Analysis of groundwater environmental background values in the Yellow River lateral seepage impact zone in Henan Province
-
摘要:
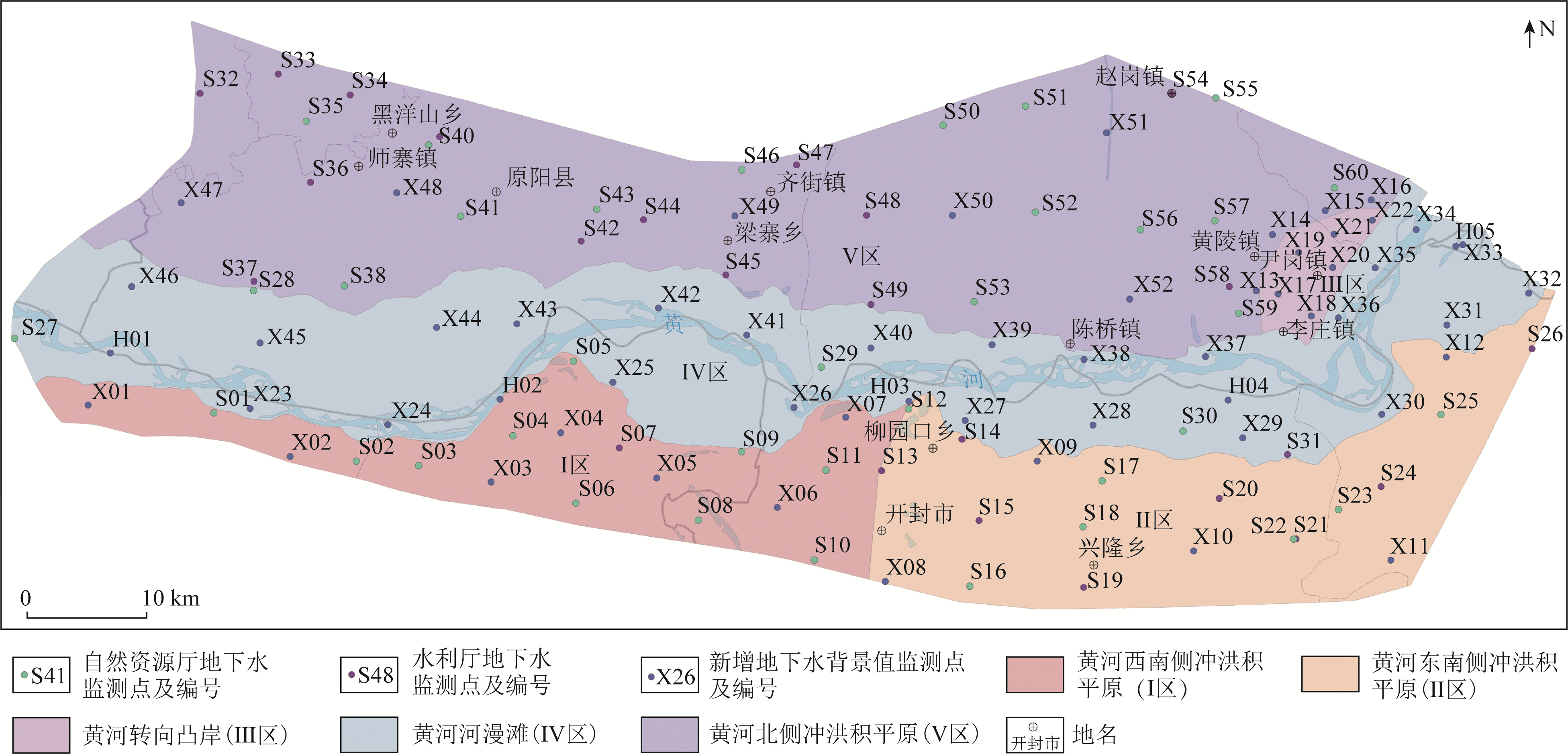
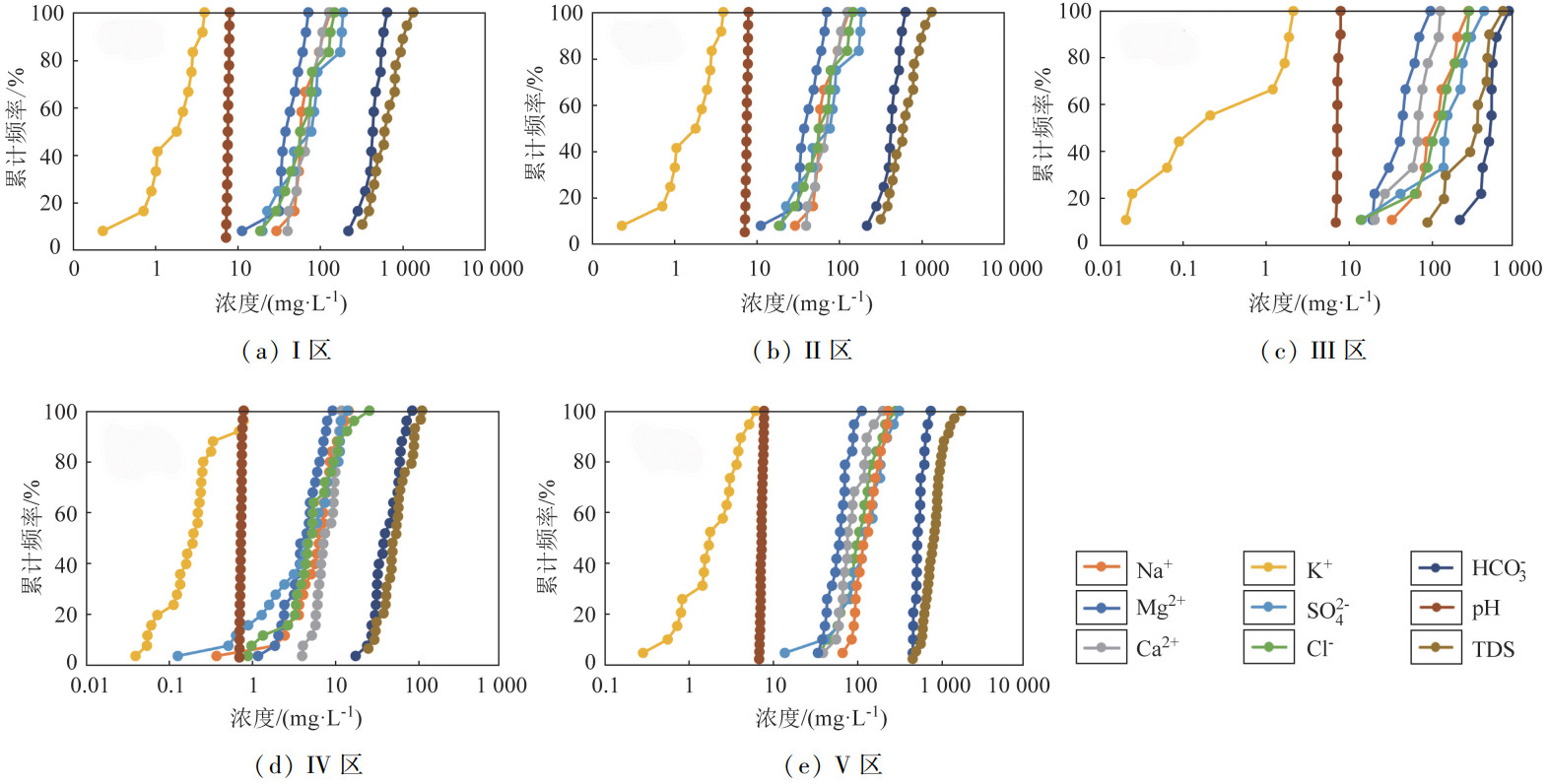
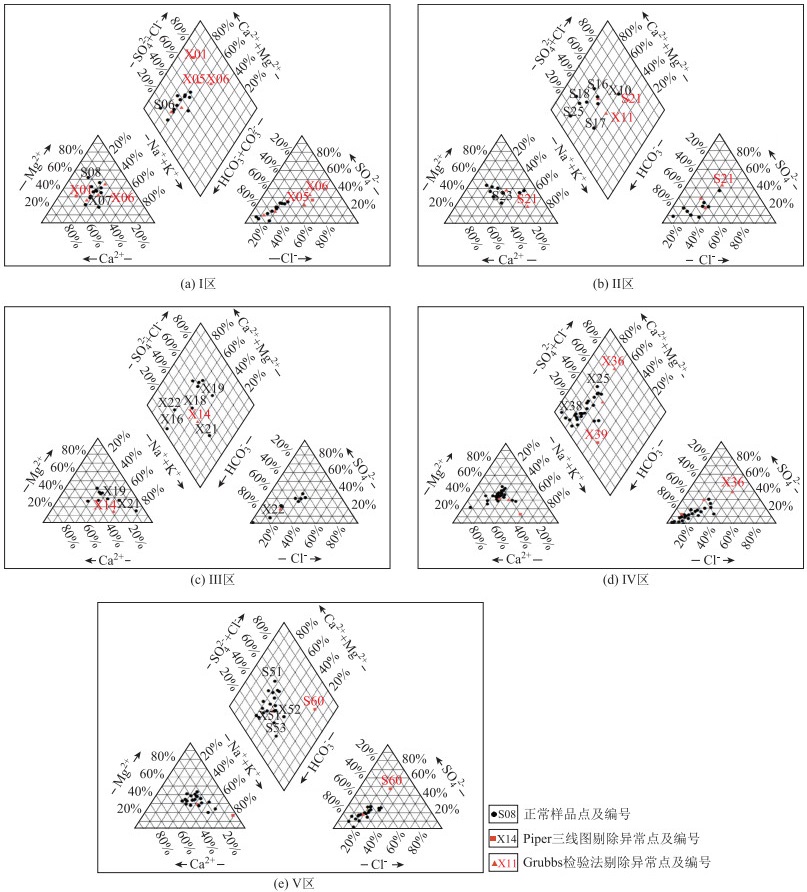
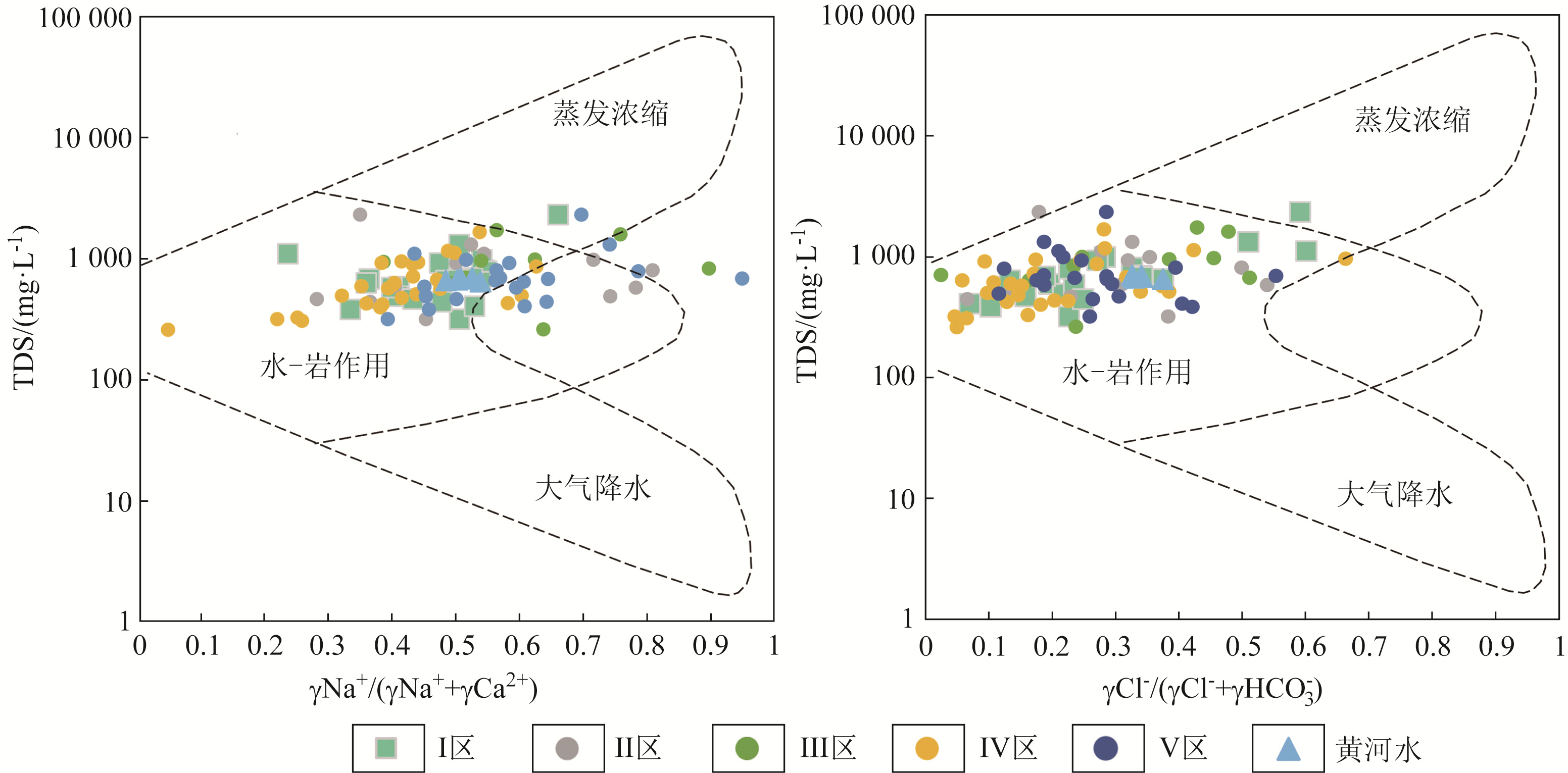
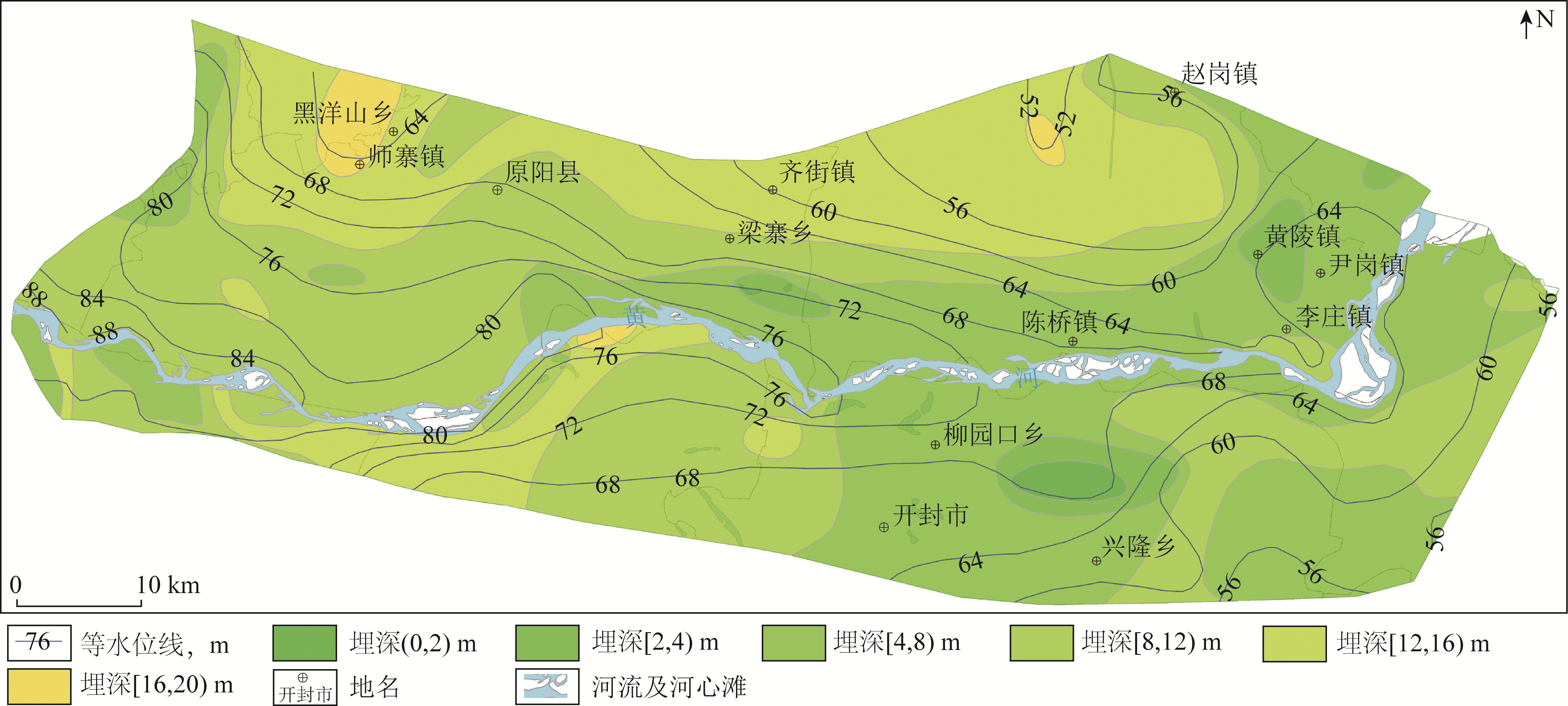
地下水环境背景值是衡量地下水是否遭受污染的重要依据,确定区域内地下水环境背景值是评价该地区地下水可持续发展的重要标尺。针对河南省黄河下游侧渗影响带水文地质与地下水化学特征,划分5个地下水环境背景值单元分区,运用数理统计方法计算各个分区8种地下水化学指标的地下水环境背景值和范围。研究结果表明: 黄河阶地Ⅳ区的地下水背景值最低,地处黄河南岸的Ⅰ区、Ⅱ区地下水背景值较低,黄河北岸的Ⅴ区和位于黄河流向自EW向转为SW向凸岸处的Ⅲ区地下水背景值较高; 研究区主要地下水类型为HCO3--Ca2+·Mg2+·Na+型、HCO3--Mg2+·Ca2+·Na+型和HCO3--Mg2+·Na+·Ca2+型,研究区内Ca2+、Mg2+、Na+、SO42-、Cl-、溶解性总固体(total dissolved solids,TDS)值存在高背景值区,Ca2+、Mg2+的高背景值区可能是由于矿物溶解和阳离子交换作用所导致,农业面源污染形成了Cl-和SO42-的高背景值区,TDS值高背景值区是由于该区域蒸发浓缩作用强所导致; Gibbs图解显示研究区地下水主要受到原生地层中矿物风化溶解作用的影响,也受到部分蒸发浓缩作用的影响。研究结果查明了河南省黄河下游侧渗影响带的水质分布规律,提升对该区域的地下水水质形成演化机理的认识,为维护区域地下水可持续发展提供了重要支撑。
Abstract:The groundwater environmental background value is an important basis for measuring whether the groundwater is polluted, and the groundwater environmental background value is an important yardstick for evaluating the sustainable development level of groundwater in this region. Five groundwater background value unit zonings were divided in this paper based on the hydrogeological and groundwater chemical characteristics of lateral seepage impact zone in the lower reaches of the Yellow River in Henan Province. The groundwater environmental background values and ranges of 8 groundwater chemical indicators in each zoing were calculated using mathematical and statistical methods. The results show that the groundwater background value of Zone Ⅳ in the Yellow River terrace is the lowest, while that of Zone Ⅰ and Zone Ⅱ on the southem bank of the Yellow River is lower. The background values of Zone Ⅴ on the northem bank of the Yellow River and Zone Ⅲ, where the Yellow River turns from east-west to south-west, are higher. The main groundwater types in the study area are HCO3--Ca2+·Mg2+·Na2+, HCO3--Mg2+·Ca2+·Na+ and HCO3--Mg2+·Na+·Ca2+ water. There are high background value areas for Ca2+, Mg2+, SO42-, Cl-, TDS and other indicators in the study area. The high background value area of Ca2+ and Mg2+ may be caused by mineral dissolution and cation exchange, and that of SO42- and Cl- may be caused by agricultural non-point source pollution. The high background value area of TDS is caused by strong evaporation and concentration in this area. The Gibbs diagram shows that the groundwater in this area is mainly affected by the weathering and dissolution of minerals in the original strata, and is also affected by partial evaporation and concentration. The water quality distribution law of the lateral seepage impact zone in the lower reaches of the Yellow River in Henan Province was identified, and the understanding of the formation and evolution mechanism of groundwater quality in this region was improved. The research results could provide important support for maintaining the sustainable development of regional groundwater.
-

-
表 1 研究区典型指标地下水环境背景值统计
Table 1. Typical indicators statistical of groundwater environmental background values of the study area
分区 指标 ω(HCO3-)/(mg·L-1) ω(Cl-)/(mg·L-1) ω(SO42-)/(mg·L-1) ω(K+)/(mg·L-1) ω(Ca2+)/(mg·L-1) ω(Na+)/(mg·L-1) ω(Mg2+)/(mg·L-1) pH值 TDS/(mg·L-1) Ⅰ区 中位数 431.13 64.35 79.97 1.99 72.08 57.81 39.97 7.57 632.14 背景值 437.04 72.59 87.06 1.97 73.07 69.74 43.58 7.57 686.67 背景值下限(5%) 251.58 24.36 21.32 0.50 40.40 39.52 22.35 7.21 369.20 背景值上限(95%) 606.56 139.80 183.12 3.84 116.67 120.92 68.78 7.88 1142.00 分布类型 正态 正态 正态 正态 正态 正态 正态 正态 正态 样本数/个 12 12 12 12 12 12 12 18 17 Ⅱ区 中位数 527.82 121.01 100.86 1.81 99.00 110.40 55.40 7.60 772.05 背景值 503.94 112.82 121.95 2.34 88.66 102.14 59.38 7.61 842.26 背景值下限(5%) 297.78 35.31 47.24 0.55 34.53 42.82 36.40 7.19 488.20 背景值上限(95%) 675.23 197.72 241.20 5.13 134.84 168.20 92.21 7.96 1480.10 分布类型 正态 正态 正态 正态 正态 正态 正态 正态 正态 样本数/个 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 20 20 Ⅲ区 中位数 553.02 140.03 162.01 0.22 72.60 126.04 46.80 7.55 886.50 背景值 532.89 150.42 195.19 0.84 76.63 138.39 50.34 7.67 928.80 背景值下限(5%) 303.03 34.94 26.46 0.022 24.20 48.22 20.58 7.32 409.60 背景值上限(95%) 791.20 288.80 394.80 2.12 130.60 259.60 90.12 8.07 1348.40 分布类型 正态 正态 正态 正态 正态 正态 正态 正态 正态 样本数/个 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 10 10 Ⅳ区 中位数 415.02 54.59 54.80 2.01 78.20 66.30 46.90 7.54 567.50 背景值 472.86 70.89 60.54 1.85 84.11 68.75 47.93 7.55 614.11 背景值下限(5%) 258.60 10.86 5.56 0.55 44.58 20.55 19.80 7.23 310.00 背景值上限(95%) 752.40 168.8 121.6 7.92 120.04 131.6 82.38 7.73 920.79 分布类型 正态 正态 正态 对数正态 正态 正态 正态 正态 正态 样本数/个 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 29 29 Ⅴ区 中位数 543.08 109.19 130.00 1.83 79.83 139.10 64.52 7.50 854.50 背景值 573.28 123.84 142.77 2.46 96.60 144.57 65.87 7.50 855.33 背景值下限(5%) 477.06 44.84 39.46 0.54 56.13 86.60 39.16 7.08 563.16 背景值上限(95%) 721.10 230.10 284.60 5.43 167.60 235.60 96.89 7.96 1376.05 分布类型 正态 正态 正态 正态 正态 正态 正态 正态 正态 样本数/个 19 19 19 19 19 19 19 35 34 -
[1] 中华人民共和国生态环境部. 关于印发《地下水环境背景值统计表征技术指南(试行)》的通知[EB/OL]. (2023-10-23).
Ministry of Ecology and Environment, PRC. Guidelines for statistical characterization of groundwater environmental background values (Trial version)[EB/OL]. (2023-10-23).
[2] 寇文杰, 谢振华, 赵立新, 等. 探讨地下水背景值确定方法及其容易忽视的几个问题[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2013, 41(8): 3603-3605. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2013.08.112
Kou W J, Xie Z H, Zhao L X, et al. On several methods for determining the groundwater background value and some easily neglected problems[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 41(8): 3603-3605. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2013.08.112
[3] 江西省地矿局环境地质大队. 长江中下游重点地区地下水环境背景值调查研究[R]. 南昌: 江西省地矿局环境地质大队, 1991.
Environmental Geology Research Institute of Jiangxi Provincial Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources. Investigation and Study on Groundwater Environmental Background Values in Key Areas of the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River[R]. 1991.
[4] 何宝南, 何江涛, 孙继朝, 等. 区域地下水污染综合评价研究现状与建议[J]. 地学前缘, 2022, 29(3): 51-63.
He B N, He J T, Sun J C, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of regional groundwater pollution: research status and suggestions[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2022, 29(3): 51-63.
[5] 高迪, 潘国营, 钟福平, 等. 新乡市地下水化学背景值研究[J]. 露天采矿技术, 2006(4): 51-54.
Gao D, Pan G Y, Zhong F P, et al. Study of groundwater chemical background value in Xinxiang city[J]. Opencast Mining Technology, 2006(4): 51-54.
[6] 刘左, 潘欢迎. 湖北省平原岗区地下水环境背景值初步研究[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2023, 30(3): 208-221.
Liu Z, Pan H Y. Preliminary study on groundwater environmental background value in plain area of Hubei Province[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2023, 30(3): 208-221.
[7] 齐万秋, 周金龙. 石河子市地下水环境背景值[J]. 干旱环境监测, 1994, 8(1): 14-16.
Qiu W Q, Zhou J L. Environmental background values of the groundwater of Shihezi city[J]. Arid Environmental Monitoring, 1994, 8(1): 14-16.
[8] 张英, 孙继朝, 黄冠星, 等. 珠江三角洲地区地下水环境背景值初步研究[J]. 中国地质, 2011, 38(1): 190-196.
Zhang Y, Sun J C, Huang G X, et al. A preliminary study of natural background levels of groundwater in the Zhujiang River Delta[J]. Geology in China, 2011, 38(1): 190-196.
[9] 朱晓星. 泉州市沿海地区地下水锰环境背景值研究[J]. 黑龙江环境通报, 2022, 35(3): 17-22.
Zhu X X. Study on environmental background value of manganese in groundwater in Quanzhou coastal area[J]. Heilongjiang Huanjing Tongbao, 2022, 35(3): 17-22.
[10] 曾颖. 秦皇岛柳江盆地浅层地下水常规组分背景值研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015.
Zeng Y. Study on Natural Background Levels of Conventional Components in Shallow Groundwater of the Liujiang River Basin in Qinhuangdao[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2015.
[11] 张兆吉, 费宇红, 郭春艳, 等. 华北平原区域地下水污染评价[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2012, 42(5): 1456-1461.
Zhang Z J, Fei Y H, Guo C Y, et al. Regional groundwater contamination assessment in the North China Plain[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2012, 42(5): 1456-1461.
[12] Kim K H, Yun S T, Kim H K, et al. Determination of natural backgrounds and thresholds of nitrate in South Korean groundwater using model-based statistical approaches[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 148: 196-205.
[13] Preziosi E, Parrone D, Del Bon A, et al. Natural background level assessment in groundwaters: probability plot versus pre-selection method[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 143: 43-53.
[14] Parrone D, Ghergo S, Preziosi E. A multi-method approach for the assessment of natural background levels in groundwater[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 659: 884-894.
[15] Lee L, Helsel D. Baseline models of trace elements in major aquifers of the United States[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2005, 20(8): 1560-1570.
[16] 方媛, 吴昊, 霍晨琛, 等. 石嘴山市浅层地下水的环境背景值[J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(7): 1361-1371.
Fang Y, Wu H, Huo C C, et al. Environment background levels of phreatic water in Shizuishan[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 35(7): 1361-1371.
[17] 刘文波, 冯翠娥, 高存荣. 河套平原地下水环境背景值[J]. 地学前缘, 2014, 21(4): 147-157.
Liu W B, Feng C E, Gao C R. Background value of groundwater environment in Hetao Plain[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2014, 21(4): 147-157.
[18] 耿婷婷, 李颖智, 张涛, 等. 西藏"一江三河"地区地下水环境背景值初步研究[J]. 地质与资源, 2018, 27(5): 480-487.
Geng T T, Li Y Z, Zhang T, et al. Preliminary study on the environmental background values of groundwater in middle Yarlung Zangbo River Basin, Tibet[J]. Geology and Resources, 2018, 27(5): 480-487.
[19] 郭高轩, 辛宝东, 刘文臣, 等. 我国地下水环境背景值研究综述[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2010, 37(2): 95-98.
Guo G X, Xin B D, Liu W C, et al. Review on the study of the environment background values of groundwater in China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2010, 37(2): 95-98.
[20] 邱汉学, 黄巧珍. 地下水环境背景值及其确定方法[J]. 青岛海洋大学学报, 1994(S3): 16-20.
Qiu H X, Huang Q Z. The concept of groundwater environment background and its determination[J]. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao, 1994(S3): 16-20.
[21] 赵云章, 邵景力, 崔亚莉, 等. 黄河悬河段影响带远景水源地可采资源评价[J]. 人民黄河, 2003, 25(5): 22-24.
Zhao Y Z, Shao J L, Cui Y L, et al. Evaluation on long-term exploitable water resources of effected zone in suspended section of the Yellow River[J]. Yellow River, 2003, 25(5): 22-24.
[22] 孙跃. 河南省沿黄地下水数值模拟及地下水资源评价[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2011.
Sun Y. The Study on Groundwater Numerical Simulation and Groundwater Resources Evaluation of the Area along the Yellow River in Henan Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2011.
[23] 平建华, 曹剑峰, 苏小四, 等. 同位素技术在黄河下游河水侧渗影响范围研究中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2004, 34(3): 399-404.
Ping J H, Cao J F, Su X S, et al. Application of isotopic technique in the research of the affected range of lateral seepage of the down-Yellow River water[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2004, 34(3): 399-404.
[24] 高燕燕. 关中平原地下水化学成分时空演化规律及人体健康风险评价[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2020.
Gao Y Y. Spatio-temporal Evolution of Hydrochemical Components and Human Health Risk Assessment of Groundwater in Guanzhong Plain[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2020.
[25] 河南省地质调查院. 黄河下游河南段环境地质调查评价报告[R]. 2005.
Henan Geological Survey Institute. Environmental Geological Survey and Evaluation Report of the Lower Yellow River in Henan[R]. 2005.
[26] 河南省地质调查院. 黄河下游河南段地下水资源潜力调查评价报告[R]. 郑州: 河南省地质调查院, 2003.
Henan Institute of Geological Survey. Assessment of Groundwater Resource Potential of Downstream of the Yellow River in Henan[R]. Zhengzhou: Henan Institute of Geological Survey, 2003.
[27] 中华人民共和国生态环境部. HJ 164—2020地下水环境监测技术规范[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2021.
Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China. HJ 164—2020 Technical Specifications for Environmental Monitoring of Groundwater[S]. Beijing: China Environment Press, 2021.
[28] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 14848—2017地下水质量标准[S]. 2017.
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of PRC, Standardization Administration of PRC. GB/T 14848—2017 Standard for Groundwater Quality[S]. 2017.
[29] 王瑞久. 三线图解及其水文地质解释[J]. 工程勘察, 1983(6): 6-11.
Wang R J. Piper diagrams and its hydrogeological interpretation[J]. Geotechnical Investigation and Surveying, 1983(6): 6-11.
[30] 沈照理, 朱宛华, 钟佐燊. 水文地球化学基础[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1993.
Shen Z L, Zhu W H, Zhong Z S. Hydrogeochemical Fundamentals[M]. Beijing: Geological Press, 1993.
[31] 王帅, 任宇, 郭红, 等. 河南黄河改道区浅层地下水化学特征与主控污染源解析[J]. 环境科学, 2024, 45(2): 792-801.
Wang S, Ren Y, Guo H, et al. Chemical characteristics of shallow groundwater in the Yellow River diversion area of Henan Province and identification of main control pollution sources[J]. Environmental Science, 2024, 45(2): 792-801.
[32] 金银龙, 陈昌杰, 陈西平, 等. GB 5749—2006生活饮用水卫生标准[S]北京: 中国标准出版社, 2007.
Jin Y L, Chen C J, Chen X P, et al. GB 5749—2006 Standards for Drinking Water Quality[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2007.
[33] 王亚平, 王岚, 许春雪, 等. 长江水系水文地球化学特征及主要离子的化学成因[J]. 地质通报, 2010, 29(2/3): 446-456.
Wang Y P, Wang L, Xu C X, et al. Hydro-geochemistry and genesis of major ions in the Yangtze River, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2010, 29(2/3): 446-456.
[34] 孙龙, 王莉莉, 曹文庚. 黄河下游影响带(河南段)水化学演化规律研究[J]. 人民黄河, 2021, 43(12): 91-99.
Sun L, Wang L L, Cao W G. Evolution of groundwater hydrochemical characteristics in the influence zone of the lower Yellow River in Henan[J]. Yellow River, 2021, 43(12): 91-99.
-



 下载:
下载: