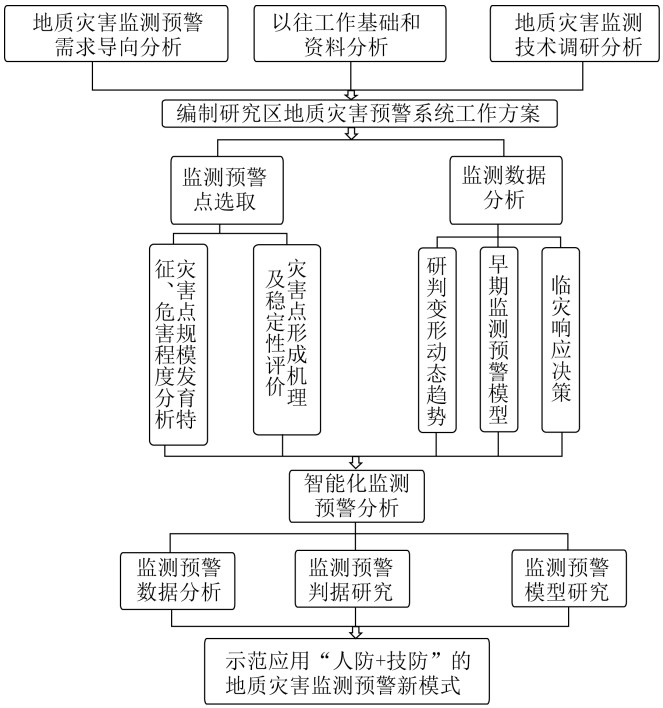
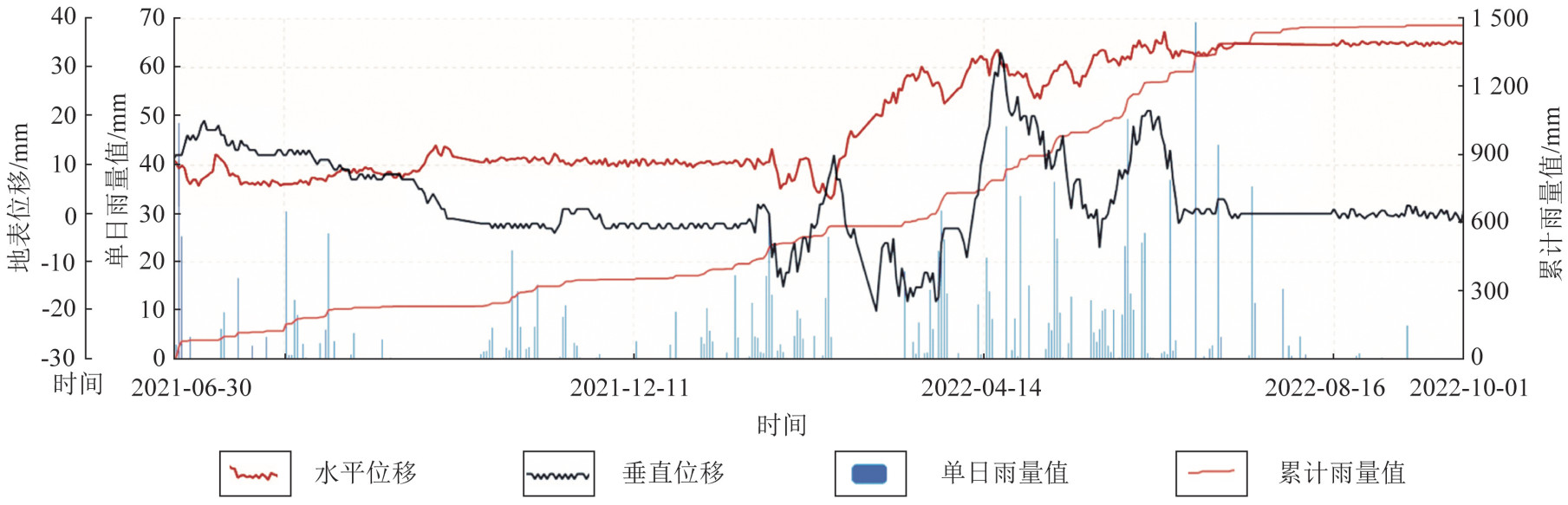
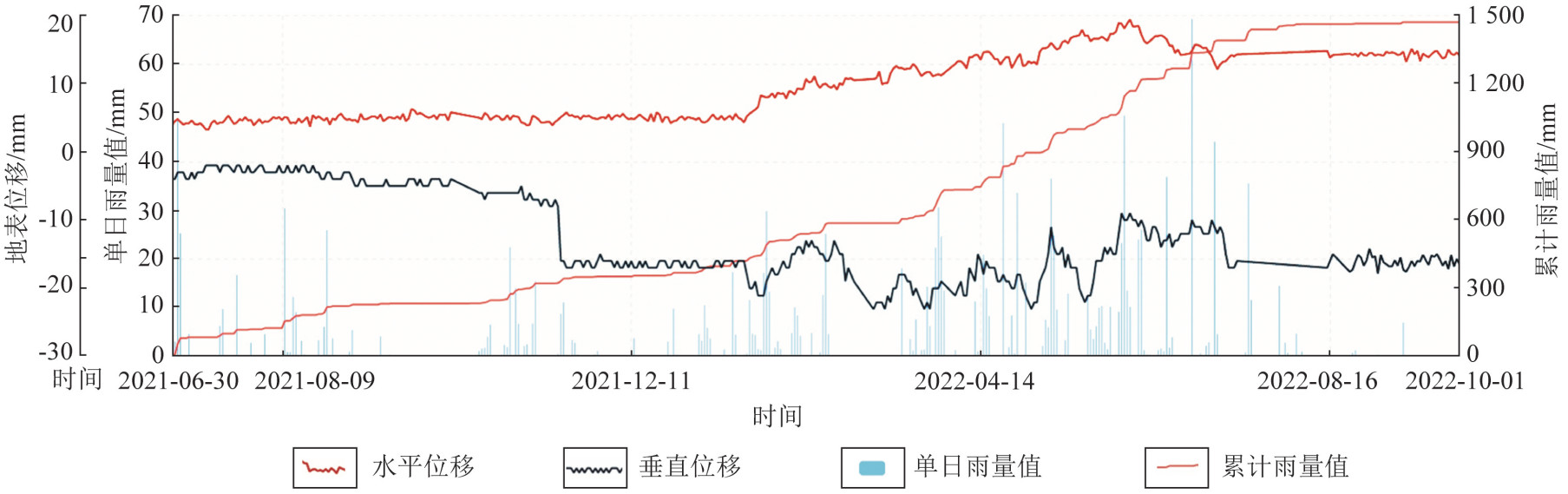
Universal monitoring and early warning for landslide geological hazard: A case study of Xupu County in Hunan Province
-
摘要:
为了满足普适型地质灾害监测预警工作的应用推广需求,以湖南省溆浦县40处滑坡地质灾害普适型监测预警示范点建设为例,介绍了普适型监测预警示范点建设与监测预警系统运行的全过程。根据研究区滑坡地质灾害发育特征、成灾模式和致灾特点,选取了40处监测预警示范点,选用雨量计、裂缝计、GNSS位移计、含水率计、倾角加速度计普适型设备,对监测预警示范点的变形特征、影响因素、滑动前兆等关键指标开展专业化监测; 聚焦雨量和变形,采用Pearson模型和监测数据分析的方法分别提出了研究区雨量判据和变形判据,建立了监测预警模型; 监测数据汇聚至系统平台,通过判据模型自动触发预警,并发送预警信息。以湾里滑坡为典型点,对监测部署方案和监测数据进行了分析,实时掌握了降雨特征、滑坡的变形特征及两者的相关特性,初步显现了普适型设备的监测成效和预警作用。研究成果可对普适型监测预警工作的推广应用提供技术支撑,同时可有效指导相关部门开展应急响应工作。
Abstract:In order to meet the application and promotion needs of universal geological disaster monitoring and early warning, the authors took the construction of 40 universal monitoring and early warning demonstration points for landslide hazard in Xupu County of Hunan Province as an example to introduce the entire process of the construction of universal monitoring and early warning demonstration points and the operation of the monitoring and early warning system. Forty monitoring and early warning demonstration points were selected according to the development characteristics, disaster modes, and disaster-causing features of landslide hazard in the study area. The universal equipment such as rain gauges, crack gauges, GNSS displacement meters, moisture meters, and inclination accelerometers were used for the professional detection of key indicators of monitoring and early warning demonstration points, including deformation characteristics, influencing factors and slide precursor. For rainfall and deformation, Pearson model and monitoring data analysis method were adopted to propose rainfall criterion and deformation criterion in the study area. And the monitoring and early warning model was established. The monitoring data were aggregated to the system platform, and the criterion model automatically triggered warnings to send warning information. Wanli landslide was taken as a typical case to analyze the monitoring deployment plan and monitoring data. The rainfall characteristics, deformation features of the landslide, and their correlation were provided in real time, and the effectiveness and early warning capabilities of the universal monitoring equipment were preliminarily demonstrated. The research results could provide technical support for the promotion and application of universal monitoring and early warning work, and it could effectively guide relevant departments to carry out emergency response work at the same time.
-
Key words:
- geological disaster /
- landslide /
- universal equipment /
- monitoring /
- early warning
-

-
表 1 研究区土质滑坡成灾模式
Table 1. Soil landslide disaster mode in the study area
滑坡类型 成灾模式 致灾特点 沿基覆界面滑移型 该类滑坡多发生在由砂页岩、砂泥岩岩组及变质岩岩组构成的地形坡度为20°~25°的斜坡中,坡体结构为顺向等倾的更易发生滑坡。斜坡坡角多因切坡有基岩出露,但斜坡主体仍为残坡积土层,因为基岩顶面相对与土体来说更隔水,容易造成地下水在基覆界面汇集,从而浸泡和软化接触带附近土体,易产生上覆残坡积土层沿下伏基岩顶面的滑动变形。滑坡形成初期往往表现为斜坡后缘发育拉裂缝,随着变形进一步发展,斜坡下半部分逐渐鼓胀、隆起,在极限降雨条件下,潜在滑移面被剪断贯通,形成滑坡 该类型滑坡一般规模较大,对滑坡体内及坡前的建筑物毁坏性较强,致灾性大 浅表层滑动型 该类型滑坡主要发生由花岗岩岩组、砂页岩岩组及变质岩岩组构成的坡度为25°~30°的斜坡中。滑体物质多为表层残坡积黏土、亚黏土与下层碎裂散体状全-强风化碎石的混合物,结构松散,厚度较薄。在持续强降雨条件下,浅表层土体饱水后强度降低,自重增大,沿边坡顶部产生小规模滑动 该类型滑坡多数规模小,致灾性小,滑坡体堆积于房后或对房屋后墙造成破坏,主要危及房屋后墙及路边行人、车辆 陡坡塌滑型 该类型滑坡主要发生由花岗岩岩组、变质岩岩组构成的坡度为30°~45°的陡坡中。原始斜坡表层岩土体在长时间风化作用下,裂隙发育,表层岩土体松散破碎。强降雨入渗导致坡体物质自重增加,坡体表层土体吸水处于饱和状态,坡体上部被裂隙分割的岩土体首先发生塌滑,滑塌岩土体冲击坡体下部松散岩土体,使得下部松散岩土体发生滑动破坏 该类型滑坡突发性强、速度快、冲击力大,致灾性高,易摧毁并掩盖房屋和道路 表 2 研究区监测预警示范点特征
Table 2. Characteristics of monitoring and early warning demonstration points in the study area
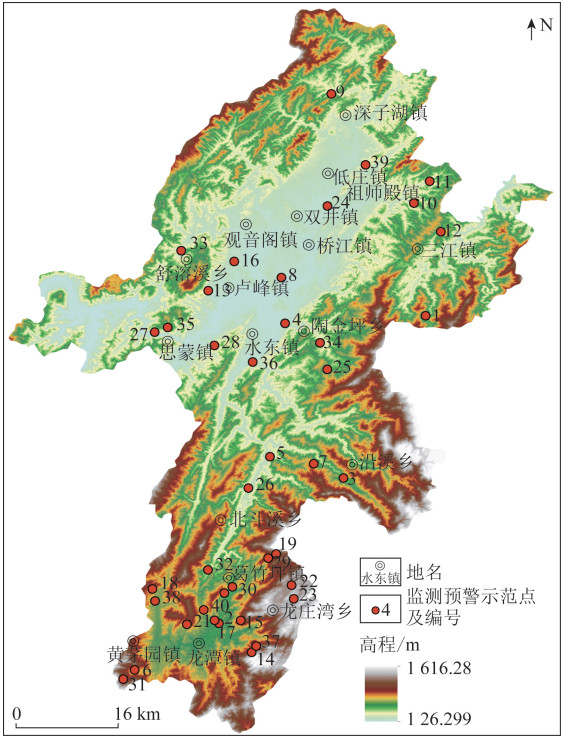
示范点编号 隐患点名称 类型 规模 稳定性 威胁人数/人 威胁财产/万元 成灾模式 1 祠屋下滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 60 130 沿基覆界面滑移型 2 红岩村1组滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 41 300 沿基覆界面滑移型 3 梅子坪滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 20 30 沿基覆界面滑移型 4 绿化社区8组滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 31 90 沿基覆界面滑移型 5 红花村3组滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 26 60 沿基覆界面滑移型 6 油麻村21组滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 60 350 沿基覆界面滑移型 7 过江坡村7组滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 22 200 沿基覆界面滑移型 8 河上坡村滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 20 138 浅表层滑动型 9 刘家坪村6组滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 64 120 沿基覆界面滑移型 10 令吉冲村12组滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 33 80 浅表层滑动型 11 青龙溪滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 31 95 陡坡塌滑型 12 金兰村12组滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 25 78 浅表层滑动型 13 红花园村7、8组滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 21 50 沿基覆界面滑移型 14 红岩村6组滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 29 100 沿基覆界面滑移型 15 圭洞村25组滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 42 120 浅表层滑动型 16 哑塘村19组滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 198 150 沿基覆界面滑移型 17 彭家滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 45 100 沿基覆界面滑移型 18 杨梅冲滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 18 60 浅表层滑动型 19 湖南田滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 52 70 沿基覆界面滑移型 20 合堂湾滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 28 100 沿基覆界面滑移型 21 筲箕湾滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 48 200 沿基覆界面滑移型 22 打戈垅组滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 32 100 陡坡塌滑型 23 金龙组滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 21 60 沿基覆界面滑移型 24 洞底湾滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 54 180 浅表层滑动型 25 老鸭田滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 12 60 陡坡塌滑型 26 叶家湾滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 29 40 沿基覆界面滑移型 27 半山滑坡 滑坡 中型 不稳定 30 40 沿基覆界面滑移型 28 麻叶冲滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 96 60 沿基覆界面滑移型 29 鸭坝塘滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 35 150 沿基覆界面滑移型 30 岩背滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 88 700 沿基覆界面滑移型 31 烂屋场滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 77 200 沿基覆界面滑移型 32 湾里滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 43 150 沿基覆界面滑移型 33 周家坪滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 31 40 陡坡塌滑型 34 贺家滑坡 滑坡 中型 不稳定 33 220 沿基覆界面滑移型 35 梅子冲滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 110 120 沿基覆界面滑移型 36 雷公坪滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 30 75 陡坡塌滑型 37 红岩村2组滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 27 180 浅表层滑动型 38 王家院子滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 80 100 陡坡塌滑型 39 后村湾滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 16 45 浅表层滑动型 40 向家冲滑坡 滑坡 小型 不稳定 67 120 沿基覆界面滑移型 表 3 研究区滑坡监测设备实施表
Table 3. Implementation of landslide monitoring equipment in the study area
设备类型 技术参数 安装位置建议 雨量计 测量精度为±3%F.S; 分辨率不低于0.2 mm; 设备类型为压电式; 采样间隔0 s~24 h; 上传间隔0 s~72 h; 输出信号支持2G/4G无线通讯,可定制NB窄带物联网、LoRa或有线传输方式; 防护等级为IP67; 供电方式为按需供电方式,满足连续30个阴雨日正常工作 布设于相对平坦且空旷区域,承雨器口至山顶的仰角不大于30°,不宜布设在陡坡上、峡谷内、有遮挡或风口处 GNSS位移计 输出信号: RS485、RS232; 静态解算精度平面不低于±2.5 mm+0.5 ppm,高程不低于±5.0 mm+0.5 ppm; 通讯为全网通+LoRa; 功耗在采样间隔不低于15 s且上传间隔不低于15 s情况下,接收机平均功耗≤2 W; 防水防尘为IP67; 数据格式: 支持RTCM32原始数据及实时动态结果数据上传; 供电为12~24 V太阳能供电; 连续不间断运行时间(MTBF)不低于32 000 h 布设于位移量较大、稳定性差的部位; 基准站需布设在滑坡外围稳定区; GNSS监测点应位置空旷,在±15°高度截止角上空不能有成片障碍物,保证搜星条件良好,周围无高压线、变电站等电磁干扰源 裂缝计 测量范围为0~500 cm; 测量精度±0.1%F·S; 采样间隔为0~7 200 s; 上传间隔为1~36 000 s; 输出信号0~5 V,RS485; 通信方式为全网通+LoRa; 防护等级为IP67; 供电方式为12~24 V太阳能供电; 触发功能为设备具备阈值触发功能,如监测数据超过阈值,可立即采集监测数据并自动上报 布设于裂缝两侧,且应布设于裂缝较宽处。对宽度大于5 m或两侧高差大于1 m的裂缝,宜安装无线裂缝计 倾角加速度计 测量精度为倾角0.005°;加速度1 mg;振动1 Hz;位移0.2%F.S;量程为倾角±180°;加速度±2 g;振动0~2 000 Hz;位移2 m; 采集方式为阈值触发加密采集; 通信方式为全网通/NB-Lot+LoRa; 供电方式为内置锂电(15 000 mAh)+外置太阳能板; 报警方式为微信、短信、语音; 防护等级为IP67; 工作湿度95%RH; 工作温度-25 ℃~85 ℃ 布设于坡顶危险岩土块体上或可能变形处及前缘存在鼓胀或滑塌区 含水率计 测量范围为干土—饱和土,测量深度不小于0.8 m; 测量精度为±4%; 采样间隔0 s~24 h; 上传间隔0 s~72 h; 支持双波段900/1 800 MHz; 支持GPRS、CDMA、北斗数据发送方式; 具有定时自检功能, 掉电数据保护、实时时钟校准; 输出参数为输出同位分层土壤含水率及土壤温度、倾斜角参数; 防护等级为IP67; 在使用时含水率不需要标定校准,若需要标定的特殊土质,设备需要支持远程设置标定参数; 供电方式为采用太阳能浮充蓄电池供电方式 布设于滑坡的中腰部位、以及某些坪台或坑洼、地下水集中入渗点部位,深度以土岩接触带以上约1 m 表 4 主要测项单参数预警判据表达式
Table 4. Single parameter early warning criterion expression for the main test items
测项 预警判据描述 预警判据表达式 GNSS 前1 h水平位移量或垂直位移量达到或超过阈值 D1h≥Gh∨D1v≥Gv。(1)
式中: D1h、D1v分别为1 h内GNSS水平、垂直位移量,mm; Gh,Gv分别为GNSS水平、垂直位移量的阈值,mm裂缝 前1 d裂缝变形量达到或超过阈值 d1≥dt,(2)
式中: d1为1 d裂缝变形量,mm; dt为裂缝变形量阈值,mm R1≥Rt。(3)
式中: R1为1 h内降雨量,mm; Rt为降雨量阈值,mm雨量 前1 h雨量值达到或超过阈值、有效降雨量达到或超过阈值 $R_e=\sum\limits_{n=1}^N P_n \alpha^n \geqslant R_{\mathrm{t}}。\text{(4)}$
式中: Re为有效降雨量,mm; Pn为前n天的降雨量,mm; Rt为降雨量阈值,mm; α为有效降雨系数; n为天数,d表 5 不同日数前期累计降雨量与滑坡相关性分析
Table 5. Correlation analysis between the accumulated rainfall with different antecedent rainfall days and the landslide
不同日数前期累计降雨量 P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 P6 P7 P8 P9 P10 相关系数 0.597 0.605 0.646 0.589 0.539 0.518 0.497 0.486 0.445 0.424 表 6 不同有效降雨系数累计前期3 d降雨量与滑坡相关性分析
Table 6. Correlation analysis between the cumulative antecedent rainfall of three days with different effective rainfall coefficients and the landslide
有效降雨系数α α=1.0 α=0.9 α=0.8 α=0.7 α=0.6 α=0.5 α=0.4 相关系数 0.636 0.641 0.704 0.656 0.563 0.547 0.539 表 7 研究区滑坡监测预警模型表
Table 7. Landslide monitoring and early warning model in the study area
预警级别 蓝色 黄色 橙色 红色 雨量判据 前1 h雨量值≥20 mm 前1 h雨量值≥30 mm 前0~24 h雨量值×1+前24~48 h雨量值×0.8+前48~72 h雨量×0.6≥80 mm 前0~24 h雨量值×1+前24~48 h雨量值×0.8+前48~72 h雨量值×0.6 ≥100 mm GNSS判据 前1 h水平位移量≥50 mm或前1 h垂直位移量≥50 mm 前1 h水平位移量≥100 mm或前1 h垂直位移量≥100 mm 前1 h水平位移量≥150 mm或前1 h垂直位移量≥150 mm 前1 h水平位移量≥200 mm或前1 h垂直位移量≥200 mm 裂缝判据 前1 d裂缝变形量≥10 mm 前1 d裂缝变形量≥15 mm 前1 d裂缝变形量≥25 mm 前1 d裂缝变形量≥35 mm 表 8 研究区滑坡监测预警模型及响应措施建议
Table 8. Monitoring and early warning model and response measure suggestions for landslide in the study area
预警级别 人防预警 监测预警模型 响应管理措施建议 蓝色预警(注意) 初始变形后缘裂缝断续产生,前缘鼓胀隆起等 雨量蓝色预警或裂缝蓝色预警或位移蓝色预警 正常监测,加强群测群防员巡查,加密观测频次; 观测时间间隔1 d/次; 专业监测人员加强数据观测,每日不少于2次 黄色预警(警示) 匀速变形后缘裂缝数量增多扩展局部有下错现象,前缘小规模崩塌等 雨量黄色预警或裂缝黄色预警或位移黄色预警 观测频次12 h/次,提醒监测人员收集其他监测数据,加强监测数据校核; 县级自然资源主管部门组织专家研判 橙色预警(警戒) 匀速变形—局部加速变形后缘裂缝加深加宽,逐渐贯通,形成下错台坎,两侧出现剪切裂缝,滑坡边界清晰等 雨量橙色预警且裂缝橙色预警或位移橙色预警 观测频次6 h/次; 综合各类监测数据; 地市级自然资源主管部门组织专家研判 红色预警(警报) 加速变形后缘与两侧裂缝完全贯通,前缘大规模崩塌,有岩土体开裂或挤压巨响声等 雨量红色预警且裂缝红色预警或位移红色预警 启动应急预案,撤离和停止危险区内一切人类活动和工程活动; 组织专家会商研判,报送上级自然资源部主管部门 表 9 湾里滑坡监测设备
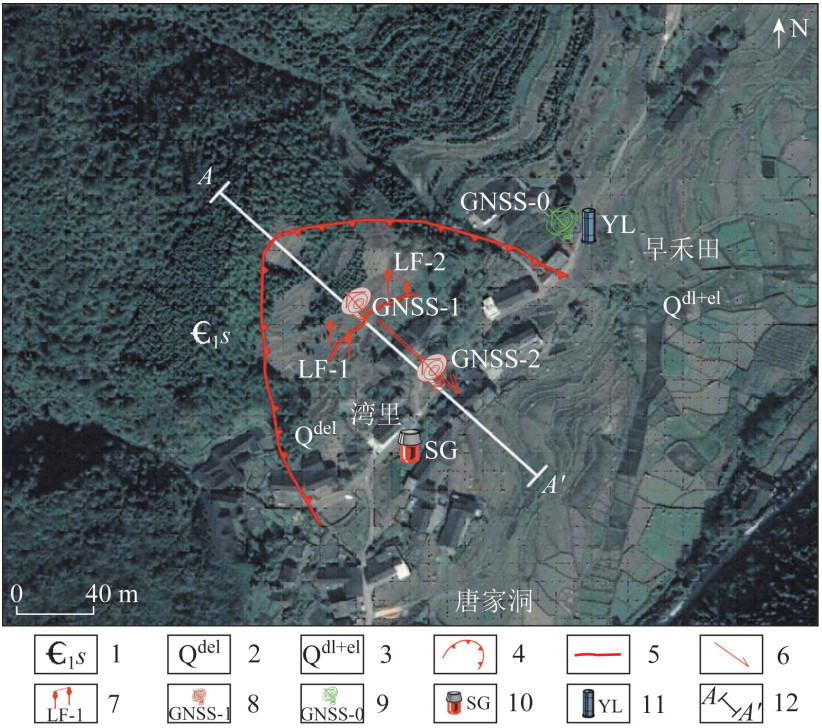
Table 9. Monitoring equipment for Wanli landslide
设备类型 编号 布设位置 监测目的 GNSS基站 GNSS-0 滑坡左侧边界外50 m 基站 GNSS测站 GNSS-1 滑坡中部 监测滑坡变形 GNSS测站 GNSS-2 滑坡前部 监测滑坡变形 裂缝计 LF-1 滑坡后缘 裂缝变形监测 裂缝计 LF-2 滑坡后缘 裂缝变形监测 雨量计 YL 滑坡左侧边界外50 m 降雨强度特征 声光报警器 SG 滑坡前缘 发布预警信息 -
[1] 黄润秋. 20世纪以来中国的大型滑坡及其发生机制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2007, 26(3): 433-454. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.03.001
Huang R Q. Large-scale landslides and their sliding mechanisms in China since the 20th century[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 26(3): 433-454. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.03.001
[2] 铁永波, 徐勇, 张勇, 等. 南方山地丘陵区地质灾害调查工程主要进展与成果[J]. 中国地质调查, 2020, 7(2): 1-12. doi: 10.19388/j.zgdzdc.2020.02.01
Tie Y B, Xu Y, Zhang Y, et al. Main progresses and achievements of geological hazards survey in hilly area of southern China[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2020, 7(2): 1-12. doi: 10.19388/j.zgdzdc.2020.02.01
[3] Yin Y P, Wang H D, Gao Y L, et al. Real-time monitoring and early warning of landslides at relocated Wushan Town, the Three Gorges Reservoir, China[J]. Landslides, 2010, 7(3): 339-349. doi: 10.1007/s10346-010-0220-1
[4] 王青超, 方美平, 梁恩妙. 贵州龙家岩滑坡稳定性监测及防治方法分析[J]. 地基处理, 2020, 2(6): 516-521.
Wang Q C, Fang M P, Liang E M. Stability monitoring and control methods of Longjiayan landslide in Guizhou province[J]. Chinese Journal of Ground Improvement, 2020, 2(6): 516-521.
[5] Han B, Tong B, Yan J K, et al. The monitoring-based analysis on deformation-controlling factors and slope stability of reservoir landslide: Hongyanzi landslide in the southwest of China[J]. Geofluids, 2018, 2018: 7391517. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/326322432_The_Monitoring-Based_Analysis_on_Deformation-Controlling_Factors_and_Slope_Stability_of_Reservoir_Landslide_Hongyanzi_Landslide_in_the_Southwest_of_China
[6] 侯圣山, 李昂, 韩冰, 等. 四川雅安地质灾害预警预报及分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2014, 25(4): 134-138.
Hou S S, Li A, Han B, et al. An approach of geo-hazard warning system in Ya'an, Sichuan and its analysis[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2014, 25(4): 134-138.
[7] 关凤峻. 地质灾害防治和地质环境保护"四大体系"建设[J]. 中国国土资源经济, 2016, 29(10): 4-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6995.2016.10.002
Guan F J. Prevention and control of geological hazards and construction of "four systems" of geological environment protection[J]. Natural Resource Economics of China, 2016, 29(10): 4-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6995.2016.10.002
[8] 许强, 董秀军, 李为乐. 基于天-空-地一体化的重大地质灾害隐患早期识别与监测预警[J]. 武汉大学学报·信息科学版, 2019, 44(7): 957-966.
Xu Q, Dong X J, Li W L. Integrated space-air-ground early detection, monitoring and warning system for potential catastrophic geohazards[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(7): 957-966.
[9] 王文涛. 倾斜航空摄影技术在茂密植被山区地质灾害调查中的应用[J]. 中国地质调查, 2024, 11(2): 116-122. doi: 10.19388/j.zgdzdc.2024.02.14
Wang W T. Application of oblique aerial photography technology in the geological hazard investigation in dense vegetation mountainous areas[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2024, 11(2): 116-122. doi: 10.19388/j.zgdzdc.2024.02.14
[10] 马娟, 赵文祎, 齐干, 等. 基于普适型监测的多参数预警研究: 以三峡库区卡门子湾滑坡为例[J]. 西北地质, 2021, 54(3): 259-269.
Ma J, Zhao W Y, Qi G, et al. Study on the multi-parameter early warning based on universal equipment: A case study of Kamenziwan landslide in the Three Gorges reservoir[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2021, 54(3): 259-269.
[11] 王国卫, 李明波, 吴浪辉, 等. 湖南省溆浦县1/5万地质灾害详细调查报告[R]. 怀化: 湖南省地质环境监测总站, 2014: 51-53.
Wang G W, Li M B, Wu L H, et al. Detailed Geological Disaster Investigation Report at 1∶ 50, 000 Scale in Xupu County, Hunan Province[R]. Huaihua: Geological Environment Monitoring Station of Hunan Province, 2014: 51-53.
[12] 中华人民共和国自然资源部. DZ/T 0460—2023地质灾害自动化仪器监测预警规范[S]. 2023.
Ministry of Natural Resources, People's Republic of China. DZ/T 0460—2023 Specification for Geological Hazard Monitoring and Early Warning by Automation Equipment[S]. 2023.
[13] 侯圣山, 李昂, 陈亮, 等. 基于普适型仪器的滑坡监测预警初探: 以甘肃兰州岷县三处滑坡为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2020, 31(6): 47-53.
Hou S S, Li A, Chen L, et al. Application of universal geo-hazard monitoring instruments in landslides and early warning of three landslides in Gansu Province: A case study of Minxian County and Lanzhou City of Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(6): 47-53.
[14] 张茂省, 贾俊, 王毅, 牛千, 等. 基于人工智能(AI)的地质灾害防控体系建设[J]. 西北地质, 2019, 52(2): 103-116.
Zhang M S, Jia J, Wang Y, et al. Construction of geological disaster prevention and control system based on AI[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2019, 52(2): 103-116.
[15] 贾俊, 张茂省, 冯立, 等. 流态破坏型黄土滑坡滑带土临界特征[J]. 西北地质, 2019, 52(2): 136-147.
Jia J, Zhang M S, Feng L, et al. Critical characteristics of slip zone soil in loess landslide with flow failure pattern[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2019, 52(2): 136-147.
[16] 段钊, 彭建兵, 陈伟, 等. 泾河下游黄土台塬区滑崩灾害空间分异研究[J]. 西北地质, 2018, 51(3): 214-222. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2018.03.020
Duan Z, Peng J B, Chen W, et al. Distribution difference of landslide and collapse in the loess tableland area at the downstream of Jing river[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2018, 51(3): 214-222. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2018.03.020
[17] 丁继新, 尚彦军, 杨志法, 等. 降雨型滑坡预报新方法[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2004, 23(21): 3738-3743. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.21.030
Ding J X, Shang Y J, Yang Z F, et al. New method of predicting rainfall-induced landslides[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 23(21): 3738-3743. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.21.030
[18] 孙世国, 苏振华, 王杰, 等. 滑坡变形组合预测方法的研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2016, 24(6): 1041-1047.
Sun S G, Su Z H, Wang J, et al. Research on the synthetical prediction method of landslip deformation[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2016, 24(6): 1041-1047.
-



 下载:
下载: