Numerical simulation of groundwater pollution caused by leakage of urban pipe network: a case study on an interfluve in Shenzhen City
-
摘要:
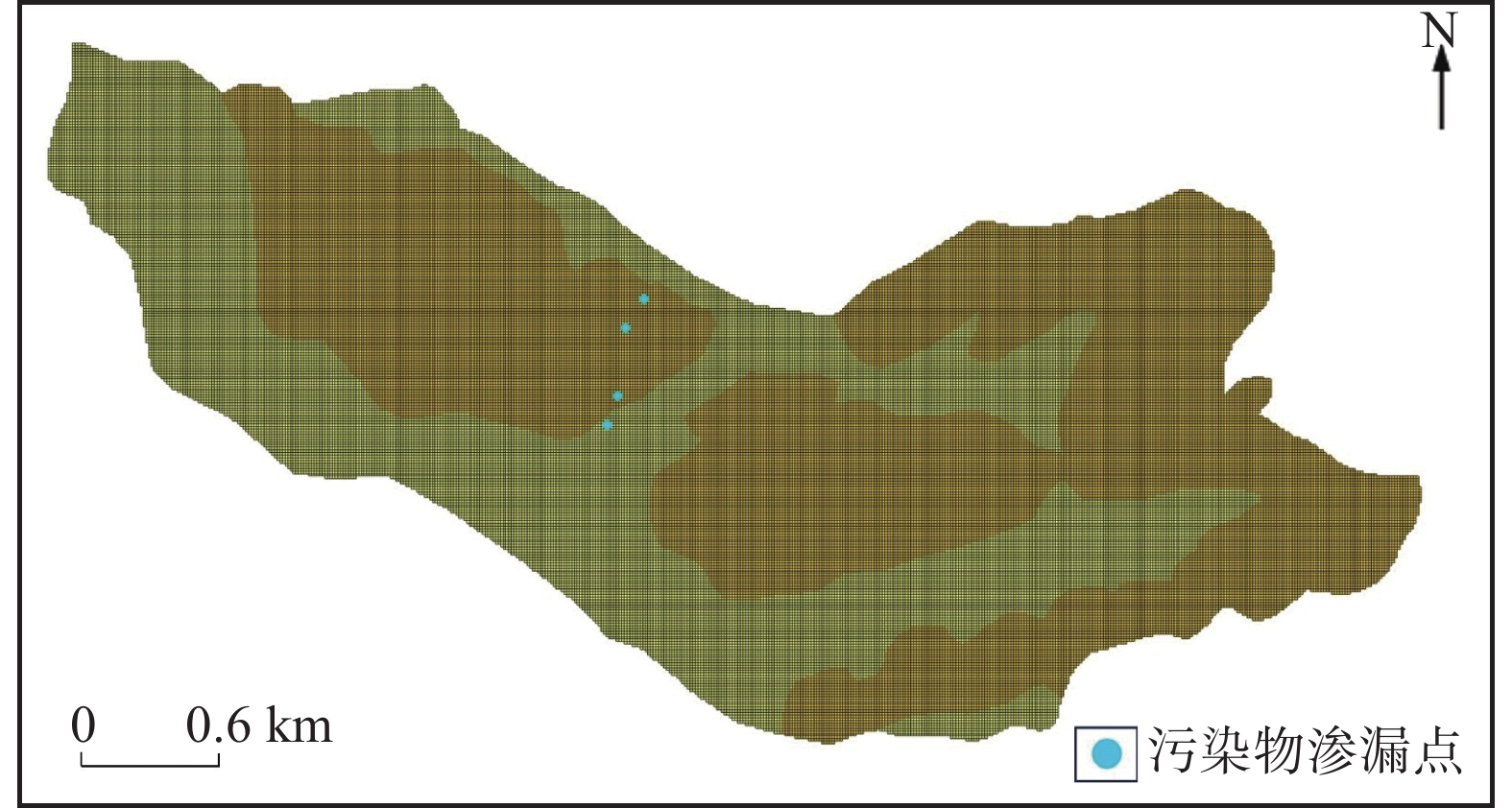
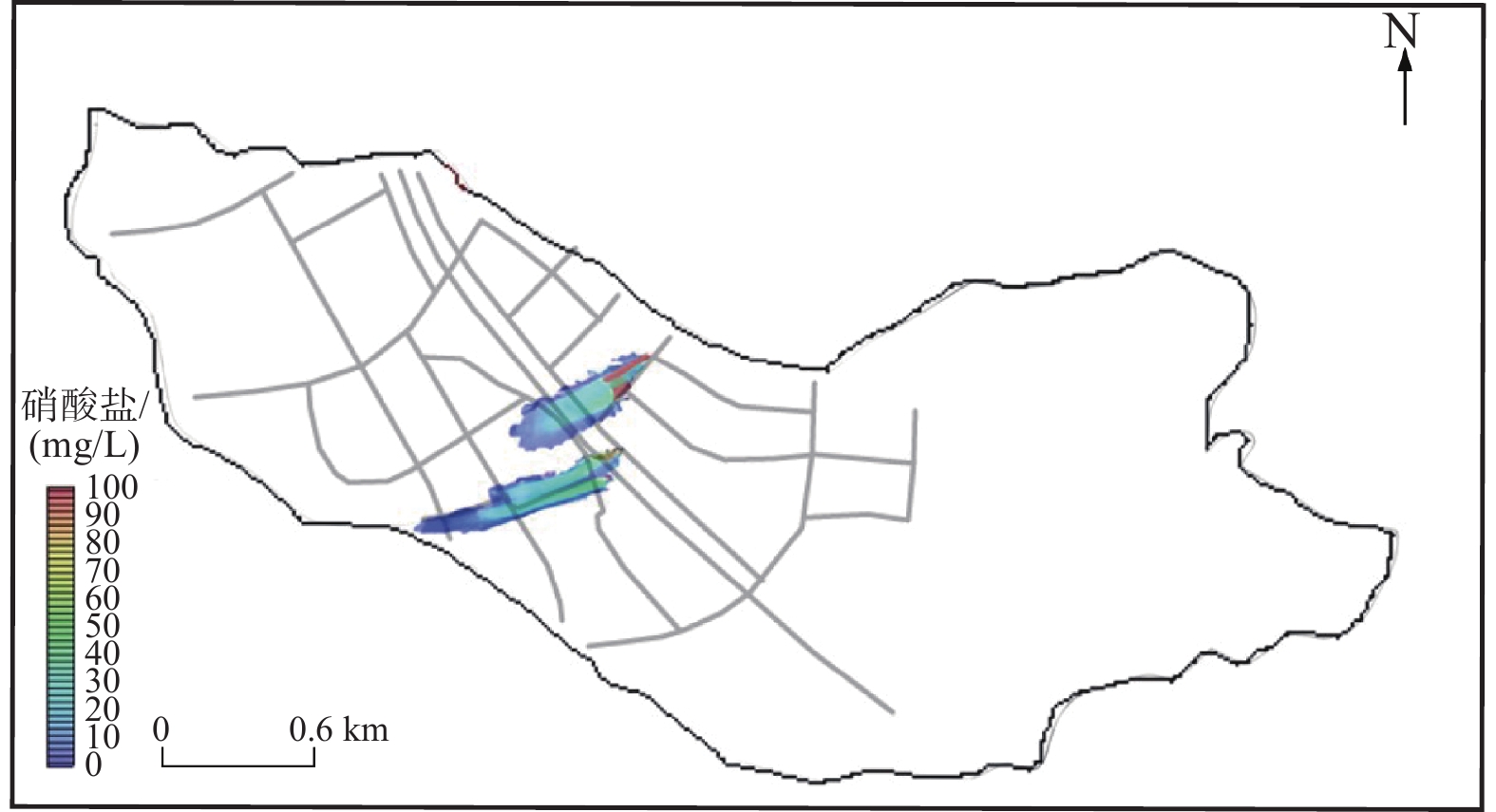
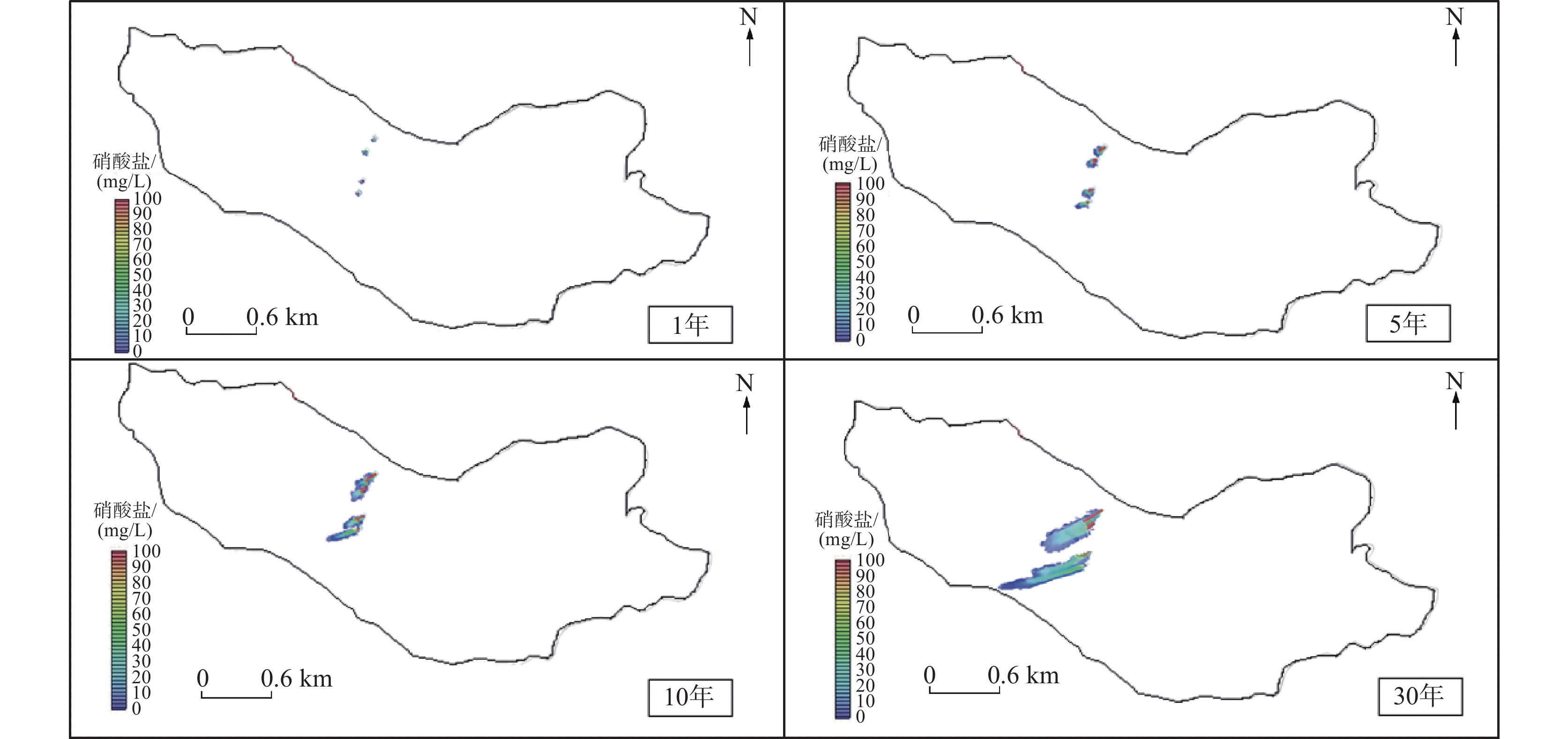
针对现阶段城市地下管网渗漏导致的地下水体污染问题,文章选取深圳市光明区某河间地块作为研究区域,并进行了详细的地下水环境背景调查。基于调查结果,利用数值模拟软件(Groundwater Modeling System,GMS)建立了研究场地的水文地质模型和三维溶质运移数值模型,研究了复杂环境下市政排水设施的渗漏情况及污染物的迁移过程。结果表明:研究区地下水背景水质存在污染风险,主要污染指标包括硝酸盐、氯化物、亚硝酸盐、总大肠菌群和锰离子等,其中,硝酸盐浓度达25 mg/L;管网渗漏区域的污染物迁移方向受地形影响,总体由东北向西南流动,迁移速率约为0.5 m/d。参数的敏感性分析表明:含水层渗透系数越大,地下水流动和污染物迁移扩散的程度越显著,污染羽扩散范围也越大。该研究成果为城市管网渗漏导致的地下水污染的防治提供了科学依据,有助于推动该区域及类似环境中管网渗漏问题的科学解决和管理实践。
Abstract:Regarding the underground water pollution resulting from the leakage of urban underground pipe networks, this study selected a specific interfluve in Guangming District, Shenzhen City as the research area and conducted a detailed background investigation of the groundwater environment. Based on the investigation results, we established a hydrogeological conceptual model and a three-dimensional solute transport numerical model by employing the numerical simulation software (Groundwater Modeling System, GMS) to systematically explore the leakage effects of municipal drainage facilities on migration process of groundwater pollutants. The results demonstrated that there existed a pollution risk of groundwater quality in the study area, which was mainly indicated by nitrate, chloride, nitrite, total coliform bacteria and manganese ions, etc. Among them, the nitrate concentration was as high as 25 mg/L. The migration direction of pollutants in the leakage area of the pipe network was influenced by topographic characteristics and generally flows from the northeast to the southwest, with a migration rate of approximately 0. 5 m/d. Additionally, the sensitivity analysis of aquifer parameters indicated that the larger the permeability coefficient of the sediment, the more prominent the degree of groundwater flow and pollutant migration and diffusion, and the broader the diffusion range of the pollution plume. The research findings offer a scientific basis for the prevention and control of groundwater pollution caused by urban pipe network leakage and contribute to facilitating the scientific solution and management practice of pipe network leakage issues in this area and similar environments.
-

-
表 1 三维模型不同地层参数赋值情况
Table 1. The assignment of parameters for different strata in the three-dimensional model
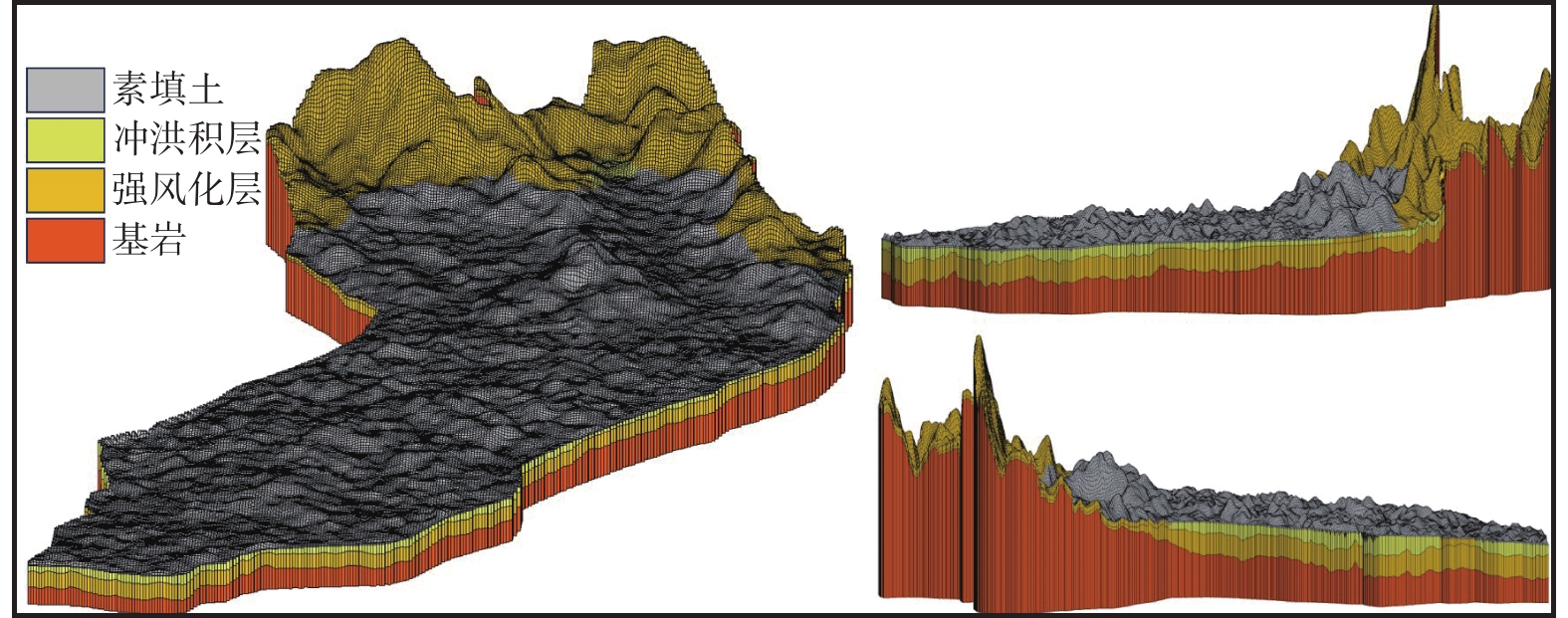
地层 水平渗透系数/(m·d−1) 水平各向异性 垂向各向异性 给水度 释水系数 纵向弥散系数 孔隙度 素填土 8.64 1 1 0.00001 0.19 0.5 0.19 冲洪积层 6.912 1 3 0.00001 0.17 0.5 0.17 强风化层 4.32 1 1 0.00001 0.2 0.5 0.2 基岩 0.00464 1 1 0.00001 0.001 0.5 0.001 -
[1] AMEUR M, AOUITI S, HAMZAOUI-AZAZA F, BEN CHEIKHA L, GUEDDARI M. 2021. Vulnerability assessment, transport modeling and simulation of nitrate in groundwater using SI method and modflow-MT3DMS software: case of Sminja aquifer, Tunisia[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,80(6):220. doi: 10.1007/s12665-021-09491-z
[2] BAO X H, YU H B, JI L. 2022. Division of two-level protection area of Changchun Qijia groundwater source based on GMS[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),52(3):955-966 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[3] DU J Y, YANG H X, SHEN Z C, GUO X D. 2018. Development of an inline vertical cross-flow turbine for hydropower harvesting in urban water supply pipes[J]. Renewable Energy,127:386-397. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2018.04.070
[4] DUAN Y, LI D C, ZHOU S K. 2023. Application of GMS in study of thallium pollutant transport in groundwater of a typical chemical industry park[J]. Journal of University of South China (Science and Technology),37(4):9-17 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[5] GAO Y X, SHEN H, ZHANG Y M, WANG L M, PENG F Q, XU X T. 2018. Groundwater pollution risk prediction research and effect evaluation of golf course based on FEFLOW[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering,49(11):144-150 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[6] GUAN J J, ZHENG Y J, CAO X H. 2024. The problems faced by groundwater resources in China and countermeasures suggestion[J]. East China Geology, 45(3): 255-263 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[7] JIANG H N. 2022. Research and application of well chamber leakage treatment measures for underground water supply and drainage network[J]. Hongshui River,41(5):117-120 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[8] JIANG Z F, LIU Y W, CUI B F, WU L. 2022. Simulation study on risk characteristics of regional groundwater pollutant transport[J]. Computer Simulation,39(10):289-293 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[9] KUANG Y P. 2023. Leakage analysis and leakage detection technology of water supply pipeline network[J]. Water Technology,17(1):11-14 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[10] LI J, ZHENG W J, LU C G. 2022. An accurate leakage localization method for water supply network based on deep learning network[J]. Water Resources Management,36(7):2309-2325. doi: 10.1007/s11269-022-03144-x
[11] LIU X S, LIAO Z L. 2021. Research progress on leakage detection and location technologies of urban water supply networks[J]. Energy Environmental Protection,35(5):16-22 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] LIU J G, XU G Z, MA X J, LEI J M, WU H. 2018. Study on comparative application of different simulation software in groundwater environmental impact[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,41(S1):359-362 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[13] MEI S J, JIANG Y H, YANG H, ZHOU Q P, CHEN Z, JIA Z Y, JIN Y, ZHANG H, ZHANG B. 2024.Deformation and seepage characteristics of the bank collapse site based on WFBG technology—a case study of Zhinan Village, Yangzhong[J]. East China Geology, 45(2): 228-239 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[14] NASIRIAN A, MAGHREBI M F, YAZDANI S. 2013. Leakage detection in water distribution network based on a new heuristic genetic algorithm model[J]. Journal of Water Resource and Protection,5(3):294-303. doi: 10.4236/jwarp.2013.53030
[15] PECHE A, GRAF T, FUCHS L, NEUWEILER I. 2019. Physically based modeling of stormwater pipe leakage in an urban catchment[J]. Journal of Hydrology,573:778-793. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.03.016
[16] PENG C L, CHEN Z, DOU Z, SHI J H, JI S S. 2019. Simulation of groundwater pollution from solid waste dump in a karst region[J]. Coal Geology of China,31(9):80-86 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[17] PUDAR R S, LIGGETT J A. 1992. Leaks in pipe networks[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,118(7):1031-1046. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1992)118:7(1031)
[18] QIU Y L. 2006. The research and application water distribution pipeline leakage prediction[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University (in Chinese with English abstract).
[19] QU S, LV J J, LIU J X. 2020. Visualization analysis for global water resources based on digital earth[J]. Journal of Coastal Research,105(SI):47-50.
[20] RAO L, WEI X P, LIU X. 2018. Numerical simulation of groundwater pollutants transport in an industrial park of Chongqing based on visual modflow[J]. Journal of Chongqing Normal University (Natural Science),35(5):72-78 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[21] SONG L Z. 2022. Research on digital simulation of leakage prediction of urban sewage pipe network[J]. Journal of Chengdu Technological University,25(4):36-41 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] SONG J M, HUANG Y. 2023. Simulation of the transport of sewage pollutants on a domestic waste landfill site[J]. Journal of Gansu Sciences,35(1):74-79 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[23] TAN W Q, SUN Q, HU J M, MA L, ZHAO Y N. 2008. Application of GMS in simulation of pollutants migration for groundwater[J]. Water Resources & Hydropower of Northeast,26(5):54-55,59 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[24] WANG P Y. 2013. Study on leakage analyses and control solutions of urban water distribution network[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University of Technology (in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] WANG P, QIU Y L, XIA Q Q, SHEN B. 2006. Combined model applied in water distribution pipeline leakage prediction[J]. China Water & Wastewater,22(17):67-69 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[26] XIE X. 2018. Study on key technologies of hydraulic model driven online leak monitoring in urban water distribution networks[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University (in Chinese with English abstract).
[27] YU B. 2012. Leakage control of urban water supply pipe network[J]. Urban Construction Theory Research (Electronic Edition), (35): 1-6 (in Chinese).
[28] ZHANG Q Z. 2013. Research on leakage detection via hydraulic model calibration in water distribution systems[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology (in Chinese with English abstract).
[29] ZHOU J, SONG B, YU L, XIE W Y, LU X H, JIANG D D, KONG L Y, DENG S P, SONG M. 2023. Numerical research on migration law of typical chlorinated organic matter in shallow groundwater of Yangtze delta region[J]. Water,15(7):1381. doi: 10.3390/w15071381
[30] ZHU C F, GONG J S, TAO X H, TAN M J, ZHOU K E, WANG H S, LI L, YE Y H.2023.Comparison of the hydrochemical characteristics of shallow groundwater in the Huaihe River Basin during a ten-year period and its significance to environmental change[J]. East China Geology, 44(3): 282-291 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[31] ZOU X, ZHANG H F, LI Y P. 2020. Analysis of the environmental impact of groundwater in Huangchuan economic development zone based on visual MODFLOW[J]. Journal of North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power (Natural Science Edition),41(6):89-96 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[32] 鲍新华, 于瀚博, 计量. 2022. 基于GMS的长春齐家地下水水源地二级保护区划分[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),52(3):955-966.
[33] 段毅, 李东春, 周书葵. 2023. GMS在某典型化工工业园区地下水铊污染物运移研究中的应用[J]. 南华大学学报(自然科学版),37(4):9-17.
[34] 高月香, 沈欢, 张毅敏, 汪龙眠, 彭福全, 许雪婷. 2018. 基于FEFLOW的高尔夫球场地下水污染风险预测研究与效果评估[J]. 水利水电技术,49(11):144-150.
[35] 官娇娇,郑跃军,曹祥会. 2024.我国地下水资源面临的问题及对策思考[J]. 华东地质,45(3):255-263.
[36] 蒋昊楠. 2022. 给排水地下管网井室渗漏处理措施的研究及应用[J]. 红水河,41(5):117-120.
[37] 姜忠峰, 刘艳伟, 崔弼峰, 吴丽. 2022. 区域地下水污染物运移风险特征仿真研究[J]. 计算机仿真,39(10):289-293.
[38] 匡亚平. 2023. 供水管网渗漏分析与漏失检测技术[J]. 供水技术,17(1):11-14.
[39] 刘小帅, 廖振良. 2021. 城镇供水管网漏损检测及定位技术研究进展[J]. 能源环境保护,35(5):16-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8759.2021.05.003
[40] 刘建国, 许光照, 马学礼, 雷佳明, 伍欢. 2018. 不同模拟软件在地下水环评中的应用对比研究[J]. 环境科学与技术,41(S1):359-362.
[41] 梅世嘉, 姜月华, 杨海, 周权平, 陈孜, 贾正阳, 金阳, 张鸿, 张博. 2024.基于WFBG技术的崩岸场地变形和渗流特征研究——以扬中指南村为例[J].华东地质, 45(2): 228-239.
[42] 彭传路, 陈舟, 窦智, 施佳会, 计顺顺. 2019. 某岩溶区固废渣场地下水污染模拟[J]. 中国煤炭地质,31(9):80-86.
[43] 邱云龙. 2006. 给水管网漏损预测的研究与应用[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学.
[44] 饶磊, 魏兴萍, 刘迅. 2018. 基于Visual Modflow的重庆某工业园区地下水污染物运移模拟[J]. 重庆师范大学学报(自然科学版),35(5):72-78.
[45] 宋雷震. 2022. 针对城市污水管网渗漏预测的数字模拟研究[J]. 成都工业学院学报,25(4):36-41.
[46] 宋旌鸣, 黄勇. 2023. 某生活垃圾填埋场地下水污染物运移模拟[J]. 甘肃科学学报,35(1):74-79.
[47] 谭文清, 孙春, 胡婧敏, 马力, 赵彦宁. 2008. GMS在地下水污染质运移数值模拟预测中的应用[J]. 东北水利水电,26(5):54-55,59.
[48] 王培永. 2013. 城市给水管网漏损分析及控制措施的研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江工业大学.
[49] 王圃, 邱云龙, 夏清泉, 沈波. 2006. 组合模型在给水管网漏损预测中的应用[J]. 中国给水排水,22(17):67-69.
[50] 谢翔. 2018. 水力模型驱动的城市供水管网漏损在线监测关键技术研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学.
[51] 于斌. 2012. 城市供水管网漏损控制[J]. 城市建设理论研究(电子版), (35): 1-6.
[52] 张清周. 2013. 基于模型校核的给水管网漏失定位研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学.
[53] 朱春芳, 龚建师, 陶小虎, 檀梦皎, 周锴锷, 王赫生, 李亮, 叶永红. 2023.淮河流域浅层地下水水化学特征10年对比分析及其环境变迁意义[J]. 华东地质, 44(3): 282-291.
[54] 邹浔, 张海丰, 李跃鹏. 2020. 基于Visual MODFLOW的潢川经济开发区地下水环境影响分析[J]. 华北水利水电大学学报(自然科学版),41(6):89-96.
-




 下载:
下载: