Simulation and prediction of Yancheng ground subsidence based on Bio-consolidation theory
-
摘要:
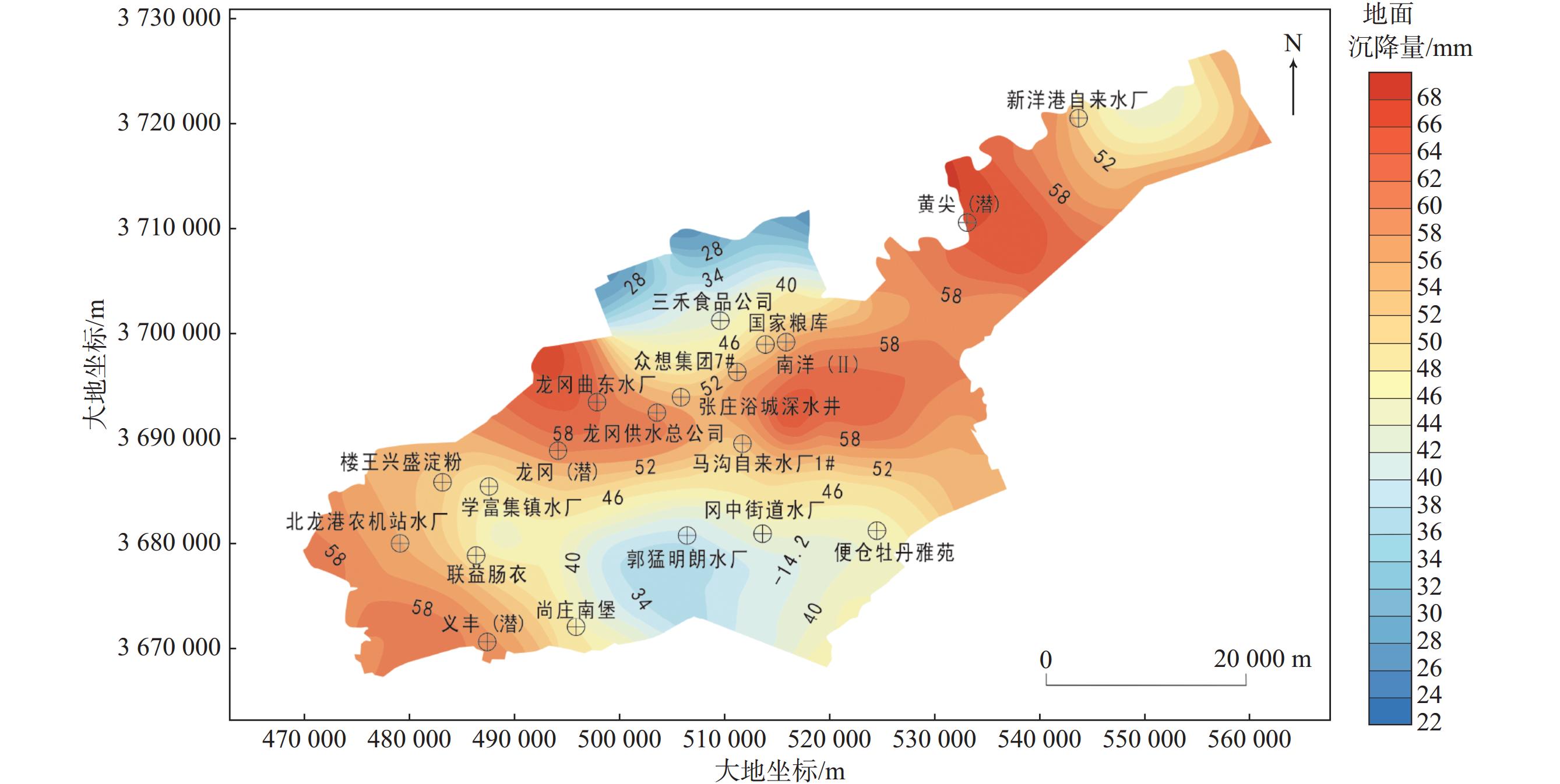
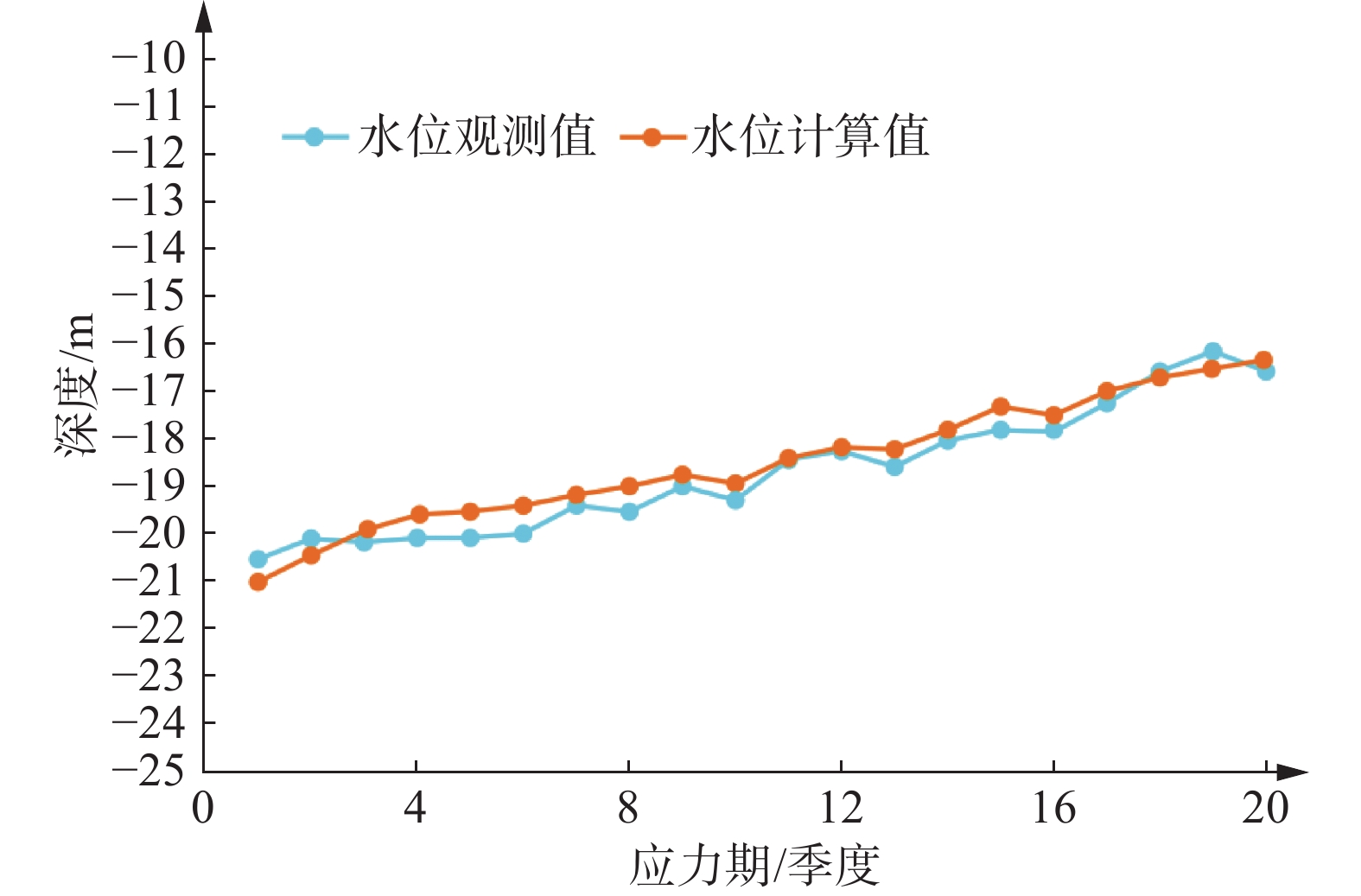
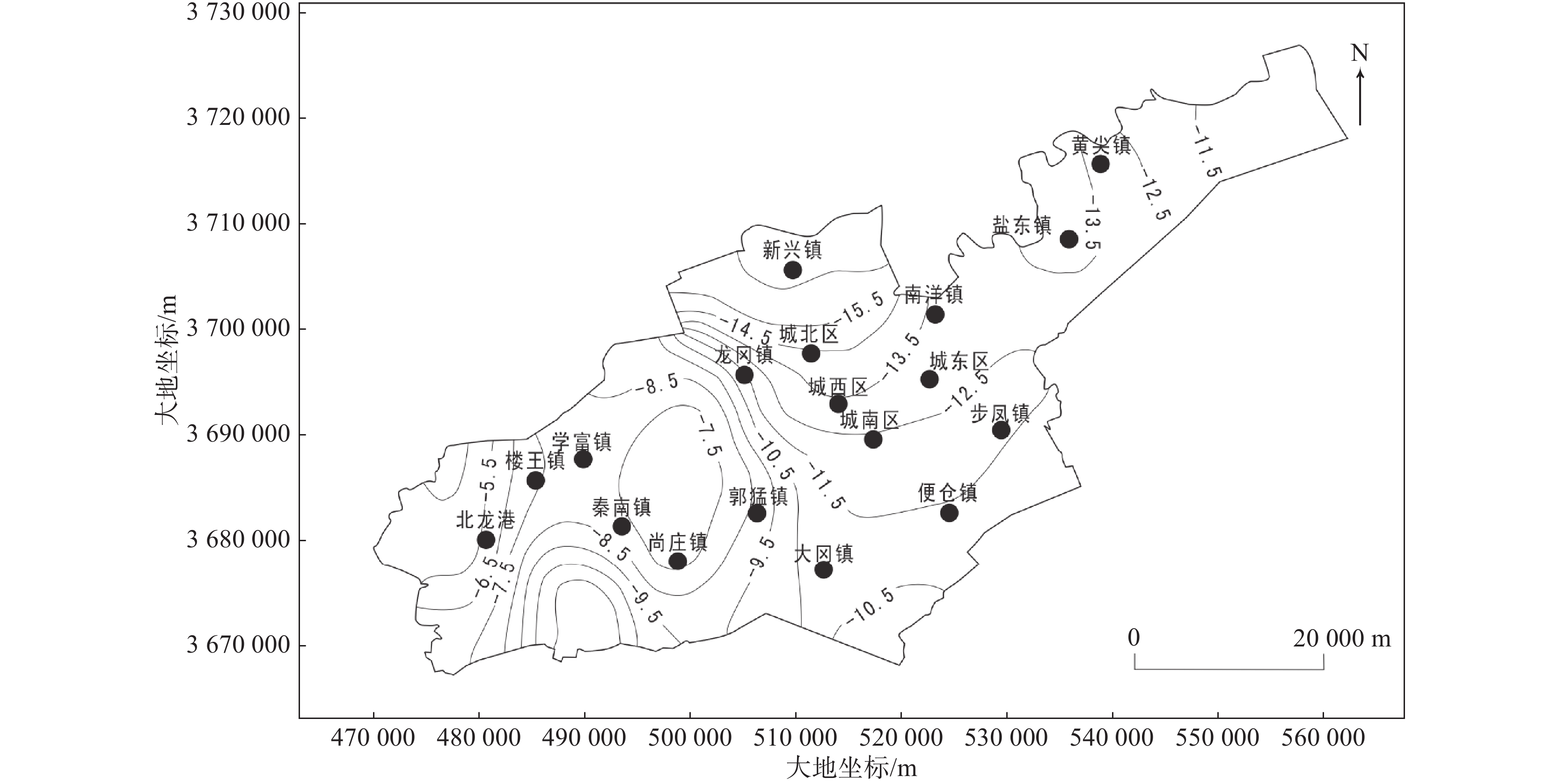
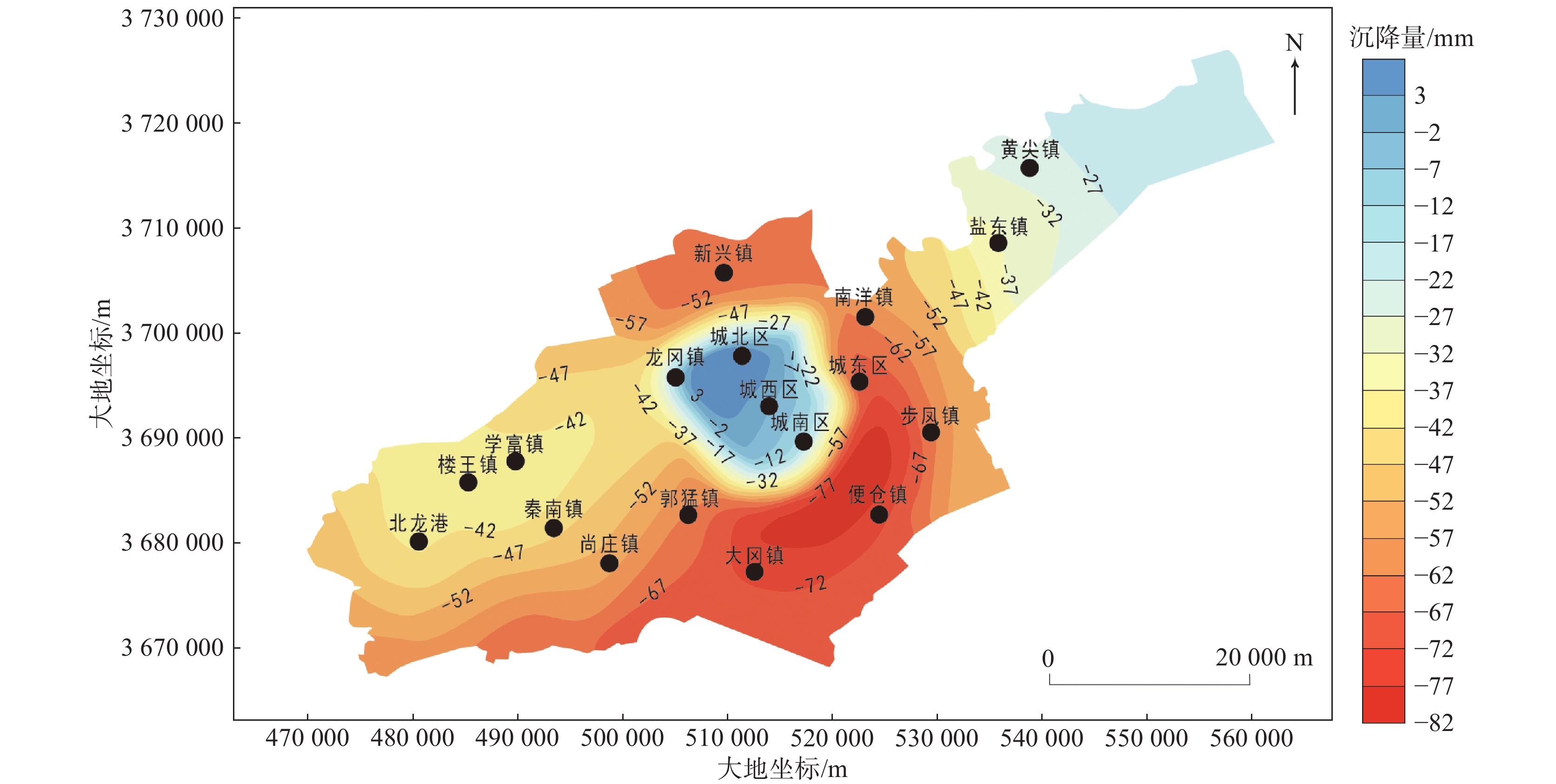
城市地面沉降可能会对建筑物和基础设施造成损坏,影响城市的整体稳定性和安全性。文章以江苏省盐城市区为研究对象,以比奥固结理论为基础,引入黏弹塑性土体本构模型,并考虑土体参数随应力状态的非线性变化,建立了盐城市建筑荷载和地下水开采与地面沉降三维变参数全耦合黏弹塑性模型。结果表明:在建筑荷载和地下水开采条件下,研究区地下水水位持续回升,整体出现回弹现象,但在建筑荷载较大的中心城区,地面回弹量较小,甚至出现轻微沉降,且2021—2023年产生的最大水平位移为15 mm。研究结果可为盐城市防治和减轻地面沉降危害提供科学依据。
Abstract:Ground subsidence occurred in urban area may cause damage to buildings and infrastructure, affecting the overall stability and safety of the city. This paper established a three-dimensional variable parameter fully-coupled viscoelastic-plastic model of building loads and groundwater mining with ground subsidence in Yancheng, Jiangsu Province based on the theory of Bio-consolidation, introduced the viscoelastic-plastic soil constitutive model, and meanwhile took the nonlinear change of soil parameters with the state of stress into account. The results show that the groundwater level in the study area continually rises under the conditions of construction loading and groundwater extracting, with an overall rebound phenomenon. However, in the centre of the city, where the building loads are high, the amount of ground rebound is small and even slight settlement occurs, and the maximum horizontal displacement produced over 10 years is 15 mm. The results of the study can provide scientific basis for the prevention and mitigation of ground subsidence hazards in Yancheng.
-
Key words:
- Yancheng /
- groundwater extraction /
- ground subsidence /
- building load /
- Bio-consolidation theory
-

-
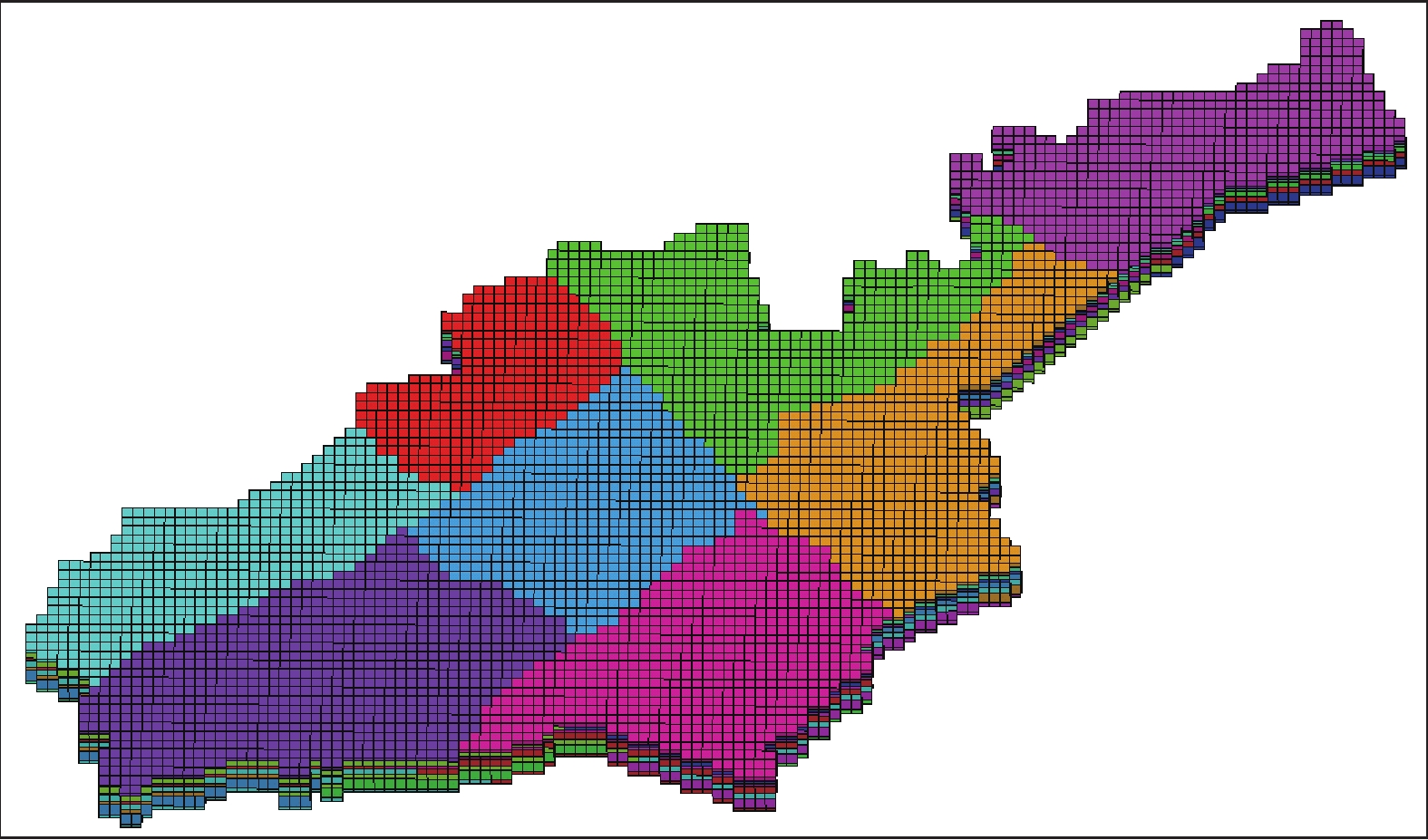
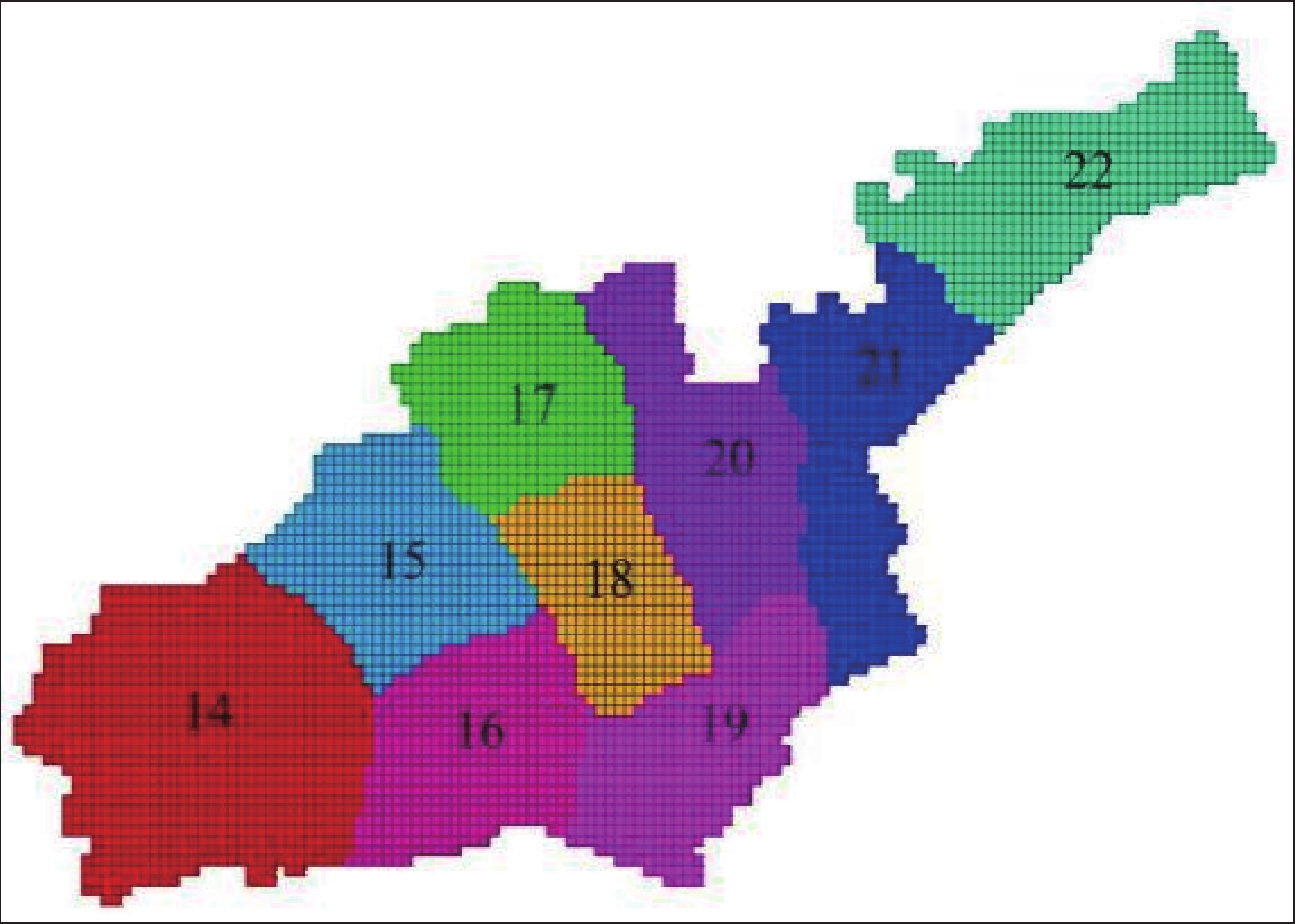
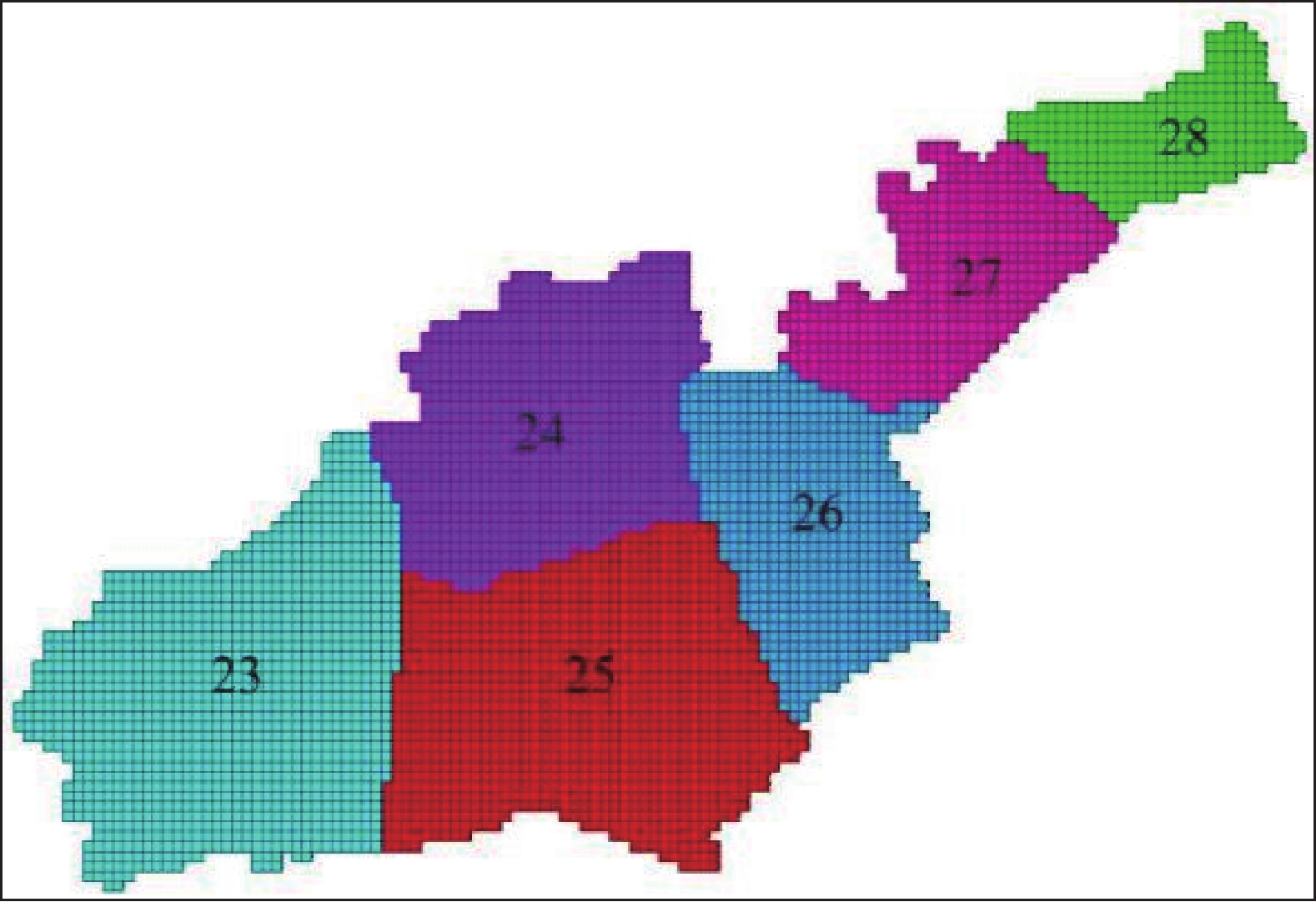
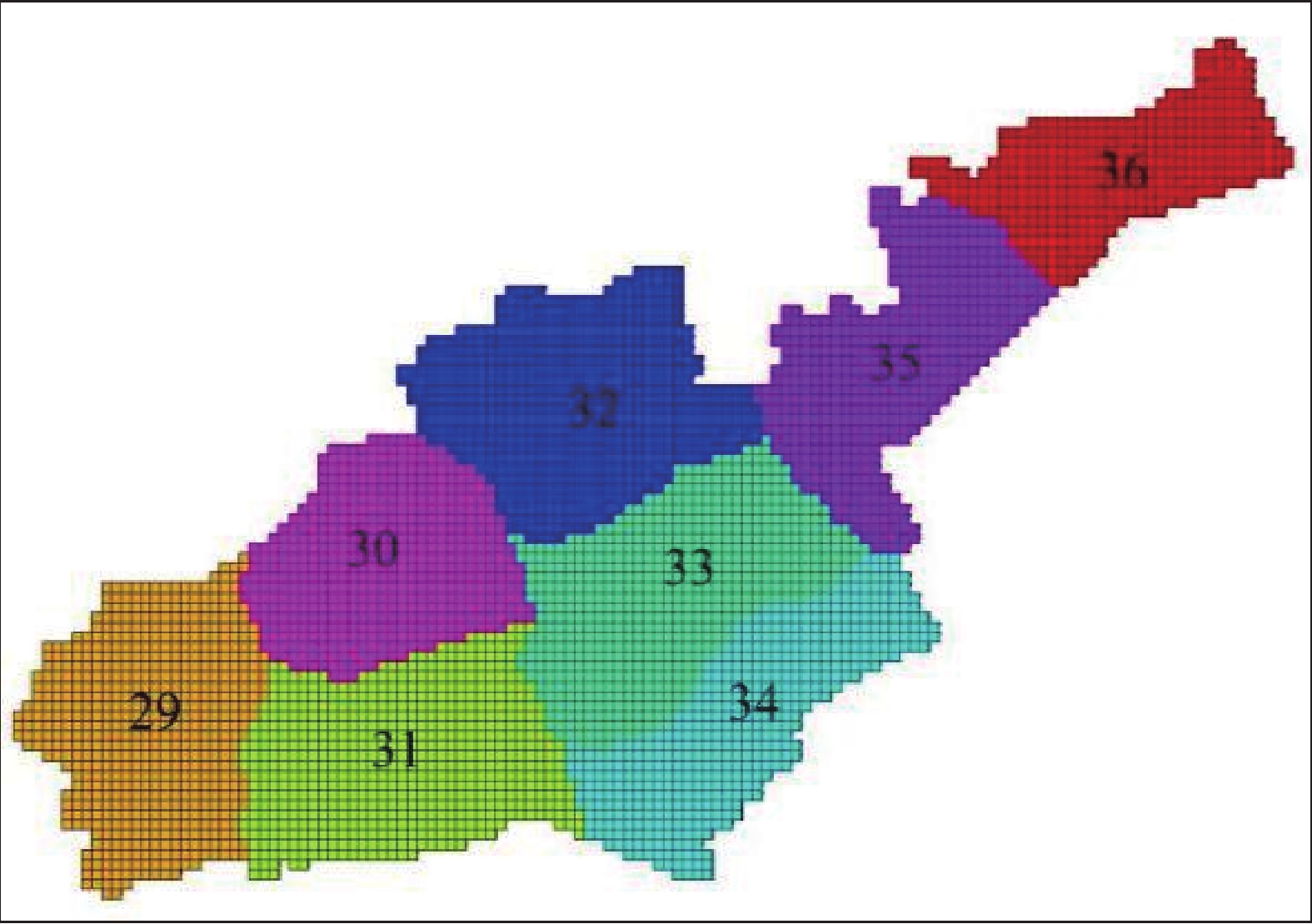
表 1 盐城市含水层参数分区表
Table 1. Parameter partition of aquifer in Yancheng
分区 主轴方向渗透系数/(m/d) 变形模量/MPa 泊松比 粘聚力/KPa 摩擦角/° 膨胀角/° 重度/(KN/m3) 有效孔隙度 Kxx Kyy Kzz E ν c φ ψ Γ n 1 3.2 3.2 0.32 27 0.40 3.0 33.6 0 20.42 0.422 2 4.4 4.4 0.44 26 0.45 5.0 34.3 0 21.54 0.418 3 2.8 2.8 0.28 24 0.39 6.0 35.1 0 20.73 0.425 4 3.5 3.5 0.35 25 0.38 8.0 35.7 0 21.41 0.416 5 3.2 3.2 0.32 23 0.36 5.5 34.8 0 19.86 0.419 6 3.6 3.6 0.36 25 0.42 4.5 34.2 0 20.28 0.428 7 4.1 4.1 0.41 27 0.47 4.0 34.0 0 19.75 0.431 8 3.4 3.4 0.34 22 0.48 3.0 33.6 0 20.64 0.418 9 5.2×10−3 5.2×10−3 5.2×10−4 18 0.48 15.0 21.5 0 21.37 0.522 10 4.3×10−3 4.3×10−3 4.3×10−4 16 0.47 17.0 23.2 0 20.68 0.518 11 4.6×10−3 4.6×10−3 4.6×10−4 15 0.48 18.0 20.9 0 20.24 0.525 12 5.0×10−3 5.0×10−3 5.0×10−4 17 0.48 14.0 21.2 0 19.57 0.516 13 5.5×10−3 5.5×10−3 5.5×10−4 19 0.48 15.0 20.8 0 19.11 0.519 14 34 34 3.4 30 0.38 4.0 34.2 0 21.32 0.437 15 33 33 3.3 28 0.40 3.5 35.1 0 20.87 0.422 16 30 30 3.0 31 0.37 4.0 34.7 0 20.55 0.416 17 28 28 2.8 29 0.39 4.3 33.6 0 20.38 0.426 18 24 24 2.4 32 0.36 5.5 33.2 0 20.14 0.430 19 35 35 3.5 33 0.35 4.8 34.0 0 21.11 0.421 20 32 32 3.2 29 0.41 4.6 34.5 0 22.13 0.419 21 40 40 4.0 27 0.42 3.8 35.0 0 20.72 0.424 22 36 36 3.6 26 0.40 3.5 35.8 0 20.16 0.417 23 2.6×10−4 2.6×10−4 2.6×10−5 25 0.44 18.2 20.6 0 19.76 0.492 24 3.0×10−4 3.0×10−4 3.0×10−5 22 0.48 17.5 20.6 0 20.33 0.488 25 3.3×10−4 3.3×10−4 3.3×10−5 21 0.46 17.2 20.6 0 19.54 0.485 26 2.8×10−4 2.8×10−4 2.8×10−5 23 0.48 16.7 20.6 0 20.48 0.506 27 2.0×10−4 2.0×10−4 2.0×10−5 24 0.47 16.1 20.6 0 21.25 0.490 28 2.4×10−4 2.4×10−4 2.4×10−5 26 0.45 16.5 20.6 0 21.66 0.483 29 5.0 5.0 0.50 36 0.38 5.3 34.2 0 20.11 0.397 30 5.6 5.6 0.56 35 0.41 4.2 35.4 0 19.83 0.382 31 6.2 6.2 0.62 34 0.39 4.8 36.6 0 19.97 0.376 32 5.3 5.3 0.53 38 0.42 6.6 31.8 0 20.42 0.390 33 5.1 5.1 0.51 39 0.40 5.8 32.4 0 20.63 0.385 34 6.0 6.0 0.60 41 0.44 6.3 36.1 0 21.37 0.388 35 4.5 4.5 0.45 38 0.41 5.7 35.5 0 20.44 0.391 36 4.8 4.8 0.48 36 0.41 5.5 35.0 0 20.71 0.393 37 2.0×10−4 2.0×10−4 2.0×10−5 32 0.48 17.6 21.1 0 20.64 0.492 38 1.6×10−4 1.6×10−4 1.6×10−5 35 0.43 18.8 20.7 0 20.52 0.488 39 1.0×10−4 1.0×10−4 1.0×10−5 34 0.46 19.4 20.5 0 20.73 0.485 40 1.2×10−4 1.2×10−4 1.2×10−5 36 0.44 18.7 20.8 0 20.16 0.506 41 1.8×10−4 1.8×10−4 1.8×10−5 35 0.42 18.2 21.2 0 19.92 0.490 42 7.0×10−5 7.0×10−5 7.0×10−6 33 0.47 17.8 20.3 0 19.63 0.483 43 9.0×10−5 9.0×10−5 9.0×10−6 32 0.45 17.5 20.4 0 19.17 0.482 44 13 13 1.3 45 0.39 5.8 34.8 0 20.18 0.435 45 12 12 1.2 46 0.41 6.2 34.2 0 20.54 0.432 46 18 18 1.8 50 0.40 6.0 33.7 0 21.62 0.426 47 20 20 2.0 48 0.38 5.9 33.4 0 20.35 0.420 48 16 16 1.6 46 0.36 6.5 32.8 0 21.24 0.433 49 12 12 1.2 53 0.39 6.4 32.5 0 21.33 0.428 50 14 14 1.4 48 0.37 6.1 33.4 0 21.17 0.419 51 9 9 0.9 49 0.41 5.8 35.5 0 20.93 0.413 52 8.5 8.5 0.85 51 0.43 5.7 36.1 0 20.54 0.417 53 3 3 0.3 47 0.45 5.3 37.0 0 20.36 0.437 54 4.5 4.5 0.45 45 0.46 5.0 37.5 0 20.22 0.422 -
[1] CHEN X P, BAI S W. 2001. The numerical analysis of visco-elastic-plastic Biot’s consolidation for soft clay foundation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,23(4):481-484 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[2] CHEN Z, LUO Z J. 2017. Sensitivity analysis of parameters on Biot's consolidation full coupled model[J]. Journal of Nanchang University (Engineering & Technology),39(4):354-360, 379 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[3] FRANCESCO R D. 2013. Exact solution of Terzaghi’s consolidation equation and extension to two/three-dimensional cases[J]. Applied Mathematics,4(4):713-717. doi: 10.4236/am.2013.44099
[4] GU S Y, YAO W J, XU M Z, WANG D. 2020. Risk evaluation of land subsidence in Yancheng of Jiangsu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,31(1):36-43 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[5] HAN S, HUI S J, SUN Q, ZHANG S, SHI L, ZHANG Y, ZHU Q W. 2023.Research on ecological restoration technology of high-steep slopes of abandoned mines based on geological safety evaluation[J]. East China Geology, 44(2): 216-227 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[6] HE H Y. 2019. Land subsidence analysis and numerical simulation of Dongguang[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing) (in Chinese with English abstract).
[7] HU X R, CAI X F, LI C B, ZHANG Z R, QU P. 2022. Triple-shear elasto-plastic constitutive models of unsaturated clays in normal consolidation[J]. Engineering Mechanics,39(1):164-174 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[8] JIANG Y H, ZHOU Q P, NI H Y, CHEN L D, CHENG H Q, LEI M T, GE W Y, MA T, SHI B, CHENG Z Y, DUAN X J, SU J W, ZHU J Q, XIU L C, XIANG F, ZHU Z M, FENG N Q, XIE Z S, TAN J M, PENG K, GUO S Q, FU Y P, REN H Y, SUN J P, YANG Q, ZHU J L, WANG D H, LI M H, LIU G N, FAN C Z, WANG X F, SHI Y J, WANG H M, DONG X Z, CHEN H Y, HAO S F, DENG Y M, LI Y, XIAO Z Y, YANG H, LIU L, JIN Y, ZHANG H, MEI S J, QI Q J, LÜ J S, HOU L L, CHEN G, CHEN Z, JIA Z Y. 2023. Progress of environmental geological investigation and research in the Yangtze River Economic Zone[J]. East China Geology,44(3):239-261 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.16788/j.hddz.32-1865/P.2023.03.001
[9] LI H. 2017. Numerical simulation of land subsidence and compression characteristics of water loss under groundwater exploitation[D]. Ji’nan: Shandong University (in Chinese with English abstract).
[10] LI W, CHEN Y F, SHEN H Z, WU M J, ZHU Y. 2015. Ground subsidence effects since groundwater exploitation restriction in Wenhuang plain[J]. Resources Survey & Environment,36(4):306-310 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[11] LUO Z J, NING D, DU J J, LU W. 2019. Influence of building load and groundwater exploitation on land subsidence in Shengze, Wujiang[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),49(2):514-525 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] LUO Y, YE S J, WU J C, YANG T L. 2018. Development and application of visualization system for numerical simulation of regional land subsidence[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition),46(10):28-33 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[13] MA Q S, LUO Z J. 2015. Numerical simulation of groundwater exploitation and land subsidence in Cangzhou City[J]. Water Resources Protection,31(4):20-26 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[14] ROGERS J D, CHUNG J W. 2016. Applying Terzaghi’s method of slope characterization to the recognition of Holocene land slippage[J]. Geomorphology,265:24-44.
[15] SU H Y. 1979. Investigation of the deformation characteristics of various soil staata under the influence of pumping out & back of ground water in Shanghai[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, first issue, 24-35 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[16] VIANOA C C. 1987. The principle of rheology in soil Mec-Hanics[M]. DU Y P. Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese).
[17] WANG Y W. 2016. Numerical simulation of regional land subsidence in coastal area of north Jiangsu[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University (in Chinese with English abstract).
[18] XIONG X F, LUO Y, SHI X Q, WU J F, WU J C. 2017. Three-dimensional Land Subsidence Modeling Based on TOUGH2-FLAC3D and Control Strategies Evaluation[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities,23(1):172-180 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[19] XUE Y Q, ZHANG Y. 2016. Land subsidence and land fissures in the southern Yangtze River Delta[J]. East China Geology,37(1):1-9 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[20] YANG H W, ZHANG F L. 2016. Analysis of groundwater exploitation and utilization in Yancheng[J]. Water Resources Protection and Management, (1): 43-45 (in Chinese).
[21] ZHU C F, GONG J S, TAO X H, TAN M J, ZHOU K E, WANG H S, LI L, YE Y H. 2023. Comparison of the hydrochemical characteristics of shallow groundwater in the Huaihe River Basin during a ten-year period and its significance to environmental change[J]. East China Geology,44(3):282-291 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.16788/j.hddz.32-1865/P.2023.03.004
[22] ZHANG Y, XUE Y Q, SHI X Q, SONG Z. 2005. Study on nonlinear creep model for saturated sand[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,26(12):1869-1873 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[23] ZONG M F. 2021. Theoretical and experimental study on one-dimensional nonlinear consolidation of soft soil based on continuous drainage boundary[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences (in Chinese with English abstract).
[24] 陈晓平, 白世伟. 2001. 软粘土地基粘弹塑性比奥固结的数值分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,23(4):481-484. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2001.04.021
[25] 陈卓, 骆祖江. 2017. 比奥固结全耦合模型参数灵敏度分析[J]. 南昌大学学报(工科版),39(4):354-360, 379.
[26] 顾晟彦, 姚维军, 徐明钻, 王丹. 2020. 江苏盐城地面沉降风险评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,31(1):36-43.
[27] 韩帅, 惠淑君, 孙强, 张帅, 时磊, 张颖, 朱庆伟.2023.基于地质安全评价的废弃矿山高陡边坡生态修复技术研究[J]. 华东地质, 44(2): 216-227.
[28] 何宏宇. 2019. 东光地面沉降分析及数值模拟研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京).
[29] 胡小荣, 蔡晓锋, 李春博, 章志荣, 瞿鹏. 2022. 正常固结非饱和黏性土的三剪弹塑性本构模型[J]. 工程力学,39(1):164-174. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2020.12.0910
[30] 姜月华, 周权平, 倪化勇, 陈立德, 程和琴, 雷明堂, 葛伟亚, 马腾, 施斌, 程知言, 段学军, 苏晶文, 朱锦旗, 修连存, 向芳, 朱志敏, 冯乃琦, 谢忠胜, 谭建民, 彭轲, 郭盛乔, 伏永朋, 任海彦, 孙建平, 杨强, 朱继良, 王东辉, 李明辉, 刘广宁, 范晨子, 王新峰, 史玉金, 王寒梅, 董贤哲, 陈焕元, 郝社峰, 邓娅敏, 李云, 肖则佑, 杨海, 刘林, 金阳, 张鸿, 梅世嘉, 齐秋菊, 吕劲松, 侯莉莉, 陈刚, 陈孜, 贾正阳. 2023. 长江经济带环境地质调查研究进展[J]. 华东地质,44(3):239-261. doi: 10.16788/j.hddz.32-1865/P.2023.03.001
[31] 李辉. 2017. 地下水诱发地面沉降数值模拟分析研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学.
[32] 黎伟, 陈远法, 沈慧珍, 吴孟杰, 诸烨. 2015. 浙江温黄平原地下水控采后地面沉降效应分析[J]. 资源调查与环境,36(4):306-310.
[33] 骆祖江, 宁迪, 杜菁菁, 陆玮. 2019. 吴江盛泽地区建筑荷载和地下水开采对地面沉降的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),49(2):514-525.
[34] 罗跃, 叶淑君, 吴吉春, 杨天亮. 2018. 区域地面沉降数值模拟可视化系统开发及应用[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版),46(10):28-33.
[35] 马青山, 骆祖江. 2015. 沧州市地下水开采-地面沉降数值模拟[J]. 水资源保护,31(4):20-26. doi: 10.3880/j.issn.1004-6933.2015.04.004
[36] 苏河源. 1979. 抽、灌水作用下上海土层变形特征的探讨[J]. 岩土工程学报, 创刊号:24-35.
[37] 王艺伟. 2016. 苏北沿海地区区域地面沉降模拟研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学.
[38] 维亚洛夫. 1987. 土力学的流变原理[M]. 杜余培, 译. 北京: 科学出版社.
[39] 熊小锋, 罗跃, 施小清, 吴剑锋, 吴吉春. 2017. 基于TOUGH2-FLAC3D耦合的三维地面沉降数值模拟及控制策略研究[J]. 高校地质学报,23(1):172-180.
[40] 薛禹群, 张云. 2016. 长江三角洲南部地面沉降与地裂缝[J]. 华东地质,37(1):1-9.
[41] 杨红尉, 张凤莲. 2016. 盐城地下水开采及利用情况分析[J]. 水政水资源,(1):43-45.
[42] 朱春芳, 龚建师, 陶小虎, 檀梦皎, 周锴锷, 王赫生, 李亮, 叶永红. 2023. 淮河流域浅层地下水水化学特征10年对比分析及其环境变迁意义[J]. 华东地质,44(3):282-291. doi: 10.16788/j.hddz.32-1865/P.2023.03.004
[43] 张云, 薛禹群, 施小清, 宋震. 2005. 饱和砂性土非线性蠕变模型试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,26(12):1869-1873. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2005.12.001
[44] 宗梦繁. 2021. 连续排水边界下软土一维非线性固结理论与试验研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉).
-



 下载:
下载: