Structural sedimentary characteristics and oil & gas exploration potentials of Paleogene System in Sanmenxia basin of Henan Province
-
摘要:
为了查明三门峡盆地的构造演化、古近系沉积特征及油气地质条件,依据二维地震解释、钻井测井、露头、实验数据等资料,对三门峡盆地构造演化、断层发育和沉积相特征进行研究,并探讨其油气勘探潜力。结果表明,三门峡盆地发育3个活动期次的正断层: 第一期断裂为形成于燕山运动末期的控盆断裂; 第二期断裂为形成于喜山期的盆内控凸、控凹断裂; 第三期断裂为形成于更新世的盆内调节断层。三门峡盆地经历了5个演化阶段: 前寒武纪变质基底和坳陷槽形成阶段、古生代海侵及造山阶段、中生代地堑式断陷盆地形成阶段、古近纪断陷盆地发展阶段和盆地定型阶段。通过分析共识别出冲积扇相、曲流河相、三角洲相和湖相4种沉积相以及9种沉积亚相和15种沉积微相。古近系小安组暗色泥岩有机碳含量平均值为2.7%,具有较好的生烃物质基础,镜质体反射率分布范围为0.7%~1.1%,烃源岩进入主力生烃阶段,有机质类型以Ⅱ型为主,部分为Ⅲ型,综合评价为中—好烃源岩; 三角洲相、冲积扇相砂岩为储层发育奠定基础,平均孔隙度为19.79%,渗透率分布范围为(5~150)×10-3 μm2,为中孔—中低渗储层,物性较好; 发育“下生上储、自生自储”生储盖组合,推测发育“新生古储”的生储盖组合,具备油气形成和富集的物质基础和地质条件,豫峡地1井钻获工业油流,进一步证实了三门峡盆地具有一定的油气勘探潜力。
Abstract:In order to identify the structural evolution, Paleogene sedimentary characteristics, and hydrocarbon conditions of Sanmenxia basin, the authors studied the structural evolution, fault development, and sedimentary facies characteristics of Sanmenxia basin based on the two-dimensional seismic interpretation, drilling logging data, outcrop features, experimental data, and other data. And the potentials for oil and gas exploration were discussed. The results show that normal faults under 3 active periods were developed in Sanmenxia basin. The first-period faults are basin-controlling faults at the end stage of Yanshanian orogenic movement. The second-period faults are basin internal control concave faults in the Himalayan period. The third-period faults are intra-basin tear faults in Pleistocene System. Sanmenxia basin has experienced five evolutional stages: Precambrian metamorphic basement and depression trough formation stage, Paleozoic transgression and orogeny stage, the formation stage of Mesozoic graben type faults basin, the development stage of Paleogene faults basin and basin finalization stage. Four sedimentary facies, including alluvial fan facies, meandering river facies, delta facies and lacustrine facies, 9 sedimentary subfacies and 15 sedimentary microfacies were identified. Organic carbon content of dark mudstone in Xiao'an Formation is 2.7%, indicating good material base for hydrocarbon generation. The distribution range of vitrinite reflectrance is 0.7%~1.1%, Hydracarbon Source rocks enter the main hydrocarbon production stage, and the organic matter type is mainly type Ⅱ with some of type Ⅲ, indicating medium-good source rock. The delta facies and alluvial fan facies lay the foundation for reservoir development, with the average porosity of 19.79% and the permeability of (5~150)×10-3 μm2, indicating medium porosity -medium low permeability reservoir with good physical properties. The source-reservoir-cap assemblage of lower-source and upper-reservoir model and self-generation and self-storage model was developed. It is speculated that the type of new source and old reservoir model is also developed, meaning it has material basis and geological conditions for the formation and enrichment of oil and gas. The industrial oil flow was obtained during the drilling of Yushandi No.1 well, which further confirms that Sanmenxia basin has certain potentials for oil and gas exploration.
-

-
图 1 研究区构造单元划分(a)和断裂分布图(b)[4]
Figure 1.
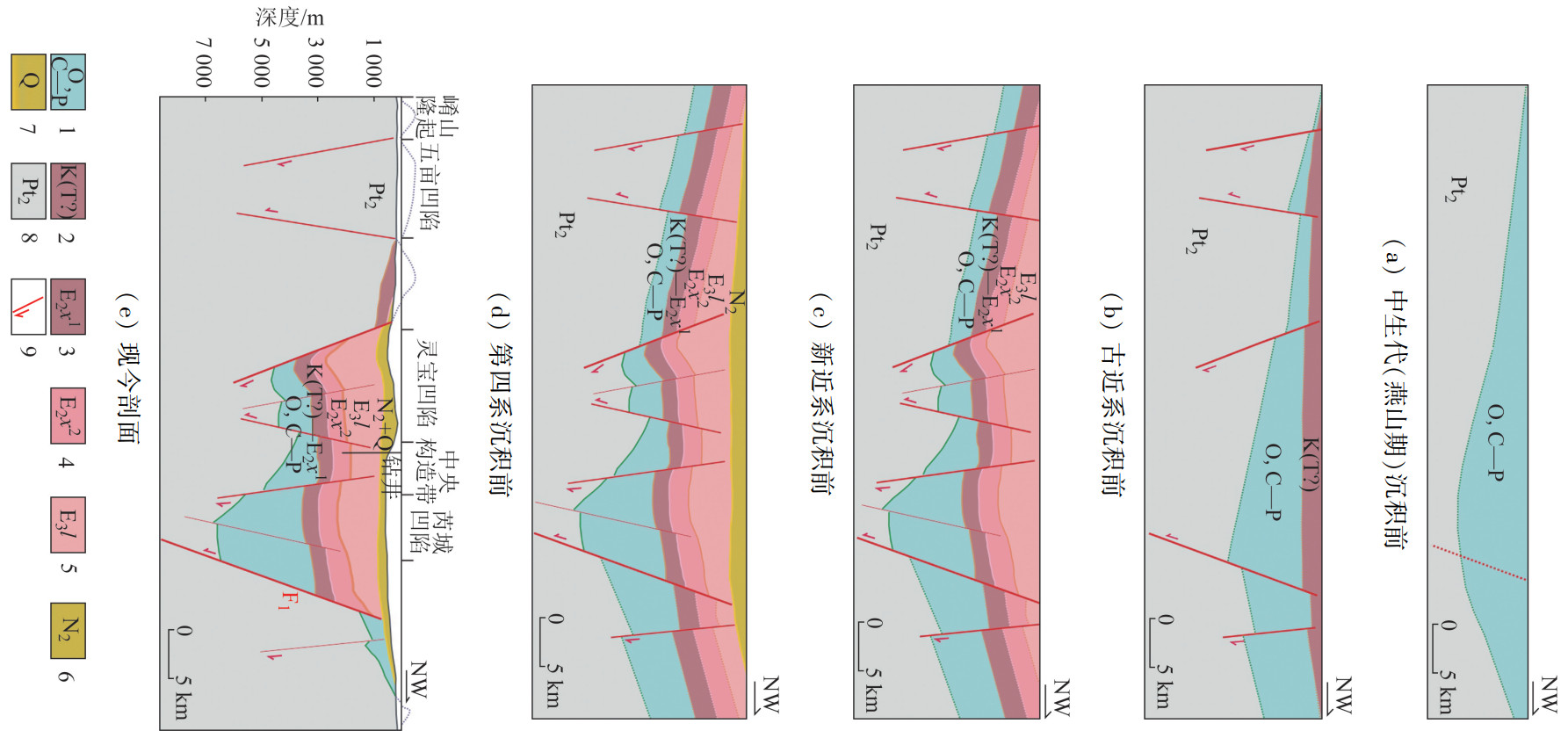
图 2 三门峡盆地构造演化模式(剖面位置见图 1 AA′)
Figure 2.
图 3 三门峡盆地野外露头和沉积相特征(露头位置见图 1)
Figure 3.
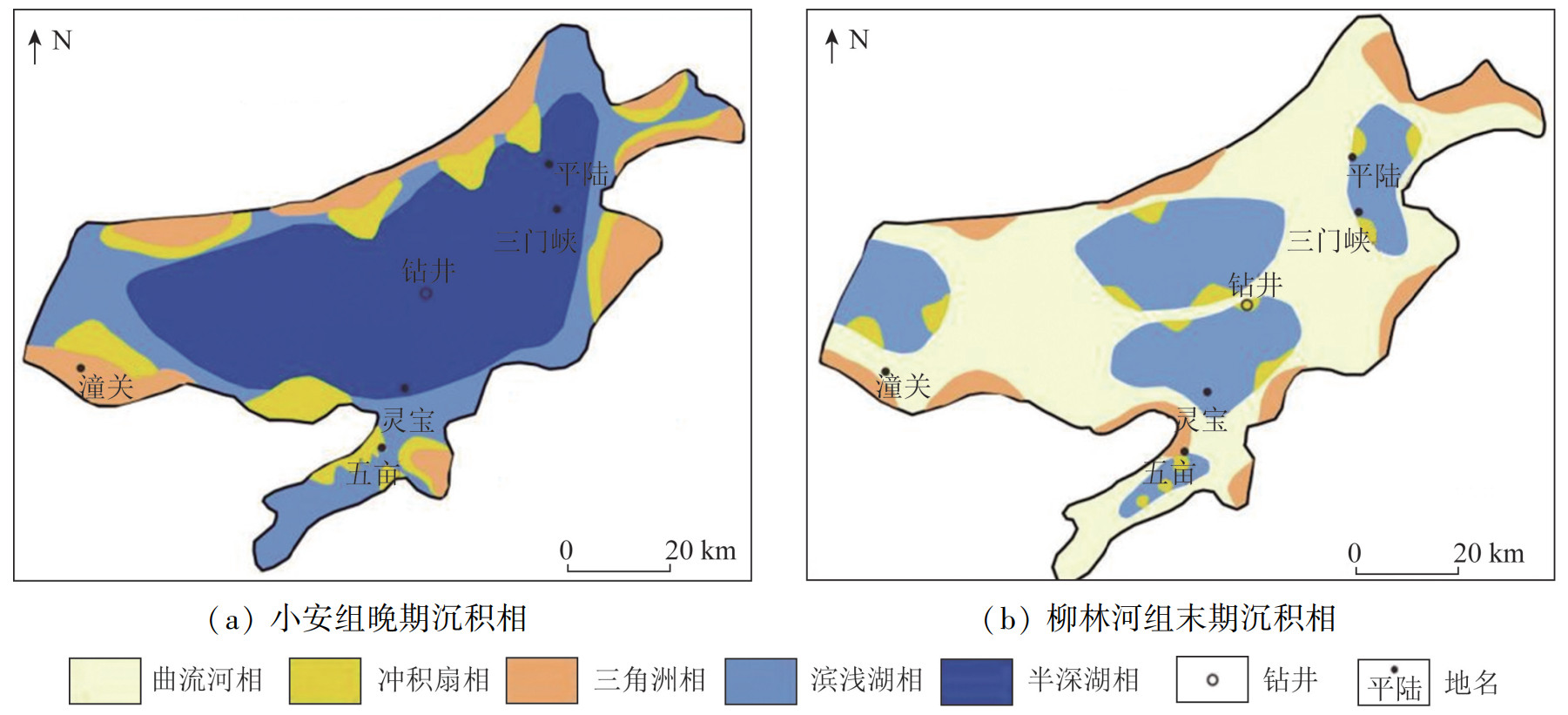
图 5 三门峡盆地古近系测井曲线和沉积相特征(钻井位置见图 1)
Figure 5.
-
[1] 王宏语, 李瑞磊, 朱建峰, 等. 松辽盆地梨树断陷构造沉积学特征及发育机制[J]. 地学前缘, 2023, 30(4): 112-127.
Wang H Y, Li R L, Zhu J F, et al. Tectono-sedimentary characteristics and formation mechanism of the Lishu rift depression, Songliao Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2023, 30(4): 112-127.
[2] 王建强, 刘池洋, 高飞, 等. 陕西渭河盆地前新生界地质特征及其油气意义[J]. 地质通报, 2015, 34(10): 1981-1991. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.10.024
Wang J Q, Liu C Y, Gao F, et al. Pre-Cenozoic geological characteristics and oil-gas significance in Weihe basin, Shaanxi Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2015, 34(10): 1981-1991. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.10.024
[3] 油田石油地质志编写组. 中国石油地质志卷七[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1993.
Oilfield Petroleum Geology Compilation Team. Petroleum Geology of China VOL. 7[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1993.
[4] 王丹丹, 张交东, 刘旭锋, 等. 河南三门峡盆地构造格架及其油气资源远景分析[J]. 中国地质, 2024, 51(3): 719-727.
Wang D D, Zhang J D, Liu X F, et al. Structural framework of Sanmenxia Basin, Henan Province and its oil and gas resources potential analysis[J]. Geology in China, 2024, 51(3): 719-727.
[5] 张瑞胜. 河南灵宝盆地中新生代陆相地层的新划分与对比研究[J]. 资源调查与环境, 2014, 35(2): 114-119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4814.2014.02.004
Zhang R S. A newly stratigraphic division-correlation of Mesozoic-Cenozoic continental strata of Lingbao basin in Henan Pro\|vince[J]. Resources Survey and Environment, 2014, 35(2): 114-119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4814.2014.02.004
[6] 王现国, 杨国华, 谷芳莹, 等. 三门峡盆地地下水化学成分演化机理与模拟[J]. 人民黄河, 2018, 40(6): 82-86.
Wang X G, Yang G H, Gu F Y, et al. Evolution mechanism and simulation of chemical composition of groundwater in Sanmenxia Basin[J]. Yellow River, 2018, 40(6): 82-86.
[7] 王建一, 胡望水, 汤济广, 等. 豫西地区中古生代构造特征与油气前景评价[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2015, 15(5): 207-215. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2015.05.037
Wang J Y, Hu W S, Tang J G, et al. Structural characteristics of Mesozoic and Palaeozoic and exploration prospects of the West He'nan region[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2015, 15(5): 207-215. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2015.05.037
[8] 王飞, 胡望水, 汤济广, 等. 豫西地区构造样式与成藏模式[J]. 长江大学学报: 自科版, 2015, 12(11): 1-7.
Wang F, Hu W S, Tang J G, et al. Tectonic styles and hydrocarbon accumulation pattern in the western Henan area[J]. Journal of Yangtze University: Natural Science Edition, 2015, 12(11): 1-7.
[9] 葛勋, 汤济广, 姜天阳, 等. 豫西地区中新生代差异构造变形[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2018, 38(4): 703-711.
Ge X, Tang J G, Jiang T Y, et al. Mesozoic-Cenozoic different tectonic deformation in western Henan[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 2018, 38(4): 703-711.
[10] 冯兴祥. 三门峡盆地的新构造运动与地震活动[J]. 河南师大学报, 1982(1): 49-55.
Feng X X. Neotectonics movement and eaethquake activity in Sanmenxia basin[J]. Journal of Henan University, 1982(1): 49-55.
[11] 贾海民. 河南省三门峡市灵宝市地质与矿产调查研究[J]. 世界有色金属, 2016, 41(S9): 51-52.
Jia H M. Sanmenxia city in Henan Lingbao city geology and mineral investigation[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2016, 41(S9): 51-52.
[12] 刘恩然, 刘成林, 石砥石, 等. 南华北盆地周口坳陷东北部上古生界泥岩孔隙非均质性及主控因素[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2022, 53(9): 3773-3790.
Liu E R, Liu C L, Shi D S, et al. Characterization and controlling factors of pore structural heterogeneity of mudstone: A case of upper Paleozoic in northeast Zhoukou Depression, Southern North China Basin[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2022, 53(9): 3773-3790.
[13] 韩宇春, 黄晓梅. 华北南部地区古生界构造演化及其油气远景[J]. 海相油气地质, 1997, 2(3): 11-15.
Han Y C, Huang X M. Structural evolution and hydrocarbon prospects of Paleozoic in southern part of North China[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 1997, 2(3): 11-15.
[14] 徐汉林, 赵宗举, 杨以宁, 等. 南华北盆地构造格局及构造样式[J]. 地球学报, 2003, 24(1): 27-33.
Xu H L, Zhao Z J, Yang Y N, et al. Structural pattern and structural style of the southern North China Basin[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 2003, 24(1): 27-33.
[15] 吴奇, 许立青, 李三忠, 等. 华北地块中部活动构造特征及汾渭地堑成因探讨[J]. 地学前缘, 2013, 20(4): 104-114.
Wu Q, Xu L Q, Li S Z, et al. Active tectonics in the Central North China Block and the cause of the formation of the Fenwei Graben[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(4): 104-114.
[16] 吴伟, 王雨涵, 曹高社, 等. 南华北盆地豫西地区C-P烃源岩地球化学特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2015, 26(1): 128-136.
Wu W, Wang Y H, Cao G S, et al. The geochemical characteristics of the carboniferous and Permian source rocks in the western Henan, the southern North China Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2015, 26(1): 128-136.
[17] 刘艳杰, 程党性, 邱庆伦, 等. 南华北盆地下二叠统泥页岩孔隙特征及控制因素[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(10): 1501-1513.
Liu Y J, Cheng D X, Qiu Q L, et al. Characteristics of pores and controlling factors of Lower Permian shales in Southern North China Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2020, 31(10): 1501-1513.
[18] 宋佳佳, 田晓峰, 王帅军, 等. 南华北块体及邻区地质结构构造研究进展[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2021, 36(3): 940-952.
Song J J, Tian X F, Wang S J, et al. Research progress of geolo\|gical structure in the South north China and adjacent areas[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2021, 36(3): 940-952.
[19] 李明培, 邵龙义, 李智学, 等. 华北地区石炭一二叠纪下煤组聚煤期岩相古地理[J]. 煤炭学报, 2020, 45(7): 2399-2410.
Li M P, Shao L Y, Li Z X, et al. Lithofacies palaeogeography of lower coal group accumulation period of Carboniferous Permian in North China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(7): 2399-2410.
[20] 王丹丹, 李世臻, 周新桂, 等. 大兴安岭地区突泉盆地高精度重磁电特征及其构造格架[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2016, 46(1): 240-253.
Wang D D, Li S Z, Zhou X G, et al. Lithology lithofacies identification and deep structure of Tuquan Basin in great Xinggan range area based on high-precision gravity-magnetic-electrical survey[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2016, 46(1): 240-253.
[21] 王丹丹, 赵松, 张文浩, 等. 松辽盆地外围通化地区高精度重磁电特征及其构造格架[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(4): 1056-1068.
Wang D D, Zhao S, Zhang W H, et al. Lithofacies identification and deep structure of Tonghua area in the periphery of Songliao Basin based on high-precision gravity-magnetic electrical survey[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(4): 1056-1068.
[22] 刘卫彬, 李世臻, 徐兴友, 等. 松辽外围火山-沉积盆地非常规油气调查发现及启示意义——以双阳盆地为例[J]. 煤炭学报, 2022, 47(6): 2396-2406.
Liu W B, Li S Z, Xu X Y, et al. Discovery of unconventional oil and gas in volcanic sedimentary basins around Songliao and its enlightenment: Take Shuangyang Basin as an example[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(6): 2396-2406.
[23] 曹高社, 徐国强, 高立祥, 等. 豫西南晚白垩世盆地断裂构造和沉积特征的自相似性分析[J]. 河南理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2012, 31(6): 674-678, 701.
Cao G S, Xu G Q, Gao L X, et al. Similarity analysis of rift structure and sedimentary characteristics in basins of southwestern Henan province, Upper Cretaceous[J]. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University: Natural Science, 2012, 31(6): 674-678, 701.
[24] 曲志成, 贾会冲, 田刚, 等. 三门峡盆地重力异常特征与构造格局[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2022, 22(24): 10425-10433.
Qu Z C, Jia H C, Tian G, et al. Gravity anomaly characteristics and tectonic framework in Sanmenxia Basin[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2022, 22(24): 10425-10433.
[25] 杜建军, 马寅生, 黎敦朋. 渭河盆地东南缘主要断裂晚更新世以来的活动性及灾害效应[J]. 地球学报, 2017, 38(S1): 55-58.
Du J J, Ma Y S, Li D P. Activity of main faults since the late Pleistocene and related geohazard effects in southeast of Weihe Basin[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2017, 38(S1): 55-58.
[26] 薛晓东. 1815平陆63/4级地震发震构造初步研究[J]. 山西建筑, 2016, 42(17): 44-45.
Xue X D. Prelim inary study on seismogenic structure of Pinglu 63/4 earthquake in 1815[J]. Shanxi Architecture, 2016, 42(17): 44-45.
[27] 何发岐, 於文辉, 马超, 等. 三门峡断陷盆地及邻区深部结构及成因-来自深地震反射与大地电磁测深的证据[J]. 地质学报, 2024, 98(4): 1088-1100.
He F Q, Yu W H, Ma C, et al. Deep structure and genesis of Sanmenxia fault basin and its adjacent area: evidence from deep seismic reflection and magnetotelluric sounding[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2024, 98(4): 1088-1100.
[28] 李清瑶, 高永进, 陈夷, 等. 北方重要盆地油气资源战略选区调查工作进展[J]. 中国地质调查, 2024, 11(1): 1-8. doi: 10.19388/j.zgdzdc.2024.01.01
Li Q Y, Gao Y J, Chen Y, et al. Progress in the strategic selection investigation of oil and gas resources in northern important basins[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2024, 11(1): 1-8. doi: 10.19388/j.zgdzdc.2024.01.01
[29] 包书景, 郭天旭, 白忠凯, 等. 中国地质调查局新一轮找矿突破战略行动油气调查工作成果与进展[J]. 中国地质, 2024, 51(3): 封2.
Bao S J, Guo T X, Bai Z K, et al. The achievements and progress of oil and gas survey work in the new round of exploration breakthrough strategy action by the China geological survey bureau[J]. Geology in China, 2024, 51(3): 封2.
[30] 陆鹿, 陈树光, 李壮福, 等. 河套盆地临河坳陷白垩纪—古近纪沉积环境演化及油气地质意义[J]. 古地理学报, 2022, 24(2): 308-331.
Lu L, Chen S G, Li Z F, et al. Sedimentary evolution and petroleum potential of the Cretaceous to Paleogene in Linhe depression, Hetao Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography (Chinese Edition), 2022, 24(2): 308-331.
-




 下载:
下载: