Composition of deep water in the northwestern Indian Ocean: Evidence from Nd isotopes and redox sensitive elements of surface sediments
-
摘要:
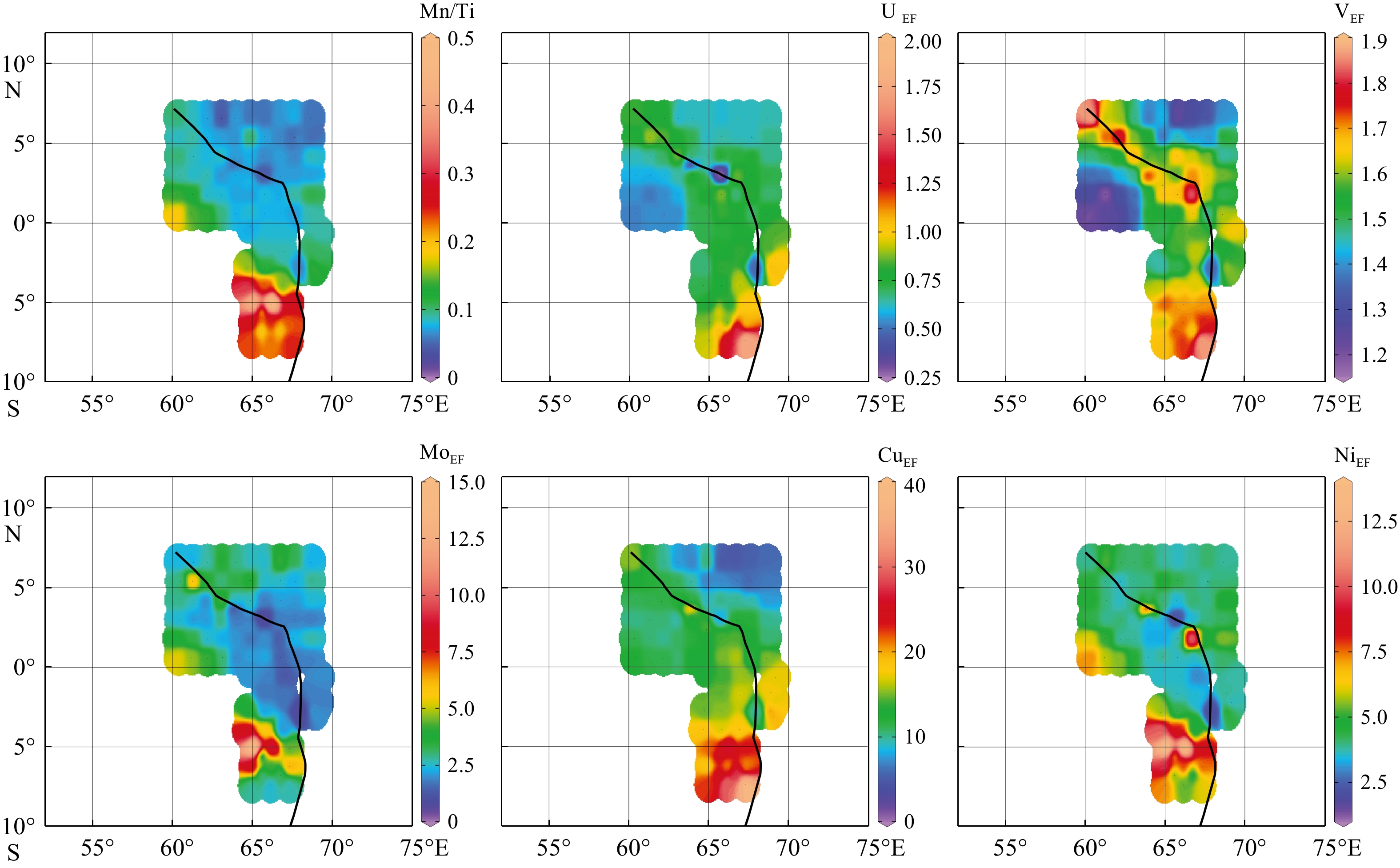
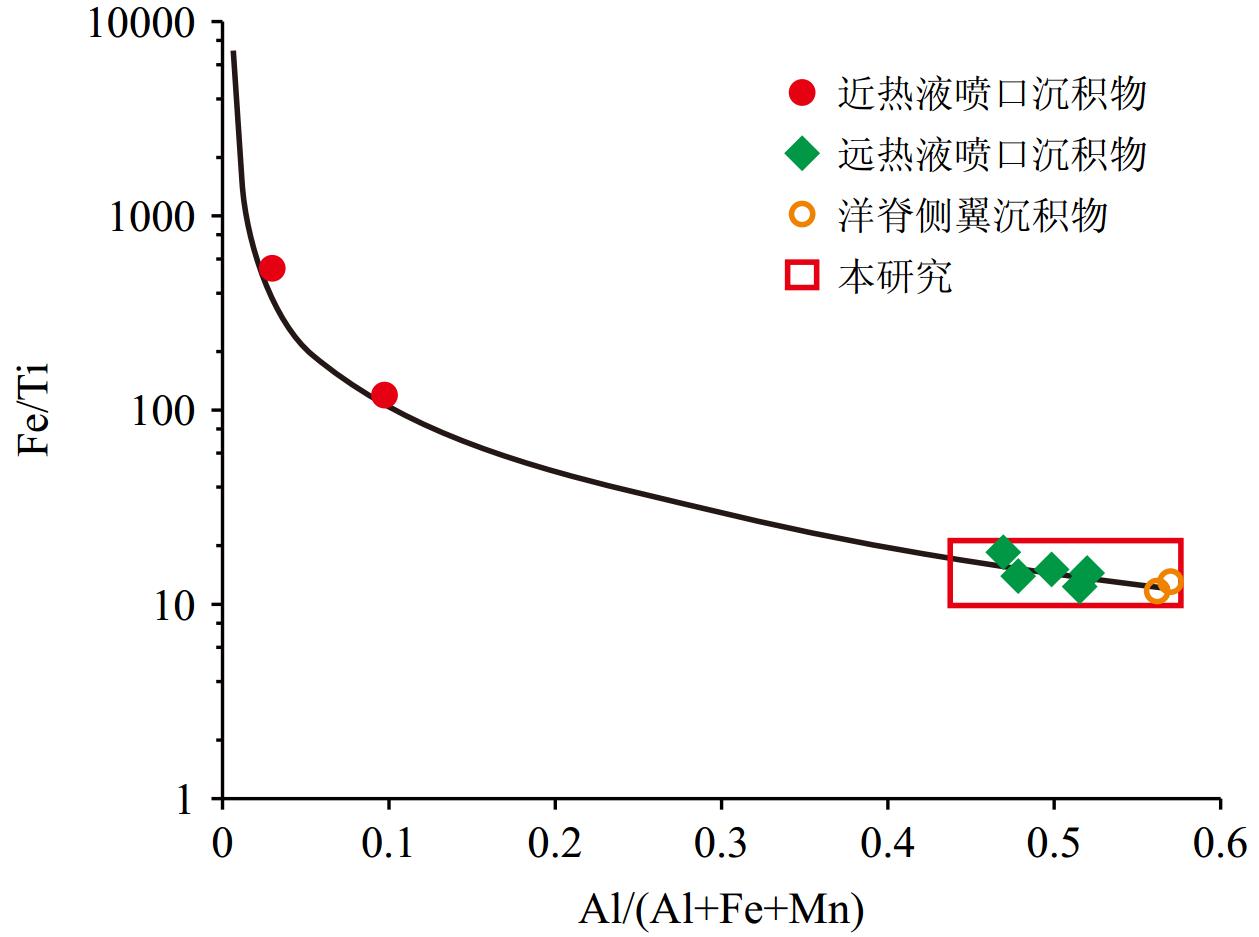
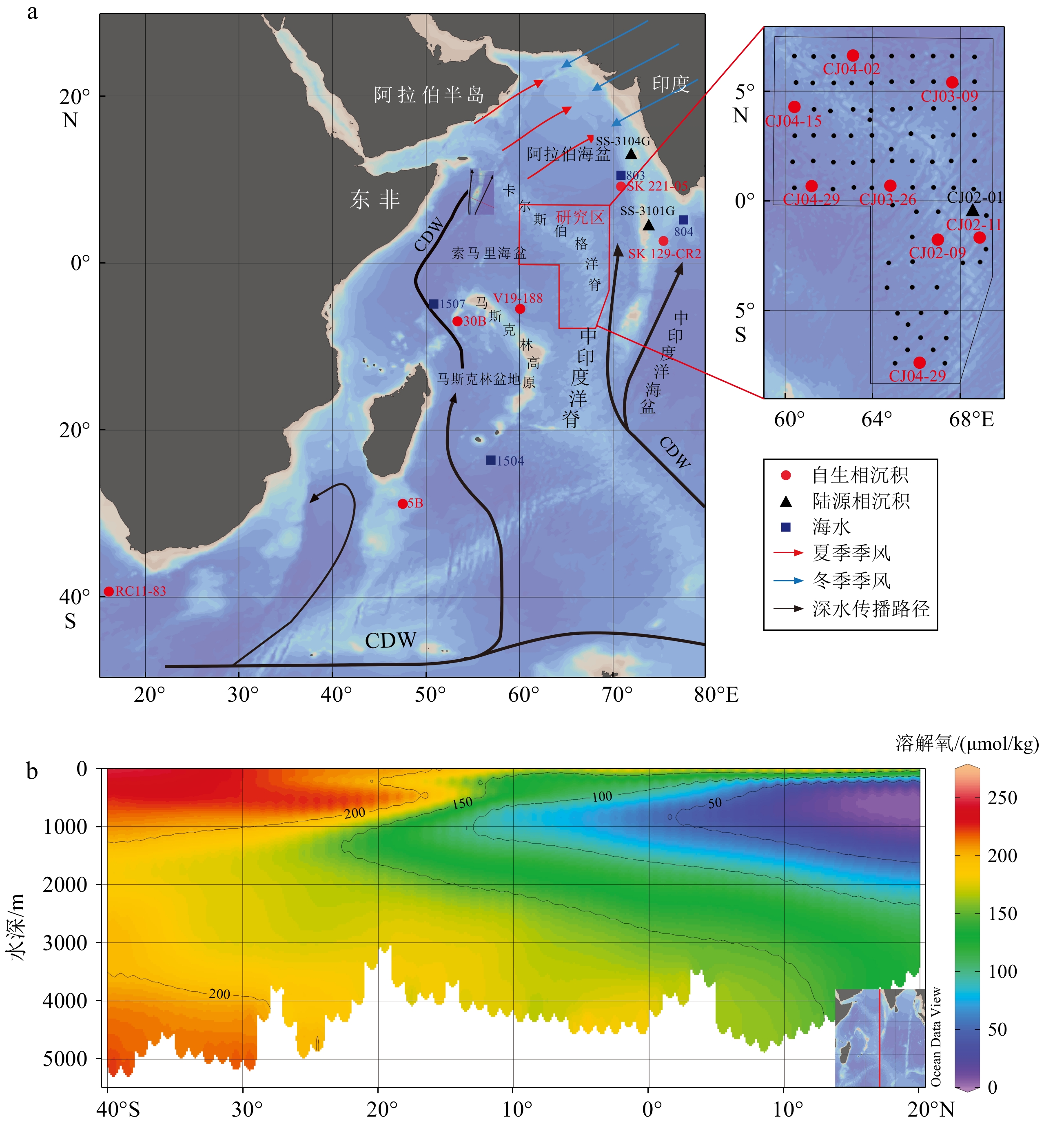
作为全球大洋循环的重要组成部分,印度洋底层水是当前深水物质循环与环境变化研究的热点,主要由南极底层水(AABW)和北大西洋深层水(NADW)组成。本研究通过对西北印度洋表层沉积物Nd同位素、氧化还原敏感元素、TOC等指标的分析,探讨了底层水的氧化还原状态与水团组成。结果表明Mn、Mo和Ni等敏感元素的富集指示研究区整体为氧化环境,在洋脊南部存在强氧化区域。εNd的分布范围为−7.16~−8,指示该区底层水团主要由AABW组成。与邻近区域的Nd同位素记录相比更重,这主要是受到一定风尘输入的影响。研究区南部较重的εNd指示了AABW贡献的增加,这可能是受到了索马里盆地内赤道强东向流的影响。本研究初步揭示了区域氧化还原状态和εNd的空间分布变化特征及其可能的影响因素,为后续对底层水的深入研究提供了重要的参考依据。
Abstract:The Indian Ocean deep water, as an important part of the global ocean circulation, is composed of mainly the Antarctic Bottom Water (AABW) and North Atlantic Deep Water (NADW), which is currently a research hot topic of marine substance circulation and environmental changes. We discussed the deep water redox state and composition of the bottom water through the analyses of Nd isotopes, redox-sensitive elements, total organic carbon of surface sediments in the northwestern Indian Ocean. Results show that sensitive elements such as Mn, Mo, and Ni indicated that the study area was generally in an oxidizing environment, and there was a strongly oxidizing area in the south side of the ridge. The εNd ranged from −7.16 to −8, indicating that the bottom water were mainly composed of AABW, and almost no NADW. Due to a certain amount of dust input, the study area has heavier εNd records compared with adjacent areas. The heavier εNd is indicative of an increased AABW contribution in the south, which may be influenced by the strong equatorial eastward flow within the Somali Basin. We revealed the characteristics of redox-sensitive elements and Nd isotopes of surface sediment and their possible influencing factors, and especially provided an important reference for subsequent in-depth research on bottom water.
-

-
表 1 经方差极大旋转后的沉积物元素因子荷载矩阵
Table 1. Sediment element factor-loading matrix after varimax rotation
F1 F2 F3 F4 TiO2 0.9716 − 0.0017 0.2228 − 0.0685 Fe2O3 0.9589 − 0.0027 0.2611 − 0.0992 MnO 0.8044 − 0.0130 0.1926 − 0.5572 CaO 0.3284 − 0.0884 0.9353 − 0.0834 TOC −0.002 − 0.9988 0.0488 0.0040 Mo 0.9042 − 0.0080 0.1071 − 0.3773 U 0.9499 − 0.0120 0.2934 − 0.0548 V 0.9553 − 0.0006 0.2863 − 0.0594 Cu 0.8289 − 0.0137 0.3937 − 0.3671 Ni 0.9132 − 0.0035 0.1966 − 0.3434 表 2 印度洋表层沉积物和海水的εNd数据统计
Table 2. εNd data of surface sediments and sea water collected in Indian Ocean
站位 深度/m 地理位置 εNd 样品类型 文献来源 02-09站 3483 中印度洋脊西侧 −7.77 铁锰氧化相 本研究 02-11站 3733 中印度洋脊东侧 −7.48 02-29站 3519 中印度洋脊西侧 −7.27 03-09站 4206 卡尔斯伯格脊东侧 −8.0 03-26站 3996 卡尔斯伯格脊西侧 −7.86 04-02站 4022 卡尔斯伯格脊东侧 −7.74 04-15站 4085 卡尔斯伯格脊西侧 −7.89 04-29站 4900 卡尔斯伯格脊西侧 −7.16 SK221-05站 2700 东南阿拉伯海 −8.8 Lathika[21] SK129-CR2站 3800 查戈斯-拉克代夫海岭东侧 −9.3 Piotrowski[19] V19-188站 − 马斯克林台地东北侧 −8.1 Pahnke[40] 5B站 3684 马达加斯加盆地 −8.32 Wilson[20] 30B站 3950 马斯克林盆地 −8.38 RC11-83站 4718 开普盆地 −8.39 Rutberg[52] 02-01站 3508 中印度洋脊东侧 −10.26 去碳酸盐残留相 何州天[41] SS-3101G站 − 查戈斯-拉克代夫海岭东侧 −13.0 Goswami[44] SS-3104G站 − 东南阿拉伯海 −9.9 803站 2504 查戈斯-拉克代夫海岭西北侧 −10.2 海水 Goswami[1] 804站 2350 印度大陆南端 −10.6 1504站 4500 马达加斯加盆地 −8.5 Bertram & Elderfield[17] 1507站 4000 索马里盆地 −8.6 -
[1] Goswami V, Singh S K, Bhushan R. Impact of water mass mixing and dust deposition on Nd concentration and εNd of the Arabian Sea water column[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2014, 145:30-49. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2014.09.006
[2] Manabe S, Stouffer R J. The rôle of thermohaline circulation in climate[J]. Tellus B: Chemical and Physical Meteorology, 1999, 51(1):91-109. doi: 10.3402/tellusb.v51i1.16262
[3] Rahmstorf S. Ocean circulation and climate during the past 120 000 years[J]. Nature, 2002, 419(6903):207-214. doi: 10.1038/nature01090
[4] Clark P U, Pisias N G, Stocker T F, et al. The role of the thermohaline circulation in abrupt climate change[J]. Nature, 2002, 415(6874):863-869. doi: 10.1038/415863a
[5] Talley L D. Closure of the global overturning circulation through the Indian, Pacific, and Southern Oceans: schematics and transports[J]. Oceanography, 2013, 26(1):80-97. doi: 10.5670/oceanog.2013.07
[6] Mantyla A W, Reid J L. On the origins of deep and bottom waters of the Indian Ocean[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1995, 100(C2):2417-2439. doi: 10.1029/94JC02564
[7] Johnson G C, Rudnick D L, Taft B A. Bottom water variability in the Samoa passage[J]. Journal of Marine Research, 1994, 52(2):177-196. doi: 10.1357/0022240943077118
[8] Schmiedl G, Leuschner D C. Oxygenation changes in the deep western Arabian Sea during the last 190, 000 years: Productivity versus deepwater circulation[J]. Paleoceanography, 2005, 20(2):PA2008.
[9] Tyson R V, Pearson T H. Modern and ancient continental shelf anoxia: an overview[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1991, 58(1):1-24. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1991.058.01.01
[10] Tribovillard N, Algeo T J, Lyons T, et al. Trace metals as paleoredox and paleoproductivity proxies: an update[J]. Chemical Geology, 2006, 232(1-2):12-32. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.02.012
[11] Pattan J N, Pearce N J G. Bottom water oxygenation history in southeastern Arabian Sea during the past 140ka: results from redox-sensitive elements[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2009, 280(3-4):396-405. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2009.06.027
[12] Nambiar R, Bhushan R, Raj H. Paleoredox conditions of bottom water in the northern Indian Ocean since 39 ka[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2022, 586:110766. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2021.110766
[13] Amsler H E, Thöle L M, Stimac I, et al. Bottom water oxygenation changes in the southwestern Indian Ocean as an indicator for enhanced respired carbon storage since the last glacial inception[J]. Climate of the Past, 2022, 18(8):1797-1813. doi: 10.5194/cp-18-1797-2022
[14] Tachikawa K, Jeandel C, Roy-Barman M. A new approach to the Nd residence time in the ocean: the role of atmospheric inputs[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1999, 170(4):433-446. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(99)00127-2
[15] Bender M L. Tracers in the sea[J]. BioScience, 1984, 34(7):452.
[16] Albarède F, Goldstein S L. World map of Nd isotopes in sea-floor ferromanganese deposits[J]. Geology, 1992, 20(8):761-763. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0761:WMONII>2.3.CO;2
[17] Bertram C J, Elderfield H. The geochemical balance of the rare earth elements and neodymium isotopes in the oceans[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1993, 57(9):1957-1986. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(93)90087-D
[18] Dileep Kumar M, Li Y H. Spreading of water masses and regeneration of silica and 226Ra in the Indian Ocean[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 1996, 43(1):83-110. doi: 10.1016/0967-0645(95)00084-4
[19] Piotrowski A M, Banakar V K, Scrivner A E, et al. Indian Ocean circulation and productivity during the last glacial cycle[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2009, 285(1-2):179-189. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2009.06.007
[20] Wilson D J, Piotrowski A M, Galy A, et al. A boundary exchange influence on deglacial neodymium isotope records from the deep western Indian Ocean[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2012, 341-344:35-47. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2012.06.009
[21] Lathika N, Rahaman W, Tarique M, et al. Deep water circulation in the Arabian Sea during the last glacial cycle: implications for paleo-redox condition, carbon sink and atmospheric CO2 variability[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2021, 257:106853. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2021.106853
[22] Singh S P, Singh S K, Goswami V, et al. Spatial distribution of dissolved neodymium and εNd in the Bay of Bengal: role of particulate matter and mixing of water masses[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2012, 94:38-56. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2012.07.017
[23] Bang S, Huh Y, Khim B K, et al. Deep-water circulation over the last two glacial cycles reconstructed from authigenic neodymium isotopes in the equatorial Indian Ocean (Core HI1808-GPC04)[J]. Ocean Science Journal, 2022, 57(2):324-333. doi: 10.1007/s12601-021-00046-8
[24] Zhang H D, Luo Y M, Yu J M, et al. Indian Ocean sedimentary calcium carbonate distribution and its implications for the glacial deep ocean circulation[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2022, 284:107490. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2022.107490
[25] 余星, 韩喜球, 邱中炎, 等. 西北印度洋脊的厘定及其地质构造特征[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(2):626-639
YU Xing, HAN Xiqiu, QIU Zhongyan, et al. Definition of northwest Indian ridge and its geologic and tectonic signatures[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(2):626-639.]
[26] Gordon A L, Ma S B, Olson D B, et al. Advection and diffusion of Indonesian Throughflow water within the Indian Ocean South Equatorial Current[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1997, 24(21):2573-2576. doi: 10.1029/97GL01061
[27] You Y Z. Implications of the deep circulation and ventilation of the Indian Ocean on the renewal mechanism of North Atlantic Deep Water[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2000, 105(C10):23895-23926. doi: 10.1029/2000JC900105
[28] He Z T, Qiao S Q, Jin L N, et al. Clay mineralogy and geochemistry of surface sediments in the equatorial western Indian Ocean and implications for sediment sources and the Antarctic bottom water inputs[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2023, 254:105741. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2023.105741
[29] Cai M J, Colin C, Xu Z K, et al. Climate and sea level forcing of terrigenous sediments input to the eastern Arabian Sea since the last glacial period[J]. Marine Geology, 2022, 450:106860.
[30] Kumar A, Suresh K, Rahaman W. Geochemical characterization of modern aeolian dust over the Northeastern Arabian Sea: implication for dust transport in the Arabian Sea[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 729:138576.
[31] Johnson G C, Warren B A, Olson D B. Flow of bottom water in the Somali Basin[J]. Deep Sea Research Part A. Oceanographic Research Papers, 1991, 38(6):637-652. doi: 10.1016/0198-0149(91)90003-X
[32] Ewing M, Eittreim S, Truchan M, et al. Sediment distribution in the Indian Ocean[J]. Deep Sea Research and Oceanographic Abstracts, 1969, 16(3):231-248.
[33] Murray R W, Leinen M. Scavenged excess aluminum and its relationship to bulk titanium in biogenic sediment from the central equatorial Pacific Ocean[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(20):3869-3878.
[34] Algeo T J, Liu J S. A re-assessment of elemental proxies for paleoredox analysis[J]. Chemical Geology, 2020, 540:119549.
[35] Li Y H, Schoonmaker J E. Chemical composition and mineralogy of marine sediments[J]. Treatise on Geochemistry, 2003, 7:1-35.
[36] Algeo T J, Tribovillard N. Environmental analysis of paleoceanographic systems based on molybdenum–uranium covariation[J]. Chemical Geology, 2009, 268(3-4):211-225.
[37] 何连花, 张辉, 刘季花, 等. MC-ICP-MS测定海洋沉积物中钕同位素的化学分离方法[J]. 矿产与地质, 2020, 34(5):1018-1022
HE Lianhua, ZHANG Hui, LIU Jihua, et al. Chemical separation method for MC-ICP-MS determination of Nd isotopes in marine sediment[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2020, 34(5):1018-1022.]
[38] Tanaka T, Togashi S, Kamioka H, et al. JNdi-1: a neodymium isotopic reference in consistency with LaJolla neodymium[J]. Chemical Geology, 2000, 168(3-4):279-281.
[39] Jacobsen S B, Wasserburg G J. Sm-Nd isotopic evolution of chondrites and achondrites, II[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1984, 67(2):137-150.
[40] Pahnke K, Goldstein S L, Hemming S R. Abrupt changes in Antarctic Intermediate Water circulation over the past 25, 000 years[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2008, 1(12):870-874.
[41] 何州天. MIS 7期以来赤道西印度洋沉积物特征及其对物源和古环境的指示意义[D]. 自然资源部第一海洋研究所硕士学位论文, 2023
HE Zhoutian. Characteristics of sediments in the equatorial western Indian Ocean since MIS 7 and implications for sediment sources and paleoenvironment[D]. Master Dissertation of the First Institute of Oceanography, MNR, 2023.]
[42] McLennan S M. Relationships between the trace element composition of sedimentary rocks and upper continental crust[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2001, 2(4):2000GC000109.
[43] Boström K. Origin and fate of ferromanganoan active ridge sediments[M]//Hsü K J, Jenkyns H C. Pelagic Sediments: on Land and under the Sea. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific, 1974: 401-401.
[44] Qiu Z Y, Fan W J, Han X Q, et al. Distribution, speciation and mobility of metals in sediments of the Tianxiu hydrothermal field, Carlsberg Ridge, Northwest Indian Ocean[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 2023, 237:103826.
[45] Qiu Z Y, Han X Q, Li M, et al. The temporal variability of hydrothermal activity of Wocan hydrothermal field, Carlsberg Ridge, northwest Indian Ocean[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2021, 132:103999.
[46] Goswami V, Singh S K, Bhushan R, et al. Temporal variations in 87Sr/86Sr and ɛNd in sediments of the southeastern Arabian Sea: impact of monsoon and surface water circulation[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2012, 13(1):Q01001.
[47] Kohfeld K E, Harrison S P. DIRTMAP: the geological record of dust[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2001, 54(1-3):81-114.
[48] Mahowald N M, Muhs D R, Levis S, et al. Change in atmospheric mineral aerosols in response to climate: last glacial period, preindustrial, modern, and doubled carbon dioxide climates[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2006, 111(D10):D10202.
[49] Halliday A N, Davidson J P, Holden P, et al. Metalliferous sediments and the scavenging residence time of Nd near hydrothermal vents[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1992, 19(8):761-764.
[50] Lacan F, Jeandel C. Tracing Papua New Guinea imprint on the central Equatorial Pacific Ocean using neodymium isotopic compositions and Rare Earth Element patterns[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2001, 186(3-4):497-512.
[51] Tachikawa K, Athias V, Jeandel C. Neodymium budget in the modern ocean and paleo-oceanographic implications[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2003, 108(C8):3254.
[52] Rutberg R L, Hemming S R, Goldstein S L. Reduced North Atlantic Deep Water flux to the glacial Southern Ocean inferred from neodymium isotope ratios[J]. Nature, 2000, 405(6789):935-938.
[53] Johnson G C, Musgrave D L, Warren B A, et al. Flow of bottom and deep water in the Amirante Passage and Mascarene Basin[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1998, 103(C13):30973-30984.
-



 下载:
下载: