Geochemical characteristics and upwelling origin of siliceous source rocks in the Permian Gufeng Formation of the South Yellow Sea area
-
摘要:
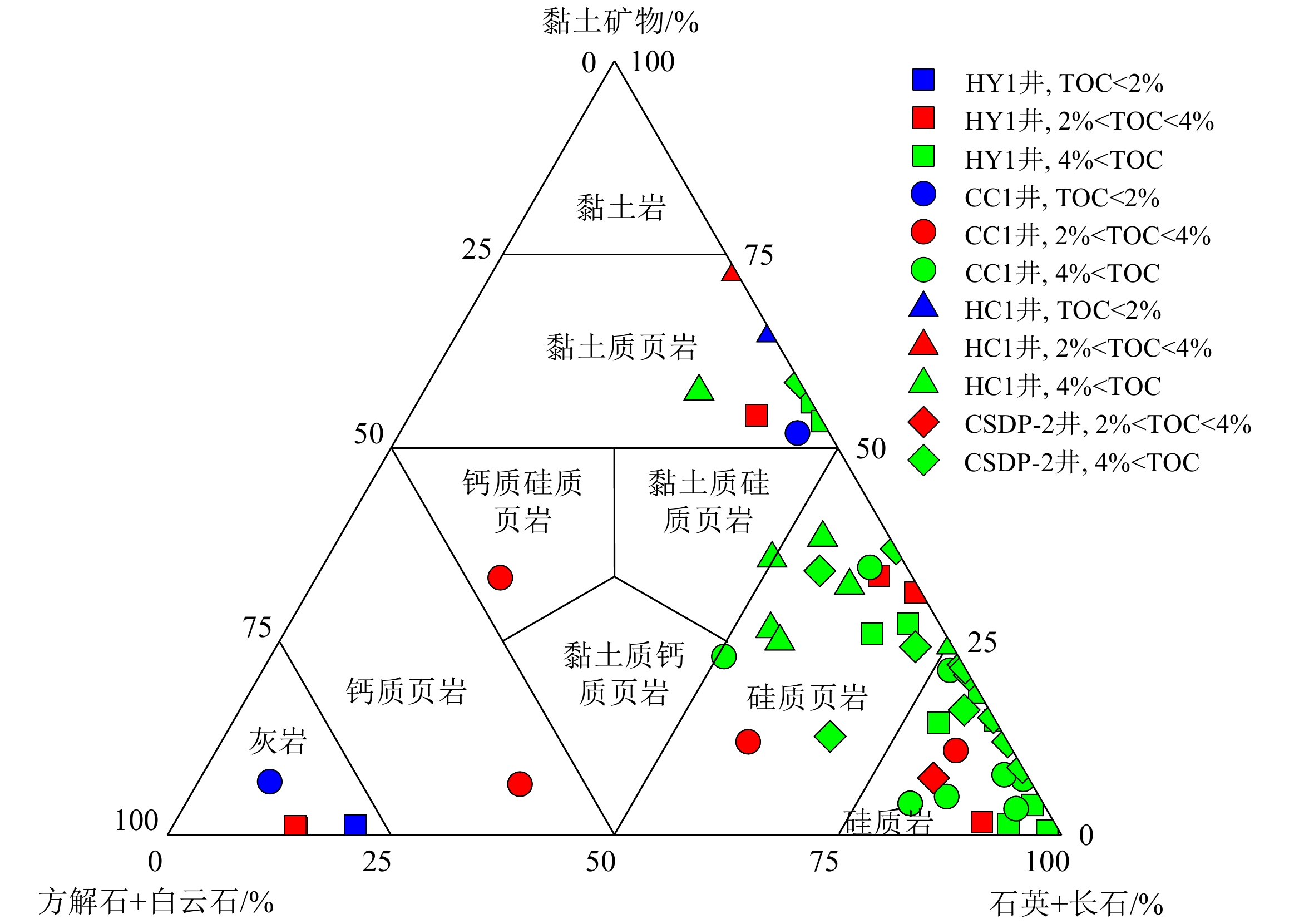
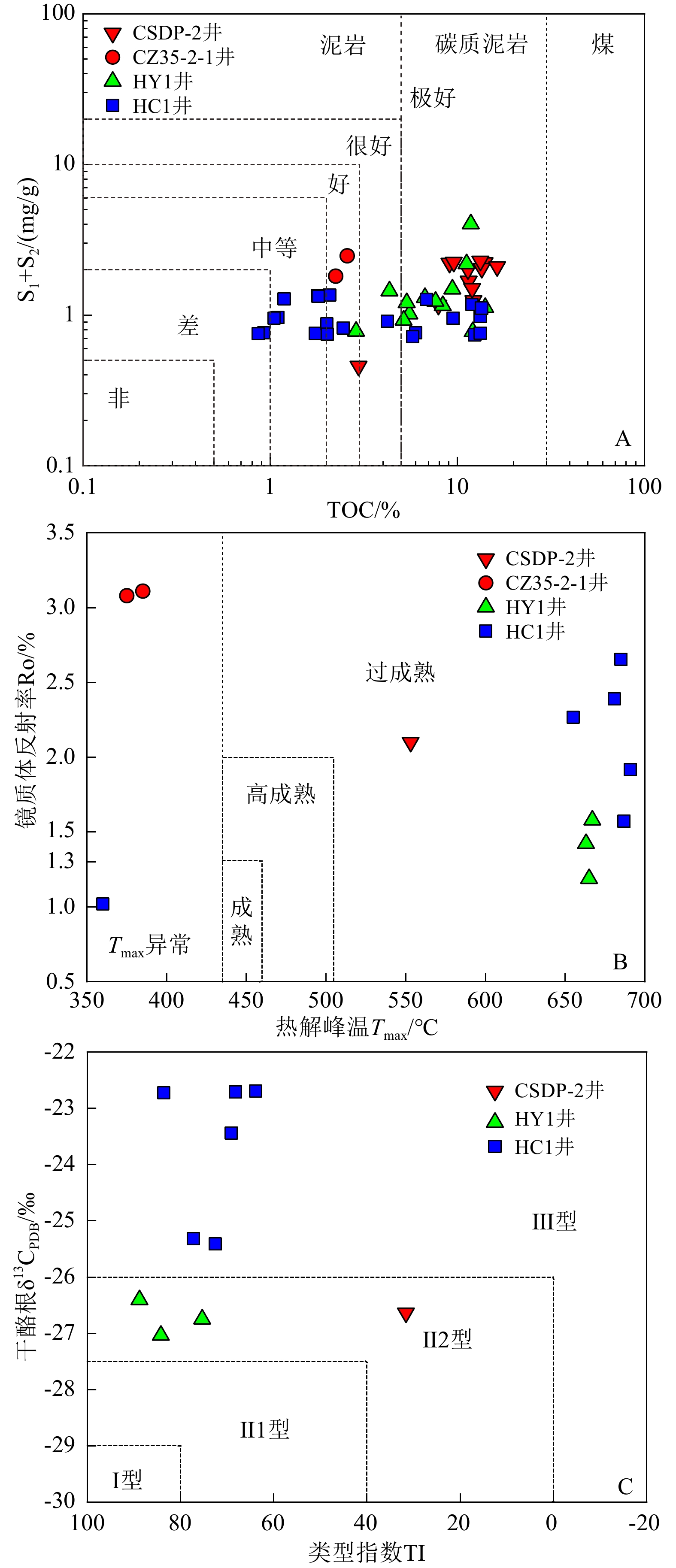
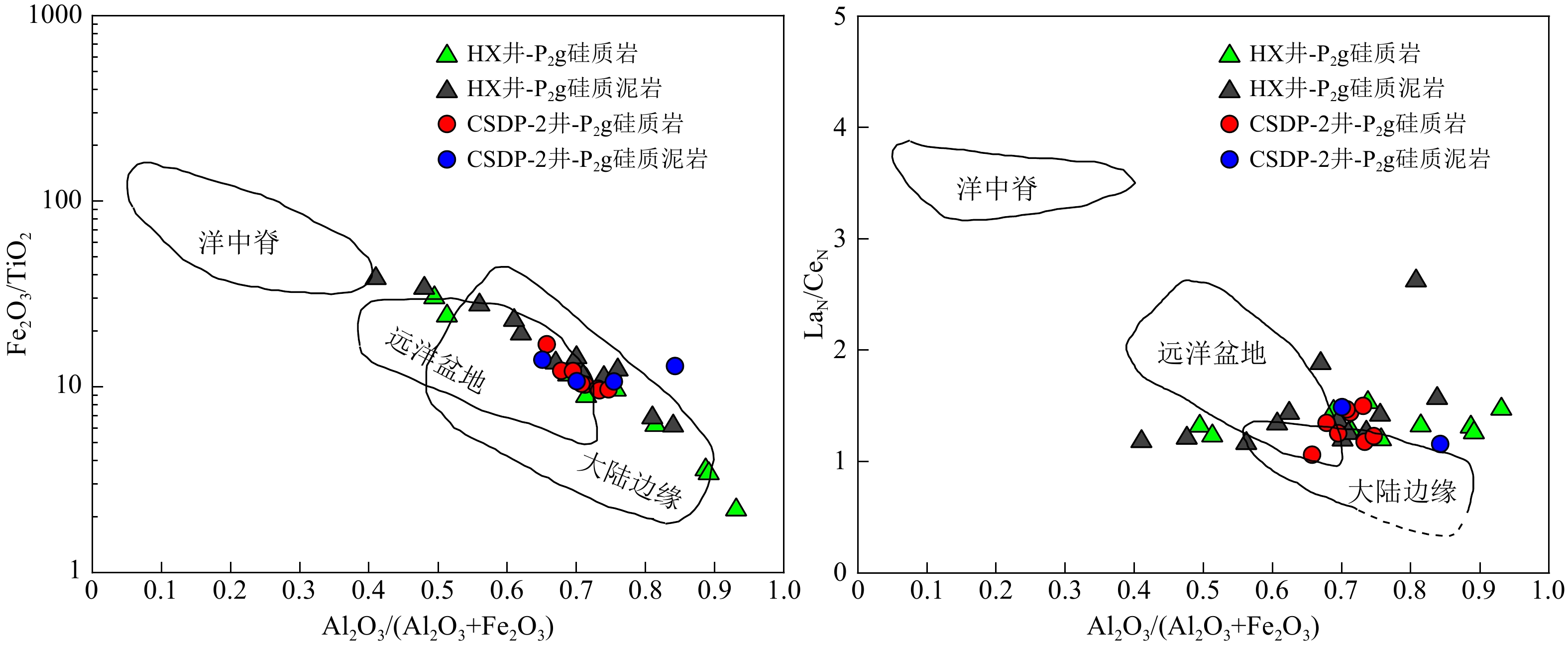
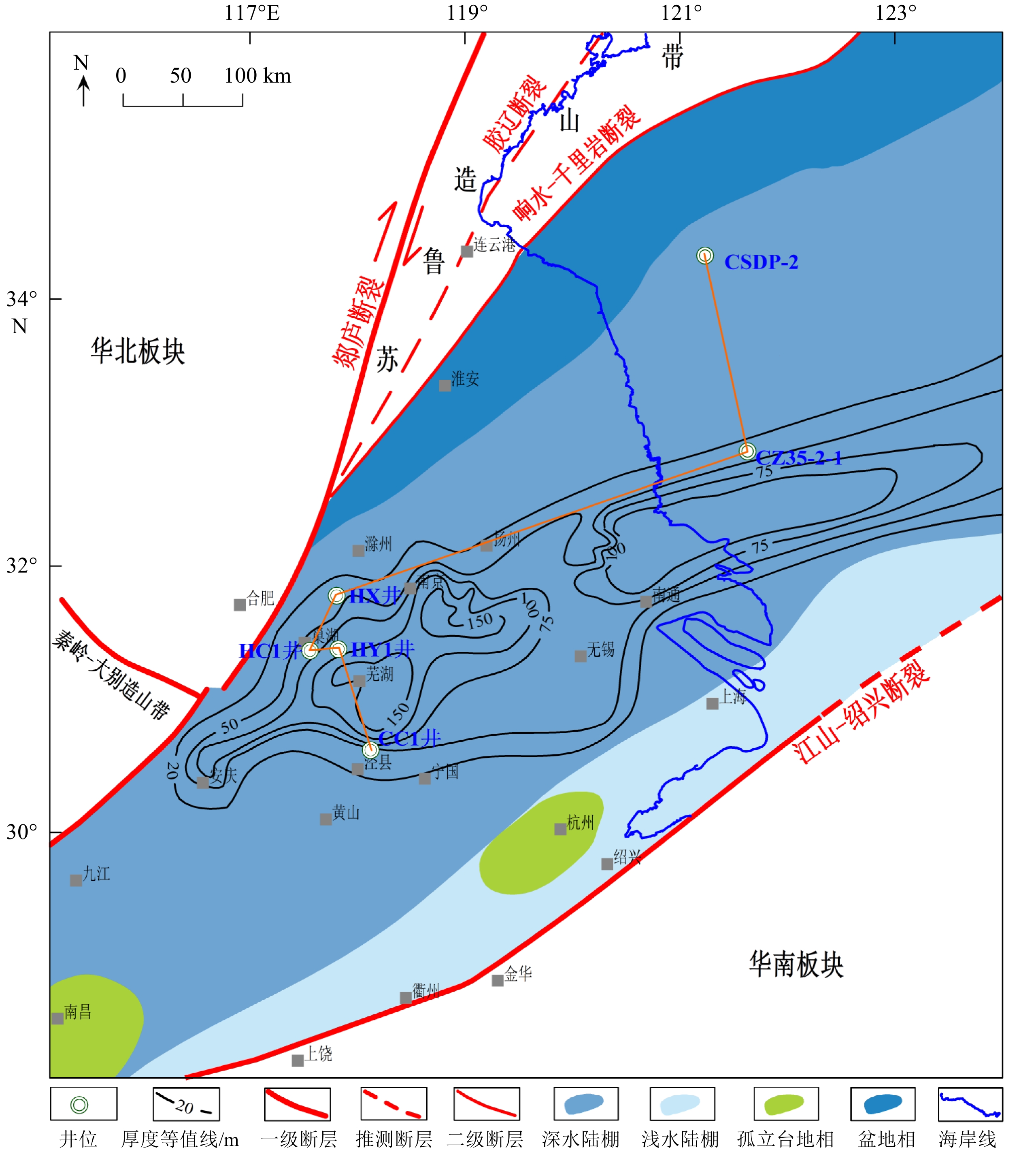
前人对南黄海地区中二叠统孤峰组层状硅质岩的生烃潜力和成因研究较少,本文利用下扬子-南黄海地区的5口钻井资料,对二叠系孤峰组硅质烃源岩进行了详细的矿物学和地球化学研究,并通过与现代秘鲁上升流区的沉积物进行元素含量对比,分析了南黄海地区孤峰组硅质烃源岩的生烃潜力和成因机制。结果显示,下扬子-南黄海地区孤峰组具有硅质岩和硅质泥岩不等厚互层的特征,是一套呈SWW-NEE向展布的过成熟偏腐殖型优质烃源岩。在地球化学特征方面,南黄海地区孤峰组硅质烃源岩和秘鲁上升洋流沉积物均表现出还原性敏感元素和生产力敏感元素相对富集,K、Ti、Mn相对亏损,具有Co×Mn<0.4、Cd/Mo>0.1的特征,显示为大陆边缘的上升流成因。研究显示,南黄海地区孤峰组硅质烃源岩的有机质富集主要受高生产力控制,形成于中等滞留的缺氧-硫化环境。与硅质泥岩相比,孤峰组硅质岩的陆源碎屑输入和Co×Mn值较低,Zr/Rb值较高,这意味着硅质岩沉积时期的上升流活动强度大于硅质泥岩。此外,部分探井中的孤峰组硅质泥岩相对于硅质岩具有较高的化学蚀变指数,说明古气候变暖是造成上升流活动减弱和硅质沉积含量减少的主要原因。
Abstract:Few studies regarding the hydrocarbon generation potential and genesis of the layered siliceous source rocks in the Mid-Permian Gufeng Formation (GFF) of the South Yellow Sea (SYS) has been conducted. The mineralogy and geochemistry of the siliceous source rocks in the GFF were studied in detail based on the borehole data of five wells located in the Lower Yangtze to South Yellow Sea area, and the element content were compared with those of the sediments in the modern upwelling area of Peru, from which the hydrocarbon generation potential of the GFF siliceous source rocks in the SYS and its origin were revealed. Geological data shows that the GFF in the SYS area is characterized by interbeds of siliceous rocks and siliceous mudstones in unequal thickness, and is a set of over-mature and slightly humic high-quality source rocks extending in the SWW-NEE direction. In terms of geochemistry, both the siliceous rocks and Peruvian upwelling deposits show enrichment in the elements that are sensitive to reduction and productivity, but relative depletion in K, Ti and Mn, and have Co×Mn value lower than 0.4, Cd/Mo value higher than 0.1, indicating their origin of upwelling on continental margin. This study shows that the enrichment of organic matter in the GFF siliceous source rocks in the SYS area is mainly controlled by high productivity and is formed in anoxic to euxinic environment with moderate retention. Compared with siliceous mudstone in the GFF, the terrigenous clastic input and Co×Mn value are lower and Zr/Rb value is higher in the siliceous rocks, which means that the upwelling intensity of the siliceous rocks during sedimentation is greater than that of siliceous mudstones. In addition, the siliceous mudstone of the GFF have higher chemical alteration index than the GFF siliceous rocks in some wells, which suggests that the paleoclimate warming is the main cause for the weakening of upwelling activity and the reduction of siliceous sediment content.
-
Key words:
- siliceous rocks /
- upwelling current /
- geochemical characteristics /
- South Yellow Sea /
- Gufeng Formation
-

-
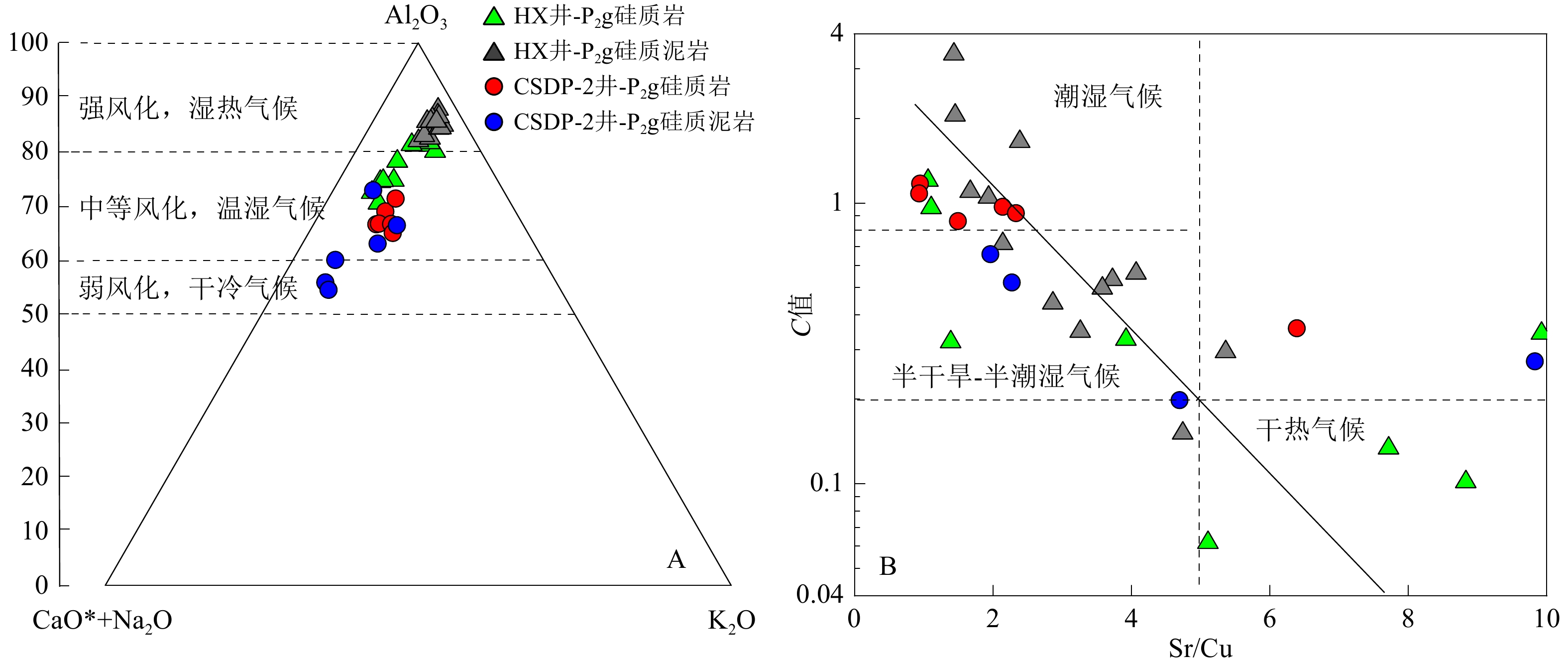
图 10 下扬子-南黄海地区孤峰组硅质岩的A-CN-K图解 [72]、Sr/Cu、气候指数C值判别古气候
Figure 10.
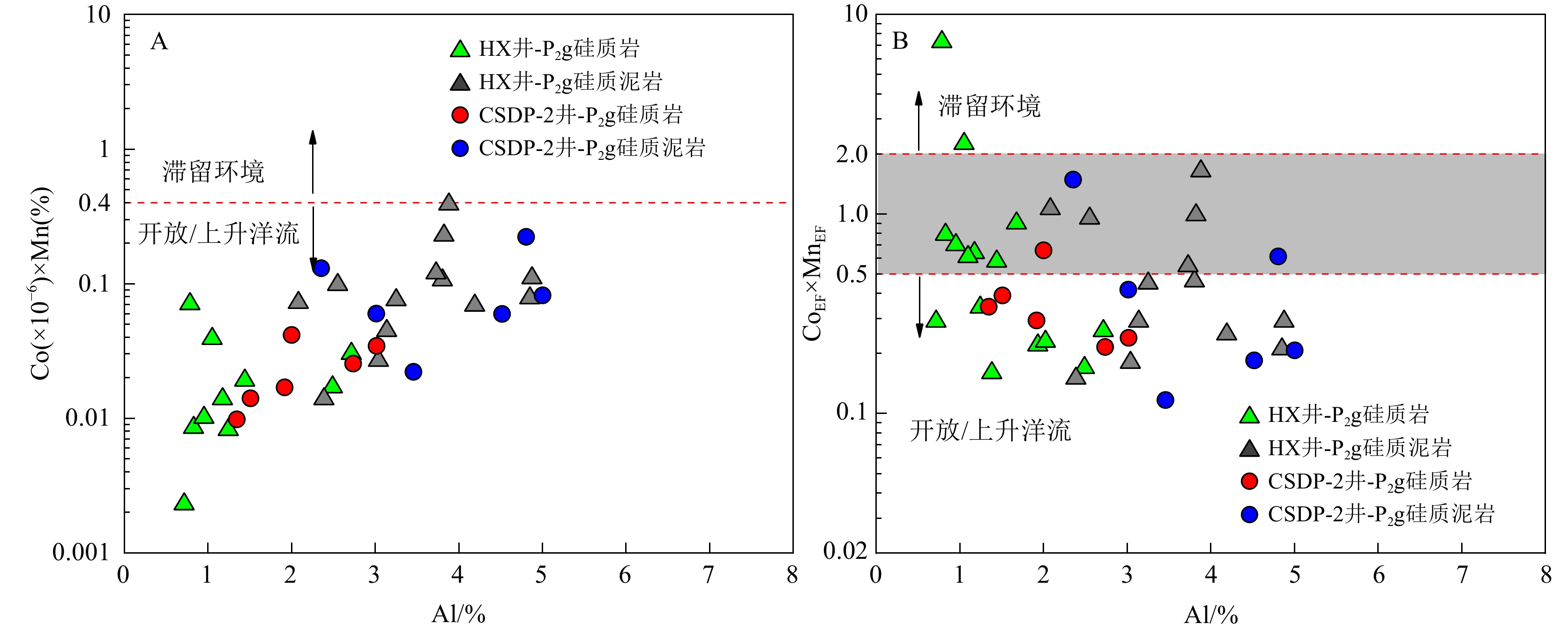
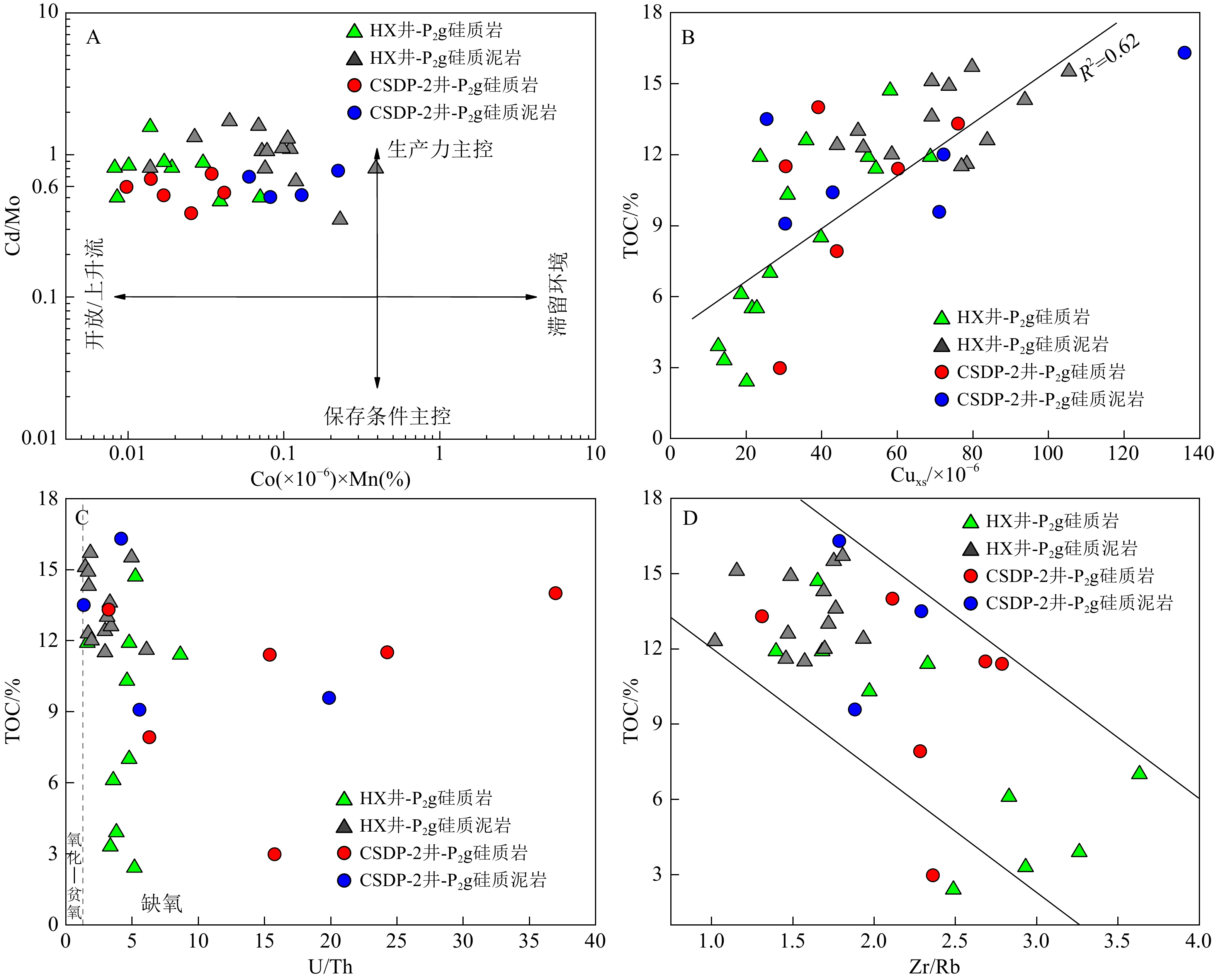
图 11 下扬子-南黄海地区孤峰组硅质烃源岩的Cd/Mo-Co×Mn联合图版 [78]及Cuxs、U/Th、Zr/Rb与TOC的相关关系
Figure 11.
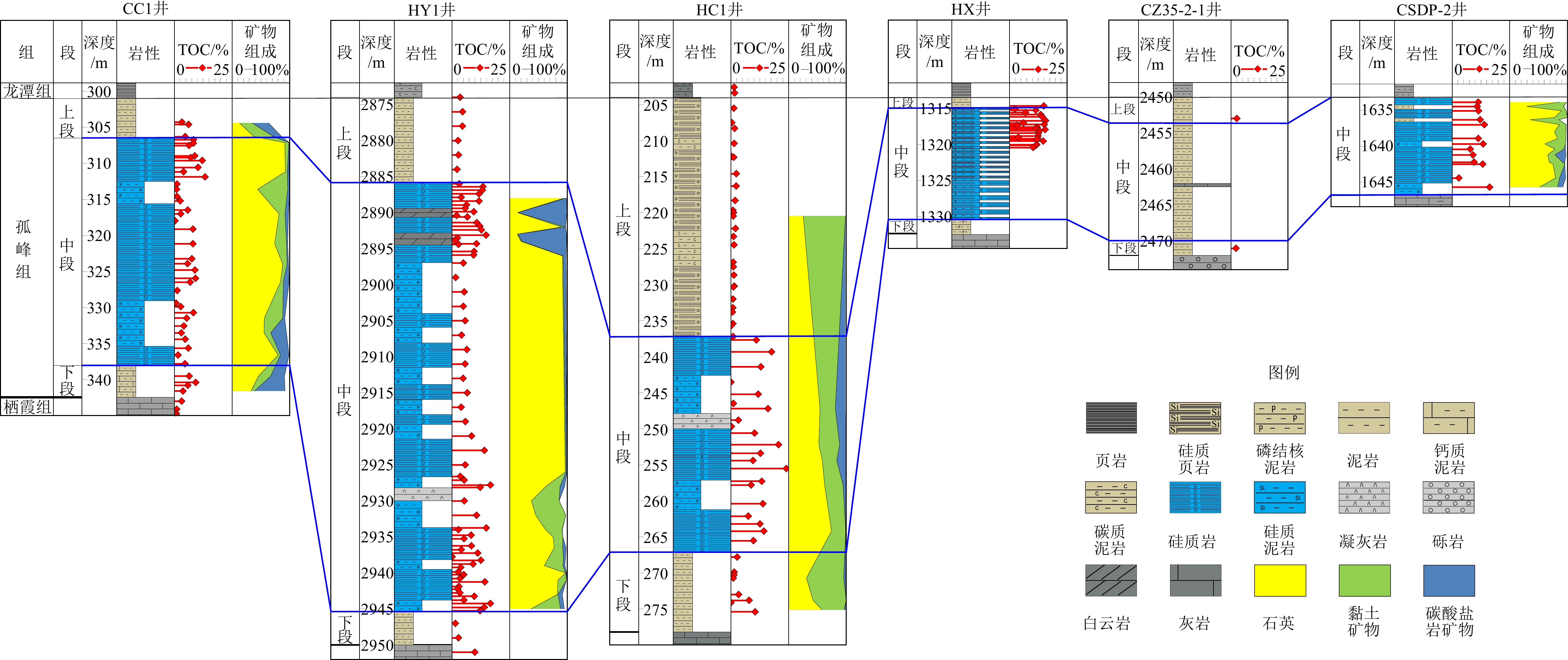
表 1 CSDP-2井孤峰组硅质烃源岩的有机碳、岩石热解及全岩矿物分析数据
Table 1. Analytical data of TOC, Rock-Eval, and whole-rock mineral composition of siliceous source rocks in the Gufeng Formation in Well CSDP-2
样品号 深度/m 岩性 TOC/% S1+S2
/(mg/g)Tmax/℃ 矿物含量/% 石英 长石 碳酸盐 黄铁矿 黏土矿物 DP2-1 1633.9 硅质岩 11.4 1.18 548.3 75.1 11.5 0 1.7 11.7 DP2-2 1634.5 硅质泥岩 10.9 2.19 504.7 10.3 19.2 0 6.3 64.2 DP2-3 1635.1 硅质岩 11.5 1.62 527.8 89.3 0.0 0 2.2 8.5 DP2-4 1636.3 硅质泥岩 12.2 1.18 514.7 24.1 11.5 0 14.3 50.1 DP2-5 1636.0 硅质岩 — — — 67.6 10.4 0 0 22.0 DP2-6 1637.0 硅质岩 14 2.18 529.7 86.4 0 0 1.8 11.8 DP2-7 1638 硅质岩 — — — 77.3 0 0 2.6 20.1 DP2-8 1638.9 硅质岩 11.4 1.95 535 82.1 0.7 0 2.4 14.8 DP2-9 1639.7 硅质泥岩 13.5 2.00 533.1 44.6 16.3 0 3.4 35.7 DP2-10 1640.4 硅质岩 7.92 1.11 531.7 75.6 2.7 2.7 3.4 15.6 DP2-11 1641.2 硅质泥岩 9.08 2.16 529.6 62.1 3.9 19 2.6 12.4 DP2-12 1642.2 硅质泥岩 9.58 2.18 520.8 66.8 1.5 4 4.5 23.2 DP2-13 1642.5 硅质岩 13.3 2.23 526.3 73.1 1.9 0 4.4 20.6 DP2-14 1644.4 硅质岩 2.97 0.42 540.5 77.1 2.3 10.3 3.2 7.1 DP2-15 1645.7 硅质泥岩 16.3 2.03 533.8 45.5 6.0 9.2 7.9 31.4 表 2 HX井与CSDP-2井孤峰组硅质岩的主量元素百分含量
Table 2. Mass percentage fractions of the main elements of siliceous rocks in the Gufeng Formation in Wells HX and CSDP-2
井位 样品号 岩性 深度/m TOC
/%主量元素/% SiO2 TiO2 Al2O3 TFe2O3 MnO MgO CaO Na2O K2O P2O5 CDSP-2井 DP2-3 硅质岩 1635.1 11.5 81.62 0.11 2.85 1.15 0.005 0.34 0.33 0.26 0.39 0.148 DP2-6 硅质岩 1637.0 14 82.33 0.10 2.54 1.05 0.003 0.31 0.39 0.27 0.35 0.21 DP2-8 硅质岩 1638.9 11.4 76.33 0.14 3.62 1.33 0.004 0.30 0.28 0.28 0.50 0.174 DP2-9 硅质泥岩 1639.7 13.5 64.53 0.14 9.45 1.76 0.032 2.71 3.17 0.82 0.77 0.11 DP2-10 硅质岩 1640.4 7.92 73.86 0.20 5.17 1.88 0.005 0.52 0.53 0.54 0.75 0.138 DP2-11 硅质泥岩 1641.2 9.08 66.78 0.16 4.45 1.51 0.034 3.09 4.38 0.89 0.53 0.104 DP2-12 硅质泥岩 1642.2 9.58 67.37 0.22 5.69 2.70 0.009 1.06 1.70 0.69 1.00 0.31 DP2-13 硅质岩 1642.5 13.3 72.01 0.21 5.70 2.50 0.005 0.37 0.47 0.58 0.98 0.109 DP2-14 硅质岩 1644.4 2.97 75.19 0.12 3.78 1.97 0.009 0.49 3.97 0.38 0.72 0.19 DP2-15 硅质泥岩 1645.7 16.3 54.71 0.36 9.08 3.88 0.02 0.86 4.26 0.84 1.69 0.34 DP2-16 硅质泥岩 1644.0 10.4 51.99 0.26 8.54 2.78 0.01 7.03 10.70 1.44 0.89 0.10 DP2-17 硅质泥岩 1644.2 12 62.54 0.25 6.53 3.50 0.00 1.83 7.80 1.35 0.93 0.25 HX井 HX0-12 硅质岩 1320.4 10.3 85.31 0.084 2.35 0.3 0.002 0.33 0.5 0.13 0.21 0.043 HX0-8 硅质岩 1320.1 11.4 80.29 0.106 2.72 1.23 0.001 0.22 0.76 0.09 0.31 0.212 HX0-7 硅质岩 1320.0 11.9 74.53 0.211 4.7 1.88 0.002 0.46 0.42 0.13 0.69 0.057 HX0-3 硅质岩 1319.5 14.7 63.78 0.189 5.13 1.82 0.004 0.56 4.91 0.14 0.64 0.069 HX0-1 硅质岩 1319.3 11.9 72.55 0.079 2.22 0.27 0.007 0.33 9.23 0.15 0.24 0.043 HX1-2 硅质岩 1319.0 3.9 82.12 0.046 1.35 0.1 0.001 0.35 5.55 0.12 0.11 0.035 HX1-13 硅质岩 1317.3 3.3 82.67 0.052 1.56 0.5 0.002 1.45 4 0.12 0.13 0.037 HX1-15 硅质岩 1317.0 6.1 73.38 0.066 1.8 0.41 0.005 2.53 5.95 0.07 0.17 0.041 HX1-25 硅质岩 1315.5 7 67.4 0.05 1.48 1.51 0.008 3.59 8.95 0.11 0.13 0.039 HX1-28 硅质岩 1315.0 2.4 81.94 0.078 1.98 1.88 0.003 0.82 4.41 0.18 0.22 0.049 HX1-1 硅质泥岩 1319.2 12.3 69.64 0.207 5.93 1.41 0.008 0.53 3.52 0.06 0.58 0.065 HX1-3 硅质泥岩 1318.8 12.4 65.94 0.141 4.51 0.87 0.002 0.5 6.08 0.15 0.46 0.062 HX1-6 硅质泥岩 1318.4 12.6 56.81 0.234 7.22 7.95 0.008 0.63 3.37 0.09 0.75 0.084 HX1-8 硅质泥岩 1318.1 13 66.38 0.144 3.93 1.94 0.004 0.47 6.3 0.1 0.47 0.075 HX1-9 硅质泥岩 1317.9 15.5 59.63 0.192 6.14 3.7 0.004 0.75 3.9 0.17 0.65 0.08 HX1-10 硅质泥岩 1317.8 11.6 54.66 0.306 9.21 4.04 0.013 1.75 4.95 0.12 1.16 0.207 HX1-11 硅质泥岩 1317.5 12 65 0.137 4.82 3.12 0.004 0.66 4.9 0.1 0.45 0.079 HX1-14 硅质泥岩 1317.2 15.1 65.91 0.213 7.19 3.06 0.004 0.7 1.84 0.12 0.71 0.086 HX1-17 硅质泥岩 1316.7 15.7 63.8 0.283 7.92 3.24 0.007 0.9 1.32 0.13 0.97 0.102 HX1-21 硅质泥岩 1316.1 14.3 52.79 0.274 7.33 10.53 0.011 0.65 1.44 0.11 0.92 0.14 HX1-23 硅质泥岩 1315.8 13.6 64.58 0.183 5.74 2.06 0.002 0.68 3.83 0.07 0.62 0.083 HX1-27 硅质泥岩 1315.2 11.5 64.81 0.198 7.04 5.48 0.003 0.66 1.22 0.13 0.7 0.077 HX1-31 硅质泥岩 1314.6 14.9 55.22 0.24 9.16 2.96 0.007 1.11 4.99 0.14 1 0.155 注:HX井样品数据引自文献[14];DP2-16、DP2-17号样品数据引自文献[28]。 表 3 HX井与CSDP-2井孤峰组硅质岩的微量元素含量
Table 3. Mass fractions of the trace elements of siliceous rocks in the Gufeng Formation from Wells HX and CSDP-2
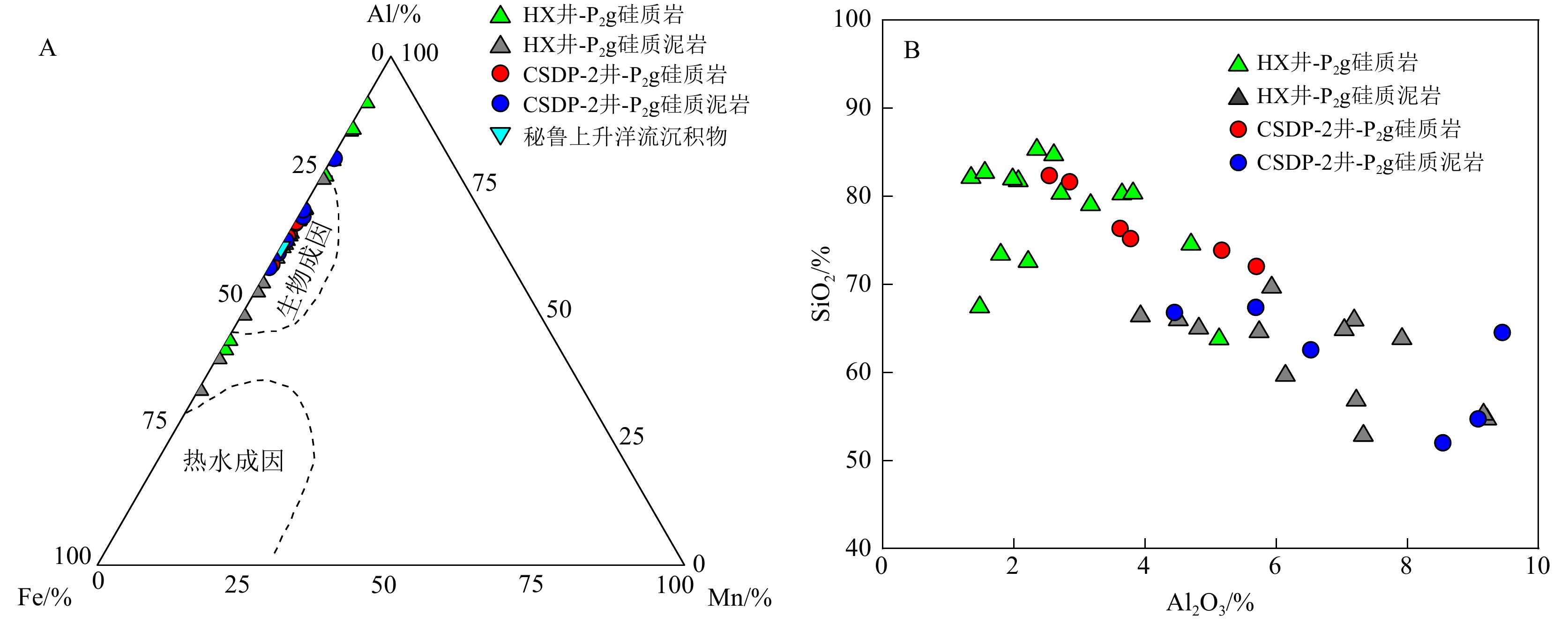
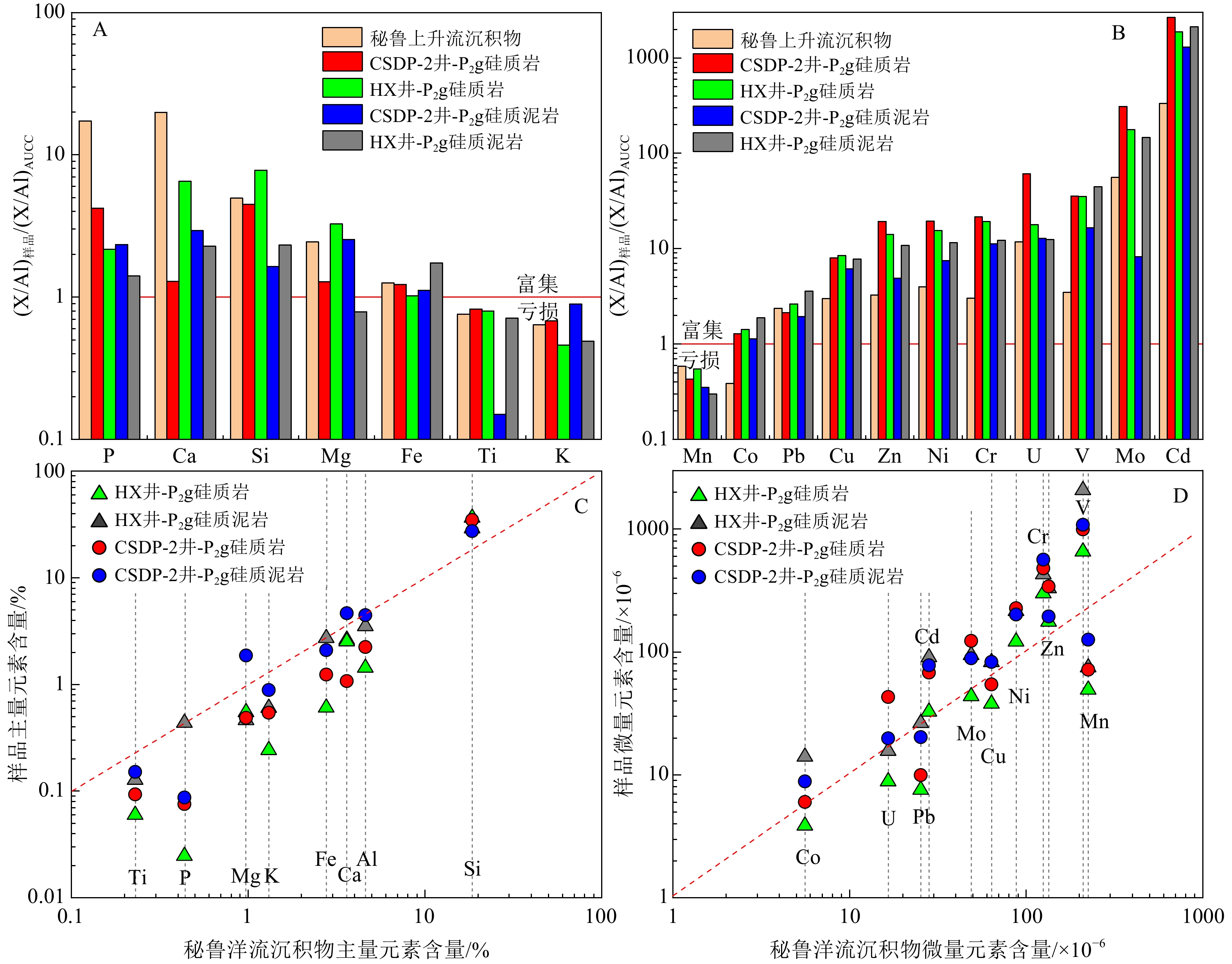
井位 样品号 微量元素/×10−6 Cd/Mo LaN/CeN CIA C值 V Cr Co Ni Cu Zn U Mo Cd Th Sr Zr Rb CSDP-2井 DP2-3 786 391 3.62 186 35.2 369 40.3 76.2 51.6 1.66 75.4 44.3 16.5 0.68 1.44 68.92 0.97 DP2-6 1004 423 4.21 218 43.3 398 66.6 110 65.5 1.8 101 35.3 16.7 0.60 1.47 66.57 0.92 DP2-8 1672 649 5.47 304 66.2 654 37.4 220 114 2.43 62.7 62.7 22.5 0.52 1.50 71.31 1.17 DP2-9 1093 365 3.3 156 41 257 19.4 118 59.6 14.4 403 68.3 29.8 0.51 1.16 72.81 0.27 DP2-10 1059 383 6.57 279 52.5 264 28.2 218 84.7 4.47 78.5 71.5 31.3 0.39 1.18 66.66 0.86 DP2-11 800 317 4.94 189 37.7 265 19.6 108 56.3 3.53 177 68.1 22.6 0.52 1.23 55.87 0.20 DP2-12 1191 775 8.58 243 80.5 317 105 114 79.9 5.28 158 74 39.3 0.70 1.35 63.03 0.66 DP2-13 1126 697 8.88 291 85.5 337 14 90.5 66.5 4.33 79.8 50.6 38.6 0.73 1.25 66.64 1.08 DP2-14 289 193 5.95 101 35.2 119 33.1 47.4 25.7 2.1 225 45.6 19.3 0.54 1.06 64.98 0.36 DP2-15 1073 763 14.4 247 151 292 27.8 124 95.8 6.66 343 110 61.6 0.77 1.49 66.40 0.52 DP2-16 − − 6.0 − 57.0 75.6 16.3 35.9 − − − − − − − 59.96 0.14 DP2-17 − − 5.0 − 83.0 154.0 15.9 76.3 − − − − − − − 54.50 0.29 HX井 HX0-12 191.3 264.5 1.7 115.3 34.9 168.3 7.2 18.2 14.8 1.57 48.5 40.9 20.7 0.81 1.31 78.19 0.32 HX0-8 619.2 386.8 4.5 164.6 58.9 210.2 20.4 62.4 50.77 2.36 65.0 74.3 31.9 0.81 1.45 81.13 0.96 HX0-7 917.7 857.3 5.5 198.7 76.6 401.7 15.2 49.2 43.86 3.18 81.3 43.0 30.8 0.89 1.27 79.98 1.20 HX0-3 1324.5 419.4 7.7 213.0 66.6 237.9 18.1 92.7 81.84 3.45 261.0 52.1 31.5 0.88 1.53 81.62 0.33 HX0-1 399.5 146.8 1.8 82.1 27.4 136.5 2.6 21.9 34.42 1.63 − 47.2 28.17 1.57 1.26 74.65 0.04 HX1-2 293.1 119.7 0.9 57.9 14.8 54.0 3.9 22.6 15.58 1.03 − 19.5 6 0.69 1.47 72.42 0.03 HX1-13 337.7 104.4 2.3 56.8 16.8 95.6 4.4 32.8 16.23 1.31 148.5 21.1 7.2 0.49 1.20 74.43 0.10 HX1-15 504.8 192.5 1.6 85.1 21.7 210.5 4.7 44.8 37.37 1.32 110.7 24.1 8.5 0.83 1.32 81.27 0.06 HX1-25 950.9 114.6 8.4 80.4 28.8 120.1 6.2 50.8 25.19 1.3 222.1 63.8 17.6 0.50 1.32 74.63 0.13 HX1-28 325.8 115.5 7.4 75.7 23.4 105.5 8.29 48.7 22.99 1.6 232.6 28.1 11.3 0.47 1.23 70.44 0.34 HX1-1 1382.1 371.8 5.6 135.4 60.8 195.3 7.6 44.7 76.97 4.54 198.2 63.5 62.2 1.72 2.62 87.76 0.35 HX1-3 1081.1 450.4 4.1 177.5 51.5 136.6 11.3 57.1 46.35 3.83 244.2 43.8 22.7 0.81 1.57 81.96 0.15 HX1-6 1486.8 373.2 28.7 273.3 95.7 225.2 21.1 140.3 49.46 6.18 228.4 53.8 36.6 0.35 1.21 86.68 1.65 HX1-8 1569.4 233.0 8.2 170.5 56.1 161.1 8.0 66.4 70.65 2.55 300.7 85.8 49.9 1.06 1.88 82.41 0.29 HX1-9 1465.0 463.2 16.1 286.0 115.5 679.5 22.4 151.4 121.89 4.51 247.2 55.8 31.9 0.81 1.43 82.92 0.72 HX1-10 1300.9 361.6 10 219.9 93.6 362.0 43.2 109.2 119.56 7.1 348.9 76.7 52.6 1.09 1.36 84.78 0.53 HX1-11 2233.9 313.2 10.2 193.8 66.5 241.3 7.4 75.8 83.85 3.83 270.5 83.3 49.1 1.11 1.34 85.50 0.56 HX1-14 3299.3 607.7 11.1 216.5 81 268.5 9.2 76.6 99.26 6.3 156.6 65.5 56.6 1.30 1.19 86.05 1.05 HX1-17 3086.0 488.4 11.3 237 92.8 361.6 10.3 73.2 116.77 5.62 155.4 91.0 50.4 1.60 1.25 84.25 1.10 HX1-21 31105 454.9 40 173 105.8 407.7 11.7 150.1 119.77 6.86 151.7 82.4 48.7 0.80 1.18 84.35 3.38 HX1-23 1256.0 523.9 5.7 218.6 78.6 5723 14.2 80.3 107 4.27 225.2 55.0 31.2 1.33 1.26 86.41 0.44 HX1-27 1277.5 423.7 22.0 252.6 88.6 394.6 21.4 104.9 68.48 7.22 128.8 55.3 35.2 0.65 1.16 85.57 2.05 HX1-31 4403.5 488.7 9.8 236.3 88.8 259.4 15.5 91 96.36 9.27 317.9 72.7 48.9 1.06 1.42 85.56 0.50 注:LaN/CeN是样品经过北美上地壳页岩组合的元素含量[71]标准化后计算的比值,计算公式为LaN/CeN=(Las样品/LaAUCC)/(Ce样品/CeAUCC);元素富集系数按照XEF=(X/Al)样品/(X/Al)AUCC公式计算,过剩Cuxs=Cu样品−Al样品×(Cu/Al)AUCC;CIA指数计算方法见文献[72];C指数计算方法见文献[28]。 -
[1] 谈昕, 邱振, 卢斌, 等. 华南地区不同时代硅质岩地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2018, 18(2):7-19
TAN Xin, QIU Zhen, LU Bin, et al. Geochemical characteristics for siliceous rocks of different ages in south china and their geological significance [J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2018, 18(2): 7-19.
[2] 姚旭, 周瑶琪, 李素, 等. 硅质岩与二叠纪硅质沉积事件研究现状及进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2013, 28(11):1189-1200
YAO Xu, ZHOU Yaoqi, LI Su, et al. Research status and advances in chert and Permian chert event [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2013, 28(11): 1189-1200.
[3] Murchey B L, Jones D L. A mid-Permian chert event: widespread deposition of biogenic siliceous sediments in coastal, island arc and oceanic basins [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1992, 96(1-2): 161-174. doi: 10.1016/0031-0182(92)90066-E
[4] 程成, 李双应, 赵大千, 等. 扬子地台北缘中上二叠统层状硅质岩的地球化学特征及其对古地理、古海洋演化的响应[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2015, 34(1):155-166 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2015.01.018
CHENG Cheng, LI Shuangying, ZHAO Daqian, et al. Geochemical characteristics of the middle-upper Permian bedded cherts in the northern margin of the Yangtze block and its response to the evolution of paleogeography and Paleo-Ocean [J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2015, 34(1): 155-166. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2015.01.018
[5] 吴勘, 马强分, 冯庆来. 扬子板块北缘孤峰组地层划分及空间分布特征[J]. 地层学杂志, 2015, 39(1):33-39 doi: 10.19839/j.cnki.dcxzz.2015.01.003
WU Kan, MA Qiangfen, FENG Qinglai. Stratigraphic division and spatial distribution of the Middle Permian KuhFeng Formation in the Northern Yangtze Block [J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2015, 39(1): 33-39. doi: 10.19839/j.cnki.dcxzz.2015.01.003
[6] 杨玉卿, 冯增昭. 华南下二叠统层状硅岩的形成及意义[J]. 岩石学报, 1997, 13(1):112-120
YANG Yuqing, FENG Zengzhao. Formation and Significance of the Bedded Siliceous Rocks of the Lower Permian in South China [J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 1997, 13(1): 112-120.
[7] 夏邦栋, 钟立荣, 方中, 等. 下扬子区早二叠世孤峰组层状硅质岩成因[J]. 地质学报, 1995, 69(2):125-137
XIA Bangdong, ZHONG Lirong, FANG Zhong, et al. The origin of cherts of the Early Permian Gufeng Formation in the Lower Yangtze Area, Eastern China [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1995, 69(2): 125-137.
[8] 加娜提古丽·吾斯曼, 周瑶琪, 姚旭, 等. 安徽省巢湖地区二叠纪栖霞组、孤峰组硅质岩地球化学特征对比及大地构造背景分析[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(4):734-745
JIANATIGULI W, ZHOU Yaoqi, YAO Xu, et al. Geochemical characteristics comparison and tectonic background analysis of siliceous rocks from Qixia Formation and Gufeng Formation of Permian in Chaohu Area, Anhui Province [J]. Geoscience, 2017, 31(4): 734-745.
[9] 韩宗珠, 肖楠, 李安龙, 等. 安徽巢湖下二叠统孤峰组硅质岩沉积地球化学特征与沉积环境分析[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2014, 44(4):78-85,99
HAN Zongzhu, XIAO Nan, LI Anlong, et al. Geochemistry and sedimentary environments analysis of siliceous rocks from the Gufeng Formation of Lower Permian in Chaohu Region, Anhui Province [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2014, 44(4): 78-85,99.
[10] 李红敬, 林正良, 解习农. 下扬子地区古生界硅岩地球化学特征及成因[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2015, 27(5):232-239
LI Hongjing, LIN Zhengliang, XIE Xinong. Geochemical characteristics and origin of Palaeozoic siliceous rocks in Lower Yangtze area [J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2015, 27(5): 232-239.
[11] 吕炳全, 瞿建忠. 下扬子地区早二叠世海进和上升流形成的缺氧环境的沉积[J]. 科学通报, 1990, 35(14):1193-1198
LV Bingquan, QU Jianzhong. Sedimentation of anoxic environments under transgression and upwelling process in Early Permian in Lower Yangtze area [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1990, 35(14): 1193-1198.
[12] 鄢菲, 胡望水, 吕炳全, 等. 下扬子中二叠统上升流相与烃源岩的关系研究[J]. 海洋石油, 2008, 28(2):62-67 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2008.02.011
YAN Fei, HU Wangshui, LV Bingquan, et al. Relationship between middle Permian upwelling facies and hydrocarbon in lower Yangtze area [J]. Offshore Oil, 2008, 28(2): 62-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2008.02.011
[13] Kametaka M, Takebe M, Nagai H, et al. Sedimentary environments of the Middle Permian phosphorite–chert complex from the northeastern Yangtze platform, China; the Gufeng Formation: a continental shelf radiolarian chert [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2005, 174(3-4): 197-222. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2004.12.005
[14] Zhang B L, Yao S P, Wignall P, et al. Widespread coastal upwelling along the Eastern Paleo-Tethys Margin (South China) during the Middle Permian (Guadalupian): Implications for organic matter accumulation [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 97: 113-126. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.06.025
[15] 姚旭. 东古特提斯洋大陆边缘二叠纪硅质岩成因研究[D]. 中国石油大学(华东)博士学位论文, 2016
YAO Xu. Research on origin of Permian cherts from continental marginal sea of eastern Paleo-Tethys ocean[D]. Doctor Dissertation of China University of Petroleum (East China), 2016.
[16] 赵振洋, 李双建, 王根厚. 中下扬子北缘中二叠统孤峰组层状硅质岩沉积环境、成因及硅质来源探讨[J]. 地球科学进展, 2020, 35(2):137-153 doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2020.003
ZHAO Zhenyang, LI Shuangjian, WANG Genhou. Discussion on sedimentary environments, origin and source of Middle Permian Gufeng Formation bedded cherts in the northern margin of the Middle-Lower Yangtze area [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2020, 35(2): 137-153. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2020.003
[17] Shi L, Feng Q L, Shen J, et al. Proliferation of shallow-water radiolarians coinciding with enhanced oceanic productivity in reducing conditions during the Middle Permian, South China: evidence from the Gufeng Formation of western Hubei Province [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2016, 444: 1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2015.11.031
[18] Yao X, Zhou Y Q, Hinnov L A. Astronomical forcing of a Middle Permian chert sequence in Chaohu, South China [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2015, 422: 206-221. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2015.04.017
[19] Ito T, Takahashi K, Matsuoka A, et al. The Guadalupian (Permian) Gufeng formation on the north margin of the South China block: a review of the Lithostratigraphy, Radiolarian biostratigraphy, and geochemical characteristics [J]. Paleontological Research, 2019, 23(4): 261-280. doi: 10.2517/2018PR025
[20] 吕炳全, 王红罡, 胡望水, 等. 扬子地块东南古生代上升流沉积相及其与烃源岩的关系[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2004, 24(4):29-35 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2004.04.005
LV Bingquan, WANG Honggang, HU Wangshui, et al. Relationship between Paleozoic upwelling Facies and hydrocarbon in Southeastern Marginal Yangtze Block [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2004, 24(4): 29-35. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2004.04.005
[21] 张水昌, 张宝民, 边立曾, 等. 中国海相烃源岩发育控制因素[J]. 地学前缘, 2005, 12(3):39-48
ZHANG Shuichang, ZHANG Baomin, BIAN Lizeng, et al. Development constraints of marine source rocks in China [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2005, 12(3): 39-48.
[22] 王汝建, 沈高平, SASHIDA K. 苏皖地区孤峰组放射虫动物群及其古环境意义[J]. 同济大学学报, 1997, 25(5):559-564
WANG Rujian, SHEN Gaoping, SASHIDA K. Studies on radiolarian fauna from Gufeng formation in Anhui and Jiangsu provinces, East China and its paleoenvironmental significance [J]. Journal of Tongji University, 1997, 25(5): 559-564.
[23] 张尚锋, 许光彩, 朱锐, 等. 上升流沉积的研究现状和发展趋势[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2012, 34(1):7-11,30 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2012.01.002
ZHANG Shangfeng, XU Guangcai, ZHU Rui, et al. Research status and development tendency of upwelling sediments [J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2012, 34(1): 7-11,30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2012.01.002
[24] 翟刚毅, 王玉芳, 刘国恒, 等. 中国二叠系海陆交互相页岩气富集成藏特征及前景分析[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2020, 40(3):102-117 doi: 10.19826/j.cnki.1009-3850.2020.07003
ZHAI Gangyi, WANG Yufang, LIU Guoheng, et al. Enrichment and accumulation characteristics and prospect analysis of the Permian marine conticental multiphase shale gas in China [J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2020, 40(3): 102-117. doi: 10.19826/j.cnki.1009-3850.2020.07003
[25] 廖圣兵, 石刚, 李建青, 等. 安徽望江地区WWD1井钻遇二叠系孤峰组页岩气[J]. 中国地质, 2021, 48(5):1657-1658
LIAO Shengbing, SHI Gang, LI Jianqing, et al. Shale gas drilled by well WWD1 in the Wangjiang area of Anhui Province [J]. Geology in China, 2021, 48(5): 1657-1658.
[26] 陈建文, 雷宝华, 梁杰, 等. 南黄海盆地油气资源调查新进展[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(3):1-23 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2018.03.001
CHEN Jianwen, LEI Baohua, LIANG Jie, et al. New progress of petroleum resources survey in South Yellow Sea basin [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(3): 1-23. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2018.03.001
[27] Cai L X, Xiao G L, Guo X W, et al. Assessment of Mesozoic and Upper Paleozoic source rocks in the South Yellow Sea Basin based on the continuous borehole CSDP-2 [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 101: 30-42. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.11.028
[28] Chen G, Chang X C, Guo X W, et al. Geochemical characteristics and organic matter enrichment mechanism of Permian black mudstone in the South Yellow Sea Basin, China [J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2022, 208: 109248. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2021.109248
[29] 叶舟, 马力, 梁兴, 等. 下扬子独立地块与中生代改造型残留盆地[J]. 地质科学, 2006, 41(1):81-101 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2006.01.008
YE Zhou, MA Li, LIANG Xing, et al. The independent Lower Yangtze block and Mesozoic reformed residual basins [J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2006, 41(1): 81-101. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2006.01.008
[30] 蔡乾忠. 中国东部与朝鲜大地构造单元对应划分[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1995, 15(1):7-24 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.1995.01.001
CAI Qianzhong. Corresponding division of geotectonic units of eastern China and Korea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1995, 15(1): 7-24. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.1995.01.001
[31] 吴根耀, 陈焕疆, 马力, 等. 苏皖地块: 特提斯演化阶段独立的构造单元[J]. 古地理学报, 2002, 4(2):77-87 doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2002.02.010
WU Genyao, CHEN Huanjiang, MA Li, et al. Su-Wan block: an independent tectonic unit during period of Tethyan evolution [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2002, 4(2): 77-87. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2002.02.010
[32] 陈建文, 张银国, 欧光习, 等. 南黄海古生界油气多期成藏的包体证据[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2018, 34(2):69-70 doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2018.02010
CHEN Jianwen, ZHANG Yinguo, OU Guangxi, et al. Inclusion evidence of multi-stage hydrocarbon accumulation in the Paleozoic of South Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2018, 34(2): 69-70. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2018.02010
[33] 高顺莉, 谭思哲, 陈春峰, 等. 下扬子-南黄海二叠纪岩相古地理特征及油气勘探启示[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2021, 37(4):53-60 doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2021.019
GAO Shunli, TAN Sizhe, CHEN Chunfeng, et al. Permian Lithofacies paleogeography of the South Yellow Sea area, Lower Yangtze plate and its implications for petroleum exploration [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2021, 37(4): 53-60. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2021.019
[34] 郭念发, 赵红格, 陈红, 等. 下扬子地区海相地层油气赋存条件分析及选区评价[J]. 西北大学学报:自然科学版, 2002, 32(5):526-530
GUO Nianfa, ZHAO Hongge, CHEN Hong, et al. Oil-gas occurrence conditions and evaluation of chosen belts of the marine strata in Yangtze Area [J]. Journal of Northwest University:Natural Science Edition, 2002, 32(5): 526-530.
[35] 顾忠安, 郑荣才, 黄建良, 等. 苏皖地区二叠系页岩气成藏地质条件[J]. 成都理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2014, 41(3):274-282
GU Zhong’an, ZHENG Rongcai, HUANG Jianliang, et al. Geological conditions of Permian shale gas accumulation in Jiangsu-Anhui of China [J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology:Science & Technology Edition, 2014, 41(3): 274-282.
[36] 金之钧, 刘光祥, 方成名, 等. 下扬子区海相油气勘探选区评价研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2013, 35(5):473-479,486 doi: 10.11781/sysydz201305473
JIN Zhijun, LIU Guangxiang, FANG Chengming, et al. Evaluation of selected areas for petroleum exploration in marine strata of Lower Yangtze region [J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 2013, 35(5): 473-479,486. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201305473
[37] 冯增昭, 杨玉卿, 金振奎, 等. 中国南方二叠纪岩相古地理[J]. 沉积学报, 1996, 14(2):1-11 doi: 10.14027/j.cnki.cjxb.1996.02.001
FENG Zengzhao, YANG Yuqing, JIN Zhenkui, et al. Lithofacies paleogeography of the Permian of South China [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1996, 14(2): 1-11. doi: 10.14027/j.cnki.cjxb.1996.02.001
[38] 朱光, 徐嘉炜, 刘国生, 等. 下扬子地区前陆变形构造格局及其动力学机制[J]. 中国区域地质, 1999, 18(1):73-79
ZHU Guang, XU Jiawei, LIU Guosheng, et al. Tectonic pattern and dynamic mechanism of the foreland deformation in the Lower Yangtze Region [J]. Regional Geology of China, 1999, 18(1): 73-79.
[39] 郭彤楼. 下扬子地区中古生界叠加改造特征与多源多期成藏[J]. 石油实验地质, 2004, 26(4):319-323 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2004.04.002
GUO Tonglou. Superimposition and modification of the Mesozoic and Paleozoic Basins and multi-stages of hydrocarbon accumulation with multiple source rocks in Lower Yangtze area [J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2004, 26(4): 319-323. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2004.04.002
[40] 姚永坚, 夏斌, 冯志强, 等. 南黄海古生代以来构造演化[J]. 石油实验地质, 2005, 27(2):124-128 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2005.02.005
YAO Yongjian, XIA Bin, FENG Zhiqiang, et al. Tectonic evolution of the South Yellow Sea since the Paleozoic [J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2005, 27(2): 124-128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2005.02.005
[41] 罗志立, 金以钟, 朱夔玉, 等. 试论上扬子地台的峨眉地裂运动[J]. 地质论评, 1988, 34(1):11-24 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1988.01.002
LUO Zhili, JIN Yizhong, ZHU Kuiyu, et al. On Emei taphrogenesis of the Upper Yangtze platform [J]. Geological Review, 1988, 34(1): 11-24. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1988.01.002
[42] 杜叶龙, 李双应, 孔为伦, 等. 安徽泾县-南陵地区二叠纪沉积相与沉积环境分析[J]. 地层学杂志, 2010, 34(4):431-444
DU Yelong, LI Shuangying, KONG Weilun, et al. The Permian sedimentary facies and depositional environment analysis in the Jingxian-Nanling region of Anhui [J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2010, 34(4): 431-444.
[43] 朱文博, 张训华, 周道容, 等. 下扬子地区二叠系海相页岩孔隙特征新认识及页岩气勘探启示[J]. 天然气工业, 2021, 41(7):41-55 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2021.07.005
ZHU Wenbo, ZHANG Xunhua, ZHOU Daorong, et al. New cognition on pore structure characteristics of Permian marine shale in the Lower Yangtze Region and its implications for shale gas exploration [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(7): 41-55. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2021.07.005
[44] 胡世忠. 对孤峰组的新认识[J]. 火山地质与矿产, 2000, 21(1):63-68
HU Shizhong. New consideration of Gufong Formation by stratigraphy check up [J]. Volcanology & Mineral Resources, 2000, 21(1): 63-68.
[45] 廖志伟. 下扬子地区二叠纪晚期沉积环境演化与烃源岩发育特征研究[D]. 南京大学博士学位论文, 2016
LIAO Zhiwei. A study of source rock features and sedimentary environmental evolution during the late Permian in the Lower Yangtze Region, Southeastern China[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Nanjing University, 2016.
[46] 庞玉茂. 基于CSDP-2井的南黄海中部隆起构造热演化史研究[D]. 中国科学院大学博士学位论文, 2017
PANG Yumao. Tectonic thermal evolution history of the central uplift of the South Yellow Sea Basin from CSDP-2 drilling well[D]. Doctor Dissertation of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017.
[47] 顾忠安. 苏皖地区二叠系页岩气成藏地质条件分析[D]. 成都理工大学硕士学位论文, 2014
GU Zhong’an. Geological conditions of Permian shale gas accumulation in Jiangsu-Anhui area[D]. Master Dissertation of Chengdu University of Technology, 2014.
[48] 祁江豪, 温珍河, 张训华, 等. 南黄海地区与上扬子地区海相中—古生界岩性地层对比[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2013, 33(1):109-119
QI Jianghao, WEN Zhenhe, ZHANG Xunhua, et al. Lithostratigraphic correlation of Mesozoic and Palaeozoic Marine strata between South Yellow Sea and Upper Yangtze region [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2013, 33(1): 109-119.
[49] 付小东, 陈娅娜, 罗冰, 等. 四川盆地北部中二叠统茅口组孤峰段优质烃源岩特征及其油气地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(6):1903-1920 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.06.016
FU Xiaodong, CHEN Ya’na, LUO Bing, et al. Characteristics and petroleum geological significance of the high-quality source rocks in the Gufeng Member of the Middle Permian Maokou Formation in the northern Sichuan basin [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(6): 1903-1920. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.06.016
[50] 马永生, 陈洪德, 王国力, 等. 中国南方层序地层与古地理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009
MA Yongsheng, CHEN Hongde, WANG Guoli, et al. Sequence stratigraphy and paleogeography of Southern China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009.
[51] 白卢恒, 石万忠, 张晓明, 等. 下扬子皖南宣泾地区二叠系海相页岩特征及其沉积环境[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(6):2204-2217
BAI Luheng, SHI Wanzhong, ZHANG Xiaoming, et al. Characteristics of Permian marine shale and its sedimentary environment in Xuanjing Area, South Anhui province, Lower Yangtze area [J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(6): 2204-2217.
[52] 邱振, 王清晨. 湘黔桂地区中上二叠统硅质岩的地球化学特征及沉积背景[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(12):3612-3628
QIU Zhen, WANG Qingchen. Geochemistry and sedimentary background of the Middle-Upper Permian cherts in the Xiang-Qian-Gui region [J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2010, 26(12): 3612-3628.
[53] 姚素平, 吴聿元, 余文端, 等. 下扬子区孤峰组—大隆组露头剖面特征与岩相变化[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2022, 12(1):215-232,245 doi: 10.13809/j.cnki.cn32-1825/te.2022.01.019
YAO Suping, WU Yuyuan, YU Wenduan, et al. Outcrop characteristic and lithofacies changes of both Gufeng and Dalong Formations in Lower Yangtze Region [J]. Petroleum Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2022, 12(1): 215-232,245. doi: 10.13809/j.cnki.cn32-1825/te.2022.01.019
[54] 袁飞. 下扬子巢湖-宣城地区二叠系泥页岩储层特征研究[D]. 长江大学硕士学位论文, 2018
YUAN Fei. Study on the characteristics of Permian shale reservoir in the lower Yangtze Chaohu-Xuancheng area[D]. Master Dissertation of Yangtze University, 2018.
[55] 曹涛涛, 宋之光, 罗厚勇, 等. 下扬子地区二叠系海陆过渡相页岩孔隙体系特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(7):1332-1345 doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2016.07.1332
CAO Taotao, SONG Zhiguang, LUO Houyong, et al. Pore system characteristics of Permian transitional shale reservoir in the Lower Yangtze region, China [J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(7): 1332-1345. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2016.07.1332
[56] 梁峰. 中上扬子地区五峰组—龙马溪组页岩气富集模式及有利区优选评价[D]. 中国矿业大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2018
LIANG Feng. The research on shale gas enrichment pattern and the favorable area optimizing of Wufeng-Longmaxi shale in middle and upper Yangtze Region[D]. Doctor Dissertation of China University of Mining & Technology, Beijing, 2018.
[57] 陈建平, 梁狄刚, 张水昌, 等. 中国古生界海相烃源岩生烃潜力评价标准与方法[J]. 地质学报, 2012, 86(7):1132-1142
CHEN Jianping, LIANG Digang, ZHANG Shuichang, et al. Evaluation criterion and methods of the hydrocarbon generation potential for China's Paleozoic marine source rocks [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2012, 86(7): 1132-1142.
[58] 傅宁, 刘英丽, 熊斌辉, 等. CZ35-2-1井古生界烃源岩地球化学参数异常分析[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 2003, 17(2):93-98
FU Ning, LIU Yingli, XIONG Binhui, et al. An Analysis of abnormal geochemical parameters of Palaeozoic source rocks in CZ35-2-1 well, the Southern Yellow Sea [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 2003, 17(2): 93-98.
[59] 赵青芳, 王建强, 陈建文, 等. 下扬子区海相古生界高成熟烃源岩评价指标的优选[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(2-3):330-340
ZHAO Qingfang, WANG Jianqiang, CHEN Jianwen, et al. Optimization of evaluation index of Paleozoic high mature marine source rock in the Lower Yangze region [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2021, 40(2-3): 330-340.
[60] 白帆. 下扬子西部地区中二叠统孤峰组气源岩发育特征及控制因素[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(3):468-475 doi: 10.11781/sysydz202103468
BAI Fan. Characteristics and controlling factors of natural gas source rocks of Middle Permian Gufeng Formation in western part of Lower Yangtze Platform, China [J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 2021, 43(3): 468-475. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202103468
[61] 梁狄刚, 郭彤楼, 陈建平, 等. 中国南方海相生烃成藏研究的若干新进展(一): 南方四套区域性海相烃源岩的分布[J]. 海相油气地质, 2008, 13(2):1-16 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2008.02.001
LIANG Digang, GUO Tonglou, CHEN Jianping, et al. Some progresses on studies of hydrocarbon generation and accumulation in marine sedimentary regions, Southern China (Part 1): distribution of four suits of regional marine source rocks [J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2008, 13(2): 1-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2008.02.001
[62] Boström K, Kraemer T, Gartner S. Provenance and accumulation rates of opaline silica, Al, Ti, Fe, Mn, Cu, Ni and Co in Pacific pelagic sediments [J]. Chemical Geology, 1973, 11(2): 123-148. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(73)90049-1
[63] Murray R W, Ten Brink M R B, Gerlach D C, et al. Rare earth, major, and trace elements in chert from the Franciscan Complex and Monterey Group, California: Assessing REE sources to fine-grained marine sediments [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1991, 55(7): 1875-1895. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(91)90030-9
[64] Murray R W. Chemical criteria to identify the depositional environment of chert: general principles and applications [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1994, 90(3-4): 213-232. doi: 10.1016/0037-0738(94)90039-6
[65] 肖斌, 刘树根, 冉波, 等. 基于元素Mn、Co、Cd、Mo的海相沉积岩有机质富集因素判别指标在四川盆地北缘的应用[J]. 地质论评, 2019, 65(6):1316-1330 doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2019.06.002
XIAO Bin, LIU Shugen, RAN Bo, et al. Identification of organic matter enrichment factors in marine sedimentary rocks based on elements Mn, Co, Cd and Mo: application in the northern margin of Sichuan Basin, South China [J]. Geological Review, 2019, 65(6): 1316-1330. doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2019.06.002
[66] Algeo T J, Tribovillard N. Environmental analysis of paleoceanographic systems based on molybdenum-uranium covariation [J]. Chemical Geology, 2009, 268(3-4): 211-225. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.09.001
[67] Algeo T, Lyons T. Mo-total organic carbon covariation in modern anoxic marine environments: Implications for analysis of paleoredox and paleohydrographic conditions [J]. Paleoceanography, 2006, 21(1): PA1016.
[68] Scott C, Lyons T. Contrasting molybdenum cycling and isotopic properties in euxinic versus non-euxinic sediments and sedimentary rocks: Refining the paleoproxies [J]. Chemical Geology, 2012, 324-325: 19-27. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.05.012
[69] Paulmier A, Ruiz-Pino D. Oxygen minimum zones (OMZs) in the modern ocean [J]. Progress in Oceanography, 2009, 80(3-4): 113-128. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2008.08.001
[70] Tribovillard N, Algeo T J, Baudin F, et al. Analysis of marine environmental conditions based onmolybdenum–uranium covariation—Applications to Mesozoic paleoceanography [J]. Chemical Geology, 2012, 324-325: 46-58. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2011.09.009
[71] Mclennan S M. Relationships between the trace element composition of sedimentary rocks and upper continental crust [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2001, 2(4): 1021.
[72] 牟传龙, 葛祥英, 余谦, 等. 川西南地区五峰—龙马溪组黑色页岩古气候及物源特征: 来自新地2井地球化学记录[J]. 古地理学报, 2019, 21(5):835-854 doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2019.05.057
MOU Chuanlong, GE Xiangying, YU Qian, et al. Palaeoclimatology and provenance of black shales from Wufeng-Longmaxi Formations in southwestern Sichuan Province: From geochemical records of Well Xindi-2 [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2019, 21(5): 835-854. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2019.05.057
[73] Adachi M, Yamamoto K, Sugisaki R. Hydrothermal chert and associated siliceous rocks from the northern Pacific their geological significance as indication of ocean ridge activity [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1986, 47(1-2): 125-148. doi: 10.1016/0037-0738(86)90075-8
[74] Dean W E, Leinen M, Stow D A V. Classification of deep-sea, fine-grained sediments [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1985, 55(2): 250-256.
[75] 朱如凯, 李梦莹, 杨静儒, 等. 细粒沉积学研究进展与发展方向[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(2):251-264 doi: 10.11743/ogg20220201
ZHU Rukai, LI Mengying, YANG Jingru, et al. Advances and trends of fine-grained sedimentology [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(2): 251-264. doi: 10.11743/ogg20220201
[76] Böning P, Brumsack H J, Böttcher M E, et al. Geochemistry of Peruvian near-surface sediments [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2004, 68(21): 4429-4451. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2004.04.027
[77] Zhang B L, Wignall P, Yao S P, et al. Collapsed upwelling and intensified euxinia in response to climate warming during the Capitanian (Middle Permian) mass extinction [J]. Gondwana Research, 2021, 89: 31-46. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2020.09.003
[78] Sweere T, Van Den Boorn S, Dickson A J, et al. Definition of new trace-metal proxies for the controls on organic matter enrichment in marine sediments based on Mn, Co, Mo and Cd concentration [J]. Chemical Geology, 2016, 441: 235-245. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2016.08.028
[79] Nesbitt H W, Young G M. Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites [J]. Nature, 1982, 299(5885): 715-717. doi: 10.1038/299715a0
[80] Nesbitt H W, Young G M. Prediction of some weathering trends of plutonic and volcanic rocks based on thermodynamic and kinetic considerations [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1984, 48(7): 1523-1534. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(84)90408-3
[81] 赵占仑, 温小浩, 汤连生, 等. 化学蚀变指数指示古气候变化的适用性探讨[J]. 沉积学报, 2018, 36(2):343-353 doi: 10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2018.026
ZHAO Zhanlun, WEN Xiaohao, TANG Liansheng, et al. Applicability of chemical alteration index to indication of paleoclimate change by different sedimentary facies [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2018, 36(2): 343-353. doi: 10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2018.026
[82] 颜佳新, 赵坤. 二叠-三叠纪东特提斯地区古地理、古气候和、古海洋演化与地球表层多圈层事件耦合[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2001, 44(11):968-978 doi: 10.1007/BF02875390
YAN Jiaxin, ZHAO Kun. Permo-Triassic paleogeographic, paleoclimatic and paleoceanographic evolutions in eastern Tethys and their coupling [J]. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences, 2001, 44(11): 968-978. doi: 10.1007/BF02875390
[83] Zhang B L, Yao S P, Hu W X, et al. Development of a high-productivity and anoxic-euxinic condition during the late Guadalupian in the Lower Yangtze region: Implications for the mid-Capitanian extinction event [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2019, 531: 108630. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2018.01.021
[84] Jones B, Manning D. Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of palaeoredox conditions in ancient mudstones [J]. Chemical Geology, 1994, 111(1-4): 111-129. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(94)90085-X
[85] 秦建中, 腾格尔, 付小东. 海相优质烃源层评价与形成条件研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2009, 31(4):366-372,378 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2009.04.010
QIN Jianzhong, TENGER, FU Xiaodong. Study of forming condition on marine excellent source rocks and its evaluation [J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2009, 31(4): 366-372,378. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2009.04.010
[86] 腾格尔, 刘文汇, 徐永昌, 等. 海相地层无机参数与烃源岩发育环境的相关研究: 以鄂尔多斯盆地为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2005, 26(4):411-421 doi: 10.11743/ogg20050403
TENGER, LIU Wenhui, XU Yongchang, et al. Study on relation between inorganic parameters in marine deposits and developmental environment of hydrocarbon source rocks: taking Ordos basin as an example [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2005, 26(4): 411-421. doi: 10.11743/ogg20050403
[87] 刘喜停, 颜佳新, 薛武强, 等. 华南中二叠统栖霞组海相烃源岩形成的地球生物学过程[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2014, 57(5):957-964 doi: 10.1007/s11430-013-4764-5
LIU Xiting, YAN Jiaxin, XUE Wuqiang, et al. The geobiological formation process of the marine source rocks in the Middle Permian Chihsia Formation of South China [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2014, 57(5): 957-964. doi: 10.1007/s11430-013-4764-5
[88] 朱伟林, 陈春峰, 张伯成, 等. 南黄海古生代盆地原型演变与烃源岩发育特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(5):728-741 doi: 10.11781/sysydz202005728
ZHU Weilin, CHEN Chunfeng, ZHANG Bocheng, et al. Paleozoic basin prototype evolution and source rock development in the South Yellow Sea [J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(5): 728-741. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202005728
[89] 陈建文, 龚建明, 李刚, 等. 南黄海海相中-古生界油气资源潜力巨大[J]. 海洋地质前言, 2016, 32(1):1-7
CHEN Jianwen, GONG Jianming, LI Gang, et al. Great Resources potential of the Marine Mesozoic-Paleozoic in the South Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2016, 32(1): 1-7.
[90] 陈建文, 梁杰, 张银国, 等. 中国海域油气资源潜力分析与黄东海海域油气资源调查进展[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2019, 39(6):1-29 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2019112001
CHEN Jianwen, LIANG Jie, ZHANG Yinguo, et al. Regional evaluation of oil and gas resources in offshore China and exploration of marine Paleo-Mesozoic oil and gas in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2019, 39(6): 1-29. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2019112001
[91] 陈建文, 杨长清, 张莉, 等. 中国海域前新生代地层分布及其油气勘探方向[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2022, 42(1):1-25
CHEN Jianwen, YANG Changqing, ZHANG Li, et al. Distribution of Pre-Cenozoic strata and petroleum prospecting directions in China Seas [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2022, 42(1): 1-25.
-



 下载:
下载: