Study on the compression and consolidation properties of soil in the key area of land subsidence in Hangzhou: a case study of test hole HZ22J06
-
摘要:
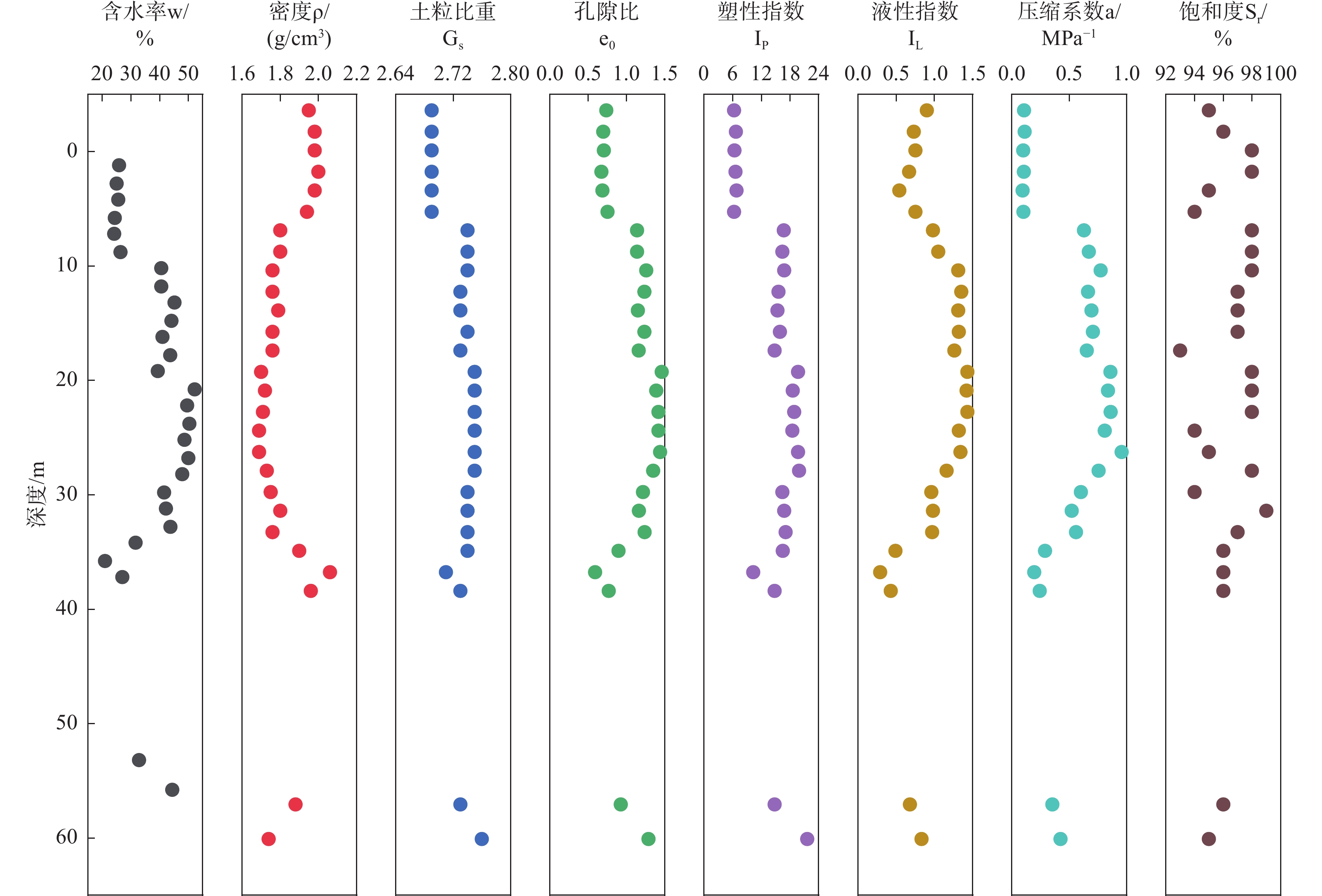
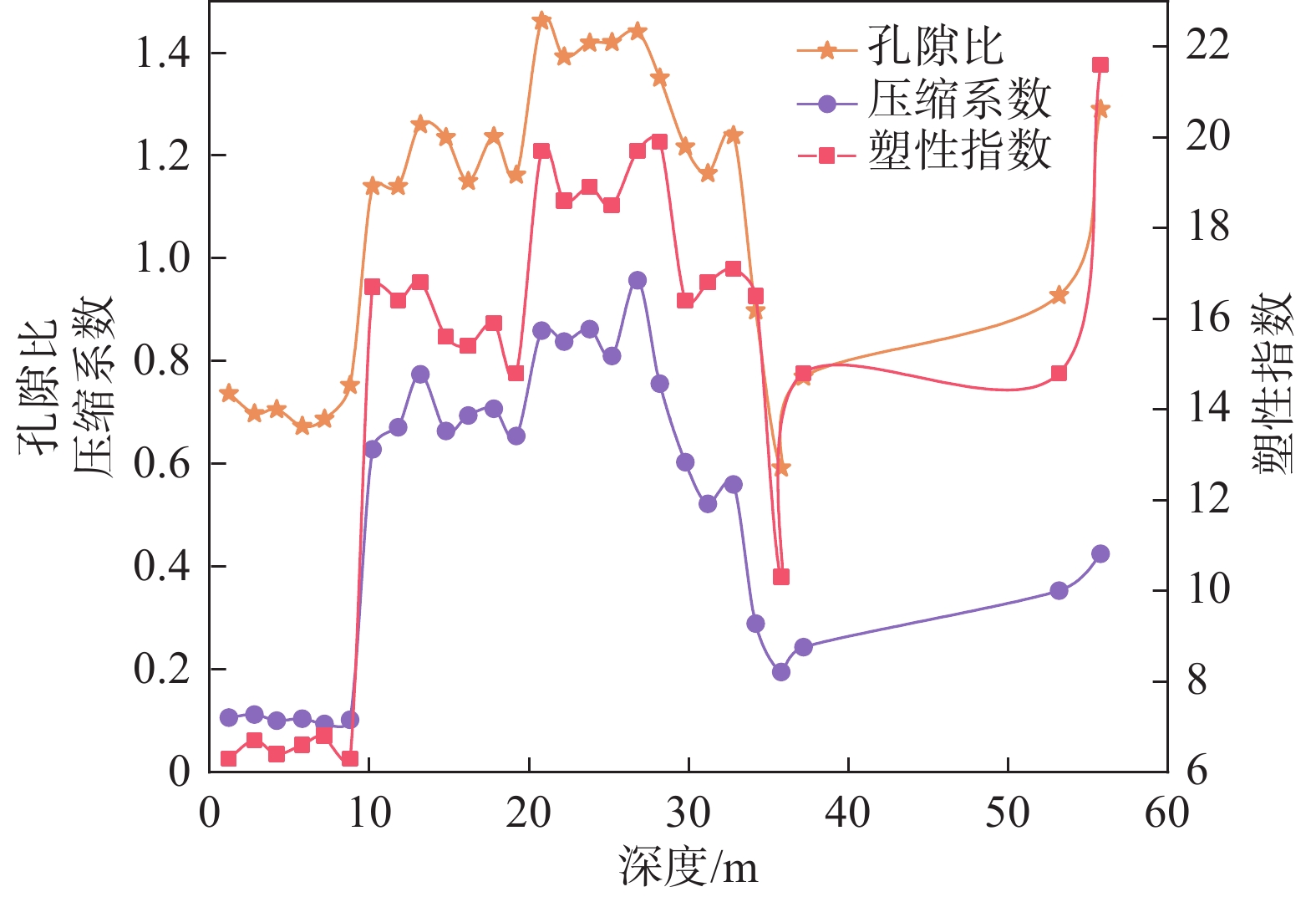
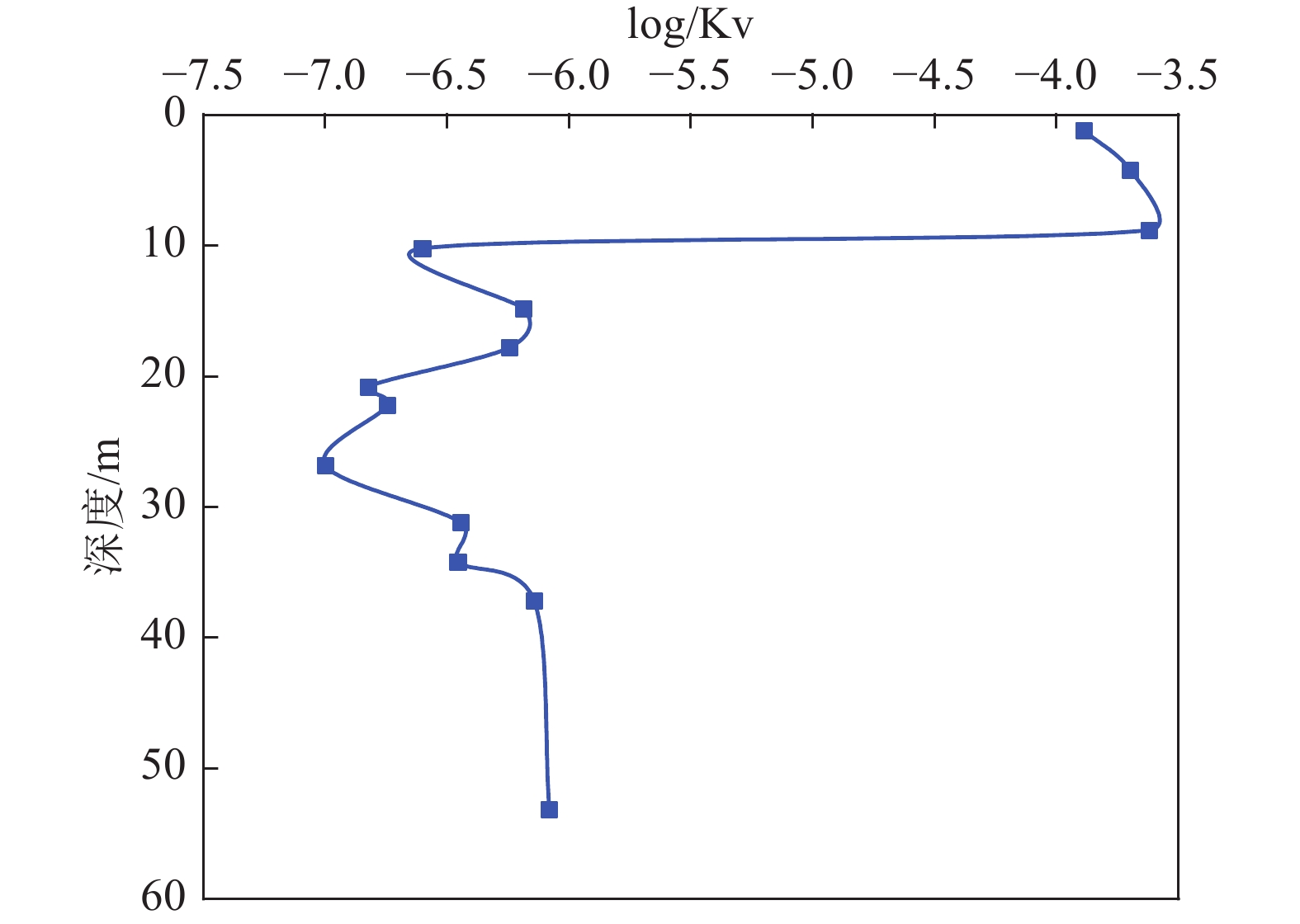
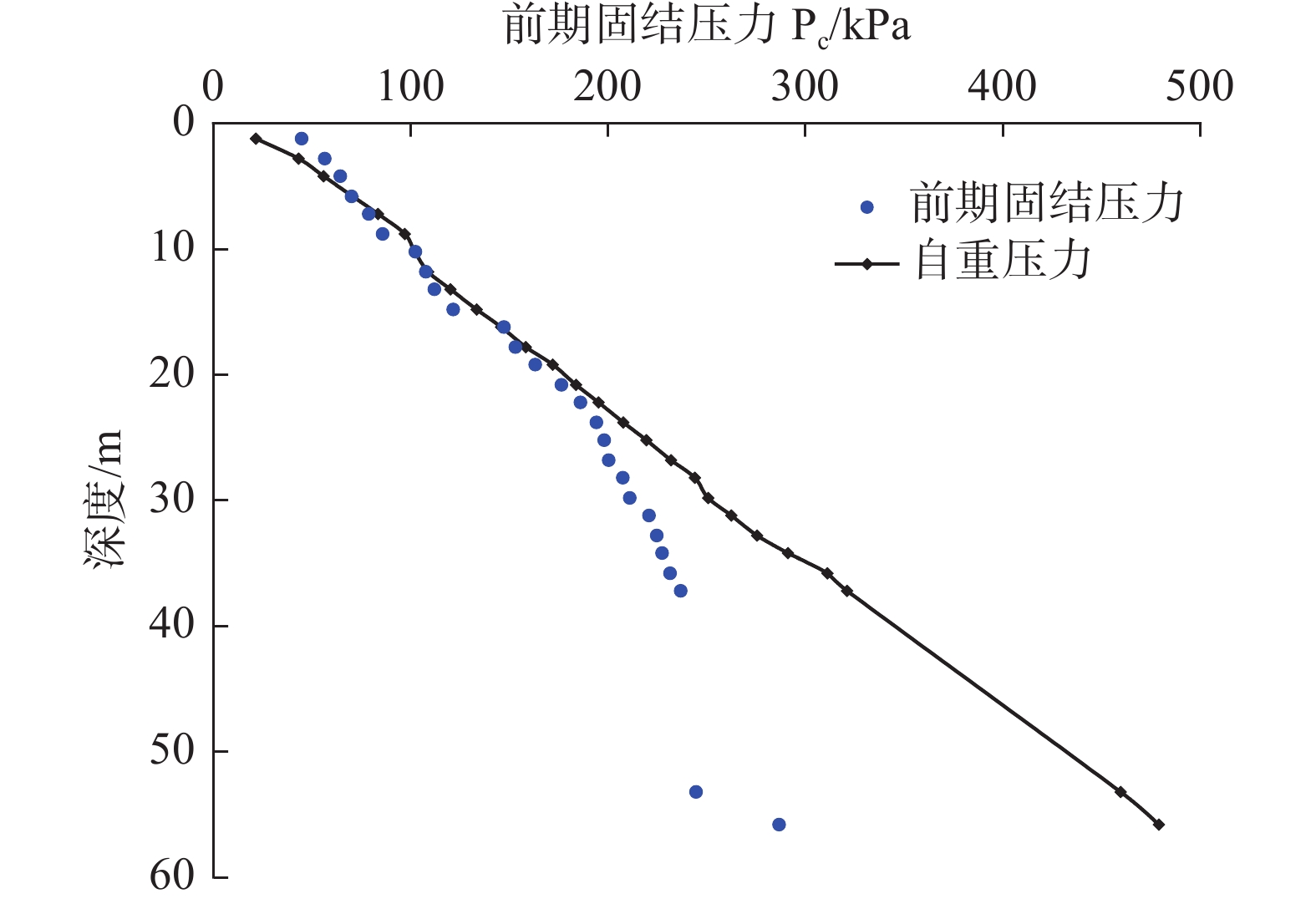
开展土体压缩固结特性研究,从宏观上分析土体变形影响因素,是探究地面沉降成因的重要内容。文章以杭州市地面沉降重点区水文地质工程地质综合试验孔HZ22J06土样为研究对象,通过室内试验对土体的物理力学性质、压缩变形及固结特征进行分析研究。结果表明:试验孔土体各物理指标之间存在显著的相关性,土体含水率、土粒比重、孔隙比、塑性指数、液性指数和压缩系数等指标随深度的增加总体上呈现先增大后减小的趋势;土样压缩系数随压力的增大呈现减小的趋势,且浅部土样压缩系数高于深部土样;土体固结系数与渗透系数之间存在密切的关联性,相同压力下不同类型土样的固结系数大小变化符合粉土>粉质黏土>淤泥质粉质黏土>淤泥质黏土的规律,这与土体渗透系数大小变化规律相一致;试验孔大多数土样处于欠固结状态,在现有自重压力作用下会进一步固结压密,易引发地面沉降。研究成果可为杭州市地面沉降成因规律研究和风险防控提供科学依据。
Abstract:To investigate the soil compression and consolidation properties and analyze the influencing factors of soil deformation from a macro perspective is an important aspect for exploring the causes of land subsidence. Taking soil samples from the hydrogeology and engineering geological comprehensive test hole HZ22J06 in the key area of land subsidence in Hangzhou as an example, and the physical properties, compression deformation and consolidation characteristics of the soil were analyzed and studied by indoor testing. The results reveal a significant correlation among the physical indexes of the soil in the test holes, and the parameters of water content, specific gravity of soil grains, void ratio, plasticity index, liquidity index and compression coefficient show an overall trend of first increasing and then decreasing with the increase of depth. The compression coefficient of the soil samples generally decreases with increasing pressure, with shallow samples having higher compression coefficients compared to deeper ones. Furthermore, there is a close correlation between the consolidation coefficient and hydraulic conductivity of soil. Under the same pressure, the variation of the consolidation coefficient of different types of soil samples follows the law of silt>silty clay>muddy silty clay>soft clay, which is consistent with the variation law of hydraulic conductivity. Additionally, most of the soil samples in the test holes are in an under-consolidated state, which may cause further consolidation and compaction, leading to land subsidence. The research results could provide scientific basis for the study of the causes of land subsidence and risk prevention and control in Hangzhou city.
-

-
表 1 试验孔HZ22J06土体软硬程度与压缩系数统计表
Table 1. Statistical table of soil hardness and compression coefficient for test borehole HZ22J06
孔号 土体软硬状态 土样数/个 土样所占比例/% 平均含水率/% 平均液性指数 平均压缩系数/MPa−1 HZ22J06 0.25<IL≤0.75 可塑 9 33.3 26.4 0.59 0.18 0.75<IL≤1 软塑 6 22.2 39.8 0.94 0.48 IL>1 流塑 12 44.4 46.1 1.31 0.77 -
[1] BAGHERI-GAVKOSH M, HOSSEINI S M, ATAIE-ASHTIANI B, SOHANI Y, EBRAHIMIAN H, MOROVAT F, ASHRAFI S. 2021. Land subsidence: a global challenge[J]. Science of the Total Environment,778:146193. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146193
[2] DANG F N, SONG J Y, ZHOU M, ZHANG L. 2022. Consolidation theory of saturated soil considering permeability coefficient variation and its rationality verification[J]. Journal of China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research,20(6):506-515 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[3] DI S T. 2020. Research on macro-mesoscopic evolution mechanism of whole process and trend prediction of land subsidence caused by groundwater exploitation[D]. Ji’nan: Shandong University (in Chinese with English abstract).
[4] DI S T, JIA C, DING P P, ZHU X. 2022. Microstructural variation of clay during land subsidence and the correlation between macroscopic and microscopic parameters[J]. Materials,15(5):1817. doi: 10.3390/ma15051817
[5] DUAN X F, SUN X X, YANG Y B, LIU Y. 2018. Present condition and mechanism analysis on land subsidence in northern Shandong Plain[J]. Shandong Land and Resources,34(10):86-92 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[6] FANG Y L, REN J W, LI Y P, BAI H J. 2004. Empirical relationship between compression coefficient and pore ratio of soils in Kaifeng area[J]. Journal of Yellow River Conservancy Technical Institute, 16(1): 43-44 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[7] GUO H P, BAI J B, ZHANG Y Q, WANG L Y, SHI J S, LI W P, ZHANG Z C, WANG Y L, ZHU J Y, WANG H G. 2017. The evolution characteristics and mechanism of the land subsidence in typical areas of the North China Plain[J]. Geology in China,44(6):1115-1127 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[8] HUANG D H. 2023. Land subsidence monitoring in Yungang mining area in Datong City based on InSAR technology[J]. East China Geology,44(4):476-484 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.16788/j.hddz.32-1865/P.2023.04.011
[9] GUO H P, DING G P, ZHU J Y, TIAN X W, LEI J T, WANG Y L. 2014. Compression deformation and permeability characteristics of clay in land subsidence area of Cangzhou[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology,36(5):111-117 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[10] JIANG W H, ZHAN L T, YANG C. 2020. Analytical solution for one-dimensional large strain consolidation of saturated soft soils with continuous drainage boundary[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology),51(5):1289-1298 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[11] JU J, LIU S Y, LIU Z B, CAI G J. 2012. Degree of underconsolidation determination method of in-situ soft soil through pore pressure dissipation test[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,33(3):957-960 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] KONG L Y, XU Y Z, ZHAO G Z, LIU W H, XIE S M. 2023. Study on the structural characteristics of riverbed lithology based on the joint inversion of multiple methods[J]. East China Geology,44(2):150-159.
[13] LEI H W. 2010. Study on characteristics, mechanism and numerical simulation of land subsidence in XX City[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences (in Chinese).
[14] LI C X, WANG P X. 1998. The study of the estuarine stratigraphy of the late Quaternary in the Yangtze River[M]. Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese).
[15] LI X G, XU R Q, WANG X C, RONG X N. 2013. Assessment of engineering properties for marine and lacustrine soft soil in Hangzhou[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science),47(8):1346-1352 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[16] LIU D P, YOU X W, BAI B. 2005. Geotechnics[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press (in Chinese).
[17] MINISTRY OF HOUSING AND URBAN-RURAL DEVELOPMENT OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA. 2019. GB/T 50123-2019 Standard for geotechnical testing method[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 85-91 (in Chinese).
[18] PEI J T, YANG L, LUO Z J. 2023. Cause analysis of land subsidence in Haimen area of Jiangsu Province[J]. East China Geology,44(4):467-475 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.16788/j.hddz.32-1865/P.2023.04.010
[19] QIAO Y. 2019. Erodibility of bed sediments in the Yangtze Estuary[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University (in Chinese).
[20] SU H Y. 1981. Study on deformation characteristics and deformation mechanism of soil layer in land subsidence in Shanghai[J]. Shanghai Land and Resources, (2): 56-69 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[21] SUN D C. 2016. The dynamic analysis on the pearl marine with different degree of consolidation[D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University (in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] TIAN L C. 2010. Research on consolidation of different depths clay in Hengshui[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology,8(2):31-34 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[23] TIAN Y, ZHANG J B, MA L. 2020. Experimental study on variation law of tailings sand consolidation coefficient[J]. Journal of Xiʼan University of Architecture & Technology (Natural Science Edition), 52(1): 92-97 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[24] WANG Y L, GUO H P, MENG J, CHEN Y, ZANG X S, ZHU J Y, FAN G D. 2020. A study on compression and consolidation behaviors of soils in typical landsubsidence area in Cangzhou[J]. Geological Survey and Research,43(3):246-250,278 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] WANG M Z, WAN J W, BAI T, LIU Y, SHEN F. 2021. The influence of geothermal resources exploitation of sandstone thermal reservoir on land subsidence in Decheng District, Dezhou City[J]. East China Geology,42(2):202-209 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[26] WANG Z B, YANG S Y, WANG Q, ZHANG Z X, ZHANG X H, LAN X H, LI R H, HUANG L. 2014. Late Quaternary stratigraphic evolution on the outer shelf of the East China Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research,90:5-16. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2014.04.015
[27] XU Y S, SHEN J S, ZHOU A N, ARULRAJAH A. 2018. Geological and hydrogeological environment with geohazards during underground construction in Hangzhou: a review[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences,11(18):544. doi: 10.1007/s12517-018-3894-7
[28] XUE Y Q, ZHANG Y. 2016. Land subsidence and land fissures in the southern Yangtze River Delta[J]. East China Geology,37(1):1-9 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[29] YUAN M, BAI J W, QIN Y K. 2016. A review on land subsidence research[J]. Journal of Suzhou University of Science and Technology (Natural Science),33(1):1-5 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[30] ZHAO J K, WU M J, LIU S X, SHEN H Z. 2006. The relation between groundwater exploitation and land subsidence in the coast plain of Zhejiang Province[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities,12(2):185-194 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[31] ZHAO Y B, LIU Q J, HUANG X J. 2022. Characteristics of karst development and the law of groundwater enrichment in Shazhouba area of Ruijin City[J]. East China Geology,43(2):227-234(in Chinese with English abstract).
[32] ZHU J Y, GUO H P, LI W P, TIAN X W. 2014. Relationship between land subsidence and deep groundwater yield in the North China Plain[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology,12(3):165-169 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[33] 党发宁, 宋靖宇, 周玫, 张乐. 2022. 饱和土的变渗透系数固结理论及其合理性验证[J]. 中国水利水电科学研究院学报(中英文),20(6):506-515.
[34] 狄胜同. 2020. 地下水开采导致地面沉降全过程宏细观演化机理及趋势预测研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学.
[35] 段晓飞, 孙晓晓, 杨亚宾, 刘毅. 2018. 鲁北平原地面沉降现状与机理分析[J]. 山东国土资源,34(10):86-92.
[36] 方永伦, 任建伟, 李亚平, 白宏洁. 2004. 开封地区土的压缩系数和孔隙比的经验关系[J]. 黄河水利职业技术学院学报,16(1):43-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-486X.2004.01.016
[37] 郭海朋, 白晋斌, 张有全, 王丽亚, 石菊松, 李文鹏, 张作辰, 王云龙, 朱菊艳, 王海刚. 2017. 华北平原典型地段地面沉降演化特征与机理研究[J]. 中国地质,44(6):1115-1127. doi: 10.12029/gc20170606
[38] 郭海朋, 丁国平, 朱菊艳, 田小伟, 雷建涛, 王云龙. 2014. 沧州地面沉降区粘土压缩变形和渗透特征研究[J]. 武汉理工大学学报,36(5):111-117.
[39] 黄德华. 2023. 基于InSAR技术的大同市云冈矿区地面沉降监测[J]. 华东地质,44(4):476-484. doi: 10.16788/j.hddz.32-1865/P.2023.04.011
[40] 江文豪, 詹良通, 杨策. 2020. 连续排水边界条件下饱和软土一维大变形固结解析解[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),51(5):1289-1298.
[41] 居俊, 刘松玉, 刘志彬, 蔡国军. 2012. 现场软土欠固结程度孔压消散试验评价方法[J]. 岩土力学,33(3):957-960. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2012.03.048
[42] 孔令莹, 徐远志, 赵贵章, 刘文辉, 谢思敏. 2023. 基于多种方法联合反演的河床岩性结构特征研究[J]. 华东地质,44(2):150-159.
[43] 雷宏武. 2010. XX城地面沉降特征与机理分析及数值模拟研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学.
[44] 李从先, 汪品先. 1998. 长江晚第四纪河口地层学研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社.
[45] 李雪刚, 徐日庆, 王兴陈, 荣雪宁. 2013. 杭州地区海、湖相软土的工程特性评价[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版),47(8):1346-1352. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2013.08.004
[46] 刘大鹏, 尤晓暐, 白冰. 2005. 土力学[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社.
[47] 裴江涛, 杨璐, 骆祖江. 2023. 江苏海门地区地面沉降成因分析[J]. 华东地质,44(4):467-475. doi: 10.16788/j.hddz.32-1865/P.2023.04.010
[48] 乔宇. 2019. 长江口表层沉积物侵蚀特性研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学.
[49] 苏河源. 1981. 上海地面沉降中土层变形特征与变形机理的研究[J]. 上海地质,(2):56-69.
[50] 孙东晨. 2016. 不同固结程度珠江海洋土动力特性分析[D]. 广州: 广州大学.
[51] 田利川. 2010. 衡水沉降区不同深度黏土固结特性研究[J]. 南水北调与水利科技,8(2):31-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1683.2010.02.009
[52] 田园, 张敬博, 马林. 2020. 尾矿砂固结系数变化规律试验研究[J]. 西安建筑科技大学学报(自然科学版),52(1):92-97.
[53] 王云龙, 郭海朋, 孟静, 陈晔, 臧西胜, 朱菊艳, 樊高栋. 2020. 沧州典型地面沉降区土体压缩与固结特征研究[J]. 地质调查与研究,43(3):246-250,278.
[54] 王明珠, 万军伟, 白通, 刘毅, 沈芳. 2021. 德州市德城区砂岩热储地热资源开采对地面沉降的影响[J]. 华东地质,42(2):202-209.
[55] 薛禹群, 张云. 2016. 长江三角洲南部地面沉降与地裂缝[J]. 华东地质,37(1):1-9.
[56] 袁铭, 白俊武, 秦永宽. 2016. 国内外地面沉降研究综述[J]. 苏州科技学院学报(自然科学版),33(1):1-5.
[57] 赵建康, 吴孟杰, 刘思秀, 沈慧珍. 2006. 浙江省滨海平原地下水开采与地面沉降[J]. 高校地质学报,12(2):185-194. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2006.02.005
[58] 赵毅斌, 刘前进, 黄旭娟. 2022. 瑞金市沙洲坝地区岩溶发育特征与地下水富集规律[J]. 华东地质,43(2):227-234.
[59] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 2019. GB/T 50123—2019 土工试验方法标准[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 85-91.
[60] 朱菊艳, 郭海朋, 李文鹏, 田小伟. 2014. 华北平原地面沉降与深层地下水开采关系[J]. 南水北调与水利科技,12(3):165-169.
-




 下载:
下载: