Distribution, source, and transport of particulate organic carbon in the Yellow River estuary as affected by the water-sediment regulation
-
摘要:
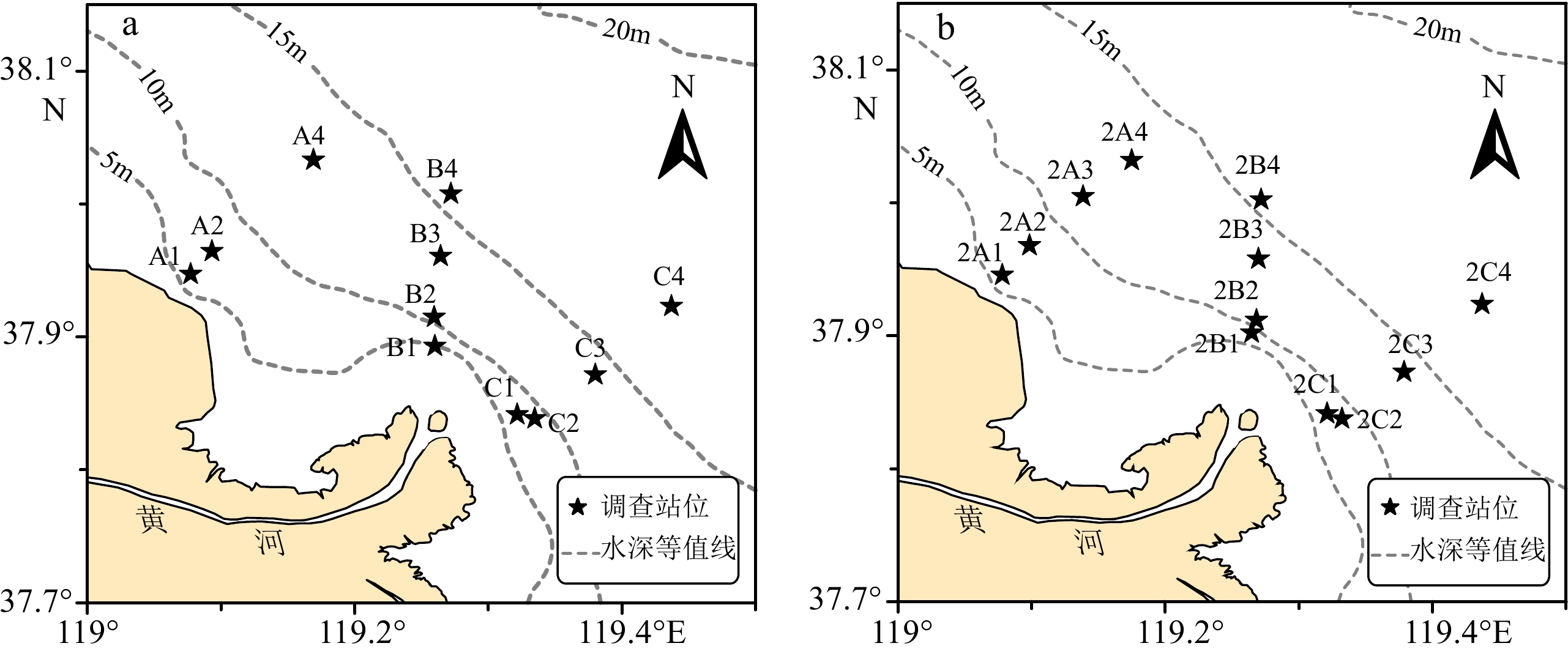
黄河是全球输沙量最大的河流之一,陆源颗粒有机碳通量高。然而,近年来流域水库调控对黄河下游水文格局和颗粒有机碳输送产生了重要影响,小浪底水库调水调沙时期成为黄河水沙和有机碳入海的关键时段。为揭示水库调控对河口水动力和有机碳分布的影响机制,基于2020年7月调水期和调沙期黄河口的水动力观测结果,结合沉积物有机碳测试结果,研究了水库调控不同阶段下河口沉积物粒度参数和表层沉积物有机碳的时空分布。研究结果表明,水库不同阶段下悬浮颗粒物的物源和主要扩散、沉积区域的变化,使得黄河口表层沉积物的粒度组成特征发生明显变化;在高径流量的调水期期间,粗颗粒泥沙携带颗粒有机碳在河口距离口门12 km范围内大量埋藏,河口区域表层沉积物的有机碳含量相较于调沙期明显偏低。调水期黄河口陆源有机碳主要来自下游河床冲刷,颗粒较粗,调沙期则转变为水库释放的细颗粒有机碳和流域C3维管植物碎屑。水库调控的不同阶段使得黄河下游河流水动力格局和泥沙运输机制改变,从而引起黄河口沉积有机碳来源和分布的显著变化。因此,人类活动对调节有机碳向海洋的输送及其在近岸海域的分布具有主导性作用。
Abstract:The Yellow River, one of the highest sediment-laden rivers, discharges a huge amount of terrestrial particulate organic carbon (POC) to the sea. However, the reservoir regulations over recent decades have significantly affected the downstream hydrology and POC delivery. The Water-Sediment Regulation Scheme (WSRS) has become a critical time window for the impulse discharges of water, sediment, and POC to the estuary. We investigated the impacts of the WSRS on the estuarine dynamics and POC distribution based on the sampling and observations in the Yellow River estuary in July 2020 corresponding to the two stages (water-regulation stage and sediment-regulation stage) of the WSRS. The distributions of grain-size composition and POC content of surface sediments were presented according to the datasets of in-laboratory analysis. Results indicated that there was a clear turning point of variation in sediment source, grain-size composition, and the POC distribution at the two stages. At the water-regulation stage, the water discharge was high and sediments were relatively coarser and mostly deposited nearshore (<12 km off the river mouth) with low POC content, while at the sediment-regulation stage, fine-gained sediments were delivered offshore with significant increase in POC content. POC in surface sediments at the water-regulation stage was sourced maily from the lower river erosion, while that at the sediment-regulation stage was composed of the dam-released soil carbon and C3 vascular plant debris. The rapid changes in POC source and distribution in the Yellow River estuary were controlled by the reservoir regulation, which significantly changed the downstream hydrology and sediment transport. Therefore, human intervention can play an important role in regulating the seaward POC delivery and distribution in the coastal sea.
-
Key words:
- Water-Sediment Regulation /
- POC /
- sediment transport /
- Yellow River estuary
-

-
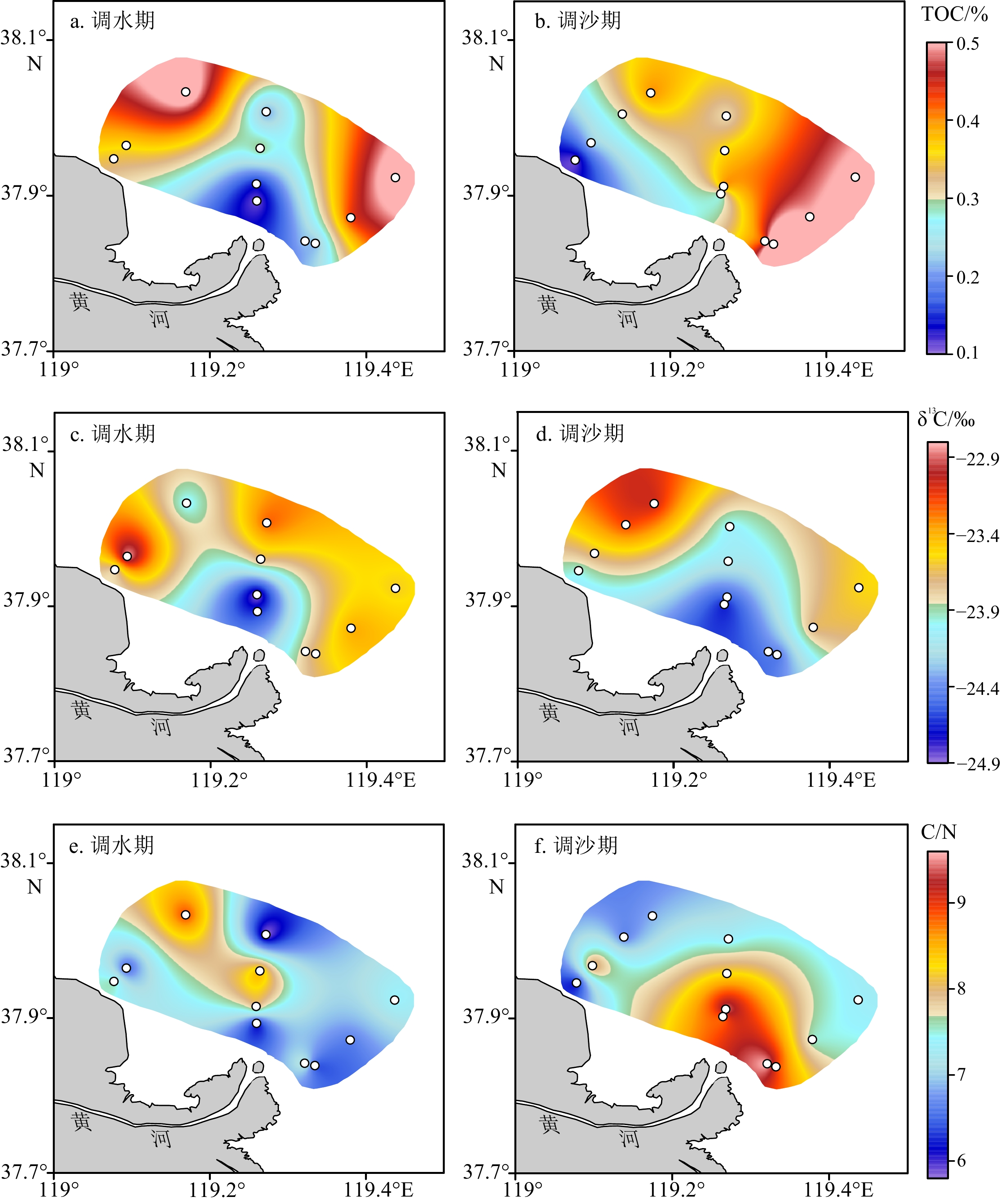
表 1 TOC含量与各粒级组分含量相关性分析
Table 1. Correlations of TOC content and each fractional percentage of sediment
不同时期黄河口表层沉积物TOC含量 砂含量 粉砂含量 黏土含量 调水期 −0.54 0.10 0.75** 调沙期 −0.90** 0.50 0.94** 注:*为 p<0.05,** 为p<0.01。 -
[1] Galy V, Peucker-Ehrenbrink B, Eglinton T. Global carbon export from the terrestrial biosphere controlled by erosion [J]. Nature, 2015, 521(7551): 204-207. doi: 10.1038/nature14400
[2] Milliman J D, Meade R H. World-wide delivery of river sediment to the oceans [J]. The Journal of Geology, 1983, 91(1): 1-21. doi: 10.1086/628741
[3] Cauwet G, Mackenzie F T. Carbon inputs and distribution in estuaries of turbid rivers: the Yang Tze and Yellow rivers (China) [J]. Marine Chemistry, 1993, 43(1-4): 235-246. doi: 10.1016/0304-4203(93)90229-H
[4] 杨作升, 李国刚, 王厚杰, 等. 55年来黄河下游逐日水沙过程变化及其对干流建库的响应[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2008, 28(6):9-18
YANG Zuosheng, LI Guogang, WANG Houjie, et al. Variation of daily water and sediment discharge in the yellow river lower reaches in the past 55 years and its response to the dam operation on its main stream [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2008, 28(6): 9-18.
[5] 胡春宏, 陈建国, 孙雪岚, 等. 黄河下游河道健康状况评价与治理对策[J]. 水利学报, 2008, 39(10):1189-1196
HU Chunhong, CHEN Jianguo, SUN Xuelan, et al. Health assessment of river course in Lower Yellow River and measures for regulation [J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2008, 39(10): 1189-1196.
[6] 李松, 王厚杰, 张勇, 等. 黄河在调水调沙影响下的入海泥沙通量和粒度的变化趋势[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2015, 31(7):20-27
LI Song, WANG Houjie, ZHANG Yong, et al. Variation in sediment load and grain-size under the influence of Water and Sediment Regulation Scheme (WSRS) of The Huanghe (Yellow) River [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2015, 31(7): 20-27.
[7] Bi N S, Wang H J, Yang Z S. Recent changes in the erosion-accretion patterns of the active Huanghe (Yellow River) delta lobe caused by human activities [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2014, 90: 70-78. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2014.02.014
[8] 于帅, 毕乃双, 王厚杰, 等. 黄河调水调沙影响下河口入海泥沙扩散及沉积效应[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2015(2):155-163
YU Shuai, BI Naishuang, WANG Houjie, et al. Suspended sediment dispersal off the Huanghe (Yellow River) river mouth and its sedimentary effects under impact of the water-sediment regulation scheme [J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2015(2): 155-163.
[9] 王苗苗, 孙志高, 卢晓宁, 等. 调水调沙工程长期实施对黄河口近岸沉积物粒度分布与黏土矿物组成特征的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(4):1256-1262
WANG Miaomiao, SUN Zhigao, LU Xiaoning, et al. Effects of long-term implementation of the flow-sediment regulation scheme on grain and clay compositions of inshore sediments in the Yellow River estuary [J]. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(4): 1256-1262.
[10] 葛雷, 娄广艳, 张军锋, 等. 2010年黄河调水调沙对河口近海盐度影响[J]. 河南水利与南水北调, 2013, 42(1):61-62
GE Lei, LOU Guangyan, ZHANG Junfeng, et al. Effects of the water and sediment regulation scheme from the Yellow River on salinity near the estuary in 2010 [J]. Henan Water Resources and South-to-North Water Diversion, 2013, 42(1): 61-62.
[11] 孙珊, 苏博, 李凡, 等. 调水调沙对黄河口及邻近海域环境状况的影响[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2019, 38(3):399-406
SUN Shan, SU Bo, LI Fan, et al. Effects of water and sediment discharge regulation on environment in the Yellow River Estuary and adjacent waters [J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2019, 38(3): 399-406.
[12] 袁萍, 毕乃双, 吴晓, 等. 现代黄河三角洲表层沉积物的空间分布特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(2):49-57
YUAN Ping, BI Naishuang, WU Xiao, et al. Surface sediments at the subaqueous Yellow River delta: classification and distribution [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2016, 36(2): 49-57.
[13] Wang Y Z, Fan Y B, Bu F, et al. Quantifying effects of water and sediment regulation scheme on the sand bar in the Yellow River estuary in 2014 [J]. Ecohydrology & Hydrobiology, 2020, 20(4): 475-484.
[14] Liu D Y, Li X, Emeis K C, et al. Distribution and sources of organic matter in surface sediments of Bohai Sea near the Yellow River Estuary, China [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2015, 165: 128-136. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2015.09.007
[15] 高立蒙, 姚鹏, 王金鹏, 等. 渤海表层沉积物中有机碳的分布和来源[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 38(6):8-20
GAO Limeng, YAO Peng, WANG Jinpeng, et al. Distribution and sources of organic carbon in surface sediments from the Bohai Sea [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2016, 38(6): 8-20.
[16] Bigot M, Saliot A, Cui X, et al. Organic geochemistry of surface sediments from the Huanghe estuary and adjacent Bohai Sea(China) [J]. Chemical Geology, 1989, 75(4): 339-350. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(89)90006-5
[17] 吴丹, 姚鹏, 黄新莹, 等. 黄河2017特枯年入海有机碳的输运特征[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2020, 50(S1):118-127
WU Dan, YAO Peng, HUANG Xinying, et al. Transport of organic carbon in the lower Yellow River in the extreme drought year of 2017 [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2020, 50(S1): 118-127.
[18] Tao S Q, Eglinton T I, Zhang L, et al. Temporal variability in composition and fluxes of Yellow River particulate organic matter [J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2018, 63(S1): S119-S141. doi: 10.1002/lno.10727
[19] Zhao B, Yao P, Li D, et al. Effects of river damming and delta erosion on organic carbon burial in the Changjiang Estuary and adjacent East China Sea inner shelf [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 793: 148610. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148610
[20] Wang H J, Wu X, Bi N S, et al. Impacts of the dam-orientated water-sediment regulation scheme on the lower reaches and delta of the Yellow River (Huanghe): A review [J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2017, 157: 93-113. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2017.08.005
[21] Wang H J, Bi N S, Saito Y, et al. Recent changes in sediment delivery by the Huanghe (Yellow River) to the sea: Causes and environmental implications in its estuary [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2010, 391(3-4): 302-313. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.07.030
[22] Wu X, Bi N S, Syvitski J, et al. Can reservoir regulation along the Yellow River be a sustainable way to save a sinking delta? [J]. Earth's Future, 2020, 8(11): e2020EF001587.
[23] 于永贵, 石学法, 迟万清, 等. 调水调沙期间黄河口羽状流的逐时变化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(5):41-51
YU Yonggui, SHI Xuefa, CHI Wanqing, et al. Hourly change in sediment plume at the Yellow River mouth during the water-sediment regulation [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(5): 41-51.
[24] Zhang J, Huang W W, Shi M C. Huanghe (Yellow River) and its estuary: Sediment origin, transport and deposition [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 1990, 120(1-4): 203-223. doi: 10.1016/0022-1694(90)90150-V
[25] 党亚爱, 李世清, 王国栋, 等. 黄土高原典型土壤有机碳和微生物碳分布特征的研究[J]. 自然资源学报, 2007, 22(6):936-945
DANG Aiya, LI Shiqing, WANG Guodong, et al. Distribution characteristics of soil organic carbon and microbial biomass carbon on the Loess Plateau [J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2007, 22(6): 936-945.
[26] Zhang L J, Wang L, Cai W J, et al. Impact of human activities on organic carbon transport in the Yellow River [J]. Biogeosciences, 2013, 10(4): 2513-2524. doi: 10.5194/bg-10-2513-2013
[27] Ran L, Lu X X, Xin Z. Erosion-induced massive organic carbon burial and carbon emission in the Yellow River basin, China [J]. Biogeosciences, 2014, 11(4): 945-959. doi: 10.5194/bg-11-945-2014
[28] 乔淑卿, 石学法, 白亚之, 等. 黄河口及邻近渤海海域悬浮体和沉积物中有机碳、氮的分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 沉积学报, 2011, 29(2):354-362
QIAO Shuqing, SHI Xuefa, BAI Yazhi, et al. Distribution of organic carbon, nitrogen in suspended and surface sediments and their controlling factors off the Huanghe (Yellow River) mouth and the Nearby Bohai Sea [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2011, 29(2): 354-362.
[29] 于广磊, 李斌, 李凡, 等. 黄河口附近海域沉积物中碳氮元素地球化学特征及有机质来源研究[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2019, 38(6):862-867
YU Guanglei, LI Bin, LI Fan, et al. Carbon, nitrogen geochemical character and organic matter source study in the coastal sediment of Yellow River Estuary [J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2019, 38(6): 862-867.
[30] Canfield, D E. Factors influencing organic carbon preservation in marine sediments [J]. Chemical Geology, 1994, 114(3-4): 315-329. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(94)90061-2
[31] Hedges J I, Keil R G. Sedimentary organic matter preservation: an assessment and speculative synthesis [J]. Marine Chemistry, 1995, 49(2-3): 81-115. doi: 10.1016/0304-4203(95)00008-F
[32] Meyers P A. Organic geochemical proxies of paleoceanographic, paleolimnologic, and paleoclimatic processes [J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1997, 27(5-6): 213-250. doi: 10.1016/S0146-6380(97)00049-1
[33] 胡利民, 邓声贵, 郭志刚, 等. 夏季渤海湾及邻近海域颗粒有机碳的分布与物源分析[J]. 环境科学, 2009, 30(1):39-46 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2009.01.007
HU Limin, DENG Shenggui, GUO Zhigang, et al. Distribution and source of particulate organic carbon in the Bohai Bay and its adjacent Bohai Sea, China [J]. Environmental Science, 2009, 30(1): 39-46. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2009.01.007
[34] 刘卫国, 宁有丰, 安芷生, 等. 黄土高原现代土壤和古土壤有机碳同位素对植被的响应[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2005, 48(1):93-99 doi: 10.1360/02yd0148
LIU Weiguo, NING Youfeng, AN Zhisheng, et al. Carbon isotopic composition of modern soil and paleosol as a response to vegetation change on the Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences, 2005, 48(1): 93-99. doi: 10.1360/02yd0148
[35] 胡利民. 大河控制性影响下的陆架海沉积有机质的“源—汇”作用: 以渤、黄海为例[D]. 中国海洋大学博士学位论文, 2010
HU Limin. Sources and sinks of sedimentary organic matter in the river-dominated continental shelves: a case study in the Bohai and Yellow Seas[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2010.
-



 下载:
下载: