Constraints of organic carbon burial on sedimentary mercury in the Bohai Sea over the past century
-
摘要:
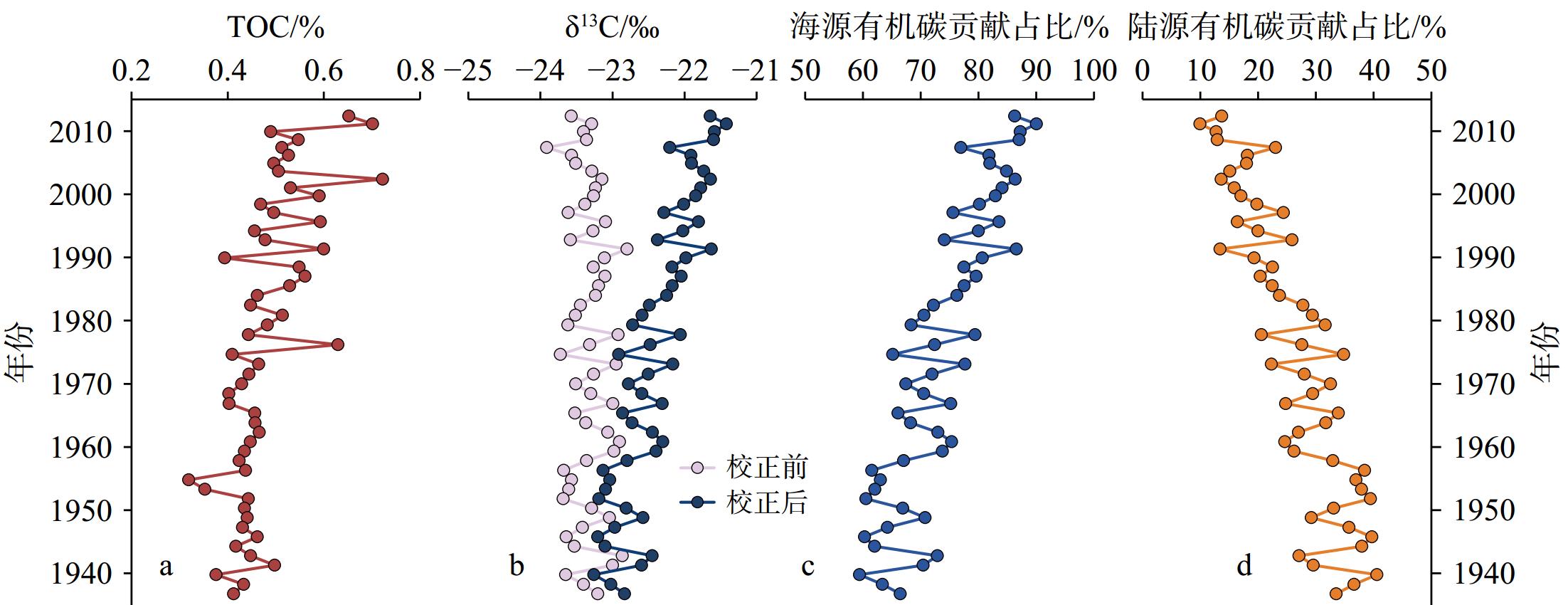
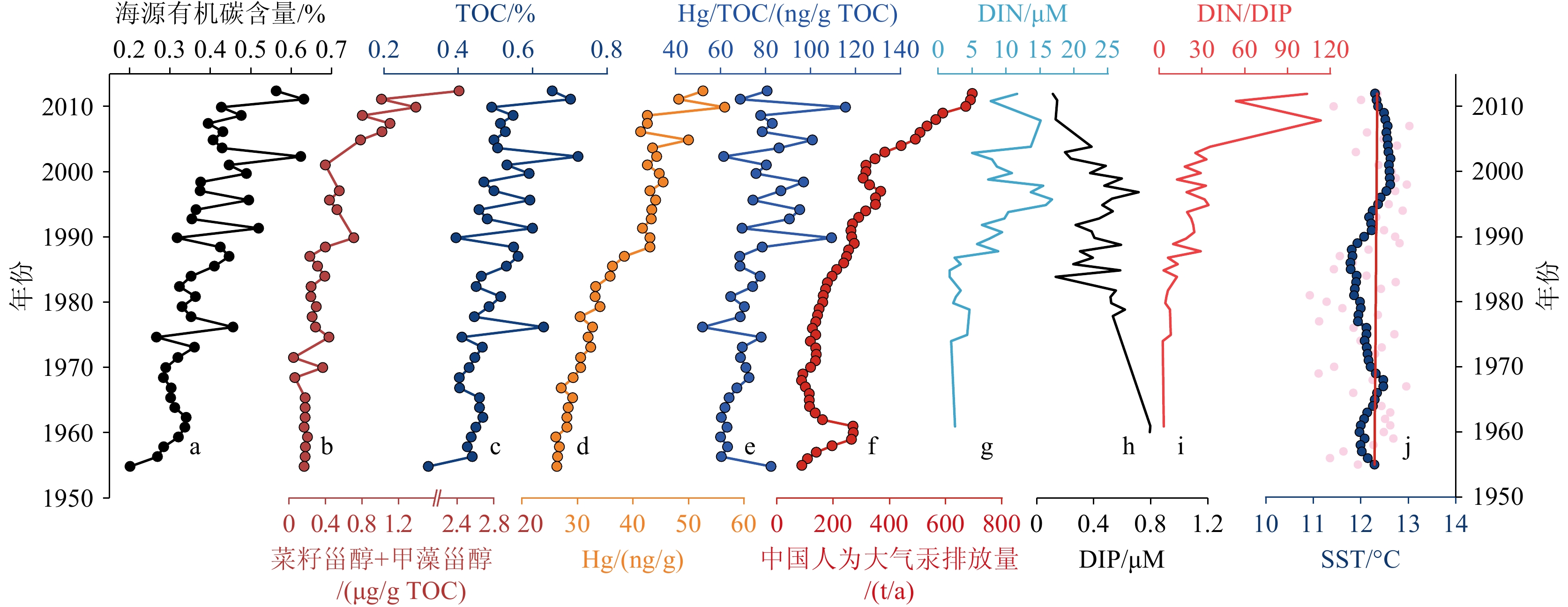
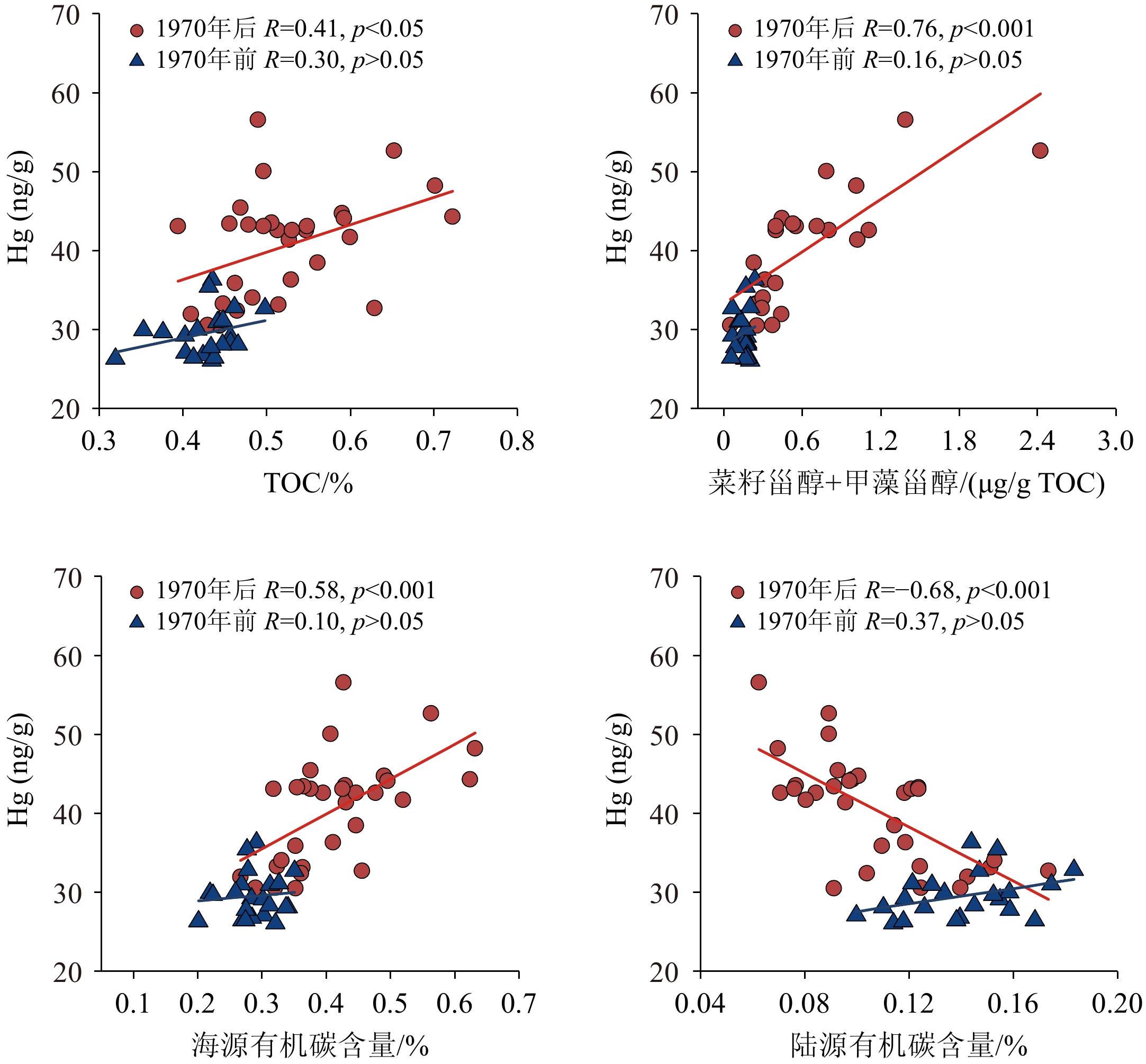
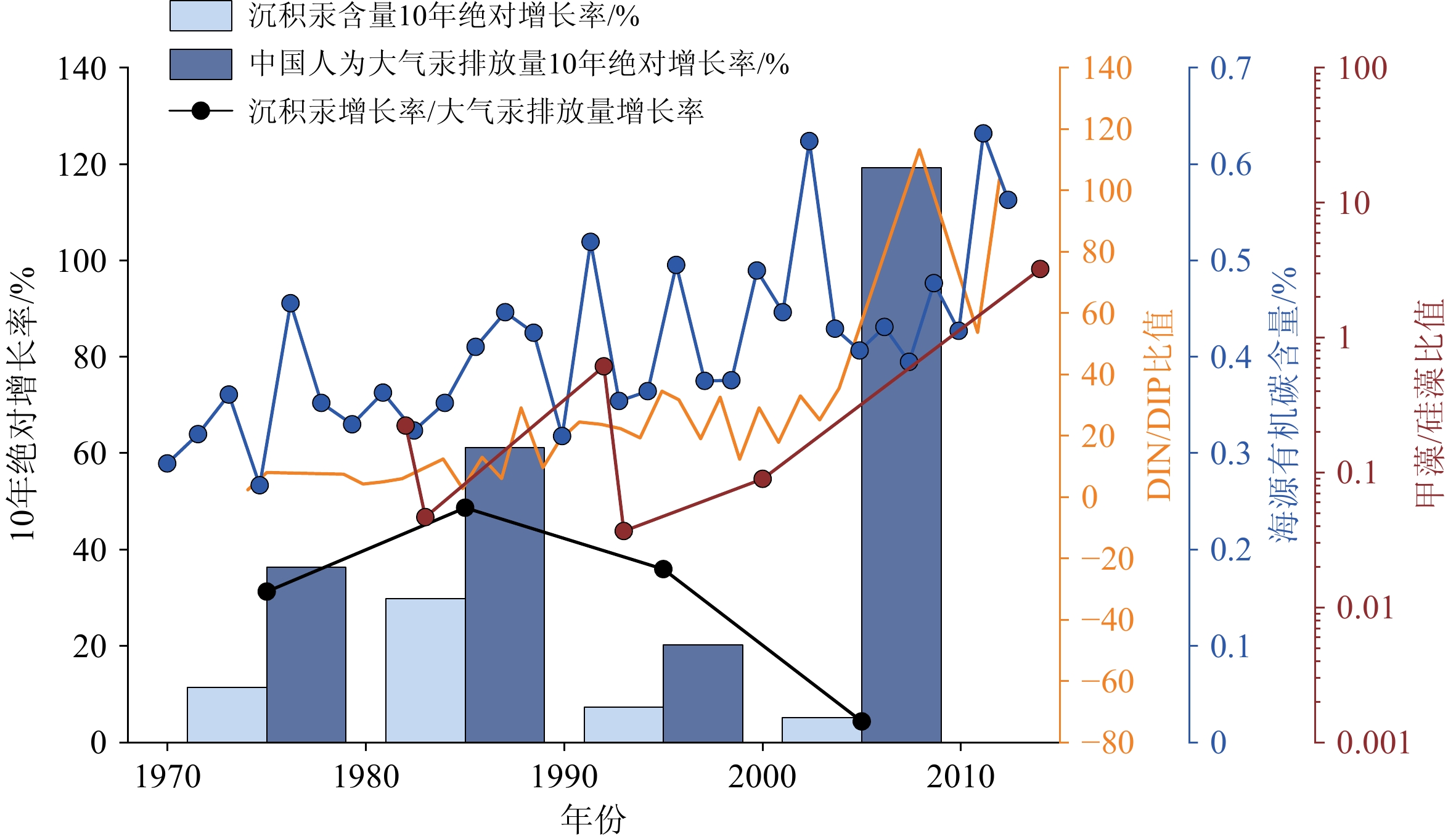
全球变暖背景下,近海陆架有机碳埋藏及其环境效应不仅是海洋碳循环的关键环节,而且对全面认识人类活动对近海生态系统的影响也具有重要意义。本研究基于2013年在渤海中部泥质区由箱式取样器采集的53 cm长的沉积岩芯,综合分析了近百年来总有机碳(TOC)及其稳定碳同位素(δ13C)、生物标志物和沉积汞等指标的高分辨率沉积记录,探讨了不同来源有机碳的演变特征及其对沉积汞埋藏的约束作用。通过对有机碳δ13C进行Suess效应校正,并利用双端元混合模型,估算得到海源有机碳贡献率约为59%~90%,且自1970年以来显著增加。海源有机碳与菜籽甾醇和甲藻甾醇的演化趋势基本一致,指示自1970年以来海洋初级生产力显著增加,可能与营养物质输入和气候变暖有关。沉积汞的埋藏记录与上述生产力参数的变化趋势总体一致,并与1970年后的海源有机碳等指标呈显著的正相关,表明近几十年浮游植物生产力的增加可能对沉积汞的累积具有重要作用,因此生物作用可能对近海汞的沉积和归宿具有不可忽视的影响。进一步对比了近期人为大气汞的排放量和沉积汞埋藏量的相对变化,发现大约2000s以后,沉积汞埋藏的比率明显下降(相对于排放量),这可能与同期营养盐和浮游植物群落结构改变(如甲藻显著增加)导致的生物对汞的清除作用效率降低有关。
Abstract:In the global warming scheme, organic carbon burial and its environmental effects on coastal shelves are important in the marine carbon cycle, and a window for understanding the impact of modern human activities on coastal ecosystems. A 53-cm long core was acquired by box-coring in 2013 from the central mud deposition area of the Bohai Sea, North China. The high-resolution sedimentary records of total organic carbon (TOC), stable carbon isotopes (δ13C), biomarkers, and sedimentary mercury over the past century were comprehensively analyzed, and the evolutionary characteristics of organic carbon from various sources and constraining effects on mercury burial were clarified. By correcting the δ13C of organic carbon for the Suess effect and applying a two-endmember mixing model, we estimated that marine organic carbon contributes approximately 59% to 90%, with a marked increase since the 1970. The trends of marine organic carbon align closely with those of brassicasterol and dinosterol, indicating a significant increase in marine primary productivity since the 1970, due likely to increased nutrient input and climate warming. The burial records of sedimentary mercury are generally consistent with the trends of the aforementioned productivity parameters and exhibit a significant positive correlation with marine organic carbon and other indicators since the 1970. This suggests that the increase in phytoplankton productivity in recent decades may have played a crucial role in the accumulation of sedimentary mercury. Therefore, biological processes may have a significant impact on the sequestration and fate of mercury in coastal areas. A further comparison of the relative changes in recent anthropogenic atmospheric mercury emissions and sedimentary mercury burial rates revealed a significant decline in the burial efficiency relative to emissions after the 2000s. This decline may be related to concurrent changes in nutrient levels and phytoplankton community structure, such as a notable increase in dinoflagellates, which potentially reduced the efficiency of biological mercury scavenging.
-
Key words:
- organic carbon /
- sedimentary record /
- biological pump /
- sedimentary mercury /
- Bohai Sea
-

-
图 1 研究区概况及取样站位 [34]
Figure 1.
-
[1] Bauer J E, Cai W J, Raymond P A, et al. The changing carbon cycle of the coastal ocean[J]. Nature, 2013, 504(7478):61-70. doi: 10.1038/nature12857
[2] Sun X S, Hu L M, Sun X, et al. Mercury burial in modern sedimentary systems of the East China marginal seas: the role of coastal oceans in global mercury cycling[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2023, 37(9):e2023GB007760. doi: 10.1029/2023GB007760
[3] Yin R S, Guo Z G, Hu L M, et al. Mercury inputs to Chinese marginal seas: impact of industrialization and development of China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2018, 123(8):5599-5611. doi: 10.1029/2017JC013691
[4] Cao Y L, Bi R, Wang X C, et al. The sources and burial of marine organic carbon in the eastern China marginal seas[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2022, 9:824181. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.824181
[5] 张桂成, 孙军. 渤海环境污染现状及研究进展[J]. 环境化学, 2023, 42(3):918-930 doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2022101805
ZHANG Guicheng, SUN Jun. State of environmental pollution in the Bohai Sea, China: a review[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2023, 42(3):918-930.] doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2022101805
[6] 王焕松, 雷坤, 李子成, 等. 辽东湾北岸主要入海河流污染物入海通量及其影响因素分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2011, 33(6):110-116
WANG Huansong, LEI Kun, LI Zicheng, et al. Analysis of major pollutants flux into the sea and influencing factors on the north shore of the Liaodong Gulf[J]. Acta Oceanological Sinica, 2011, 33(6):110-116.]
[7] Zhou Q X, Wang S M, Liu J Q, et al. Geological evolution of offshore pollution and its long-term potential impacts on marine ecosystems[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2022, 13(5):101427. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2022.101427
[8] Azoury S, Tronczyński J, Chiffoleau J F, et al. Historical records of mercury, lead, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons depositions in a dated sediment core from the eastern mediterranean[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(13):7101-7109.
[9] Zhu A M, Liu J H, Qiao S Q. Quantitative source apportionment of heavy metals in sediments from the Bohai Sea, China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2023, 196:115620. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2023.115620
[10] Tian H Z, Zhu C Y, Gao J J, et al. Quantitative assessment of atmospheric emissions of toxic heavy metals from anthropogenic sources in China: historical trend, spatial distribution, uncertainties, and control policies[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2015, 15(17):10127-10147. doi: 10.5194/acp-15-10127-2015
[11] Filgueiras A V, Lavilla I, Bendicho C. Evaluation of distribution, mobility and binding behaviour of heavy metals in surficial sediments of Louro River (Galicia, Spain) using chemometric analysis: a case study[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2004, 330(1-3):115-129. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.03.038
[12] Bartoli G, Papa S, Sagnella E, et al. Heavy metal content in sediments along the Calore river: relationships with physical–chemical characteristics[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2012, 95:S9-S14. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2011.02.013
[13] Le Faucheur S, Campbell P G C, Fortin C, et al. Interactions between mercury and phytoplankton: speciation, bioavailability, and internal handling[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2014, 33(6):1211-1224. doi: 10.1002/etc.2424
[14] Outridge P M, Sanei L H, Stern G A, et al. Evidence for control of mercury accumulation rates in Canadian High Arctic lake sediments by variations of aquatic primary productivity[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(15):5259-5265.
[15] Stern G A, Sanei H, Roach P, et al. Historical interrelated variations of mercury and aquatic organic matter in lake sediment cores from a subArctic lake in Yukon, Canada: further evidence toward the algal-mercury scavenging hypothesis[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009, 43(20):7684-7690.
[16] Wu F C, Xu L B, Liao H Q, et al. Relationship between mercury and organic carbon in sediment cores from Lakes Qinghai and Chenghai, China[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2013, 13(6):1084-1092. doi: 10.1007/s11368-013-0694-2
[17] Chakraborty P, Sarkar A, Vudamala K, et al. Organic matter — A key factor in controlling mercury distribution in estuarine sediment[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2015, 173:302-309. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2014.10.005
[18] Zaferani S, Biester H. Biogeochemical processes accounting for the natural mercury variations in the southern Ocean diatom ooze sediments[J]. Ocean Science, 2020, 16(3):729-741. doi: 10.5194/os-16-729-2020
[19] Chen B, Hu L M, Liu J H, et al. High-resolution depositional records of lead isotopes and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Bohai Sea, China: implications for a sediment footprint of anthropogenic impact[J]. Marine Geology, 2021, 432:106396. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2020.106396
[20] Liu L, Wang J Y, Wang L J, et al. Vertical distributions of mercury in marine sediment cores from central and southern part of Bohai Sea, China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 170:399-406. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.12.003
[21] Zhou D, Yu M, Yu J B, et al. Impacts of inland pollution input on coastal water quality of the Bohai Sea[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 765:142691. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142691
[22] Fang Y, Chen Y J, Lin T, et al. Spatiotemporal trends of elemental carbon and char/soot ratios in five sediment cores from eastern China marginal seas: indicators of anthropogenic activities and transport patterns[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(17):9704-9712.
[23] 李凤业, 高抒, 贾建军, 等. 黄、渤海泥质沉积区现代沉积速率[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2002, 33(4):364-369 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2002.04.004
LI Fengye, GAO Shu, JIA Jianjun, et al. Contemporary deposition rates of fine-grained sediment in the Bohai and Yellow Seas[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2002, 33(4):364-369.] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2002.04.004
[24] Song J M, Duan L Q. Chapter 17 - The Bohai sea[M]//Sheppard C. World Seas: an Environmental Evaluation. 2nd ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2019: 377-394.
[25] Ding X K, Guo X Y, Zhang C, et al. Water conservancy project on the Yellow River modifies the seasonal variation of chlorophyll-a in the Bohai Sea[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 254:126846. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126846
[26] 赵海萍, 李清雪, 陶建华. 渤海湾表层水质时空变化及污染源识别[J]. 水力发电学报, 2016, 35(10):21-30 doi: 10.11660/slfdxb.20161003
ZHAO Haiping, LI Qingxue, TAO Jianhua. Spatio-temporal water quality variations and identification of surface water pollutant sources in Bohai Bay[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering, 2016, 35(10):21-30.] doi: 10.11660/slfdxb.20161003
[27] 陶磊, 孙健, 刘海英, 等. 潮汐和季风作用下渤海湾水交换研究[J]. 水力发电学报, 2020, 39(5):99-107 doi: 10.11660/slfdxb.20200510
TAO Lei, SUN Jian, LIU Haiying, et al. Study on water exchange in Bohai Bay under effects of tides and seasonal winds[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering, 2020, 39(5):99-107.] doi: 10.11660/slfdxb.20200510
[28] Ding X K, Guo X Y, Gao H W, et al. Seasonal variations of nutrient concentrations and their ratios in the central Bohai Sea[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 799:149416. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149416
[29] Ding X K, Shi J, Guo X Y, et al. Interannual variations in the nutrient cycle in the central Bohai Sea in response to anthropogenic inputs[J]. Chemosphere, 2023, 313:137620. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.137620
[30] Gao X L, Zhou F X, Chen C T A. Pollution status of the Bohai Sea: an overview of the environmental quality assessment related trace metals[J]. Environment International, 2014, 62:12-30. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2013.09.019
[31] Wang J J, Yu Z G, Wei Q S, et al. Long-term nutrient variations in the Bohai Sea over the past 40 years[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2019, 124(1):703-722. doi: 10.1029/2018JC014765
[32] Xin M, Wang B D, Xie L P, et al. Long-term changes in nutrient regimes and their ecological effects in the Bohai Sea, China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 146:562-573. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.07.011
[33] 郭术津, 李彦翘, 张翠霞, 等. 渤海浮游植物群落结构及与环境因子的相关性分析[J]. 海洋通报, 2014, 33(1):95-105 doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2014.01.013
GUO Shujin, LI Yanqiao, ZHANG Cuixia, et al. Phytoplankton community in the Bohai Sea and its relationship with environmental factors[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2014, 33(1):95-105.] doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2014.01.013
[34] Hu L M, Guo Z G, Shi X F, et al. Temporal trends of aliphatic and polyaromatic hydrocarbons in the Bohai Sea, China: evidence from the sedimentary record[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2011, 42(10):1181-1193. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2011.08.009
[35] Xu Y P, Zhou S Z, Hu L M, et al. Different controls on sedimentary organic carbon in the Bohai Sea: River mouth relocation, turbidity and eutrophication[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 2018, 180:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2017.12.004
[36] Li L, Wang Y J, Liu D Y. Phytoplankton shifts in the Central Bohai Sea over the last 250 years reflect eutrophication and input from the Yellow River[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2021, 126:107676. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107676
[37] Wang Y J, Liu D Y, Xiao W P, et al. Coastal eutrophication in China: trend, sources, and ecological effects[J]. Harmful Algae, 2021, 107:102058. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2021.102058
[38] Hu L M, Shi X F, Guo Z G, et al. Sources, dispersal and preservation of sedimentary organic matter in the Yellow Sea: the importance of depositional hydrodynamic forcing[J]. Marine Geology, 2013, 335:52-63. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2012.10.008
[39] Xia P, Meng X W, Yin P, et al. Eighty-year sedimentary record of heavy metal inputs in the intertidal sediments from the Nanliu River estuary, Beibu Gulf of South China Sea[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2011, 159(1):92-99. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2010.09.014
[40] Schelske C L, Hodell D A. Using carbon isotopes of bulk sedimentary organic matter to reconstruct the history of nutrient loading and eutrophication in Lake Erie[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 1995, 40(5):918-929. doi: 10.4319/lo.1995.40.5.0918
[41] Keeling C D, Bacastow R B, Carter A F, et al. A three-dimensional model of atmospheric CO2 transport based on observed winds: 1. Analysis of observational data[M]//Peterson D H. Aspects of Climate Variability in the Pacific and the Western Americas. Washington: American Geophysical Union, 1989: 165-236.
[42] Friedli H, Lötscher H, Oeschger H, et al. Ice core record of the 13C/12C ratio of atmospheric CO2 in the past two centuries[J]. Nature, 1986, 324(6094):237-238. doi: 10.1038/324237a0
[43] Jia G D, Xu S D, Chen W F, et al. 100-year ecosystem history elucidated from inner shelf sediments off the Pearl River estuary, China[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2013, 151:47-55. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2013.02.005
[44] Zonneveld K A F, Versteegh G J M, Kasten S, et al. Selective preservation of organic matter in marine environments; processes and impact on the sedimentary record[J]. Biogeosciences, 2010, 7(2):483-511. doi: 10.5194/bg-7-483-2010
[45] Minoura K, Hoshino K, Nakamura T, et al. Late Pleistocene-Holocene paleoproductivity circulation in the Japan Sea: sea-level control on δ13C and δ15N records of sediment organic material[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1997, 135(1-4):41-50. doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(97)00026-6
[46] 宋逸群, 王传远, 靳文静, 等. 渤海辽东湾海域表层沉积物有机质特征、来源及环境评价分析[J]. 生态科学, 2022, 41(2):84-90 doi: 10.32846/2306-9716/2022.eco.2-41.14
SONG Yiqun, WANG Chuanyuan, JIN Wenjing, et al. Characteristics, sources of organic matter in surface sediments and environmental assessment of Liaodong Bay, Bohai Sea[J]. Ecological Science, 2022, 41(2):84-90.] doi: 10.32846/2306-9716/2022.eco.2-41.14
[47] Fry B, Sherr E B. δ13C measurements as indicators of carbon flow in marine and freshwater ecosystems[J]. Contributions in Marine Science, 1984, 27:13-47.
[48] Xing L, Zhao M X, Zhang T, et al. Ecosystem responses to anthropogenic and natural forcing over the last 100 years in the coastal areas of the East China Sea[J]. The Holocene, 2016, 26(5):669-677. doi: 10.1177/0959683615618248
[49] Zimmerman A R, Canuel E A. Sediment geochemical records of eutrophication in the mesohaline Chesapeake Bay[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2002, 47(4):1084-1093. doi: 10.4319/lo.2002.47.4.1084
[50] Kuypers M M M, Pancost R D, Nijenhuis I A, et al. Enhanced productivity led to increased organic carbon burial in the euxinic North Atlantic Basin during the Late Cenomanian oceanic anoxic event[J]. Paleoceanography, 2002, 17(4):1051.
[51] Algeo T J, Henderson C M, Tong J N, et al. Plankton and productivity during the Permian–Triassic boundary crisis: an analysis of organic carbon fluxes[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2013, 105:52-67. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2012.02.008
[52] Krumhardt K M, Lovenduski N S, Long M C, et al. Potential predictability of net primary production in the ocean[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2020, 34(6):e2020GB006531. doi: 10.1029/2020GB006531
[53] Wang H J, Yang Z S, Saito Y, et al. Interannual and seasonal variation of the Huanghe (Yellow River) water discharge over the past 50 years: connections to impacts from ENSO events and dams[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2006, 50(3-4):212-225. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2006.01.005
[54] 邢磊, 赵美训, 张海龙, 等. 二百年来黄海浮游植物群落结构变化的生物标志物记录[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2009, 39(2):317-322
XING Lei, ZHAO Meixun, ZHANG Hailong, et al. Biomarker records of phytoplankton community structure changes in the yellow sea over the Last 200 Years[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2009, 39(2):317-322.]
[55] 丁玲, 邢磊, 赵美训. 生物标志物重建浮游植物生产力及群落结构研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2010, 25(9):981-989
DING Ling, XING Lei, ZHAO Meixun. Applications of biomarkers for reconstructing phytoplankton productivity and community structure changes[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2010, 25(9):981-989.]
[56] 于培松, 张海生, 扈传昱, 等. 利用沉积生物标志物分析南极普里兹湾浮游植物群落结构变化[J]. 极地研究, 2012, 24(2):143-150
YU Peisong, ZHANG Haisheng, HU Chuanyu, et al. Using biomarkers in sediments as indicators to rebuild the phytoplankton community in Prydz Bay, Antarctica[J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2012, 24(2):143-150.]
[57] 冯旭文, 段杉杉, 石学法, 等. 浙江近岸泥质区百年来浮游植物生产力的变化及对环境的响应[J]. 海洋学报, 2013, 35(4):155-161 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2013.04.018
FENG Xuwen, DUAN Shanshan, SHI Xuefa, et al. Changes in phytoplankton productivity and impacts on environment in the Zhejiang coastal mud area during the last 100 years[J]. Acta Oceanological Sinica, 2013, 35(4):155-161.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2013.04.018
[58] Xiong W, Mei X, Meng X J, et al. Phytoplankton biomarkers in surface sediments from Liaodong Bay and their potential as indicators of primary productivity[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2020, 159:111536. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111536
[59] Volkman J K. A review of sterol markers for marine and terrigenous organic matter[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1986, 9(2):83-99. doi: 10.1016/0146-6380(86)90089-6
[60] Song Y Y, Guo Y Y, Liu H J, et al. Water quality shifts the dominant phytoplankton group from diatoms to dinoflagellates in the coastal ecosystem of the Bohai Bay[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2022, 183:114078. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2022.114078
[61] Malone T C, Newton A. The globalization of cultural eutrophication in the coastal ocean: causes and consequences[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2020, 7:670. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2020.00670
[62] 冉祥滨, 韦钦胜, 于志刚. 中国近海营养盐结构失衡与磷消耗问题及其生态环境效应的研究进展[J]. 海洋科学, 2023, 47(8):75-89
RAN Xiangbin, WEI Qinsheng, YU Zhigang. Stoichiometric imbalance in the rates of nutrient and phosphorus depletion in coastal China with implications for the ecological environment[J]. Marine Sciences, 2023, 47(8):75-89.]
[63] De Senerpont Domis L N, Van de Waal D B, Helmsing N R, et al. Community stoichiometry in a changing world: combined effects of warming and eutrophication on phytoplankton dynamics[J]. Ecology, 2014, 95(6):1485-1495. doi: 10.1890/13-1251.1
[64] 李磊. 黄河口邻近海域浮游植物百年演变特征及与环境变化的响应关系[D]. 华东师范大学博士学位论文, 2021
LI Lei. A century-long phytoplankton shift and environmental responses in the adjacent sea of the Yellow River Estuary[D]. Doctor Dissertation of East China Normal University, 2021.]
[65] Hutchins D A, Tagliabue A. Feedbacks between phytoplankton and nutrient cycles in a warming ocean[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2024, 17(6):495-502. doi: 10.1038/s41561-024-01454-w
[66] Wang F, Li X G, Tang X H, et al. The seas around China in a warming climate[J]. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 2023, 4(8):535-551.
[67] Wan N N, Zhang R P, Kong X L, et al. Effect of aquatic organic matter and global warming on accumulation of PAHs in lakes, East China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 2022, 127(11):e2022JG007167. doi: 10.1029/2022JG007167
[68] Lee J H, Kwon S Y, Lee H, et al. Climate-associated changes in mercury sources in the arctic fjord sediments[J]. ACS Earth and Space Chemistry, 2021, 5(9):2398-2407. doi: 10.1021/acsearthspacechem.1c00095
[69] Manceau A, Nagy K L. Thiols in natural organic matter: molecular forms, acidity, and reactivity with mercury(II) from first-principles calculations and high energy-resolution X-ray absorption near-edge structure spectroscopy[J]. ACS Earth and Space Chemistry, 2019, 3(12):2795-2807. doi: 10.1021/acsearthspacechem.9b00278
[70] 栾青杉, 康元德, 王俊. 渤海浮游植物群落的长期变化(1959~2015)[J]. 渔业科学进展, 2018, 39(4):9-18
LUAN Qingshan, KANG Yuande, WANG Jun. Long-term changes in the phytoplankton community in the Bohai Sea (1959~2015)[J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2018, 39(4):9-18.]
[71] 孙军, 刘东艳, 杨世民, 等. 渤海中部和渤海海峡及邻近海域浮游植物群落结构的初步研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2002, 33(5):461-471 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2002.05.002
SUN Jun, LIU Dongyan, YANG Shimin, et al. The preliminary study on phytoplankton community structure in the central Bohai Sea and the Bohai Strait and its adjacent area[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2002, 33(5):461-471.] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2002.05.002
[72] Egge J K. Are diatoms poor competitors at low phosphate concentrations?[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 1998, 16(3-4):191-198. doi: 10.1016/S0924-7963(97)00113-9
[73] Xiao W P, Liu X, Irwin A J, et al. Warming and eutrophication combine to restructure diatoms and dinoflagellates[J]. Water Research, 2018, 128:206-216. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.10.051
[74] Spilling K, Olli K, Lehtoranta J, et al. Shifting diatom—dinoflagellate dominance during spring bloom in the baltic sea and its potential effects on biogeochemical cycling[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2018, 5:327. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2018.00327
[75] Fowler S W, Knauer G A. Role of large particles in the transport of elements and organic compounds through the oceanic water column[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 1986, 16(3):147-194. doi: 10.1016/0079-6611(86)90032-7
-



 下载:
下载: