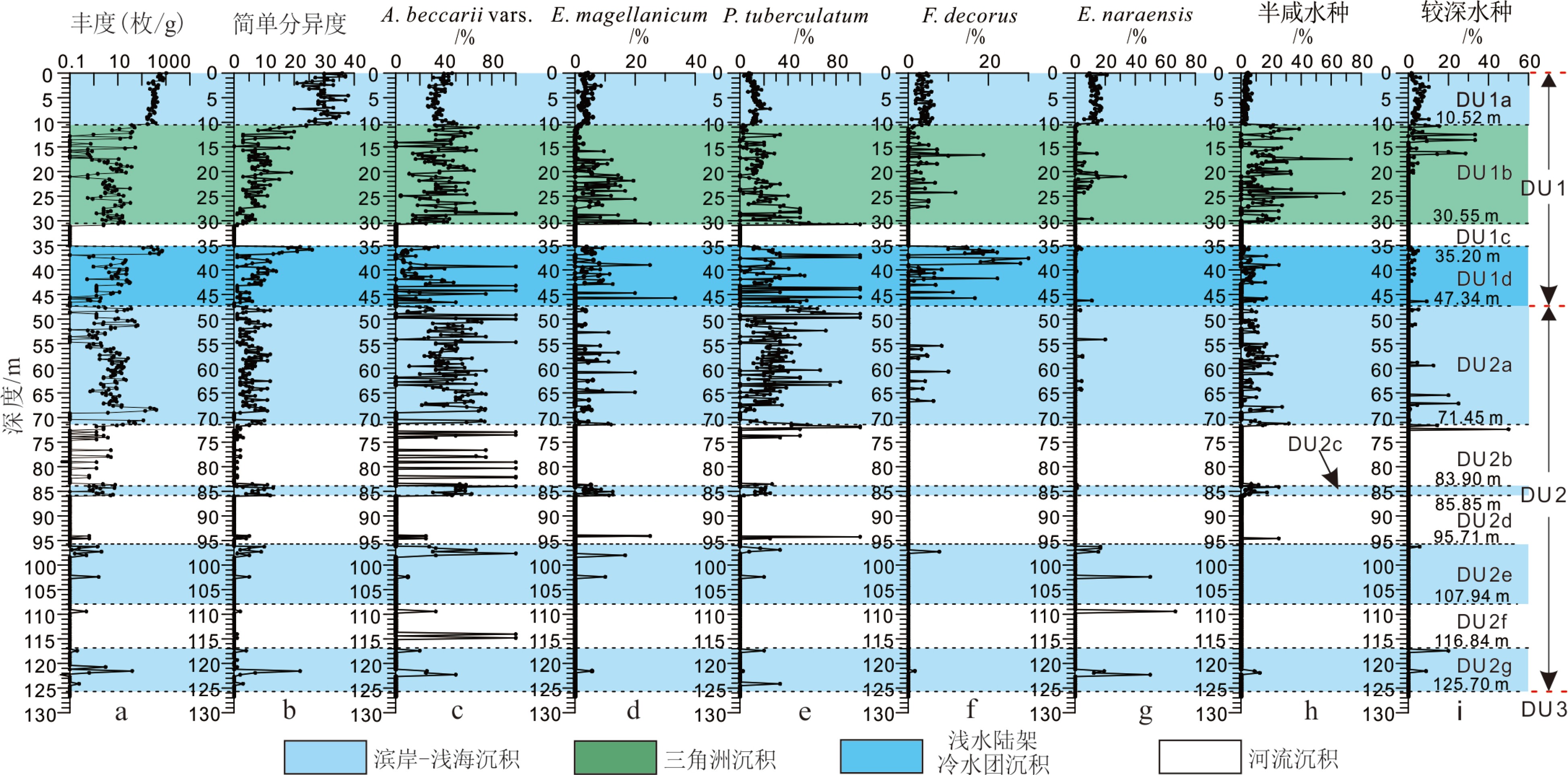
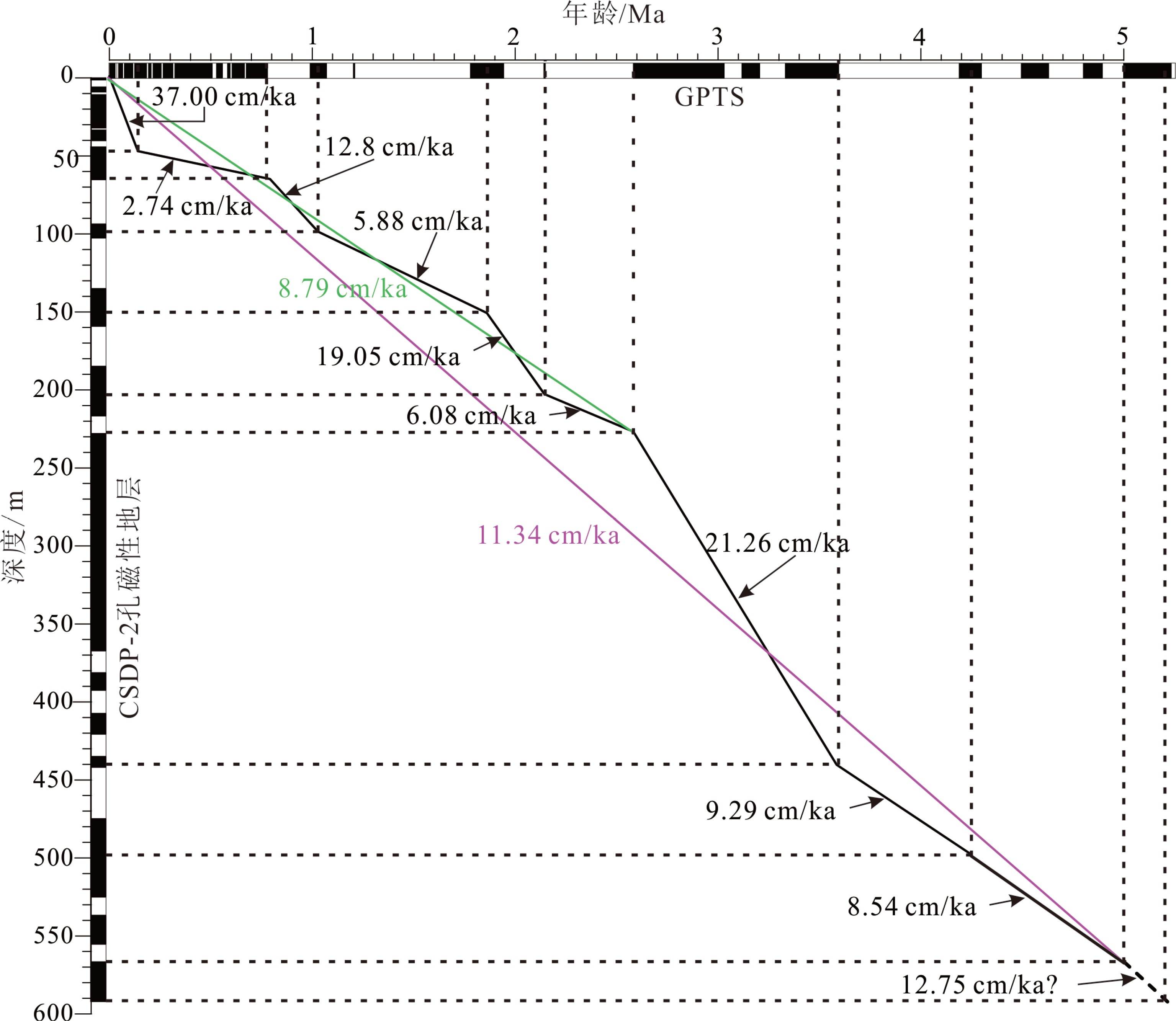
CSDP-2孔位于南黄海中部隆起,其孔深超过2800 m。该孔中下部中—古生代的固结成岩地层已被深入研究,但其最上部592 m未固结成岩的沉积序列尚未有研究报道。为了确定这部分沉积序列的地层划分,揭示其沉积演化历史,我们对其开展了古地磁测试、光释光测年、底栖有孔虫鉴定和沉积相分析,并与南黄海及其邻近海岸地区以往钻孔岩心分析成果进行对比研究。结果表明,CSDP-2孔0~592.00 m沉积序列最初形成于约5.2 Ma,其第四系底界位于孔深约227.91 m(年龄为2.59 Ma),下/中更新统界线位于孔深约65.23 m(年龄为0.78 Ma),中/上更新统界线位于孔深47.34 m(年龄约128 ka);自晚更新世以来形成的地层又可划分出MIS 5、MIS 4、MIS 3和MIS 1的沉积层段, MIS 2沉积缺失。南黄海中部隆起区在新近纪的剥蚀止于约5.2 Ma,从约5.2 Ma至约1.7 Ma发育河流沉积;由于浙闽隆起的逐渐沉降,约1.7 Ma发生自新生代以来的首次海侵,直至约0.83 Ma,发育潮坪—滨岸沉积与河流沉积的互层;从约0.83 Ma开始至今,浙闽隆起进一步沉降使得南黄海中部隆起区在间冰期高海平面时期的海洋环境基本接近现今环境;南黄海西部陆架在MIS 5发育范围比现今更广的冷水团沉积,在MIS 4、MIS 3早期、MIS 3晚期至MIS 2和MIS1分别依次发育河流、三角洲、河流和滨岸—内陆架环境。该沉积序列主要受控于区域构造沉降和海平面变化,其全新统、更新统及整个地层序列的沉积速率呈现依次明显下降的趋势,主要归因于地层时代越老其连续性越差,特别是晚更新世之前的地层有显著侵蚀的现象。本文的研究成果为深入理解南黄海西部陆架区晚新近纪以来的沉积环境演化进程和沉积地层的形成机制提供了新证据。
Abstract:The Core of CSDP-2, which is more than 2800 m long, was retrieved from the Central Uplift of the South Yellow Sea, of which the Mesozoic-Paleozoic strata of the core have become a hot topic under research. However, research results of the uppermost sequence, 592 m in thickness made up of unconsolidated loose sediments, have not yet been reported so far. We have carried out paleomagnetic measurements, optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) dating, identification of benthic foraminifera and analyses of sedimentary facies for the sequence, in order to make its stratigraphic classification and reveal its history of sedimentary evolution. The results indicate that the 592 m- thick sequence came into being about 5.2 Ma, with its Quaternary bottom boundary at ~227.91 m of 2.59 Ma, the Lower and Middle Pleistocene boundary at ~65.23 m of 0.78 Ma, and the Middle - Upper Pleistocene boundary at 47.34 m of 128 ka, and covered by the Upper Pleistocene, which could be further subdivided into several sedimentary intervals formed during MIS 5, MIS 4, MIS 3 and MIS 1, while the MIS 2 deposits are missing. Also the results demonstrate that the denudation took place on the Central Uplift during Neogene and came to an end at ~5.2 Ma, followed by the deposition of fluvial deposits from ~5.2 to ~1.7 Ma, which was ceased as the first marine transgression took place in the region since Cenozoic presumably due to subsidence of the Zhe-Min Uplift. From ~1.7 to ~0.83 Ma, there was an alternation of tidal-flat and coastal deposits, and then from ~0.83 to the present the marine environments during high sea-level stands of the interglacial times were close to the marine environment of today in the region, due to the further subsidence of the Zhe-Min Uplift. On the western shelf of the South Yellow Sea, there was a cold water mass during MIS 5, which is broader than that of nowadays, and fluvial, deltaic, fluvial and coastal to inner-shelf environments prevailed successively during MIS 4, early MIS 3, late MIS 3 to MIS 2, and MIS 1. The sedimentary sequence was primarily controlled by tectonic subsidence and sea-level changes, and the sedimentation rates decreased evidently from the Holocene deposits to the Pleistocene and to the whole sequence, owing to the incompleteness of the older sediments comparing to the younger ones. Especially the pre-Late Pleistocene strata are marked by distinct erosion. The results of this study have provided new evidence for better understanding the evolution of sedimentary environments and the formation mechanism of strata in the western South Yellow Sea shelf since late Neogene.
-

-
表 1 本文涉及的南黄海海岸带-陆架区钻孔信息
Table 1. Details of the sediment cores in the coastal to shelf areas of the South Yellow sea as described in this paper
钻孔编号 位置 水深/m 孔深/m 资料来源 CSDP-2 34°33′18.9″N、121°15′41″E 22.00 2809.88 本文 CSDP-1 34°18′10.7730″N、122°22′0.4896″E 52.50 300.10 [7] QC2 34°18′N、122°16′E 49.05 108.83 [22] SYS-0701 34°39.7535′N、121°27.0000′E 33.00 70.20 [23] SYS-0702 34°18.0919′N、122°05.7459′E 32.00 70.25 [23] GZK01 34°10′N、119°29′E - 285 [24] XH-1 32°45′N、119°51′N - 350 [25] 表 2 CSDP-2孔沉积物样品OSL测年结果
Table 2. Optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) dating results for sediment samples of core CSDP-2
孔深/m 粒径/μm U/10−6 Th/10−6 K/% 含水率/% 等效剂量/Gy 剂量率/(Gy/ka) 年代/ka 0.47 38~63 1.59 ± 0.3 9.17 ± 0.6 1.94 ± 0.03 19 ± 5 2.71 ± 0.03 2.69 ± 0.12 1.0 ± 0.1 1.06 38~63 1.35 ± 0.3 9.03 ± 0.6 1.77 ± 0.03 22 ± 5 2.57 ± 0.04 2.27 ± 0.12 1.1 ± 0.1 1.78 38~63 1.42 ± 0.3 8.43 ± 0.6 1.86 ± 0.03 20 ± 5 2.70 ± 0.03 1.81 ± 0.09 1.1 ± 0.1 3.03 38~63 1.52 ± 0.3 9.77 ± 0.6 2.10 ± 0.04 19 ± 5 3.96 ± 0.07 2.77 ± 0.12 1.4 ± 0.1 3.9 38~63 1.47 ± 0.3 10.05 ± 0.7 2.06 ± 0.04 20 ± 5 5.91 ± 0.12 2.42 ± 0.11 2.4 ± 0.1 7.87 38~63 1.56 ± 0.3 9.67 ± 0.6 2.11 ± 0.04 25 ± 5 10.82 ± 0.20 2.59± 0.11 4.2 ± 0.2 9.38 38~63 2.23 ± 0.4 11.53 ± 0.7 2.16 ± 0.04 23 ± 5 11.85 ± 0.39 2.9 ± 0.13 4.0 ± 0.2 17.75 38~63 1.98 ± 0.3 11.04 ± 0.7 2.14 ± 0.04 21 ± 5 193.4 ± 18.1 2.82 ± 0.12 68.5 ± 7.1 18.82 38~63 3.09± 0.4 11.97 ± 0.7 1.91 ± 0.03 18 ± 5 197.2 ± 18.2 2.99 ± 0.14 65.9 ± 6.8 24.72 38~63 2.04 ± 0.4 12.69 ± 0.7 1.87 ± 0.03 18 ± 5 225.3 ±15.7 2.78 ± 0.13 81.1 ± 6.8 26.31 38~63 1.57 ± 0.3 8.88 ± 0.6 1.93 ± 0.03 16 ± 5 169.2 ± 17.1 2.55 ± 0.12 66.3 ± 7.4 27.02 38~63 1.75 ± 0.3 10.16 ± 0.7 1.77 ± 0.03 15 ± 5 205.4 ± 20.0 2.56 ± 0.12 80.4 ± 8.7 30.29 38~63 1.60 ± 0.3 9.93 ± 0.6 1.81 ± 0.03 17 ± 5 196.0 ± 14.6 3.00 ± 0.10 65.4 ± 5.3 31.15 38~63 1.0 ± 0.3 6.14 ± 0.6 2.02 ± 0.04 16 ± 5 169.5 ± 11.1 2.33 ± 0.12 72.6 ±6.1 32.16 38~63 1.59 ± 0.3 9.45 ± 0.6 1.68 ± 0.03 14 ± 5 188.0 ± 21.0 2.42 ± 0.12 77.7 ± 9.5 37.05 38~63 1.70 ± 0.3 8.65 ± 0.6 2.01 ± 0.04 16 ± 5 241 ± 16 2.62 ± 0.13 92 ± 7* 38.74 38~63 1.79 ± 0.3 9.39 ± 0.6 2.01 ± 0.04 19 ± 5 266 ± 21 2.61 ± 0.12 102 ± 9* 39.96 38~63 1.91 ± 0.3 9.59 ± 0.6 1.86 ± 0.03 18 ± 5 244 ± 11 2.54 ± 0.12 96 ± 6.* 48.31 38~63 1.83 ± 0.3 11.49 ± 0.7 1.97 ± 0.03 18 ± 5 286 ± 19 2.73 ± 0.12 105 ± 12* 49.5 38~63 1.03 ± 0.3 6.55 ± 0.6 1.94 ± 0.03 12 ± 5 291 ± 19 2.39 ± 0.13 122 ± 10* -
[1] 庞玉茂, 张训华, 肖国林, 等. 下扬子南黄海沉积盆地构造地质特征[J]. 地质论评, 2016, 62(3):604-616
PANG Yumao, ZHANG Xunhua, XIAO Guolin, et al. Structural and geological characteristics of the South Yellow Sea Basin in lower Yangtze block [J]. Geological Review, 2016, 62(3): 604-616.
[2] 庞玉茂, 张训华, 郭兴伟, 等. 南黄海北部盆地中、新生代构造热演化史模拟研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2017, 60(8):3177-3190 doi: 10.6038/cjg20170824
PANG Yumao, ZHANG Xunhua, GUO Xingwei, et al. Mesozoic and Cenozoic tectono-thermal evolution modeling in the Northern South Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2017, 60(8): 3177-3190. doi: 10.6038/cjg20170824
[3] 姚永坚, 夏斌, 冯志强, 等. 南黄海古生代以来构造演化[J]. 石油实验地质, 2005, 27(2):124-128 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2005.02.005
YAO Yongjian, XIA Bin, FENG Zhiqiang, et al. Tectonic evolution of the South Yellow Sea since the Paleozoic [J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2005, 27(2): 124-128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2005.02.005
[4] 侯方辉, 张志珣, 张训华, 等. 南黄海盆地地质演化及构造样式地震解释[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2008, 28(5):61-68
HOU Fanghui, ZHANG Zhixun, ZHANG Xunhua, et al. Geologic evolution and tectonic styles in the South Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2008, 28(5): 61-68.
[5] 杨长清, 董贺平, 李刚. 南黄海盆地中部隆起的形成与演化[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2014, 30(7):17-21,33
YANG Changqing, DONG Heping, LI Gang. Formation and tectonic evolution of the central uplift of the South Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2014, 30(7): 17-21,33.
[6] Pang Y M, Guo X W, Han Z Z, et al. Mesozoic–Cenozoic denudation and thermal history in the Central Uplift of the South Yellow Sea Basin and the implications for hydrocarbon systems: constraints from the CSDP-2 borehole [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 99: 355-369. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.10.027
[7] Liu J X, Liu Q S, Zhang X H, et al. Magnetostratigraphy of a long Quaternary sediment core in the South Yellow Sea [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2016, 144: 1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2016.05.025
[8] Liu J, Zhang X H, Mei X, et al. The sedimentary succession of the last ~ 3.50 Myr in the western South Yellow Sea: paleoenvironmental and tectonic implications [J]. Marine Geology, 2018, 399: 47-65. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2017.11.005
[9] Zhang J, Wan S M, Clift P D, et al. History of Yellow River and Yangtze River delivering sediment to the Yellow Sea since 3.5 Ma: tectonic or climate forcing? [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2019, 216: 74-88. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2019.06.002
[10] 张晓华, 张训华, 吴志强, 等. 南黄海中部隆起中-古生代地层发育新认识: 基于大陆架科学钻探CSDP-02井钻探成果[J]. 地球物理学报, 2018, 61(6):2369-2379 doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0124
ZHANG Xiaohua, ZHANG Xunhua, WU Zhiqiang, et al. New understanding of Mesozoic-Paleozoic strata in the central uplift of the South Yellow Sea basin from the drilling of well CSDP-02 of the “continental shelf drilling program” [J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2018, 61(6): 2369-2379. doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0124
[11] 郭兴伟, 朱晓青, 牟林, 等. 南黄海中部隆起二叠纪-三叠纪菊石的发现及其意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(3):121-128
GUO Xingwei, ZHU Xiaoqing, MU Lin, et al. Discovery of Permian-Triassic ammonoids in the central uplift of the South Yellow Sea and its geological implications [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(3): 121-128.
[12] 蔡来星, 郭兴伟, 徐朝晖, 等. 南黄海盆地中部隆起上古生界沉积环境探讨[J]. 沉积学报, 2018, 36(4):695-705
CAI Laixing, GUO Xingwei, XU Zhaohui, et al. Depositional environment of upper Paleozoic in the central uplift of the South Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2018, 36(4): 695-705.
[13] Cai L X, Xiao G L, Guo X W, et al. Assessment of Mesozoic and Upper Paleozoic source rocks in the South Yellow Sea Basin based on the continuous borehole CSDP-2 [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 101: 30-42. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.11.028
[14] Guo X W, Xu H H, Zhu X Q, et al. Discovery of Late Devonian plants from the southern Yellow Sea borehole of China and its palaeogeographical implications [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2019, 531: 108444. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2017.08.039
[15] 吴志强, 郭兴伟, 祁江豪, 等. 大陆架科学钻探南黄海CSDP-2井的垂直地震剖面资料采集技术[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(3):199-207
WU Zhiqiang, GUO Xingwei, QI Jianghao, et al. Vertical seismic profiling data acquisition from Well CSDP-2 in the Central uplift of South Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(3): 199-207.
[16] 许薇龄. 论南黄海区的两个新生代盆地[J]. 海洋地质研究, 1982, 2(1):66-78
XU Weiling. Discussion on the two Cenozoic Basins of the South Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geological Research, 1982, 2(1): 66-78.
[17] 陈沪生, 张永鸿, 徐师文, 等. 下扬子及邻区岩石圈结构构造特征与油气资源评价[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1999: 1-287
CHEN Husheng, ZHANG Yonghong, XU Shiwen, et al. The Lithospheric Textural and Structural Features as Well as Oil and Gas Evaluation in the Lower Yangtze Area and its Adjacent Region, China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1999: 1-287. ]
[18] 邱检生, 胡建, 李真, 等. 大别—苏鲁造山带变质岩原岩组合与闽浙沿海晚中生代岩浆岩组合的对比: 对扬子板块北东缘新元古构造属性的启示[J]. 高校地质学报, 2010, 16(4):413-425 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2010.04.001
QIU Jiansheng, HU Jian, LI Zhen, et al. Comparison of protolith assemblages of metamorphic rocks in the Dabie-Sulu Orogen and the late Mesozoic magmatic rock associations in the coastal region of Zhejiang and Fujian provinces: implications for the neoproterozoic tectonic setting of northeastern Yangtze Block [J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2010, 16(4): 413-425. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2010.04.001
[19] 侯方辉, 郭兴伟, 吴志强, 等. 南黄海有关地层与构造的研究进展及问题讨论[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2019, 49(1):96-105
HOU Fanghui, GUO Xingwei, WU Zhiqiang, et al. Research progress and discussion on formation and tectonics of South Yellow Sea [J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2019, 49(1): 96-105.
[20] Jin X L, Yu P Z. Tectonics of the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea[M]//C. A. O. S. IOCAS (Institute of Oceanology). Beijing: The Geology of the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea Science Press, 1982: 1-22.
[21] 沈淑敏, 郑芳芳, 刘文英. 中国东南大陆边缘地区中、新生代构造特点与构造应力场[J]. 中国地质科学院地质力学研究所所刊, 1986(8):9-34
SHEN Shumin, ZHENG Fangfang, LIU Wenying. Mesozoic-Cenozoic tectonic features of southeast China continental margin and the tectonic stress field [J]. Bulletin of the Institute of Geomechanics CAGS, 1986(8): 9-34.
[22] 杨子赓. Olduvai亚时以来南黄海沉积层序及古地理变迁[J]. 地质学报, 1993, 67(4):357-366
YANG Zigeng. The sedimentary sequence and palaeogeographic changes of the South Yellow Sea since the Olduvai subchron [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1993, 67(4): 357-366.
[23] Liu J, Saito Y, Kong X H, et al. Delta development and channel incision during marine isotope stages 3 and 2 in the western South Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 2010, 278(1-4): 54-76. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2010.09.003
[24] Gao X B, Ou J, Guo S Q, et al. Sedimentary history of the coastal plain of the south Yellow Sea since 5.1 Ma constrained by high-resolution magnetostratigraphy of onshore borehole core GZK01 [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2020, 239: 106355. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2020.106355
[25] 舒强, 萧家仪, 赵志军, 等. 苏北盆地XH-1钻孔0.78 Ma以来的气候环境变化记录[J]. 地层学杂志, 2010, 34(1): 27-34
SHU Qiang, XIAO Jiayi, ZHAO Zhijun, et al. Environmental records in XH-1 core in northern Jiangsu Basin since about 780 ka B. P. [J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2010, 34(1): 27-34.
[26] Murray A S, Wintle A G. Luminescence dating of quartz using an improved single-aliquot regenerative-dose protocol [J]. Radiation Measurements, 2000, 32(1): 57-73. doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(99)00253-X
[27] Roberts H M, Duller G A T. Standardised growth curves for optical dating of sediment using multiple-grain aliquots [J]. Radiation Measurements, 2004, 38(2): 241-252. doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2003.10.001
[28] Lai Z P. Testing the use of an OSL standardised growth curve (SGC) for De determination on quartz from the Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. Radiation Measurements, 2006, 41(1): 9-16. doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2005.06.031
[29] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. GB/T 12763.8-2007 海洋调查规范 第8部分: 海洋地质地球物理调查[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008: 7-9
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China. GB/T 12763.8-2007 Specifications for oceanographic survey—Part 8: marine geology and geophysics survey[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008: 7-9. ]
[30] Amorosi A, Pavesi M, Lucchi M R, et al. Climatic signature of cyclic fluvial architecture from the Quaternary of the central Po Plain, Italy [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2008, 209(1-4): 58-68. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2008.06.010
[31] Guion P D, Fulton I M, Jones N S. Sedimentary facies of the coal-bearing Westphalian A and B north of the Wales-Brabant High [J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1995, 82: 45-78. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1995.082.01.03
[32] Duan Z Q, Liu Q S, Shi X F, et al. Reconstruction of high-resolution magnetostratigraphy of the Changjiang (Yangtze) River Delta, China [J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2016, 204(2): 948-960. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggv497
[33] Duan Z Q, Liu Q S, Gai C C, et al. Magnetostratigraphic and environmental implications of greigite (Fe3S4) formation from Hole U1433A of the IODP Expedition 349, South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 2017, 394: 82-97. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2017.02.008
[34] Kirschvink J L. The least-squares line and plane and the analysis of palaeomagnetic data [J]. Geophysical Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society, 1980, 62(3): 699-718. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.1980.tb02601.x
[35] Gradstein F M, Ogg J G, Schmitz M D, et al. The Geologic Time Scale[M]. Boston: Elsevier, 2012: 1-1144.
[36] 张茂恒, 李吉均, 舒强, 等. 兴化XH-1孔记录的苏北盆地晚新生代沉积体系及环境变化过程[J]. 地理研究, 2011, 30(3):513-522
ZHANG Maoheng, LI Jijun, SHU Qiang, et al. The sediments sequence and environmental oscillation of the core XH-1 in Subei Basin since late Cenozoic [J]. Geographical Research, 2011, 30(3): 513-522.
[37] Miller K G, Kominz M A, Browning J V, et al. The Phanerozoic record of global sea-level change [J]. Science, 2005, 310(5752): 1293-1298. doi: 10.1126/science.1116412
[38] 杨子赓, 林和茂, 王圣洁, 等. 对末次间冰期南黄海古冷水团沉积的探讨[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1998, 18(1):47-58
YANG Zigeng, LIN Hemao, WANG Shengjie, et al. A study of the ancient Cold Water Mass sediments in South Yellow Sea during Last Interglacial [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1998, 18(1): 47-58.
[39] Chappell J, Omura A, Esat T, et al. Reconciliaion of late Quaternary sea levels derived from coral terraces at Huon Peninsula with deep sea oxygen isotope records [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letter, 1996, 141(1-4): 227-236. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(96)00062-3
[40] Liu J, Qiu J D, Saito Y, et al. Formation of the Yangtze Shoal in response to the post-glacial transgression of the paleo-Yangtze (Changjiang) estuary, China [J]. Marine Geology, 2020, 423: 106080. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2019.106080
[41] Sommerfield C K. On sediment accumulation rates and stratigraphic completeness: lessons from Holocene ocean margins [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2006, 26(17-18): 2225-2240. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2006.07.015
[42] 管秉贤. 黄、东海浅海水文学的主要特征[J]. 黄渤海海洋, 1985, 3(4):1-10
HUANG Bingxian. Major features of the shallow water hydrography in the East China Sea and Huanghai Sea [J]. Journal of Oceanography of Huanghai & Bohai Seas, 1985, 3(4): 1-10.
[43] 庞玉茂, 郭兴伟, 韩作振, 等. 南黄海中部隆起晚白垩世以来地层剥蚀的磷灰石裂变径迹分析[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(6):1921-1930
PANG Yumao, GUO Xingwei, HAN Zuozhen, et al. Apatite fission track constrains on denudation since late cretaceous in central uplift, South Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(6): 1921-1930.
-




 下载:
下载: