Characteristics of organic carbon isotope and the paleoenvironmental significances of loess in Shengshan Island during the Last Glacial Period
-
摘要:
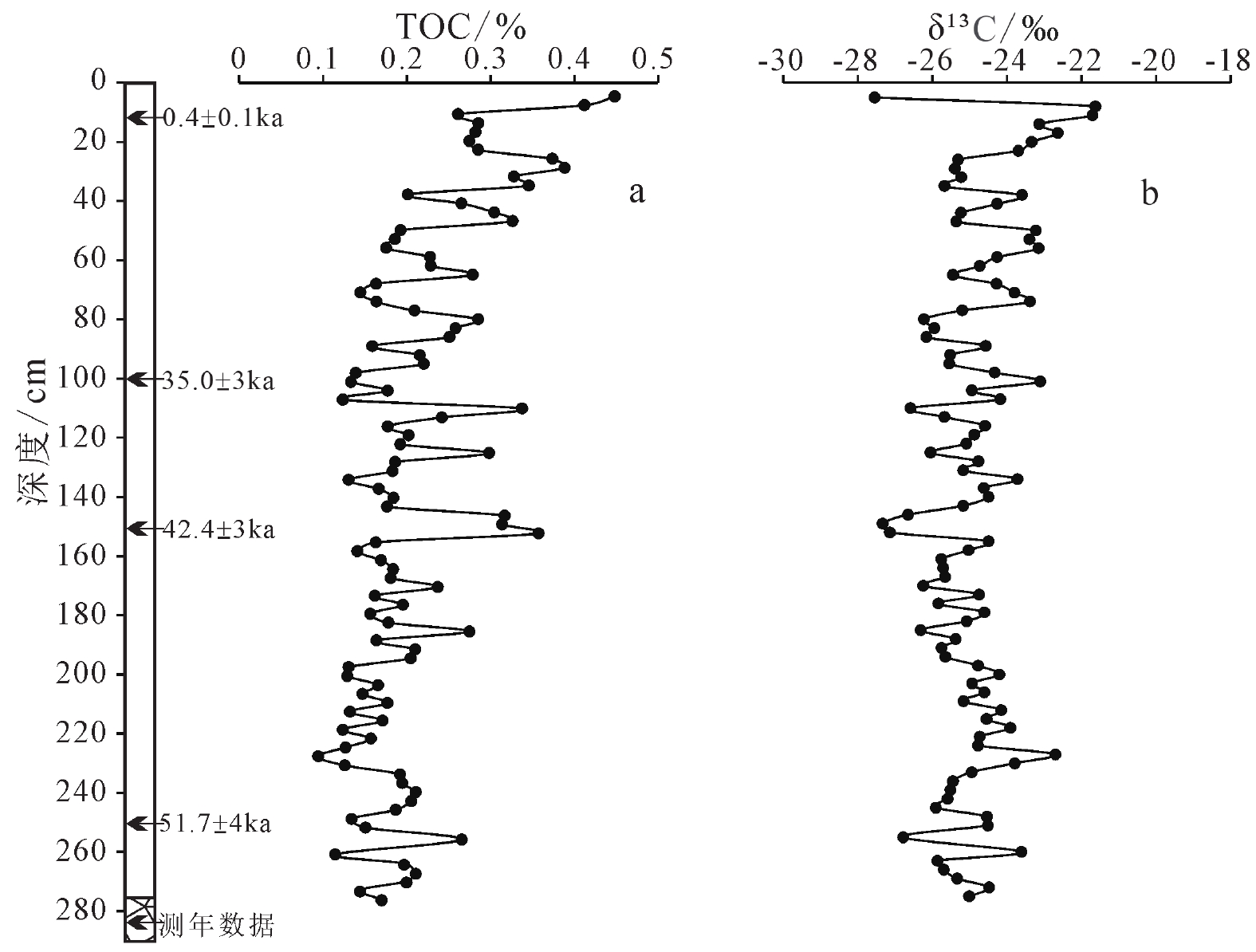
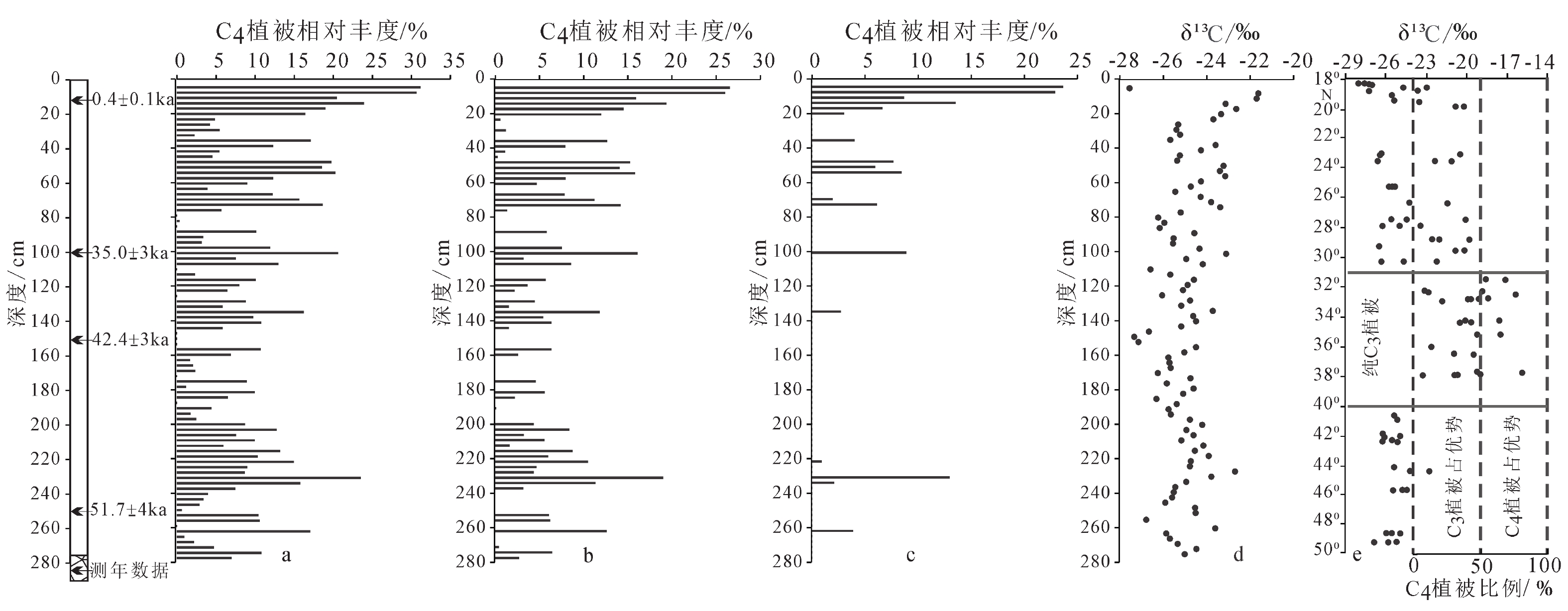
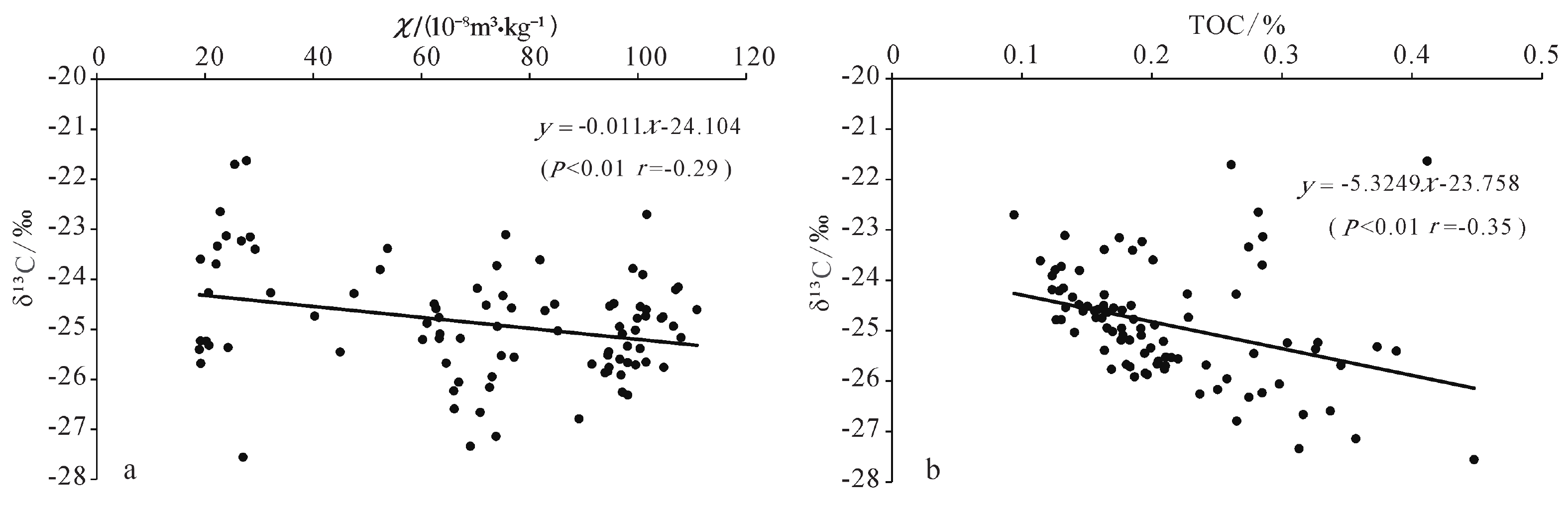
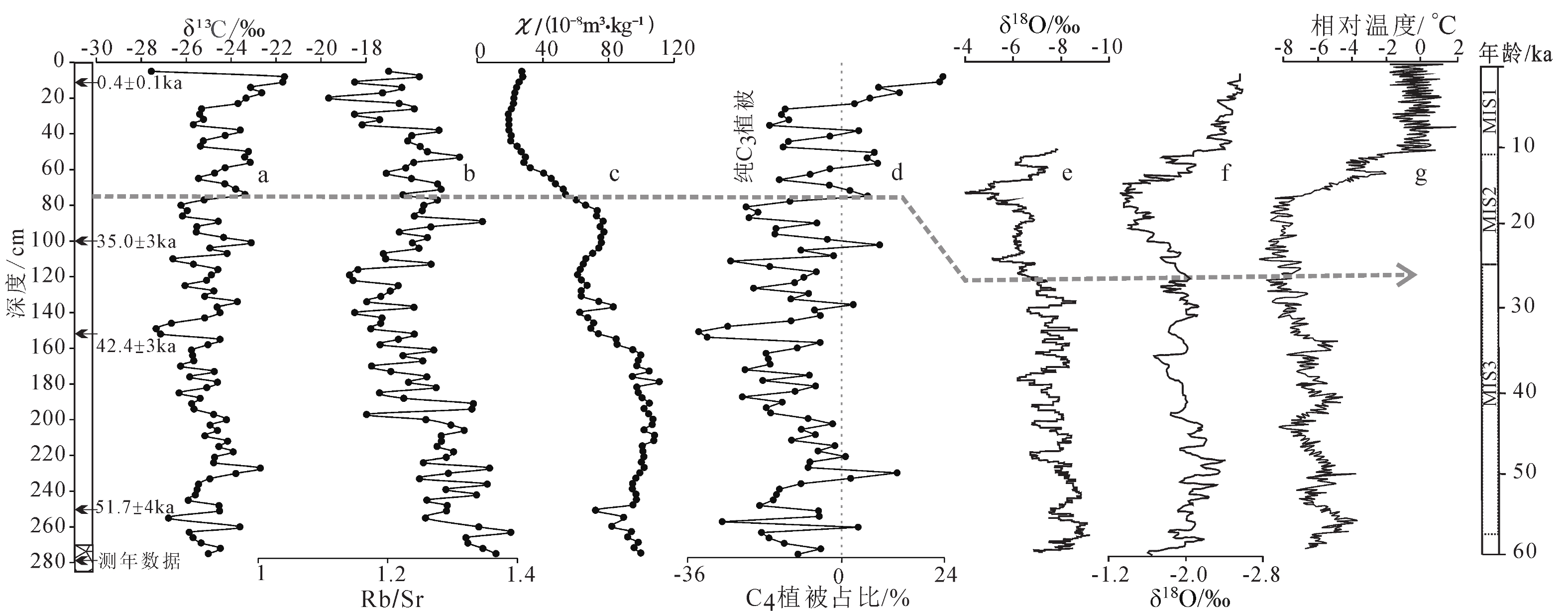
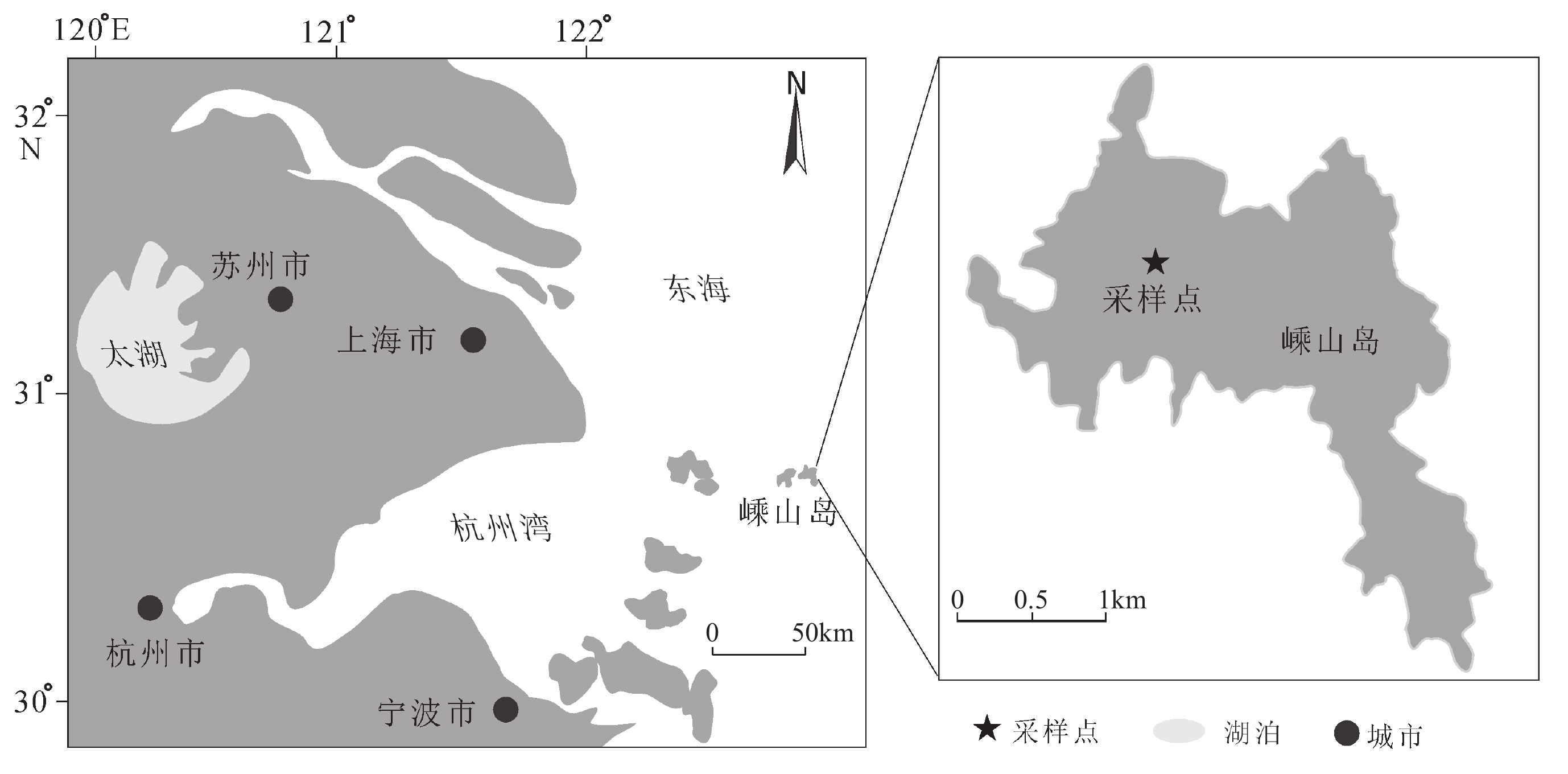
黄土沉积中有机碳同位素组成与古气候关系密切,对研究区域环境演变具有重要意义。本文聚焦我国东海嵊山岛末次冰期黄土地层,在磁化率和元素地球化学指标特征分析基础上,开展有机碳同位素组成特征研究。研究结果表明:嵊山岛黄土沉积剖面有机碳同位素组成波动范围−21.63‰~−27.56‰,平均值为−24.88‰,剖面有机碳同位素组成波动偏正;利用端元法对嵊山岛黄土沉积环境中C3/C4植被相对丰度进行估算,揭示沉积地层记录的植被类型是以C3型植被为主导,C4型植被对沉积地层中有机碳同位素的贡献有限;与南京洞穴石笋、苏禄海海洋沉积以及南极Vostok冰芯氧同位素记录对比,显示末次冰期间冰阶时期嵊山岛黄土沉积中有机碳同位素波动是以C3型植被为主导的植被碳同位素对降水条件改变的响应,降水可能是这一时期黄土沉积中有机碳同位素变化的主要影响因素;在末次冰消期阶段,温度有利于C4植被的发育,导致区域C4型植被丰度有所上升,并对沉积地层中有机碳同位素变动的贡献增加。
Abstract:The organic carbon isotope composition in loess deposits is closely related to paleoclimate, which is of great significance to the study of regional environmental evolution. The loess deposit of the Last Glacial Period in Shengshan Island in the East China Sea off the East China was studied. The magnetic susceptibility and element geochemistry were analyzed, based on which the organic carbon isotope composition was scrutinized. Results show that since the Last Glaciation, the organic carbon isotope composition in the loess fluctuated from −21.63‰ to −27.56‰ on average of −24.88‰. In general, the value of organic carbon isotope decreased with the increase in burial depth of the loess. In addition, the relative abundance of C3/C4 vegetation in Shengshan Island was estimated by using the end-member method. It was revealed that the C3 plants dominated in the island since the Last Glacial Period, and C4 plants were very limited in the contribution to the organic carbon isotope in the loess deposit. In comparison with the oxygen isotope data of the cave stalagmites in Nanjing, marine sediments from Sulu Sea, and Antarctic Vostok ice core, the loess was deposited during the interstage of the Last Glaciation, and the fluctuation in organic carbon isotope value was resulted mainly from the responses of local ancient C3 plant-dominated vegetation to the variation of precipitation condition. The precipitation was the main influential factor on the organic carbon isotope variation during the period. In the last deglaciation stage, the paleo-temperature favored C4 plants booming, thus the relative abundance of C4 plants increased, and so did their contribution to the fluctuation of organic carbon isotopes in the loess deposits in the island.
-

-
表 1 嵊山岛黄土剖面光释光年代测定结果
Table 1. OSL (optically stimulated luminescence) dating results of the loess in Shengshan Island
深度/cm U/(μg/g) Th/(μg/g) K/% 实测含水量/% 环境剂量率/(Gy/ka) 等效剂量/Gy 年龄/ka 10 2.83 14.3 1.49 14.45 3.05 1.2±0.3 0.4±0.1 100 2.98 15.1 1.69 11.86 3.34 117±4 35.03±3 150 2.94 14.4 1.56 8.18 3.23 137±8 42.41±4 250 2.93 14.3 1.62 16.49 3.00 152±5 51.67±4 -
[1] 刘东生. 黄土与环境[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1985
LIU Tungsheng. Loess and the Environment[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1985.
[2] Maher B A. Palaeoclimatic records of the loess/palaeosol sequences of the Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2016, 154: 23-84. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2016.08.004
[3] Yang H, Li G Q, Gou S Y et al. The close-space luminescence dated loess record from SW Junggar Basin indicates persistent aridity during the last glacial-interglacial cycle in lowlands of Central Asia [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2021, 584: 110664. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2021.110664
[4] Li P, Zhang C X, Wu H B et al. Geochemical characteristics of Holocene loess-paleoslol sequences in central Chinese Loess Plateau and their implications for East Asian monsoon evolution [J]. Quaternary International, 2022, 616: 99-108. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2021.10.017
[5] Xu X W, Qiang X K, Hu S et al. Records of the Mid-Brunhes Event in Chinese loess-paleosol sequences [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2020, 543: 109596. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2020.109596
[6] Mir J A, Dar R A, Vinnepand M et al. Environmental reconstruction potentials of loess-paleosol-sequences in Kashmir through high-resolution proxy data [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2022, 601: 111100. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2022.111100
[7] Wang Y, Guo F, Ma L et al. Millennial-scale summer monsoon oscillations over the last 260 ka revealed by high-resolution elemental results of the Mangshan loess-palaeosol sequence from the southeastern Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. Quaternary International, 2020, 552: 164-174. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2020.05.039
[8] 周家兴, 于娟, 杨丽君, 等. 铜川地区早中全新世黄土沉积特征及其古气候意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(1):160-166
ZHOU Jiaxing, YU Juan, YANG Lijun et al. Sedimentary characteristics of the early and middle Holocene loess in Tongchuan area and their implications for paleoclimate [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(1): 160-166.
[9] Ding Z L, Yu Z W, Yang S L et al. Coeval changes in grain size and sedimentation rate of eolian loess, the Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2001, 28(10): 2097-2100. doi: 10.1029/2000GL006110
[10] Kong X H, Zhou W J, Beck J W et al. Loess magnetic susceptibility flux: A new proxy of East Asian monsoon precipitation [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2020, 201: 104489. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2020.104489
[11] 刘秀铭, 刘东生, Heller F, 等. 黄土频率磁化率与古气候冷暖变换[J]. 第四纪研究, 1990,10(1):42-50 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1990.01.005
LIU Xiuming, LIU Tungsheng, Heller F et al. Frequency-dependent susceptibility of loess and quaternary paleoclimate [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1990,10(1): 42-50. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1990.01.005
[12] 石 浩, 岳大鹏, 赵景波, 等. 陕西绥德地区黄土-古土壤序列地球化学特征及其环境指示意义[J]. 地球与环境, 2022, 50(1):1-13
SHI Hao, YUE Dapeng, ZHAO Jingbo et al. Geochemical characteristics of loess paleosol sequence and its environmental implications in Suide area, Shanxi [J]. Earth and Environment, 2022, 50(1): 1-13.
[13] 田庆春, 郝晓龙, 韩军青, 等. 临汾盆地黄土沉积微量元素地球化学特征及其气候意义[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2022, 36(5):87-93 doi: 10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2022.123
TIAN Qingchun, HAO Xiaolong, HAN Junqing et al. Geochemical characteristics and climatic significance of trace elements in loess of Linfen basin [J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2022, 36(5): 87-93. doi: 10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2022.123
[14] Yang S L, Liu L, Chen H et al. Variability and environmental significance of organic carbon isotopes in Ganzi loess since the last interglacial on the eastern Xizang Plateau [J]. Catena, 2021, 196: 104866. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2020.104866
[15] Zhou B, Wali G, Peterse F et al. Organic carbon isotope and molecular fossil records of vegetation evolution in central Loess Plateau since 450 kyr [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2016, 59(6): 1206-1215. doi: 10.1007/s11430-016-5276-x
[16] An Z S, Huang Y S, Liu W G et al. Multiple expansions of C4 plant biomass in East Asia since 7 Ma coupled with strengthened monsoon circulation [J]. Geology, 2005, 33(9): 705-708. doi: 10.1130/G21423.1
[17] O’Leary M H. Carbon isotope fractionation in plants [J]. Phytochemistry, 1981, 20(4): 553-567. doi: 10.1016/0031-9422(81)85134-5
[18] O’Leary M H. Carbon isotope in photosynthesis [J]. BioScience, 1988, 38(5): 328-336. doi: 10.2307/1310735
[19] Kohn M J. Carbon isotope compositions of terrestrial C3 plants as indicators of (paleo)ecology and (paleo)climate [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(46): 19691-19695. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1004933107
[20] Liu W G, Huang Y S. Reconstructing in-situ vegetation dynamics using carbon isotopic composition of biopolymeric residues in the central Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 249(3-4): 348-356. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.01.010
[21] Liu W G, Yang H, Ning Y F et al. Contribution of inherent organic carbon to the bulk δ13C signal in loess deposits from the arid western Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2007, 38(9): 1571-1579. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2007.05.004
[22] 饶志国, 郭文康, 薛骞, 等. 黄土高原西部地区黄土地层有机质主要来源分析[J]. 第四纪研究, 2015, 35(4):819-827 doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2015.04.04
RAO Zhiguo, GUO Wenkang, XUE Qian et al. Assessment on primary provenance of organic matter in loess/paleosol sequences in the western Chinese Loess Plateau: local biomass or bedrocks in dust source regions? [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2015, 35(4): 819-827. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2015.04.04
[23] Zhang Z H, Zhao M X, Lu H Y et al. Lower temperature as the main cause of C4 plant declines during the glacial periods on the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 214(3-4): 467-481.
[24] 饶志国, 陈发虎, 曹洁, 等. 黄土高原西部地区末次冰期和全新世有机碳同位素变化与C3 /C4植被类型转换研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2005, 25(1):107-114 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2005.01.015
RAO Zhiguo, CHEN Fahu, CAO Jie et al. Variation of soil organic carbon isotope and C3/C4 vegetation type transition in the western loess plateau during the last glacial and Holocene periods [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2005, 25(1): 107-114. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2005.01.015
[25] Liu W G, Yang H, Sun Y B et al. δ13C values of loess total carbonate: A sensitive proxy for Asian summer monsoon in arid northwestern margin of the Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. Chemical Geology, 2011, 284(3-4): 317-322. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2011.03.011
[26] Yang S L, Ding Z L, Li Y Y et al. Warming-induced northwestward migration of the East Asian monsoon rain belt from the Last Glacial Maximum to the mid-Holocene [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(43): 13178-13183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1504688112
[27] 林本海, 刘荣谟. 最近800ka黄土高原夏季风变迁的稳定同位素证据[J]. 科学通报, 1992(18):1691-1693 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1992.18.023
LIN Benhai, LIU Rongmo. Stable isotopic evidence of the summer monsoon evolution during the last 800ka in Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1992(18): 1691-1693. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1992.18.023
[28] Vidic N J, Montañez I P. Climatically driven glacial-interglacial variations in C3 and C4 plant proportions on the Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. Geology, 2004, 32(4): 337-340. doi: 10.1130/G20222.2
[29] Chen F H, Rao Z G, Zhang J W et al. Variations of organic carbon isotopic composition and its environmental significance during the last glacial on western Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2006, 51(13): 1593-1602. doi: 10.1007/s11434-006-2003-6
[30] Liu W G, Huang Y S, An Z S et al. Summer monsoon intensity controls C4/C3 plant abundance during the last 35 ka in the Chinese Loess Plateau: Carbon isotope evidence from bulk organic matter and individual leaf waxes [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2005, 220(3-4): 243-254. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2005.01.001
[31] Hatté C, Fontugne M, Rousseau D D et al. δ13C variations of loess organic matter as a record of the vegetation response to climatic changes during the Weichselian [J]. Geology, 1998, 26(7): 583-586. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1998)026<0583:CVOLOM>2.3.CO;2
[32] 郑祥民, 刘飞. 长江三角洲与东海岛屿黄土研究综述[J]. 华东师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 2006(6):9-24
ZHENG Xiangmin, LIU Fei. Review of research on loess in the Yangtze River delta and the East China Sea islands [J]. Journal of East China Normal University(Natural Science), 2006(6): 9-24.
[33] 石娇星. 舟山群岛植被分类与制图[D]. 华东师范大学硕士学位论文, 2021: 62-63
SHI Jiaoxing. Vegetation classification and mapping of Zhoushan archipelago[D]. Master Dissertation of East China Normal University, 2021: 62-63.
[34] Farquhar G D, Ehleringer J R, Hubick K T. Carbon isotope discrimination and photosynthesis [J]. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, 1989, 40: 503-537. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pp.40.060189.002443
[35] 饶志国, 朱照宇, 贾国东, 等. 环北太平洋地区现代植被中C3/C4 植物相对丰度与气候条件关系研究[J]. 科学通报, 2010, 55(18):1931-1936 doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3101-z
RAO Zhiguo, ZHU Zhaoyu, JIA Guodong et al. Relationship between climatic conditions and the relative abundance of modern C3 and C4 plants in three regions around the North Pacific [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010, 55(18): 1931-1936. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3101-z
[36] Tieszen L L, Reed B C, Bliss N B et al. NDVI, C3 and C4 production and distributions in Great Plains grassland land cover classes [J]. Ecological Applications, 1997, 7(1): 59-78.
[37] Bird M I, Pousai P. Variations of δ 13C in the surface soil organic carbon pool [J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 1997, 11(3): 313-322. doi: 10.1029/97GB01197
[38] 饶志国, 贾国东, 朱照宇, 等. 中国东部表土总有机质碳同位素和长链正构烷烃碳同位素对比研究及其意义[J]. 科学通报, 2008, 53(24):3921-3927 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2008.17.013
RAO Zhiguo JIA Guodong ZHU Zhaoyu et al. Comparison of the carbon isotope composition of total organic carbon and long-chain n-alkanes from surface soils in Eastern China and their significance [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2008, 53(24): 3921-3927. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2008.17.013
[39] 何勇, 秦大河, 任贾文, 等. 塬堡黄土剖面末次间冰期古土壤有机质碳同位素记录的夏季风演化历史[J]. 科学通报, 2002, 47(15):1289-1291 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2002.12.013
HE Yong, QIN Dahe, REN Jiawen et al. The summer monsoon evolution recorded by carbon isotope of organic matter from the Yuanbao loess section during the last Interglaciation [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2002, 47(15): 1289-1291. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2002.12.013
[40] Wang G A, Feng X, Han J et al. Paleovegetation reconstruction using δ13C of soil organic matter [J]. Biogeosciences, 2008, 5: 1325-1337. doi: 10.5194/bg-5-1325-2008
[41] Quade J, Cerling T E, Bowman J R. Development of Asian monsoon revealed by marked ecological shift during the latest Miocene in northern Pakistan [J]. Nature, 1989, 342(6246): 163-166. doi: 10.1038/342163a0
[42] Cerling T E. The stable isotopic composition of modern soil carbonate and its relationship to climate [J]. Earth and Planetary Science letters, 1984, 71(2): 229-240. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(84)90089-X
[43] 刘卫国, 宁有丰, 安芷生, 等. 黄土高原现代土壤和古土壤有机碳同位素对植被的响应[J]. 中国科学D辑, 2005, 48(10):93-99
LIU Weiguo, NING Youfeng, AN Zhisheng, et al. Carbon isotopic composition of modern soil and paleosol as a response to vegetation change on the Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences, 2005, 48(10): 93-99.
[44] Lyu A Q, Lu H Y, Zeng L et al. Vegetation variation of loess deposits in the southeastern Inner Mongolia, NE China over the past ~1.08 million years [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 155: 174-179. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.11.013
[45] 张月馨, 迟云平, 谢远云, 等. 中更新世以来哈尔滨黄土有机碳同位素组成及其古气候意义[J]. 地球学报, 2020, 41(4):525-534 doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2020.040602
ZHANG Yuexin, CHI Yunping, XIE Yuanyun et al. Organic carbon isotope composition of Harbin loess since the Mid-Pleistocene and its paleoclimatic significance [J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2020, 41(4): 525-534. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2020.040602
[46] 匡欢传, 周浩达, 胡建芳, 等. 末次盛冰期和全新世大暖期湖光岩玛珥湖沉积记录的正构烷烃和单体稳定碳同位素分布特征及其古植被意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2013, 33(6):1222-1233 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2013.06.18
KUANG Huanchuan ZHOU Haoda, HU Jianfang et al. Variations of n-alkanes and compound-specific carbon isotopes in sediment from Huguangyan Maar Lake during the last glacial maximum and Holocence optimum: Implications for paleovegetation [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2013, 33(6): 1222-1233. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2013.06.18
[47] 顾兆炎, 刘强, 许冰, 等. 气候变化对黄土高原末次盛冰期以来的C3/C4 植物相对丰度的控制[J]. 科学通报, 2003, 48(12):1271-1276 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2003.12.008
GU Zhaoyan, LIU Qiang, XU Bing et al. Climate as the dominant control on C3 and C4 plant abundance in the Loess Plateau: Organic carbon isotope evidence from the last glacial-interglacial loess-soil sequences [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2003, 48(12): 1271-1276. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2003.12.008
[48] Diefendorf A F, Mueller K E, Wing S L et al. Global patterns in leaf 13C discrimination and implications for studies of past and future climate [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(13): 5738-5743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0910513107
[49] Ehleringer J R, Cooper T A. Correlations between carbon isotope ratio and microhabitat in desert plants [J]. Oecologia, 1988, 76(4): 562-566. doi: 10.1007/BF00397870
[50] 王国安, 韩家懋, 刘东生. 中国北方黄土区C-3草本植物碳同位素组成研究[J]. 中国科学D辑, 2003, 46(10):1069-1076 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-9267.2003.06.008
WANG Guoan, HAN Jiamao, LIU Tungsheng. The carbon isotope composition of C3 herbaceous plants in loess area of northern China [J]. Science in China series D:Earth Sciences, 2003, 46(10): 1069-1076. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-9267.2003.06.008
[51] Liu W G, Feng X H, Ning Y F et al. δ13C variation of C3 and C4 plants across an Asian monsoon rainfall gradient in arid northwestern China [J]. Global Change Biology, 2005, 11(7): 1094-1100. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2005.00969.x
[52] Wang G A, Li J Z, Liu X Z et al. Variations in carbon isotope ratios of plants across a temperature gradient along the 400 mm isoline of mean annual precipitation in north China and their relevance to paleovegetation reconstruction [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2013, 63: 83-90. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2012.12.004
[53] An Z S, Kukla G J, Porter S C et al. Magnetic susceptibility evidence of monsoon variation on the Loess Plateau of central China during the last 130, 000 years [J]. Quaternary Research, 1991, 36(1): 29-36. doi: 10.1016/0033-5894(91)90015-W
[54] 宁有丰, 刘卫国, 安芷生. 甘肃西峰黄土-古土壤剖面的碳酸盐与有机碳的碳同位素差值(Δδ13C)的变化及其古环境意义[J]. 科学通报, 2006, 51(11):1350-1354 doi: 10.1007/s11434-006-1350-7
NING Youfeng, LIU Weiguo, AN Zhisheng. Variation of soil Δδ13C values in Xifeng loess-paleosol sequence and its paleoenvironmental implication [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2006, 51(11): 1350-1354. doi: 10.1007/s11434-006-1350-7
[55] Wang G A, Zhang L L, Zhang X Y et al. Chemical and carbon isotopic dynamics of grass organic matter during litter decompositions: A litterbag experiment [J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2014, 69: 106-113. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2014.02.012
[56] Feng X H, Epstein S. Carbon isotopes of trees from arid environments and implications for reconstructing atmospheric CO2 concentration [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(12): 2599-2608. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00152-2
[57] Jouzel J, Lorius C, Petit J R et al. Vostok ice core: a continuous isotope temperature record over the last climatic cycle(160 000 years) [J]. Nature, 1987, 329(6138): 403-408. doi: 10.1038/329403a0
[58] SeltzerA M, Ng J, Aeschbach W et al. Widespread six degrees Celsius cooling on land during the Last Glacial Maximum [J]. Nature, 2021, 593(7858): 228-232. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03467-6
[59] 陈骏, 汪永进, 季峻峰, 等. 陕西洛川黄土剖面的Rb/Sr值及其气候地层学意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 1999, 19(4):350-356 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1999.04.007
CHEN Jun, WANG Yongjin, JI Junfeng et al. Rb/Sr variations and its climatic stratigraphical significance of a loess-paleosol profile from Louchuan, Shanxi province [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1999, 19(4): 350-356. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1999.04.007
[60] Peng W B, Nie J S, Wang Z et al. A major change in precipitation gradient on the Chinese Loess Plateau at the Pliocene-Quaternary boundary [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 155: 134-138. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.10.031
[61] Hatté C, Antoine P, Fontugne M et al. δ13C of loess organic matter as a potential proxy for paleoprecipitation [J]. Quaternary Research, 2001, 55(1): 33-38. doi: 10.1006/qres.2000.2191
[62] Wang Y J, Cheng H, Edwards R L et al. A high-resolution absolute-dated late Pleistocene monsoon record from Hulu Cave, China [J]. Science, 2001, 294(5550): 2345-2348. doi: 10.1126/science.1064618
[63] Linsley B K. Oxygen-isotope record of sea level and climate variations in the Sulu Sea over the past 150, 000 years [J]. Nature, 1996, 380(6571): 234-237. doi: 10.1038/380234a0
[64] Petit J R, Jouzel J, Raynaud D et al. Climate and atmospheric history of the past 420, 000 years from the Vostok ice core, Antarctica [J]. Nature, 1999, 399(6735): 429-436. doi: 10.1038/20859
[65] 饶志国, 陈发虎, 张晓, 等. 末次冰期以来全球陆地植被中C3/C4植物相对丰度时空变化基本特征及其可能的驱动机制[J]. 科学通报, 2012, 57(31):4024-4035 doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5233-9
RAO Zhiguo, CHEN Fahu, ZHANG Xiao et al. Spatial and temporal variations of C3/C4 relative abundance in global terrestrial ecosystem since the Last Glacial and its possible driving mechanisms [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(31): 4024-4035. doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5233-9
-



 下载:
下载: