Cause and prevention model of typical river-blocking debris flow disaster: A case study of Qingjia gully debris flow in Pingwu County
-
摘要:
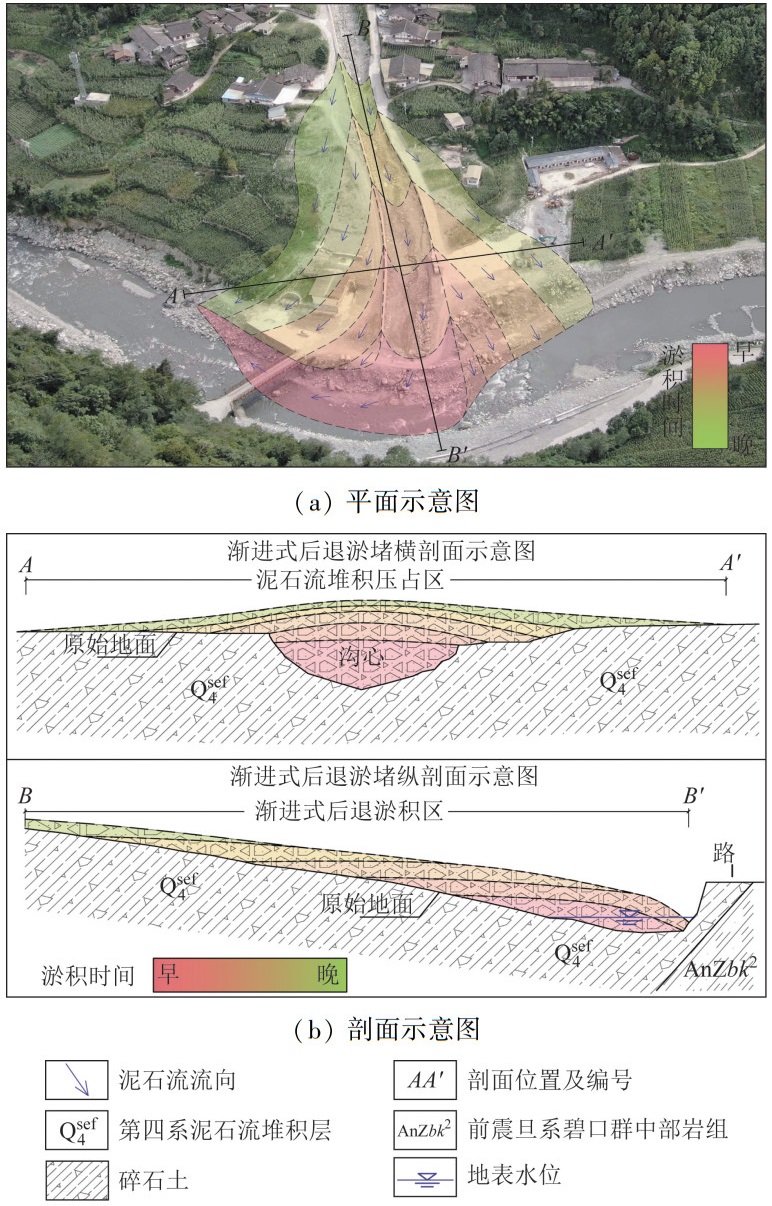
为探寻典型堵河型泥石流致灾和防治模式,以涪江流域中上游典型堵河型泥石流卿家沟为例,通过调查走访、实地测量、综合论证等方法,总结出了典型堵河型泥石流4种主要致灾模式: 主河上游淹没及次生灾害、主河下游洪水及次生灾害、主河异岸冲蚀和淹没、泥石流沟口渐进式后退淤堵。基于该型泥石流的基本特征和致灾机理,提出了两种防治模式: 一是中上游拦砂固源,沟口原沟排导模式; 二是堆积区沟道改移防治模式。结果表明,两种模式在防灾技术层面上均具有较高的可行性。研究可为堵河型泥石流灾害的防治提供新的视角和方法,对类似特征泥石流灾害防治具有借鉴意义。
Abstract:In order to explore the cause and prevention model of typical river-blocking debris flow disaster, the authors took Qingjia gully debris flow, a typical river-blocking debris flow in the middle and upper reaches of Fu river basin as a study case, and adopted the investigation, field measurement, and comprehensive analysis methods. Four main disaster-causing modes of typical river-blocking debris flow were summarized, including upstream inundation and secondary disaster, downstream flooding and secondary disaster, cross-shore erosion and inundation of the main river, and progressive retreat and siltation in the debris flow channel mouth. Two prevention and control models were proposed based on the fundamental characteristics and disaster-causing mechanisms of this type of debris flow. The first model is sediment interception and source stabilization in the middle and upper reaches, and original channel diversion at the mouth of the gully. The second model is deposition area channel relocation and control. The results show that both models have high feasibility at the technical level of disaster prevention. This study could offer new perspectives and methods for the prevention and control of river-blocking debris flow disasters, and has significant reference value for the prevention and control of debris flow disasters with similar characteristics.
-

-
表 1 研究区不同设防频率下雨强值
Table 1. Rainfall intensity calculation results for different fortification frequencies in the study area
频率P/% 平均值/(mm·h-1) 变差系数Cv1 模比系数Kp 设计雨强/(mm·h-1) 1 2.872 57.44 2 2.522 50.44 5 20 0.53 2.050 41.00 10 1.696 33.92 20 1.336 26.72 表 2 卿家沟泥石流流量
Table 2. Debris flow discharge calculation for Qingjia gully
频率P/% 泥沙修正系数φ 暴雨洪水流量QP/(m3·s-1) 堵塞系数Dc 泥石流洪峰流量Qc/(m3·s-1) 1 0.67 55.57 2.5 231.56 2 0.67 47.02 2.5 195.93 5 0.67 35.86 2.5 149.40 10 0.67 27.78 2.5 115.74 20 0.67 19.90 2.5 82.93 表 3 泥石流过流量和固体物质冲出量
Table 3. Debris flow excess flow and solid matter flushing output
频率P/% 泥石流过流量Q/104 m3 固体物质冲出量QH/104 m3 1 14.67 5.87 2 12.41 4.97 5 9.47 3.79 10 7.33 2.93 20 5.25 2.10 表 4 根据流量堵塞涪江判别结果
Table 4. Assessment results for Fu river blockage based on discharge
频率/% 主河单宽流量QM/(m3·s-1) 泥石流单宽流量QB/(m3·s-1) 交角θ/(°) 判别系数CF 2 5 16.33 90° -6.36 5 5 12.45 90° -6.09 表 5 根据规模堵塞涪江判别结果
Table 5. Assessment results for Fu river blockage based on scale
主河水面宽B/m 水下安息角φw/(°) 沟口原堆积扇或岸坡的坡度α/(°) 泥石流堆积体纵坡φc/(°) 主河水深h/m 三角形堵河所需泥石流体积Qs/m3 30 18° 6° 4.5° 2.5 5 952.94 表 6 拦砂坝设置基本情况
Table 6. Basic information of sediment storage dam design
有效坝高/m 回淤面积/m2 回淤长度/m 库容/104 m3 15 8 929 114~130 5.09 表 7 设坝后下游排导工程流量设计参数
Table 7. Downstream conveyance project flow parameters after dam design
频率P/% 泥石流重度γc/(t·m-3) 泥沙修正系数 堵塞系数Dc 泥石流洪峰流量Qc/(m3·s-1) 2 1.660(1.50) 0.67(0.43) 2.5(1.8) 195.93(121.44) 5 1.660(1.50) 0.67(0.43) 2.5(1.8) 149.40(92.60) 注: “()”内为设置拦砂坝后下游泥石流流量特征参数。 表 8 不同泥石流治理模式优缺点对比表
Table 8. Comparison table of advantages and disadvantages of different debris flow prevention and control models
治理方案 治理效果 经济性 优点 缺点 中上游拦砂固源、沟口原沟排导模式 拦砂固源条件较好时,两者相当; 条件较差时,模式二更优 模式一多设拦砂坝,后期仍需定期清淤。模式二改沟长度一般短于原自然沟道,排导工程长度更小。模式一工程建设和维护成本一般较高 ①治理工程几乎不改变原沟道位置和形态;
②治理工程征地协调工作难度小①工程建设规模大,拦砂坝需定期清淤,工程建设和维护成本较高;
②中上游拦砂固源工程布设条件较差时,仍存在堵河风险;
③交汇角改变幅度小,主河水动力条件差,主河宽度窄,除减少固体物质冲数量外,其余堵河基本要素改变有限堆积区沟道改移防治模式 ①改沟后纵坡较陡,堆积区淤积条件改善;
②改沟后交汇角大幅减小,主河变宽,主河水动力条件更强,泥石流堵溃主河情况得到根本改善;
③改沟方案圬工量小,维护成本低①改沟可能占用房屋或耕地,拆迁或征地难度较大;
②改沟后需要对原沟道进行复垦,耕地占补平衡手续复杂 -
[1] 杨顺, 黄海, 田尤, 等. 涪江上游泥石流灾损土地资源化利用模式[J]. 中国地质调查, 2019, 6(5): 124-130. doi: 10.19388/j.zgdzdc.2019.05.14
Yang S, Huang H, Tian Y, et al. Land utilization modes of debris flow disaster areas in the upper reaches of Fujiang River[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2019, 6(5): 124-130. doi: 10.19388/j.zgdzdc.2019.05.14
[2] 张金山, 沈兴菊, 谢洪. 泥石流堵河影响因素研究——以岷江上游为例[J]. 灾害学, 2007, 22(2): 82-86.
Zhang J S, Shen X J, Xie H. Study on factors affecting the river-blocking due to debris-flow in the upper reaches of Minjiang river[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2007, 22(2): 82-86.
[3] 张金山, 谢洪. 岷江上游泥石流堵河可能性的经验公式判别[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2008, 17(4): 651-655.
Zhang J S, Xie H. Calculation of the possibility of river-blocking due to debris flow in the upper reaches of Minjiang river[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2008, 17(4): 651-655.
[4] 陈德明, 王兆印, 何耘. 泥石流入汇对河流影响的实验研究[J]. 泥沙研究, 2002, 27(3): 22-28.
Chen D M, Wang Z Y, He Y. Experimental study on the fluvial process of debris flow discharging into a river[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2002, 27(3): 22-28.
[5] 胡卸文, 罗刚, 王军桥, 等. 唐家山堰塞体渗流稳定及溃决模式分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2010, 29(7): 1409-1417.
Hu X W, Luo G, Wang J Q, et al. Seepage stability analysis and dam-breaking mode of Tangjiashan barrier dam[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2010, 29(7): 1409-1417.
[6] 刘翠容. 泥石流堵塞大河判据及沿河线减灾对策[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2014.
Liu C R. Critera of Blocking Large River by Debris Flow and Diaster Reduction Countermeasures in Highways Along Rivers[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014.
[7] 刘志刚, 邢忠信, 王孟科, 等. 震后地质灾害特征与防治研究: 以汶川地震灾区为例[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2014.
Liu Z G, Xing Z X, Wang M K, et al. Characteristics of Post-Earthquake Geological Hazards and Prevention Research: A Case Study of the Wenchuan Earthquake Disaster Area[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2014.
[8] 四川省水文水资源勘测局. 四川省暴雨统计参数图集[Z]. 成都: 四川省水文水资源勘测局, 2010.
Sichuan Hydrological and Water Resources Survey Center. Atlas of Statistical Parameters for Rainstorm in Sichuan Province[Z]. Chengdu: Sichuan Hydrological and Water Resources Survey Center, 2010.
[9] 杨东旭, 游勇, 陈晓清, 等. 强震-暴雨叠加区小岗剑泥石流灾害特征与防治关键技术[J]. 兰州大学学报: 自然科学版, 2015, 51(6): 898-903.
Yang D X, You Y, Chen X Q, et al. Disaster characteristics and key technologies for treatment of Xiaogangjian debris flow in severe earthquake and intense rainstorm areas[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences), 2015, 51(6): 898-903.
[10] 中国地质灾害防治工程行业协会. T/CAGHP 006—2018泥石流灾害防治工程勘查规范(试行)[S]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2018.
China Geological Hazard Prevention Engineering Industry Association. T/CAGHP 006—2018 Specification of Geological Investigation for Debris Flow Stabilization[S]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2018.
[11] 郭志学, 曹叔尤, 刘兴年, 等. 泥石流堵江影响因素试验研究[J]. 水利学报, 2004, 35(11): 39-45.
Guo Z X, Cao S Y, Liu X N, et al. Experimental study on parameters affecting the river-blocking due to debris flow[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2004, 35(11): 39-45.
[12] 蒋忠信. 震后泥石流治理工程设计简明指南[M]. 成都: 西南交通大学出版社, 2014: 400-401.
Jiang Z X. Concise Guide to the Design of Post-Earthquake Debris Flow Control Engineering[M]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University Press, 2014: 400-401.
[13] 何易平. 泥石流对山区河流河床演变的影响[D]. 成都: 中国科学院成都山地灾害与环境研究所, 2003.
He Y P. The Impact of Debris Flows on the Evolution of Mountain River Beds[D]. Chengdu: Institute of Mountain Hazards and Environment, CAS, 2003.
[14] 蒋忠信. 震后山地地质灾害治理工程勘查设计实用技术[M]. 成都: 西南交通大学出版社, 2018: 68-70.
Jiang Z X. Practical Techniques for Investigation and Design of Geological Hazard Mitigation Engineering in Mountainous Areas After Earthquakes[M]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University Press, 2018: 68-70.
[15] 文强, 胡卸文, 刘波, 等. 四川丹巴梅龙沟"6·17"泥石流成灾机理分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2022, 33(3): 23-30.
Wen Q, Hu X W, Liu B, et al. Analysis on the mechanism of debris flow in Meilong valley in Danba County on June 17, 2020[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(3): 23-30.
[16] 唐川, 李为乐, 丁军, 等. 汶川震区映秀镇"8·14"特大泥石流灾害调查[J]. 中国地质大学学报: 地球科学版, 2011, 36(1): 172-180.
Tang C, Li W L, Ding J, et al. Field investigation and research on giant debris flow on August 14, 2010 in Yingxiu Town, epicenter of Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2011, 36(1): 172-180.
-



 下载:
下载: