Fault characteristics and evolution of Diaobei sag in the East China Sea shelf basin
-
摘要:
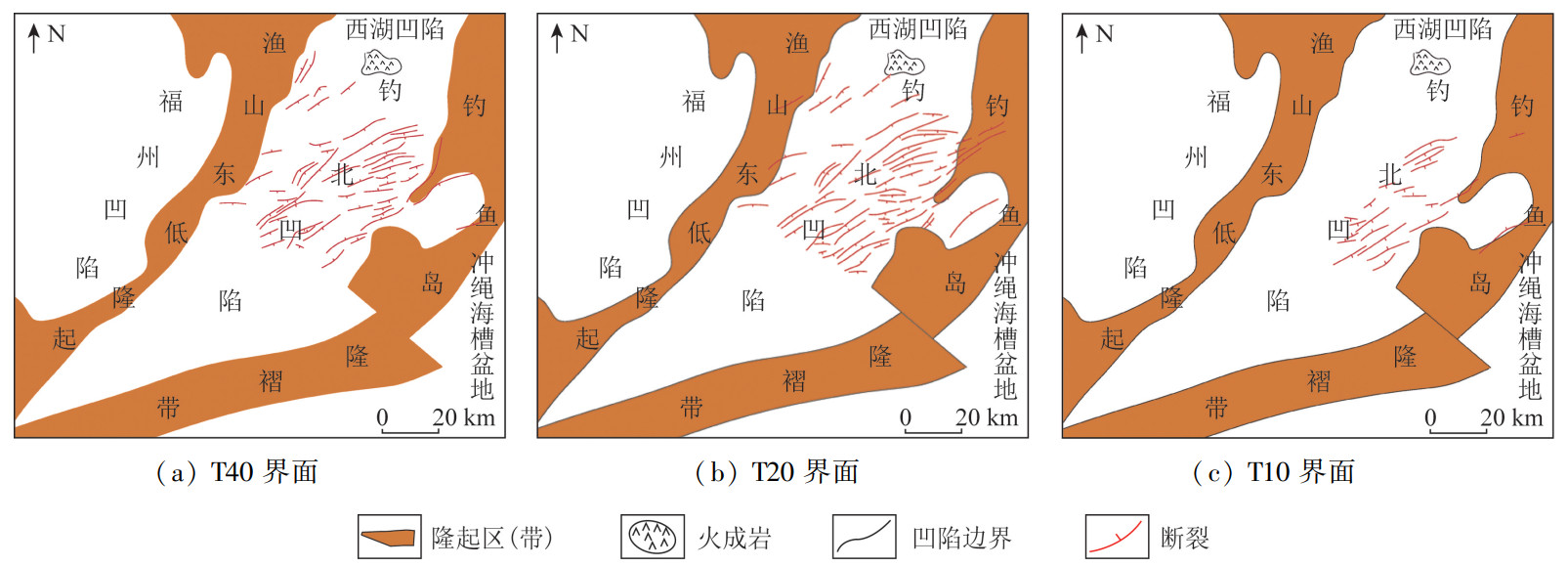
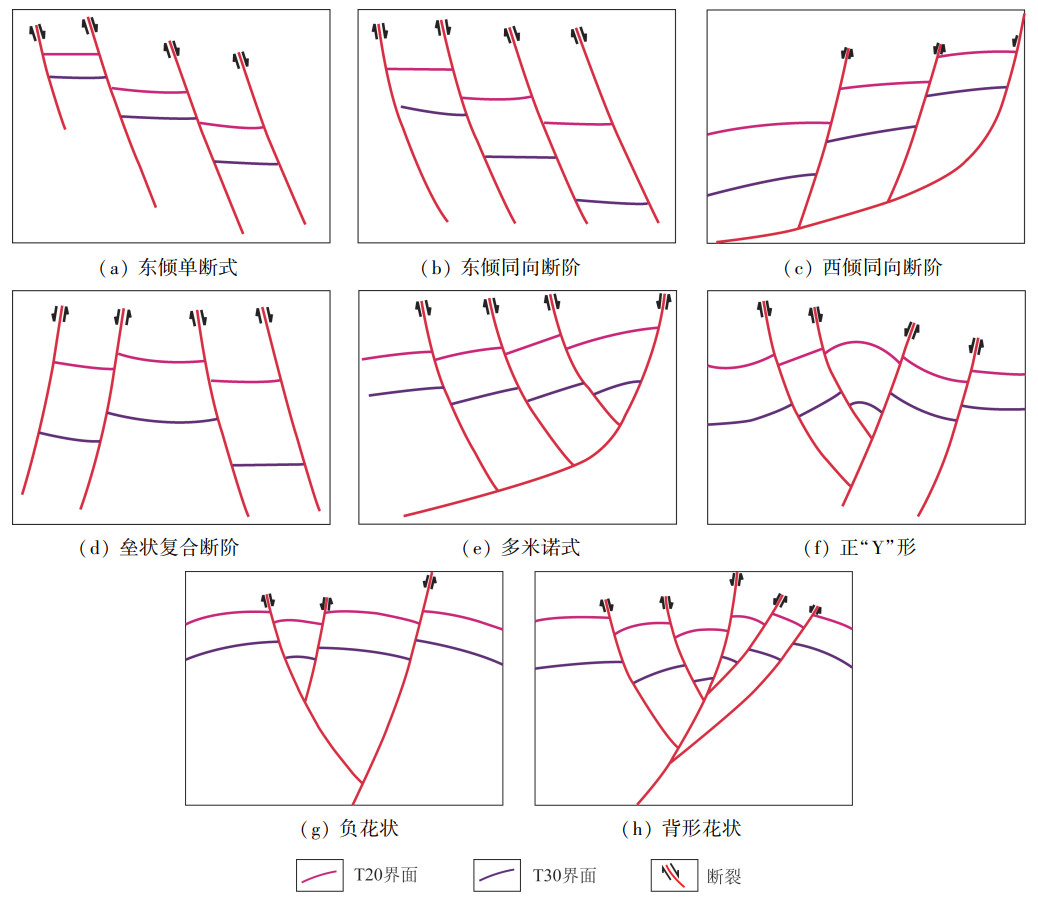
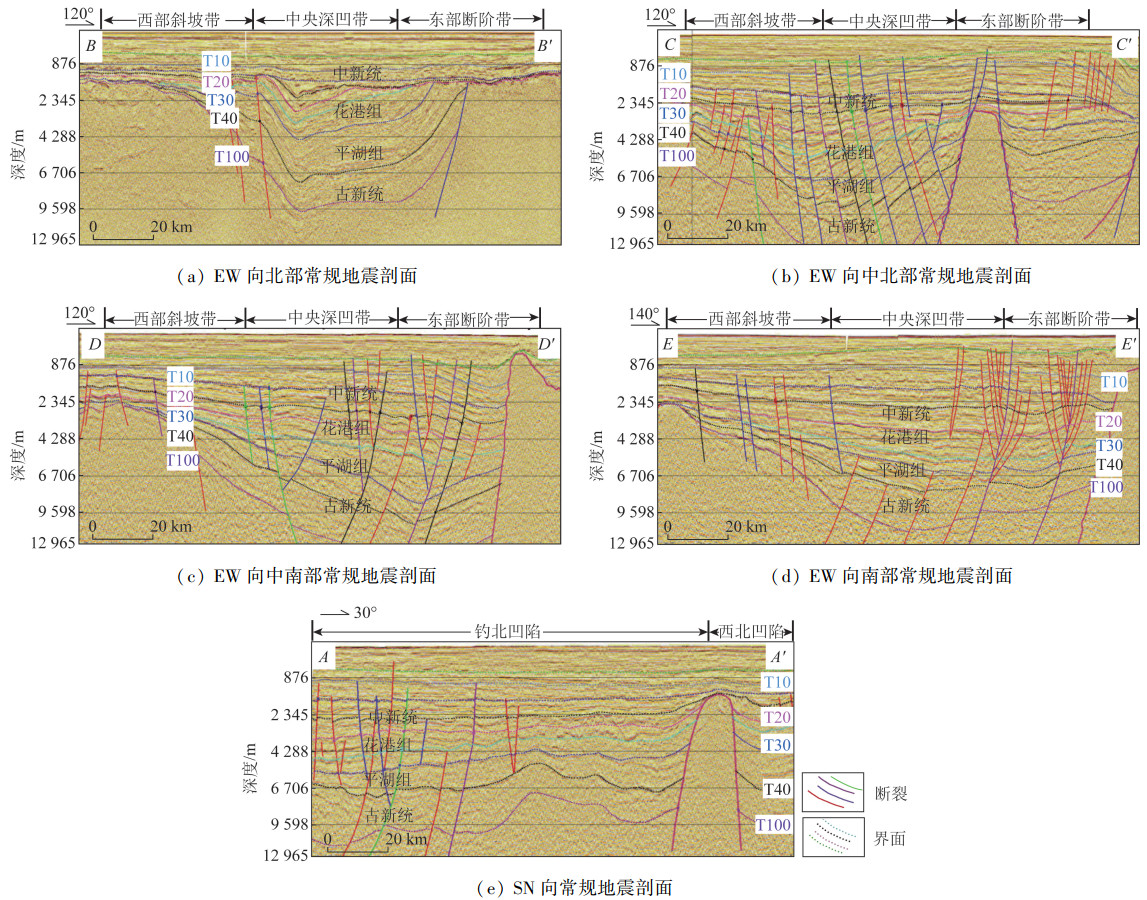
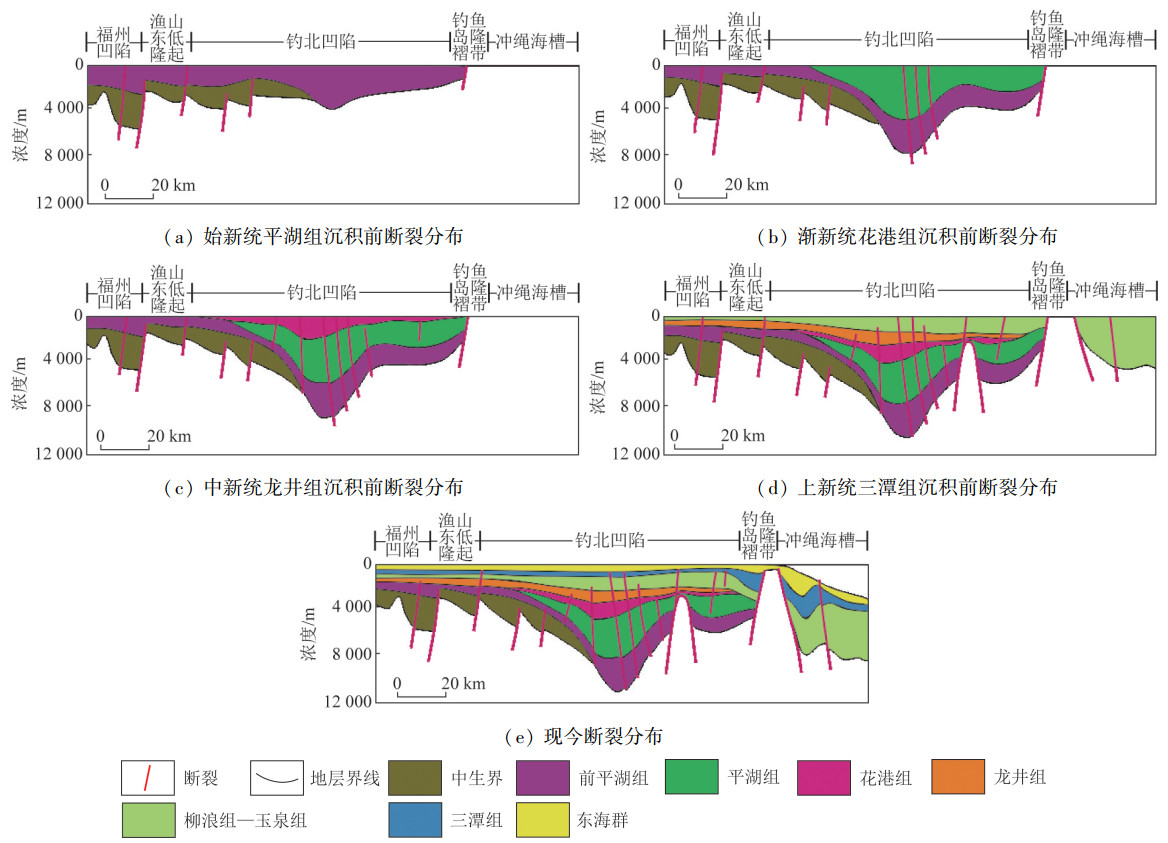
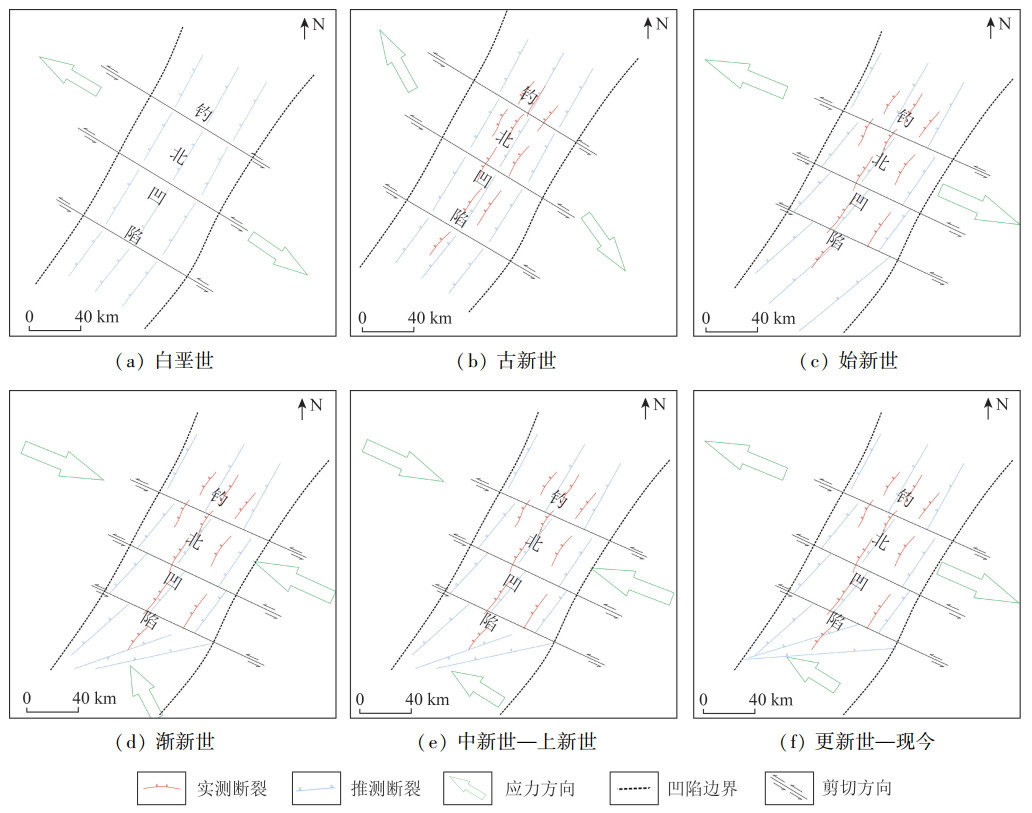
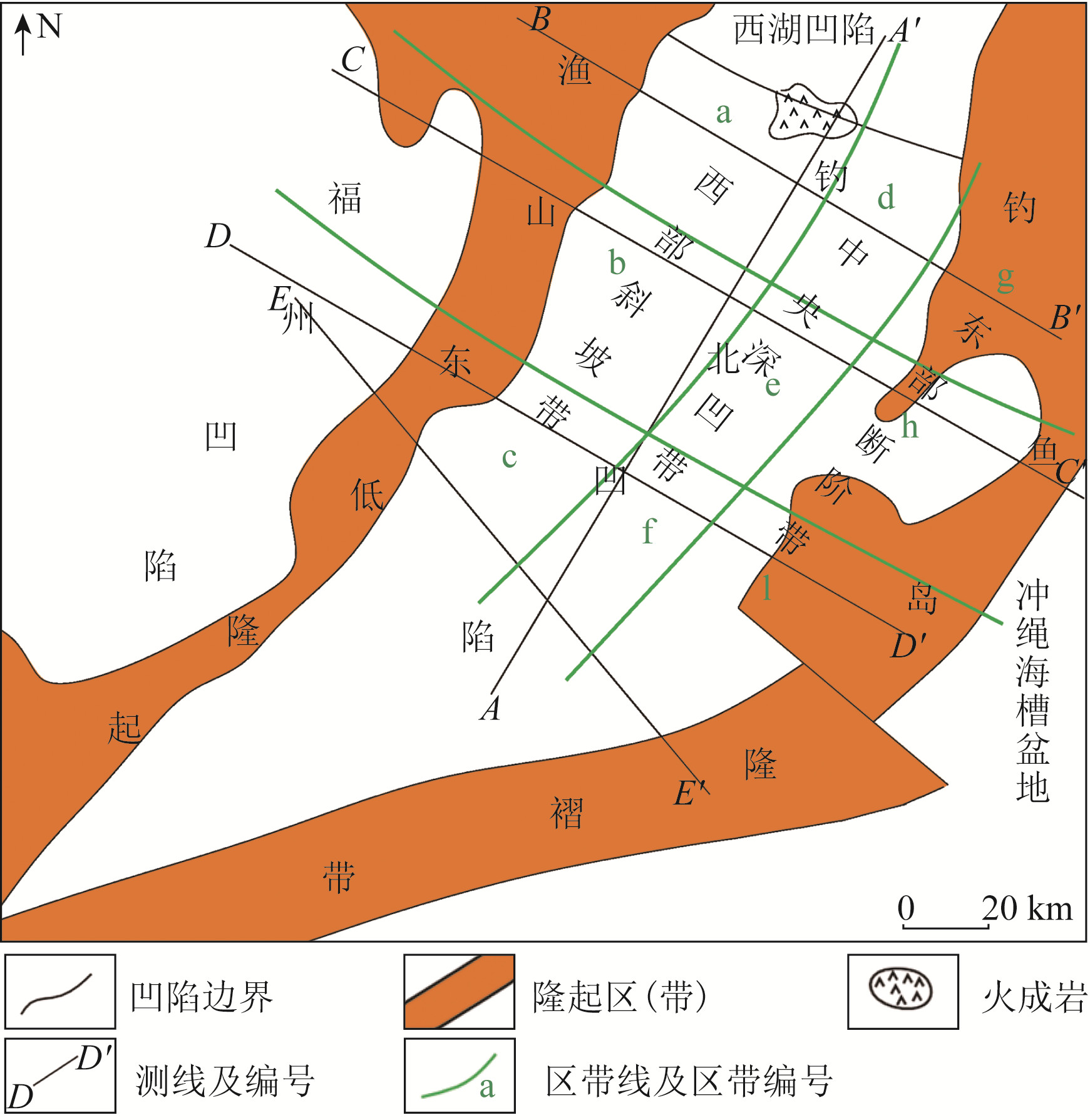
东海陆架盆地钓北凹陷断裂系统复杂,断裂组合样式多样,但针对整个凹陷断裂系统及其演化方面的研究较少。基于二维地震资料解释成果,系统研究该区域断裂的展布和演化特征,探讨钓北凹陷的断裂演化模式。研究结果表明: 以渐新统花港组底界和上新统三潭组底界为界,可以在垂向上将断裂系统分为下部张性、中部压性和上部张剪性3套断裂系统; 下部张性断裂主要有单断式、同向断阶、垒状复合断阶等断裂组合样式,主要形成于钓北凹陷的断陷期和断拗期,断裂控制了沉积地层的发育; 中部压性断裂主要有正“Y”形、反“Y”形、负花状等断裂组合样式,主要形成于凹陷的断拗期和拗陷反转期,地层具有明显的上拱形态特征; 上部张剪性断裂主要为层间断裂,平面上呈带状或雁列状展布,形成于区域沉降期,对地层的控制作用较微弱。依据钓北凹陷断裂样式和特征,将钓北凹陷分为西部斜坡带、中央深凹带和东部断阶带。从断裂演化期次来看,断裂系统可划分为断陷-断拗期断裂系统、断拗-拗陷反转期断裂系统和区域沉降期断裂系统。研究对钓北凹陷的石油勘探开发及地质研究具有一定的指导意义。
Abstract:Diaobei sag in the East China Sea shelf basin is characterized by a complex fault systems and multiple fault configurations, and there is little research on the whole fault system and its evolution. The distribution and evolution characteristics of faults in this area were systematically studied based on 2D seismic data, and the fault evolution model in Diaobei sag was discussed in this paper. The results show that the fault system can be grouped vertically into three fault systems, that is the lower(extensional), the middle(compressional), and the upper(extensional shear)fault systems, with the bottom of Oligocene Huagang Formation and the bottom of Upper Miocene Santana Formation as the boundaries. The fault configuration of the lower extensional fault system mainly include single fault type, same-directim stepover, composite horst stepover and other fault combination, which mainly formed in the rifting and say stage of the depression, and the faults controlled the development of sedimentary strata. The fault configurations of the middle compressional fault system are mainly Y-shaped, anti-Y-shaped and negative flower-shaped, and they mainly formed in the say and subsidence inversion stage of the sag. The strata have obvious characteristics of upper arch. The fault configurations of upper extensional fault system are mainly interlayer faults, with the banded and echelon distribution on plane. The fault formed in the subsidence stage of the sag, and its control of the formation is weak. Diaobei sag can be divided into western slope zone, central deep depression zone and eastern fault terrace zone according to fault styles and characteristics. From the perspective of fault evolution stages, the fault systems of Diaobei sag can be diveded into fault depression-say system, fault say-subsidence inversion system, and the regional subsidence system. This research could provide references for the petroleum exploration, exploitation and geology research.
-
Key words:
- Diaobei sag /
- fault system /
- fault evolution model /
- formation mechanism
-

-
表 1 钓北凹陷主要地层单元
Table 1. Main stratigraphic units in Diaobei sag
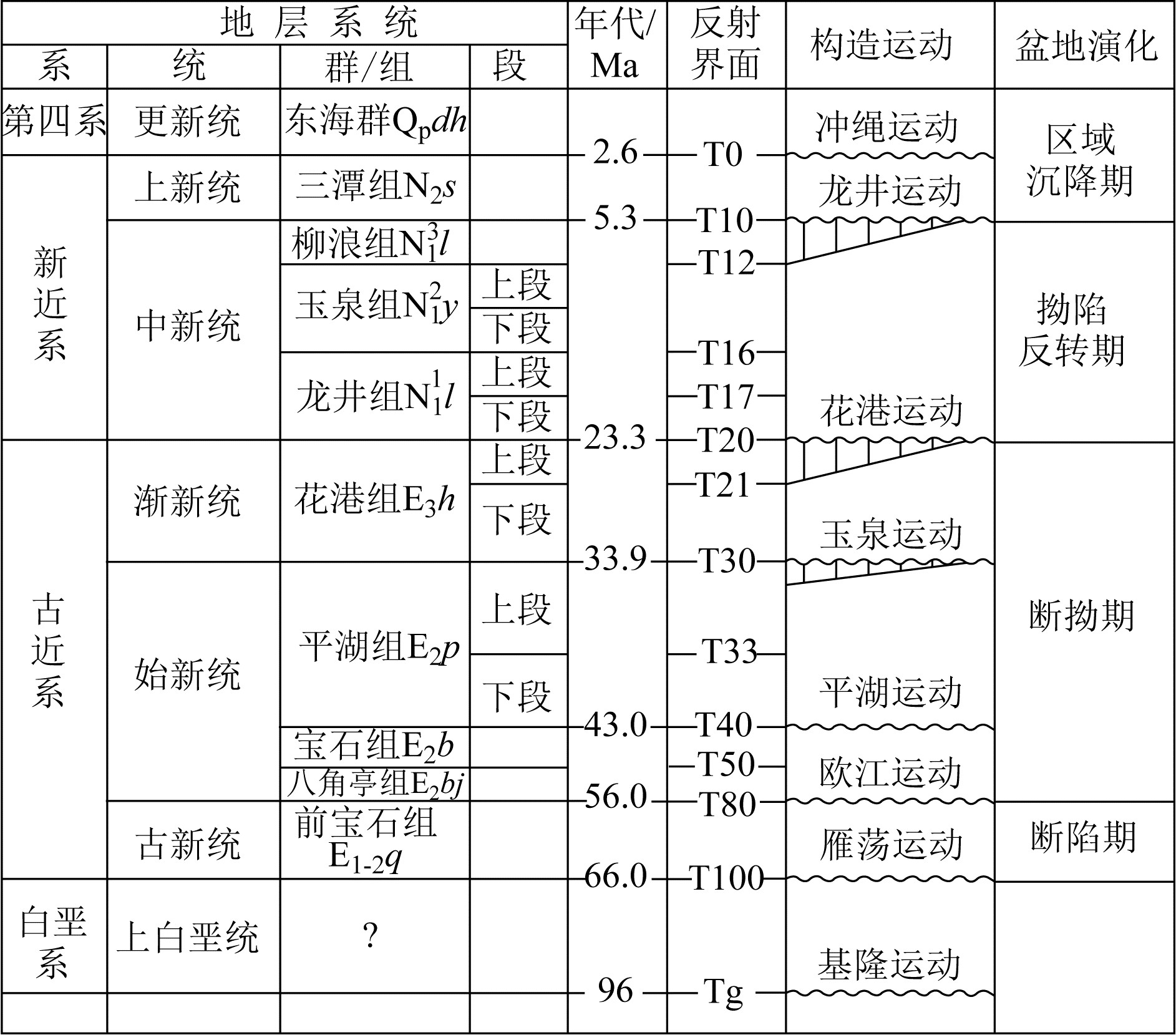
表 2 钓北凹陷各级次断裂要素
Table 2. Fault elements of each level in Diaobei sag
断裂级别 断开层位 延伸长度/km 垂直断距/m 一级控凹 T16~Tg 10~100 10~400 二级控带 T16~T40 10~50 10~200 三级复杂 T10~T20 10~30 10~120 -
[1] 王宁, 明承栋, 杨晨艺, 等. 白云凹陷东部深水区混源油定量解析[J]. 山东科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2022, 41(6): 24-31.
Wang N, Ming C D, Yang C Y, et al. Quantitative study on mixed source oil in deep water area of eastern Baiyun sag[J]. Journal of Shandong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science), 2022, 41(6): 24-31.
[2] 张敏强, 钟志洪, 夏斌, 等. 东海西湖凹陷中南部晚中新世构造反转与油气运聚[J]. 中国海上油气, 2005, 17(2): 73-79.
Zhang M Q, Zhong Z H, Xia B, et al. Late Miocene tectonic inversion and hydrocarbon migration and accumulation in central and southern Xihu sag, East China Sea[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2005, 17(2): 73-79.
[3] 张建培, 张涛, 刘景彦, 等. 西湖凹陷反转构造分布与样式[J]. 海洋石油, 2008, 28(4): 14-20.
Zhang J P, Zhang T, Liu J Y, et al. Distribution and style of inversed structures in Xihu Depression[J]. Offshore Oil, 2008, 28(4): 14-20.
[4] 张绍亮, 张建培, 唐贤君, 等. 东海西湖凹陷断裂系统几何学特征及其成因机制[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2014, 34(1): 87-94.
Zhang S L, Zhang J P, Tang X J, et al. Geometry characteristic of the fault system in Xihu Sag in East China Sea and its formation mechanism[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2014, 34(1): 87-94.
[5] 姜雄鹰, 傅志飞. 东海陆架盆地基隆凹陷构造演化特征及勘探前景[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2010, 24(2): 21-24.
Jiang X Y, Fu Z F. Tectonic evolution features and exploration prospect of Jilong sag, the East China sea shelf basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2010, 24(2): 21-24.
[6] 刘金水, 许怀智, 蒋一鸣, 等. 东海盆地中、新生代盆架结构与构造演化[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(3): 675-691.
Liu J S, Xu H Z, Jiang Y M, et al. Mesozoic and Cenozoic basin structure and tectonic evolution in the East China Sea basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(3): 675-691.
[7] 郭令智, 施央申, 马瑞士. 西太平洋中、新生代活动大陆边缘和岛弧构造的形成及演化[J]. 地质学报, 1983, 57(1): 11-21.
Guo L Z, Shi Y S, Ma R S. On the formation and evolution of the Mesozoic-Cenozoic active continental margin and island arc tectonics of the Western Pacific Ocean[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1983, 57(1): 11-21.
[8] 闫桂京, 肖国林, 陈建文, 等. 基隆凹陷油气资源潜力[J]. 海洋地质动态, 2003, 19(8): 24-26.
Yan G J, Xiao G L, Chen J W, et al. Potentials of petroleum resources in Jilong depression[J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2003, 19(8): 24-26.
[9] 赵金海. 东海中、新生代盆地成因机制和演化(上)[J]. 海洋石油, 2004, 24(4): 6-14.
Zhao J H. The forming factors and evolvement of the Mesozoic and Cenozoic basin in the East China Sea[J]. Offshore Oil, 2004, 24(4): 6-14.
[10] 赵金海. 东海中、新生代盆地成因机制和演化(下)[J]. 海洋石油, 2005, 25(1): 1-10.
Zhao J H. The forming factors and evolvement of the Mesozoic and Cenozoic basin in the East China Sea[J], Offshore Oil, 2005, 25(1): 1-10.
[11] 李培廉, 朱平. 试论东海陆架盆地的基底构造演化和盆地形成机制[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1992, 12(3): 37-43.
Li P L, Zhu P. Basement tectonic evolution and basin formation mechanism of the East China Sea shelf basin[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1992, 12(3): 37-43.
[12] 蔡华, 张建培, 唐贤君. 西湖凹陷断裂系统特征及其控藏机制[J]. 天然气工业, 2014, 34(10): 1-9.
Cai H, Zhang J P, Tang X J. Characteristics of the fault systems and their control on hydrocarbon accumulation in the Xihu Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(10): 1-9.
[13] 张国华, 张建培. 东海陆架盆地构造反转特征及成因机制探讨[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(1): 260-270.
Zhang G H, Zhang J P. A discussion on the tectonic inversion and its genetic mechanism in the East China Sea shelf basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2015, 22(1): 260-270.
[14] 索艳慧, 李三忠, 戴黎明, 等. 东亚及其大陆边缘新生代构造迁移与盆地演化[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(8): 2602-2618.
Suo Y H, Li S Z, Dai L M, et al. Cenozoic tectonic migration and basin evolution in East Asia and its continental margins[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(8): 2602-2618.
[15] 唐杰, 许文良, 王枫, 等. 古太平洋板块在欧亚大陆下的俯冲历史: 东北亚陆缘中生代—古近纪岩浆记录[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2018, 48(5): 549-583.
Tang J, Xu W L, Wang F, et al. Subduction history of the Paleo-Pacific slab beneath Eurasian continent: Mesozoic-Paleogene magmatic records in Northeast Asia[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2018, 61(5): 527-559.
[16] 王国纯. 东海盆地构造区划及其特征[J]. 台湾海峡, 1992, 11(3): 218-226.
Wang G C. Tectonic districts and its characteristics in East China Sea Basin[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 1992, 11(3): 218-226.
[17] 孙晶, 杨长清, 王建强, 等. 基隆凹陷构造演化特征及油气资源潜力[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2017, 33(4): 38-42.
Sun J, Yang C Q, Wang J Q, et al. Tectonic evolution of the Jilong Sag and its petroleum potential[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2017, 33(4): 38-42.
[18] 何将启, 梁世友, 陈拥锋, 等. 东海盆地西湖凹陷新生代构造演化对油气的控制作用——以平湖组油气响应为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2008, 30(3): 221-226.
He J Q, Liang S Y, Chen Y F, et al. Control on petroleum by Cenozoic tectonic evolution in the Xihu sag, the East China Sea Basin: Taking petroleum response of the Pinghu formation as an example[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2008, 30(3): 221-226.
[19] 李祖武. 中国东部北西向构造[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 1992.
Li Z W. The Westnorthern Structural of Eastern China[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press, 1992.
[20] 万天丰. 中国大地构造学纲要[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2004.
Wan T F. The Geotectonic Outline of China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2004.
[21] 许浚远, 张凌云. 西北太平洋边缘新生代盆地成因(上): 成盆机制述评[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2000, 21(2): 93-98.
Xu J Y, Zhang L Y. Genesis of Cenozoic Basins in northwest pacific ocean margin (1): Comments on basin-forming mechanism[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2000, 21(2): 93-98.
[22] 杨长清, 杨传胜, 李刚, 等. 东海陆架盆地南部中生代构造演化与原型盆地性质[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(3): 105-111.
Yang C Q, Yang C S, Li G, et al. Mesozoic tectonic evolution and prototype basin characters in the southern East China Sea shelf basin[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(3): 105-111.
[23] 赵志刚, 王鹏, 祁鹏, 等. 东海盆地形成的区域地质背景与构造演化特征[J]. 地球科学, 2016, 41(3): 546-554.
Zhao Z G, Wang P, Qi P, et al. Regional background and tectonic evolution of East China Sea Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2016, 41(3): 546-554.
[24] 钟锴, 朱伟林, 高顺莉, 等. 东海陆架盆地形成演化及油气成藏关键地质问题[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(10): 3485-3497.
Zhong K, Zhu W L, Gao S L, et al. Key geological questions of the formation and evolution and hydrocarbon accumulation of the East China Sea shelf basin[J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(10): 3485-3497.
[25] 刘金水, 廖宗廷, 贾健谊, 等. 东海陆架盆地地质结构及构造演化[J]. 上海地质, 2003(3): 1-6.
Liu J S, Liao Z T, Jia J Y, et al. The geological structure and tectonic evolution of the East China Sea shelf basin[J]. Shanghai Geology, 2003(3): 1-6.
[26] 祝建军, 王琪, 梁建设, 等. 东海陆架盆地南部新生代地质结构与构造演化特征研究[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2012, 23(2): 222-229.
Zhu J J, Wang Q, Liang J S, et al. Cenozoic geological structure and tectonic evolution of southern East China Sea shelf basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2012, 23(2): 222-229.
[27] Sibuet J C, Hsu S K. How was Taiwan created?[J]. Tectonophysics, 2004, 379(1/2/3/4): 159-181.
-



 下载:
下载: